Undergraduate Teaching Audit and Evaluation Using an Extended ORESTE Method with Interval-Valued Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Sets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Researches on Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Methods
2.2. Researches on ORESTE Improvement
2.3. Researches on UTAE
3. Preliminaries
- (1)
- The set is ordered: , if i > j;
- (2)
- There is a negation operator: satisfying i + j = 2t.
- (1)
- (2)
- ;
- (3)
- .
- (1)
- If E(α1) > E(α2), then α1 > α2.
- (2)
- If E(α1) = E(α2), then:
- (a)
- if D(α1) > D(α2), then α1 > α2;
- (b)
- if D(α1) = D(α2), then α1 = α2.
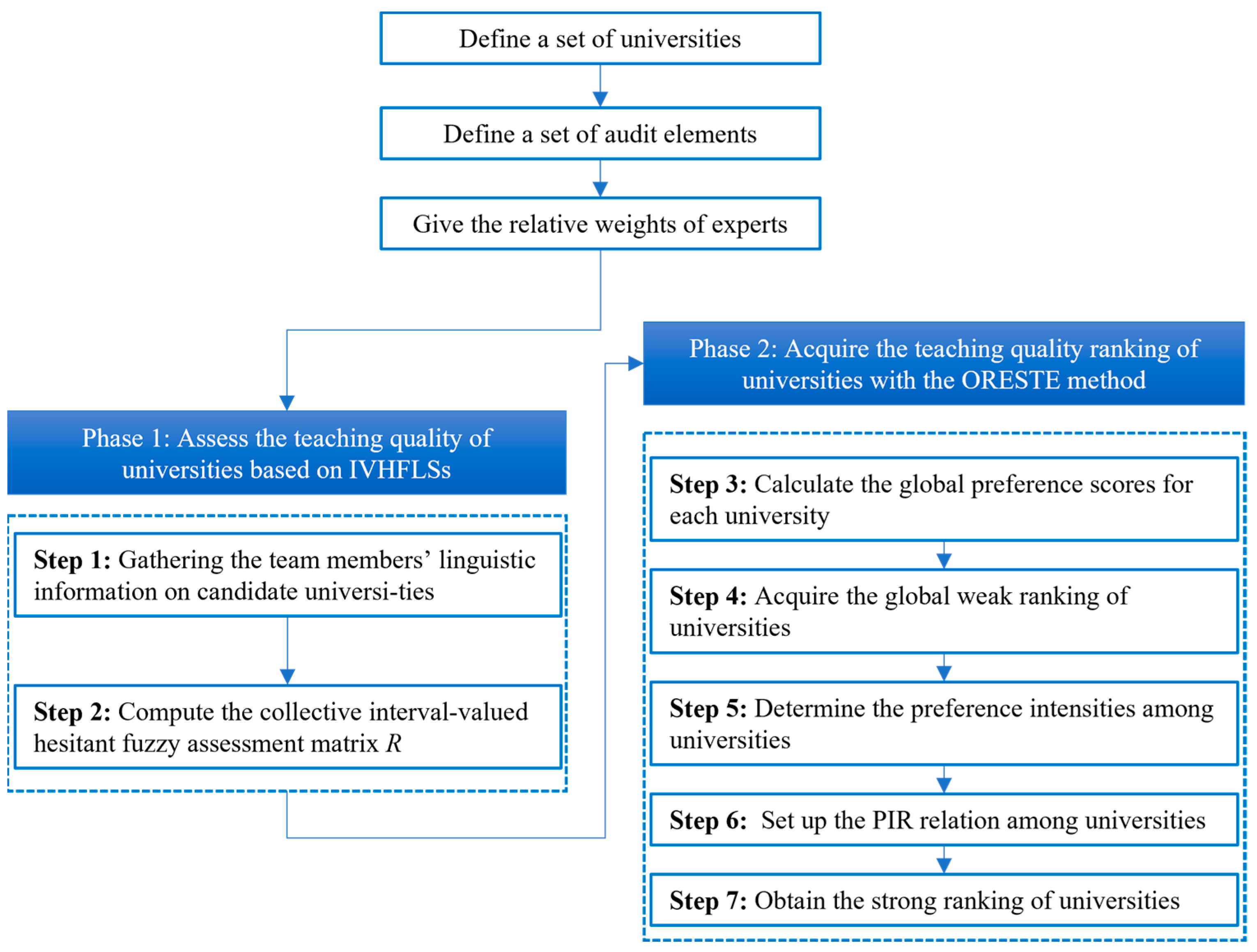
4. The Proposed UTAE Methodology
- (1)
- If , then
- (a)
- Ui I Up, if and ;
- (b)
- Ui R Up, if or .
