Mechanical Performance of Bentonite Plugs in Abandonment Operations of Petroleum Wells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Plugs Preparation
- Offshore Plugs
- Onshore Plugs
2.2.2. Mechanical Tests
- Compressive Strength
- Adhesion
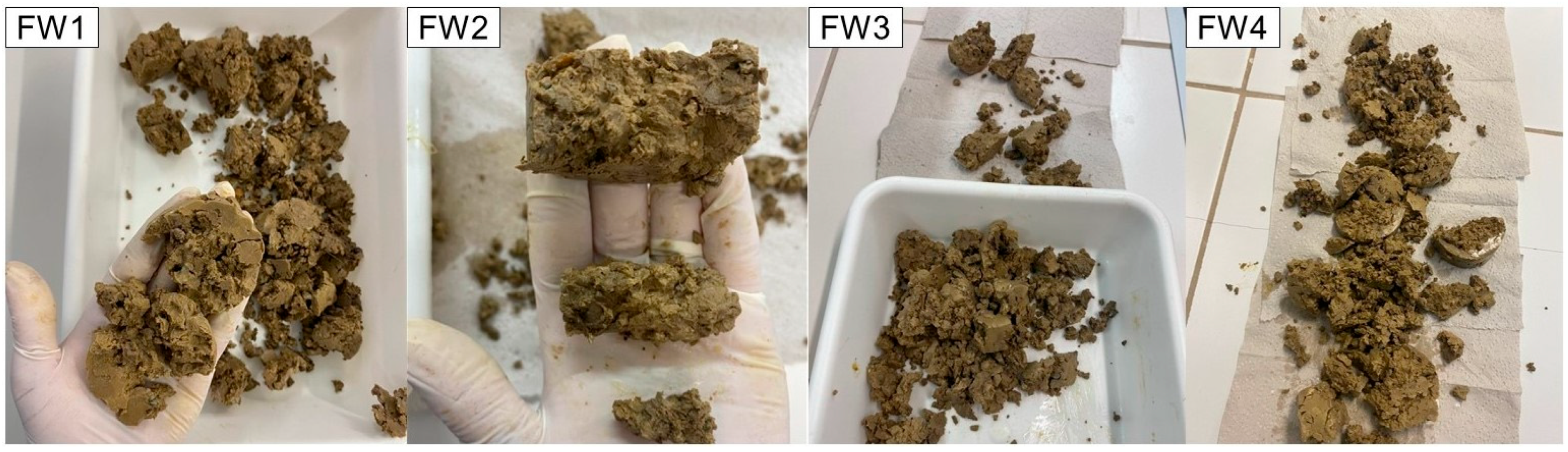
2.2.3. Plugs Interaction with Formation Waters
3. Results and Discussion
