Community Characteristics and Potential Risk of Nekton in Waters Adjacent to Ningde Nuclear Power Plant in Fujian, China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
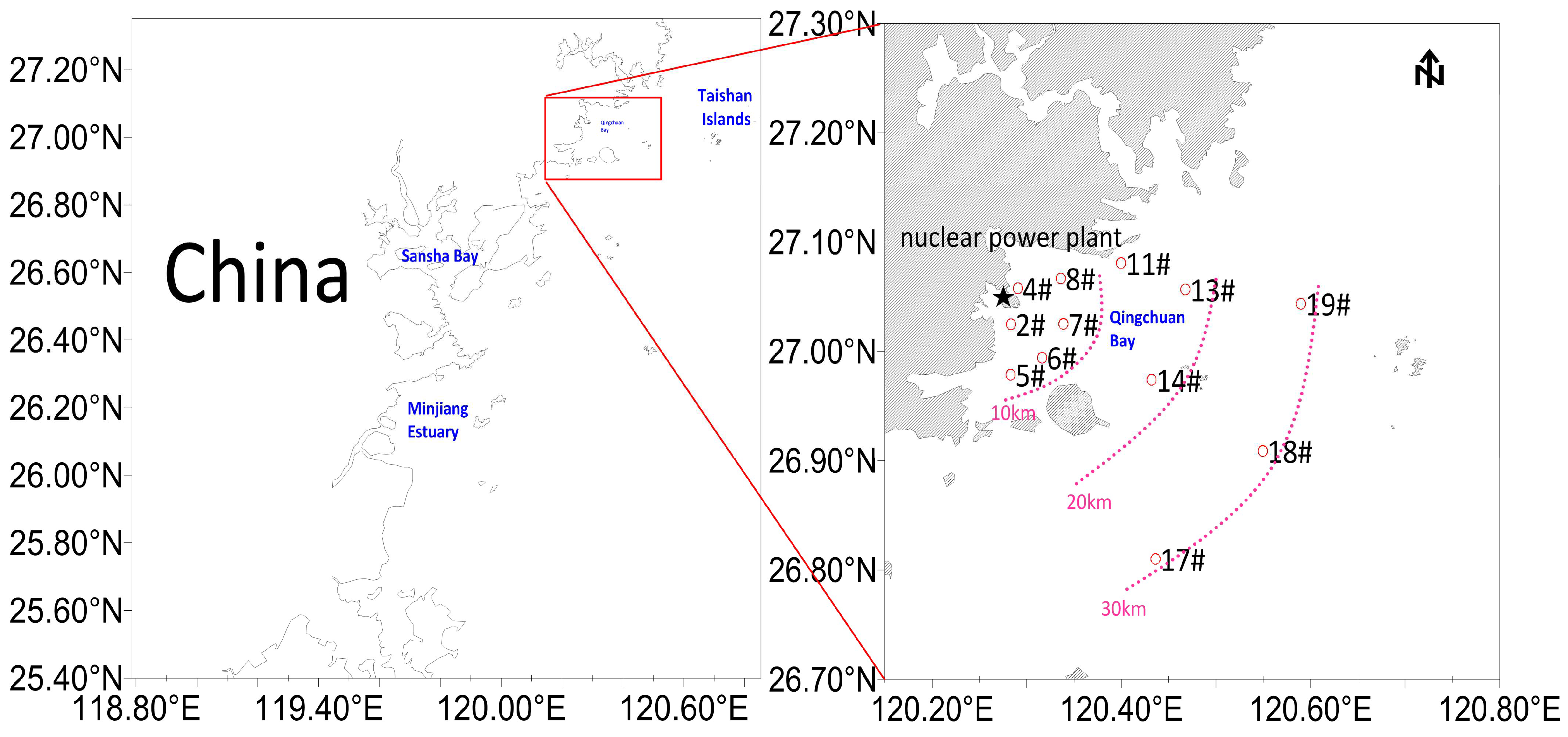
2.1. Sample Collection, Identification, and Classification
2.2. Measurements of Environmental Variables
2.3. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Nekton Species Collected During the Surveys
3.2. Seasonal Changes in Dominant Species of Nekton
3.3. Seasonal Changes in Nekton Diversity Indexes
3.4. Seasonal Changes in the Volume of Nekton
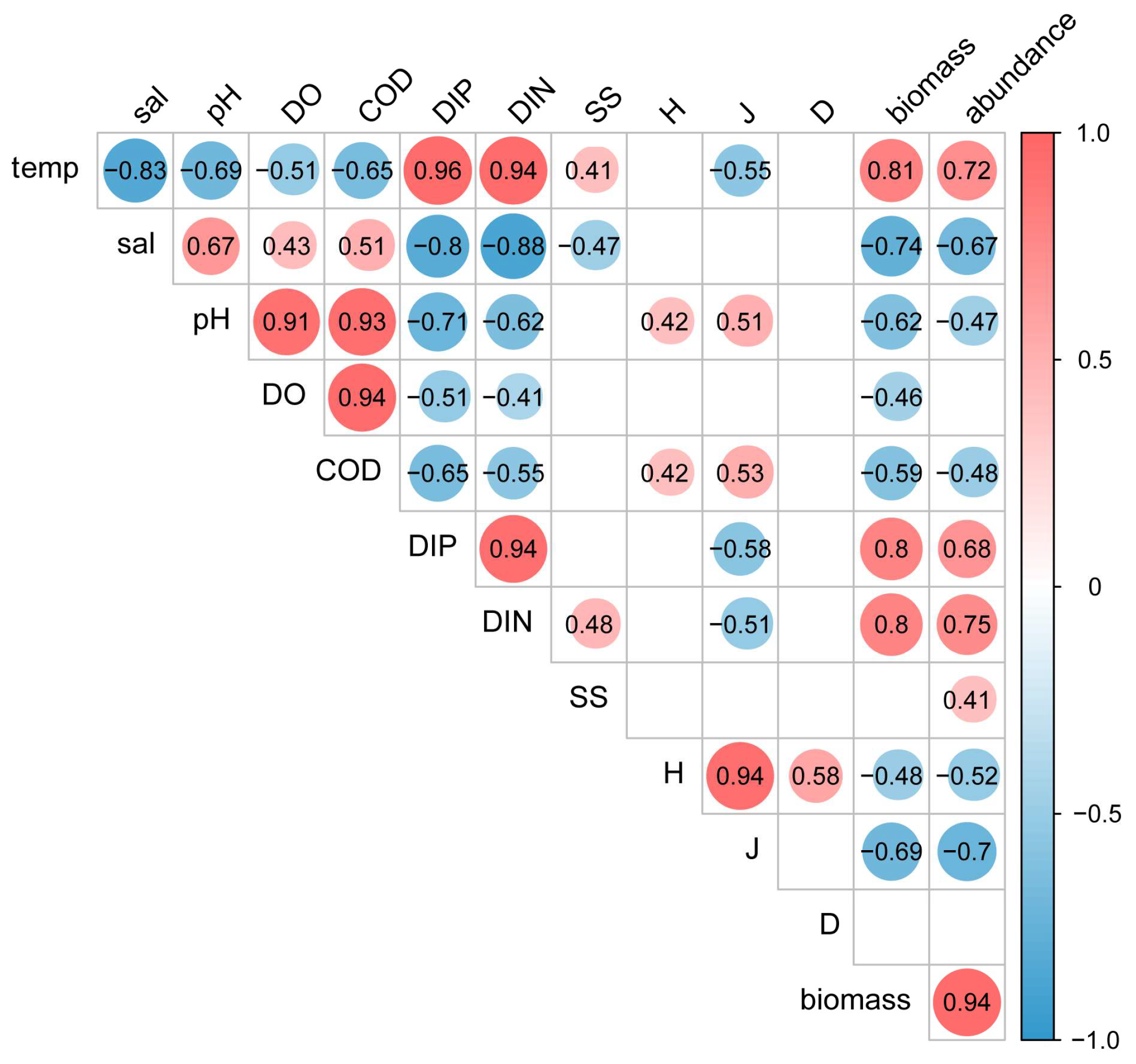
3.5. Spatial Distribution of Nekton and Its Correlation with Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Composition of the Nekton Community
4.2. Dominant Species of Nekton in the Study Area
4.3. Nekton Diversity in the Study Area
4.4. Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Nekton and Their Correlation with Environmental Factors
4.5. Potential Risks of Nekton to the Safety of the Cooling Water System of the Ningde NPP
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dagnall, S. Nuclear fission: Continuing evolution of a future generation. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. 2005, 158, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S. Role of nuclear energy to a future society of shortage of energy resources and global warming. J. Nucl. Mater. 2010, 398, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Ma, F.Q.; Xue, Y.; Jiao, C.S.; Yang, Z.G. Failure analysis on leaked titanium tubes of seawater heat exchangers in recirculating cooling water system of coastal nuclear power plant. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 101, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Jordan, C.; Jain, P.; Robb, K.; Bindra, H.; Eckels, S.J. Experimental investigation on the coolability of nuclear reactor debris beds using seawater. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 184, 122347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.S.; Zhang, S.Y.; Cao, R.R.; Yu, S.H.; Bai, W.; Zhang, R.Y.; Yang, J.; Dai, L.; Chen, J.X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A review on the risk, prevention and control of cooling water intake blockage in coastal nuclear power plants. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2023, 56, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.H.; Cheng, F.; Jin, X.X.; Sun, L.; Bao, R.Y.; Liu, Y. An automatic marine-organism monitoring system for the intake water of the nuclear power plant. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2017, 109, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.P.; Yu, X.B.; Meng, B.F.; Wu, C.C. Classification and Characteristic Analysis of Risky Organisms in the Cooling Water Intake Area of Coastal Nuclear Power Plants. Mar. Sci. 2023, 47, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.W.; Guan, C.J.; Xu, P.; Liu, G.Z.; Xu, Q.M.; Ye, J.Q.; Wang, X.; Zhao, B.Q. Analysis of Risky Organisms in the Cooling Water Intake Area of Nuclear Power Plants in the Eastern Part of Liaodong Bay. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Xu, B.T.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y.M.; Zhang, H.Y.; Peng, Y. Analysis of the Impact of Marine Organism Outbreaks on the Cooling Water System of Nuclear Power Plants and Countermeasures. Water Supply Drain. 2018, 44, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Chae, J.; Choi, H.W.; Lee, W.J.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.H. Distribution of a pelagic tunicate, Salpa fusiformis in warm surface current of the eastern Korean waters and its impingement on cooling water intakes of Uljin nuclear power plant. J. Environ. Biol. 2008, 29, 585–590. [Google Scholar]
