Abstract
Heritage crimes can result in the significant loss of cultural relics and predicting them is crucial. To address the issues of inconsistent textual information format and the challenge of preventing and combating heritage crimes, this paper develops a system that extracts crime elements and predict heritage crime occurrences. The system comprises two deep-learning models. The first model, Bi-LSTM + CRF, is constructed to automatically extract crime elements and perform spatio-temporal analysis of crimes based on them. By integrating routine activity theory, social disorder theory, and practical field experience, the research reveals that holidays and other special days (SD) perform a critical role as influential factors in heritage crimes. Building upon these findings, the second model, LSTM + SD, is constructed to predict excavation-type heritage crimes. The results demonstrate that the model with the introduction of the holiday factor improves the RMSE and MAE by 6.4% and 47.8%, respectively, when compared to the original LSTM model. This paper presents research aimed at extracting crime elements and predicting excavation-type heritage crimes. With the ongoing expansion of data volume, the practical significance of the proposed system is poised to escalate. The results of this study are expected to provide decision-making support for heritage protection departments and public security authorities in preventing and combating crimes.
1. Introduction
Cultural heritage comprises relics and vestiges that have significant historical, artistic, and scientific value, left behind by human beings during their social activities [1]. It is a vital medium for individuals to explore their traditional culture and derive spiritual nourishment [2]. Given the high risk of irreparable damage that heritage crimes pose to these non-renewable cultural objects, it is imperative to enhance all measures to combat heritage crimes [3].
Currently, the incessant excavation and smuggling of cultural heritage, driven by enormous illegal interests, pose a significant threat to cultural heritage security. Protecting cultural heritage has become an arduous task due to this situation. As heritage is non-renewable, prevention of heritage crimes should be prioritized over traditional post-event measures.
Excavation-type heritage crimes, unlike traditional crimes, are typically superstitious and perpetrated by gangs [4]. During the Three Kingdoms period, the “gold-digging captain” post was established to plunder tomb treasures for military expenses. However, social unrest and other factors led to the formation of a more complex group of tomb raiders, including scattered soldiers, professional soldiers, bandits, and geomancers. As a result, the method of crime shifted from manual excavation to explosive tomb raiding [5]. Today, heritage crimes have become more professional and organized, with sophisticated tools, such as infrared detectors, military compasses, and infrared binoculars [6]. This has resulted in the formation of an integrated upstream and downstream criminal chain and network, posing new challenges to the protection of cultural heritage and the fight against heritage crimes. To combat this serious and complex situation, public security authorities must enhance the scientific and technological content of their methods to protect heritage and combat heritage crimes.
The Department of Heritage Protection is increasingly gaining a better understanding of heritage crimes, and research on heritage protection is producing practical outcomes. However, most research remains stuck in legal discussions or analyses of current situations related to heritage crimes, with very few scholars engaged in researching the prediction and detection of heritage crimes. The prediction of heritage crimes combines historical data and investigative experience with other elements to analyze the spatial and temporal characteristics of heritage crimes, then predict their incidence or provide support for guiding practical work [7]. Heritage crimes typically lack obvious victims, and law enforcement is often unmotivated to investigate cases involving small amounts of money [8]. Crime data platforms in various locations also fail to analyze heritage crime data in depth, leading to the possibility of a certain criminal “dark figure” in heritage crimes and limited exploration and application of heritage crime data. Moreover, because heritage crimes are relatively infrequent compared to frequent property crimes, it is difficult to statistically analyze the development of the crime situation over a relatively short period, which explains the paucity of quantitative studies on heritage crimes. Traditional crime prediction models perform well in dealing with complex crime data involving multiple crimes, but they may struggle to demonstrate their advantages when dealing with sparse crime data [9]. Deep learning is a complex machine learning method that can extract features from complex data through multi-layer neural networks. It is characterized by learning ability, adaptability, wide applicability, and portability, and it can effectively solve problems, such as sparse crime data and overcome limitations of other machine learning methods. When it comes to tackling the challenge of sparse data, deep learning exhibits unique advantages. Unlike traditional machine learning methods that may struggle with limited data, deep learning models can effectively learn and extract meaningful patterns and representations from sparse datasets. By employing multiple layers of interconnected neurons, deep learning algorithms can automatically discover hierarchical representations of data, enabling them to capture intricate relationships and dependencies within the dataset. This ability to learn complex features and representations allows deep learning models to effectively generalize from limited data, enhancing their performance even when faced with sparse crime data. Furthermore, deep learning models excel at handling larger datasets and achieving high levels of generalization. With its multi-layer architecture, deep learning can leverage the vast amount of information contained in larger datasets. By learning multiple levels of abstraction, deep learning models can recognize and extract high-level features that are representative of the entire dataset, thus achieving better performance on larger and more diverse datasets. Therefore, it is necessary to combine traditional crime prediction methods with advanced technological methods, such as data mining and machine learning to build prediction models that can analyze massive amounts of data and achieve accurate predictions of future heritage crimes in time, space, and trends.
In summary, this study highlights the need to aggregate and analyze data on heritage crimes in conjunction with other relevant factors that may influence such crimes. Deep learning methods should then be employed to identify trends in crime patterns. This approach involves using criminological theory, social disorder theory, and field sector experience to select the relevant factors. The paper is organized as follows: Section 2 presents the research aims. Section 3 discusses the current state of research on heritage crime and crime prediction. Section 4 describes the system developed in this study and presents its experimental results. Finally, Section 5 concludes the paper and identifies key areas for further research.
2. Research Aims
The research aim of this paper is to develop a system for extracting crime elements and predicting excavation-type heritage crimes.
Natural language processing techniques are utilized to extract information from the structured textual data of excavation-type heritage crimes. The extracted temporal and spatial information are then analyzed to determine the characteristics of the crime in both spatial and temporal aspects. Crime hotspots are identified for time-series prediction. Currently, serious learning-based crime spatiotemporal prediction models exhibit high prediction accuracy. However, these studies often suffer from the inherent “black box” limitation, causing considerable uncertainty when applying them to new environments for crime prediction. Previous studies have primarily focused on constructing models with high accuracy by utilizing crime data with substantial volume, often overlooking the interpretation of characteristic variables. This study undertakes the construction of the excavation-type heritage crime prediction model based on LSTM as an endeavor to address these limitations. To analyze the factors affecting excavation-type heritage crimes, this study combines criminological theory, social disorder theory, and field experience and builds a predictive model for crimes.
The findings of this research can offer ideas and recommendations for heritage protection departments and public security authorities in preventing and combating crimes.
3. Related Works
3.1. Heritage Crime
Scholars have conducted extensive research on heritage crimes in various countries and regions, primarily focusing on the characteristics of heritage crime and combating strategies. Louise Grove provided a systematic account of heritage crime, offering insights into its definition, patterns, and different types. The research also underscored the significance of establishing the database and conducting comprehensive analyses of heritage crime. Furthermore, Grove highlighted the potential efficacy of employing situational prevention strategies to address heritage crime [10]. Bryant, R. et al. examined the spatial and temporal characteristics of crimes within, at, or close to heritage sites in Kent and Medway. It utilized crime mapping and the global Moran index to analyze the distribution of crime in the area and employed models, such as Prophet to analyze crime in terms of spatial and temporal characteristics. The study aimed to assess the impact of heritage action zones on the frequency of crimes within, at, or close to heritage sites in these areas and conducted a more localized analysis of CWACHS. Separate temporal and spatial analyses were conducted for three Heritage Action Zones, namely, Leeds and Hollingbourne, Ramsgate, and Swanscombe and Greenhithe. It is worth noting that the research analyzed reported crime at, within, or near a building or location with historical value and importance. Clearly, this was not the same as analyzing ‘heritage crime’ per se [11]. Manacorda et al. have published a book of research on the crime of illicit trafficking in art. The book provided a detailed exploration of the process of this crime and strategies to combat it. The research team also drew on the practical experience of frontline staff, such as those at Interpol and UNESCO, to make recommendations for improving the prevention, control, and detection of heritage crime [12]. Neil Brodie analyzed two criminal cases involving transnational trade in cultural objects. The study examined the activities of Subhash Kapoor, a dealer based in New York, and the activities of two dealers who transported cultural objects from Dubai Freeport to destination markets in London and New York. The analysis shed light on the potential modus operandi and criminal networks involved in the illicit trade of cultural objects and other cultural goods [13]. Liu analyzed the current situation of heritage crimes, which mainly included the number of crimes, types of crimes, subjects of crimes, objects of crimes, places of crimes, and means of crimes, and put forward relevant suggestions to improve the system of combating excavation-type heritage crimes [14]. M Balcells Magrans analyzed the tomb raiders in Italy from a criminological perspective, focusing on the history of tomb raiders, the relationship between criminal gangs and organized crime, the internal structure of criminal gangs, and the technical means used by tomb raiders [15]. From the perspective of investigation work mechanism, Some scholars have also described the practices of the Italian Carabinieri Command for the Protection of Cultural Heritage in the fight against heritage crimes, which include the creation of a rapidly deployable unit, the Task Force Unite4Heritage (TF U4H), and the construction of a database of illegally removed cultural artifacts, “Leonardo”, the biggest database of stolen works of art in the world [16]. Xu optimized the investigation work mechanism of cultural relics crime based on analyzing the existing work difficulties and reasons, mainly including strengthening the collection of information, breaking down the work barriers of investigation departments, improving the professional quality of investigators, and strengthening the guidance mechanism of public opinion [17].
Crime situations are dynamic and subject to various factors, making it difficult to predict future situations based solely on historical crime data. Therefore, incorporating criminological theory and practical experience is essential to identify the factors that influence crime situations, ultimately improving the interpretability and validity of crime prediction models.
A large body of criminological research has shown a relationship between the environment and crime, and Quilter investigated the number of crimes committed at different times and found that crime patterns varied with the seasons [18]. Eileen G. COHN found that different weather conditions (such as heat, rain, and wind) had different effects on various crimes [19]. Peng et al. found that under extreme weather conditions, robbery crimes decreased, while burglaries increased during the day [20]. Anna Bruederle et al. found that temperature had a short-term effect on violent crime [21]. Just as bus pickpockets often choose to commit their crimes in weather with poor air quality [22], excavators often choose to take advantage of bad weather, such as rain and snow, to facilitate their actions.
