Abstract
Emollients plus are defined as topical formulations containing active ingredients with no pharmacological effect. They are designed to target multiple mechanisms in AD pathophysiology. The objective of the present study was to assess the efficacy of emollient plus medical device cream by performing a post-marketing surveillance study. It was carried out in cooperation with 88 members of the Polish Association for Atopic Diseases who were diagnosed with AD and voluntarily fulfilled the questionnaire after 14 days of product use. Additionally, the medical device underwent in vitro/ex vivo testing. Cytotoxicity was assessed by in vitro studies: direct MTT assay and indirect Agarose Overlay Assay. An ex vivo EpiDerm™ culture (EPI-200) was used to investigate the irritation potential, and culture medium was collected after 18 h of contact with the skin model to perform a flow cytometric for the analysis of inflammatory cytokines. A dermatological assessment with the local SCORAD was employed to confirm the efficacy of the cream. It was found that 86% of patients with AD observed an improvement in their skin condition during the two-week testing period. In vitro/ex vivo assays confirmed that the product is safe, non-irritant, and does not stimulate the production of proinflammatory cytokines. According to the local SCORAD, the symptoms of AD were alleviated. Moreover, preliminary studies indicated its efficacy in eliminating S. aureus on patients’ skin.
1. Introduction
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a relapsing, inflammatory skin disease that can emerge in distinct stages of life. Nonetheless, it is mostly prevalent in patients before the age of six [1]. Alterations in the composition of essential lipids and structural proteins in the upper layer of the skin (stratum corneum) lead to the impairment of the skin’s barrier function [2]. Disturbances in skin integrity trigger increased transepidermal water loss (TEWL), reduced hydration, enhanced percutaneous penetration of allergens, and disruptions in the composition of the cutaneous microbiota [3,4,5]. The development of atopic dermatitis (AD) is a complex and multifactorial process characterized by a heterogeneous immune response that can vary depending on the disease subtype and the patient’s age [6]. Clinically, AD is characterized by various signs and symptoms, including erythema, oozing, lichenification, xerosis, and dry skin. These manifestations can be localized to different body areas depending on the patient’s age and the severity of the disease [7,8]. Patients with atopic dermatitis (AD) suffer from itching, pain, and sleep disturbances, leading to significant physical and social impacts that lower their quality of life [9]. AD is associated with both atopic comorbidities, such as allergic asthma, rhinitis, conjunctivitis, and food allergies, as well as non-atopic comorbidities, including cardiovascular, neurological, and psychosomatic disorders [10]. The symptoms of AD, along with its comorbidities, are distressing and contribute to social stigma. Patients with moderate to severe AD experience a high disease burden and many are undertreated, resulting in inadequate symptom control. Patient satisfaction is crucial in the management of chronic diseases, and in the case of AD, the level of dissatisfaction with disease management is particularly high [11]. For this reason, a holistic approach to the patient’s problems is advocated, addressing not only dermatological treatment but also fulfilling their overall needs, including their willingness to use emollients [12,13].
Currently, six novel systemic therapies for AD have received approval in Europe: the biologics dupilumab, tralokinumab, and lebrikizumab along with the oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors targeting JAK1/2 (baricitinib) and JAK1 (upadacitinib and abrocitinib). These treatments are prescribed according to the disease’s severity [10]. According to the latest European guidelines and consensus on AD management, topical emollients and moisturizers are considered fundamental components of treatment [14]. Adherence among patients with atopic dermatitis (AD) is a significant concern that is influenced by various factors including patient frustration with medication efficacy and a dislike of prescribed emollients, which should not be underestimated [13,15,16]. Regardless of the disease severity, the use of emollients is recommended alongside systemic treatment [17]. Furthermore, the daily application of emollients during the post-inflammatory stages may mitigate the frequency of flare recurrences and prolong periods of remission. The primary objective of emollient therapy is to maintain skin hydration and safeguard it against potential extrinsic irritants. This is accomplished through the occlusive barrier created by the emollients [18]. Based on their composition and mechanism of action, emollients are classified into three generations. In addition to performing fundamental occlusive functions (I generation), some emollients assist in the restoration of the skin’s barrier function (II generation) and promote reparative processes (II generation) [14]. In 2018, a novel generation of emollients, known as ‘emollients plus’, was introduced. These are topical formulations that incorporate active ingredients without pharmacological effects. Consequently, their occlusive and barrier functions are augmented by the effects of these active ingredients. Currently, the most commonly used active ingredients in these formulations include bacterial lysates, saponins, flavonoids, riboflavins, and synthetic derivatives of menthol [14,17,18,19,20]. Finally, the products are designed to target multiple mechanisms in the pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis (AD), including the reduction of transepidermal water loss (TEWL), the facilitation of skin barrier restoration, and selective bacteriostatic and prebiotic activities. Maintaining a proper skin microbiome balance is critical, as numerous studies have demonstrated an increased predominance of Staphylococcus aureus during flare-ups [4,21,22,23]. The pathogenic mechanism of Staphylococcus aureus involves triggering alterations in lipid and protein composition upon penetrating the dermal layer of the skin. Consequently, this leads to the overexpression of proinflammatory Th2 cytokines. The impaired immune response facilitates further colonization of pathogenic S. aureus and results in a reduction in the biodiversity of the skin microbiota [24,25]. Początek formularzaDół formularza.
