Matrix Metalloproteases in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Key Drivers of Disease Progression?
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Tumor Microenvironment of PDAC
1.2. Matrix Metalloproteases in the Tumor Microenvironment
1.3. Overview of Matrix Metalloproteases
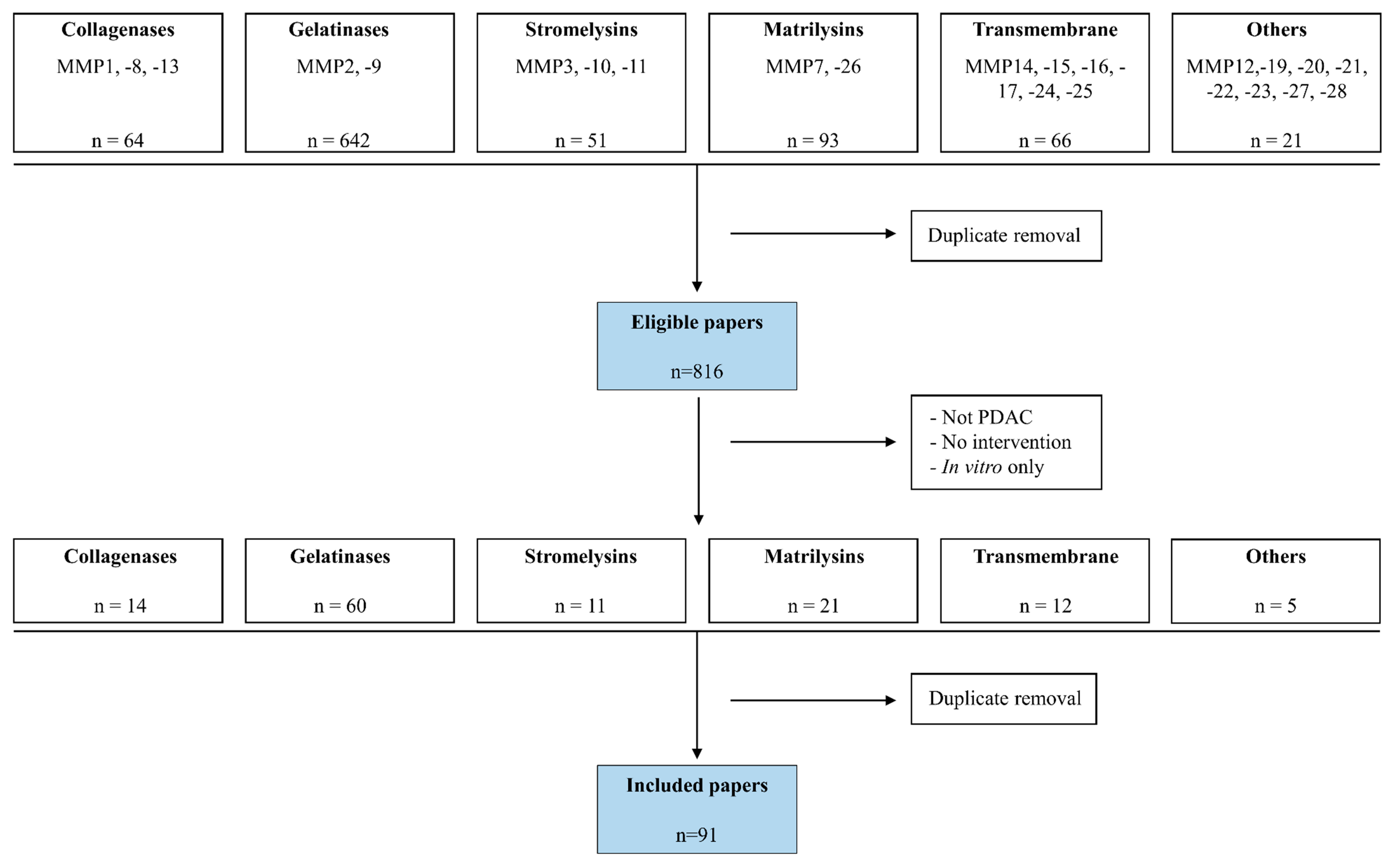
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Collagenases in PDAC
3.2. Gelatinases in PDAC
3.3. Stromelysins in PDAC
3.4. Matrilysins in PDAC
3.5. Membrane-Type MMPs in PDAC
3.6. Other MMPs in PDAC
3.7. Clinical Trials with MMP Inhibitors in PDAC
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neoptolemos, J.P.; Urrutia, R.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Büchler, M.W. (Eds.) Pancreatic Cancer; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume XXXIII, pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Gaduputi, V. Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: Global Trends, Etiology and Risk Factors. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, E.P.; Ward, E.M.; Siegel, R.; Jemal, A. Cancers with increasing incidence trends in the United States: 1999 through 2008. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2012, 62, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burris, H.A., III; Moore, M.J.; Andersen, J.; Green, M.R.; Rothenberg, M.L.; Modiano, M.R.; Cripps, M.C.; Portenoy, R.K.; Storniolo, A.M.; Tarassoff, P.; et al. Improvements in survival and clinical benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with advanced pancreas cancer: A randomized trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 1997, 15, 2403–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, D.; Chau, I.; Stocken, D.D.; Valle, J.W.; Smith, D.; Steward, W.; Harper, P.G.; Dunn, J.; Tudur-Smith, C. Phase III randomized comparison of gemcitabine versus gemcitabine plus capecitabine in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5513–5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, V.; Quietzsch, D.; Gieseler, F.; Gonnermann, M.; Schönekäs, H.; Rost, A.; Neuhaus, H.; Haag, C.; Clemens, M.; Heinrich, B.; et al. Randomized phase III trial of gemcitabine plus cisplatin compared with gemcitabine alone in advanced pancreatic cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 3946–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louvet, C.; Labianca, R.; Hammel, P.; Lledo, G.; Zampino, M.G.; André, T.; Zaniboni, A.; Ducreux, M.; Aitini, E.; Taïeb, J.; et al. Gemcitabine in combination with oxaliplatin compared with gemcitabine alone in locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer: Results of a GERCOR and GISCAD phase III trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 3509–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reni, M.; Cordio, S.; Milandri, C.; Passoni, P.; Bonetto, E.; Oliani, C.; Luppi, G.; Nicoletti, R.; Galli, L.; Bordonaro, R.; et al. Gemcitabine versus cisplatin, epirubicin, fluorouracil, and gemcitabine in advanced pancreatic cancer: A randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2005, 6, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, N.; Zhang, C.; Schwarz, A.M.; Hinz, S.; Wang, C.; Williams, N.S.; Schwarz, M.A.; Schwarz, R.E. Comparative benefits of Nab-paclitaxel over gemcitabine or polysorbate-based docetaxel in experimental pancreatic cancer. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2361–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, V.; Haas, M.; Boeck, S. Systemic treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2012, 38, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombouts, S.J.; Mungroop, T.H.; Heilmann, M.N.; van Laarhoven, H.W.; Busch, O.R.; Molenaar, I.Q.; Besselink, M.G.; Wilmink, J.W. FOLFIRINOX in Locally Advanced and Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer: A Single Centre Cohort Study. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 1861–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suker, M.; Beumer, B.R.; Sadot, E.; Marthey, L.; Faris, J.E.; Mellon, E.A.; El-Rayes, B.F.; Wang-Gillam, A.; Lacy, J.; Hosein, P.J.; et al. FOLFIRINOX for locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and patient level meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, M. Pancreatic cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1605–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijlsma, M.; van Laarhoven, H. The conflicting roles of tumor stroma in pancreatic cancer and their contribution to the failure of clinical trials: A systematic review and critical appraisal. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015, 34, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, R.O. The extracellular matrix: Not just pretty fibrils. Science 2009, 326, 1216–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Weaver, V.M.; Werb, Z. The extracellular matrix: A dynamic niche in cancer progression. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipe, E.C.; Chitty, J.L.; Cox, T.R. Charting the unexplored extracellular matrix in cancer. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 99, 58–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, B.C.; Pentcheva-Hoang, T.; Carstens, J.L.; Zheng, X.; Wu, C.; Simpson, T.R.; Laklai, H.; Sugimoto, H.; Kahlert, C.; Novitskiy, S.V.; et al. Depletion of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and fibrosis induces immunosuppression and accelerates pancreas cancer with reduced survival. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, A.D.; Oberstein, P.E.; Thomas, D.H.; Mirek, E.T.; Palermo, C.F.; Sastra, S.A.; Dekleva, E.N.; Saunders, T.; Becerra, C.P.; Tattersall, I.W.; et al. Stromal elements act to restrain, rather than support, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catenacci, D.V.; Junttila, M.R.; Karrison, T.; Bahary, N.; Horiba, M.N.; Nattam, S.R.; Marsh, R.; Wallace, J.; Kozloff, M.; Rajdevet, L.; et al. Randomized Phase Ib/II Study of Gemcitabine Plus Placebo or Vismodegib, a Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitor, in Patients With Metastatic pancreatic cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 4284–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massova, I.; Kotra, L.P.; Fridman, R.; Mobashery, S. Matrix metalloproteinases: Structures, evolution, and diversification. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 1075–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brew, K.; Dinakarpandian, D.; Nagase, H. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: Evolution, structure and function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1477, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.; Lapiere, C. Collagenolytic activity in amphibian tissues: A tissue culture assay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1962, 48, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.; Patel, A.P.; Debs, L.H.; Nguyen, D.; Patel, K.; Grati, M.; Mittal, J.; Yan, D.; Chapagain, P.; Liu, X.Z. Intricate Functions of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Physiological and Pathological Conditions. J. Cell Physiol. 2016, 231, 2599–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juurikka, K.; Butler, G.S.; Salo, T.; Nyberg, P.; Åström, P. The Role of MMP8 in Cancer: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, C.J.; Kuliopulos, A. Mouse Matrix metalloprotease-1a (Mmp1a) Gives New Insight into MMP Function. J. Cell Physiol. 2014, 229, 1875–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.H.; Law, C.H.; Kuo, P.H.; Hu, R.Y.; Yang, C.C.; Chung, T.W.; Li, J.M.; Lin, L.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Liao, E.C.; et al. MMP13 is involved in oral cancer cell metastasis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 17144–171161. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, T.; Ito, M.; Shiozawa, J.; Naito, S.; Kanematsu, T.; Sekine, I. Expression of the MMP-1 in Human Pancreatic Carcinoma: Relationship with Prognostic Factor. Mod. Pathol. 1999, 12, 669–674. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, A.; Smith, M.J.; Doolan, P.; Clarke, C.; Clynes, M.; Murphy, J.F.; McDermott, A.; Swan, N.; Crotty, P.; Ridgway, P.F.; et al. Invasive Markers Identified by Gene Expression Profiling in pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology 2012, 12, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, H.; Sato, K.; Yamazaki, Y.; Ohyama, T.; Horiguchi, N.; Hashizume, H.; Kakizaki, S.; Takagi, H.; Ozaki, I.; Arai, H.; et al. Transforming Growth Factor-α Activates Pancreatic Stellate Cells and May Be Involved in Matrix metalloproteinase-1 Upregulation. Lab. Investig. 2013, 93, 720–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lian, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Su, Y.; Li, J.; et al. MMP1/PAR1/SP/NK1R paracrine loop modulates early perineural invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3074–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlund, D.; Ardnor, B.; Oman, M.; Naredi, P.; Sund, M. Expression pattern and circulating levels of endostatin in patients with pancreas cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 2805–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramhall, S.R.; Neoptolemos, J.P.; Stamp, G.W.; Lemoine, N.R. Imbalance of expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of the matrix metalloproteinases (TIMPs) in human pancreatic carcinoma. J. Pathol. 1997, 182, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.E.; Humphreys, M.J.; Campbell, F.; Neoptolemos, J.P.; Boyd, M.T. Comprehensive analysis of matrix metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitor expression in pancreatic cancer: Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase-7 predicts poor survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 2832–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlert, C.; Fiala, M.; Musso, G.; Halama, N.; Keim, S.; Mazzone, M.; Lasitschka, F.; Pecqueux, M.; Klupp, F.; Schmidt, T.; et al. Prognostic Impact of a Compartment-Specific Angiogenic Marker Profile in Patients With pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 12978–12989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Itoh, F.; Iku, S.; Adachi, Y.; Fukushima, H.; Sasaki, S.; Mukaiya, M.; Hirata, K.; Imai, K. Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinases in Human Pancreatic Adenocarcinomas: Clinicopathologic and Prognostic Significance of Matrilysin Expression. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moz, S.; Basso, D.; Padoan, A.; Padoan, A.; Bozzato, D.; Fogar, P.; Zambon, C.F.; Pelloso, M.; Sperti, C.; Vigili de Kreutzenberg, S.; et al. Blood expression of matrix metalloproteinases 8 and 9 and of their inducers S100A8 and S100A9 supports diagnosis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer -associated diabetes mellitus. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 456, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tréhoux, S.; Duchêne, B.; Jonckheere, N.; Van Seuningen, I. The MUC1 oncomucin regulates pancreatic cancer cell biological properties and chemoresistance. Implication of p42–44 MAPK, Akt, Bcl-2 and MMP13 pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 456, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fa, Y.; Gan, Y.; Shen, Y.; Cai, X.; Song, Y.; Zhao, F.; Yao, M.; Gu, J.; Tu, H. Leptin signaling enhances cell invasion and promotes the metastasis of human pancreatic cancer via increasing MMP-13 production. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 16120–16134. [Google Scholar]
- Long, K.B.; Gladney, W.L.; Tooker, G.M.; Graham, K.; Fraietta, J.A.; Beatty, G.L. IFNγ and CCL2 Cooperate to Redirect Tumor-Infiltrating Monocytes to Degrade Fibrosis and Enhance Chemotherapy Efficacy in Pancreatic Carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, L.L.; Cai, C.Y.; Wu, Y.; Tang, Z.G. Correlation and prognostic significance of MMP-2 and TFPI-2 differential expression in pancreatic carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 682–691. [Google Scholar]
- Ellenrieder, V.; Alber, B.; Lacher, U.; Hendler, S.F.; Menke, A.; Boeck, W.; Wagner, M.; Wilda, M.; Friess, H.; Büchler, M.; et al. Role of MT-MMPs and MMP-2 in pancreatic cancer progression. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 85, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, M.; Ochi, K.; Ichimura, M.; Mizushima, T.; Shinji, T.; Koide, N.; Tsurumi, T.; Hasuoka, H.; Harada, M. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 in pancreatic juice for diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2002, 24, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juuti, A.; Lundin, J.; Nordling, S.; Louhimo, J.; Haglund, C. Epithelial MMP-2 expression correlates with worse prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Oncology 2006, 71, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, X.D.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zhu, J.; Xiong, Y.; Li, K.; Dong, J.H.; Li, X. Interaction between cancer cells and stromal fibroblasts is required for activation of the uPAR-uPA-MMP-2 cascade in pancreatic cancer metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 3115–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekstan, A.; Lampe, P.; Lewin-Kowalik, J.; Olakowski, M.; Jablonska, B.; Labuzek, K.; Jedrzejowska-Szypulka, H.; Olakowska, E.; Gorka, D.; Filip, I.; et al. Concentrations and activities of metalloproteinases 2 and 9 and their inhibitors (TIMPS) in chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 63, 589–599. [Google Scholar]