- (2)
- If , then
- (a)
- Ui R Up, if
- (b)
- Ui P Up, if and ;
- (c)
- Up P Ui, if and .
5. Illustrative Example
5.1. Application
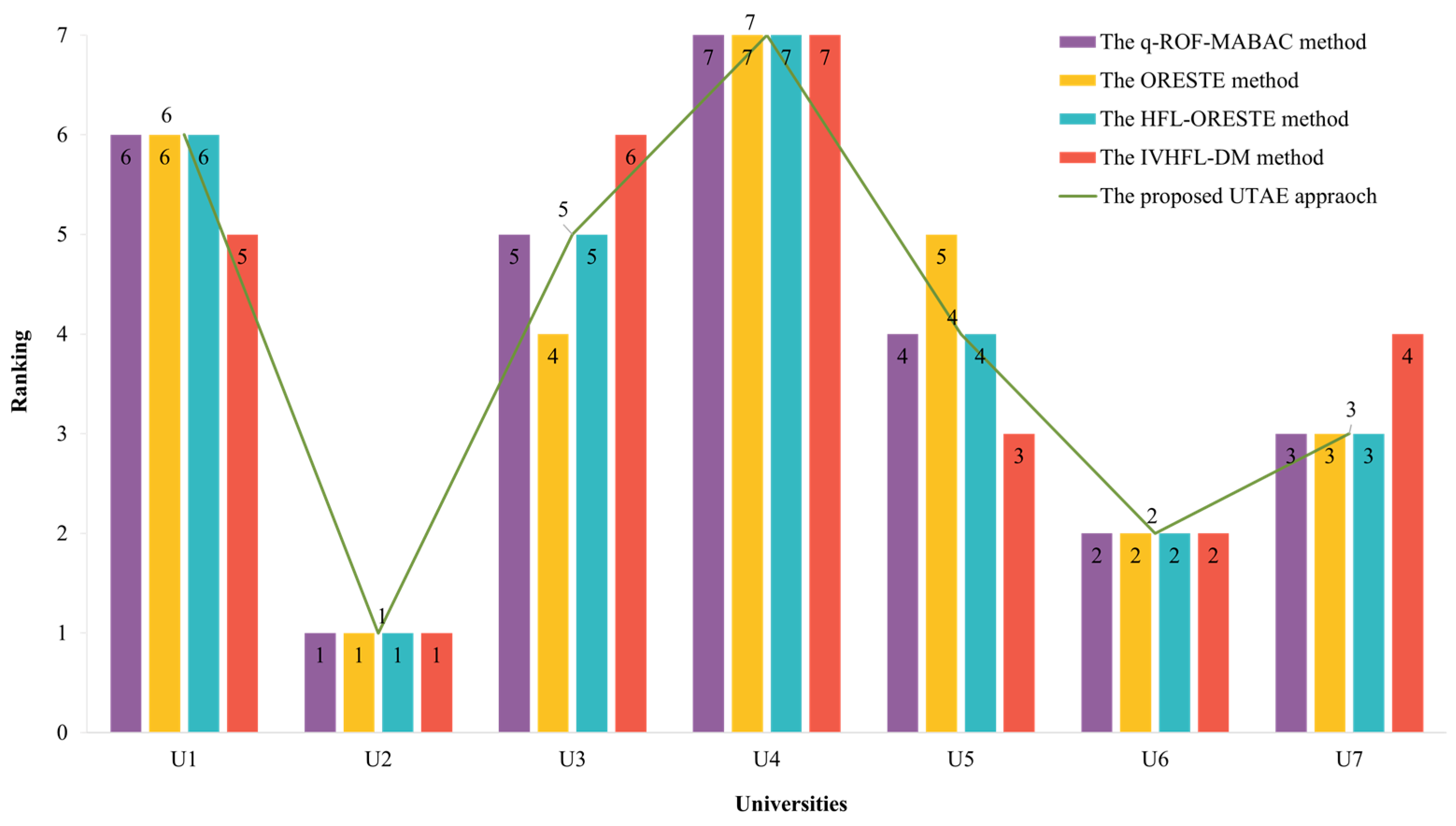
5.2. Comparative Analysis
- (1)
- The proposed approach can reduce information loss when aggregating multiple-expert evaluations and increase the flexibility of eliciting and displaying experts’ linguistic assessment information by utilizing the IVHFLSs. Decision makers can now communicate their opinions more clearly and realistically.
