Spatiotemporal Analysis of the Coupling Coordination Degree between Haze Disaster and Urbanization Systems in China from 2000 to 2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Index System Construction
2.3.2. Determination of the Index Weights
2.3.3. Calculation of the Comprehensive Index
2.3.4. Calculation of the Coupling Coordination Degree Index
3. Results
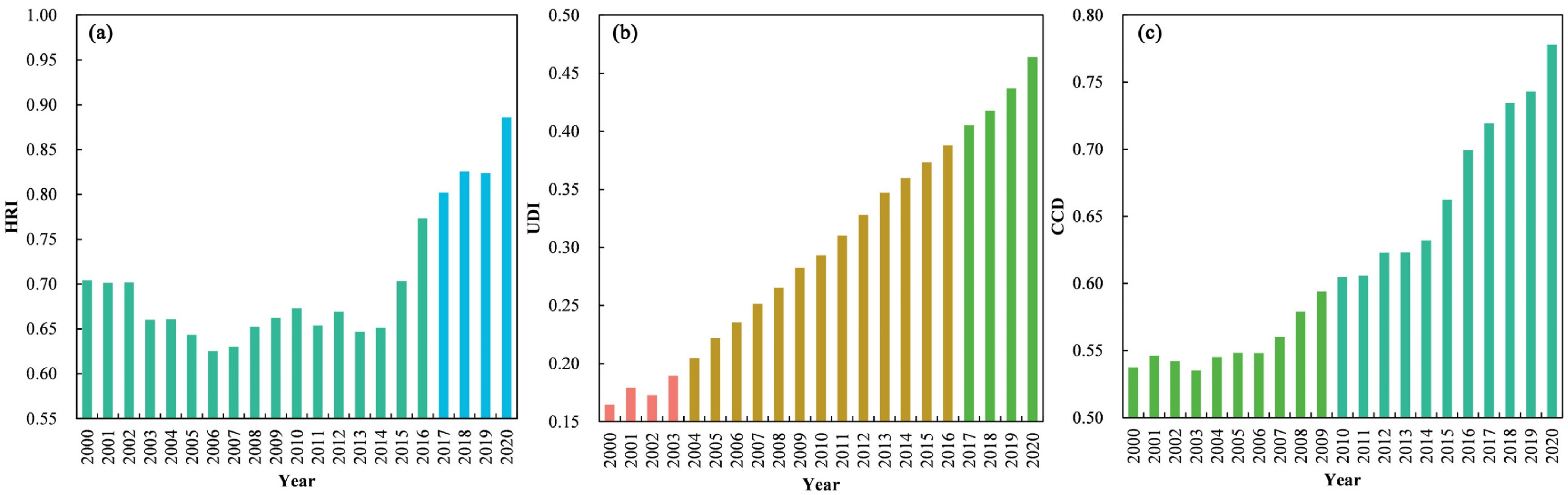
3.1. Time Series Change Characteristics of Haze Disaster Risk Level, Urbanization Development Level and the Coupling Coordination between the Two
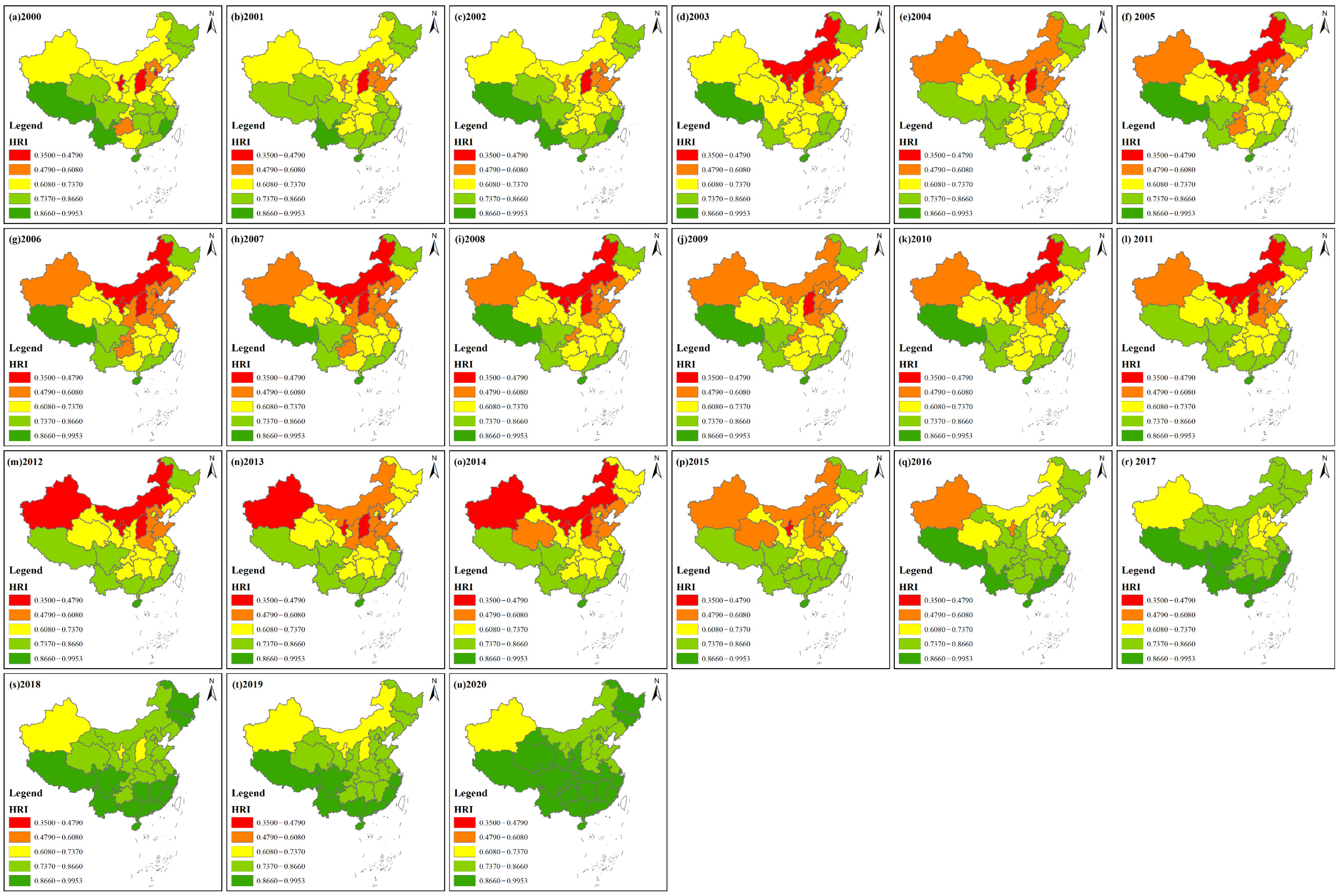
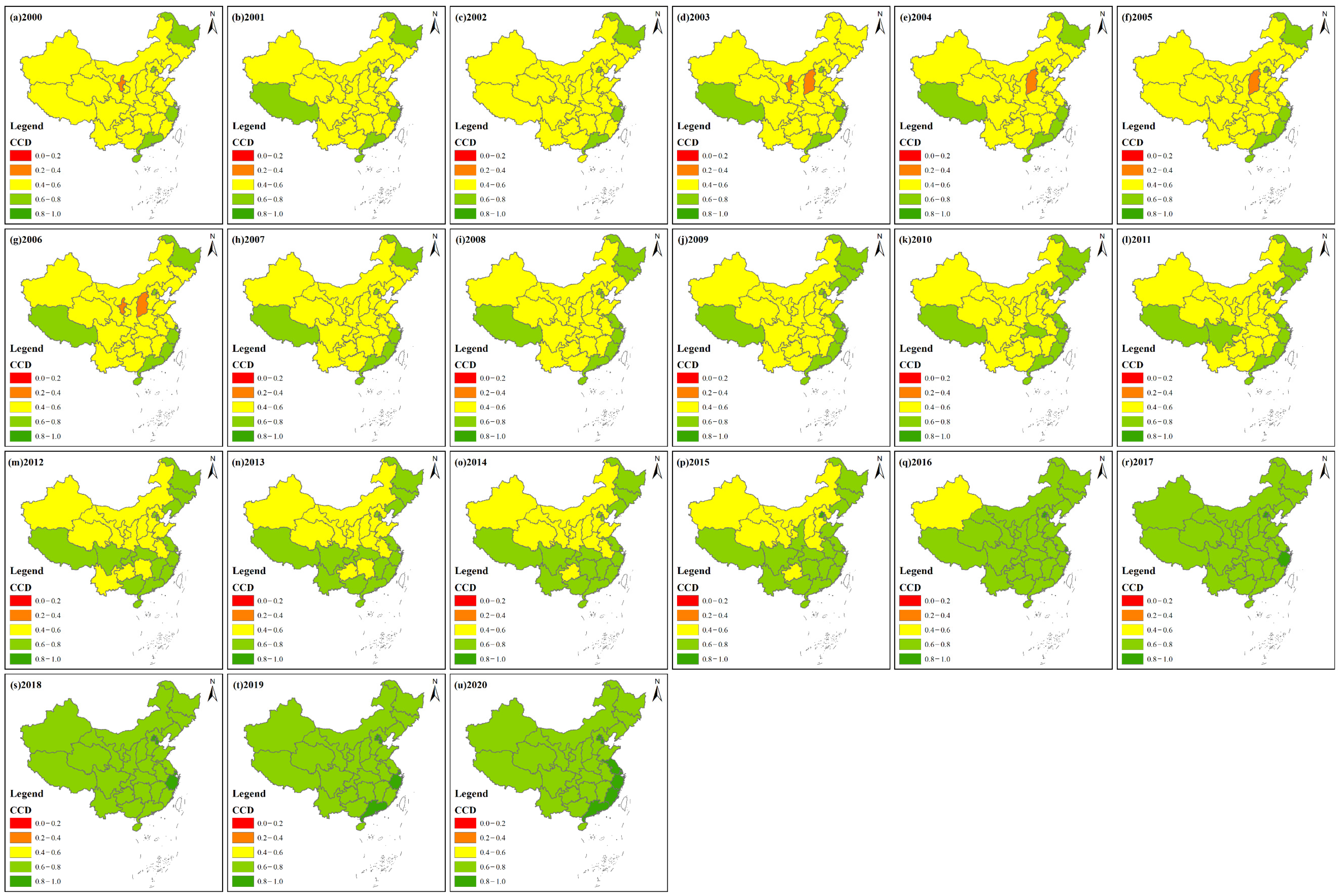
3.2. Spatial Change Characteristics of Haze Disaster Risk Level, Urbanization Development Level and the Coupling Coordination Degree of the Two
3.2.1. Spatial Change Characteristics of Haze Disaster Risk Level
3.2.2. Characteristics of Changes in the Spatial Sequence of Urbanization Development Level
3.2.3. Spatial Sequence Variation in Coupling Coordination
4. Discussion
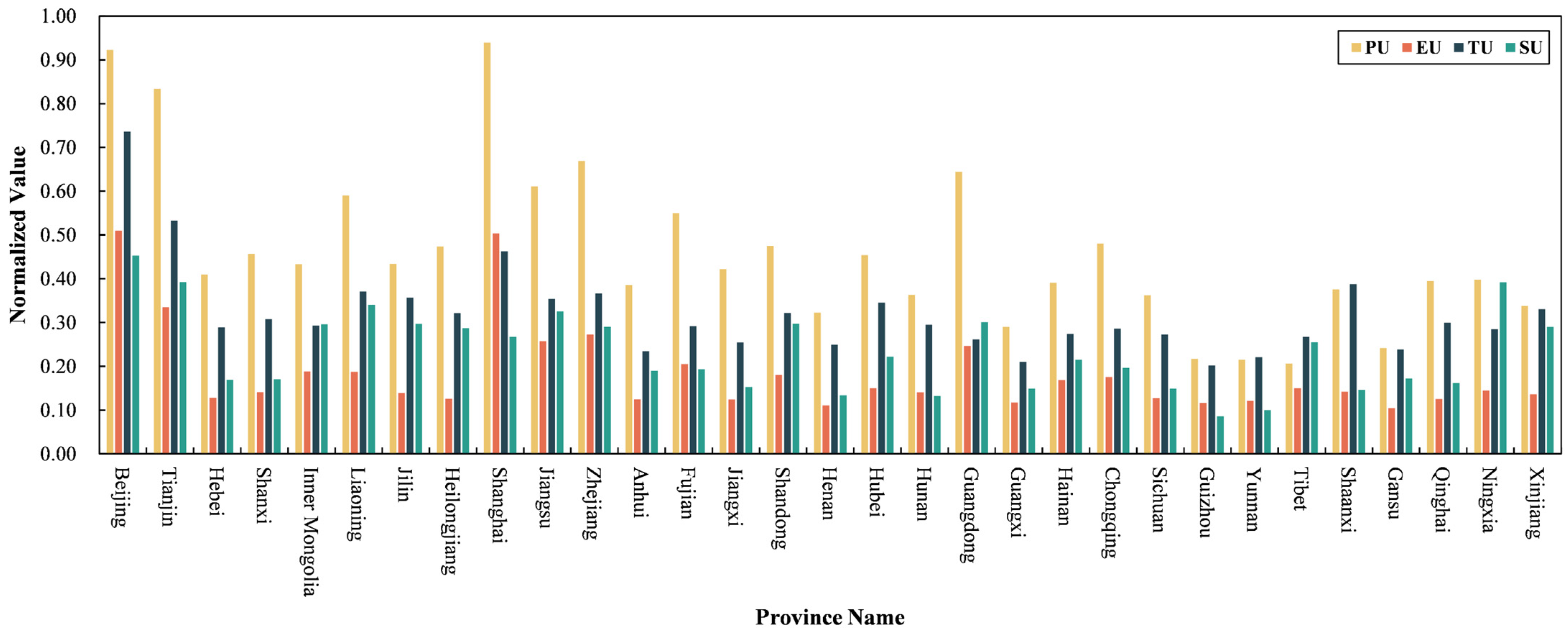
4.1. Validation of Four Aspects of Urbanization
4.2. Comparison with Existing Studies about HRI, UDI and CCD
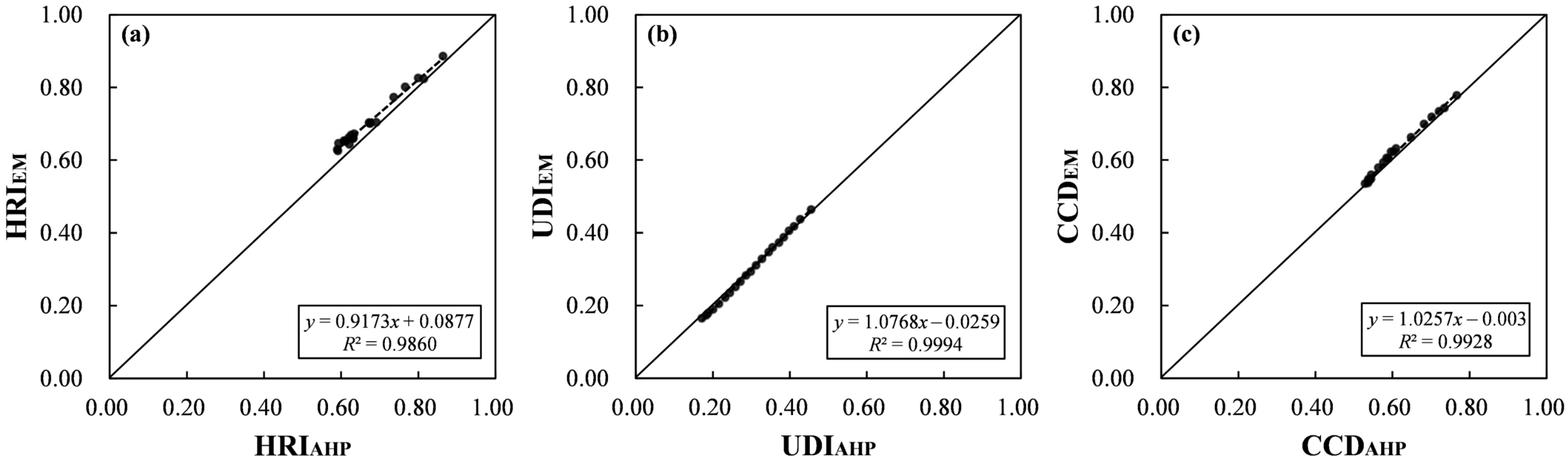
4.3. Comparison with HRI, UDI and CCD Results Using AHP Method
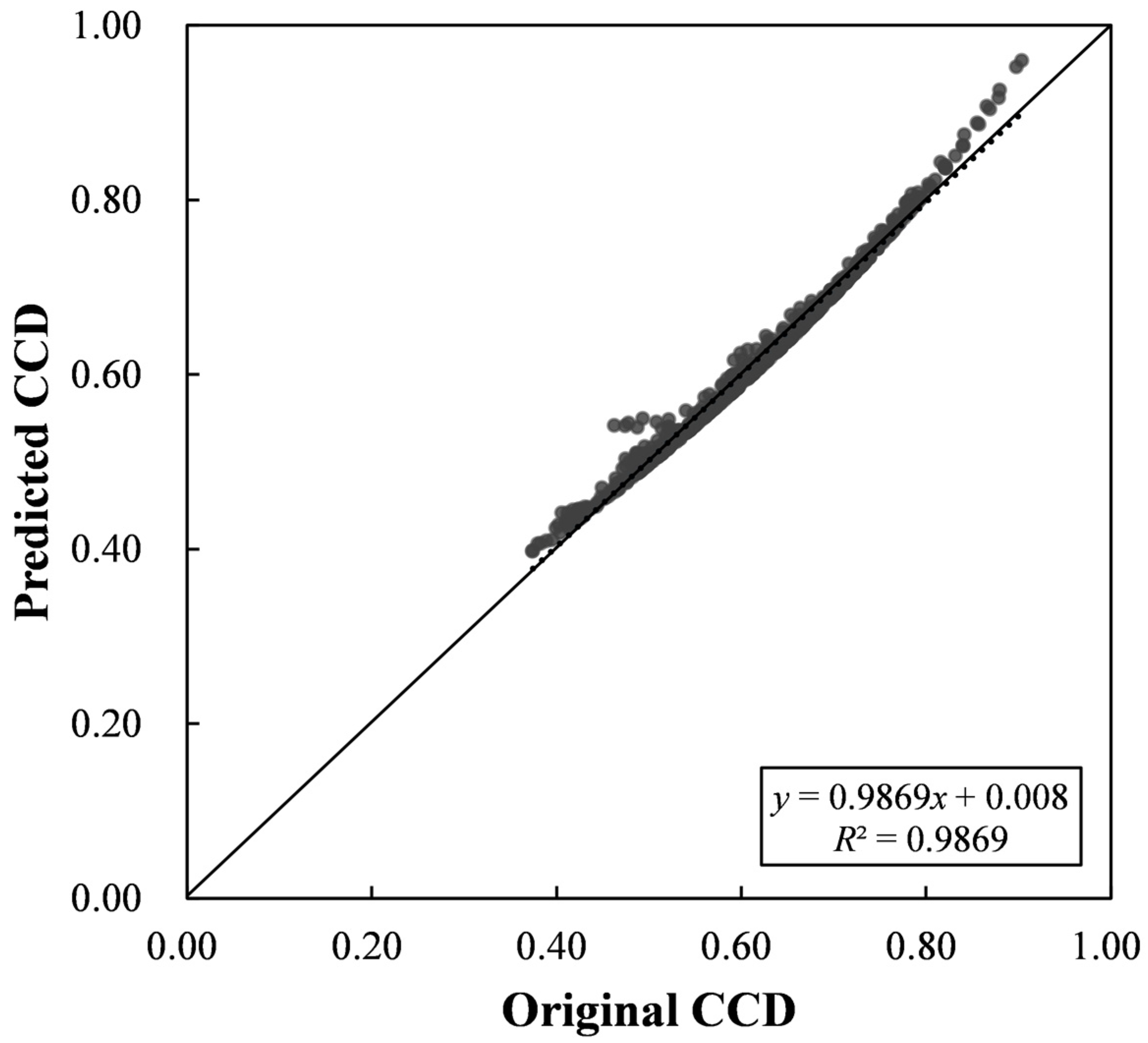
4.4. Relationship Exploration among the HRI, UDI and CCD
4.5. Policy Implications, Limitations and Further Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHP | Analytic hierarchy process | A subjective method to determine indicator’s weight |
| AOD | Aerosol optical depth | A measure of aerosols distribution within a column of air from the instrument to the top of the atmosphere |
| CCD | Coupling coordination degree | A measure of coupling coordination level between systems |
| CCDM | Coupling coordination degree model | A model of calculating coupling coordination degree |
| EU | Economy urbanization | An indicator of reflecting regional economy urbanization level |
| HRI | Haze disaster risk index | A measure of regional haze disaster risk level |
| PCA | Principal component analysis | A method of aggregating multi-dimensional information |
| PU | Population urbanization | An indicator of reflecting regional population urbanization level |
| SU | Spatiality urbanization | An indicator of reflecting regional spatiality urbanization level |