- Śmigielski, J.; Piskorz, Ł.; Talar-Wojnarowska, R.; Malecka-Panas, E.; Jabłoński, S.; Brocki, M. The estimation of metaloproteinases and their inhibitors blood levels in patients with pancreatic tumors. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 11, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Das, P.; Datta Gupta, S.; Sahni, P.; Pandey, R.M.; Gupta, S.; Chauhan, S.S.; Saraya, A. Prognostic significance of extracellular matrix degrading enzymes-cathepsin L and matrix metalloproteases-2 [MMP-2] in human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Investig. 2013, 31, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ding, X.; Tan, H.; Qian, J. Correlation between B7-H3 expression and matrix metalloproteinases 2 expression in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.; Zurakowski, D.; Wischhusen, J.; Frauenhoffer, C.; Hooshmand, S.; Kulke, M.; Moses, M.A. Urinary TIMP-1 and MMP-2 levels detect the presence of pancreatic malignancies. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1772–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, T.; Xia, X.; Yan, W. Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinases-2/-9 is Associated with Microvessel Density in Pancreatic Cancer. Am. J. Ther. 2017, 24, e431–e434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubowska, K.; Pryczynicz, A.; Januszewska, J.; Sidorkiewicz, I.; Kemona, A.; Niewiński, A.; Lewczuk, L.; Kędra, B.; Guzińska-Ustymowicz, K. Expressions of Matrix Metalloproteinases 2, 7, and 9 in Carcinogenesis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Dis. Markers 2016, 2016, 9895721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Gupta, S.; Pandey, R.M.; Sahni, P.; Chauhan, S.S.; Saraya, A. Prognostic significance of plasma matrix metalloprotease-2 in pancreatic cancer patients. Indian J. Med. Res. 2017, 146, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Le, S.; Jin, X.; Liu, G.; Chen, J.; Hu, J. CSN5 promotes the invasion and metastasis of pancreatic cancer by stabilization of FOXM1. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 374, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, T.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Pancreatic Stellate Cells Activation and Matrix Metallopeptidase 2 Expression Correlate With Lymph Node Metastasis in Pancreatic Carcinoma. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 357, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.L.; Huang, Q. Overexpression of the SMYD3 Promotes Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Pancreatic Cancer. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gress, T.M.; Müller-Pillasch, F.; Lerch, M.M.; Friess, H.; Büchler, M.; Adler, G. Expression and in-situ localization of genes coding for extracellular matrix proteins and extracellular matrix degrading proteases in pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Cancer 1995, 62, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshiba, T.; Hosotani, R.; Wada, M.; Fujimoto, K.; Lee, J.U.; Doi, R.; Arii, S.; Imamura, M. Detection of matrix metalloproteinase activity in human pancreatic cancer. Surg. Today 1997, 27, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshiba, T.; Hosotani, R.; Wada, M.; Miyamoto, Y.; Fujimoto, K.; Lee, J.U.; Doi, R.; Arii, S.; Imamura, M. Involvement of matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity in invasion and metastasis of pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer 1998, 82, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuniyasu, H.; Ellis, L.M.; Evans, D.B.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Fenoglio, C.J.; Bucana, C.D.; Cleary, K.R.; Tahara, E.; Fidler, I.J. Relative expression of E-cadherin and type IV collagenase genes predicts disease outcome in patients with resectable pancreatic carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 1999, 5, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pryczynicz, A.; Guzińska-Ustymowicz, K.; Dymicka-Piekarska, V.; Czyzewska, J.; Kemona, A. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in pancreatic ductal carcinoma is associated with tumor metastasis formation. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2007, 45, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tian, M.; Cui, Y.Z.; Song, G.H.; Zong, M.J.; Zhou, X.Y.; Chen, Y.; Han, J.X. Proteomic analysis identifies MMP-9, DJ-1 and A1BG as overexpressed proteins in pancreatic juice from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroczko, B.; Lukaszewicz-Zajac, M.; Wereszczynska-Siemiatkowska, U.; Groblewska, M.; Gryko, M.; Kedra, B.; Jurkowska, G.; Szmitkowski, M. Clinical significance of the measurements of serum matrix metalloproteinase-9 and its inhibitor (tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1) in patients with pancreatic cancer: Metalloproteinase-9 as an independent prognostic factor. Pancreas 2009, 38, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Hu, X.Q.; Feng, D.Y.; Lei, S.Y.; Hu, G.H. GPC-1 may serve as a predictor of perineural invasion and a prognosticator of survival in pancreatic cancer. Asian J. Surg. 2013, 36, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Jiang, P.; Wu, G.; Chen, K.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. The co-expression of MMP-9 and Tenascin-C is significantly associated with the progression and prognosis of pancreatic cancer. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 10, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukaszewicz-Zając, M.; Gryko, M.; Pączek, S.; Szmitkowski, M.; Kędra, B.; Mroczko, B. Matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) and its tissue inhibitor 2 (TIMP-2) in pancreatic cancer (PC). Oncotarget 2019, 10, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.D.; Kang, E.S.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, K.T.; Lee, K.H.; Park, Y.S.; Park, J.O.; Lee, J.; Heo, J.S.; Choi, S.H. Serum CA19-9, cathepsin D, and matrix metalloproteinase-7 as a diagnostic panel for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Proteomics 2012, 12, 3590–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Määttä, M.; Soini, Y.; Liakka, A.; Autio-Harmainen, H. Differential expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, MMP-9, and membrane type 1-MMP in hepatocellular and pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Implications for tumor progression and clinical prognosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 2726–2734. [Google Scholar]