- (2)
- The suggested methodology, which is based on the ORESTE method, is more effective in the UTAE process and can help decision makers get rankings of alternative colleges that are fairer and more trustworthy. This improves the viability and realism of the IVHFLS-ORESTE technique.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, J.W.; Li, Q.; Yin, L.; Liu, H.C. Undergraduate teaching audit and evaluation using an extended MABAC method under q-rung orthopair fuzzy environment. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2020, 35, 1912–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Baocun, L. The undergraduate teaching evaluation system in China: Progress, problems and suggestions. Chin. Educ. Soc. 2018, 51, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q. Using neural network for the evaluation of physical education teaching in colleges and universities. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 10699–10705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alobaid, M.A.; Bin Hassan, S.A.; Alfarhan, A.H.; Ali, S.; Hameed, M.S.; Syed, S. A critical evaluation of the undergraduate endodontic teaching in dental colleges of Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X. Neutrosophic reducible weighted maclaurin symmetric mean for undergraduate teaching audit and evaluation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 18634–18648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Teaching quality monitoring and evaluation using 6G internet of things communication and data mining. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2023, 14, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, X. EDAS method for single-valued neutrosophic number multiattribute group decision-making and applications to physical education teaching quality evaluation in colleges and universities. Math. Probl. Eng. 2023, 2023, 5576217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, H. Managing multi-granularity linguistic information in qualitative group decision making: An overview. Granul. Comput. 2016, 1, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asan, U.; Kadaifci, C.; Bozdag, E.; Soyer, A.; Serdarasan, S. A new approach to DEMATEL based on interval-valued hesitant fuzzy sets. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 66, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Wu, J.T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, X.H. Interval-valued hesitant fuzzy linguistic sets and their applications in multi-criteria decision-making problems. Inf. Sci. 2014, 288, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, W.; Qiang, L. Interval-valued hesitant fuzzy linguistic multiattribute decision-making method based on three-parameter heronian mean operators. J. Math. 2021, 2021, 3634895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.B.; Hu, S.S.; Dong, J.Y.; Wan, S.P.; Xu, G.L. Multi-attribute group decision making based on cloud aggregation operators under interval-valued hesitant fuzzy linguistic environment. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 20, 2273–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, J. A two-sided stable matching model of cloud manufacturing tasks and services considering the nonlinear relationship between satisfaction and expectations. Complexity 2021, 2021, 6735210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, S.; Mousavi, S.M. A new risk evaluation methodology based on FMEA, MULTIMOORA, TPOP, and interval-valued hesitant fuzzy linguistic sets with an application to healthcare industry. Kybernetes 2021, 50, 2521–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ju, Y.; Liu, X. Multiple criteria decision analysis based on Shapley fuzzy measures and interval-valued hesitant fuzzy linguistic numbers. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2017, 105, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P. VIKOR method for intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute group decision-making and its application to teaching quality evaluation of college English. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 42, 5189–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.W.; Liu, H.C.; You, X.Y.; Yin, L. An integrated multi-criteria decision making approach with linguistic hesitant fuzzy sets for E-learning website evaluation and selection. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 102, 107118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubens, M. Preference relations on actions and criteria in multicriteria decision making. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1982, 10, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liao, H. An approach to hesitant fuzzy linguistic multiple criteria group decision making with uncertain criteria weights considering incomparability between alternatives. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Lu, K.; Jiang, L. Learning the thresholds in the ORESTE method from historical preference information. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Mao, L.X.; Li, K.; Wang, X.H.; Liu, H.C. Engineering characteristics prioritization in quality function deployment using an improved ORESTE method with double hierarchy hesitant linguistic information. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liao, H. An approach to quality function deployment based on probabilistic linguistic term sets and ORESTE method for multi-expert multi-criteria decision making. Inf. Fusion 2018, 43 (Suppl. C), 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Wu, X.; Liang, X.; Xu, J.; Herrera, F. A new hesitant fuzzy linguistic ORESTE method for hybrid multicriteria decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 26, 3793–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.P.; Liang, H.M.; Nie, R.X.; Wang, X.K.; Wang, J.Q. Data-driven multi-criteria decision support method for electric vehicle selection. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 177, 109061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Jing, X.; Martínez, L. An ELICIT information-based ORESTE method for failure mode and effect analysis considering risk correlation with GRA-DEMATEL. Inf. Fusion 2023, 93, 396–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, H.; Liu, P. Assessment of regional economic restorability under the stress of COVID-19 using the new interval type-2 fuzzy ORESTE method. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lianga, Y.; Jua, Y.; Martínezb, L.; Tuc, Y. Sustainable battery supplier evaluation of new energy vehicles using a distributed linguistic outranking method considering bounded rational behavior. J. Energy Storage 2022, 48, 103901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, D.; Liu, P. An integrated TOPSIS–ORESTE-based decision-making framework for new energy investment assessment with cloud model. Comput. Appl. Math. 2022, 41, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.M.; Martinez, L.; Herrera, F. Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2012, 20, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Tao, Y.; Chen, W. Prospects and barriers analysis framework for the development of energy storage sharing. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 89, 104368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; He, S.F.; Zamora, D.G.; Pan, X.H.; Martínez, L. A large scale group three-way decision-based consensus model for site selection of new energy vehicle charging stations. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 214, 119107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, X.; Kexin, Z. Dynamic evaluation of a post-pandemic agricultural traceability system, based on the HFLTS-DEMATEL method. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishankumar, R.; Pamucar, D.; Deveci, M.; Aggarwal, M.; Ravichandran, K.S. Assessment of renewable energy sources for smart cities’ demand satisfaction using multi-hesitant fuzzy linguistic based Choquet integral approach. Renew. Energy 2022, 189, 1428–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finger, G.S.W.; Lima-Junior, F.R. A hesitant fuzzy linguistic QFD approach for formulating sustainable supplier development programs. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2022, 247, 108428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, I.; Murat Ar, I.; Peker, I.; Searcy, C. Alleviating the impact of the barriers to circular economy adoption through blockchain: An investigation using an integrated MCDM-based QFD with hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 165, 107962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y.J.; Hou, L.X.; Liu, H.C. New method for dependence assessment in human reliability analysis based on linguistic hesitant fuzzy information. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2021, 53, 3675–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Liu, H.C.; Xu, J.Y.; Ping, Y.J. A new method for quality function deployment using double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and axiomatic design approach. Qual. Eng. 2021, 33, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishankumar, R.; Pamucar, D.; Pandey, A.; Kar, S.; Ravichandran, K.S. Double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic information based framework for personalized ranking of sustainable suppliers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 65371–65390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, Z.; Gou, X. ELECTRE II method based on the cosine similarity to evaluate the performance of financial logistics enterprises under double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic environment. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Mak. 2022, 22, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Liao, H. A social participatory allocation network method with partial relations of alternatives and its application in sustainable food supply chain selection. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 109, 107550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gou, X.; Xu, Z. Assessment of traffic congestion with ORESTE method under double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic environment. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2020, 86, 105864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Liang, W.; Zhao, G. Likelihood-based hybrid ORESTE method for evaluating the thermal comfort in underground mines. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2020, 87, 105983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.H.; Wang, Y.M.; He, S.F.; Labella, Á.; Martínez, L. An interval type-2 fuzzy ORESTE method for waste-to-energy plant site selection: A case study in China. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 136, 110092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Pang, Y. T-Spherical fuzzy ORESTE method based on cross-entropy measures and its application in multiple attribute decision-making. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 10371–10387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Li, F. Risk assessment in failure mode and effect analysis: Improved ORESTE method with hesitant pythagorean fuzzy information. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2021, 70, 2115–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Ran, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, G. Prioritization of key quality characteristics with the three-dimensional HoQ model-based interval-valued spherical fuzzy-ORESTE method. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 104, 104271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalla, M.; Facchinetti, G.; Mastroleo, G. Ordinal scales and fuzzy set systems to measure agreement: An application to the evaluation of teaching activity. Qual. Quant. 2005, 38, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.F.; Hsieh, H.N.; Do, Q.H. Evaluating teaching performance based on fuzzy AHP and comprehensive evaluation approach. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 28, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rocca, M.; Parrella, M.L.; Primerano, I.; Sulis, I.; Vitale, M.P. An integrated strategy for the analysis of student evaluation of teaching: From descriptive measures to explanatory models. Qual. Quant. 2017, 51, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, M.C.; Tarantola, S.; Carot, J.M.; Conchado, A. Sensitivity analysis: A necessary ingredient for measuring the quality of a teaching activity index. Soc. Indic. Res. 2017, 131, 931–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C. Research on a new teaching quality evaluation method based on improved fuzzy neural network for college English. Int. J. Contin. Eng. Educ. Life Long Learn. 