Dancing to Another Tune—Adhesive Moonlighting Proteins in Bacteria
Abstract
:1. Introduction—Concept of Moonlighting Proteins
2. Bacterial Moonlighting Proteins Come in Many Forms
| Moonlighting protein | Moonlighting function | Bacterial species | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolic enzymes | |||
| GAPDH | |||
| Binding to plasmin(ogen) | B. anthracis, E. coli, La. crispatus, La. plantarum, Li. monocytogens, S. aureus, St. agalactiae, St. anginosus, St. epidermis, St. equisimilis, St. oralis, St. pneumoniae, St. pyogenes, St. suis | [6,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24] | |
| Binding to urokinase receptor on human pharyngeal cells | St. pyogenes | [25] | |
| Binding to lysozyme | St. pyogenes | [6] | |
| Binding to actin | St. pyogenes, St. agalactiae | [6,22] | |
| Binding to myosin | St. pyogenes | [6] | |
| Binding to albumin | St. suis | [26] | |
| Binding to fibrinogen | St. agalactiae | [22] | |
| Binding to fibronectin | E. coli, L. plantarum, St. pyogenes | [6,14,16,27] | |
| Binding to other bacterial species | Group B Streptococcus, La. crispatus | [28,29] | |
| Binding to intestinal epithelial cells, competitive exclusion and displacement of Clostridium sporogenes and Enterococcus faecalis | La. plantarum | [30] | |
| Coadhesin of Porfyromonas gingivalis in periodontal tissue | St. oralis | [31] | |
| Binding to intestinal epithelial cells | E. coli, La. plantarum | [14,16] | |
| Binding to colonic, porcine or vaginal mucin | La. plantarum, M. genitalium | [16,32,33] | |
| Binding to A and B blood antigens | La. plantarum | [34] | |
| Binding to porcine tracheal rings | St. suis | [35] | |
| EGF-receptor | M. avium, M. tuberculosis | [36] | |
| Binding to C5a complement protein | St. pyogenes | [37] | |
| Enolase | |||
| Binding to plasmin(ogen) | B. anthracis, Bi. animalis subspecies lactis, Bi. bifidum, Bi. breve, Bi. longum, Bo. burgdorferi, La. crispatus, La. johnsonii, La. plantarum, Li. monocytogenes, M. pneumoniae, S. aureus, St. anginosus, St. mutans, St. oralis, S. pneumoniae, S. pyogenes | [16,17,19,21,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48] | |
| Binding to fibronectin | La. plantarum | [16,49] | |
| Binding to laminin | La. crispatus, La. johnsonii, S. aureus | [48,50] | |
| Binding to collagen | La. crispatus, S. aureus | [48] | |
| Binding to albumin | St. pyogenes | [51] | |
| Binding to salivary mucin | St. gordonii, St. mutans | [42,52] | |
| Binding to intestinal epithelial cells | La. plantarum, St. suis | [16,53] | |
| Binding to C4b-binding proteins | St. pneumoniae | [54] | |
| Binding to other bacterial species | La. crispatus | [28] | |
| Aldolase | |||
| Binding to flamingo cadherin | St. pneumoniae | [55] | |
| Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (GPI) | |||
| Binding to collagen | La. crispatus | [28] | |
| Binding to other bacterial species | La. crispatus | [28] | |
| Phosphofructokinase | |||
| Binding to plasmin(ogen) | St. oralis | [19] | |
| Phosphoglycerate kinase | |||
| Binding to plasmin(ogen) | St. anginosus, St. oralis, Group B streptococci | [19,56] | |
| Binding to actin | Group B streptococci | [56,57] | |
| Phosphoglycerate mutase | |||
| Binding to plasmin(ogen) | Bi. animalis subspecies lactis, St. anginosus, St. oralis | [19,58] | |
| Triosephosphate isomerase | |||
| Binding to plasmin(ogen) | St. anginosus, St. oralis | [19] | |
| Binding to intestinal epithelial cells, competitive exclusion and displacement of Clostridium sporogenes and Enterococcus faecalis | La. plantarum | [30] | |
| Glutamine synthetase | |||
| Binding to plasmin(ogen) | Bi. animalis subspecies lactis, La. crispatus, M. tuberculosis | [28,58,59] | |
| Binding to fibronectin | M. tuberculosis | [59] | |
| Binding to collagen I and laminin | La. crispatus | [28] | |
| Binding to other bacterial species | La. crispatus | [28] | |
| Ribonucleotide reductase | |||
| Binding to plasmin(ogen) | S. aureus | [44] | |
| Inosine 5′-monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) | |||
| Binding to plasmin(ogen) | S. aureus | [44] | |
| Alcohol acetaldehyde dehydrogenase | |||
| Binding to Caco-2 cells | Li. monocytogenes | [60] | |
| Binding to eukaryotic Hsp60 | Li. monocytogenes | [61] | |
| Malate synthase | |||
| Binding to laminin and fibronectin | M. tuberculosis | [62] | |
| SarA; oligopeptide-binding protein | |||
| Binding to salivary mucin | St. gordonii | [52] | |
| Pyruvate dehydrogenase | |||
| Binding to fibronectin | La. plantarum | [47] | |
| Binding to plasmin(ogen) | M. pneumoniae | [46] | |
| Binding to fibronectin | M. pneumoniae | [63] | |
| Puryvate kinase | |||
| Binding to salivary mucin | St. gordonii | [52] | |
| Bile salt hydrolase | |||
| Binding to plasmin(ogen) | Bi. animalis subspecies lactis | [58] | |
| Molecular chaperones | |||
| DnaK | |||
| Binding to plasmin(ogen) | Bi. animalis subspecies lactis, M. tuberculosis, Li. monocytogenes | [21,58,59,64] | |
| Stimulation of dendritic cell maturation by binding CCR5 | M. tuberculosis | [65] | |
| Competition with HIVfor CCR5 binding | M. tuberculosis | [65,66] | |
| Mediation of LAB adherence to yeast cells | L. lactis | [67] | |
| GroEL | |||
| Binding to intestinal HT-29 cells and mucus; stimulation of IL-8 secretion in human macrophages and HT-29 cells; aggregation of H. pylori cells | La. johnsonii | [68] | |
| Translational elongational factors | |||
| EF-Tu | |||
| Binding to plasmin(ogen) | Li. monocytogenes, Ps. aeruginosa | [21,69] | |
| Binding to plasma Factor H and Factor H-related protein 1 (FHR-1) | Ps. aeruginosa | [69] | |
| Binding to intestinal epithelial cells and HT-MTX-derived mucus | La. johnsonii | [70] | |
| Binding to salivary mucin | St. gordonii | [52] | |
| Binding to intestinal epithelial cells, competitive exclusion and displacement of Clostridium sporogenes and Enterococcus faecalis | La. plantarum | [30] | |
| Binding to fibronectin | M. pneumoniae | [63] | |
| EF-G | |||
| Binding to salivary mucin | St. gordonii | [52] | |
| Other proteins | |||
| Ag85 complex of M. tuberculosis | |||
| Binding of plasmi(ogen) | M. tuberculosis | [59] | |
| Binding to fibronectin | M. tuberculosis | [59] | |
| DNA-directed RNA polymerase beta´subunit | |||
| Binding to salivary mucin | St. gordonii | [52] | |
| Endopeptidase O | |||
| Binding of plasmin(ogen) | St. pneumoniae | [71] | |
| Binding to fibronectin | St. pneumoniae | [71] | |
| Binding and invasion to epithelial and endothelial cells | St. pneumoniae | [71] | |
| SecA | |||
| Binding to salivary mucin | St. gordonii | [52] | |
| Superoxide dismutase | |||
| Binding to epithelial cell ldolase, GAPDH and cyclophilin A | M. avidum | [72] | |
