Using 3D Imaging to Preoperatively Plan Facelift Procedures for the Lower Third of the Face and Neck
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preoperative Planning
2.1. Methods of Evaluation for Cervico-Mental Area Correction
2.2. Modern Imaging Techniques in Plastic Surgery
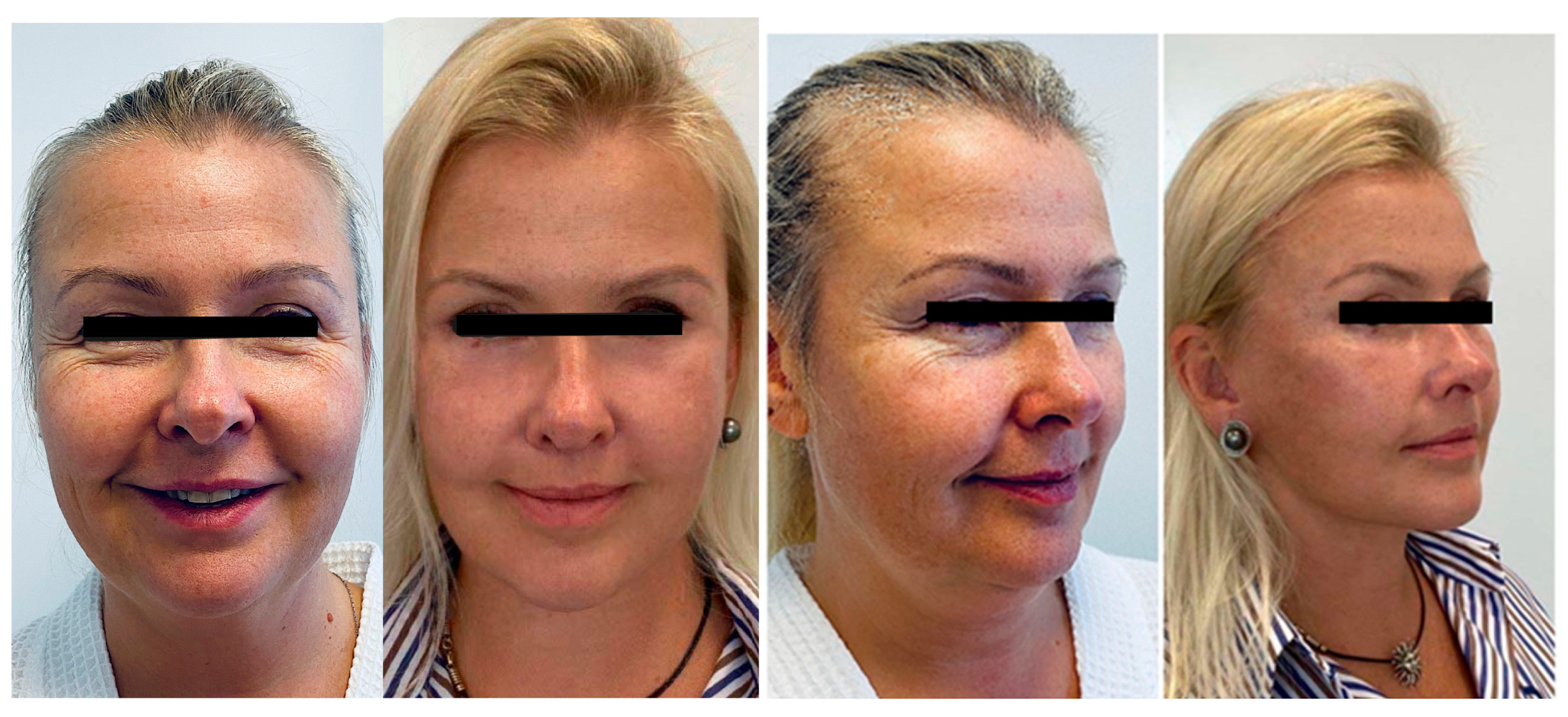
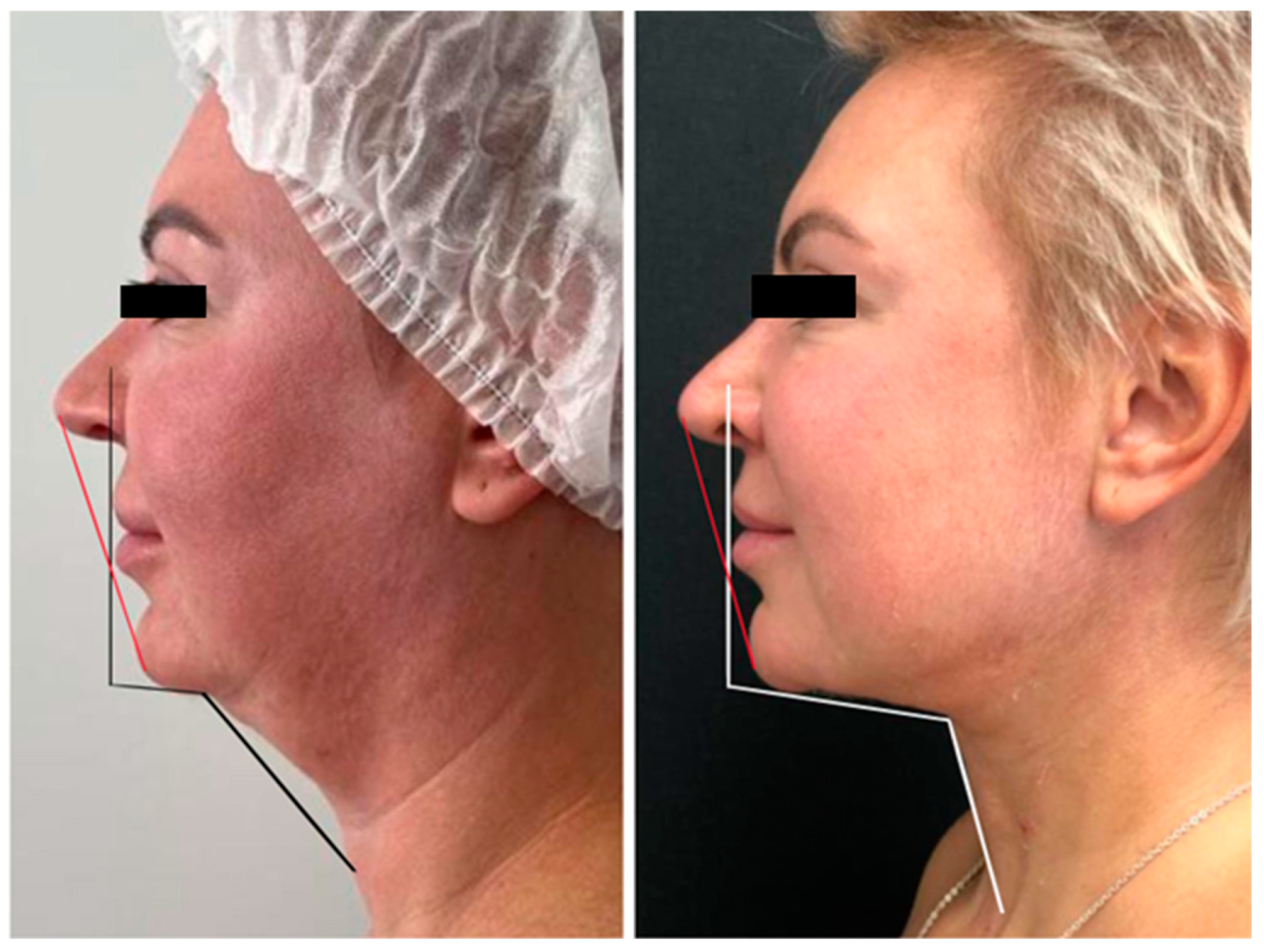
3. Clinical Cases
3.1. Case 1
3.2. Case 2
4. Discussion
- Decreased skin turgor and tone and the appearance of excess skin;
- Involutional changes in facial skeletal structures;
- Excess volume in the lower third of the face;
- Eyebrow ptosis of the eyebrow tail and displacement of soft tissues in the temporal area;
- Age-related changes in periocular soft tissues;
- Hypertonicity or hypotonicity of the chin area;
- Presence of jowls;
- Presence of an obtuse cervical-mental angle;
- Ptosis of the upper lip;
- Manifestation of deep facial wrinkles.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sinno, S.; Thorne, C. Cervical Branch of Facial Nerve: An Explanation for Recurrent Platysma Bands Following Necklift and Platysmaplasty. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2019, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orra, S.; Tadisina, K.; Charafeddine, A.; Derakhshan, A.; Halliburton, S.; Hashem, A.; Doumit, G.; Zins, J.E. The Effect of Age on Fat Distribution in the Neck Using Volumetric Computed Tomography. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 147, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisenda, J.L.; Nassif, P.S. Correction of the Lower Face and Neck. Facial Plast. Surg. 2018, 34, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raveendran, S.S.; Anthony, D.J.; Ion, L. An Anatomic Basis for Volumetric Evaluation of the Neck. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2012, 32, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendelson, B.C.; Tutino, R. Submandibular Gland Reduction in Aesthetic Surgery of the Neck: Review of 112 Consecutive Cases. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 136, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahne, A.; El-Haddad, G.; Alavi, A.; Houseni, M.; Moonis, G.; Mong, A.; Hernandez-Pampaloni, M.; Torigian, D.A. Assessment of Age-Related Morphological and Functional Changes of Selected Structures of the Head and Neck by Computed Tomography, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, and Positron Emission Tomography. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2007, 37, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Sepahdari, A.; Cohen, M. Radiologic Measurement of Submandibular Gland Ptosis. Facial Plast. Surg. 2013, 29, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, M.-S.; Lee, S.-C.; Lee, S.-S.; Choi, H.-M.; Choi, S.-C.; Park, T.-W. Quantitative Analysis of Normal Major Salivary Glands Using Computed Tomography. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2001, 92, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.; Kim, J.Y.; Lim, J.H. Anatomy of the Platysma Muscle. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2017, 28, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, R.B.; Katzel, E.B.; Koltz, P.F.; Kahn, D.M.; Puzas, E.J.; Langstein, H.N. Facial Bone Density: Effects of Aging and Impact on Facial Rejuvenation. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2012, 32, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelson, B.; Wong, C.-H. Changes in the Facial Skeleton With Aging: Implications and Clinical Applications in Facial Rejuvenation. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2012, 36, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikarev, A.; Mantardzhiev, D.; Tsinenko, D. Facial Skeleton Augmentation with Porous Implants for Long-Term Stability of Surgical Rejuvenation. Plast. Surg. Aesthetic Med. 2021, 1, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimova, S.M.; Sharobaro, V.I.; Telnova, A.V.; Stepanyan, E.E. Planning of methods of surgical correction of soft tissues of the face and neck. Med. Vis. 2021, 25, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarassoli, S.P.; Shield, M.E.; Allen, R.S.; Jessop, Z.M.; Dobbs, T.D.; Whitaker, I.S. Facial Reconstruction: A Systematic Review of Current Image Acquisition and Processing Techniques. Front. Surg. 2020, 7, 537616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaye, D.A.; Tollefson, T.T.; Strong, E.B. Use of Intraoperative Computed Tomography for Maxillofacial Reconstructive Surgery. JAMA Facial Plast. Surg. 2015, 17, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laungani, A.; Ritman, E.; Lachman, N.; Christner, J.; Vercnocke, A.; Jorgensen, S.; Anderson, J.; Regnier, T.; Saint-Cyr, M. The Use of Micro Computed Tomography in Plastic Surgery: Towards a Better Understanding of Flaps Microvascular Architecture. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 132, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.S.; Vijai, A. 3D Reconstruction of Face from 2D CT Scan Images. Procedia Eng. 2012, 30, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakowczyk, Ł.; Piotrowska-Seweryn, A.; Szymczyk, C.; Wierzgoń, J.; Oleś, K.; Ulczok, R.; Donocik, K.; Dowgierd, K.; Maciejewski, A. Virtual Surgical Planning and Cone Beamcomputed Tomography in Reconstruction Ofhead and Neck Tumors—Pilot Study. Otolaryngol. Pol. 2020, 75, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-W.; Yen, J.-H.; Chen, W.-H.; Chen, I.-C.; Lai, C.-S.; Lu, C.-T.; Song, D.-Y. Preoperative Computed Tomography Angiography for Evaluation of Feasibility of Free Flaps in Difficult Reconstruction of Head and Neck. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016, 76, S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.-Q.; Jia, X.-L.; Choi, Y.; Zhu, Z.-W.; Xu, Y.-B.; Velamuri, R.; Liu, X.-X. Three-Dimensional Scanning Technique in the Congenital Microtia Reconstruction with Tissue Expander. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 134, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markiewicz, M.R.; Bell, R.B. The Use of 3D Imaging Tools in Facial Plastic Surgery. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 19, 655–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, A.Q.; Pflibsen, L.R.; Smith, A.A.; Rebecca, A.M.; Teven, C.M. Three-Dimensional Printing in Plastic Surgery: Current Applications, Future Directions, and Ethical Implications. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2021, 9, e3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callen, A.L.; Badiee, R.K.; Phelps, A.; Potigailo, V.; Wang, E.; Lee, S.; Talbott, J.; Glastonbury, C.; Pomerantz, J.H.; Narvid, J. Facial Feminization Surgery: Key CT Findings for Preoperative Planning and Postoperative Evaluation. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 217, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimova, S.M.; Sharobaro, V.I.; Avdeev, A.E.; Sidorenkov, D.A.; Guseva, T.S. Cone-Beam Computed Tomography for Objective Diagnosis of Age-Related Soft Tissue Changes in Lower Face and Neck. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2023, 47, 2370–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, N.; Sakai, O.; Bauer, C.M.; Norbash, A.M.; Jara, H. Age-Related Relaxo-Volumetric Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Major Salivary Glands. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2013, 37, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naini, F.B.; Garagiola, U.; Wertheim, D. Analysing Chin Prominence in Relation to the Lower Lip: The Lower Lip-Chin Prominence Angle. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 47, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langsdon, P.R.; Velargo, P.A.; Rodwell, D.W.; Douglas, D. Submental Muscular Medialization and Suspension. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2013, 33, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giampapa, V.C.; Mesa, J.M. Neck Rejuvenation with Suture Suspension Platysmaplasty Technique. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2014, 41, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveikata, K.; Balciuniene, I.; Tutkuviene, J. Factors Influencing Face Aging. Literature Review. Stomatologija 2011, 13, 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Lala, B.; Shah, J.; Salvador, T.M.; Ricci, J.A. Expanding the Utilization of Low-Dose Computed Tomography in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Based on Validated Practices Among Surgical Specialties. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2021, 87, e163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghani, R.; Mukherji, S.K. Advanced Dual-Energy CT Applications for the Evaluation of the Soft Tissues of the Neck. Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugul, H.; Cigdem, M.; Kirisci, M.; Kutlubay, Z. Focused Radiofrequency and Ultrasound for Face and Neck Rejuvenation: A Retrospective Evaluation of 158 Patients. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Age | Combination of Surgical Methods | Mean Value (%) |