2018, 28, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Dai, J. Research on the assessment of classroom teaching quality with q-rung orthopair fuzzy information based on multiparametric similarity measure and combinative distance-based assessment. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2019, 34, 1588–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.L. The teaching quality evaluation of Chinese-Foreign cooperation in running schools from the perspective of education for sustainable development. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M. The quality evaluation of business English classroom teaching using improved DA-BP algorithm. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 7260914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L. College English teaching evaluation with neural network. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 6870764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Liu, L.; Kumar, B.S.; Prathik, A. An English teaching quality evaluation model based on Gaussian process machine learning. Expert Syst. 2022, 39, e12861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Velasco, M. The technical efficiency performance of the higher education systems based on data envelopment analysis with an illustration for the Spanish case. Educ. Res. Policy Pract. 2020, 19, 159–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Liu, H.C.; Wang, J.H.; Shi, H. New model for occupational health and safety risk assessment based on Fermatean fuzzy linguistic sets and CoCoSo approach. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 126, 109262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seikh, M.R.; Mandal, U. Multiple attribute decision-making based on 3,4-quasirung fuzzy sets. Granul. Comput. 2022, 7, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seikh, M.R.; Mandal, U. Multiple attribute group decision making based on quasirung orthopair fuzzy sets: Application to electric vehicle charging station site selection problem. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 115, 105299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; Wang, J.H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.Z. New success likelihood index model for large group human reliability analysis considering noncooperative behaviors and social network. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2022, 228, 108817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; Shi, H.; Li, Z.; Duan, C.Y. An integrated behavior decision-making approach for large group quality function deployment. Inf. Sci. 2022, 582, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| U1 | U2 | U3 | U4 | U5 | U6 | U7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AE1 | <s4,[0.5, 0.8]> | <s4,[0.2, 0.8]> | <s3,[0.1, 0.3]> | <s3,[0.1, 0.6]> | <s4,[0.5, 0.8]> | <s5,[0.6, 0.8]> | <s5,[0.5, 0.7]> |
| AE2 | <s3,[0.3, 0.6]> | <s5,[0.6, 0.8]> | <s3,[0.1, 0.5]> | <s2,[0.3, 0.6]> | <s5,[0.6, 0.8]> | <s4,[0.5, 0.8]> | <s3,[0.1, 0.4]> |
| AE3 | <s4,[0.4, 0.8]> | <s4,[0.4, 0.7]> | <s4,[0.5, 0.8]> | <s2,[0.2, 0.6]> | <s3,[0.4, 0.7]> | <s6,[0.5, 0.9]> | <s4,[0.5, 0.8]> |
| AE4 | <s3,[0.3, 0.9]> | <s5,[0.6, 0.8]> | <s4,[0.5, 0.8]> | <s5,[0.4, 0.6]> | <s2,[0.7, 0.8]> | <s3,[0.2, 0.6]> | <s4,[0.4, 0.8]> |
| AE5 | <s5,[0.1, 0.5]> | <s6,[0.4, 0.8]> | <s3,[0.1, 0.6]> | <s2,[0.1, 0.4]> | <s3,[0.6, 0.8]> | <s4,[0.5, 0.8]> | <s4,[0.5, 0.8]> |
| AE6 | <s1,[0.1, 0.7]> | <s4,[0.5, 0.9]> | <s2,[0.3, 0.5]> | <s1,[0.5, 0.6]> | <s3,[0.4, 0.6]> | <s5,[0.4, 0.6]> | <s3,[0.1, 0.5]> |
| AE7 | <s3,[0.3, 0.6]> | <s5,[0.2, 0.8]> | <s2,[0.2, 0.6]> | <s3,[0.3, 0.6]> | <s4,[0.5, 0.8]> | <s5,[0.5, 0.6]> | <s4,[0.5, 0.6]> |
| AE8 | <s3,[0.3, 0.6]> | <s4,[0.4, 0.7]> | <s3,[0.4, 0.8]> | <s2,[0.4, 0.9]> | <s4,[0.4, 0.8]> | <s5,[0.2, 0.8]> | <s3,[0.4, 0.7]> |
| AE9 | <s2,[0.1, 0.6]> | <s5,[0.4, 0.8]> | <s5,[0.2, 0.5]> | <s3,[0.3, 0.8]> | <s2,[0.1, 0.3]> | <s3,[0.3, 0.6]> | <s5,[0.5, 0.7]> |
| AE10 | <s3,[0.3, 0.8]> | <s6,[0.6, 0.7]> | <s4,[0.5, 0.8]> | <s2,[0.6, 0.9]> | <s2,[0.2, 0.3]> | <s3,[0.5, 0.6]> | <s2,[0.4, 0.5]> |
| U1 | U2 | U3 | U4 | U5 | U6 | U7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AE1 | <s3.58,[0.46, 0.79]> | <s3.43,[0.32, 0.78]> | <s2.94,[0.23, 0.39]> | <s3.29,[0.09, 0.68]> | <s3.98,[0.48, 0.85]> | <s5.38,[0.59, 0.74]> | <s4.89,[0.49, 0.73]> |