- Mark, S. Marine ecology: Attack of the blobs. Nature 2012, 482, 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- An, L.; Wang, L.; Ou, D.; Jia, C.; Li, W.; Ding, Y.; You, C.; Liao, J.; Huang, H. The ecological mechanisms of Acetes blooms as a threat to the security of cooling systems in coastal nuclear power plants. J. Coast. Conserv. 2021, 25, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.F. Research on Typical Disaster-Causing Organisms for Coastal Nuclear Power Operation Safety, A Case Study of Ningde Nuclear Power Plant; Shanghai Ocean University: Shanghai, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.H.; Wu, W.; Li, K.Z. Editorial: Nuclear power cooling-water system disaster-causing organisms, outbreak and aggregation mechanisms, early-warning monitoring, prevention and control. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1218776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huo, J.L.; Song, Y.Z.; Yang, L.; Liu, S.T. An integrated monitoring system for disaster-causing organisms in the water intake areas of coastal nuclear power plants. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1089699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Chen, H.; Dai, L.; Ji, J.; Lin, J.; Yu, T.; Xiao, Y. Early warning and monitoring of the safety risk of coastal nuclear power plant cold source under the stress from Phaeocystis globosa blooms. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2024, 75, MF23179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jylhä, K.; Kämäräinen, M.; Fortelius, C.; Gregow, H.; Helander, J.; Hyvärinen, O.; Johansson, M.; Karppinen, A.; Korpinen, A.; Kouznetsov, R. Recent meteorological and marine studies to support nuclear power plant safety in Finland. Energy 2018, 165, 1102–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.C.; Du, F.L.; Pu, X.; Wang, X.; Han, F.Z. Analysis on Critical Factors of Marine Organism Impacts on Water Intake Safety at Nuclear Power Plants. J. Nucl. Eng. Radiat. Sci. 2020, 6, 041101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.C.; Du, F.L.; Huang, X.D.; Pei, J.; Zhang, Z.L.; Xing, X.F.; Pu, X. Cooling water intake system safety analysis based on impingement probability. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1133187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.S. Real-Time Detection System for Underwater Disaster-Causing Organisms in Coastal Nuclear Power Plants; Xiamen University: Xiamen, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.H.; Hu, L.S.; Li, J.W.; Zhang, J.F. Research on Marine Biological Monitoring Technology to Improve the Cold Source Safety of Nuclear Power Plant. Electr. Saf. Technol. 2019, 21, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Howe, B.M.; Miksis-Olds, J.; Rehm, E.; Sagen, H.; Worcester, P.F.; Haralabus, G. Observing the Oceans Acoustically. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desidera, E.; Guidetti, P.; Panzalis, P.A.; Navone, A.; Valentini-Poirrier, C.A.; Boissery, P.; Gervaise, C.; Di Iorio, L. Acoustic Fish Communities: Sound Diversity of Rocky Habitats Reflects Fish Species Diversity. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 608, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, K.; Kamiya, K.; Yamashita, K.; Hayashi, F.; Watanabe, I.; Murao, Y.; Miyasaka, H.; Kamimura, N.; Nogami, M. Genetic polymorphism of the adult medusae invading an electric power station and wild polyps of Aurelia aurita in Wakasa Bay, Japan. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2005, 85, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.J.; Ming, H.X.; Liu, S.Y.; Lang, X.L.; Jin, Y.; Fan, J.F. Full-length 16S rRNA gene sequencing reveals the operating mode and chlorination-aggravated SWRO biofouling at a nuclear power plant. Water Sci. Technol. 2024, 90, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.Z.; Rao, Y.Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Yang, D.Y.; Lin, J.X.; Fu, S.J.; Zhou, X.P. Two risk indices for benthic macrofauna entrapment evaluation on the water intake systems in coastal nuclear power plants. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2022, 41, 655–662. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.C.; Jin, Q.Q.; Yang, L.; Jia, C.; Guan, C.J.; Wang, H.N.; Guo, H. Aggregation process of two disaster-causing jellyfish species, Nemopilema nomurai and Aurelia coerulea, at the intake area of a nuclear power cooling-water system in Eastern Liaodong Bay, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1098232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, L.S.; Mills, C.E.; Hirano, Y.M.; Collins, A.G.; Marques, A.C. A review of the global diversity and natural history of stalked jellyfishes (Cnidaria, Staurozoa). Mar. Biodivers. 2018, 48, 1695–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Xu, Z.J.; Zhang, H.L.; Li, B.L.; Wen, G.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Sha, J.J.; Du, X.Y.; Bao, M.M.; Sun, Z.N.; et al. Characteristics of small medusae community correlated with environment-al factors in the southwest of Bohai Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2023, 45, 66–75. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.J. Analysis on the community characteristics and influencing factors of jellyfish in a Nuclear Power Plant. Environ. Ecol. 2022, 4, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.P.; Wang, T.T.; Xiong, M.S.; Yang, S.L.; Zhang, H.; Ying, J.; Shi, Y.C.; Zhao, G.Q.; Zhang, X.M.; Liu, X.D.; et al. Analysis of the Distribution Characteristics of Jellyfish and Environmental Factors in the Seawater Intake Area of the Haiyang Nuclear Power Plant in China. Biology 2024, 13, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.Y.; Song, X.X.; Yu, F.; Wang, K.; Song, S.Q.; Yu, Z.M. Potential risk and prevention of phytoplankton outbreak to water-cooling system in nuclear power plant in Fangchenggang, Guangxi. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2019, 50, 700–706. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Lin, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.Y.; Chang, L.; Tang, X.M.; Xiang, P.; Lin, H.S. Potential risk from and prevention of phytoplankton outbreaks in blocking the cooling water system in a nuclear power plant on the Southeast China coast. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1034876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Yang, L.; Ren, H.T.; Liu, Z.W.; Jia, Z.Y. Analysis of the Invasion of Acetes into the Water Intake of the Daya Bay Nuclear Power Base. Water 2022, 14, 3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.S.; Wang, J.J.; Liu, W.; Liu, K.; Zhang, S.Y.; He, X.B.; Huang, Y.Q.; Lin, J.H.; Mou, J.F.; Zheng, C.X. Fouling community characteristics in subtropical coastal waters of the southwestern East China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 10, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.S.; Huang, Y.Q.; Lin, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.Y.; Yu, S.H.; Liu, K.; Mou, J.F.; Lin, J.H.; He, X.B.; Fu, S.J.; et al. Biofouling characteristics in Xinghua Bay of Fujian, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1107087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpathy, K.K. Biofouling control measures in power plant cooling systems, A brief overview. In Marine Biofouling and Power Plants; Bhabha Atomic Research Centre Press: Bombay, India, 1990; pp. 153–166. [Google Scholar]
- Arefiev, N.; Mikhalev, M.; Zotov, D.; Zotov, K.; Vatin, N.; Nikonova, O.; Skvortsova, O.; Pavlov, S.; Chashina, T.; Kuchurina, T. Physical Modeling of Suspended Sediment Deposition in Marine Intakes of Nuclear Power Plants. Procedia Eng. 2015, 117, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.P.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, B.; Shangguan, Z.H.; Sha, X.D. Prediction of Sea Ice Melting and Environmental Impact Assessment by Thermal Effluent from Nuclear Power Plant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 35 (Suppl. S2), 330–333. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.; Xu, N.; Wang, Y.L.; Sun, S.S.; Zhao, B.Q.; Yuan, S.; Shi, W.Q.; Ma, Y.X. Risk Assessment and Case Analysis of Sea Ice Dynamic Accumulation in Water Intakes of Nuclear Power Plants. Int. J. Offshore Polar Eng. 2022, 32, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Guo, Y.C.; Liu, W.; Zheng, B.Q.; Huang, Q.Z.; Wang, H.; Cheng, H.; Xun, F. Risk Analysis of the Aggregation Behavior of Acaudina Molpadioides on Nuclear Power Plant Cold Source. Nucl. Saf. 2024, 23, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, B.P.