The social disorder theory posits that the organization of a community, and the mobility and heterogeneity of the people within it, can lead to changes in its internal environment that increase the likelihood of crime in certain circumstances [23]. Consequently, applying this theory, the holiday season could result in disorder within the protected heritage unit area, potentially impacting the crime situation in the region.
During the investigation process of such cases, public security authorities investigating excavation-type heritage crimes have found that while the tendency to professionalize the crime and update criminal methods has increased, criminal gangs almost always include a geomancer who considers many superstitious factors. These factors include the geomancy of the area around the tomb, the lunar calendar, the topography of the area, and even the growth of wheat in winter, which guide the gang in their excavation activities. Due to the differences between geomancers and the location of the crime, there is no consistent standard for the geomancy of each place, and the only constant factor is the “auspiciousness” in the Lunar Calendar. Therefore, the Lunar Calendar may have had a significant influence on the tomb raiders.
3.2. Crime Prediction
Current communication methods are mainly enabled by telephone, face-to-face meetings, or the Internet. Most of the content of these communications is saved or converted to written text, then archived in digital format, which makes it more complex and difficult to manually sift through valid information, but also provides opportunities for automated text analysis using NLP technology [24]. Currently, NLP is becoming a popular technology for analyzing police data as the policing model is transformed into “smart policing”. For example, Chih-Hao Ku et al. used NLP to extract elements from crime reports, then used machine learning algorithms, such as Bayes to build a decision model for smart policing [25]. Areeba Umair et al. extracted crime data from eight years of news reports in Pakistan and further predicted the crime situation [26]. Xiang et al. extracted data from 25,000 first-instance judgments on online fraud in China from China Judgements Online and conducted a study on the spatial and temporal distribution of online fraud in China at the county scale [27].
After extracting the elements of crimes, crime dynamics can be analyzed in various aspects, of which crime time series prediction is an important part [28]. Time series analysis is a data mining technique based on historical time data [29]. Time series prediction of crime is an important branch of current spatio-temporal crime prediction research. Different time series models can extract the occurrence characteristics of different crime types, which can provide decision support for police in police force allocation, patrol route planning, etc. [30].
Current research methods for crime time-series prediction include the following two main types: (1) Single feature crime time-series prediction. The traditional time series analysis method is used to make simple predictions, such as the number of different types of crimes. The advantage of this method is that it can account for the volatility of crime data. For example, Chen et al. used a time series model, ARIMA, to make short-term predictions of property crime in a Chinese city. Based on a given 50 weeks of property crime data, an ARIMA model was determined and can predict the amount of crime 1 week in advance. The results showed that the ARIMA model had higher accuracy than the exponential smoothing model [31]. FENG et al found that using crime data from San Francisco, Chicago, and Philadelphia over three years to train the Prophet model was able to achieve better results than traditional neural networks [32]. Shoesmith employed the ST-AR model to forecast rates of violent crime and property crime across multiple countries and regions spanning a 15-year period (1955–2009). The study revealed that the ST-AR model exhibited superior predictive capabilities compared to other models, particularly in terms of property crime predictions rather than violent crime [33]. (2) Crime time-series prediction with multiple features. Crime prediction using machine learning or neural network methods can perform excellently with large amounts of data or unstable data, and multi-dimensional predictions that incorporate geographic and economic factors that may have an impact on the occurrence of crime. However, high-dimensional variables cannot explain the crime phenomenon, and the issue of how to ensure convergence and consistency of the operating rate should also be considered in the parameter setting process. Alexander Stec et al. used crime data from Chicago and Portland, along with local weather, census, and public transport data, to predict crime counts using a deep learning approach, and their best models achieved accuracy rates of 75.6% and 65.3%, respectively [7]. Bitzel Cortez et al. found that an LSTM-based prediction model could be used for Guatemala City emergencies with better prediction results [34]. Jha et al. conducted a study with two million crime data from India over the past decade and found that the improved neural network model had better training results when dealing with large amounts of data [35]. Lin et al. leveraged the automatic feature extraction capability of DNN models to train DNN-tuning models. These models were developed by combining vehicle theft data with 84 types of geographic data, resulting in promising outcomes [36]. Zhang et al. utilized crime data, environmental data, demographic data, and XGBoost models to predict incidents of public theft, specifically at XT police stations in ZG. To enhance the interpretability of the predicted results, they employed the SHAP method to assess the contribution of each variable and offer a more meaningful interpretation [37].
Each of the aforementioned methods has its own advantages and disadvantages. Prediction methods that solely rely on crime data are able to capture the volatility of the data, but they do not elucidate the relationship between crime and other factors, and their performance may be suboptimal for crime types with limited data availability. On the other hand, crime prediction based on deep learning methods incorporating external data sources often grapples with the inherent blackbox nature of machine learning. Even when employing interpretable machine learning models, such as SHAP, the introduction of variables still lacks a solid theoretical foundation, often leading to their interpretation solely from an algorithmic standpoint. Moreover, the introduction of additional variables renders the model less interpretable and may even lead to “dimensional disasters” when the number of variables increases, thereby diminishing prediction performance [38]. In summary, research on heritage crimes is relatively restricted when compared to other forms of criminal activities, with a notable dearth of quantitative analysis specifically focused on Chinese heritage crimes, especially excavation-type heritage crimes. This limitation primarily stems from the challenges associated with accessing criminal data pertaining to cultural relics and the potential disparities between such data and information obtained from conventional sources like media coverage and official news. Consequently, a thorough exploration of historical data on cultural heritage crimes, accompanied by a comprehensive integration of theoretical frameworks and practical experiences, is crucial. The identification of influential factors that contribute to the occurrence of excavation-type heritage crimes is essential, as is the application of scientific, statistical analysis and big data analysis, among other methodologies, to analyze and predict the trajectory of cultural heritage crimes. These efforts will yield more effective strategies for combating cultural heritage crimes.
4. The System for Extracting Crime Elements and Predicting Excavation-Type Heritage Crimes
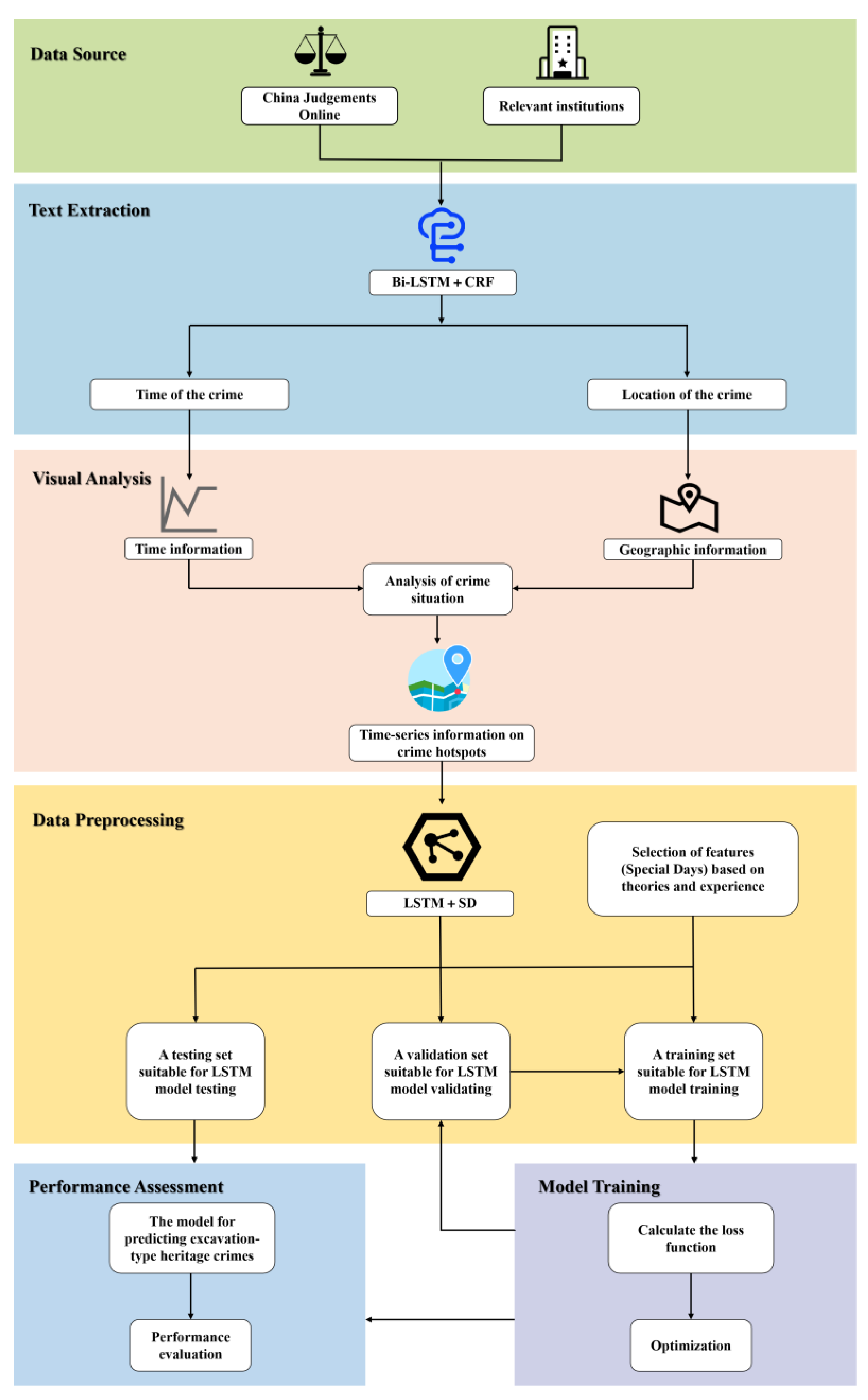
In this study, the system for extracting crime elements and predicting excavation-type heritage crimes is constructed. The technical route of the system is shown in Figure 1.