| AE2 | <s2.13,[0.23, 0.72]> | <s4.12,[0.43, 0.79]> | <s2.69,[0.13, 0.51]> | <s1.99,[0.22, 0.63]> | <s5.18,[0.62, 0.84]> | <s3.46,[0.47, 0.86]> | <s3.79,[0.12, 0.46]> |
| AE3 | <s3.79,[0.42, 0.80]> | <s3.80,[0.39, 0.72]> | <s4.12,[0.49, 0.76]> | <s2.35,[0.19, 0.61]> | <s3.39,[0.41, 0.74]> | <s5.66,[0.49, 0.87]> | <s3.87,[0.56, 0.85]> |
| AE4 | <s4.52,[0.36, 0.60]> | <s5.36,[0.59 0.76]> | <s4.68,[0.57, 0.89]> | <s5.06,[0.41 0.55]> | <s2.63,[0.74, 0.81]> | <s3.11,[0.21, 0.57]> | <s4.03,[0.45, 0.84]> |
| AE5 | <s5.21,[0.22, 0.62]> | <s5.97,[0.42, 0.79]> | <s3.08,[0.24, 0.71]> | <s2.48,[0.36, 0.87]> | <s3.46,[0.62, 0.77]> | <s4.18,[0.47, 0.80]> | <s3.96,[0.16, 0.83]> |
| AE6 | <s0.89,[0.22, 0.53]> | <s3.69,[0.55, 0.86]> | <s2.92,[0.32, 0.57]> | <s1.24,[0.45, 0.62]> | <s3.25,[0.49, 0.55]> | <s5.03,[0.49, 0.63]> | <s3.07,[0.09, 0.43]> |
| AE7 | <s2.78,[0.32, 0.55]> | <s5.01,[0.31, 0.87]> | <s1.85,[0.29, 0.81]> | <s3.31,[0.31, 0.79]> | <s3.86,[0.52, 0.84]> | <s4.99,[0.51, 0.62]> | <s3.80,[0.52, 0.66]> |
| AE8 | <s3.31,[0.31, 0.65]> | <s3.69,[0.43, 0.76]> | <s5.09,[0.15, 0.59]> | <s2.27,[0.58, 0.69]> | <s3.58,[0.46, 0.79]> | <s5.36,[0.19, 0.77]> | <s3.14,[0.41, 0.73]> |
| AE9 | <s2.54,[0.16, 0.58]> | <s5.45,[0.42, 0.86]> | <s3.58,[0.46, 0.79]> | <s3.96,[0.41, 0.72]> | <s1.85,[0.08 0.79]> | <s3.46,[0.28, 0.61]> | <s5.03,[0.56, 0.70]> |
| AE10 | <s3.64,[0.34, 0.77]> | <s5.81,[0.56, 0.73]> | <s3.98,[0.45, 0.74]> | <s2.30,[0.49, 0.95]> | <s2.34,[0.17, 0.36]> | <s3.90,[0.47, 0.61]> | <s2.09,[0.43, 0.53]> |
| U1 | U2 | U3 | U4 | U5 | U6 | U7 | |
| AE1 | 27.5 | 42.5 | 63 | 54 | 16 | 5.5 | 10 |
| AE2 | 59 | 22 | 64.5 | 64.5 | 2 | 27.5 | 57 |
| AE3 | 25.5 | 36.5 | 19.5 | 61.5 | 41 | 1 | 14 |
| AE4 | 34.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 23.5 | 38.5 | 55.5 | 19.5 |
| AE5 | 34.5 | 5.5 | 51.5 | 50 | 23.5 | 16 | 40 |
| AE6 | 70 | 19.5 | 53 | 68 | 46.5 | 12.5 | 66.5 |
| AE7 | 55.5 | 11 | 59 | 44.5 | 16 | 12.5 | 31 |
| AE8 | 48.5 | 31 | 42.5 | 51.5 | 31 | 19.5 | 44.5 |
| AE9 | 61.5 | 8 | 31 | 31 | 66.5 | 48.5 | 9 |
| AE10 | 38.5 | 3 | 25.5 | 46.5 | 69 | 36.5 | 59 |
| D(rij) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AE1 | 19.83 | 30.30 | 44.72 | 38.38 | 11.96 | 5.50 | 8.07 |
| AE2 | 41.90 | 16.04 | 45.77 | 45.77 | 4.14 | 19.83 | 40.49 |
| AE3 | 18.05 | 25.82 | 13.81 | 43.49 | 29.00 | 1.00 | 9.92 |
| AE4 | 24.89 | 6.29 | 6.29 | 17.34 | 27.67 | 39.56 | 14.65 |
| AE5 | 25.40 | 8.07 | 37.10 | 36.06 | 18.06 | 13.34 | 29.15 |
| AE6 | 49.90 | 15.19 | 38.01 | 48.50 | 33.49 | 10.89 | 47.45 |
| AE7 | 39.65 | 9.62 | 42.10 | 31.97 | 12.65 | 10.49 | 22.64 |
| AE8 | 34.32 | 21.97 | 30.09 | 36.44 | 21.97 | 13.86 | 31.50 |
| AE9 | 43.56 | 6.17 | 22.06 | 22.06 | 47.09 | 34.38 | 6.83 |
| AE10 | 27.22 | 2.12 | 18.03 | 32.88 | 48.79 | 25.81 | 41.72 |
| Strong Ranking | Universities | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1 | U2 | U3 | U4 | U5 | U6 | U7 | |
| r(Ui) | 6 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, L.-X.; Lan, J.; Li, Z.; Shi, H. Undergraduate Teaching Audit and Evaluation Using an Extended ORESTE Method with Interval-Valued Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Sets. Systems 2023, 11, 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11050216
Mao L-X, Lan J, Li Z, Shi H. Undergraduate Teaching Audit and Evaluation Using an Extended ORESTE Method with Interval-Valued Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Sets. Systems. 2023; 11(5):216. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11050216
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Ling-Xiang, Jing Lan, Zifeng Li, and Hua Shi. 2023. "Undergraduate Teaching Audit and Evaluation Using an Extended ORESTE Method with Interval-Valued Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Sets" Systems 11, no. 5: 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11050216
APA StyleMao, L.-X., Lan, J., Li, Z., & Shi, H. (2023). Undergraduate Teaching Audit and Evaluation Using an Extended ORESTE Method with Interval-Valued Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Sets. Systems, 11(5), 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11050216