The primary objective of the present study was to evaluate the efficacy of the recently developed emollient plus medical device cream, Emotopic Bacteria Control S.O.S. Cream, through a post-marketing surveillance study. This study was conducted in collaboration with 88 members of the Polish Association for Atopic Diseases who were diagnosed with atopic dermatitis (AD) and voluntarily completed a questionnaire (Supplementary Materials) after 14 days of product use. Additionally, the medical device underwent in vitro and ex vivo testing to confirm its safety in accordance with OECD guidelines.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Medical Device Cream Characteristics
The emollient medical device cream (index 16926) underwent extensive safety evaluation through a series of in vitro tests prior to its launch in Poland in 2022. This product is a conventional oil-in-water emulsion (pH 5–6) composed of 29.4% emollients and 8.4% humectants. The key components include natural-origin oils containing free fatty acids: canola oil (2%), hempseed oil (3%), castor oil (3.5%), humectants, ceramides, and active non-medicated substances capable of influencing the skin microbiota, such as acetyl heptapeptide and root extract of Ophiopogon japonicus. Following the product launch, an in vivo test in the form of a post-marketing questionnaire was conducted to gather user feedback. This study is not a post-market clinical follow-up investigation as defined by the European Union Medical Device Regulation (MDR Annex XIV, Part B, Section 6.2). Therefore, this non-interventional study was designed to evaluate patient-reported experiences with the medical device emollient cream.
2.2. In Vitro Safety Assessment of Medical Device Emollient Cream
2.2.1. Direct MTT Assay
A total of 105 L929 cells were seeded in each well of a 96-well plate 24 h prior to the assay to achieve confluency (0.04 × 106) the following day. According to ISO 10993-5:2009 standards [26] for the biological evaluation of medical devices, cytotoxicity testing was performed using the direct MTT assay, with sample preparation (medical device extracts) conducted in accordance with ISO 10993-12:2012 [27]. The concentrations evaluated were 1%, 0.1%, 0.01%, and 0.001%. Briefly, cellular activity was measured after 24 h of exposure to the tested extracts using a colorimetric assay. MTT (1 mg/mL in complete DMEM medium) was added to the cells, and after a 3-h incubation at 37 °C with 5% CO2, formazan crystals formed. Subsequently, 100 μL of isopropanol was added to each well, and the plate was wrapped and shaken on an orbital shaker for 10 min. Occasionally, pipetting was performed to fully dissolve the formazan. The absorbance at 570 nm was measured using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (BioTek, Epoch, Gen5 v.3.13.15).
2.2.2. Indirect Cytotoxicity Assessment with Agarose Overlay
The indirect evaluation of cytotoxicity potential was performed using the Agarose Overlay assay. This method is based on determining the cytotoxicity of the product 24 h after its application on the surface of an agarose gel in contact with an L929 cell monolayer. Specifically, 4 mL of 1% low melting point agarose in complete medium was prepared and applied directly to a 60 mm cell culture dish. After the agarose solidified, 10 mg of the tested product was applied to a sterile cellulose filter paper disc (6 mm in diameter), which was then placed directly on the agarose layer. The setup was incubated at 37 °C with 5% CO2 for 24 h. After the incubation period, both the paper disc and the agarose gel were gently removed using a fine spatula, and the cell culture was rinsed with PBS. Subsequently, 2 mL of MTT at a concentration of 0.5 mg/mL was added to the culture. Following contrast staining, a non-colored lysis zone was investigated to assess its diameter, which corresponds to the level of cytotoxicity of the tested product. The test product (16926) was assessed in quadruplicate. The negative control (NC) used in the assay was sterile PBS, and the positive control (PC) was 3% SDS. The evaluation was performed in accordance with ISO 10993-5 standards [26].
2.2.3. Irritation Potential of Medical Device Emollient Cream
The irritation potential of the product was assessed according to the in vitro skin irritation test OECD 439 [28]. The test was conducted in accordance with the manufacturer’s protocol for medical devices, the ISO 10993-23:2021 standard [29], and the OECD 439 guidelines.
Additionally, during the assay, culture medium was collected after 18 h of contact with EpiDerm™ to perform ELISA analyses of inflammatory cytokines released post-exposure. The samples were tested in triplicate, with 5% SDS serving as the positive control (PC) and a blend of parabens with known irritant potential as the reference sample (REF). The concentration of IL-18 was assessed using the Human IL-18/IL-1F4/Interleukin-18 ELISA Kit (Biorbyt Ltd., Cambridge, UK) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The IL-18 concentration in the samples was determined spectrophotometrically at 450 nm using the Epoch Microplate Spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA).
In addition to the quantification of IL-18, flow cytometric analysis of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12p70, and TNF-α) was performed using a sandwich ELISA with the Human Inflammatory Cytokines Kit (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s protocol. For this assay, the BD FACSCanto II cytometer (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) with FACSDiva v.6.1.3 software (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) was used for reading the results, and FCAPArray v.3 software (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) was employed for the analysis. Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism v.8.4.3.
2.3. Patients’ Self-Evaluation of Product Efficacy
In the study, 88 patients (members of the Polish Association for Atopic Diseases) were enrolled to assess the efficacy of the product. The inclusion criteria for participation were the presence of atopic dermatitis, erythema of unspecified etiology, scaling skin, and pruritus. The study participants used the product for 14 days according to the manufacturer’s instructions, applying it to symptomatic skin lesions twice daily. At the end of the two-week trial, the participants were asked to complete a pre-set online questionnaire specifying the age bracket (4–12 months, 12–36 months, 3–12 years, 13–18 years, 18+ years) and gender. For underage patients, a parent or legal guardian who consented to the child’s participation in the study completed the questionnaire after the trial. The participants were also asked if they used the product in combination with other products, including drugs and cosmetics. Additionally, they were queried about the time frame in which the first signs of skin improvement appeared (after the first use, after 3 days, within the first week, after the first week, after 2 weeks, no improvement noticed). A 5-grade scale was designed to assess the product efficacy in terms of symptom reduction/alleviation, where 1 indicates “worsened” and 5 indicates “significantly improved”. Using this scale, the patients evaluated the product’s efficacy in reducing pruritus, improving sleep, skin dryness, erythema, exudates and scabs, and burning sensation. Furthermore, the participants were asked to assess the moisturizing properties of the tested product (no difference, felt well moisturized, felt very well moisturized) and its protective effect against external factors (no difference, felt well protected, felt very well protected). The questionnaire also included questions regarding the clarity and understandability of the product labeling (Yes, No, Patient comments) and the user-friendliness of the packaging and tube (Yes, No, Patient comments). Additionally, the users were asked to evaluate the acceptability of the lack of fragrance in the formulation (1—not acceptable, 2—acceptable, 3—very acceptable, 4—excellent). Początek formularza
The online questionnaire was anonymized and did not include any questions that would collect personal identifying data. The following study is based on descriptive statistics gathered from 88 participants who agreed to complete the online questionnaire.