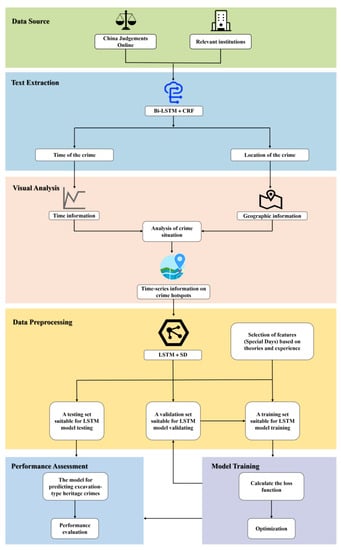
Figure 1.
The system for extracting crime elements and predicting excavation-type heritage crimes.
The paper presents a six-step process, which includes data source, text extraction, visual analysis, data preprocessing, model training, and performance assessment. First, the case descriptions of heritage crimes related to excavation are obtained from China Judgements Online and relevant institutions. Second, the Bi-LSTM + CRF model is employed to process the obtained case descriptions, from which the time and location of the crimes are extracted. Then, the crime situation is visualized using software, such as ArcGIS Pro 2.8.4, and the LSTM model is applied to predict the number of crimes in the crime hot spots. Based on this, classical criminological theories and field experience are incorporated to develop the LSTM + SD model.
4.1. Data
The study used crime data obtained from China Judgements Online, which publishes judgment documents that have come into effect and are accessible to the public from all levels of people’s courts in China. With over 100 million documents, the website covers a wide range of fields, including criminal and civil law, and has been visited over 80 billion times. To reflect the real situation of heritage crimes, this study focused on excavation-type heritage crimes in China from 2011 to 2020, using first-instance verdict documents of criminal cases crawled from the website, combined with data from relevant official institutions. The study also chose XS Province in China as an example due to the limited access to crime data sources.
Historical weather data is downloaded from the official website of the Weather Post. The historical weather data provided by this website have been used in some scholars’ studies and thus possess a certain degree of credibility [39]. The holiday arrangement notice issued by the State Council is used as the standard for determining the dates of holidays. The data of the Lunar Calendar is crawled from the official website of Baidu Calendar. The dates involved in this part of the data are referred to as Special Days (SD).
4.2. The Model of Extracting Crime Elements: Bi-LSTM + CRF Model
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is an interdisciplinary field at the intersection of computer science, artificial intelligence, and linguistics. Its main objective is to develop theories and methods for effective communication between humans and computers using natural language. NLP has gained popularity in machine translation, sentiment analysis, information extraction, and text classification [24]. Among various tasks in information extraction, named entity recognition, relationship extraction, and entity disambiguation are common methods to extract structured data from unstructured text [40]. The application of NLP technology enables the rapid extraction of a large number of case elements, which can be further analyzed for in-depth crime analysis.
Named entity recognition (NER) is a fundamental task in natural language processing that involves identifying words in a text directed by specific naming conventions, such as the names of people, places, and organizations. The most successful and commonly used modeling approach to date is to frame this task as a sequence annotation problem, where the input sequence is labeled with a corresponding sequence of tags.
The labeling system in NER involves two types of tags: the first type represents the category to which the named entity belongs, such as a person (PER), location (LOC), or organization (ORG). The second type represents the position of a word within a named entity. The most widely used standard for this is the BIO annotation system, which employs three tags: named entity beginning (B), named entity internal (I), and non-named entity (O). There are two annotation schemes for named entity recognition: the first is a word-based annotation scheme, and the second is a character-based annotation scheme, which greatly affects the recognition performance. For the Chinese, the more commonly used method for named entity recognition tasks with more research value and potential is the character-based annotation scheme.
This study adopts a mature and advanced Chinese-named entity recognition model, which is currently recognized as the more effective Bi-LSTM + CRF approach, i.e., character-level distributed representation (Char Embedding layer), followed by deep neural network model training (Bi-LSTM encoder layer), feature extraction, and finally, by conditional random field model. The CRF layer predicts the category to which each character belongs.
The Conditional Random Field (CRF) layer has the capability to learn some global constraints from the training corpus, such as the requirement that the entity tag should begin with “B-” rather than “I-” in a sentence, that tags of different classes should not be connected, and that recognized entities of people, places, and organizations should not be mixed and matched. These constraints ensure that the labels of different classes are not interconnected and that named entities are identified with precision.
The input sequence is and the output probability matrix after distributed representation and the Bi-LSTM module is , where k is the number of tags. refers to the probability that is tagged with the jth label. refers to the probability of transferring the ith label to the jth label in the probability transfer matrix.
For the sequence of labels to be output , the path score formulae are defined as and .
The CRF model uses a dynamic programming algorithm to find the highest scoring path as the optimal path for sequence labeling by modeling the output label binary.
This study utilized around 10,000 magistrate documents, which is impractical to manually process such a large amount of text data. Therefore, information extraction technology was employed to overcome this challenge effectively. By employing machine-reading and parsing the adjudication documents, primary attribute information, including the crime time and location, in ancient tomb raiding adjudication documents was extracted through steps, such as Chinese word segmentation, lexical annotation, and entity recognition.
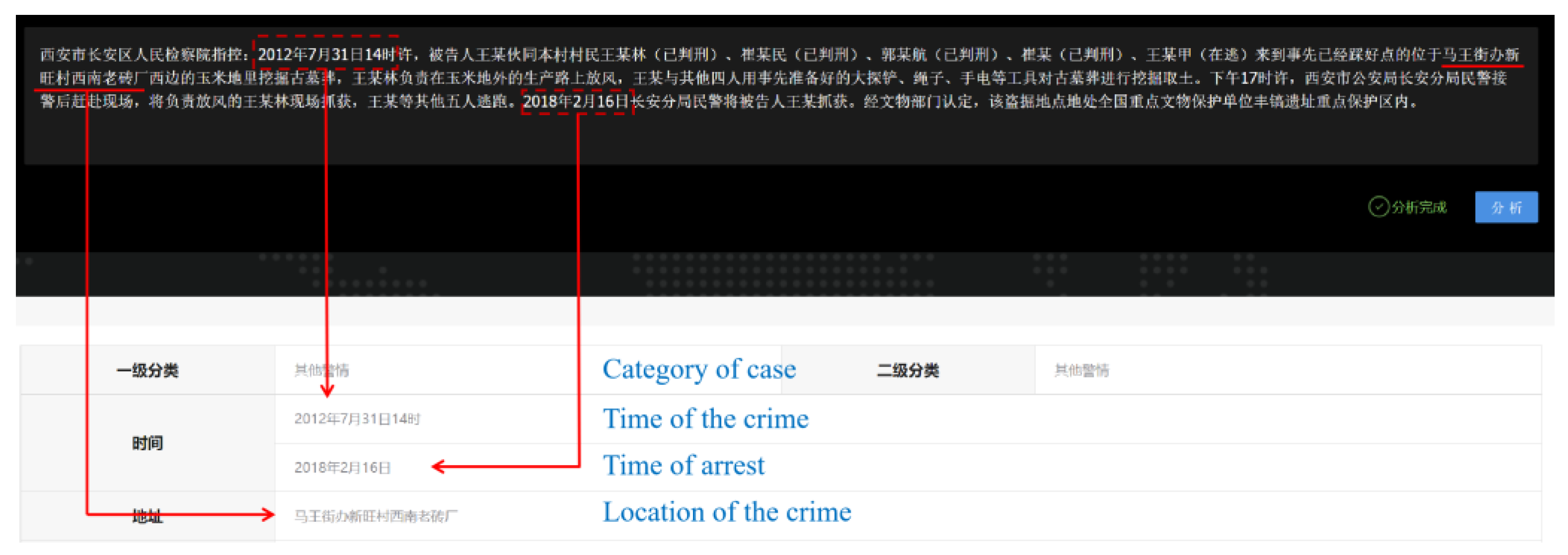
Figure 2 shows the system for the automatic crime elements extraction. The upper part of Figure 2 is a brief of the case. The specific text entered is as follows. “On 31 July 2012, at approximately 2:00 p.m., Wang, the defendant, and several other villagers from the same village, including Wang Moulin (arrested), Cui Moumin (arrested), Guo Mouhang (arrested), Cui Mou (arrested), and Wang Moujia (still at large), arrived at a cornfield situated west of the old brick factory in the southwest of Xinwang Village, Ma Wang Street Office. They had previously marked the location as a burial site. Wang Moulin was tasked with keeping watch on the production road outside the cornfield, while Wang and the other four utilized tools such as large shovels, ropes, and flashlights that they had prepared beforehand to excavate and remove soil from the burial site. At approximately 5:00 p.m. that afternoon, the police from the Chang’an Branch of the Xi’an Public Security Bureau rushed to the scene after receiving a report and arrested Wang Moulin, who was responsible for keeping watch. Meanwhile, Wang and the other five individuals fled. On 16 February 2018, police from the Chang’an Branch apprehended the defendant, Wang. According to the Cultural Relics Department, the robbed tomb site is situated within the key protection area of the Fenghao archaeological site, a nationally protected cultural relics site”.
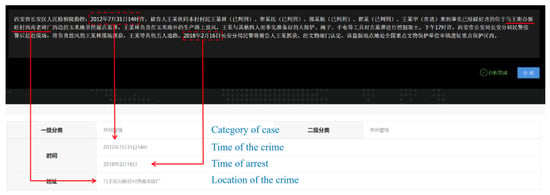
Figure 2.
Crime elements extraction system.
Taking the aforementioned content as an exemplification, our training process primarily encompasses the following steps. First, it is imperative to annotate the time and location information. In the provided content, “14:00 on 31 July 2012” is designated as the recorded incident time. The first “2” is marked as B-time, and each subsequent number and Chinese character is marked as I-time. Similarly, the “Mawang Street Office Southwest Old Brick Factory” is identified as the incident location. “Ma” is marked as B-location, and each subsequent Chinese character is marked as I-time. Additionally, 16 February 2018 is recorded as the time of the arrest. The first “2” is marked as B-arrest time, followed by the subsequent numbers and characters marked as I-arrest time. All other contents in the provided text, including punctuation marks, are marked with O. Second, the texts are randomly divided into three sets: training and testing sets. The division ratio is set at 8:2 for training and testing purposes. Lastly, F1-score is utilized as the evaluation criteria for assessing the performance of our model. In this study, the constructed model achieved an F1-score of 0.911. With the continuous expansion of our data volume, the efficacy of our model training will be further enhanced.