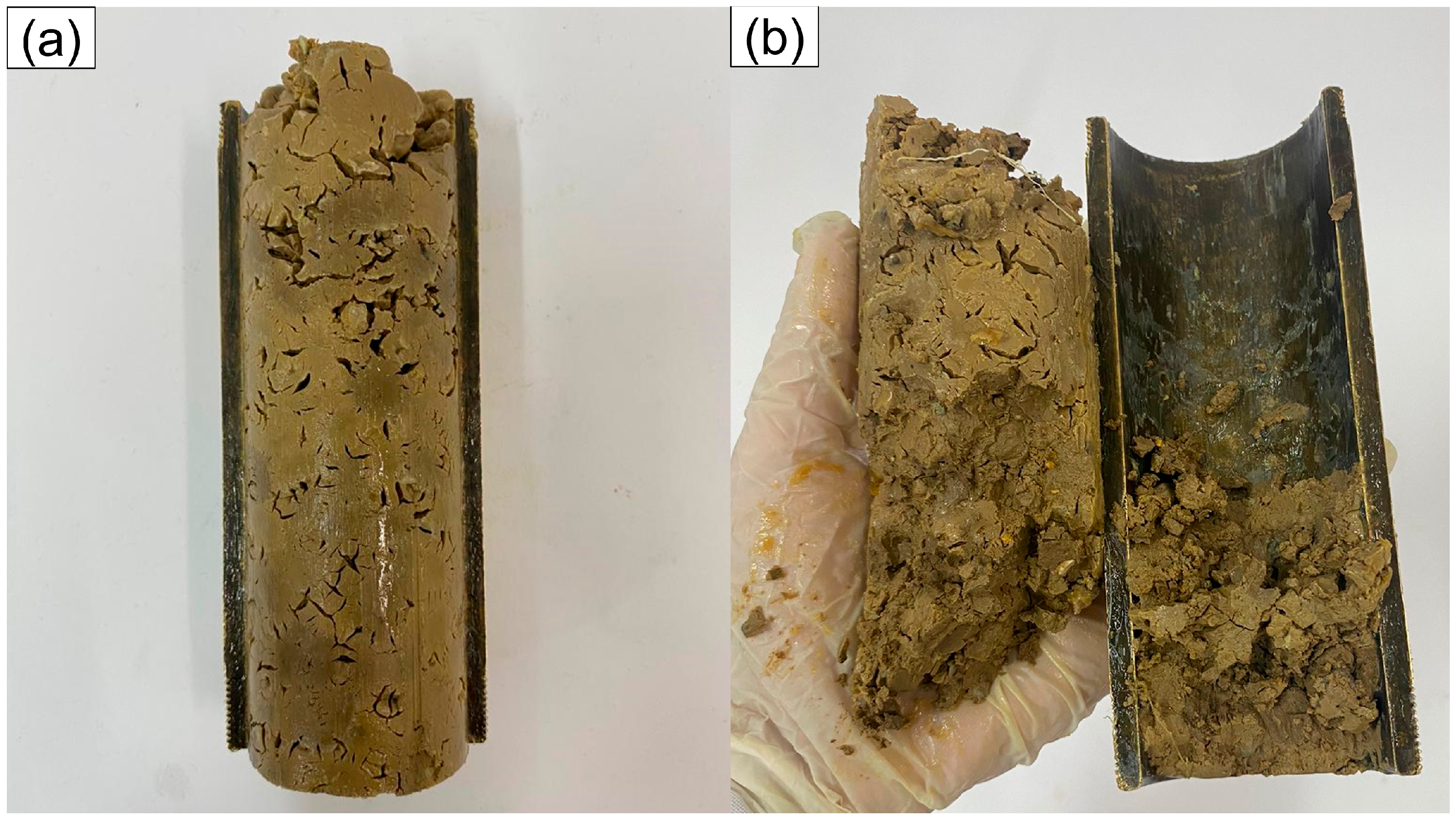
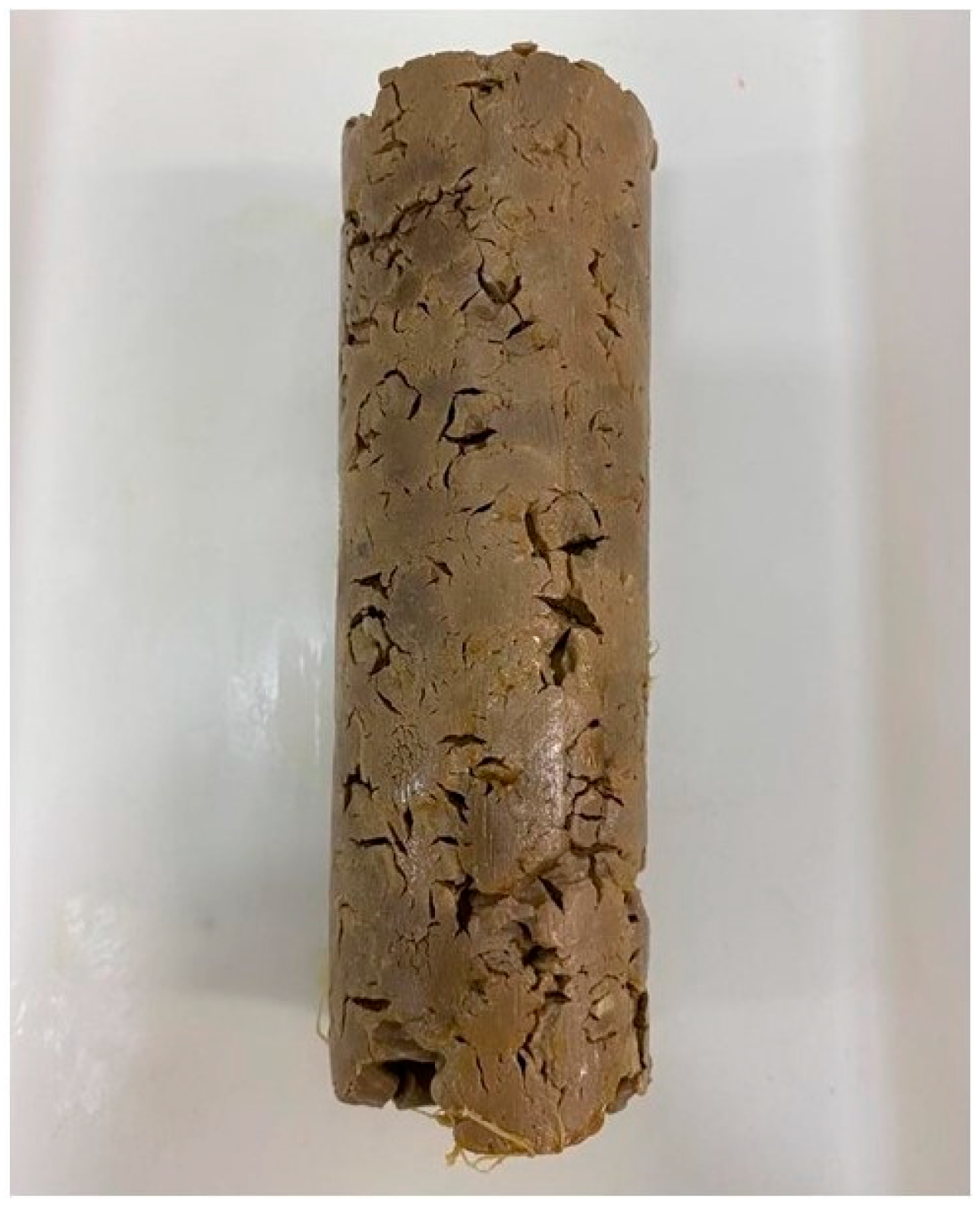
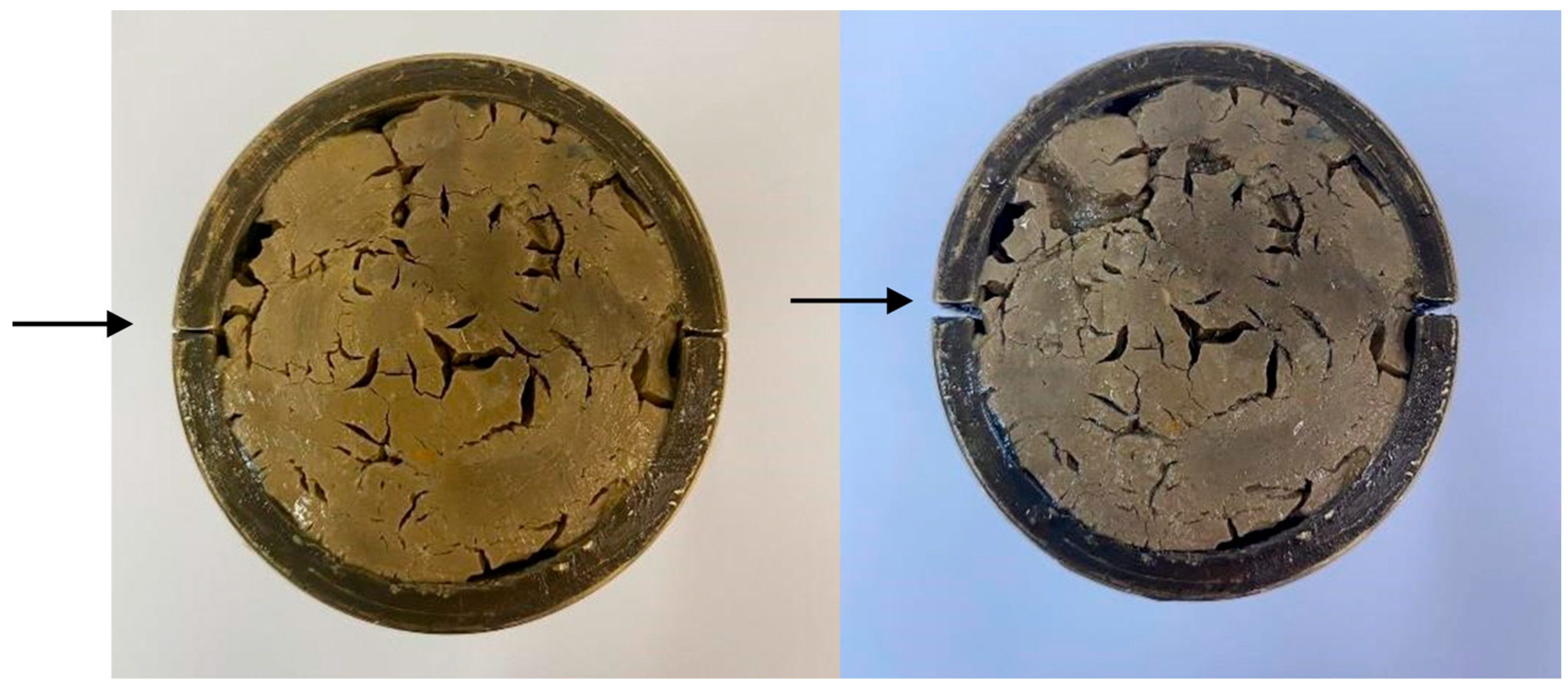
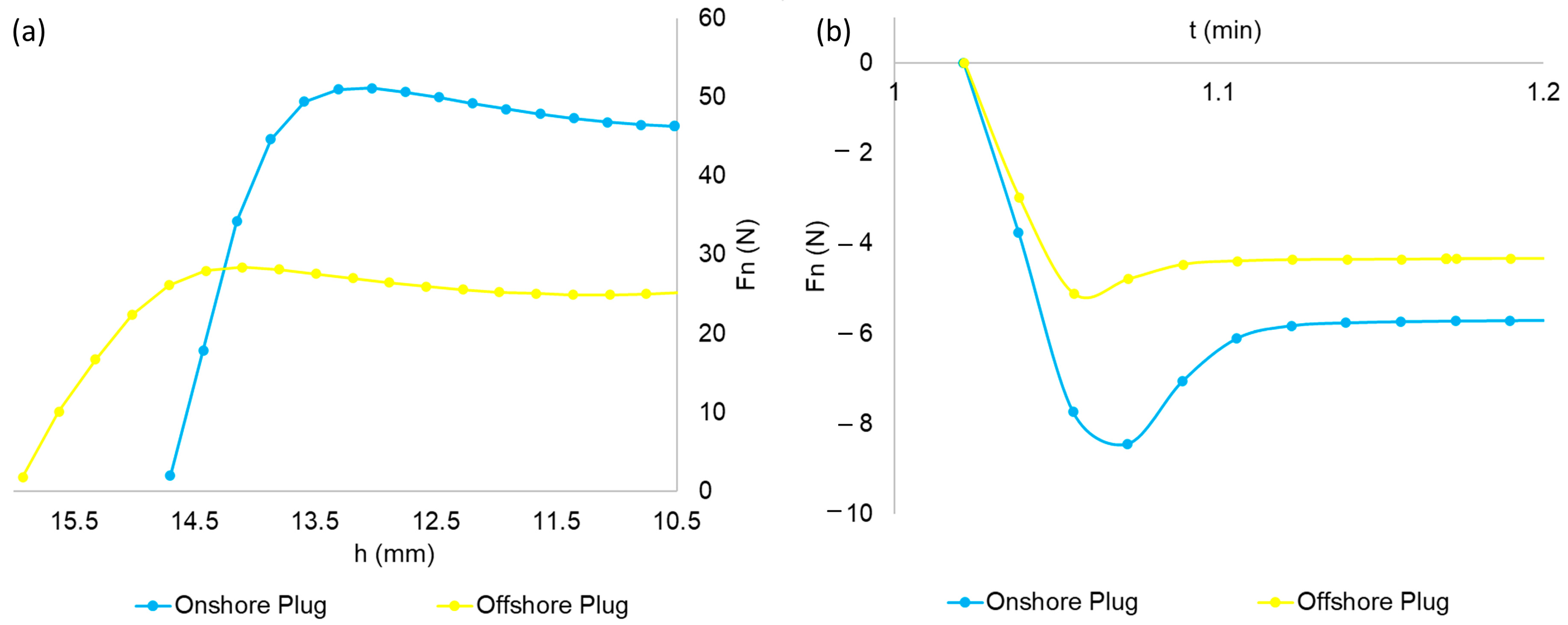
3.1. Aspect and Mechanical Properties of Offshore and Onshore Plugs
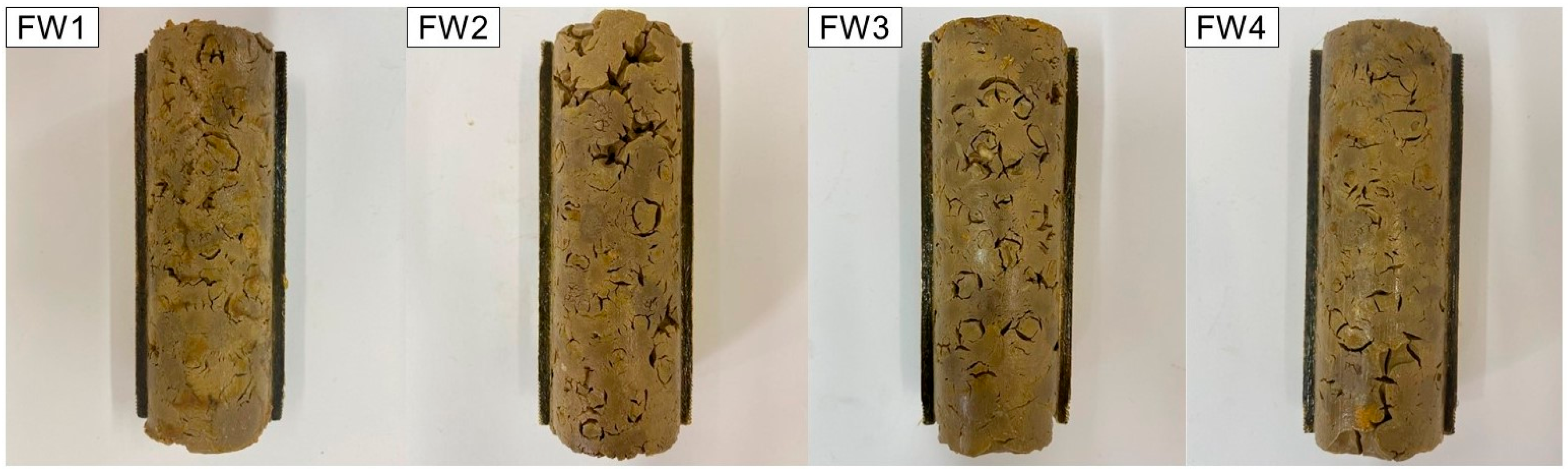
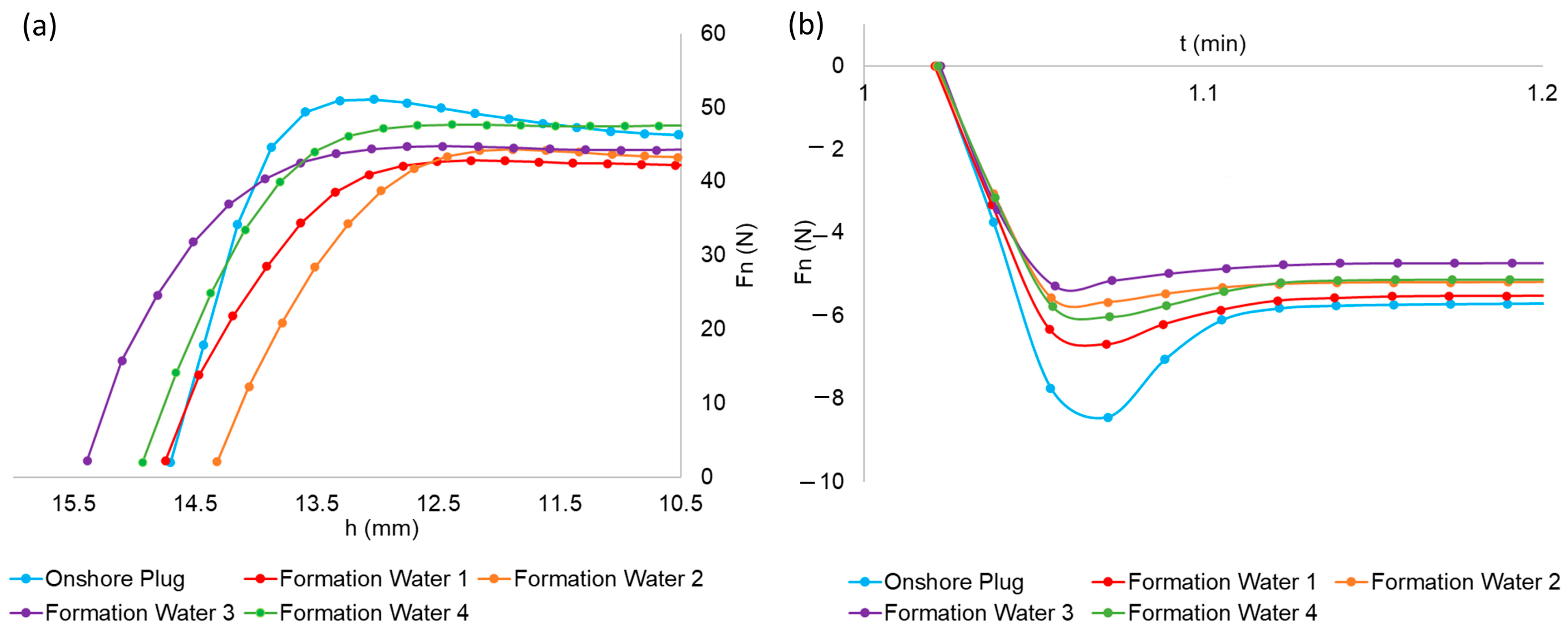
3.2. Aspect and Mechanical Properties of Plugs after Interaction with Formation Waters
4. Conclusions
- Prior analysis of the mechanical properties of the plug is a determining factor in the appropriate choice of the operational procedure and, in the case of offshore wells, of the type of displacement fluid used to dispose the pellets inside the well in the design of abandonment operations.
- Contact with organic fluids used to displace the pellets in offshore wells reduces the mechanical properties of bentonite plugs; however, this reduction compromises significantly only the stability of plugs formed by pellets previously immersed in olefin. Consequently, plugs formed by pellets previously immersed in diesel are promising alternatives for offshore abandonment operations.
- The onshore plug presents satisfactory mechanical resistance to contact with formation waters, so that the plug’s capacity to support loads, represented by compressive strength, presents a maximum reduction of 13% after exposure to this condition, although the adhesion property presents more pronounced reductions.