3. How Can the Separate Functions Be Arranged in a Moonlighting Protein?
4. Are Moonlighting Proteins Secreted or Are They Released from Traumatized Cells?
5. Adhesive Properties in Bacterial Moonlighting Proteins
5.1. GAPDH
5.2. Enolase
5.3. Molecular Chaperones
6. Moonlighting Proteins of Lactobacilli: Ionic Interactions Are Important in Anchorage and Activity

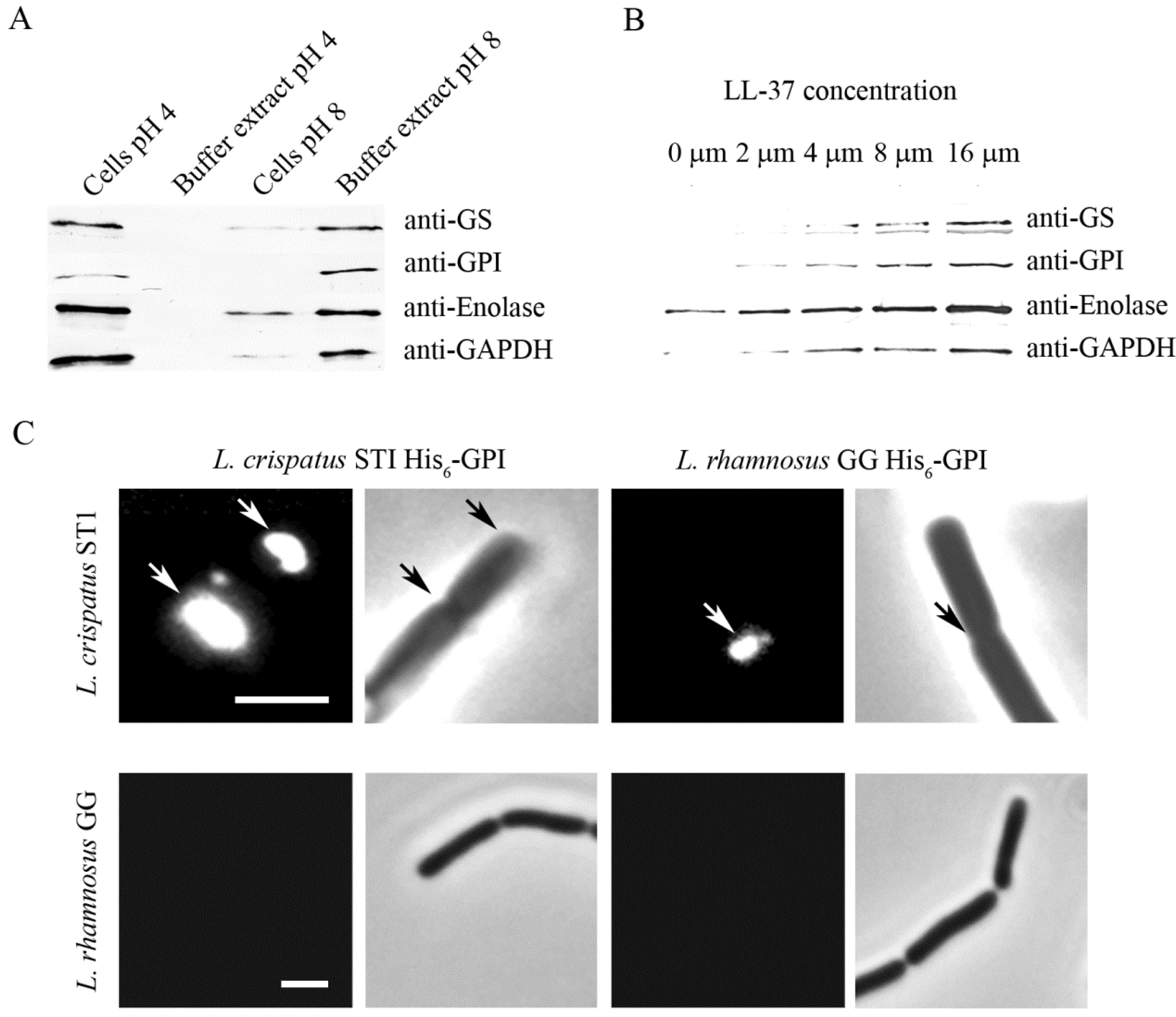
7. Adhesive Moonlighting Goes in Several Directions: Multitasking in Fimbriae, Flagella, and Surface Proteases
8. Conclusions

Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Copley, S.D. Moonlighting is Mainstream: Paradigm Adjustment Required. Bioessays 2012, 34, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompa, P.; Szasz, C.; Buday, L. Structural Disorder Throws New Light on Moonlighting. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005, 30, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaput, M.; Claes, V.; Portetelle, D.; Cludts, I.; Cravador, A.; Burny, A.; Gras, H.; Tartar, A. The Neurotrophic Factor Neuroleukin is 90% Homologous with Phosphohexose Isomerase. Nature 1988, 332, 454–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wistow, G.J.; Lietman, T.; Williams, L.A.; Stapel, S.O.; de Jong, W.W.; Horwitz, J.; Piatigorsky, J. Tau-crystallin/alpha-Enolase: One Gene Encodes both an Enzyme and a Lens Structural Protein. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 107, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworschack, R.G.; Wickerham, L.J. Production of Extracellular and Total Invertase by Candida Utilis, Saccharomyces Cerevisiae, and Other Yeasts. Appl. Microbiol. 1961, 9, 291–294. [Google Scholar]
- Pancholi, V.; Fischetti, V.A. A Major Surface Protein on Group A Streptococci is a Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate-Dehydrogenase with Multiple Binding Activity. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 176, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commichau, F.M.; Rothe, F.M.; Herzberg, C.; Wagner, E.; Hellwig, D.; Lehnik-Habrink, M.; Hammer, E.; Volker, U.; Stulke, J. Novel Activities of Glycolytic Enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: Interactions with Essential Proteins Involved in mRNA Processing. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2009, 8, 1350–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huberts, D.H.; van der Klei, I.J. Moonlighting Proteins: An Intriguing Mode of Multitasking. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1803, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, C.J. Moonlighting Proteins—An Update. Mol. Biosyst. 2009, 5, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, B.; Martin, A. Bacterial Virulence in the Moonlight: Multitasking Bacterial Moonlighting Proteins are Virulence Determinants in Infectious Disease. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 3476–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, A.; Hernandez, S.; Amela, I.; Pinol, J.; Cedano, J.; Querol, E. Do Protein-Protein Interaction Databases Identify Moonlighting Proteins? Mol. Biosyst. 2011, 7, 2379–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Chitale, M.; Rayon, C.; Kihara, D. Evaluation of Function Predictions by PFP, ESG, and PSI-BLAST for Moonlighting Proteins. BMC Proc. 2012, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, S.; Rohde, M.; Chhatwal, G.S.; Hammerschmidt, S. Characterization of Plasmin(Ogen) Binding to Streptococcus pneumoniae. Indian J. Med. Res. 2004, 119, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Egea, L.; Aguilera, L.; Gimenez, R.; Sorolla, M.A.; Aguilar, J.; Badia, J.; Baldoma, L. Role of Secreted Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase in the Infection Mechanism of Enterohemorrhagic and Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli: Interaction of the Extracellular Enzyme with Human Plasminogen and Fibrinogen. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 1190–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gase, K.; Gase, A.; Schirmer, H.; Malke, H. Cloning, Sequencing and Functional Overexpression of the Streptococcus equisimilis H46A gapC Gene Encoding a Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase that also Functions as a Plasmin(Ogen)-Binding Protein. Purification and Biochemical Characterization of the Protein. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 239, 42–51. [Google Scholar]
- Glenting, J.; Beck, H.C.; Vrang, A.; Riemann, H.; Ravn, P.; Hansen, A.M.; Antonsson, M.; Ahrne, S.; Israelsen, H.; Madsen, S. Anchorless Surface Associated Glycolytic Enzymes from Lactobacillus plantarum 299v Bind to Epithelial Cells and Extracellular Matrix Proteins. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurmalainen, V.; Edelman, S.; Antikainen, J.; Baumann, M.; Lähteenmäki, K.; Korhonen, T.K. Extracellular Proteins of Lactobacillus crispatus enhance Activation of Human Plasminogen. Microbiology 2007, 153, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobin, M.C.; Brassard, J.; Quessy, S.; Gottschalk, M.; Grenier, D. Acquisition of Host Plasmin Activity by the Swine Pathogen Streptococcus suis Serotype 2. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnby, B.; Booth, N.A.; Svensater, G. Plasminogen Binding by Oral Streptococci from Dental Plaque and Inflammatory Lesions. Microbiology 2008, 154, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modun, B.; Williams, P. The Staphylococcal Transferrin-Binding Protein is a Cell Wall Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar]