The system is a comprehensive automated solution. Once the case profile is entered into the system, it undergoes automatic analysis of various crime elements. This analysis primarily encompasses the category of case, the time of arrest, the time of the crime, and the location of the crime.
4.3. Analysis of Crime Elements
4.3.1. Temporal Characteristics of Excavation-Type Heritage Crimes
To examine the temporal patterns of the crime, this study provides a comprehensive analysis of the occurrence of excavation-type heritage crimes in XS Province at four temporal scales: daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly.
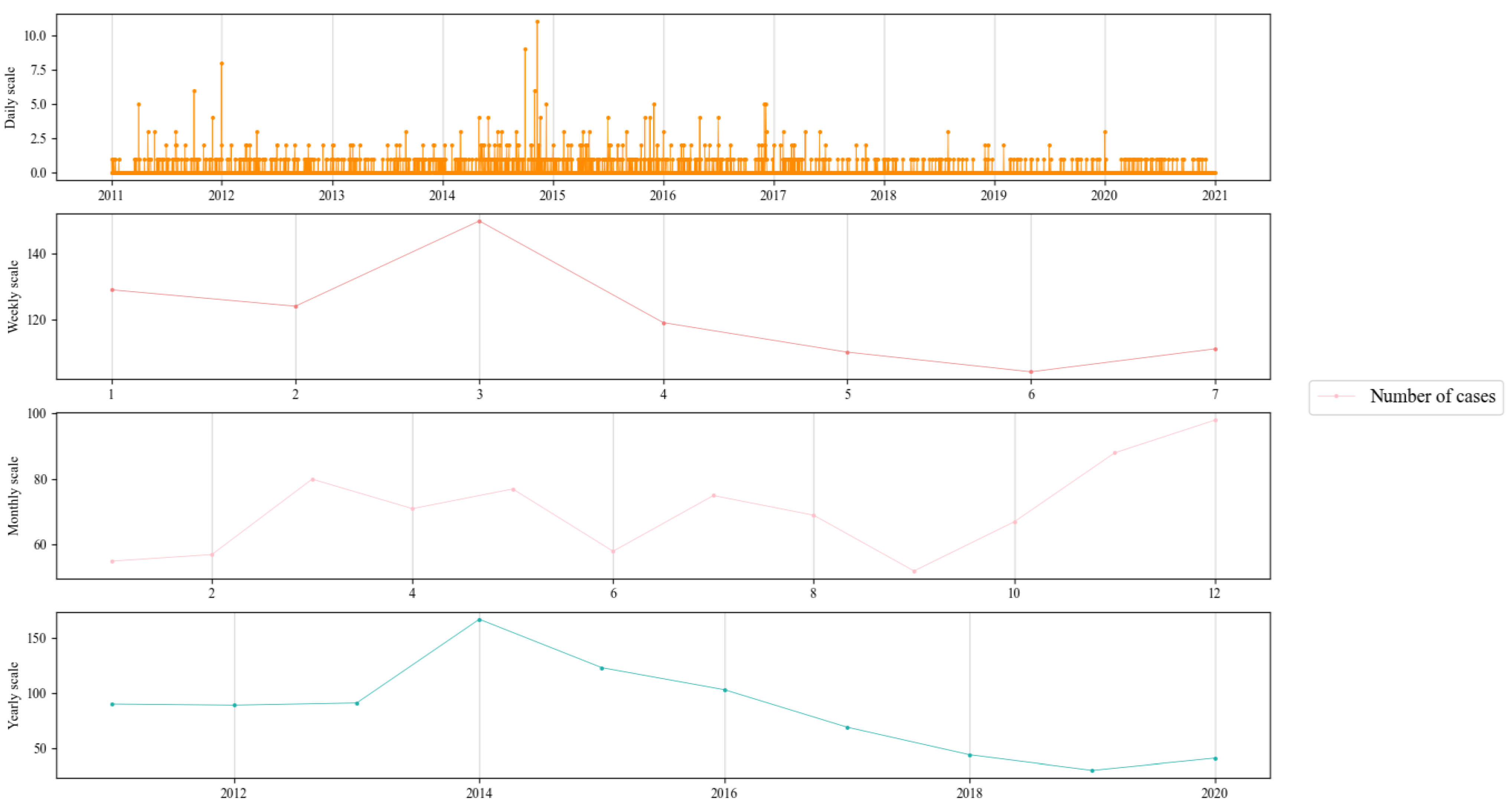
Figure 3 shows the number of crimes committed in XS province from 2011 to 2020 on different scales, with a total of 847 cases over the ten years, including 3010 days without one crime, 522 days with one crime, 82 days with two crimes, and 39 days with three or more crimes.
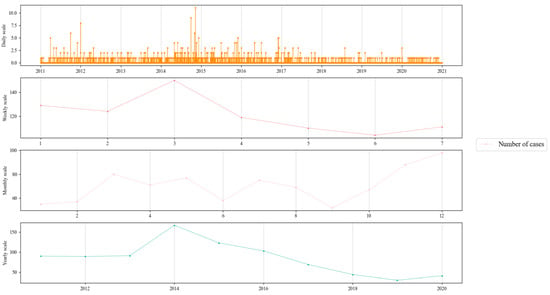
Figure 3.
Number of cases in XS province from 2011 to 2020 on different scales.
The frequency of criminal incidents occurring on non-working days is significantly lower than on working days. This can be attributed to the dispersed and unpredictable activities of individuals during their leisure time, making it more challenging for criminals to target and excavate protected heritage sites that are commonly designated as tourist attractions.
Overall, the number of crimes tends to increase from the beginning to the end of the year, with a high incidence in the spring (March–May) and at the turn of autumn and winter (November–December). This pattern indicates that the frequent special crackdowns on heritage crimes by public security authorities in winter and spring are justified. The trend is due to the majority of crimes occurring in protected heritage units and remote suburban areas. As security measures in protected heritage units increase, tomb raiders are forced to choose crime sites in fields and remote villages where security measures are weak. Moreover, perpetrators can exploit the growing or harvested crops to conceal their actions during spring and the turn of autumn and winter.
After analyzing the yearly scale data, it was found that 2014 had the highest number of excavation-type heritage crimes. However, since 2017, the number of crimes has been declining, with a slight rebound in 2020. Generally, heritage crimes are trending downward and leveling off. This can be attributed to the regular and frequent crackdowns on heritage crimes by public security authorities and other departments, and the enhancement of security systems in protected heritage units.
4.3.2. Spatial Characteristics of Excavation-Type Heritage Crimes
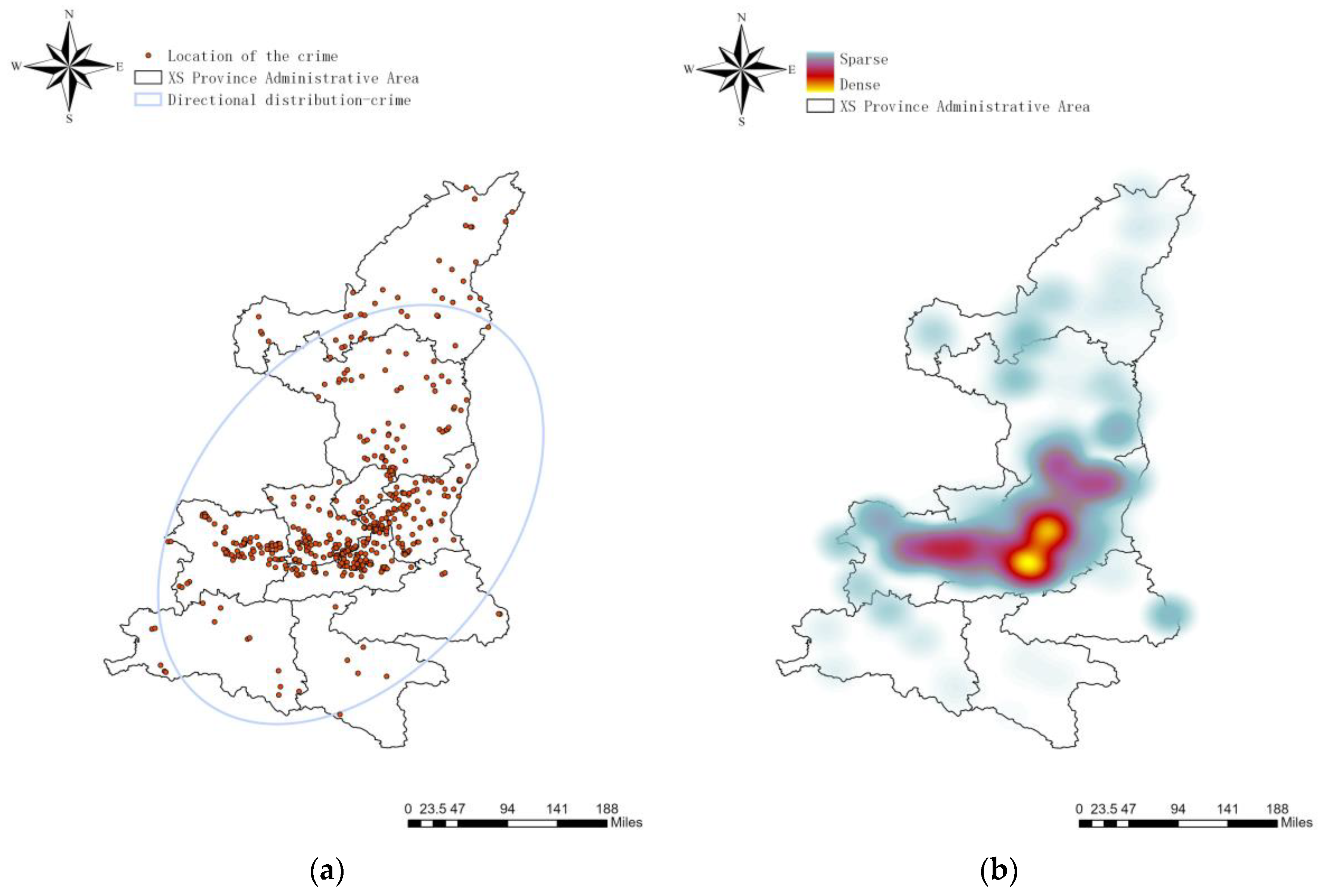
The longitude and latitude information of the crime sites is imported into ArcGIS Pro software to analyze the distribution of excavation-type heritage crimes in XS province from 2011 to 2020.