2.4. Dermatological Assessment of Product Efficacy
A dermatologist conducted a study involving 24 adult patients who were not undergoing pharmacological treatment. At the initial visit, the purpose and methodology of the medical device assessment were discussed with the patients. A site on their bodies with atopic dermatitis lesions was selected for further investigation. The patients were provided with the products and instructed to apply the medical device cream twice a day for seven days. The local SCORAD index was employed to evaluate the selected lesions prior to the commencement of emollient monotherapy and following a seven-day period of product use.
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Safety Assessment of Medical Device Emollient Cream
The direct MTT assay indicated that the device extracts at concentrations below or equal to 0.01% were not cytotoxic towards L929 cells, with a mean cell viability of 72.9% at 0.01%. Any concentration higher than 0.01% was cytotoxic, with cell viability dropping below 70% (Figure 1). In the indirect method for determining the cytotoxic potential of the product (Agarose Overlay Assay), it was found that the product did not form a lysis zone in the monolayer of the L929 culture. However, the morphology of the cells was slightly disturbed directly under the filter paper disc where the tested product was applied (Figure 2).
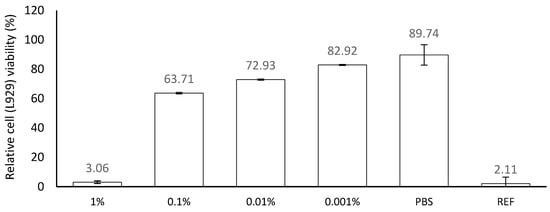
Figure 1.
Cytotoxicity of Emollient Medical Device Cream on L929 cells. Values are presented as percentage of mean viability in NC ± SD. Viability < 70% of the control—cytotoxic potential. Ref—0.5% SDS.
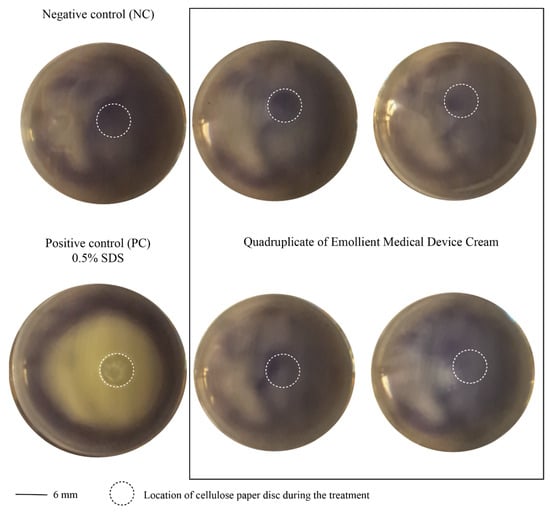
Figure 2.
Cytotoxicity of Emollient Medical Device Cream (16926) in L929 cells investigated through Agarose Overlay Assay. Circle with dashed line corresponds to the place where cellulose disc for treatment was located. Cytotoxicity of a product was excluded due to lack of lysis zone in cell monolayer below the paper disc where tested product was applied.
The quantification of EpiDerm™ viability through the MTT assay indicated that treatment with the undiluted tested product preparation did not result in a decrease in viability after exposure and post-treatment incubation when compared to untreated EpiDerm™ samples (NC). According to the OECD protocol, a sample is non-irritant if the mean relative viability after incubation (18 h for medical devices) is higher than or equal to 50% compared to the negative control. Thus, the emollient cream medical device can be considered safe and non-irritant for the skin (Figure 3).
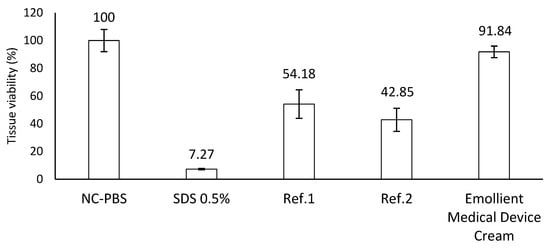
Figure 3.
Skin irritation potential of Emollient Medical Device Cream on EpiDerm™ model. PC—5% SDS—irritant. Ref 1—naphthalene acetic acid (CAS86-87-3)—non-classified (non-irritant). Ref 2—cyclamen aldehyde (CAS 103-95-7)—classified (irritant, Cat. 2). Tissue viability ≤ 50% of the control (PBS)—irritant. Tissue viability ≥ 50% of the control—non-irritant.
Analysis of interleukin concentration after 18 h of exposure to EpiDerm™ to the tested medical device revealed that the levels of IL-10, IL-12p70, and TNF-α were below the detection threshold. Nevertheless, mean concentrations of IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, and IL-18 were successfully determined, with detailed results presented in Figure 4. Statistical differences between the experimental groups and the control group (NC) were determined using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a post-hoc Dunnett test.
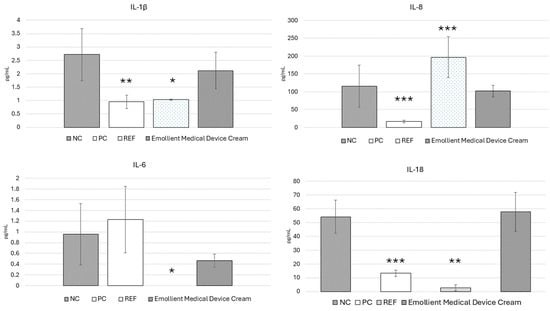
Figure 4.