- The salinity of the formation water has a significant influence on the mechanical properties of the bentonite plug, adversely affecting these parameters, especially the adhesion properties.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leporini, M.; Marchetti, B.; Corvaro, F.; Polonara, F. Reconversion of offshore oil and gas platforms into renewable energy sites production: Assessment of different scenarios. Renew. Energy 2019, 135, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaleo, G.; Nardo, F.; Azzellino, A.; Vicinanza, D. Decommissioning of offshore platforms in Adriatic Sea: The total removal option from a life cycle assessment perspective. Energies 2019, 15, 9325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, A.S.; Love, M.S. Worldwide oil and gas platform decommissioning: A review of practices and reefing options. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2018, 168, 274–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Lian, X.; Luo, J.; Liang, C.; Ma, H. Dynamic risk assessment of plugging and abandonment operation process of offshore wells based on Dynamic Bayesian Network. Ocean Eng. 2023, 270, 113625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruivo, F.M.; Morooka, C.K. Decommissioning Offshore Production Facilities. In Proceedings of the Engineering Technology Conference on Energy, Houston, TX, USA, 4–5 February 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainguy, M.; Longuemare, P.; Audibert, A.; Lécolier, E. Analyzing the risk of well plug failure after abandonment. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 2007, 62, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towler, B.F.; Firouzi, M.; Mortezapour, A.; Hywel-Evans, P.D. Plugging CSG wells with bentonite: Review and preliminary lab results. In Proceedings of the SPE Asia Pacific Unconventional Resources Conference and Exhibition, Brisbane, Australia, 9–11 November 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, E.S.; Lemos, M.J. A thermal study of a new oil well plugging & abandonment operation. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2020, 155, 106421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towler, B.F.; Firouzi, M.; Holl, H.G.; Gandhi, R.; Thomas, A. Field trials of plugging oil and gas wells with hydrated bentonite. In Proceedings of the SPE Asia Pacific Oil & Gas Conference and Exhibition, Perth, Australia, 25–27 October 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achang, M.; Yanyao, L.; Radonjic, M. A review of past, present, and future technologies for permanent plugging and abandonment of wellbores and restoration of subsurface geologic barriers. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2020, 37, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrålstad, T.; Saasen, A.; Fjær, E.; Øia, T.; Ytrehus, J.D.; Khalifeh, M. Plug & abandonment of offshore wells: Ensuring long-term well integrity and cost-efficiency. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 173, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, B.M.; Strutt, J.E.; Eden, R.D. Long Term Well Plug Integrity Assurance–A Probabilistic Approach. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 6–9 May 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, M.C. Using coarse ground bentonite to plug abandoned holes. Water Well J. 1996, 50, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.; Cho, W.; Lee, C.; Kim, G.Y. Thermal conductivity of Korean compacted bentonite buffer materials for a nuclear waste repository. Energies 2018, 11, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, R.C.; Ravi, K. A review on the impact of thermal history on compacted bentonite in the context of nuclear waste management. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarck, J.; Salsbury, B. Well Abandonment Using Highly Compressed Sodium Bentonite-An Australian Case Study. In Proceedings of the Exploration and Production Environmental Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, 10–12 March 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.T.; Opitz, L.A.; Sundstrom, E.; Taylor, J.F. Plugging Wells with Hydrated Bentonite, Part 3: Further Lab Results; University of Wyoming: Laramie, WY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ogden, F.L.; Ruff, J.F. Strength of bentonite water-well annulus seals in confined aquifers. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1993, 119, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towler, B.F.; Ehlers, G.C. Friction factors for hydrated bentonite plugs. In Proceedings of the SPE Rocky Mountain Regional Meeting, Casper, WY, USA, 18–21 May 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifeh, M.; Hodne, H.; Saasen, A.; Vralstad, T. Techniques and materials for North Sea plug and abandonment operations. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 6–9 May 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, W.R.P.; Oliveira, L.R.C.; Nóbrega, K.C.; Costa, A.C.A.; Gonçalves, R.L.N.; Lima, M.C.S.; Nascimento, R.C.A.M.; Souza, E.A.; Oliveira, T.A.; Barros, M.; et al. Evaluation of Saline Solutions and Organic Compounds as Displacement Fluids of Bentonite Pellets for Application in Abandonment of Offshore Wells. Processes 2023, 11, 3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worden, R.H.; Manning, D.A.C.; Bottrell, S.H. Multiple generations of high salinity formation water in the Triassic Sherwood Sandstone: Wytch Farm oilfield, onshore UK. Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 455–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towler, B.F.; Hywel-Evans, D.; Firouzi, M. Failure modes for hydrated bentonite plugs used in well decommissioning operations. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 184, 105385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaji, T.A.; Oti, M.N.; Onyekonwu, M.O.; Bamidele, T.; Osuagwu, M.; Chiejina, L.; Elendu, P. Preliminary geochemical characterization of saline formation water from Miocene reservoirs, offshore Niger Delta. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, W.R.P.; Amorim, L.V.; Nobrega, K.C.; Nascimento, R.C.A.M.; Costa, A.C.A.; Duarte, A.B.M.; Lima, M.C.S. Stability of inverse olefin emulsions: Influence of the incorporation of fine solids of different chemical natures. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2022, 43, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazacheva, E.N.; Uspenskaya, M.V.; Strelnikova, I.E. Bentonite acrylic copolymers modified as effective oil absorbents. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 196, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S.; Ebadi, T.; Maknoon, R.; Amiri, M. Predicting variations in the permeability and strength parameters of a sand-bentonite mixture (SBM) contaminated simultaneously with lead (II) and diesel. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 157, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komine, H.; Yasuhara, K.; Murakami, S. Reply to Discussion by Kaya et al. on “Swelling characteristics of bentonite in artificial seawater”. Can. Geotech. J. 2009, 46, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Niu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wei, X.; Chen, X.; Pan, D.; Wu, W. Kinetic determination of sedimentation for GMZ bentonite colloids in aqueous solution: Effect of pH, temperature and electrolyte concentration. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 184, 105393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.M.; Zheng, Z.J.; Chen, B.; Chen, Y.G.; Cui, Y.J.; Wang, J. Effects of pH and temperature on the swelling pressure and hydraulic conductivity of compacted GMZ01 bentonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 101, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcbride, M. Environmental Chemistry of Soils; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 63–116. [Google Scholar]