- Pezzilli, R.; Corsi, M.M.; Barassi, A.; Morselli-Labate, A.M.; Dogliotti, G.; Casadei, R.; Corinaldesi, R.; D’Eril, G.M. The role of inflammation in patients with intraductal mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas and in those with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 3801–3805. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagakawa, Y.; Aoki, T.; Kasuya, K.; Tsuchida, A.; Koyanagi, Y. Histologic features of venous invasion, expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and matrix metalloproteinase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9, and the relation with liver metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2002, 24, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.K.; Kim, M.A.; Ryu, J.K.; Yoon, Y.B.; Kim, S.W.; Han, H.S.; Kang, G.H.; Kim, H.; Hwang, J.H.; Kim, Y.T. Postoperative prognostic predictors of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Clinical analysis and immunoprofile on tissue microarrays. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 2664–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, M.; Shafii, A.; Zervos, E.E.; Rosemurgy, A.S. Addition of matrix metalloproteinase inhibition to conventional cytotoxic therapy reduces tumor implantation and prolongs survival in a murine model of human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 3207–3211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zervos, E.E.; Norman, J.G.; Gower, W.R.; Franz, M.G.; Rosemurgy, A.S. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition attenuates human pancreatic cancer growth in vitro and decreases mortality and tumorigenesis in vivo. J. Surg. Res. 1997, 69, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervox, E.E.; Franz, M.G.; Salhab, K.F.; Shafii, A.E.; Menendez, J.; Gower, W.R.; Rosemurgy, A.S. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition improves survival in an orthotopic model of human pancreatic cancer. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2000, 4, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervos, E.E.; Shafii, A.E.; Rosemurgy, A.S. Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibition selectively decreases type II MMP activity in a murine model of pancreatic cancer. J. Surg. Res. 1999, 81, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, R.E.; Hartwig, W.; Antoniu, B.A.; Compton, C.C.; Warshaw, A.L.; Fernández-Del Castillo, C. Effect of matrix metalloproteinase inhibition on pancreatic cancer invasion and metastasis: An additive strategy for cancer control. Ann. Surg. 2000, 231, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.C.; Gong, B.G.; Wu, J.B.; Cheng, P.G.; Xu, H.Y.; Song, D.K.; Li, F. MMI-166, a selective matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, promotes apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, A.; Onda, M.; Uchida, E.; Maekawa, R.; Yoshioka, T. Antitumor effect of a new selective matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, MMI-166, on experimental pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 92, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, M.; Gregor, J.I.; Heukamp, I.; Hanel, M.; Ahlgrimm, M.; Schimke, I.; Kristiansen, G.; Ommer, A.; Walz, M.L.; Jacobi, C.A.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor RO 28-2653 decreases liver metastasis by reduction of MMP-2 and MMP-9 concentration in BOP-induced ductal pancreatic cancer in Syrian Hamsters: Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases in pancreatic cancer. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2006, 75, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iki, K.; Tsutsumi, M.; Kido, A.; Sakitani, H.; Takahama, M.; Yoshimoto, M.; Motoyama, M.; Tatsumi, K.; Tsunoda, T.; Konishi, Y. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2), membrane-type 1 MMP and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 and activation of proMMP-2 in pancreatic duct adenocarcinomas in hamsters treated with N-nitrosobis(2-oxopropyl)amine. Carcinogenesis 1999, 20, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, P.; Yang, Y.; Hosaka, K.; Zhang, Y.; Fischer, C.; Braun, H.; Liu, S.; Yu, G.; Liu, S.; Beyaert, R.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of IL-33-mediated stromal interactions in cancer metastasis. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e122375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koikawa, K.; Ohuchida, K.; Ando, Y.; Kibe, S.; Nakayama, H.; Takesue, S.; Endo, S.; Abe, T.; Okumura, T.; Iwamoto, C.; et al. Basement membrane destruction by pancreatic stellate cells leads to local invasion in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2018, 425, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Zheng, M.; Zhu, Y.; Sha, M.; Wu, Y.; Han, X. Selection of peptide inhibitor to matrix metalloproteinase-2 using phage display and its effects on pancreatic cancer cell lines PANC-1 and CFPAC-1. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, S.; Mira, E.; Muneer, S.; Korpanty, G.; Beck, A.W.; Holloway, S.E.; Mañes, S.; Brekken, R.A. Forced expression of MMP9 rescues the loss of angiogenesis and abrogates metastasis of pancreatic tumors triggered by the absence of host SPARC. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2008, 233, 860–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, N.; Mikels-Vigdal, A.J.; Stefanutti, E.; Schwarz, M.A.; Monahan, S.; Smith, V.; Schwarz, R.E. Therapeutic efficacy of anti-MMP9 antibody in combination with nab-paclitaxel-based chemotherapy in pre-clinical models of pancreatic cancer. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3878–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bausch, D.; Pausch, T.; Krauss, T.; Hopt, U.T.; Fernandez-del-Castillo, C.; Warshaw, A.L.; Thayer, S.P.; Keck, T. Neutrophil granulocyte derived MMP-9 is a VEGF independent functional component of the angiogenic switch in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Angiogenesis 2011, 14, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Kuwai, T.; Kim, J.S.; Fan, D.; Kim, S.J.; Fidler, I.J. Stromal metalloproteinase-9 is essential to angiogenesis and progressive growth of orthotopic human pancreatic cancer in parabiont nude mice. Neoplasia 2007, 9, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünwald, B.; Vandooren, J.; Gerg, M.; Ahomaa, K.; Hunger, A.; Berchtold, S.; Akbareian, S.; Schaten, S.; Knolle, P.; Edwards, D.R.; et al. Systemic Ablation of MMP-9 Triggers Invasive Growth and Metastasis of Pancreatic Cancer via Deregulation of IL6 Expression in the Bone Marrow. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bournet, B.; Pointreau, A.; Souque, A.; Muscari, F.; Lepage, B.; Senesse, P.; Barthet, M.; Lesavre, N.; Hammel, P.; Levy, P.; et al. Gene expression signature of advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using low density array on endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration samples. Pancreatology 2012, 12, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.H. Identification of Matrix Metalloproteinase 11 as a Prognostic Biomarker in Pancreatic Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 5963–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Marschall, Z.; Riecken, E.O.; Rosewicz, S. Stromelysin 3 is overexpressed in human pancreatic carcinoma and regulated by retinoic acid in pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Gut 1998, 43, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehner, C.; Miller, E.; Khauv, D.; Nassar, A.; Oberg, A.L.; Bamlet, W.R.; Zhang, L.; Waldmann, J.; Radisky, E.S.; Crawford, H.C.; et al. Tumor cell-derived MMP3 orchestrates Rac1b and tissue alterations that promote pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehner, C.; Miller, E.; Nassar, A.; Bamlet, W.R.; Radisky, E.S.; Radisky, D.C. Tumor cell expression of MMP3 as a prognostic factor for poor survival in pancreatic, pulmonary, and mammary carcinoma. Genes Cancer 2015, 6, 480–489. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.J.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, K.L.; Peng, Y.P.; Tao, J.Q.; Tang, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, Z.K.; Dai, C.C.; Qian, Z.Y.; et al. Yin Yang-1 suppresses invasion and metastasis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by downregulating MMP10 in a MUC4/ErbB2/p38/MEF2C-dependent mechanism. Mol. Cancer. 2014, 13, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Itoh, F.; Nakamura, H.; Min, Y.; Horiuchi, S.; Iku, S.; Sasaki, S.; Imai, K. Association of matrilysin mRNA expression with K-ras mutations and progression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Carcinogenesis 2001, 22, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, H.C.; Scoggins, C.R.; Washington, M.K.; Matrisian, L.M.; Leach, S.D. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 is expressed by pancreatic cancer precursors and regulates acinar-to-ductal metaplasia in exocrine pancreas. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Wei, Z.M.; Meng, Y.X.; Ji, X.R. Beta-catenin up-regulates the expression of cyclinD1, c-myc and MMP-7 in human pancreatic cancer: Relationships with carcinogenesis and metastasis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 2117–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, K.F.; van Till, J.W.; Boermeester, M.A.; de Reuver, P.R.; Tzvetanova, I.D.; Offerhaus, G.J.; ten Kate, F.J.; Busch, O.R.; van Gulik, T.M.; Gouma, D.J.; et al. Evaluation of matrix metalloproteinase 7 in plasma and pancreatic juice as a biomarker for pancreatic cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2007, 16, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yuan, P.; He, X.H.; Rong, Y.F.; Cao, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.P.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Lou, W.; Liu, M.F. KRAS/NF-κB/YY1/miR-489 Signaling Axis Controls Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banaei, N.; Foley, A.; Houghton, J.M.; Sun, Y.; Kim, B. Multiplex detection of pancreatic cancer biomarkers using a SERS-based immunoassay. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 455101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resovi, A.; Bani, M.R.; Porcu, L.; Anastasia, A.; Minoli, L.; Allavena, P.; Cappello, P.; Novelli, F.; Scarpa, A.; Morandi, E.; et al. Soluble stroma-related biomarkers of pancreatic cancer. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, e8741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Cong, X.; Ren, M.; Sun, H.; Liu, T.; Chen, G.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Yu, S.; Yang, Q. Circular RNA hsa_circRNA_0007334 is Predicted to Promote MMP7 and COL1A1 Expression by Functioning as a miRNA Sponge in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 7630894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, A.; Wang, S.C.; Morris, J.P., IV; Folias, A.E.; Liou, A.; Kim, G.E.; Akira, S.; Boucher, K.M.; Firpo, M.A.; Mulvihill, S.J.; et al. Stat3 and MMP7 contribute to pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma initiation and progression. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bister, V.; Skoog, T.; Virolainen, S.; Kiviluoto, T.; Puolakkainen, P.; Saarialho-Kere, U. Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinases-21 and -26 and TIMP-4 in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2007, 20, 1128–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Krantz, S.B.; Shields, M.A.; Dangi-Garimella, S.; Cheon, E.C.; Barron, M.R.; Hwang, R.F.; Rao, M.R.; Grippo, P.J.; Bentrem, D.J.; Munshi, H.G. MT1-MMP cooperates with Kras(G12D) to promote pancreatic fibrosis through increased TGF-β signaling. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangi-Garimella, S.; Krantz, S.B.; Barron, M.R.; Shields, M.A.; Heiferman, M.J.; Grippo, P.J.; Bentrem, D.J.; Munshi, H.G. Three-dimensional collagen I promotes gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer through MT1-MMP-mediated expression of HMGA2. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, L.; Cao, H.; Chen, J.; Weller, S.G.; Krueger, E.W.; Zhang, L.; Razidlo, G.L.; McNiven, M.A. Pancreatic tumor cell metastasis is restricted by MT1-MMP binding protein MTCBP-1. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviano, A.J.; Sun, L.; Ananthanarayanan, V.; Munshi, H.G. Extracellular matrix-mediated membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase expression in pancreatic ductal cells is regulated by transforming growth factor-beta1. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7032–7040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaz, P.; Friess, H.; Kondo, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zimmermann, A.; Büchler, M.W. Human macrophage metalloelastase worsens the prognosis of pancreatic cancer. Ann. Surg. 2002, 235, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, L.L.; Wu, Y.; Cai, C.Y.; Huang, Q.; Tang, Z.G. High-Level Expression and Prognostic Significance of Matrix Metalloprotease-19 and Matrix Metalloprotease-20 in Human Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2016, 45, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, M.; Idichi, T.; Seki, N.; Wada, M.; Yamada, Y.; Fukuhisa, H.; Toda, H.; Kita, Y.; Kawasaki, Y.; Tanoue, K.; et al. Gene Regulation by Antitumor miR-204-5p in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: The Clinical Significance of Direct RACGAP1 Regulation. Cancers 2019, 11, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bramhall, S.R.; Schulz, J.; Nemunaitis, J.; Brown, P.D.; Baillet, M.; Buckels, J.A. A double-blind placebo-controlled, randomised study comparing gemcitabine and marimastat with gemcitabine and placebo as first line therapy in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 87, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.J.; Hamm, J.; Dancey, J.; Dagenais, M.; Fields, A.; Hagan, K.; Greenberg, B.; Colwell, B.; Zee, B.; Tuet, D.; et al. Comparison of gemcitabine versus the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor BAY 12-9566 in patients with advanced or metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas: A phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 3296–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, G.B. The Rebirth of Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors: Moving Beyond the Dogma. Cells 2019, 8, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winer, A.; Adams, S.; Mignatti, P. Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy: Turning Past Failures into Future Successes. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, N.; Mouri, N.; Iwata, K.; Ohuchi, E.; Okada, Y.; Hayakawa, T. A one-step sandwich enzyme immunoassay for human matrix metalloproteinase 2 (72-kDa gelatinase/type IV collagenase) using monoclonal antibodies. Clin. Chim. Acta 1993, 221, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Wang, X.; Jie, Z.; Hong, X.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Yu, Y. Inhibitory effects of miR-146b-5p on cell migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer by targeting MMP16. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technolog. Med. Sci. 2011, 31, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannopoulos, G.; Pavlakis, K.; Parasi, A.; Kavatzas, N.; Tiniakos, D.; Karakosta, A.; Tzanakis, N.; Peros, G. The expression of matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -9 and their tissue inhibitor 2 in pancreatic ductal and ampullary carcinoma and their relation to angiogenesis and clinicopathological parameters. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.; Hwang, J.H.; Shin, E.; Lee, H.S.; Hwang, D.W.; Cho, J.Y.; Yoon, Y.S.; Han, H.S.; Cha, B.H. CD24 and S100A4 expression in resectable pancreatic cancers with earlier disease recurrence and poor survival. Pancreas 2014, 43, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.C.; Parekh, J.R.; Porembka, M.R.; Nathan, H.; D’Angelica, M.I.; DeMatteo, R.P.; Fong, Y.; Kingham, T.P.; Jarnagin, W.R.; Allen, P.J. A Pilot Study Evaluating Serum MMP7 as a Preoperative Prognostic Marker for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Patients. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2016, 20, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Horita, S.; Senmaru, N.; Miyasaka, Y.; Gohda, T.; Inoue, Y.; Fujita, M.; Meguro, T.; Morita, T.; Nagashima, K. Association of matrilysin expression with progression and poor prognosis in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2002, 9, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, S.R.; Hurd, T.C.; Markus, G.; Martinick, M.I.; Penetrante, R.M.; Tan, D.; Venkataraman, P.; DeSouza, N.; Sait, S.N.; Driscoll, D.L.; et al. Evaluation of urinary plasminogen activator, its receptor, matrix metalloproteinase-9, and von Willebrand factor in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 4935–4943. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.; Matsuda, Y.; Ueda, J.; Uchida, E.; Naito, Z.; Ishiwata, T. Keratinocyte growth factor induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and correlates with venous invasion in pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 40, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Sheng, W.; Dong, M.; Dong, X.; Dong, Q.; Li, F. Gli1 promotes transforming growth factor-beta1- and epidermal growth factor-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells. Surgery 2015, 158, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.K.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhong, S.; Wu, H.Q.; Wang, B.; Fan, P.; Xiong, J.X.; Yang, H.J.; Wu, H.S. Overexpression of membrane-type 2 matrix metalloproteinase induced by hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in pancreatic cancer: Implications for tumor progression and prognosis. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 2, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinathan, A.; Morton, J.P.; Jodrell, D.; Sansom, O.J. GEMMs as preclinical models for testing pancreatic cancer therapies. Dis. Model. Mech. 2015, 8, 1185–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swayden, M.; Soubeyran, P.; Iovanna, J. Upcoming Revolutionary Paths in Preclinical Modeling of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 9, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biankin, A.V.; Waddell, N.; Kassahn, K.S.; Gingras, M.C.; Muthuswamy, L.B.; Johns, A.L.; Miller, D.K.; Wilson, P.J.; Patch, A.M.; Wu, J.; et al. Pancreatic cancer genomes reveal aberrations in axon guidance pathway genes. Nature 2012, 491, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Member | Patient Number | Method | Difference | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMP1 | 45 PC, 10 CO | IHC | no difference | [36] |
| MMP1 | 8 PC, 8 CO | RNA | no difference | [59] |
| MMP1 | 248 PC, 216 CO | Serum | no difference | [69] |
| MMP1 | 46 PC, 5 CO | IHC | up vs healthy | [30] |
| MMP1 | 25 PC | RNA | up vs adjacent CO | [31] |
| MMP1 | 10 PC, 12 CP, 5 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [32] |
| MMP1 | 45 PC | RNA | up vs adjacent CO | [33] |
| MMP1 | 30 PC | IHC | up vs adjacent CO | [33] |
| MMP1 | 104 PC, 62 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [34] |
| MMP1 | 17 PC, 17 CO | RNA | up vs CO | [35] |
| MMP1 | 18 PC, 8 CO | RNA | up vs healthy | [36] |
| MMP2 | 75 PC, 10 CO | IHC | no difference | [36] |
| MMP2 | 18 PC, 8 CO | RNA | no difference | [36] |
| MMP2 | 70 PC and 10 CO | IHC | no difference | [38] |
| MMP2 | 92 PC, 43 CP, 91 CO | Serum | no difference | [68] |
| MMP2 | 35 PC | RNA/IHC | no difference | [70] |
| MMP2 | 46 PC, 13 CO | Serum | no difference | [71] |
| MMP2 | 104 PC, 62 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [34] |
| MMP2 | 17 PC, 17 CO | RNA | upvsCO | [35] |
| MMP2 | 122 PC | IHC | up vs adjacent CO | [43] |
| MMP2 | 18 PC, 9 CP, 9 CO | RNA | up vs both others | [44] |
| MMP2 | 12 PC, 11 CP, 7 CO | pancreatic juice | up vs both others | [45] |
| MMP2 | 127 PC | IHC | up vs CO | [46] |
| MMP2 | 20 PC | IHC | up vs CO | [47] |
| MMP2 | 32 PC, 31 CP | ELISA on tissue | up vs CP | [48] |
| MMP2 | 110 PC, 24 BT | Plasma | up vs BT | [49] |
| MMP2 | 37 PC, 7 CP | IHC | up vs CP and CO | [50] |
| MMP2 | 45 PC | IHC | up vs CO | [51] |
| MMP2 | 51 PC, 60 CO | Urine | up vs CO | [52] |