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.B.; Qin, Y.T.; Xia, L.H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.F.; Jiang, X.S.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.T.; et al. Analysis on the community characteristics and potential ecological risk of jellyfish in the Qingchuan Bay of Ningde, Fujian Province. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2020, 42, 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Shi, Z.Z.; Yu, Z.F.; Zhou, K.L.; Lin, J.; Wu, J.Y.; Mu, J.L. Spatio-temporal variations of zooplankton and correlations with environmental parameters around Tiaowei Island, Fujian, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.B.; Sun, W.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.B.; Zheng, B.Q.; Lu, C.; Li, J.; Mu, J.L. Ecological environment and the potential hazard-causing organisms in the sea area near the nuclear power plant. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2022, 46, 32–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.Z.; Chen, D.G. Marine Fishes of China, Volumes I, II, & III.; Ocean University of China Press: Qingdao, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.T.; Yu, C.G.; Xue, L.J.; Yao, G.Z. East China Sea Economic Shrimp And Crab; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.G.; Lin, M. Atlas of Marine Organisms in China (Volume VI); Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.T.; Ding, T.M.; Xu, K.D. East China Sea Economic Cephalopods; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Gao, S. Seasonal variation in the trophic structure of food webs in coastal waters of Jiangsu Province based on stable isotope techniques. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2022, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- GB17378.3-2007; The Specification for Marine Monitoring Part 3: Sample Collection, Storage and Transportation. The General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Pinkas, L.M.S. Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna, and bonito in California waters. Calif. Dep. Fish Game Fish Bull. 1971, 152, 1–105. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Yu, Z.F.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, J.; Cheng, H.; Fan, L.J.; Wang, F.P.; Mu, J.L. Fish assemblage structure and spatio-temporal variation in Qingchuan bay, Ningde, Fujian. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2022, 41, 738–744. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Wang, X.B.; Zhang, G.H.; Han, Q.X. Community characteristics of nekton assemblages in Oujiang River estuary and its relationship with environmental factors, Zhejiang, East China. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2023, 54, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, B.; Yan, Y.R.; Li, Z.L.; Hou, G. On fishery resources survey in deepwater areain the sea with construction project. Mar. Fish. 2017, 39, 393–400. [Google Scholar]
- SCT9110-2007; Technical Regulations for Impact Assessment of Construction Projects on Marine Living Resources. The Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Liu, J.H.; Li, Y.; Cao, L.; Xu, L.L.; Dou, S.Z. Spatio-temporal Patterns of Nekton Community Composition, Resource Quantity, and Biodiversity in the Coastal Waters of East Fujian Province. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2020, 51, 931–942. [Google Scholar]