- Santamarina, J.C. Soil behavior at the microscale: Particle forces. In Proceedings of the Soil Behavior and Soft Ground Construction, Cambridge, MA, USA, 5–6 October 2001; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.K. Fundamentals of Soil Behavior; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1976; pp. 283–338. [Google Scholar]
- Corina, A.N.; Wollenweber, J.; Fischer, H.; Van der Valk, K.; Castelein, K.; Moghadam, A.; Heerens, G.J. Evaluation of Bentonite Application for the Abandonment of Deep Geo-energy Wells. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2023, 56, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



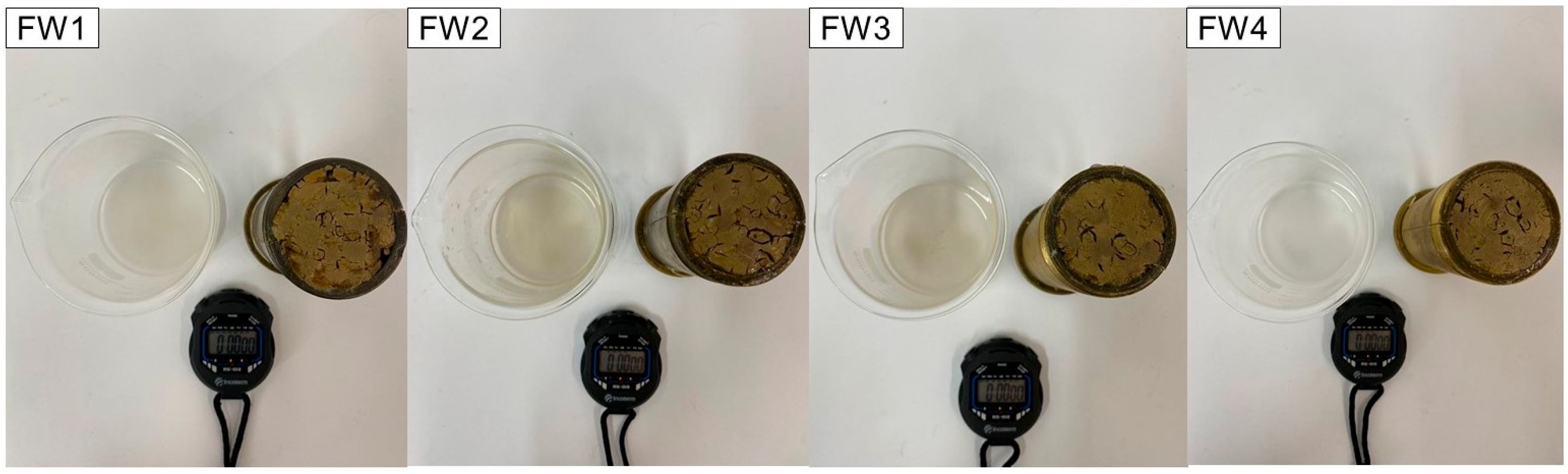
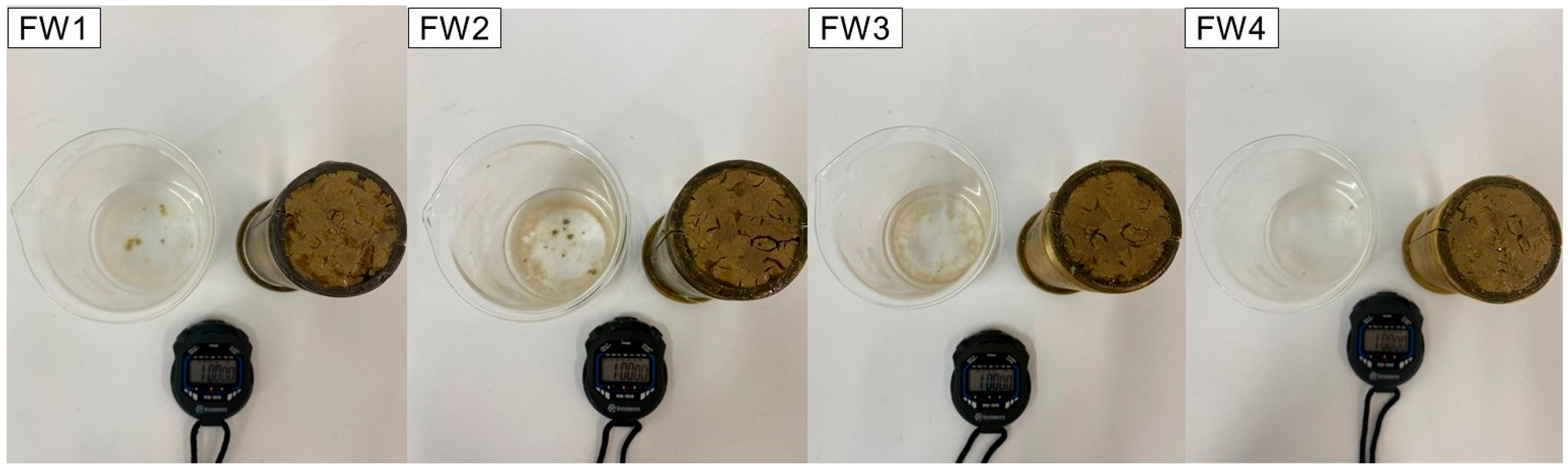


| FW1 | FW2 | FW3 | FW4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Compound | Concentration (mg/L) | Concentration (mg/L) | Concentration (mg/L) | Concentration (mg/L) |
| NaCl | 31,001.00 | 158,176.75 | 116,391.32 | 32,945.00 |
| CaCl2 | 1603.70 | 2693.34 | 0 | 1009.00 |
| NaHCO3 | 6590.00 | 436.44 | 996.79 | 4806.35 |
| MgCl2 | 1478.89 | 0 | 0 | 1112.75 |
| MgO | 60.06 | 829.22 | 575.54 | 0 |
| Ca(OH)2 | 0 | 43.02 | 959.44 | 0 |
| HCl | 0 | 25.00 | 62.00 | 0 |
| KCl | 1359.00 | 3622.63 | 3769.45 | 1940.96 |
| NaOH | 0 | 0 | 851.37 | 0 |
| CaCO3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 780.70 |
| Formation Water | FW1 | FW2 | FW3 | FW4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absorbed Volume (mL) | 3.5 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 3.5 |
| Onshore Plug | Formation Water 1 | Formation Water 2 | Formation Water 3 | Formation Water 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compressive strength (N) | 51.1 | 42.9 | 44.6 | 44.8 | 47.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, L.R.C.d.; Lima, M.C.d.S.; Costa, W.R.P.d.; Gonçalves, R.L.d.N.; Costa, A.C.A.; Nóbrega, K.C.; Souza, E.A.d.; Amorim, L.V. Mechanical Performance of Bentonite Plugs in Abandonment Operations of Petroleum Wells. Resources 2024, 13, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources13080103
Oliveira LRCd, Lima MCdS, Costa WRPd, Gonçalves RLdN, Costa ACA, Nóbrega KC, Souza EAd, Amorim LV. Mechanical Performance of Bentonite Plugs in Abandonment Operations of Petroleum Wells. Resources. 2024; 13(8):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources13080103
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Laura Rafaela Cavalcanti de, Mário César de Siqueira Lima, Waleska Rodrigues Pontes da Costa, Ruth Luna do Nascimento Gonçalves, Anna Carolina Amorim Costa, Karine Castro Nóbrega, Elessandre Alves de Souza, and Luciana Viana Amorim. 2024. "Mechanical Performance of Bentonite Plugs in Abandonment Operations of Petroleum Wells" Resources 13, no. 8: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources13080103
APA StyleOliveira, L. R. C. d., Lima, M. C. d. S., Costa, W. R. P. d., Gonçalves, R. L. d. N., Costa, A. C. A., Nóbrega, K. C., Souza, E. A. d., & Amorim, L. V. (2024). Mechanical Performance of Bentonite Plugs in Abandonment Operations of Petroleum Wells. Resources, 13(8), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources13080103