| TU | Society urbanization | An indicator of reflecting regional society urbanization level |
| UDI | Urbanization development index | A measure of regional urbanization level |
References
- Wen, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, L.; Zhao, X.; Liu, F.; Xu, J.; Yi, L.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Zuo, L.; et al. Extraction of basic trends of urban expansion in China over past 40 years from satellite images. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. China Statistical Yearbook (2021); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2013 Revision; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, P.; Niu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Dong, G.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Du, M.; Jiang, H.; et al. A systematic assessment of city-level climate change mitigation and air quality improvement in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Sheng, L.; Chen, G. Climatological intraseasonal oscillation of the summertime haze-fog in eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 244, 117951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Qin, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, W. Evaluation of haze press risk in China based on PM2.5. Acta Sci. Circu. 2017, 37, 4503–4510. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.; Yuan, H. Haze pollution and economic fluctuations: An empirical analysis of Chinese cities. Clean. Environ. Syst. 2021, 2, 100010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, J.; Zheng, W.; Yin, L. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of haze and pollution particles in China based on spatial statistics. Urban Clim. 2022, 41, 101031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Cao, T. Urbanization level, industrial structure adjustment and spatial effect of urban haze pollution: Evidence from China’s Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tan, B.; Zhang, K.; Wu, J. Risk assessment of urban haze disaster in Hunan province based on principal component analysis. J. Catas. 2021, 36, 76–81. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dotse, S.; Dagar, L.; Petra, M.; Silva, L. Influence of southeast Asian haze episodes on high PM10 concentrations across Brunei Darussalam. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Gao, J.; Jiang, J.; Lu, H.; Huang, J. Normalized difference haze index: A new spectral index for monitoring urban air pollution. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Yao, F.; Zhang, J.; Waqar, M.; Zha, Y.; He, J. Haze detection by using modified normalized difference haze index in Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei province. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 025025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Liu, Y. The influential factors of urban PM2.5 concentrations in China: A spatial econometric analysis. J. Clean Prod. 2016, 112, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tang, D.; Yang, X. Investigating the spatio-temporal variations of the impact of urbanization on haze pollution using multiple indicators. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2021, 35, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Fan, H.; Qian, Y. Modeling and efficient quantified risk assessment of haze causation system in China related to vehicle emissions with uncertainty consideration. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Wen, Y.; Yu, B.; Wu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Qiu, X. Evolution characteristics of fog and haze disaster weather in Hengshui city of Hebei province. J. Catas. 2015, 30, 79–84. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Aladağ, C. Opinions of geography and social sciences student-teachers on the concepts of urbanization and urbanizing. Educ. Urban Soc. 2019, 51, 351–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; He, S.; Li, G. Interaction between urbanization and the eco-environment in the Pan-Third Pole region. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 148011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lei, J.; Li, S.; Yang, Z.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, S.; Duan, Z. Spatiotemporal analysis of the relationship between urbanization and the eco-environment in the Kashgar metropolitan area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariken, M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, K.; Fang, C.; Kung, H. Coupling coordination analysis of urbanization and eco-environment in Yanqi Basin based on multi-source remote sensing data. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Zhuo, H.; Song, H.; Wang, J.; Ren, L. Examination of a coupling coordination relationship between urbanization and the eco-environment: A case study in Qingdao, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 23981–23993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Caloz, C.; Chang, C.; Itoh, T. Forward coupling phenomena between artificial left-handed transmission lines. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 5560–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Fang, C.; Zhang, Q. Coupling coordinated development between social economy and ecological environment in Chinese provincial capital cities-assessment and policy implications. J. Clean Prod. 2019, 229, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H. Spatio-temporal variation of the coupling relationship between urbanization and air quality: A case study of Shandong Province. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Jin, B.; Xi, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, R.; Guo, B.; Xu, Z.; et al. Spatiotemporal and multiscale analysis of the coupling coordination degree between economic development equality and eco-environmental quality in China from 2001 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Qian, T.; Sheng, C.; Xi, C.; Wang, J. Analysis of Differences in the Spatial Distribution among Terrestrial Mammals Using Geodetector—A Case Study of China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Cribb, M.; Huang, W.; Xue, W.; Sun, L.; Guo, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, J.; Lyapustin, A.; et al. Improved 1 km resolution PM2.5 estimates across China using enhanced space-time extremely randomized trees. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 3273–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Lyapustin, A.; Sun, L.; Peng, Y.; Xue, W.; Su, T.; Cribb, M. Reconstructing 1-km-resolution high-quality PM2.5 data records from 2000 to 2018 in China: Spatiotemporal variations and policy implications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J. Literature review and economic analysis of haze pollution. Financ. Econ. 2015, 14, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, G.; Huang, J.; Zhang, H. The impact of PM2.5 on kidney. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2022, 42, 4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Wang, Z.; Wei, L.; Wang, Z. Multidimensional effects of urbanization on PM2.5 concentration in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Shi, J. Urbanization and its environmental effects in Shanghai, China. Urban Clim. 2012, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Schäfer, K.; Shao, L.; Schnelle-Kreis, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Liu, Z.; Emeis, S.; Schmid, H. Chemical characteristics of PM2.5 during haze episodes in spring 2013 in Beijing. Urban Clim. 2017, 22, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Jiang, J. Urban Sprawl and Haze Pollution: Based on Raster Data of Haze PM2.5 Concentrations in 283 Cities in Mainland China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 929558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xu, H.; Yu, S. Estimating PM2.5 concentrations in Yangtze River Delta region of China using random forest model and the Top-of-Atmosphere reflectance. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 272, 111061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Bao, C.; Li, F. The effect of natural and anthropogenic factors on haze pollution in Chinese cities: A spatial econometrics approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Song, W.; Xiu, C.; Liang, Z. Non-coordination in China’s Urbanization: Assessment and Affecting Factors. Chin. Geogra. Sci. 2013, 23, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liang, L.; Sun, Z.; Wang, X. Spatiotemporal differentiation and the factors influencing urbanization and ecological environment synergistic effects within the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 243, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Xie, S.; Cheng, X. Coupling coordination analysis and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between urbanization and ecosystem health in Chongqing municipality, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Shang, J.; Ali, R.; Rehman, R. The Coupling Coordinated Relationship Between New-type Urbanization, Eco-Environment and its Driving Mechanism: A Case of Guanzhong, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 638891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, N.; Wu, X.; Zhang, P. Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of coordinated development of urbanization and ecological environment in eastern Russia—Perspectives from the 3D global trend and 2D plane analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Ding, L.; Li, D.; Altan, O.; Huq, M.; Li, C. Exploring the Relationship between Urbanization and Ecological Environment Using Remote Sensing Images and Statistical Data: A Case Study in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Zhu, J.; Lou, K.; Yang, L. Coupling coordination and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between urbanization and ecological environment in Shaanxi Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, A.; Cao, Y.; Xie, Y.; Guo, L. Interaction between Urbanization and Eco-Environment in Hebei Province, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, X. Investigation of a coupling model of coordination between urbanization and the environment. J. Environ. Manage. 2012, 98, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, L. Spatiotemporal Change and Coordinated Development Analysis of “Population-Society-Economy-Resource-Ecology-Environment” in the Jing-Jin-Ji Urban Agglomeration from 2000 to 2015. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fang, C.; Wang, Y. Quantitative investigation of the interactive coupling relationship between urbanization and eco-environment. Acta. Ecol. Sinica 2015, 35, 2244–2254. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, P.; Huang, J.; Zhou, H.; Fang, C.; Zhan, Y.; Huang, W. Local and telecoupling coordination degree model of urbanization and the eco-environment based on RS and GIS: A case study in the Wuhan urban agglomeration. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. Coupling coordination and spatiotemporal dynamic evolution between urbanization and geological hazards-A case study from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Cheng, J.; Xu, S.; Geng, J.; Yang, F.; Fang, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; et al. Understanding the Relationship between China’s Eco-Environmental Quality and Urbanization Using Multisource Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Hadi, A. Regression Analysis by Example, 4th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Chen, L.; Sun, R.; Kong, P. Science of