- Underwood, A.J. Experiments in Ecology: Their Logical Design and Interpretation Using Analysis of Variance; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Jonathan, H. Community Structure of Aquatic Insects in the Esparza River, Costa Rica. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2013, 57, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dixon, P.M. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.S.; Yoklavich, M.; Schroeder, D.M. Demersal fish assemblages in the Southern California Bight based on visual surveys in deep water. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2009, 84, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.R.; Jia, G.D.; Chen, L.H.; Jin, H.Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Feng, W.H.; Zhang, Y.Z. Seasonal succession and spatial heterogeneity of the nekton community associated with environmental factors in Hangzhou Bay, China. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2022, 49, 102108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.R.; Lin, Z.J.; Chen, Y.X.; Chen, P.M. Eco-Dynamic Analysis of the Community Structure of Nekton in the Northern South China Sea. Fishes 2023, 8, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, D.L.; Posey, M.H. Salt Marsh Habitat Size and Location Do Matter, the Influence of Salt Marsh Size and Landscape Setting on Nekton and Estuarine Finfish Community Structure. Estuar. Coast. 2019, 42, 1353–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, L.G.; Wang, X.H.; Van Damme, K.; Ning, J.J.; Li, Y.F.; Huang, D.L.; Liu, S.S.; Li, H.; Du, F.Y. Spatial and temporal variabilities of coastal nekton community structure and phylogenetic diversity in Daya and Dapeng Bay, Southern China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.C.; Shui, Y.Y.; Qin, H.L.; Ji, M.M.; Hu, C.Y.; Li, L.; Shui, B.N. Community characteristics of swimming animal in the waters of Qixing Islands in spring and autumn. J. Fish. China 2017, 41, 382–391. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.; He, X.B.; Zhao, C.X. Functional diversity of fishes in the Minjiang Estuary, Southeast China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 3589–3595. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.C. Fish community composition and diversity in Sansha Bay of Fujian. Mar. Fish. 2011, 33, 258–264. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, S.T.; Yang, L.; Ju, P.L.; Yang, S.Y.; Tu, Z.S. Community structure characteristics of fishery stock in the sea of Taishan Islands in Fujian Province. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2020, 39, 531–541. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Guo, X.F.; Fang, J.; Li, Q.S. Characteristics of seasonal spatial expansion of Fujian and Zhejiang Coastal Current and their bay effects. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2018, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tsou, T.S.; Matheson, R.E. Seasonal changes in the nekton community of the Suwannee River estuary and the potential impacts of freshwater withdrawal. Estuaries 2002, 25, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.S.; Shan, X.J.; Li, X.S.; Wang, J.; Cui, Y.; Zuo, T. Long-term changes in the fishery ecosystem structure of Laizhou Bay, China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Q.K.; Lu, Y.Z.; Mi, H.J.; Yu, Y.G.; Gu, D.X.; You, H.Z.; Hao, S. Feeding intensity and molecular prey identification of the mantis shrimp, Oratosquilla oratoria (De Haan, 1844), in the Tianjin coastal zone of Bohai Bay. Mar. Ecol. 2020, 41, e12594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneib, R.T.; Knowlton, M.K. Stage-structured interactions between seasonal and permanent residents of an estuarine nekton community. Oecologia 1995, 103, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magurran, A.E. Measuring Biological Diversity; John Wiley & Sons Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Song, P.Q.; Zhang, J.; Lin, L.S.; Xu, Z.C.; Zhu, X.M. Nekton species composition and biodiversity in Taiwan Strait. Biodivers. Sci. 2012, 20, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Desrita, D.; Muhtadi, A.; Leidonald, R.; Sibagariang, R.D.; Nurfadillah. Biodiversity of nekton in Batangtoru River and its tributaries in North Sumatra, Indonesia. Biodiversitas 2020, 21, 2344–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.Q.; Lin, L.S.; Li, Y.; Zhong, Z.H.; Zhang, R. Species composition and stability of nekton community