Expression of proinflammatory interleukins in culture medium of EpiDerm™ after treatment with Emollient Medical Device Cream. NC—negative control PC—5% SDS—irritant/non-sensitizer. REF—Paraben blend (Phenoxyethanol, Methylparaben, Ethylparaben, Propylparaben, Butylparaben)—irritant/sensitizer. * corresponds to p value (* <0.033, ** <0.002, *** <0.001).
For IL-1β, statistically significant differences compared to the negative control (NC) were observed for the paraben blend (REF) and positive control (PC), where the concentration of IL-1β was lower than in the NC. The expression of IL-6 was not confirmed only in the case of the REF sample, which was the only statistically significant difference. In terms of IL-18 expression, a statistically significant difference compared to the NC was only observed for the REF. The highest and statistically significant IL-8 concentration compared to the negative control (NC) was recorded for the REF sample, while the lowest and statistically significant IL-8 concentration was observed for the positive control (PC) sample.
3.2. Patients’ Characteristics in Self-Evaluation Product Efficacy
The surveillance study was conducted from 23 November 2022 to 28 December 2022. All the participants completed the online questionnaire, with the gender distribution favoring female users over male patients (F = 57, M = 31). The majority of users of the tested formulation were pediatric patients under the age of 18 (n = 59), while adults were represented by 29 participants. The age distribution of the volunteers and their dermatological diagnoses are presented in Figure 5. The vast majority of study participants were diagnosed with AD. Among the 88 patients, 43 were using the tested emollient medical device cream as a monotherapy, 34 used other dermatological creams in addition to the tested product, and 31 were undergoing medical treatment. No adverse effects were reported during the use of the product.
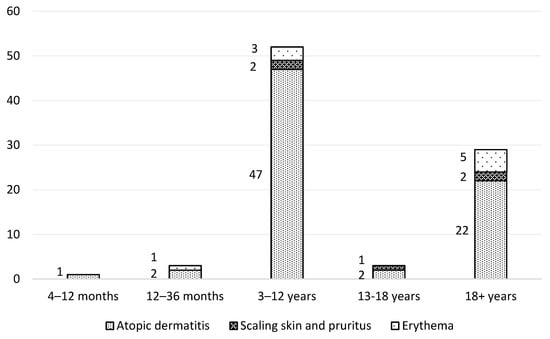
Figure 5.
Age structure of study participants and their skin conditions.
3.3. Patients’ Self-Evaluation of Product Efficacy
The study found that 86% of patients (n = 76) noticed an improvement in their skin condition during the testing period of two weeks. Specifically, 11 patients (13%) observed an improvement after the first use, 25 patients (28%) after 3 days, 29 patients (33%) within the first week, 9 patients (10%) after 7 days and 2 patients (2%) after 14 days, as shown in Figure 6.
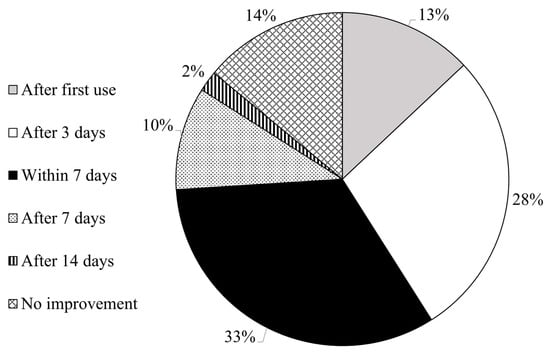
Figure 6.
Improvement (if any) in patients’ skin conditions and time of product use needed to observe it.
The remaining questions were answered using a 5-grade scale proposed by the researchers, with the detailed results summarized in Figure 7. Regarding the product’s efficacy in reducing pruritus, only the patients affected by this issue (n = 74) responded. No patients reported increased pruritus intensity (grade 1), while 9 patients (12%) reported no improvement (grade 2). Pruritus was reduced in 65 patients (87%) to varying degrees: 12 patients (16%) reported a significant reduction (grade 5), 24 patients (33%) reported a reduction (grade 4), and 29 patients (40%) reported a slight reduction (grade 3). For the question on sleep quality improvement, 36 patients who reported sleep problems responded. In total, 1 patient (3%) reported worsened sleep quality, 12 patients (33%) reported no improvement (grade 2), 14 patients (39%) reported a slight improvement (grade 3), and 9 patients (25%) found a noticeable improvement (grade 4). None of the patients reported a significant improvement in sleep quality.
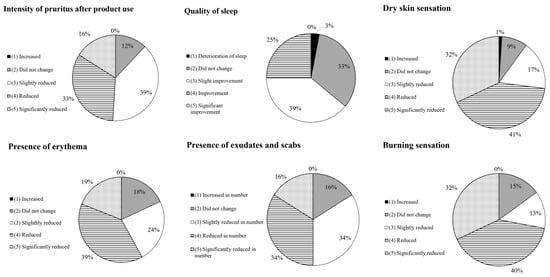
Figure 7.
Self-evaluation of skin characteristics on a 5-grade scale after 14 days of product use.
Skin dryness reduction was assessed by 74 patients. In total, 1 person (1%) reported increased dryness (grade 1), 7 patients (9%) did not observe any change (grade 2), and 66 patients (89%) reported an improvement in dryness reduction. Erythema was assessed by 74 patients reporting such a condition. There were no reports of increased redness intensity. Erythema was reduced in 61 patients (82%) (grades 3, 4, and 5). Among the 32 volunteers who had exudates and scabs, 5 (16%) did not report any changes (grade 2), while 27 subjects (84%) observed an improvement (grades 3, 4, and 5). A burning sensation was reported by 47 patients. In total, 7 patients (15%) did not experience any improvement, while 40 patients (85%) reported a decrease in the burning sensation. Within this group, 15 patients (32%) reported a significant reduction.