the Total Environment Land use changes and socio-economic development strongly deteriorate river ecosystem health in one of the largest basins in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Systems | Attributes | Indicators | Trend | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haze disaster risk index | Haze disaster | PM2.5 annual average concentration (μg/m3) | Negative | 0.4447 |
| Sulfur dioxide emissions per 10,000 people (t) | Negative | 0.3464 | ||
| Smoke and dust emissions per 10,000 people (t) | Negative | 0.2089 | ||
| Urbanization development index | Population urbanization | Proportion of urban population (%) | Positive | 0.1316 |
| Proportion of employees in secondary and tertiary industries (%) | Positive | 0.1179 | ||
| Economy urbanization | Per capita GDP (yuan) | Positive | 0.0635 | |
| Share of tertiary sector in GDP (%) | Positive | 0.0326 | ||
| Per urban resident disposable income (yuan) | Positive | 0.0554 | ||
| Per capita fiscal revenue (yuan) | Positive | 0.0945 | ||
| Society urbanization | Number of doctors per 10,000 people (person) | Positive | 0.0967 | |
| Number of university students per 10,000 people (person) | Positive | 0.0927 | ||
| Number of public transport vehicles per 10,000 people (unit) | Positive | 0.0651 | ||
| Spatiality urbanization | Per capita built-up area (m2) | Positive | 0.1376 | |
| Per capita paved road area (m2) | Positive | 0.1124 |
| CCD Classification Criteria | CCD Level |
|---|---|
| 0.0 < CCD ≤ 0.2 | Serious incoordination |
| 0.2 < CCD ≤ 0.4 | Moderate incoordination |
| 0.4 < CCD ≤ 0.6 | Low coordination |
| 0.6 < CCD ≤ 0.8 | Moderate coordination |
| 0.8 < CCD ≤ 1.0 | High coordination |
| Indicators | Weight |
|---|---|
| PM2.5 annual average concentration (μg/m3) | 0.6333 |
| Sulfur dioxide emissions per 10,000 people (t) | 0.2605 |
| Smoke and dust emissions per 10,000 people (t) | 0.1062 |
| Proportion of urban population (%) | 0.1673 |
| Proportion of employees in secondary and tertiary industries (%) | 0.1324 |
| Per capita GDP (yuan) | 0.0336 |
| Share of tertiary sector in GDP (%) | 0.0162 |
| Per urban resident disposable income (yuan) | 0.0250 |
| Per capita fiscal revenue (yuan) | 0.0566 |
| Number of doctors per 10,000 people (person) | 0.0566 |
| Number of university students per 10,000 people (person) | 0.0566 |