- Schaumburg, J.; Diekmann, O.; Hagendorff, P.; Bergmann, S.; Rohde, M.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Jänsch, L.; Wehland, J.; Kärst, U. The Cell Wall Subproteome of Listeria monocytogenes. Proteomics 2004, 4, 2991–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, K.N.; McArthur, W.P.; Bleiweis, A.S.; Brady, L.J. Characterization of Group B Streptococcal Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase: Surface Localization, Enzymatic Activity, and Protein-Protein Interactions. Can. J. Microbiol. 2003, 49, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winram, S.B.; Lottenberg, R. The Plasmin-Binding Protein Plr of Group A Streptococci is Identified as Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase. Microbiology 1996, 142, 2311–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, S.K.; Agarwal, S.; Bhatnagar, R. Surface Localized and Extracellular Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase of Bacillus anthracis is a Plasminogen Binding Protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1804, 2111–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Song, Y.P.; Boel, G.; Kochar, J.; Pancholi, V. Group A Streptococcal Surface GAPDH, SDH, Recognizes uPAR/CD87 as its Receptor on the Human Pharyngeal Cell and Mediates Bacterial Adherence to Host Cells. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 350, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quessy, S.; Busque, P.; Higgins, R.; Jacques, M.; Dubreuil, J.D. Description of an Albumin Binding Activity for Streptococcus suis Serotype 2. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1997, 147, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, B.; Schmitter, J.M.; Urdaci, M.C. Identification of Novel Proteins Secreted by Lactobacillus plantarum that Bind to Mucin and Fibronectin. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 17, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainulainen, V.; Loimaranta, V.; Pekkala, A.; Edelman, S.; Antikainen, J.; Kylväjä, R.; Laaksonen, M.; Laakkonen, L.; Finne, J.; Korhonen, T.K. Glutamine Synthetase and Glucose-6-Phosphate Isomerase are Adhesive Moonlighting Proteins of Lactobacillus crispatus Released by Epithelial Cathelicidin LL-37. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 2509–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.; Madureira, P.; Andrade, E.B.; Bouaboud, A.; Morello, E.; Ferreira, P.; Poyart, C.; Trieu-Cuot, P.; Dramsi, S. Group B Streptococcus GAPDH is Released upon Cell Lysis, Associates with Bacterial Surface, and Induces Apoptosis in Murine Macrophages. PLoS One 2012, 7, e29963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramiah, K.; van Reenen, C.A.; Dicks, L.M. Surface-Bound Proteins of Lactobacillus plantarum 423 that Contribute to Adhesion of Caco-2 Cells and their Role in Competitive Exclusion and Displacement of Clostridium Sporogenes and Enterococcus Faecalis. Res. Microbiol. 2008, 159, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Nagata, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Tanaka, J.; Minamino, N.; Shizukuishi, S. Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase of Streptococcus oralis Functions as a Coadhesin for Porphyromonas gingivalis Major Fimbriae. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, H.; Uchida, H.; Kawai, Y.; Kawasaki, T.; Wakahara, N.; Matsuo, H.; Watanabe, M.; Kitazawa, H.; Ohnuma, S.; Miura, K.; et al. Cell Surface Lactobacillus plantarum LA 318 Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (GAPDH) Adheres to Human Colonic Mucin. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.A.; Blaylock, M.W.; Baseman, J.B. Surface Localized Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase of Mycoplasma genitalium Binds Mucin. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 48, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, H.; Wakahara, N.; Watanabe, M.; Kawasaki, T.; Matsuo, H.; Kawai, Y.; Kitazawa, H.; Ohnuma, S.; Miura, K.; Horii, A.; et al. Cell Surface Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (GAPDH) of Lactobacillus plantarum LA 318 Recognizes Human A and B Blood Group Antigens. Res. Microbiol. 2008, 159, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassard, J.; Gottschalk, M.; Quessy, S. Cloning and Purification of the Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase and its Involvement as an Adhesin. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 102, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez, L.E.; Petrofsky, M.; Shelton, K. Epidermal Growth Factor-Binding Protein in Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A Possible Role in the Mechanism of Infection. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 2917–2922. [Google Scholar]
- Terao, Y.; Yamaguchi, M.; Hamada, S.; Kawabata, S. Multifunctional Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase of Streptococcus pyogenes is Essential for Evasion from Neutrophils. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 14215–14223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Kulshreshtha, P.; Bambah Mukku, D.; Bhatnagar, R. Alpha-Enolase Binds to Human Plasminogen on the Surface of Bacillus anthracis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1784, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, S.; Rohde, M.; Chhatwal, G.S.; Hammerschmidt, S. Alpha-Enolase of Streptococcus pneumoniae is a Plasmin(Ogen)-Binding Protein Displayed on the Bacterial Cell Surface. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 40, 1273–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, M.; Biagi, E.; Centanni, M.; Turroni, S.; Vici, M.; Musiani, F.; Vitali, B.; Bergmann, S.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Brigidi, P. Bifidobacterial Enolase, a Cell Surface Receptor for Human Plasminogen Involved in the Interaction with the Host. Microbiology 2009, 155, 3294–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floden, A.M.; Watt, J.A.; Brissette, C.A. Borrelia burgdorferi Enolase is a Surface-Exposed Plasminogen Binding Protein. PLoS One 2011, 6, e27502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Catt, D.M.; Gregory, R.L. Streptococcus mutans Surface Alpha-Enolase Binds Salivary Mucin MG2 and Human Plasminogen. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 6748–6752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itzek, A.; Gillen, C.M.; Fulde, M.; Friedrichs, C.; Rodloff, A.C.; Chhatwal, G.S.; Nitsche-Schmitz, D.P. Contribution of Plasminogen Activation Towards the Pathogenic Potential of Oral Streptococci. PLoS One 2010, 5, e13826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mölkänen, T.; Tyynelä, J.; Helin, J.; Kalkkinen, N.; Kuusela, P. Enhanced Activation of Bound Plasminogen on Staphylococcus aureus by Staphylokinase. FEBS Lett. 2002, 517, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancholi, V.; Fischetti, V.A. Alpha-Enolase, a Novel Strong Plasmin(Ogen) Binding Protein on the Surface of Pathogenic Streptococci. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 14503–14515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Jacobs, E.; Dumke, R. Characterization of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Subunit B and Enolase as Plasminogen-Binding Proteins in Mycoplasma Pneumoniae. Microbiology 2013, 159, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastano, V.; Capri, U.; Candela, M.; Siciliano, R.A.; Russo, L.; Renda, M.; Sacco, M. Identification of Binding Sites of Lactobacillus plantarum Enolase Involved in the Interaction with Human Plasminogen. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antikainen, J.; Kuparinen, V.; Lähteenmäki, K.; Korhonen, T.K. Enolases from Gram-Positive Bacterial Pathogens and Commensal Lactobacilli Share Functional Similarity in Virulence-Associated Traits. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 51, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldo, C.; Vastano, V.; Siciliano, R.A.; Candela, M.; Vici, M.; Muscariello, L.; Marasco, R.; Sacco, M. Surface Displaced Alfa-Enolase of Lactobacillus plantarum is a Fibronectin Binding Protein. Microb. Cell. Fact. 2009, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, C.R.; Postol, E.; Nomizo, R.; Reis, L.F.; Brentani, R.R. Identification of Enolase as a Laminin-Binding Protein on the Surface of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbes Infect. 2004, 6, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornblatt, M.J.; Kornblatt, J.A.; Hancock, M.A. The Interaction of Canine Plasminogen with Streptococcus Pyogenes Enolase: They Bind to One another but what is the Nature of the Structures Involved? PLoS One 2011, 6, e28481. [Google Scholar]
- Kesimer, M.; Kilic, N.; Mehrotra, R.; Thornton, D.J.; Sheehan, J.K. Identification of Salivary Mucin MUC7 Binding Proteins from Streptococcus gordonii. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Pan, X.; Sun, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Shao, Z.; Ge, J.; Zheng, F.; et al. Streptococcus suis Enolase Functions as a Protective Antigen Displayed on the Bacterial Cell Surface. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Malm, S.; Bergmann, S.; Riesbeck, K.; Blom, A.M. Enolase of Streptococcus pneumoniae Binds Human Complement Inhibitor C4b-Binding Protein and Contributes to Complement Evasion. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 3575–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, K.; Portnoi, M.; Shagan, M.; Kaganovich, A.; Rom, S.; Kafka, D.; Chalifa Caspi, V.; Porgador, A.; Givon-Lavi, N.; Gershoni, J.M.; et al. Flamingo Cadherin: A Putative Host Receptor for Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 195, 1828–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, T.J.; Burnham, C.A.; Tyrrell, G.J. Binding of Group B Streptococcal Phosphoglycerate Kinase to Plasminogen and Actin. Microb. Pathog. 2011, 51, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, C.A.; Shokoples, S.E.; Tyrrell, G.J. Phosphoglycerate Kinase Inhibits Epithelial Cell Invasion by Group B Streptococci. Microb. Pathog. 2005, 38, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, M.; Bergmann, S.; Vici, M.; Vitali, B.; Turroni, S.; Eikmanns, B.J.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Brigidi, P. Binding of Human Plasminogen to Bifidobacterium. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 5929–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xolalpa, W.; Vallecillo, A.J.; Lara, M.; Mendoza-Hernandez, G.; Comini, M.; Spallek, R.; Singh, M.; Espitia, C. Identification of Novel Bacterial Plasminogen-Binding Proteins in the Human Pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proteomics 2007, 7, 3332–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeesan, B.; Koo, O.K.; Kim, K.P.; Burkholder, K.M.; Mishra, K.K.; Aroonnual, A.; Bhunia, A.K. LAP, an Alcohol Acetaldehyde Dehydrogenase Enzyme in Listeria, Promotes Bacterial Adhesion to Enterocyte-Like Caco-2 Cells Only in Pathogenic Species. Microbiology 2010, 156, 2782–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.P.; Jagadeesan, B.; Burkholder, K.M.; Jaradat, Z.W.; Wampler, J.L.; Lathrop, A.A.; Morgan, M.T.; Bhunia, A.K. Adhesion Characteristics of Listeria Adhesion Protein (LAP)-Expressing Escherichia coli to Caco-2 Cells and of Recombinant LAP to Eukaryotic Receptor Hsp60 as Examined in a Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 256, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinhikar, A.G.; Vargas, D.; Li, H.; Mahaffey, S.B.; Hinds, L.; Belisle, J.T.; Laal, S. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Malate Synthase is a Laminin-Binding Adhesin. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 60, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallo, S.F.; Kannan, T.R.; Blaylock, M.W.; Baseman, J.B. Elongation Factor Tu and E1 Beta Subunit of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex Act as Fibronectin Binding Proteins in Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 46, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, M.; Centanni, M.; Fiori, J.; Biagi, E.; Turroni, S.; Orrico, C.; Bergmann, S.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Brigidi, P. DnaK from Bifidobacterium animalis Subsp. lactis is a Surface-Exposed Human Plasminogen Receptor Upregulated in Response to Bile Salts. Microbiology 2010, 156, 1609–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floto, R.A.; MacAry, P.A.; Boname, J.M.; Mien, T.S.; Kampmann, B.; Hair, J.R.; Huey, O.S.; Houben, E.N.; Pieters, J.; Day, C.; et al. Dendritic Cell Stimulation by Mycobacterial Hsp70 is Mediated through CCR5. Science 2006, 314, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaahmady, K.; Oehlmann, W.; Singh, M.; Lehner, T. Inhibition of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection of Human CD4+ T Cells by Microbial HSP70 and the Peptide Epitope 407–426. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 3354–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katakura, Y.; Sano, R.; Hashimoto, T.; Ninomiya, K.; Shioya, S. Lactic Acid Bacteria Display on the Cell Surface Cytosolic Proteins that Recognize Yeast Mannan. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergonzelli, G.E.; Granato, D.; Pridmore, R.D.; Marvin-Guy, L.F.; Donnicola, D.; Corthésy-Theulaz, I.E. GroEL of Lactobacillus johnsonii La1 (NCC 533) is Cell Surface Associated: Potential Role in Interactions with the Host and the Gastric Pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunert, A.; Losse, J.; Gruszin, C.; Huhn, M.; Kaendler, K.; Mikkat, S.; Volke, D.; Hoffmann, R.; Jokiranta, T.S.; Seeberger, H.; et al. Immune Evasion of the Human Pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Elongation Factor Tuf is a Factor H and Plasminogen Binding Protein. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 2979–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Granato, D.; Bergonzelli, G.E.; Pridmore, R.D.; Marvin, L.; Rouvet, M.; Corthésy-Theulaz, I.E. Cell Surface-Associated Elongation Factor Tu Mediates the Attachment of Lactobacillus johnsonii NCC533 (La1) to Human Intestinal Cells and Mucins. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 2160–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Kuchipudi, A.; Fulde, M.; Riesbeck, K.; Bergmann, S.; Blom, A.M. Streptococcus pneumoniae Endopeptidase O (PepO) is a Multifunctional Plasminogen- and Fibronectin-Binding Protein, Facilitating Evasion of Innate Immunity and Invasion of Host Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 6849–6863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.M.; Suleman, F.G. Mycobacterium avium-Superoxide Dismutase Binds to Epithelial Cell Aldolase, Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase and Cyclophilin A. Microb. Pathog. 2004, 36, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, C.J. Mass Spectrometry and the Search for Moonlighting Proteins. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2005, 24, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, S.; Wild, D.; Diekmann, O.; Frank, R.; Bracht, D.; Chhatwal, G.S.; Hammerschmidt, S. Identification of a Novel Plasmin(Ogen)-Binding Motif in Surface Displayed Alpha-Enolase of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 49, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cork, A.J.; Jergic, S.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Kobe, B.; Pancholi, V.; Benesch, J.L.; Robinson, C.V.; Dixon, N.E.; Aquilina, J.A.; Walker, M.J. Defining the Structural Basis of Human Plasminogen Binding by Streptococcal Surface Enolase. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 17129–17137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehinger, S.; Schubert, W.D.; Bergmann, S.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Heinz, D.W. Plasmin(Ogen)-Binding Alpha-Enolase from Streptococcus pneumoniae: Crystal Structure and Evaluation of Plasmin(Ogen)-Binding Sites. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 343, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pridmore, R.D.; Berger, B.; Desiere, F.; Vilanova, D.; Barretto, C.; Pittet, A.C.; Zwahlen, M.C.; Rouvet, M.; Altermann, E.; Barrangou, R.; et al. The Genome Sequence of the Probiotic Intestinal Bacterium Lactobacillus johnsonii NCC 533. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2512–2517. [Google Scholar]
- Siezen, R.J.; Francke, C.; Renckens, B.; Boekhorst, J.; Wels, M.; Kleerebezem, M.; van Hijum, S.A. Complete Resequencing and Reannotation of the Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 Genome. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewthwaite, J.; Skinner, A.; Henderson, B. Are Molecular Chaperones Microbial Virulence Factors? Trends Microbiol. 1998, 6, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Henderson, B.; Lund, P.A.; Tormay, P.; Ahmed, M.T.; Gurcha, S.S.; Besra, G.S.; Coates, A.R. A Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mutant Lacking the groEL Homologue cpn60.1 is Viable but Fails to Induce an Inflammatory Response in Animal Models of Infection. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cehovin, A.; Coates, A.R.; Hu, Y.; Riffo-Vasquez, Y.; Tormay, P.; Botanch, C.; Altare, F.; Henderson, B. Comparison of the Moonlighting Actions of the Two Highly Homologous Chaperonin 60 Proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 3196–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, T.B.; Thorson, L.M.; Speert, D.P.; Daffe, M.; Stokes, R.W. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Cpn60.2 and DnaK are Located on the Bacterial Surface, Where Cpn60.2 Facilitates Efficient Bacterial Association with Macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 3389–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, T.B.; Ziltener, H.J.; Speert, D.P.; Stokes, R.W. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Employs Cpn60.2 as an Adhesin that Binds CD43 on the Macrophage Surface. Cell. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1634–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewthwaite, J.C.; Coates, A.R.; Tormay, P.; Singh, M.; Mascagni, P.; Poole, S.; Roberts, M.; Sharp, L.; Henderson, B. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Chaperonin 60.1 is a More Potent Cytokine Stimulator than Chaperonin 60.2 (Hsp 65) and Contains a CD14-Binding Domain. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 7349–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancholi, V.; Chhatwal, G.S. Housekeeping Enzymes as Virulence Factors for Pathogens. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 293, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boël, G.; Jin, H.; Pancholi, V. Inhibition of Cell Surface Export of Group A Streptococcal Anchorless Surface Dehydrogenase Affects Bacterial Adherence and Antiphagocytic Properties. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 6237–6248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boël, G.; Pichereau, V.; Mijakovic, I.; Mazé, A.; Poncet, S.; Gillet, S.; Giard, J.C.; Hartke, A.; Auffray, Y.; Deutscher, J. Is 2-Phosphoglycerate-Dependent Automodification of Bacterial Enolases Implicated in their Export? J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 337, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.K.; Ewis, H.E.; Zhang, X.; Lu, C.D.; Hu, H.J.; Pan, Y.; Abdelal, A.T.; Tai, P.C. Nonclassical Protein Secretion by Bacillus subtilis in the Stationary Phase is Not due to Cell Lysis. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 5607–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, L.L.; Mohammadi, S.; Geissler, A.; Portnoy, D.A. SecA2-Dependent Secretion of Autolytic Enzymes Promotes Listeria monocytogenes Pathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12432–12437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, K.; Bron, S.; Harwood, C.R. Cellular Lysis in Bacillus subtilis; the Affect of Multiple Extracellular Protease Deficiencies. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 29, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, N.; Urdaci, M.; Vignoles, C.; Chaignepain, S.; Tallon, R.; Schmitter, J.M.; Bressollier, P. Lactobacillus plantarum 299v Surface-Bound GAPDH: A New Insight into Enzyme Cell Walls Location. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 19, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antikainen, J.; Hurmalainen, V.; Lähteenmäki, K.; Korhonen, T.K. PH-Dependent Association of Enolase and GAPDH of Lactobacillus crispatus with the Cell Wall and Lipoteichoic Acids. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 4539–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugher, J.L.; Klaenhammer, T.R. Invited Review: Application of Omics Tools to Understanding Probiotic Functionality. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 4753–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corr, S.C.; Hill, C.; Gahan, C.G. Understanding the Mechanisms by which Probiotics Inhibit Gastrointestinal Pathogens. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2009, 56, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servin, A.L. Antagonistic Activities of Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria Against Microbial Pathogens. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 28, 405–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, C.; van Hylckama Vlieg, J.E.; Janssen, D.B.; Busscher, H.J.; van der Mei, H.C.; Reid, G. Purification and Characterization of a Surface-Binding Protein from Lactobacillus fermentum RC-14 that Inhibits Adhesion of Enterococcus faecalis 1131. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 190, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurbeck, R.R.; Arvidson, C.G. Lactobacillus jensenii Surface-Associated Proteins Inhibit Neisseria gonorrhoeae Adherence to Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 3103–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Ploplis, V.A.; Castellino, F.J. Bacterial Plasminogen Receptors Utilize Host Plasminogen System for Effective Invasion and Dissemination. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lähteenmäki, K.; Edelman, S.; Korhonen, T.K. Bacterial Metastasis: The Host Plasminogen System in Bacterial Invasion. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesarman-Maus, G.; Hajjar, K.A. Molecular Mechanisms of Fibrinolysis. Br. J. Haematol. 2005, 129, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson-Smith, M.L.; de Oliveira, D.M.; Ranson, M.; McArthur, J.D. Bacterial Plasminogen Receptors: Mediators of a Multifaceted Relationship. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemens, N.; Patenge, N.; Otto, J.; Fiedler, T.; Kreikemeyer, B. Streptococcus pyogenes M49 plasminogen/plasmin Binding Facilitates Keratinocyte Invasion Via Integrin-Integrin-Linked Kinase (ILK) Pathways and Protects from Macrophage Killing. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 21612–21622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluskota, E.; Soloviev, D.A.; Bdeir, K.; Cines, D.B.; Plow, E.F. Integrin alphaMbeta2 Orchestrates and Accelerates Plasminogen Activation and Fibrinolysis by Neutrophils. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 18063–18072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attali, C.; Durmort, C.; Vernet, T.; di Guilmi, A.M. The Interaction of Streptococcus pneumoniae with Plasmin Mediates Transmigration Across Endothelial and Epithelial Monolayers by Intercellular Junction Cleavage. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 5350–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, S.; Schoenen, H.; Hammerschmidt, S. The Interaction between Bacterial Enolase and Plasminogen Promotes Adherence of Streptococcus pneumoniae to Epithelial and Endothelial Cells. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 303, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Agarwal, S.; Agarwal, S.; Pancholi, V. Surface Export of GAPDH/SDH, a Glycolytic Enzyme, is Essential for Streptococcus pyogenes Virulence. MBio 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancholi, V.; Fischetti, V.A. Regulation of the Phosphorylation of Human Pharyngeal Cell Proteins by Group A Streptococcal Surface Dehydrogenase: Signal Transduction between Streptococci and Pharyngeal Cells. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 186, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madureira, P.; Baptista, M.; Vieira, M.; Magalhães, V.; Camelo, A.; Oliveira, L.; Ribeiro, A.; Tavares, D.; Trieu-Cuot, P.; Vilanova, M.; et al. Streptococcus agalactiae GAPDH is a Virulence-Associated Immunomodulatory Protein. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, E.; Feldman, G.; Portnoi, M.; Dagan, R.; Overweg, K.; Mulholland, F.; Chalifa-Caspi, V.; Wells, J.; Mizrachi-Nebenzahl, Y. Glycolytic Enzymes Associated with the Cell Surface of Streptococcus pneumoniae are Antigenic in Humans and Elicit Protective Immune Responses in the Mouse. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 138, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhard, T.; Kronvall, G.; Ullberg, M. Surface Bound Plasmin Promotes Migration of Streptococcus pneumoniae through Reconstituted Basement Membranes. Microb. Pathog. 1999, 26, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, S.; Rohde, M.; Preissner, K.T.; Hammerschmidt, S. The Nine Residue Plasminogen-Binding Motif of the Pneumococcal Enolase is the Major Cofactor of Plasmin-Mediated Degradation of Extracellular Matrix, Dissolution of Fibrin and Transmigration. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 94, 304–311. [Google Scholar]