Figure 4a shows the distribution and direction of excavation-type heritage crimes. Figure 4b shows the heat map of excavation-type heritage crimes distribution. The study reveals that excavation-type heritage crimes are concentrated in the central cities of XS province, particularly in the province’s capital, AX city, and spread to the surrounding prefecture-level cities, with the city serving as the hot spot center. There were fewer cases reported in KA city and LS city, located in the southern part of the province. Moreover, the border areas of prefecture-level cities and the border areas between XS province and other provinces have also reported high crime rates for heritage crimes.
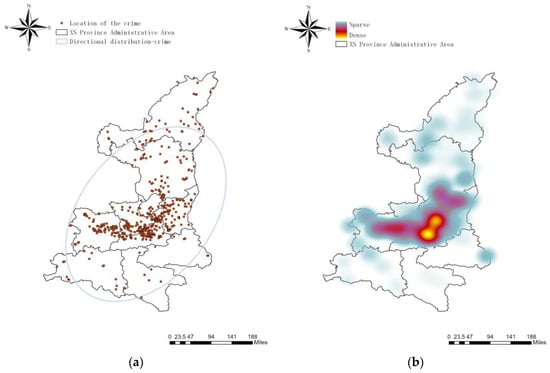
Figure 4.
Analysis of spatial characteristics of excavation-type heritage crimes. (a) Distribution of excavation-type heritage crimes in XS Province; (b) Heat map of the distribution of excavation-type heritage crimes in XS Province.
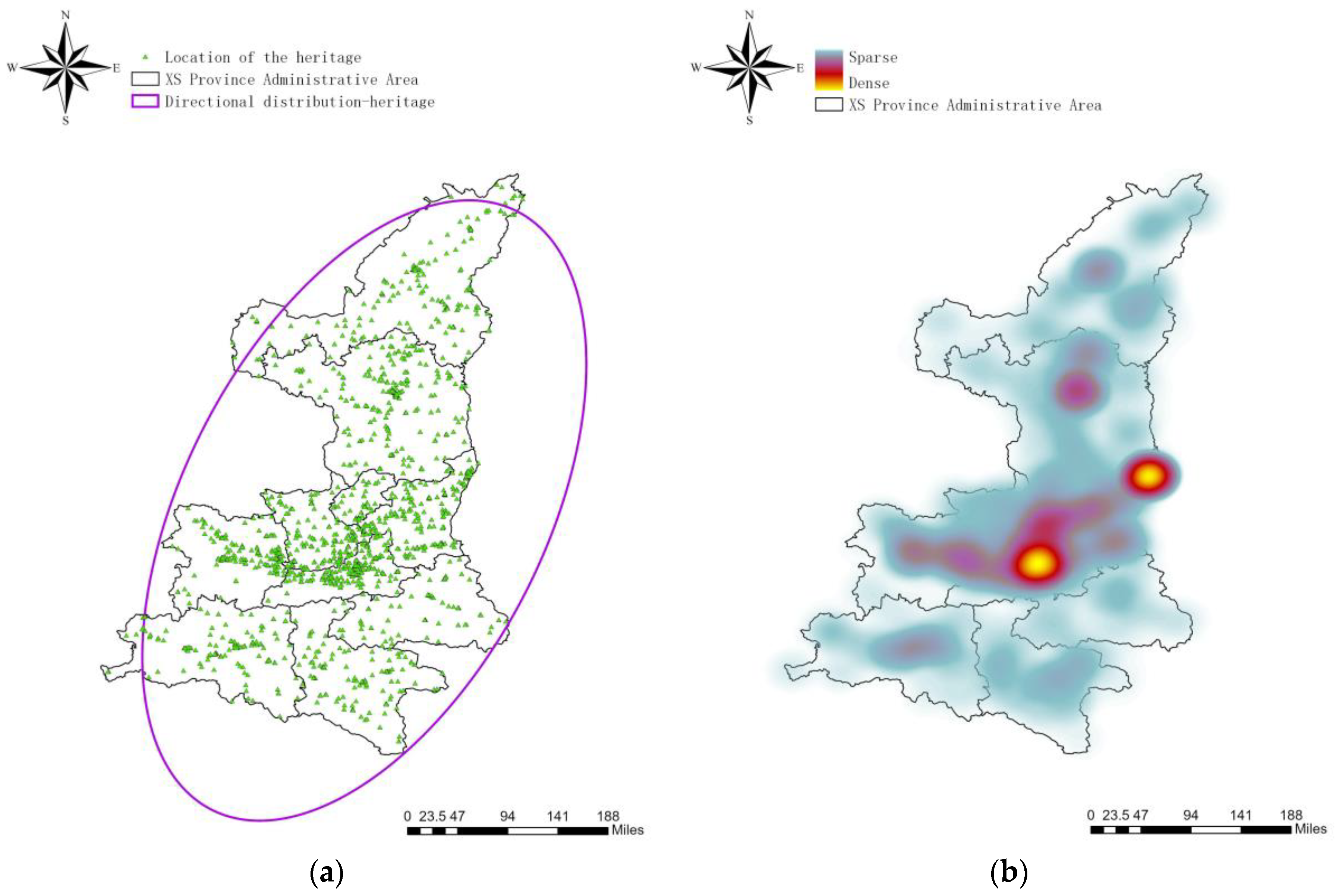
In the previous section discussing the selection of special dates, it was noted that excavation-type heritage crimes might be influenced by holidays, as these crimes are often committed at cultural heritage sites. Unlike typical theft cases, heritage crimes occur in more limited locations, many of which are designated as cultural preservation units. This phenomenon can result in fluctuations in the number of visitors during holidays, subsequently affecting the incidence of heritage crimes. In this study, the latitude and longitude information of existing artifacts in XS province are extracted by crawling the official website of the XS Provincial Bureau of Cultural Heritage. The distribution of existing cultural heritage in XS Province and the heat map are shown in Figure 5a and Figure 5b, respectively.
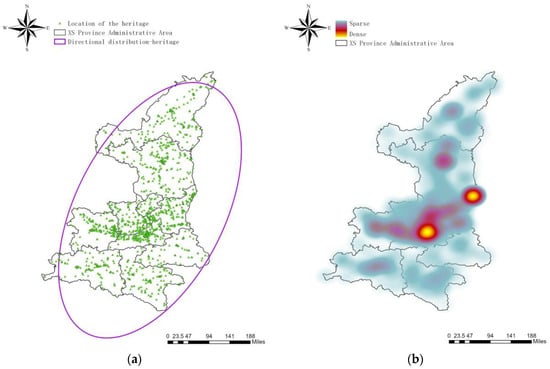
Figure 5.
Analysis of spatial characteristics of existing cultural heritage. (a) Distribution of existing cultural heritage in XS Province; (b) Heat map of the distribution of existing cultural heritage in XS Province.
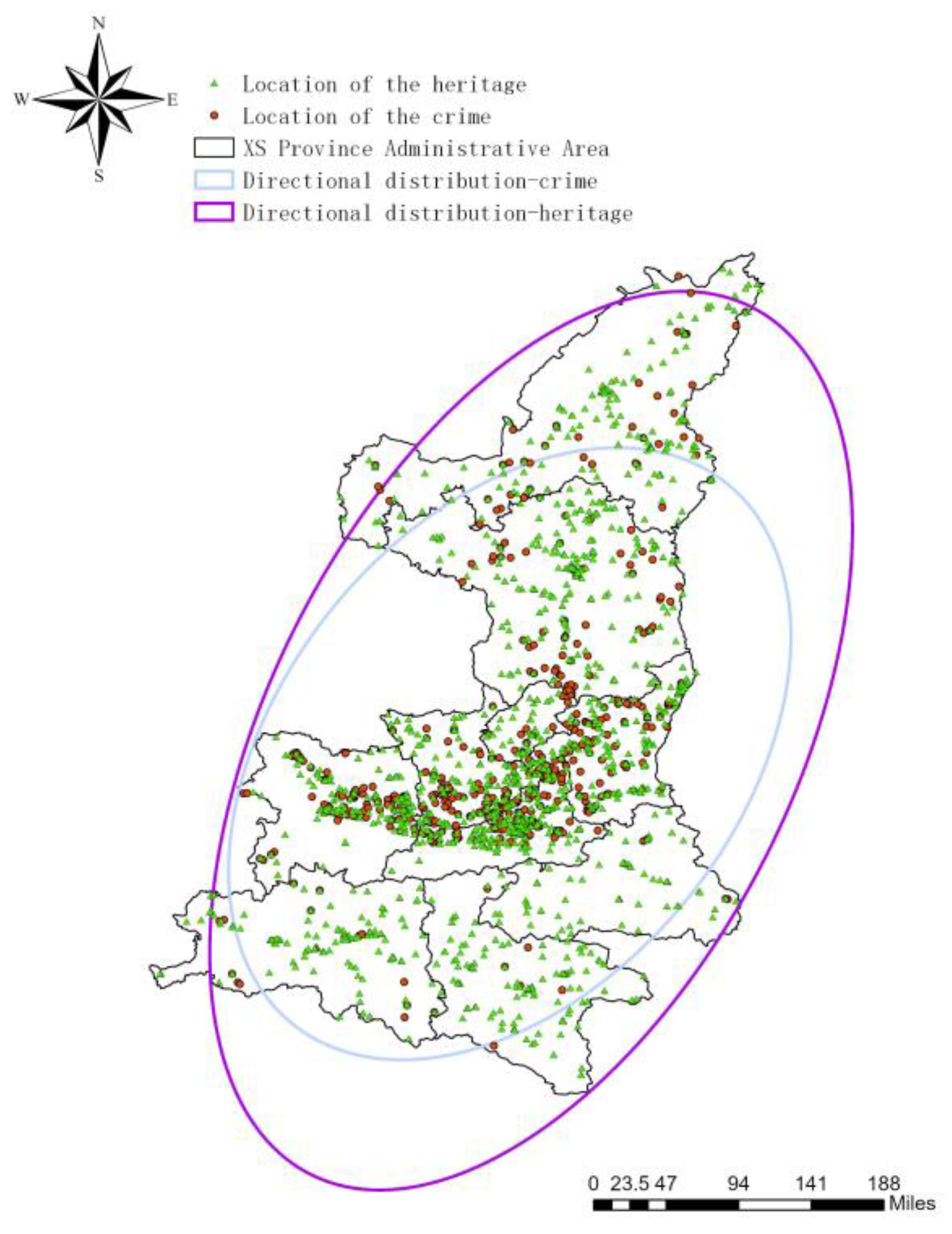
The distribution of existing cultural relics is compared with the distribution of heritage crimes, as shown in Figure 6.