structure in Sandu Bay, Fujian Province. Biodivers. Sci. 2015, 23, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonesh, J.R.; Kraus, J.M.; Rosenberg, J.S.; Chase, J.M. Predator effects on aquatic community assembly, disentangling the roles of habitat selection and post-colonization processes. Oikos 2009, 118, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelmann, C.; Hellmann, C.; Worischka, S.; Petzoldt, T.; Benndorf, J. Fish predation affects the structure of a benthic community. Freshw. Biol. 2011, 56, 1030–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollweg, T.A.; Christman, M.C.; Cebrian, J.; Wallace, B.P.; Friedman, S.L.; Ballestero, H.R.; Huisenga, M.T.; Benson, K.G. Meta-analysis of Nekton Utilization of Coastal Habitats in the Northern Gulf of Mexico. Estuar. Coast. 2020, 43, 1722–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, L.P.; Minello, T.J. Small-Scale Nekton Density and Growth Patterns Across a Saltmarsh Landscape in Barataria Bay, Louisiana. Estuar. Coast. 2015, 38, 2000–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, L.P.; Minello, T.J. Nekton Density Patterns in Tidal Ponds and Adjacent Wetlands Related to Pond Size and Salinity. Estuar. Coast. 2010, 33, 652–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, P.; Arias, A.M.; Baldó, F.; Cuesta, J.A.; Rodríguez, A.; Silva-García, A.; Sobrino, I.; Fernández-Delgado, D.; García-González, C. Spatial and temporal variation of the nekton and hyperbenthos from a temperate European estuary with regulated freshwater inflow. Estuaries 2002, 25, 451–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimatsu, A.; Hayashi, M.; Kikkawa, T. Fishes in high-CO2, acidified oceans. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 373, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.Q.; Liang, C.; Liu, C.L.; Xian, W.W. Characterizing the nektonic invertebrate communities in the Yangtze River estuary and its adjacent waters. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 45, 101847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.P.; Zhang, G.G.; Wang, T.T.; Li, M.; Ren, Z.H.; Jiang, W.L.; Lv, Z.B.; Liu, D. Community structure and seasonal variation of demersal nekton in the eastern waters of Laizhou Bay. Mar. Fish. 2024, 46, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Specziár, A.; György, Á.I.; Erős, T. Within-lake distribution patterns of fish assemblages: The relative roles of spatial, temporal and random environmental factors in assessing fish assemblages using gillnets in a large and shallow temperate lake. J. Fish Biol. 2013, 82, 840–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.B.; Du, N.; Yin, X.F. Analysis of the Impact of Wastewater Discharge from Coastal Nuclear Power Plants on Marine Ecological Environment. Sci. Technol. Vision 2023, 13, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Poornima, E.H.; Rajadurai, M.; Rao, T.S.; Anupkumar, B.; Rajamohan, R.; Rao, V.N.R. Impact of thermal discharge from a tropical coastal power plant on phytoplankton. J. Therm. Biol. 2005, 30, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, R.Y.; Zhang, W.J. Investigation of Nekton in the Waters Around a Nuclear Power Plant. Wat. Supp. Drain. 2022, 58 (Suppl. S1), 815–825. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.F.; Wang, J.H.; Cheng, H.; Zheng, B.Q.; Ma, Z.Y. Eco-environment quality assessment of macrobenthic community in the East Ningde sea waters. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 278–285, 302. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.H.; Song, H.H.; Mu, Y.Y. Reason Analysis and Improvement Measures Evaluation for Water Intake Blockage at Northern Nuclear Power Plants. Nucl. Pow. Eng. 2019, 40, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Yu, C.G.; Yu, N.J.; Zhang, P.Y.; Jiang, Q.L.; Niu, W.Z. Analysis on the status and protection of juvenile fish resources in the coastal waters of Zhoushan in spring and autumn. J. Fish. Res. 2021, 43, 121–132. [Google Scholar]