3.4. Product Characteristics Assessed by Users
All the study participants (n = 88) responded to the question regarding the moisturizing properties of the tested product. In total, 6 participants (7%) reported that their skin was not moisturized after application, whereas 82 volunteers noted a positive effect on skin hydration. Specifically, 51 patients (58%) reported that their skin was well moisturized, and 31 patients (35%) indicated that their skin was very well moisturized after application. Regarding the product’s protective properties against external factors, the responses were as follows: no difference—16 participants (18%); felt well protected—47 participants (53%); and felt very well protected—25 participants (28%). In terms of product labelling, 95% (n = 84) of users found it clear and understandable, and 97% (n = 85) found the packaging convenient and easy to use. The absence of a fragrance was accepted by 99% of the study participants: not acceptable—1 participant (1%); acceptable—5 participants (6%); very acceptable—17 participants (19%); and excellent—65 participants (74%).
3.5. Dermatological Assessment of Product Efficacy
Following the administration of the product for a period of seven days, the condition of the patient’s skin in the area selected at the initial visit was evaluated during the second medical appointment. An objective assessment was performed for five types of skin abnormalities, while two disorders were evaluated subjectively by the patients. Overall, the administration of the medical device for seven days resulted in general skin improvement and a reduction of pruritus and sleep disorders (Table 1). No adverse effects or irritation were reported.

Table 1.
Dermatological evaluation of patients (n = 24) using medical device emollient cream for 7 days, twice a day.
4. Discussion
Atopic dermatitis is a common, recurrent inflammatory skin disease that predominantly affects up to 20% of infants and children, but it can persist throughout the lifetime or develop in adulthood. The disease arises from an interplay of skin barrier dysfunction, inflammation, and dysregulation in cutaneous microbiota biodiversity. AD symptoms negatively impact a patient’s quality of life, affecting social interactions and causing daily inconveniences, ranging from stigmatization to psychological comorbidities. The high prevalence and burden of AD make it a condition of socioeconomic importance.
The management of atopic dermatitis should be conducted in accordance with dermatological guidelines, with highly recommended therapy with emollients. Considering the etiopathology of AD and the skin sensitivity of patients, an easy-to-use and safe emollient medical device enriched with saturated and unsaturated acids and additional ingredients capable of controlling the biofilm formation of pathogenic microbiota could be advantageous in AD management. Patients suffering from AD are recommended to use 250 g of emollients per week. Consequently, the amount of product used daily, at least twice a day, necessitates that manufacturers take special measures to ensure the product’s safety and lack of adverse effects.
Direct and indirect methods for verifying cytotoxicity were employed. The indirect method (Agarose Overlay) was utilized because the results of direct MTTassay were ambiguous. The MTT assay has limitations and various confounding factors must be considered when interpreting the results. To verify that the topical application of formulations does not cause irritation, special testing is crucial for designing safe products. Testing with special systems that mimic the skin barrier is highly recommended. The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) provides validated methods for assessing the irritation potential of products using skin models. Therefore, in vitro studies were extended to include an ex vivo method using the EpiDerm™ skin model following OECD instructions for medical devices, which differ from those for cosmetics in terms of the incubation time with the studied formulation (18 h instead of 1 h). The EpiDerm™ trial excluded the irritation potential of the tested product as the viability of the cells was higher (103% ± 2.32) than the 50% viability threshold of the negative control (100% ± 2.97).
The volunteers who participated in the post-marketing questionnaire study did it voluntarily and were enrolled in the study neither by a dermatologist nor by a healthcare professional. Their membership in the Polish Association for Atopic Diseases served as a credible indicator of their diagnosis of AD. According to the questionnaire, 74 out of 88 participants declared they were diagnosed with AD. The key outcome of the study was the fact that the emollient formulation, registered as a medical device, improved the skin condition in 86% of patients. Regardless of the extent of improvement, it was found that key aspects of AD, such as pruritus, erythema, a burning sensation, and skin dryness were reduced. The mechanism responsible for these improvements remains speculative; however, the product composition, including hempseed oil, canola oil, and ceramides, appears to be crucial for the process of skin barrier restoration. Studies have found that the efficacy of vegetable oils, including canola oil, in providing an occlusive layer on the skin is comparable to that of petrolatum [30]. This occlusive effect is maintained over a 6-h period, which is adequate for emollients used in the skincare management of AD, especially when applied at least twice daily [31]. Canola oil is rich in monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), including oleic acid, linoleic acid (LA), and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) [32,33]. Similarly, hempseed oil contains a balanced composition of linoleic and linolenic acids, which are known to improve skin barrier function and hydration in AD patients [34,35,36]. Importantly, the hempseed oil used in the formulation is free from CBD.
The stratum corneum (SC), the outermost layer of the epidermis, is composed of corneocytes embedded in a lipid matrix [37]. The undisturbed metabolism of SC lipids is essential for maintaining the skin’s barrier function [38]. Although some lipids can be synthesized de novo, both ALA and LA acids must be obtained externally [39]. The in vitro supplementation of ALA in combination with LA has been shown to play a crucial role in skin barrier function in reconstructed skin models [40]. Furthermore, PUFAs are recognized as gene modulators that influence the expression of proteins related to inflammation and lipid metabolism, making them valuable agents for treating various inflammatory skin diseases [38]. A topical therapeutic combination of LA and amitriptyline has been introduced to treat mild to moderate AD and prevent disease relapses [41].