- Dinis, M.; Tavares, D.; Veiga-Malta, I.; Fonseca, A.J.; Andrade, E.B.; Trigo, G.; Ribeiro, A.; Videira, A.; Cabrita, A.M.; Ferreira, P. Oral Therapeutic Vaccination with Streptococcus sobrinus Recombinant Enolase Confers Protection Against Dental Caries in Rats. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kelly, C.G.; Karttunen, J.T.; Whittall, T.; Lehner, P.J.; Duncan, L.; MacAry, P.; Younson, J.S.; Singh, M.; Oehlmann, W.; et al. CD40 is a Cellular Receptor Mediating Mycobacterial Heat Shock Protein 70 Stimulation of CC-Chemokines. Immunity 2001, 15, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, E.E.; de Vries, M.C.; Zoetendal, E.G.; Ben-Amor, K.; Akkermans, A.D.; de Vos, W.M. The Intestinal LABs. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2002, 82, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, B.; Schmitter, J.M.; Urdaci, M.C. Identification of Novel Proteins Secreted by Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Grown in De Mann-Rogosa-Sharpe Broth. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 48, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G. Lactobacillus in the Vagina: Why, how, which ones, and what do they do? In Lactobacillus Molecular Biology from Genomics to Probiotics; Ljungh, Å., Wadström, T., Eds.; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2009; p. 183. [Google Scholar]
- Durr, U.H.; Sudheendra, U.S.; Ramamoorthy, A. LL-37, the Only Human Member of the Cathelicidin Family of Antimicrobial Peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1758, 1408–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleytr, U.B.; Beveridge, T.J. Bacterial S-Layers. Trends Microbiol. 1999, 7, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierne, H.; Dramsi, S. Spatial Positioning of Cell Wall-Anchored Virulence Factors in Gram-Positive Bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, A.J.; Vollmer, W. The Physiology of Bacterial Cell Division. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1277, 8–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutkenhaus, J. The ParA/MinD Family Puts Things in their Place. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, G.; Kleinman, H.K.; George, J.; Arnaoutova, I. Multiple Uses of Basement Membrane-Like Matrix (BME/Matrigel) in vitro and in vivo with Cancer Cells. Int. J. Canc. 2011, 128, 1751–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, S.; Jonsson, H. A High-Molecular-Mass Cell-Surface Protein from Lactobacillus reuteri 1063 Adheres to Mucus Components. Microbiology 2002, 148, 433–442. [Google Scholar]
- Sochacki, K.A.; Barns, K.J.; Bucki, R.; Weisshaar, J.C. Real-Time Attack on Single Escherichia coli Cells by the Human Antimicrobial Peptide LL-37. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E77–E81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenbaum, Z.; Green, B.D.; Scott, J.R. Iron Starvation Causes Release from the Group A Streptococcus of the ADP-Ribosylating Protein Called Plasmin Receptor Or Surface Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate-Dehydrogenase. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 1956–1960. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, K.A.; Dodson, K.W.; Caparon, M.G.; Hultgren, S.J. A Tale of Two Pili: Assembly and Function of Pili in Bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proft, T.; Baker, E.N. Pili in Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Bacteria—Structure, Assembly and their Role in Disease. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 613–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkonen, M.; Saarela, S.; Lähteenmäki, K.; Hynönen, U.; Westerlund-Wikstrom, B.; Rhen, M.; Korhonen, T.K. Identification of Two Laminin-Binding Fimbriae, the Type 1 Fimbria of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium and the G Fimbria of Escherichia coli, as Plasminogen Receptors. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 4965–4970. [Google Scholar]
- Lähteenmäki, K.; Kuusela, P.; Korhonen, T.K. Bacterial Plasminogen Activators and Receptors. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 25, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkkinen, J.; Hacker, J.; Korhonen, T.K. Enhancement of Tissue Plasminogen Activator-Catalyzed Plasminogen Activation by Escherichia coli S Fimbriae Associated with Neonatal Septicaemia and Meningitis. Thromb. Haemost. 1991, 65, 483–486. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Nasr, A.; Olsen, A.; Sjobring, U.; Muller-Esterl, W.; Bjorck, L. Assembly of Human Contact Phase Proteins and Release of Bradykinin at the Surface of Curli-Expressing Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 20, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lähteenmäki, K.; Westerlund, B.; Kuusela, P.; Korhonen, T.K. Immobilization of Plasminogen on Escherichia Coli Flagella. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1993, 106, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucior, I.; Pielage, J.F.; Engel, J.N. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pili and Flagella Mediate Distinct Binding and Signaling Events at the Apical and Basolateral Surface of Airway Epithelium. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharfman, A.; Arora, S.K.; Delmotte, P.; van Brussel, E.; Mazurier, J.; Ramphal, R.; Roussel, P. Recognition of Lewis x Derivatives Present on Mucins by Flagellar Components of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 5243–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, R.W.; Reeve, K.E.; Gunn, J.S. Flagellated but Not Hyperfimbriated Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Attaches to and Forms Biofilms on Cholesterol-Coated Surfaces. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 2981–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giron, J.A.; Torres, A.G.; Freer, E.; Kaper, J.B. The Flagella of Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Mediate Adherence to Epithelial Cells. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 44, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, A.L.; Avelino, F.; Xicohtencatl-Cortes, J.; Giron, J.A. Host Protein Binding and Adhesive Properties of H6 and H7 Flagella of Attaching and Effacing Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 7426–7435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Currie, C.G.; Mackie, S.; Tree, J.; McAteer, S.; McKendrick, I.; McNeilly, T.N.; Roe, A.; La Ragione, R.M.; Woodward, M.J.; et al. An Investigation of the Expression and Adhesin Function of H7 Flagella in the Interaction of Escherichia coli O157: H7 with Bovine Intestinal Epithelium. Cell. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, G.; Yao, Y.; Kim, K.S. Flagella Promote Escherichia coli K1 Association with and Invasion of Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 2937–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troge, A.; Scheppach, W.; Schroeder, B.O.; Rund, S.A.; Heuner, K.; Wehkamp, J.; Stange, E.F.; Oelschlaeger, T.A. More than a Marine Propeller—The Flagellum of the Probiotic Escherichia coli Strain Nissle 1917 is the Major Adhesin Mediating Binding to Human Mucus. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 302, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, R.A.; Boesman-Finkelstein, M.; Chang, Y.; Hase, C.C. Vibrio cholerae hemagglutinin/protease, Colonial Variation, Virulence, and Detachment. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 472–478. [Google Scholar]
- Mel, S.F.; Fullner, K.J.; Wimer-Mackin, S.; Lencer, W.I.; Mekalanos, J.J. Association of Protease Activity in Vibrio cholerae Vaccine Strains with Decreases in Transcellular Epithelial Resistance of Polarized T84 Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 6487–6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, R.A.; Boesman-Finkelstein, M.; Holt, P. Vibrio cholerae hemagglutinin/lectin/protease Hydrolyzes Fibronectin and Ovomucin: F.M. Burnet Revisited. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 1092–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, T.K.; Haiko, J.; Laakkonen, L.; Järvinen, H.M.; Westerlund-Wikstrom, B. Fibrinolytic and Coagulative Activities of Yersinia pestis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Lähteenmäki, K.; Virkola, R.; Saren, A.; Emody, L.; Korhonen, T.K. Expression of Plasminogen Activator Pla of Yersinia pestis Enhances Bacterial Attachment to the Mammalian Extracellular Matrix. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 5755–5762. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.S.; Park, C.G.; Zhang, P.; Bartra, S.S.; Plano, G.V.; Klena, J.D.; Skurnik, M.; Hinnebusch, B.J.; Chen, T. Plasminogen Activator Pla of Yersinia pestis Utilizes Murine DEC-205 (CD205) as a Receptor to Promote Dissemination. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 31511–31521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driessen, A.J.; Nouwen, N. Protein Translocation Across the Bacterial Cytoplasmic Membrane. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008, 77, 643–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelman, S.M.; Lehti, T.A.; Kainulainen, V.; Antikainen, J.; Kylväjä, R.; Baumann, M.; Westerlund-Wikström, B.; Korhonen, T.K. Identification of a High-Molecular-Mass Lactobacillus Epithelium Adhesin (LEA) of Lactobacillus crispatus ST1 that Binds to Stratified Squamous Epithelium. Microbiology 2012, 158, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, T.; Kuparinen, V.; Koskinen, J.P.; Alatalo, E.; Holm, L.; Auvinen, P.; Edelman, S.; Westerlund-Wikström, B.; Korhonen, T.K.; Paulin, L.; et al. Genome Sequence of Lactobacillus crispatus ST1. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 3547–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, S.; Hammerschmidt, S. Fibrinolysis and Host Response in Bacterial Infections. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 98, 512–520. [Google Scholar]
- Redlitz, A.; Plow, E.F. Receptors for Plasminogen and t-PA: An Update. Baillieres Clin. Haematol. 1995, 8, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijken, D.C.; Lijnen, H.R. New Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms of the Fibrinolytic System. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguero, G.; Villena, J.; Racedo, S.; Haro, C.; Alvarez, S. Beneficial Immunomodulatory Activity of Lactobacillus casei in Malnourished Mice Pneumonia: Effect on Inflammation and Coagulation. Nutrition 2006, 22, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haro, C.; Villena, J.; Zelaya, H.; Alvarez, S.; Aguero, G. Lactobacillus casei Modulates the Inflammation-Coagulation Interaction in a Pneumococcal Pneumonia Experimental Model. J. Inflamm. (Lond.) 2009, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kainulainen, V.; Korhonen, T.K. Dancing to Another Tune—Adhesive Moonlighting Proteins in Bacteria. Biology 2014, 3, 178-204. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology3010178
Kainulainen V, Korhonen TK. Dancing to Another Tune—Adhesive Moonlighting Proteins in Bacteria. Biology. 2014; 3(1):178-204. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology3010178
Chicago/Turabian StyleKainulainen, Veera, and Timo K. Korhonen. 2014. "Dancing to Another Tune—Adhesive Moonlighting Proteins in Bacteria" Biology 3, no. 1: 178-204. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology3010178
APA StyleKainulainen, V., & Korhonen, T. K. (2014). Dancing to Another Tune—Adhesive Moonlighting Proteins in Bacteria. Biology, 3(1), 178-204. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology3010178