- Han, R.; Zhao, Y.J.; Ji, P.; Kang, Z.S.; Wu, J.X. Research on Countermeasures for Cooling Water Source Risks in Coastal Nuclear Power Plants. Wat. Supp. Drain. 2020, 56 (Suppl. S1), 17–20. [Google Scholar]






| Species Name | September 2022 | October 2022 | November 2022 | December 2022 | January 2023 | February 2023 | March 2023 | April 2023 | May 2023 | June 2023 | July 2023 | August 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loligo beka | 127 | 131 | 675 | 42 | 123 | |||||||
| Oratosquilla oratoria | 2112 | 6246 | 6939 | 484 | 7023 | 2276 | 2012 | 2805 | 1944 | 1298 | 3567 | 2022 |
| Parapenaeopsis hardwickii | 539 | 1364 | 29 | 55 | 14 | 6 | 142 | 335 | 656 | 1510 | 2799 | |
| Alpheus japonicus | 8 | 57 | 1923 | 4226 | 4106 | 1905 | 634 | 68 | 32 | 81 | ||
| Exopalaemon carinicauda | 27 | 344 | 425 | 642 | 585 | 370 | 45 | 348 | 46 | 41 | ||
| Oratosquilla interrupta | 20 | 838 | 845 | 10 | 18 | 13 | 33 | 16 | ||||
| Dictyosquilla foveolata | 443 | 851 | 112 | 22 | 66 | 337 | 345 | 188 | ||||
| Parapenaeopsis tenella | 558 | 140 | 15 | 5 | 62 | 1370 | ||||||
| Solenocera crassicornis | 1048 | 180 | 726 | 5 | 465 | |||||||
| Erugosquilla woodmasoni | 828 | 81 | ||||||||||
| Eucrate crenata | 392 | 175 | 357 | 940 | 492 | 391 | 1505 | 1777 | 607 | 772 | 1226 | 119 |
| Charybdis japonica | 1066 | 793 | 732 | 1420 | 263 | 223 | 29 | 469 | 349 | 126 | 24 | 175 |
| Portunus trituberculatus | 1406 | 1284 | 1673 | 3206 | 259 | 165 | 79 | 1251 | 1988 | 3795 | 2923 | 1219 |
| Portunus hastatoides | 15 | 43 | 35 | 42 | 148 | 131 | 885 | 21 | 18 | |||
| Charybdis bimaculata | 43 | 488 | 36 | 13 | 46 | 971 | 332 | 8 | ||||
| Portunus sanguinolentus | 462 | 1069 | 2 | 552 | 255 | |||||||
| Portunus pelagicus | 1009 | 768 | 1529 | 128 | 73 | |||||||
| Odontamblyopus rubicundus | 234 | 34 | 414 | 1974 | 519 | 75 | 493 | 400 | 647 | 219 | 762 | 240 |
| Trypanuchen uagina | 49 | 54 | 990 | 1796 | 598 | 385 | 2387 | 4750 | 1141 | 240 | 496 | 41 |
| Cynoglossus semilaevis | 30 | 15 | 468 | 156 | 702 | 85 | 39 | 84 | 29 | 60 | ||
| Johnius belangerii | 126 | 237 | 171 | 501 | 409 | 36 | 57 | 8 | 29 | 6 | ||
| Chaeturichthys stigmatias | 1887 | 4344 | 457 | 1837 | 2285 | 207 | 9 | 776 | 5 | 302 | ||
| Chaeturichthys hexanema | 76 | 585 | 834 | 1106 | 162 | 1466 | 1917 | 1300 | 3018 | 372 | ||
| Harpodou nehereus | 24 | 1424 | 177 | 16 | 89 | 1326 | 300 | 402 | 2328 | |||
| Collichthys lucidus | 6 | 379 | 128 | 487 | 5222 | 6347 | 2308 | 1204 | 581 | |||
| Chrysochir aureus | 40 | 191 | 572 | 718 | 824 | 361 | 23 | 55 | 71 | |||
| Argyrosomus argentatus | 184 | 238 | 10 | 116 | 34 | 5001 | 3310 | 3822 | ||||
| Ilisha elongata | 4234 | 867 | 7 | 13 | 145 | |||||||
| Thrissa mystax | 2908 | 792 | 37 | 8 | 313 | |||||||
| Polydactylus sextarius | 6 | 48 | 1212 | 474 | ||||||||
| Leiognathus ruconius | 2259 | 10 | 6 | |||||||||
| Saurida elongata | 9 | 552 |
| Year | Seawater | Nekton Community Structure | Survey Season | Network Mesh Size (cm) | Trawl Time (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 [65] | Sansha Bay | Fish 94 species | Spring and Autumn | 1.7 | 0.33 |
| 2012–2013 [66] | Taishan Islands | Nekton 136 species, Fish 80 species, Crustaceans 44 species, Cephalopods 9 species | Spring, Summer, Autumn and Winter | 1.3–2.5 | 0.5–1.0 |
| 2014–2015 [63] | Qixing Islands | Nekton 80 species, Fish 52 species, Crustaceans 23 species, Cephalopods 5 species | Spring and Autumn | 2.0 | 0.5 |
| 2016 [64] | Minjiang kou River | Fish 125 species, 13 orders | Spring, Summer, Autumn and Winter | 2.0 | 0.5 |
| 2020 [52] | Qingchuan Bay | Fish 55 species 11 orders 29 families 49 genera | Spring and autumn | 2.0 | 0.5 |
| 2022–2023 (This study) | Qingchuan Bay | 120 species of nekton, 72 species of fish, 23 species of crustaceans, 5 species of cephalopods | Spring, Summer, Autumn and Winter | 2.0 | 0.5 |
| 2023 year [53] | Oujiang River Estuary | 78 species of nekton, 36 species of fish, 28 species of crustaceans, 3 species of cephalopods | Spring and Autumn | 2.0 | 0.5–1.0 |