Oxidative stress is a significant factor in chronic inflammatory skin diseases, including AD, which justified the inclusion of hempseed oil in the formulation due to its antioxidant potential [42,43]. An inadequate level of ceramides, the most important class of lipids in the SC, leads to skin barrier damage and increases transepidermal water loss [44]. Thus, increased skin barrier permeability is a critical issue in AD management [45]. Inflammatory skin diseases, including AD, contribute to changes in ceramide profiles, resulting in increased skin permeability and deterioration of the AD skin condition [46]. Comparative studies have shown that topical formulations containing ceramides outperform those without them in enhancing skin barrier restoration and reducing the SCORAD index [47]. Topically applied ceramides improve barrier function through incorporation into lamellar bilayer structures in the stratum corneum and can penetrate into nucleated layers of the epidermis, significantly supporting barrier improvement [48,49]. Hence, the role of ceramides in the efficacy of the product in reducing AD symptoms in this study cannot be underestimated.
Ingredients that classify the developed product as Emollient Plus, according to the latest classification [14], include acetyl-heptapeptide-4 and Ophiopogon japonicus root extract. The latter was initially studied on a murine model, where it was found to influence the Th1/Th2 imbalance in subjects mimicking AD features [50], and has also shown efficacy in human patients of different ethnicities [51]. It has been effective in reducing the SCORAD index, including erythema and pruritus, by enhancing skin barrier function. New data on its efficacy continue to emerge [20,52]. Ophiopogon japonicus is considered a prebiotic that modulates the activity of commensal skin microbiota, which is consistent with studies demonstrating the role of prebiotics in preventing AD flare-ups. Acetyl-heptapeptide-4, which is present in the formulation, acts as a humectant and reduces the abundance of Staphylococcaceae [53]. Studies confirming the influence of emollient medical device creams on skin microbiota are ongoing. Preliminary tests performed with volunteers during remission periods (unpublished data) and flare-ups [54] showed that after seven days of product use, S. aureus was no longer present in swabbed areas where the product was applied.
Surprisingly, it was found that 35 patients (40%) reported using the tested emollient plus medical device as monotherapy, with 26 of them being diagnosed with AD. It is likely that this group was either in a remission period or had mild AD. Nonetheless, it is noteworthy that all the users in this group observed improvements in their skin conditions, specifically reductions in skin dryness and pruritus. Although this group cannot be considered representative, the findings suggest that the product itself could potentially be used as monotherapy for mild atopic dermatitis. Yet, further in-depth research is needed to substantiate such a statement.
User satisfaction with the product was highly rated. There is a growing awareness among AD patients about allergens, such as fragrances in topical emollients. In this study, 99% of the users approved of the fact that the formulation was fragrance-free. This observation aligns with studies on patient preferences for leave-on emollient products conducted in Poland [55]. Similar observations have been made worldwide, with both patients and dermatologists expecting fragrance-free products for AD skincare [56].
According to Kunkiel et al., patients prefer bottles with pumps over other types of packaging. In this study, the emollient medical device cream was delivered in tubes, and the users’ satisfaction, as expressed through the questionnaire, was 97%. Kunkel et al. found that multidose tubes are the second most preferred type of packaging preference. Interestingly, the esthetic of packaging is one of the least important factors influencing product choice, with the most crucial factor being the presence of a claim that the product is tailored to the skin [52].
The findings from the present study are very promising and form a solid basis for further research. Future studies will include patient input in the questionnaire design to enhance the validity and relevance of the data collected. Although this preliminary study employed dermatological assessments of skin improvement, the manufacturer plans to conduct extended research in collaboration with dermatologists and pharmacists to supplement the presented data with additional evidence of product efficacy. Furthermore, the impact of regular product use on patients’ skin microbiota is currently being investigated in cooperation with an independent research institute. Therefore, this research should be viewed as a preliminary but essential study, as the high acceptability of products by their users is crucial for market success. Positive patient feedback regarding the performance of the medical device cream is vital for improving patient adherence to emollient monotherapy. New data on the emollient medical device will be presented in due course.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cosmetics11040136/s1. Post-Marketing surveillance study of Emollient Plus Medical Device Cream (16926).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.D. and M.P.-P.; methodology, H.G. and M.P.-P.; software, R.C.; formal analysis, I.E.; investigation, M.R., R.D., I.M., R.C. and K.L.; data curation, I.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.R.; writing—review and editing, M.R. and K.L.; visualization, M.R.; supervision, I.E.; project administration, K.R. and R.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
As this was a post-marketing questionnaire asking for feedback from users, not a post-market clinical follow-up investigation, the European Union Medical Device Regulations did not require ethics committee approval (MDR Annex XIV, Part B, Section 6.2).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all the participants involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
All the collected data for this study are available at any request. The data are held by Dr Irena Eris S.A Company.
Acknowledgments
The main author, Michal Rachalewski, extends his gratitude to Jack White and Third Man Records for the motivational auditory stimuli derived from the albums “Fear of the Dawn” and “Entering Heaven Alive”, which provided inspiration during the author’s creative process. The final refinements were applied to recently released album, entitled “No Name”.
Conflicts of Interest
Michał Rachalewski, Monika Pasikowska-Piwko, Renata Dębowska, Iwona Marczak, Karolina Lendzion, Katarzyna Rogiewicz and Irena Eris are employees of Dr Irena Eris company. Hubert Godziątkowski and Robert Czarnomysy declare no conflict of interests.