| Number of public transport vehicles per 10,000 people (unit) | 0.0355 |
| Per capita built-up area (m2) | 0.2103 |
| Per capita paved road area (m2) | 0.2099 |
| Year | HRIAHP | UDIAHP | CCDAHP |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 0.6918 | 0.1717 | 0.5370 |
| 2001 | 0.6764 | 0.1877 | 0.5413 |
| 2002 | 0.6737 | 0.1837 | 0.5374 |
| 2003 | 0.6310 | 0.2009 | 0.5291 |
| 2004 | 0.6320 | 0.2163 | 0.5394 |
| 2005 | 0.6217 | 0.2327 | 0.5447 |
| 2006 | 0.5922 | 0.2450 | 0.5378 |
| 2007 | 0.5906 | 0.2594 | 0.5458 |
| 2008 | 0.6127 | 0.2720 | 0.5641 |
| 2009 | 0.6203 | 0.2868 | 0.5765 |
| 2010 | 0.6340 | 0.2988 | 0.5900 |
| 2011 | 0.6081 | 0.3126 | 0.5855 |
| 2012 | 0.6267 | 0.3283 | 0.6033 |
| 2013 | 0.5937 | 0.3453 | 0.5970 |
| 2014 | 0.6086 | 0.3557 | 0.6100 |
| 2015 | 0.6736 | 0.3722 | 0.6490 |
| 2016 | 0.7365 | 0.3844 | 0.6825 |
| 2017 | 0.7663 | 0.3986 | 0.7020 |
| 2018 | 0.8000 | 0.4117 | 0.7218 |
| 2019 | 0.8151 | 0.4276 | 0.7354 |
| 2020 | 0.8646 | 0.4562 | 0.7671 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, J.; Tang, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Shifaw, E.; Zhang, W.; Guo, B. Spatiotemporal Analysis of the Coupling Coordination Degree between Haze Disaster and Urbanization Systems in China from 2000 to 2020. Systems 2022, 10, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems10050150
Ji J, Tang Z, Wang L, Liu W, Shifaw E, Zhang W, Guo B. Spatiotemporal Analysis of the Coupling Coordination Degree between Haze Disaster and Urbanization Systems in China from 2000 to 2020. Systems. 2022; 10(5):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems10050150
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Jianwan, Zhanzhong Tang, Litao Wang, Wenliang Liu, Eshetu Shifaw, Weiwei Zhang, and Bing Guo. 2022. "Spatiotemporal Analysis of the Coupling Coordination Degree between Haze Disaster and Urbanization Systems in China from 2000 to 2020" Systems 10, no. 5: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems10050150
APA StyleJi, J., Tang, Z., Wang, L., Liu, W., Shifaw, E., Zhang, W., & Guo, B. (2022). Spatiotemporal Analysis of the Coupling Coordination Degree between Haze Disaster and Urbanization Systems in China from 2000 to 2020. Systems, 10(5), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems10050150