| MMP2 | 44 PC, 8 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [52] |
| MMP2 | 30 PC, 17 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [53] |
| MMP2 | 29 PC | IHC | up vs adjacent CO | [54] |
| MMP2 | 127 PC, 25 CP, 25 CO | Plasma | up vs CP and CO | [55] |
| MMP2 | 106 PC | RNA/WB | up vs adjacent CO | [56] |
| MMP2 | 40 PC, 10 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [57] |
| MMP2 | 67 PC, 20 CO | IHC | up vs adjacent CO | [58] |
| MMP2 | 8 PC, 8 CO | RNA | upvsCO | [59] |
| MMP2 | 10 PC, 3 CO | ZG | upvsCO | [60] |
| MMP2 | 33 PC, 14 CP, 13 CO | ZG/WB | upvsCO | [61] |
| MMP2 | 22 PC, 9 CP, 9 CO | RNA | up vs adjacent CO | [62] |
| MMP2 | 10 PC, 213 CO | Serum | down vs CO | [118] |
| MMP3 | 45 PC, 10 CO | IHC | no difference | [36] |
| MMP3 | 18 PC, 8 CO | RNA | no difference | [36] |
| MMP3 | 8 PC, 8 CO | RNA | no difference | [59] |
| MMP3 | 104 PC, 62 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [34] |
| MMP3 | 17 PC, 17 CO | RNA | up vs CO | [35] |
| MMP3 | 140 PC, 12 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [94] |
| MMP3 | 140 PC, 12 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [95] |
| MMP7 | 18 PC, 8 CO | RNA | no difference | [36] |
| MMP7 | 104 PC, 62 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [34] |
| MMP7 | 17 PC, 17 CO | RNA | up vs CO | [35] |
| MMP7 | 45 PC, 10 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [36] |
| MMP7 | 29 PC | IHC | up vs adjacent CO | [54] |
| MMP7 | 248 PC, 216 CO | Serum | up vs CO | [68] |
| MMP7 | 44 PC, 17 CP | RNA | up vs CP | [91] |
| MMP7 | 70 PC | RNA | up vs adjacent CO | [97] |
| MMP7 | 32 PC, ? CO | IHC | up vs CO | [98] |
| MMP7 | 47 PC, 10 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [99] |
| MMP7 | 63 PC, 31 CP | Plasma | up vs CP | [100] |
| MMP7 | 30 PC | RNA | up vs adjacent CO | [101] |
| MMP7 | 5 PC, 5 CP, 62 CO | IHC | up vs CP and CO | [102] |
| MMP7 | 131 PC, 30 CP, 131 CO | Plasma | up vs CO | [103] |
| MMP7 | 10 PC | RNA | up vs adjacent CO | [104] |
| MMP8 | 248 PC, 216 CO | Serum | no difference | [69] |
| MMP8 | 75 PC, 10 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [36] |
| MMP8 | 91 PC, 41 CP, 30 CO | RNA (PBMCs) | up vs CO | [39] |
| MMP9 | 18 PC, 8 CO | RNA | no difference | [36] |
| MMP9 | 70 PC, 10 CO | IHC | no difference | [38] |
| MMP9 | 51 PC, 60 CO | urine | no difference | [52] |
| MMP9 | 10 PC, 3 CO | ZG | no difference | [60] |
| MMP9 | 33 PC, 14 CP, 13 CO | ZG/WB | no difference | [61] |
| MMP9 | 248 PC, 216 CO | Serum | no difference | [69] |
| MMP9 | 35 PC | RNA/IHC | no difference | [70] |
| MMP9 | 104 PC, 62 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [34] |
| MMP9 | 45 PC, 10 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [36] |
| MMP9 | 91 PC, 41 CP, 30 CO | RNA (PBMCs) | up vs CP and CO | [39] |
| MMP9 | 32 PC, 31 CP | ELISA on tissue | up vs CP | [48] |
| MMP9 | 110 PC, 24 BT | Plasma | up vs BT | [49] |
| MMP9 | 30 PC, 17 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [53] |
| MMP9 | 29 PC | IHC | up vs adjacent CO | [54] |
| MMP9 | 8 PC, 8 CO | RNA | up vs CO | [59] |
| MMP9 | 22 PC, 9 CP, 9 CO | RNA | up vs adjacent CO | [62] |
| MMP9 | 36 PC | IHC | up vs CO | [63] |
| MMP9 | 9 PC, 9 CO | MS/MS | up vs CO | [64] |
| MMP9 | 78 PC, 45 CP, 70 CO | Serum | up vs both | [65] |
| MMP9 | 62 PC, 16 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [66] |
| MMP9 | 103 PC, 6 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [67] |
| MMP10 | 17 PC, 17 CO | RNA | no difference | [35] |
| MMP11 | 17 PC, 17 CO | RNA | up vs CO | [35] |
| MMP11 | 18 PC, 8 CO | RNA | up vs CO | [36] |
| MMP11 | 75 PC, 10 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [36] |
| MMP11 | 44 PC, 17 CP | RNA | up vs CP | [91] |
| MMP11 | 12 PC, 16 CO | Blood | up vs CO | [92] |
| MMP11 | 21 PC, 9 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [93] |
| MMP12 | 75 PC, 10 CO | IHC | no difference | [36] |
| MMP12 | 39 PC, 13 CO | RNA/WB/IHC | up vs CO | [111] |
| MMP13 | 104 PC, 62 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [34] |
| MMP13 | 45 PC | RNA | up vs adjacent CO | [40] |
| MMP14 | 75 PC, 10 CO | IHC | no difference | [36] |
| MMP14 | 35 PC | RNA/IHC | no difference | [111] |
| MMP14 | 18 PC, 9 CP, 9 CO | RNA | up vs both others | [44] |
| MMP14 | 64 PC, 9 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [110] |
| MMP15 | 18 PC, 9 CP, 9 CO | RNA | up vs both others | [44] |
| MMP15 | 18 PC, 8 CO | RNA | reduced vs CO | [36] |
| MMP16 | 18 PC, 9 CP, 9 CO | RNA | no difference | [44] |
| MMP16 | 12 PC | IHC | up vs adjacent CO | [119] |
| MMP19 | 102 PC | IHC | up vs adjacent CO | [112] |
| MMP20 | 102 PC | IHC | up vs adjacent CO | [112] |
| MMP21 | 25 PC, 18 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [106] |
| MMP26 | 25 PC, 18 CO | IHC | up vs CO | [106] |
| Member | Patient Number | Method | Correlation | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMP1 | 45 PC, 10 CO | IHC | no | [36] | |
| MMP1 | 70 PC | IHC | no | [38] | |
| MMP1 | 46 PC, 5 CO | IHC | OS, | LM, Size, Stage | [30] |
| MMP1 | 30 PC | IHC | PNI | [33] | |
| MMP1 | 51 PC | IHC/serum | OS | [37] | |
| MMP2 | 75 PC, 10 CO | IHC | no | [36] | |
| MMP2 | 70 PC, 10 CO | IHC | no | [38] | |
| MMP2 | 51 PC | IHC/serum | no | [37] | |
| MMP2 | 32 PC, 31 CP | ELISA on tissue | no | [48] | |
| MMP2 | 37 PC, 7 CP | IHC | no | [50] | |
| MMP2 | 29 PC | IHC | no | [54] | |
| MMP2 | 127 PC, 25 CP, 25 CO | plasma | no | [55] | |
| MMP2 | 35 PC | RNA/IHC | no | [70] | |
| MMP2 | 32 PC | IHC | no | [120] | |
| MMP2 | 67 PC | IHC | LM, | PNI, OS, DF | [121] |
| MMP2 | 122 PC | IHC | OS, DF | [43] | |
| MMP2 | 127 PC | IHC | OS, Stage | [46] | |
| MMP2 | 20 PC | IHC | LM | [47] | |
| MMP2 | 37 PC, 7 CP | IHC | LM, DM | [50] | |
| MMP2 | 45 PC | IHC | OS, LM, Stage | [51] | |
| MMP2 | 30 PC, 17 CO | IHC | LM, Stage, Size | [53] | |
| MMP2 | 106 PC | RNA/WB | DM, Stage | [56] | |
| MMP2 | 40 PC, 10 CO | IHC | LM | [57] | |
| MMP2 | 67 PC, 20 CO | IHC | LM, Stage, PNI | [58] | |
| MMP2 | 33 PC, 14 CP, 13 CO | ZG/WB | Stage | [61] | |
| MMP2 | 92 PC, 43 CP, 91 CO | serum | LM, DM | [68] | |
| MMP2 | 32 PC | IHC | VI | [72] | |
| MMP2 | 88 PC | IHC | OS | [73] | |
| MMP3 | 45 PC, 10 CO | IHC | no | [36] | |
| MMP3 | 18 PC, 8 CO | RNA | no | [36] | |
| MMP3 | 70 PC | IHC | no | [38] | |
| MMP3 | 140 PC, 12 CO | IHC | OS | [95] | |
| MMP7 | 51 PC | IHC/serum | no | [37] | |
| MMP7 | 29 PC | IHC | no | [54] | |
| MMP7 | 88 PC | IHC | no | [73] | |
| MMP7 | 45 PC, 10 CO | IHC | OS, | LM, DIF, Stage | [36] |
| MMP7 | 70 PC | IHC | OS, | Size, DIF | [38] |
| MMP7 | 134 PC | IHC | Stage, PNI, | OS | [122] |
| MMP7 | 70 PC | RNA | LM, Size | [97] | |
| MMP7 | 47 PC, 10 CO | IHC | OS, DM | [99] | |