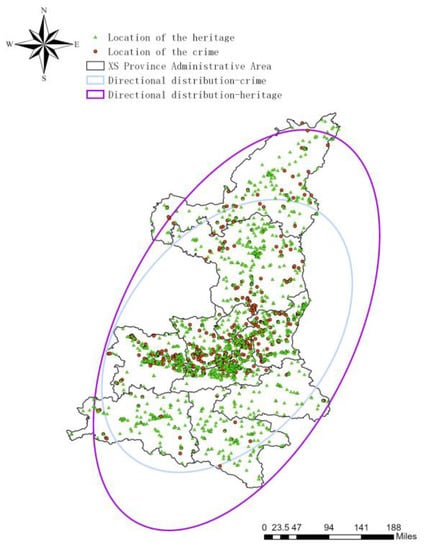
Figure 6.
Comparison of the distribution of excavation-type heritage crimes and existing cultural heritage in XS Province.
Based on the analysis, it was observed that the distribution of surviving artifacts in XS province is concentrated in the provincial capital and other central cities of XS province, which is consistent with the distribution of heritage crimes. Both are distributed in a “northeast-southwest” direction.
4.4. The Model of Crime Prediction: LSTM + SD (Special Day) Model
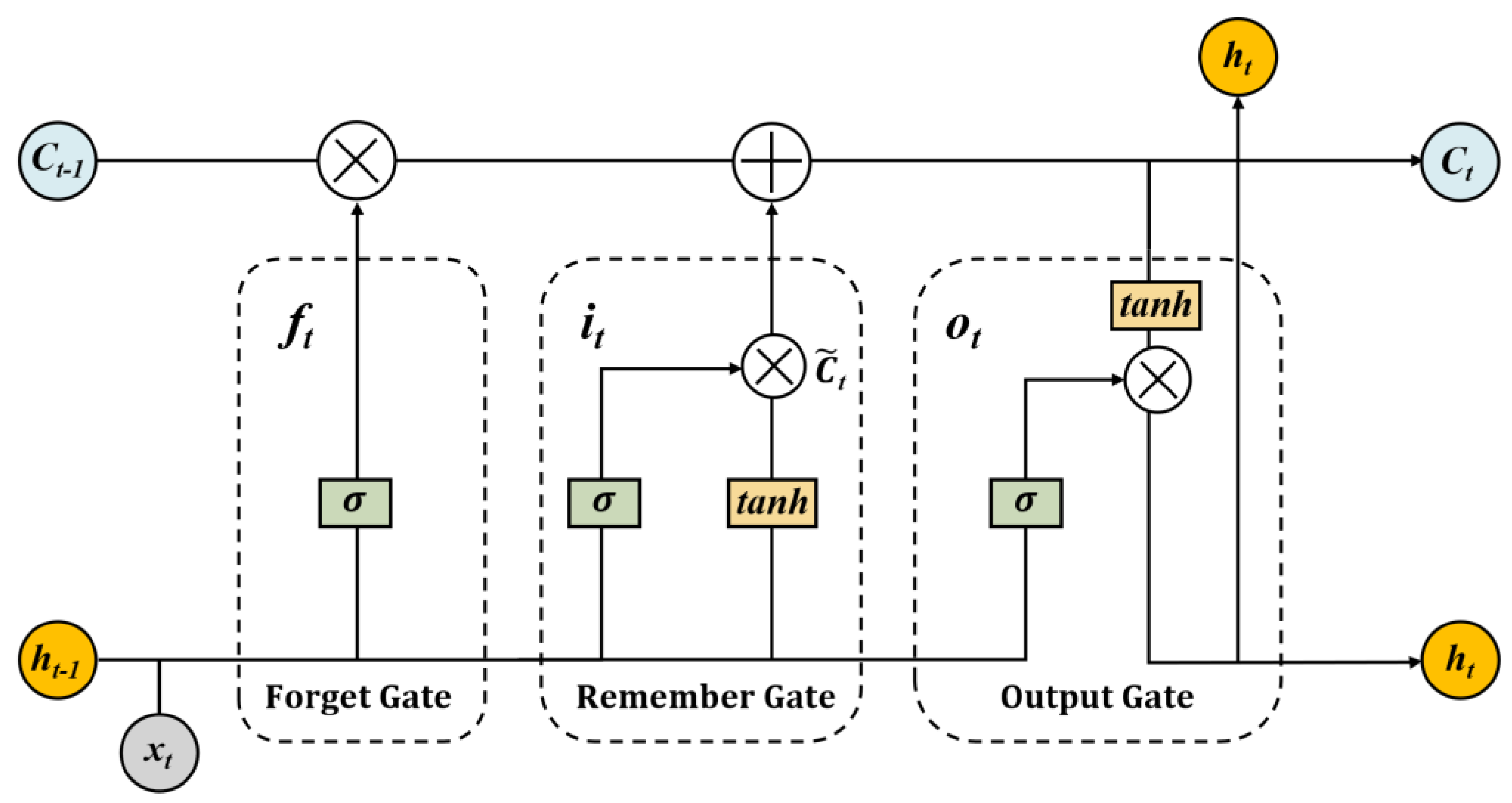
Long short-term memory (LSTM) was proposed by Sepp Hochreiter and others based on the recurrent neural network (RNN) [41]. The recurrent neural network (RNN) is a type of neural network that is particularly effective at handling time series data. However, when processing long sequences, the traditional RNN is challenged by the need to retain all of the information from the past. This not only increases the training time but also causes issues, such as gradient explosion or disappearance, which can result in a loss of historical information. To overcome these challenges, the long short-term memory (LSTM) architecture selectively retains relevant historical information by incorporating input, output, and forget gates, which effectively manage memory information in time series and address the limitations of traditional RNN [42].
When using LSTM to analyze the time series of excavation-type heritage crimes, the short-term and long-term characteristics can be better mined, and it is expected that it can be better used to predict the number of the crime on a daily scale. The structure of LSTM is shown in Figure 7.
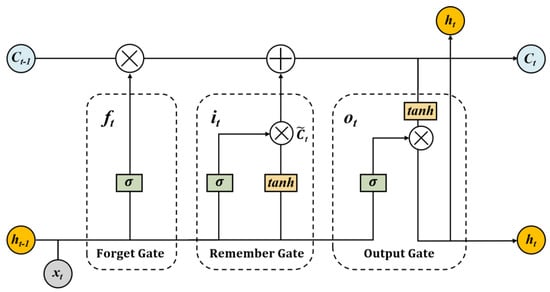
Figure 7.
LSTM cell structure.
In contrast to RNN, there is a separate calculation for the hidden state in the LSTM cell. denotes the state of the hidden layer at moment t and denotes the output at moment t, which are calculated as shown below.
In the above formulae, , , and represent the gating coefficients of the input, forget, and output gate, respectively, and the cell state, to be updated by the LSTM cell at moment t. The formulae are shown below.
where represents the non-linear activation function; represents the input at time t; , , , and represent the weight matrix; , , , and represent the corresponding deviation vectors; and represents the output at the previous time.