| Species | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Proportion of Larvae (%) | Min Biomass (kg/km2) | Max Biomass (kg/km2) | Min Abundance (×103 ind./km2) | Maximum Abundance (×103 ind./km2) | Comprehensive Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Argyrosomus argentatus | 50 | 3.34 | 22.08 | 22.90 | 58.27 | *** | ||||||||||||
| Cynoglossus semilaevis | 5 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 5.19 | 5.19 | * | ||||||||||||
| Oratosquilla interrupta | 5 | 0.62 | 1.55 | 3.38 | 13.21 | * | ||||||||||||
| Parapenaeopsis hardwickii | 10 | 1.60 | 9.40 | 5.05 | 35.07 | ** | ||||||||||||
| Portunus sanguinolentus | 0 | 0.57 | 1.43 | 3.71 | 22.78 | * | ||||||||||||
| Loligo beka | 50 | 1.69 | 1.69 | 16.27 | 16.27 | * | ||||||||||||
| Collichthys lucidus | 35 | 0.26 | 5.78 | 5.70 | 67.50 | ** | ||||||||||||
| Exopalaemon carinicauda | 5 | 0.52 | 0.69 | 2.48 | 3.35 | * | ||||||||||||
| Chrysochir aureus | 40 | 0.23 | 0.54 | 2.23 | 4.91 | * | ||||||||||||
| Trypanuchen uagina | 35 | 0.23 | 2.45 | 2.70 | 26.66 | * | ||||||||||||
| Oratosquilla oratoria | 35 | 1.45 | 10.46 | 10.96 | 110.59 | *** | ||||||||||||
| Odontamblyopus rubicundus | 10 | 0.31 | 1.31 | 0.87 | 7.76 | * | ||||||||||||
| Ilisha elongata | 5 | 1.40 | 10.34 | 15.90 | 55.69 | * | ||||||||||||
| Chaeturichthys hexanema | 25 | 0.68 | 5.91 | 2.72 | 6.86 | * | ||||||||||||
| Polydactylus sextarius | 0 | 1.38 | 1.38 | 6.85 | 6.85 | * | ||||||||||||
| Harpodou nehereus | 35 | 0.69 | 5.71 | 12.45 | 42.39 | *** | ||||||||||||
| Eucrate crenata | 5 | 0.32 | 1.75 | 4.50 | 19.79 | ** | ||||||||||||
| Leiognathus ruconius | 0 | 7.82 | 7.82 | 13.29 | 13.29 | * | ||||||||||||
| Chaeturichthys stigmatias | 25 | 1.26 | 4.17 | 4.18 | 18.12 | ** | ||||||||||||
| Portunus hastatoides | 0 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 3.18 | 3.18 | * | ||||||||||||
| Johnius belangerii | 35 | 0.48 | 0.48 | 3.15 | 3.15 | * | ||||||||||||
| Alpheus japonicus | 5 | 1.09 | 6.32 | 1.35 | 9.10 | * | ||||||||||||
| Charybdis japonica | 0 | 0.25 | 1.34 | 5.44 | 23.06 | * | ||||||||||||
| Portunus trituberculatus | 0 | 0.54 | 2.60 | 8.00 | 136.63 | ** | ||||||||||||
| Charybdis bimaculata | 0 | 1.66 | 1.66 | 2.64 | 2.64 | * | ||||||||||||
| Dictyosquilla foveolata | 5 | 1.18 | 1.18 | 17.65 | 17.65 | * | ||||||||||||
| Erugosquilla woodmasoni | 5 | 1.26 | 1.26 | 15.99 | 15.99 | * | ||||||||||||
| Parapenaeopsis tenella | 5 | 0.60 | 2.34 | 0.53 | 3.76 | * | ||||||||||||
| Portunus pelagicus | 0 | 0.32 | 1.22 | 13.04 | 22.19 | * | ||||||||||||
| Saurida elongata | 0 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 6.02 | 6.02 | * | ||||||||||||
| Thrissa mystax | 0 | 1.83 | 7.57 | 8.63 | 34.90 | * | ||||||||||||
| Solenocera crassicornis | 5 | 0.65 | 6.52 | 1.87 | 22.78 | * | ||||||||||||
| low | medium | high | extreme high |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, W.; Zheng, B.; Wen, D.; Wang, F.; Fan, L.; Yu, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhao, S. Community Characteristics and Potential Risk of Nekton in Waters Adjacent to Ningde Nuclear Power Plant in Fujian, China. Biology 2025, 14, 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050481
Huang W, Zheng B, Wen D, Wang F, Fan L, Yu Z, Liu W, Zhao S. Community Characteristics and Potential Risk of Nekton in Waters Adjacent to Ningde Nuclear Power Plant in Fujian, China. Biology. 2025; 14(5):481. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050481
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Wen, Biqi Zheng, Dong Wen, Feipeng Wang, Lijing Fan, Zefeng Yu, Wei Liu, and Shuang Zhao. 2025. "Community Characteristics and Potential Risk of Nekton in Waters Adjacent to Ningde Nuclear Power Plant in Fujian, China" Biology 14, no. 5: 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050481
APA StyleHuang, W., Zheng, B., Wen, D., Wang, F., Fan, L., Yu, Z., Liu, W., & Zhao, S. (2025). Community Characteristics and Potential Risk of Nekton in Waters Adjacent to Ningde Nuclear Power Plant in Fujian, China. Biology, 14(5), 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050481