References
- DaVeiga, S.P. Epidemiology of Atopic Dermatitis: A Review. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2012, 33, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero-Vilchez, T.; Segura-Fernández-nogueras, M.V.; Pérez-Rodríguez, I.; Soler-Gongora, M.; Martinez-Lopez, A.; Fernández-González, A.; Molina-Leyva, A.; Arias-Santiago, S. Skin Barrier Function in Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis: Transepidermal Water Loss and Temperature as Useful Tools to Assess Disease Severity. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmert, H.; Baurecht, H.; Thielking, F.; Stölzl, D.; Rodriguez, E.; Harder, I.; Proksch, E.; Weidinger, S. Stratum Corneum Lipidomics Analysis Reveals Altered Ceramide Profile in Atopic Dermatitis Patients across Body Sites with Correlated Changes in Skin Microbiome. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 1398–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demessant-Flavigny, A.L.; Connétable, S.; Kerob, D.; Moreau, M.; Aguilar, L.; Wollenberg, A. Skin Microbiome Dysbiosis and the Role of Staphylococcus Aureus in Atopic Dermatitis in Adults and Children: A Narrative Review. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 37, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danby, S.G.; Andrew, P.V.; Kay, L.J.; Pinnock, A.; Chittock, J.; Brown, K.; Williams, S.F.; Cork, M.J. Enhancement of Stratum Corneum Lipid Structure Improves Skin Barrier Function and Protects against Irritation in Adults with Dry, Eczema-Prone Skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 2022, 186, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarnowicki, T.; He, H.; Krueger, J.G.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Atopic Dermatitis Endotypes and Implications for Targeted Therapeutics. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, M.S.Y.; Yun, J.S.W.; Su, J.C. Management of Atopic Dermatitis: A Narrative Review. Med. J. Aust. 2022, 216, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grafanaki, K.; Bania, A.; Kaliatsi, E.G.; Vryzaki, E.; Vasilopoulos, Y.; Georgiou, S. The Imprint of Exposome on the Development of Atopic Dermatitis across the Lifespan: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Stengel, R.; Sun, P. Effectiveness of Emollients in the Prevention of Atopic Dermatitis in Infants: A Meta-Analysis. Dermatology 2022, 238, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Maintz, L.; Bieber, T. Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: Recently Approved Drugs and Advanced Clinical Development Programs. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 79, 1501–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicogossian, J.; Héas, S.; Thénié, C.; Noel, M.; Misery, L.; Barbarot, S.; Martin Juchat, F. Questions a Patient with Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis Would like to Be Asked: Data from a Qualitative Study Conducted by Anthropologists. In JEADV Clinical Practice; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amerio, P.; Ferrucci, S.M.; Galluzzo, M.; Napolitano, M.; Narcisi, A.; Levi, A.; Di Fino, S.; Palladino, C.; Patruno, C.; Rossi, M. A Multidisciplinary Approach Is Beneficial in Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatol. Ther. 2024, 14, 1443–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, O.G.E.; Macneill, S.; Ridd, M.J. Parent Satisfaction with Lotion, Cream, Gel and Ointment Emollient Types: Secondary Analysis of the Best Emollients for Eczema Study. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 49, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollenberg, A.; Kinberger, M.; Arents, B.; Aszodi, N.; Avila Valle, G.; Barbarot, S.; Bieber, T.; Brough, H.A.; Calzavara Pinton, P.; Christen-Zäch, S.; et al. European Guideline (EuroGuiDerm) on Atopic Eczema—Part II: Non-Systemic Treatments and Treatment Recommendations for Special AE Patient Populations. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1904–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Feldman, S. Adherence in Atopic Dermatitis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2024, 1447, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, A.; Smith, S.D. Factors Contributing to Poor Treatment Outcomes in Childhood Atopic Dermatitis. Aust. J. Dermatol. 2015, 56, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Cosmi, L.; Annunziato, F. Molecular Sciences Review From Emollients to Biologicals: Targeting Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachapelle, J.M.; Gimenez-Arnau, A.; Metz, M.; Peters, J.; Proksch, E. Best Practices, New Perspectives and the Perfect Emollient: Optimizing the Management of Contact Dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2018, 29, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quadri, M.; Lotti, R.; Bonzano, L.; Ciardo, S.; Guanti, M.B.; Pellacani, G.; Pincelli, C.; Marconi, A. A Novel Multi-Action Emollient plus Cream Improves Skin Barrier Function in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: In Vitro and Clinical Evidence. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2021, 34, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsatsi, A.; Vakirlis, E.; Kanelleas, A.; Stefanaki, I.; Kemanetzi, C.; Loizidis, C.; Pasmatzi, E. Effect of a Novel “Emollient plus” Formulation on Mild-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis and Other Dry Skin-Related Diseases as Monotherapy or Adjunctive Therapy: An Observational Study on Efficacy, Tolerance and Quality of Life in Adult Patients. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2023, 33, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrestak, D.; Matijašić, M.; Paljetak, H.Č.; Drvar, D.L.; Hadžavdić, S.L.; Perić, M. Skin Microbiota in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.H.; Oh, J.; Deming, C.; Conlan, S.; Grice, E.A.; Beatson, M.A.; Nomicos, E.; Polley, E.C.; Komarow, H.D.; Mullikin, J.; et al. Temporal Shifts in the Skin Microbiome Associated with Disease Flares and Treatment in Children with Atopic Dermatitis. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condrò, G.; Guerini, M.; Castello, M.; Perugini, P. Acne Vulgaris, Atopic Dermatitis and Rosacea: The Role of the Skin Microbiota—A Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; Thompson, A.; Jaros, J.; Blackcloud, P.; Hsiao, J.; Shi, V.Y. Updated Understanding of Staphylococcus aureus in Atopic Dermatitis: From Virulence Factors to Commensals and Clonal Complexes. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 1532–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, E.J.; Luo, C.H.; Thio, C.L.P.; Chang, Y.J. Immunomodulatory Role of Staphylococcus Aureus in Atopic Dermatitis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EN ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices. Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- EN ISO 10993-12:2012; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 12: Sample Preparation and Reference Materials. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- OECD. Test No. 439 In Vitro Skin Irritation: Reconstructed Human Epidermis Test Method. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals; OECD: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- EN ISO 10993-23:2021; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 23: Tests for Irritation. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Pinto, J.R.; Monteiro, E.; Silva, S.A.; Holsback, V.S.S.; Leonardi, G.R. Skin occlusive performance: Sustainable alternatives for petrolatum in skincare formulations. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 4775–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, A.A.; Rippke, F.; Weber, T.M.; Nicol, N.H. Efficacy of Nonprescription Moisturizers for Atopic Dermatitis: An Updated Review of Clinical Evidence. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poljšak, N.; Kočevar Glavač, N. Vegetable Butters and Oils as Therapeutically and Cosmetically Active Ingredients for Dermal Use: A Review of Clinical Studies. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 868461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Allemekinders, H.; Dansby, A.; Campbell, L.; Durance-Tod, S.; Berger, A.; Jones, P.J. Evidence of Health Benefits of Canola Oil. Nutr. Rev. 2013, 71, 370–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oomah, B.D.; Busson, M.; Godfrey, D.V.; Drover, J.C.G. Characteristics of Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Seed Oil. Food Chem. 2002, 76, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şeker, M.; Esen, Ö. The Effect of Hemp Seed Oil on Skin and Soap Performance. Int. J. Life Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 4, 420–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaway, J.C. Hempseed as a Nutritional Resource: An Overview. Euphytica 2004, 140, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Madison, K.C. Barrier Function of the Skin: “La Raison d’Être” of the Epidermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 121, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertz, P.W. Lipids and Barrier Function of the Skin. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2000, 80 Suppl. S208, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Balić, A.; Vlašić, D.; Žužul, K.; Marinović, B.; Mokos, Z.B. Omega-3 versus Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in the Prevention and Treatment of Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simard, M.; Tremblay, A.; Morin, S.; Martin, C.; Julien, P.; Fradette, J.; Flamand, N.; Pouliot, R. α-Linolenic Acid and Linoleic Acid Modulate the Lipidome and the Skin Barrier of a Tissue-Engineered Skin Model. Acta Biomater. 2022, 140, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaess, M.; Deigner, H.P. Derailed Ceramide Metabolism in Atopic Dermatitis (AD): A Causal Starting Point for a Personalized (Basic) Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Heinemann, N.; Rademacher, F.; Darvin, M.E.; Raab, C.; Keck, C.M.; Vollert, H.; Fluhr, J.W.; Gläser, R.; Harder, J.; et al. Skin Care Product Rich in Antioxidants and Anti-Inflammatory Natural Compounds Reduces Itching and Inflammation in the Skin of Atopic Dermatitis Patients. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertino, L.; Guarneri, F.; Cannavò, S.P.; Casciaro, M.; Pioggia, G.; Gangemi, S. Oxidative Stress and Atopic Dermatitis. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugroho, W.T.; Dong, Y.; Pramanik, A.; Zhang, Z.; Ramakrishna, S. Co-Influence of Nanofiller Content and 3D Printing Parameters on Mechanical Properties of Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)/Halloysite Nanotube (HNT) Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsakok, T.; Woolf, R.; Smith, C.H.; Weidinger, S.; Flohr, C. Atopic Dermatitis: The Skin Barrier and Beyond. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 180, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goleva, E.; Berdyshev, E.; Leung, D.Y.M. Epithelial Barrier Repair and Prevention of Allergy. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somjorn, P.; Kamanamool, N.; Kanokrungsee, S.; Rojhirunsakool, S.; Udompataikul, M. A Cream Containing Linoleic Acid, 5% Dexpanthenol and Ceramide in the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkers, T.; Visscher, D.; Gooris, G.S.; Bouwstra, J.A. Topically Applied Ceramides Interact with the Stratum Corneum Lipid Matrix in Compromised Ex Vivo Skin. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahle, F.F.; Metz, H.; Wohlrab, J.; Neubert, R.H.H. Polyglycerol Fatty Acid Ester Surfactant-Based Microemulsions for Targeted Delivery of Ceramide AP into the Stratum Corneum: Formulation, Characterisation, in Vitro Release and Penetration Investigation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 82, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, T.; Hamanaka, M.; Yamashita, H.; Mizukami, H. Effect of Bakumijiogan, an Herbal Formula in Traditional Chinese Medicine, on Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions Induced by Mite Antigen in NC/Jic Mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 2108–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mainzer, C.; Le Guillou, M.; Vyumvuhore, R.; Chadoutaud, B.; Bordes, S.; Closs, B. Clinical Efficacy of Oligofructans from Ophiopogon japonicus in Reducing Atopic Dermatitis Flare-Ups in Caucasian Patients. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2019, 99, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelenkova, H.; Kerob, D.; Salah, S.; Demessant-Flavigny, A.L. Impact of Daily Use of Emollient ‘plus’ on Corticosteroid Consumption in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: An Open, Randomized Controlled Study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 37, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staiano, S. Fensebiome peptide—Riconnettiti con le tue origini per avere una pelle più sana. Cosmet. Technol. Riv. Sci. Cosmetol. 2019, 22, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Pasikowska-Piwko, M.; Zapotoczna, M.; Dębowska, R.; Zyglińska, I.; Cieścińska, C.; Załuska, A.; Kołaczek, A.; Rajkowska, K.; Otlewska, A.; Rogiewicz, K.; et al. Safety and tolerability of two emollients containing complex targeting Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation. In Proceedings of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology Congress, Milan, Italy, 7–10 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kunkiel, K.; Natkańska, A.; Nędzi, M.; Zawadzka-Krajewska, A.; Feleszko, W. Patients’ Preferences of Leave-on Emollients: A Survey on Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2022, 33, 1143–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Kwa, M.; Lohman, M.E.; Evers-Meltzer, R.; Silverberg, J.I. Consumer Preferences, Product Characteristics, and Potentially Allergenic Ingredients in Best-Selling Moisturizers. JAMA Dermatol. 2017, 153, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).