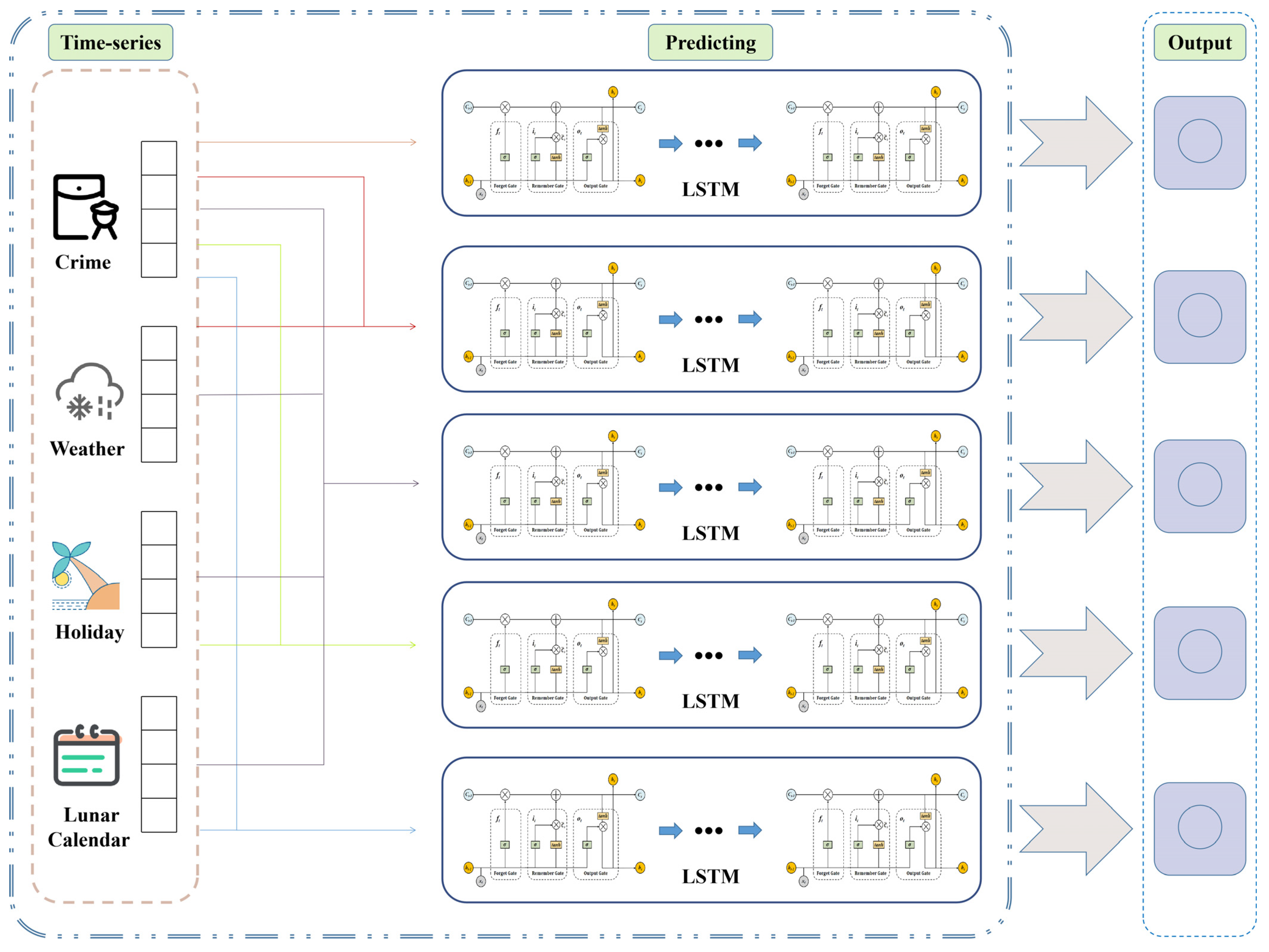
Crime can usually be location-oriented, so different regions have different criminal risks [43]. Based on the above analysis, it is crucial to examine the crime situation in AX, which is a notorious crime spot. Due to the limited availability of official weather information, the study focuses on the crime situation in AX between 2014 and 2020 for time-series prediction research. Through the theoretical analysis and field research of excavation-type heritage crimes, it is found that special days may have an impact on the development of heritage crimes. Therefore, the three variables—Special Day (SD), rain and snow conditions, holidays, and “daily taboos”, which are named , , and , are introduced in the temporal prediction of heritage crimes to improve the prediction accuracy. The structure is shown in Figure 8.
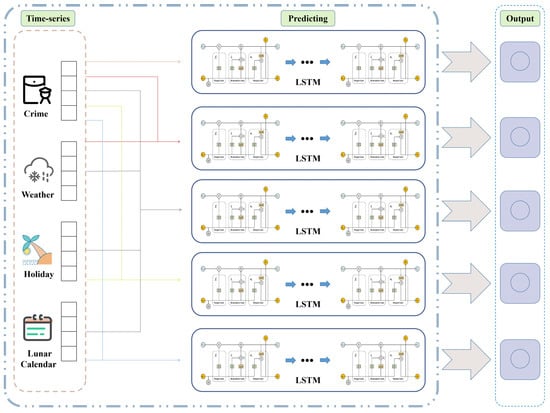
Figure 8.
The structure of the LSTM + SD model.
Prior to incorporating the aforementioned factors into the constructed model, it is necessary to preprocess the data. Since the impact factors we employ are categorical in nature rather than continuous, there is no requirement for normalization or standardization. The State Council’s notification of holiday arrangements from 2014 to 2020 is used as the standard, with holidays marked as 1 and non-holidays as 0. Historical weather conditions for AX city from 2014 to 2020 are obtained from the official weather website, with rain and snow marked as 1 and non-rain and snow as 0. These values signify that excavation-type heritage crimes are less likely to occur during holidays and non-rainy and snowy weather, while non-holidays and rainy and snowy weather are prone to excavation-type heritage crimes.
The study utilized web crawler technology to obtain data from the Baidu Lunar calendar. Based on the “daily taboo” section of the Lunar Calendar, the study selected four indicators associated with ancient burials: “repairing graves”, “starting a drill”, “breaking ground”, and “moving coffins” or “moving the bier”. If any of these indicators appeared in the daily taboo for a particular day, a value of 0 was assigned to that day to indicate that no crime would occur, while a value of 1 was assigned if the indicator was absent.
Taking the inclusion of rain and snow as a consideration in a crime prediction model as an example, the crime prediction model incorporates not only the number of crimes committed but also the rain and snow conditions of the day as inputs. Within the LSTM model, the time step parameter t, , performs a crucial role as it enables the extraction of distinct temporal features for different time steps. Consequently, the dataset is divided into specific time steps for both crime occurrences and snow conditions. Subsequently, the data is processed by LSTM layers with n neurons and connected to the Dense layer, ultimately yielding the prediction results of the number of crimes on day . This study employed an operating system of Windows 10, an Intel Xeon Silver 4112 CPU, an NVIDIA Quadro P2200 GPU, 64 GB of memory, and Python as the programming environment. In order to mitigate the risk of overfitting, the imported dataset was partitioned into three subsets: a training set, a validation set, and a test set. These subsets were allocated in the ratio of 7:1:2, respectively. To avoid complexity and draw on other research on crime prediction utilizing LSTM, three neural network layers were constructed in this study: two LSTM layers and a Dense layer. The LSTM layer comprises 100 neurons separately, and the study used an epoch of 300 and a time step of 1 [44].
Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) and Mean Absolute Error (MAE) are used as evaluation metrics to assess the accuracy of prediction models. The formulas for these metrics are presented below [45].
In the above formulas, represents the true value of the test set, represents the predicted value of the model, and n represents the number of samples predicted. The performance of the model is considered better as the values of RMSE and MAE decrease.
This study validates the performance of the LSTM model by comparing it with commonly used temporal prediction models, such as ARIMA, and traditional machine learning regression models, including Random Forest, SVR, and BP neural networks. To ensure consistency, each model is trained and evaluated based on the same training and test sets. The specific results are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Comparison of model prediction results.
Based on the experimental results, it can be observed that the temporal prediction of crime using a single feature remains consistent across the models. This is primarily due to the even distribution of data and the existence of several dates with zero occurrences, which makes it difficult to identify a clear crime pattern based solely on past incidents and therefore predict accurately.
To enhance the accuracy of the model and validate the crime factors that could affect the occurrence of excavation-type heritage crimes, each type of factor was incorporated into the LSTM model. The specific results are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
The results of the LSTM + SD model.
After introducing other factors, the accuracy of the model significantly improved with the largest improvement of 47.8% occurring after incorporating the holiday factor. This finding suggests that the holiday factor has the greatest influence on excavation-related heritage crimes, consistent with the characteristic of the crime being more prevalent on non-working days.
The experimental results above provide further explanations for the correlation between Special Day (SD) and crime, thus increasing the interpretability of the model developed in this study. Tomb raiders typically use the “Luoyang shovel”, an excavation tool, to dig soil from potential locations of ancient tombs and to determine the location and depth of the tombs based on the soil removed [46]. The choice of rainy or snowy weather for excavation is partly due to the ability to conceal one’s crime and the traces of it and partly because it affects the soil condition, greatly enhancing the efficiency of excavation.
In criminology, environmental factors, such as weather, have been shown to impact crime rates. However, holidays have also been found to have a significant relationship with crime. In a study by Sherry Towers et al. on crime in Chicago, it was found that burglary and assault-type crimes were significantly lower during holidays [47]. On the other hand, homicides in the UK between 1996 and 2015 increased significantly on Saturdays and statutory holidays [48]. This can be attributed to the fact that people tend to adopt a different lifestyle during holidays, leading to changes in the crime situation [49]. According to the routine activity theory proposed by Cohen and Felson, crime is a result of three factors: the potential and capable offender, the availability of a suitable target or victim, and the absence of a protector capable of safeguarding the target or victim [50]. Excavation crimes mainly target ancient tombs, due to the custom of “generous burial” in ancient China, which was recorded during the Western Jin Dynasty. This custom involved burying a large amount of gold, silver, and jewelry with the dead, which has attracted tomb raiders from ancient times to the present day. With the development of archaeological research and the need to better protect cultural relics, China has established three levels of cultural relics protection units at the national, provincial, and county levels. These units are gradually being established as tourist attractions open to the public, leading to an increase in the number of visitors. Criminals tend to avoid periods of high tourist traffic, particularly during holidays, when selecting excavation sites [47].
The Lunar Calendar, also known as the Traditional Chinese Calendar, is the earliest calendar in Chinese history and is primarily based on celestial observations and agricultural experience. In ancient China, it was believed that the interaction between the sun, moon, and stars in the universe contained the laws of the waxing and waning of all things, which had various positive or negative effects on human activities. Long-term observations and summaries led to the delineation of the “zodiacal auspicious day” and the “zodiacal black day” to guide people’s daily activities. China has a long-standing focus on burial culture, which involves extensive knowledge of geomancy and divination, as reflected in the Lunar Calendar. Tomb raiders may refer to it when carrying out their excavations. Therefore, it is essential to consider the Lunar Calendar when combating excavation-type crimes.
5. Conclusions
Based on data obtained from China Judgements Online and relevant institutions, this study employed NLP technology to process text data on excavation-type heritage crimes in XS province and conducted a spatio-temporal visual analysis. Additionally, the study utilized the LSTM model to predict daily occurrence rates of such crimes. In terms of time regularity, the incidence of excavation-type heritage crimes displays a declining trend, but tends to remain stable, with higher rates occurring in spring and at the turn of autumn and winter, and a pattern of occurrence on working days compared to non-working days. With respect to spatial distribution, these crimes are primarily concentrated within a city and its surrounding areas, with some also occurring within various administrative regions. In terms of predicting the time series of these crimes, the accuracy of the LSTM model was greatly enhanced through the incorporation of other feature variables. Rain and snow, holidays, and the “daily taboo” in the Lunar Calendar were identified as the main factors influencing the occurrence of these crimes, with the holiday factor having the greatest impact on the model’s accuracy.