| 35–45 years old | Liposuction of the neck and submental area in combination with medial platysmaplasty, as well as isolated corset platysmaplasty. | 20% |
| 45–55 years old | Liposuction of the neck and submental area, medial platysmaplasty; lateral platysmaplasty with and without this procedure. | 55% |
| 55–65+ years old | Liposuction of the neck and submental area, medial platysmaplasty; lateral platysmaplasty, additional fixation of soft tissues to the mylohyoid bone, elimination of submental muscle hypertrophy, and harmonization of the projection of the submental prominence. | 25% |
| BMI | Combination of Surgical Methods | Mean Value (%) |
| 19–21 | Isolated corset platysmoplasty. | 10% |
| 21–23 | Neck and submental area liposuction, medial platysmaplasty; lateral platysmaplasty and without it; additional fixation of soft tissues to the mylohyoid bone. | 63% |
| 23–25 | Neck and submental area liposuction, medial platysmaplasty; lateral platysmaplasty. | 23% |
| Type of Aging | Combined Surgical Methods | Mean Value (%) |
| Fine wrinkling type of facial aging | Isolated corset plasticy; lateral plasticy (referring to a surgical procedure called plasticy, which is used to reshape or contour the body). | 20% |
| Deformational type of facial aging | In simpler terms, this procedure involves liposuction in the neck and submental area, as well as medial platysmoplasty, lateral platysmoplasty, or a combination of both, with or without additional fixation of soft tissues to the mandibular bone for added support. | 55% |
| Mixed type of facial aging | In simpler terms, this procedure involves liposuction in the neck and submental area, as well as medial platysmoplasty or isolated corset platysmoplasty, along with lateral platysmoplasty, with or without additional fixation of soft tissues to the mandibular bone for added support. | 35% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borisenko, A.S.; Sharobaro, V.I.; Avdeev, A.E.; Burkhonova, N.S.; Fisun, A.O. Using 3D Imaging to Preoperatively Plan Facelift Procedures for the Lower Third of the Face and Neck. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11010028
Borisenko AS, Sharobaro VI, Avdeev AE, Burkhonova NS, Fisun AO. Using 3D Imaging to Preoperatively Plan Facelift Procedures for the Lower Third of the Face and Neck. Cosmetics. 2024; 11(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorisenko, Anastasiya S., Valentin I. Sharobaro, Alexey E. Avdeev, Nigora S. Burkhonova, and Anastasiya O. Fisun. 2024. "Using 3D Imaging to Preoperatively Plan Facelift Procedures for the Lower Third of the Face and Neck" Cosmetics 11, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11010028
APA StyleBorisenko, A. S., Sharobaro, V. I., Avdeev, A. E., Burkhonova, N. S., & Fisun, A. O. (2024). Using 3D Imaging to Preoperatively Plan Facelift Procedures for the Lower Third of the Face and Neck. Cosmetics, 11(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11010028