| MMP7 | 10 PC | RNA | OS | [104] | |
| MMP7 | 101 PC | serum | OS | [105] | |
| MMP7 | 39 PC | IHC | LM, OS | [123] | |
| MMP8 | 75 PC, 10 CO | IHC | no | [36] | |
| MMP8 | 91 PC, 41 CP, 30 CO | RNA (PBMCs) | no | [39] | |
| MMP9 | 45 PC, 10 CO | IHC | no | [36] | |
| MMP9 | 70 PC, 10 CO | IHC | no | [38] | |
| MMP9 | 51 PC | IHC/serum | no | [37] | |
| MMP9 | 91 PC, 41 CP, 30 CO | RNA (PBMCs) | no | [39] | |
| MMP9 | 29 PC | IHC | no | [54] | |
| MMP9 | 33 PC, 14 CP, 13 CO | ZG/WB | no | [61] | |
| MMP9 | 9 PC, 9 CO | MS/MS | no | [64] | |
| MMP9 | 35 PC | RNA/IHC | no | [70] | |
| MMP9 | 32 PC | IHC | no | [123] | |
| MMP9 | 27 PC | IHC | no | [124] | |
| MMP9 | 62 PC, 16 CO | IHC | PNI, | LM, Stage, Size | [66] |
| MMP9 | 63 PC | IHC | VI, | OS, LM, DM | [125] |
| MMP9 | 62 PC | IHC | LM, | OS | [126] |
| MMP9 | 32 PC, 31 CP | ELISA on tissue | LM | [48] | |
| MMP9 | 30 PC, 17 CO | IHC | LM, Stage, Size | [53] | |
| MMP9 | 36 PC | IHC | LM, DM | [63] | |
| MMP9 | 78 PC, 45 CP, 70 CO | serum | OS | [65] | |
| MMP9 | 103 PC, 6 CO | IHC | OS, LM, DM, VI, Stage | [67] | |
| MMP9 | 32 PC | IHC | VI | [72] | |
| MMP9 | 88 PC | IHC | OS, DF, | DM | [73] |
| MMP10 | 51 PC | IHC/serum | no | [37] | |
| MMP11 | 75 PC, 10 CO | IHC | OS, LM, | DIF, Size | [36] |
| MMP11 | not indicated | RNA | OS | [92] | |
| MMP12 | 75 PC, 10 CO | IHC | no | [36] | |
| MMP12 | 39 PC, 13 CO | RNA/WB/IHC | OS, | LM, Stage | [111] |
| MMP13 | 60 PC | IHC | LM | [41] | |
| MMP14 | 70 PC | IHC | no | [38] | |
| MMP14 | 75 PC, 10 CO | IHC | no | [36] | |
| MMP14 | 37 PC | RNA/IHC | no | [70] | |
| MMP15 | 78 PC | IHC | OS, DF, | PNI, LM, DM, Stage | [127] |
| MMP19 | 102 PC | IHC | OS, DF, PNI, Stage | [112] | |
| MMP20 | 102 PC | IHC | OS, DF, Stage, PNI | [112] | |
| MMP21 | 25 PC, 18 CO | IHC | no | [106] | |
| MMP26 | 25 PC, 18 CO | IHC | LM | [106] | |
| MMP28 | not indicated | RNA | OS | [113] | |
| Target | Model | “Treatment” | Result | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMP1 | Sciatic nerve invasion | shMMP1 PANC1 cells | Reduced perineural invasion | [33] |
| MMP2/9? | Orthotopic injection HPAC cells | Batimastat (day −7 till death/sacrifice) | Increased gemcitabine sensitivity, No effect single treatment | [74] |
| Orthotopic injection HPAC cells | Batimastat (day −4 till death/sacrifice) | Reduced tumor growth, metastasis and death | [75] | |
| Orthotopic injection HPAC cells | Batimastat (day 7 till death/sacrifice) | Reduced local invasion and death | [76] | |
| Orthotopic injection HPAC cells | Batimastat (day 7 till death/sacrifice) | Reduced tumor weight | [77] | |
| Injection AsPC1 or Capan-1 cells in spleen | Batimastat (day −7 till day 14) | Reduced metastasis and death | [78] | |
| Subcutaneous injection SW1990 cells | MMI-166 from day 7 till sacrifice at day 28 | Reduced tumor growth | [79] | |
| Orthotopic injection PGHAM cells (Syrian hamster) | MMI-166 (day 1 till sacrifice) | Reduced tumor growth, liver metastasis and MVD | [80] | |
| BOP injections (Syrian hamster) | RO28-2653 (week 6 till week 14) | Reduced liver metastasis, No effect death | [81] | |
| BOP injections (Syrian hamster) | OPB-3206 in diet from day 48 till sacrifice | Reduced invasive carcinoma | [82] | |
| Subcutaneous injection Panc02 or MIAPaca2 cells | SB-3CT (day 1 till sacrifice) | Reduced lung metastasis | [83] | |
| MMP2 | Subcutaneous injection organoid and PSC | shMMP2 PSC | Reduced tumor growth | [84] |
| Subcutaneous injection PANC-1 or CFPAC-1 cells | MMP2 blocking peptides after tumor take | Reduced growth and MVD | [85] | |
| MMP3 | Kras(G12D) mice | MMP3 overexpression | Increased neoplastic alterations | [94] |
| MMP7 | Ductal ligation | MMP7 deficient mice | Reduced ductal metaplasia | [98] |
| Pfta1-Cre/KrasG12D mice | MMP7 deficiency | No effect acinar to ductal metaplasia | [105] | |
| Pdx1-Crelate/KrasG12D mice | MMP7 deficiency | Reduced tumor development | [105] | |
| Pdx1-CreLate/KrasG12D/p53f/+ mice | MMP7 deficiency | Reduced tumor growth and metastasis | [105] | |
| Tail vein injection PANC1 cells | shMMP7 | Reduced liver and lung metastasis | [101] | |
| SCTPSPA (day −2 till day 25) | Reduced lung metastasis | [101] | ||
| MMP9 | Subcutaneous injection Panc02 cells | MMP9 deficient mice | Reduced lung metastasis | [83] |
| Orthotopic injection Panc02 cells | MMP9 overexpression | Enhanced tumor growth, No effect metastasis | [86] | |
| Subcutaneous injection AsPC-1 cells | aMMP9 antibody AB0046 (day 1 till day 14) | No effect on tumor weight | [87] | |
| Injection AsPC-1 cells in peritoneal cavity | aMMP9 antibody AB0046 (day 14 till day 56) | Increased gemcitabine/nab-paclitaxel sensitivity, No effect metastasis | [87] | |
| Subcutaneous injection Capan-1 cells | Doxycycline (day 1 till day 14) | Reduced growth and MVD | [88] | |
| Orthotopic injection L3.6pl cells | MMP9 deficient mice | Reduced tumor take, growth and MVD | [89] | |
| Pdx-1+/Cre;KrasG12D;Trp53 mice | MMP9 deficiency | Increased progression and invasive growth | [90] | |
| Intravenous injection 9801 or Panc02 cells | MMP9 deficient mice | Increased metastasis | [90] | |
| MMP14 | Subcutaneous injection organoid and PSC | shMMP14 PSC | Reduced tumor growth | [84] |
| KrasG12D mice | MMP14 overexpression | Increased number of PanIN lesions | [107] | |
| Subcutaneous injection PANC1 or HPAF-II cells | MMP14 overexpression | Reduced gemcitabine sensitivity, No effect single treatment | [108] | |
| Orthotopic injection DanG or BxPc3 cells | MTCBP-1 overexpression | Reduced metastasis, No effect tumor growth | [109] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Slapak, E.J.; Duitman, J.; Tekin, C.; Bijlsma, M.F.; Spek, C.A. Matrix Metalloproteases in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Key Drivers of Disease Progression? Biology 2020, 9, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9040080
Slapak EJ, Duitman J, Tekin C, Bijlsma MF, Spek CA. Matrix Metalloproteases in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Key Drivers of Disease Progression? Biology. 2020; 9(4):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9040080
Chicago/Turabian StyleSlapak, Etienne J., JanWillem Duitman, Cansu Tekin, Maarten F. Bijlsma, and C. Arnold Spek. 2020. "Matrix Metalloproteases in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Key Drivers of Disease Progression?" Biology 9, no. 4: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9040080
APA StyleSlapak, E. J., Duitman, J., Tekin, C., Bijlsma, M. F., & Spek, C. A. (2020). Matrix Metalloproteases in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Key Drivers of Disease Progression? Biology, 9(4), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9040080