This paper presents an endeavor to extract crime elements and predict excavation-type heritage crimes. The system primarily focuses on future conservation efforts, driven by the constraint of limited available data on cultural heritage crimes. As local police agencies and cultural protection departments construct databases, the practical implications of our system will greatly improve with the accumulation of more data in the future. The result of the current research phase is anticipated to offer decision support for specific tasks, including the adjustment of security measures and the deployment of patrol police in cultural and heritage protection departments. We anticipate that this research will inspire other scholars to explore the heritage crime field more profoundly. In future research, we can conduct further analysis and investigations into the spatial scale prediction of heritage crimes and gang crimes [51]. Additionally, in future research, when forecasting the time series of excavation-type heritage crimes, we can consider the impact of noise factors besides the impact of special days on crimes [52]. To further enhance the prediction model’s accuracy, we can introduce additional factors, such as the economy [53], regional population [54], and education [55].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.D.; Software, F.X.; Writing—original draft, H.L.; Writing—review and editing, Y.Z. and Y.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by First-Class Discipline Training Initiative in Public Security and Construction Project of Public Security Behavioral Science Lab (2023ZB02).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from China Judgements Online (https://wenshu.court.gov.cn/), the Chinese government website (https://www.gov.cn/), and the website of the Weather Post (http://www.tianqihoubao.com/).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sesana, E.; Gagnon, A.S.; Ciantelli, C.; Cassar, J.; Hughes, J.J. Climate change impacts on cultural heritage: A literature review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2021, 12, e710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, S. Understanding, Respect, and Collaboration in Cultural Heritage Preservation: A Conservator’s Developing Perspective. Libr. Trends 2007, 56, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, D.W.J. Heritage Crime Matters. Antiquity 2015, 89, 991–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinsheng, M. Tomb Robbers in the Beijing Area during the Republican Period; Beijing Archives: Beijing, China, 2012; Volume 5, pp. 48–49. [Google Scholar]
- Xuebin, W. Raiders in a chaotic world: Tomb raiding and social governance in the northern areas of the republic of China (1912–1937). J. Dalian Univ. 2021, 4, 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W. The Current Situation of Fighting and Preventing Cultural Relic Crimes in China and the Improvement of the System. J. Chin. Acad. Crim. Police 2021, 6, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stec, A.; Klabjan, D. Forecasting Crime with Deep Learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.01486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyser, B. Threatened Pasts: Police Officers, Heritage Practitioners, and Victims of Heritage Crime; Nottingham Trent University: Nottingham, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, T. Graph Deep Learning Model for Network-Based Predictive Hotspot Mapping of Sparse Spatio-Temporal Events. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2020, 79, 101403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, L. Heritocide? Defining and exploring heritage crime. Public Archaeol. 2013, 12, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R.; Kent, A.; Hills, J. Project 7708 Understanding Heritage Crime in Kent and Medway—A Data Analytical Approach. 2020. Available online: https://repository.canterbury.ac.uk/item/8wx70/project-7708-understanding-heritage-crime-in-kent-and-medway-a-data-analytical-approach (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Manacorda, S.; Duncan, C. (Eds.) Crime in the Art and Antiquities World: Illegal Trafficking in Cultural Property; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Brodie, N. The criminal organization of the transnational trade in cultural objects: Two case studies. In The Palgrave Handbook on Art Crime; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2019; pp. 439–461. [Google Scholar]
- Weijun, L. The Current Situation and Countermeasures of Fighting and Preventing Crimes against Cultural Relics in China; People’s Public Security: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Balcells Magrans, M. Contemporary Archaeological Looting: A Criminological Analysis of Italian Tomb Robbers; CUNY Academic Works: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gullotta, M.A. The Protection of Cultural Heritage: The Experience of the Italian Carabinieri Command. In Contested Holy Cities; Routledge: London, UK, 2019; pp. 184–196. [Google Scholar]
- Yumeng, X. Study on the Mechanism for Detecting Crimes of Excavation of Ancient Cultural Sites, Ancient Tombs. Ph.D. Thesis, People’s Public Security University of China, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Quetelet, L.A.J. A Treatise on Man and the Development of His Faculties; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cohn, E.G. Weather and crime. Br. J. Criminol. 1990, 30, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Shu, X.; Yuan, H.; Li, D. Assessing Temporal and Weather Influences on Property Crime in Beijing, China. Crime Law Soc. Chang. 2011, 55, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruederle, A.; Jörg, P.; Gareth, R. Weather and Crime in South Africa; RWI—Leibniz-Institut für Wirtschaftsforschung: Essen, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, N.; Zhai, Y. Crime prevention of bus pickpocketing in Beijing, China: Does air quality affect crime? Secur. J. 2021, 34, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merleau-Ponty, M.; Wild, J.D. The Structure of Behavior; Beacon Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Tan, C.-W.; Huang, Q.; Liu, H. Natural Language Processing (NLP) in Management Research: A Literature Review. J. Manag. Anal. 2020, 7, 139–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, C.-H.; Leroy, G. A Decision Support System: Automated Crime Report Analysis and Classification for e-Government. Gov. Inf. Q. 2014, 31, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umair, A.; Sarfraz, M.S.; Ahmad, M.; Habib, U.; Ullah, M.H.; Mazzara, M. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Web News Archives for Crime Prediction. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinqiao, X.; Chundong, G.; Tian, M.; Dong, J.; Mengmeng, H.; Shuai, C. Research on the spatial and temporal distribution of internet fraud in china at the county scale. Geoscience 2021, 6, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Hu, X.; Wu, H.; Shen, B.; Wu, J. Risk Prediction of Theft Crimes in Urban Communities: An Integrated Model of LSTM and ST-GCN. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 217222–217230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-T.; Baek, J.-G. Various Type of Wavelet Filters on Time Series Forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 11th International Conference on Semantic Computing (ICSC), San Diego, CA, USA, 30 January–1 February 2017; pp. 258–259. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, X.; Cai, M.; Wang, D.; Cao, L. A New Model for Predicting the Attributes of Suspects. Comput. Sci. Inf. Syst. 2020, 17, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Yuan, H.; Shu, X. Forecasting Crime Using the ARIMA Model. In Proceedings of the 2008 Fifth International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, Jinan, China, 18–20 October 2008; Volume 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Zheng, J.; Ren, J.; Hussain, A.; Li, X.; Xi, Y.; Liu, Q. Big Data Analytics and Mining for Effective Visualization and Trends Forecasting of Crime Data. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 106111–106123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoesmith, G.L. Space–Time Autoregressive Models and Forecasting National, Regional and State Crime Rates. Int. J. Forecast. 2013, 29, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, B.; Carrera, B.; Kim, Y.-J.; Jung, J.-Y. An Architecture for Emergency Event Prediction Using LSTM Recurrent Neural Networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 97, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.; Yang, E.; Almagrabi, A.O.; Bashir, A.K.; Joshi, G.P. Comparative Analysis of Time Series Model and Machine Testing Systems for Crime Forecasting. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 10621–10636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-L.; Yen, M.-F.; Yu, L.-C. Grid-Based Crime Prediction Using Geographical Features. SPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Lan, M.; Song, G.; Xiao, L.; Chen, J. Interpretable machine learning models for crime prediction. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2022, 94, 101789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Ding, N. A Systematic Review of Multi-Scale Spatio-Temporal Crime Prediction Methods. SPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lin, Y.; Su, Q.; Cheng, L. Spatial Variation of Multiple Air Pollutants and Their Potential Contributions to All-Cause, Respiratory, and Cardiovascular Mortality across China in 2015–2016. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 168, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Duan, N.; Liu, S.; Shum, H.-Y. Progress in Neural NLP: Modeling, Learning, and Reasoning. Engineering 2020, 6, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Si, X.; Hu, C.; Zhang, J. A Review of Recurrent Neural Networks: LSTM Cells and Network Architectures. Neural Comput. 2019, 31, 1235–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortley, R.; Mazerolle, L. (Eds.) Willan, Environmental Criminology and Crime Analysis: Situating the Theory, Analytic Approach and Application. In Environmental Criminology and Crime Analysis; Routledge: London, UK, 2013; pp. 23–40. ISBN 978-0-203-11821-4. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Hou, M. Predicting time series of theft crimes based on LSTM network. Data Anal. Knowl. Discov. 2020, 4, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jin, G.; Zhao, X.; Feng, Y.; Huang, J. CSAN: A Neural Network Benchmark Model for Crime Forecasting in Spatio-Temporal Scale. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2020, 189, 105120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. History of Chinese Tomb Raiding; Jiuzhou press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Towers, S.; Chen, S.; Malik, A.; Ebert, D. Factors Influencing Temporal Patterns in Crime in a Large American City: A Predictive Analytics Perspective. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, A.; While, D.; Flynn, S.; Ibrahim, S.; Kapur, N.; Appleby, L.; Shaw, J. Do Homicide Rates Increase during Weekends and National Holidays? J. Forensic Psychiatry Psychol. 2019, 30, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yin, P.; Bertozzi, A.L.; Brantingham, P.J.; Osher, S.J.; Xin, J. Deep Learning for Real-Time Crime Forecasting and Its Ternarization. Chin. Ann. Math. Ser. B 2019, 40, 949–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, L.E.; Felson, M. Social Change and Crime Rate Trends: A Routine Activity Approach. Am. Sociol. Rev. 1979, 44, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düzgün, H.S.; Polat, E. A Spatio-Temporal Crime Prediction Model for Crime Prevention. In Counter Terrorism in Diverse Communities; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 116–135. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Sun, D. DuroNet: A Dual-Robust Enhanced Spatial-Temporal Learning Network for Urban Crime Prediction. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. 2021, 21, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, S.D.; Miles, T.J. Economic Contributions to the Understanding of Crime. Annu. Rev. Law Soc. Sci. 2006, 2, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malleson, N.; Andresen, M.A. Exploring the Impact of Ambient Population Measures on London Crime Hotspots. J. Crim. Justice 2016, 46, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Stewart, K.; Fan, J. Incorporating Space and Time into Random Forest Models for Analyzing Geospatial Patterns of Drug-Related Crime Incidents in a Major US Metropolitan Area. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 87, 101599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).