Insights from Biophotonic Imaging and Biochemical Analysis on Cellular and Molecular Alterations Exhibited in Dull Skin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Skin Study #1
2.1.1. Overall Design of Skin Study #1
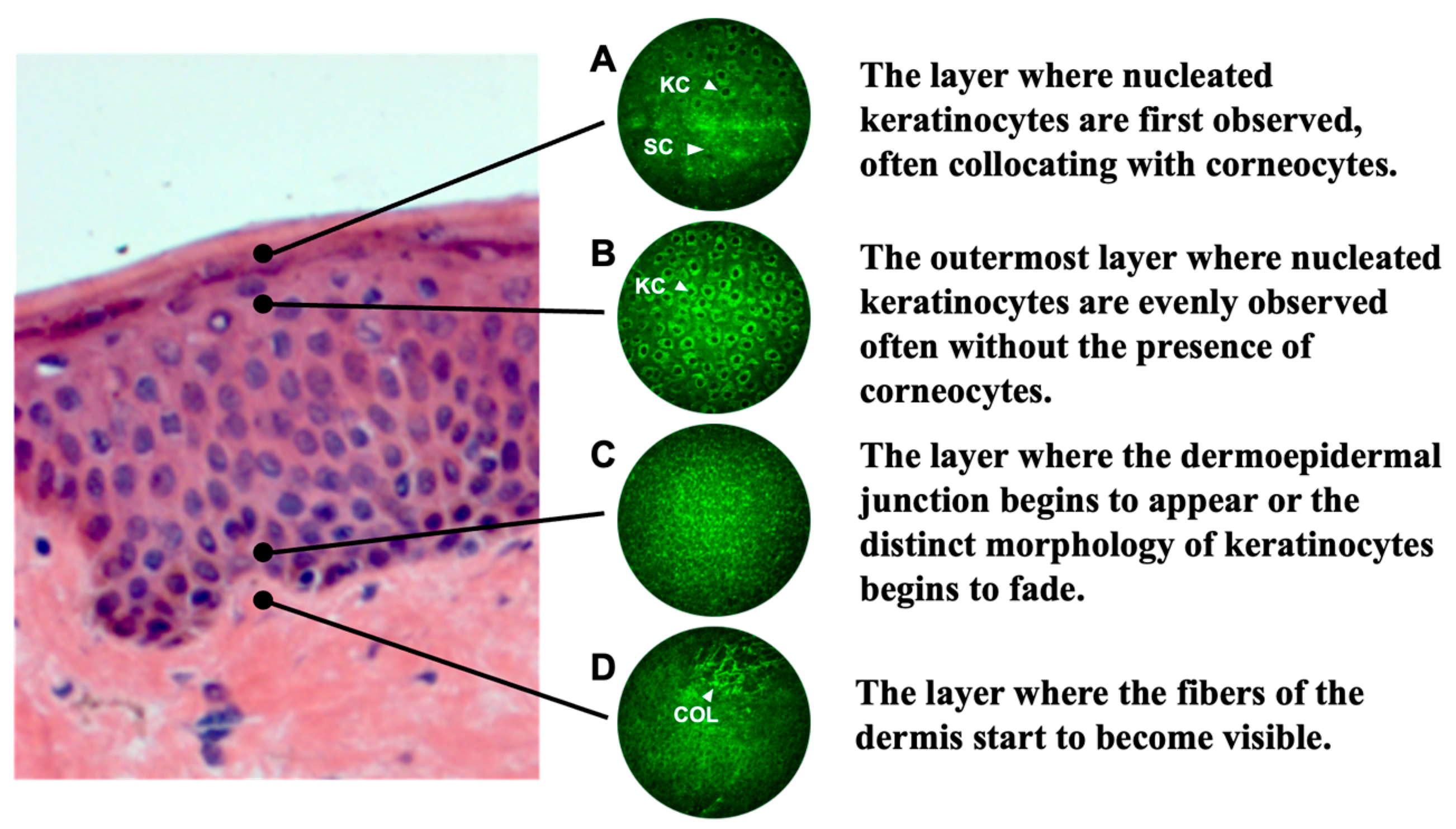
2.1.2. Multi-Photon Tomography (MPT) and Image Analysis of Cell Nuclei
2.2. Skin Study #2
2.2.1. Overall Design of Skin Study #2
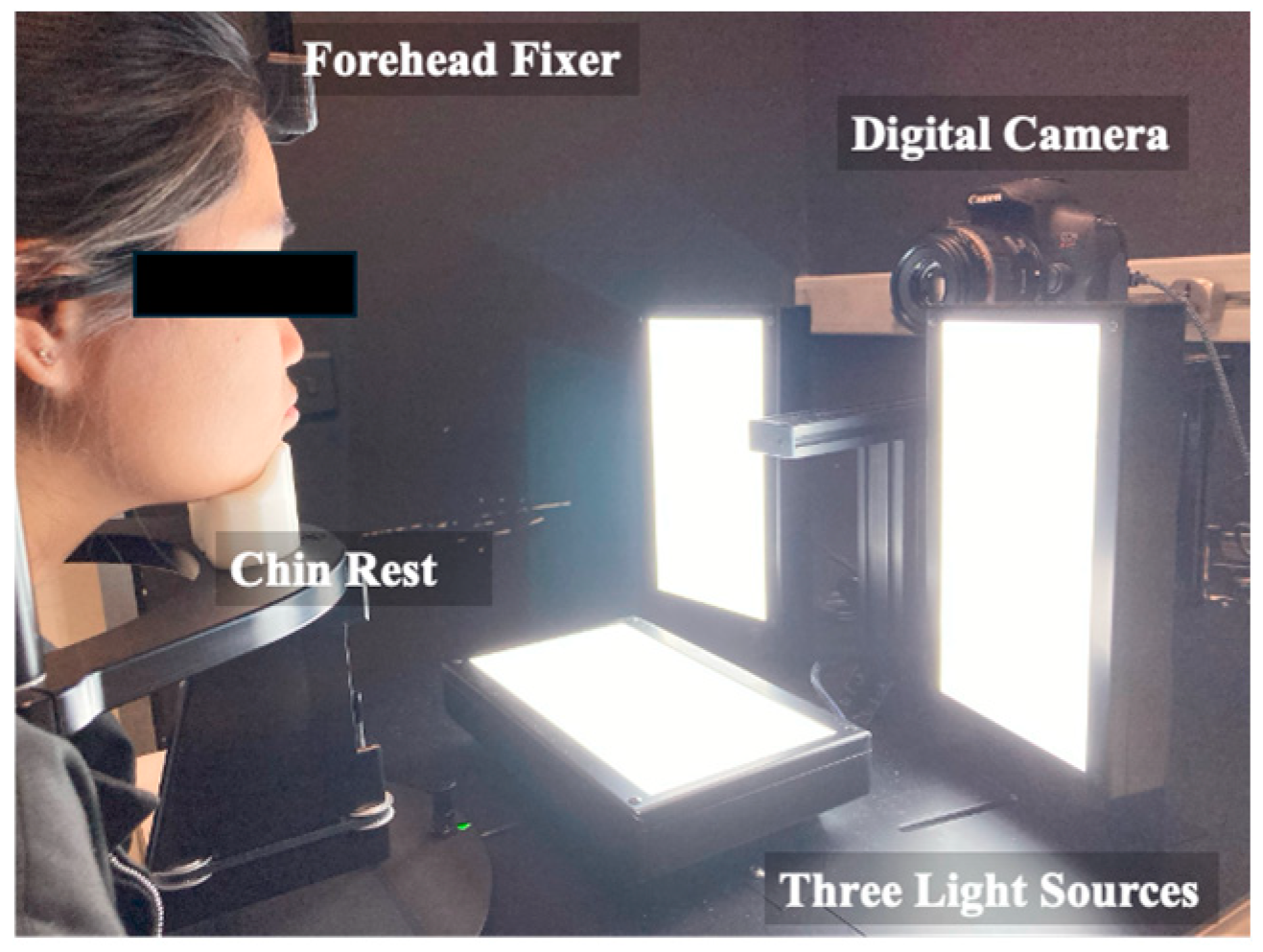
2.2.2. DTIS and Visual Grading for Skin Dullness and Radiance
2.2.3. Biochemical Composition Analysis from Tape-Strip Samples
IL-36γ Assay
Filaggrin Metabolite Assay
E-Cadherin (CDH1) Assay
2.3. Skincare Material Testing in 2D/3D Skin Models
2.3.1. Keratinocyte Culture
2.3.2. Protein Extraction
2.3.3. Skin Equivalent Culture
2.3.4. Histology and FLG Staining
2.3.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Differences at the Cellular Level Between Radiant and Dull Skin via MPT Measurement
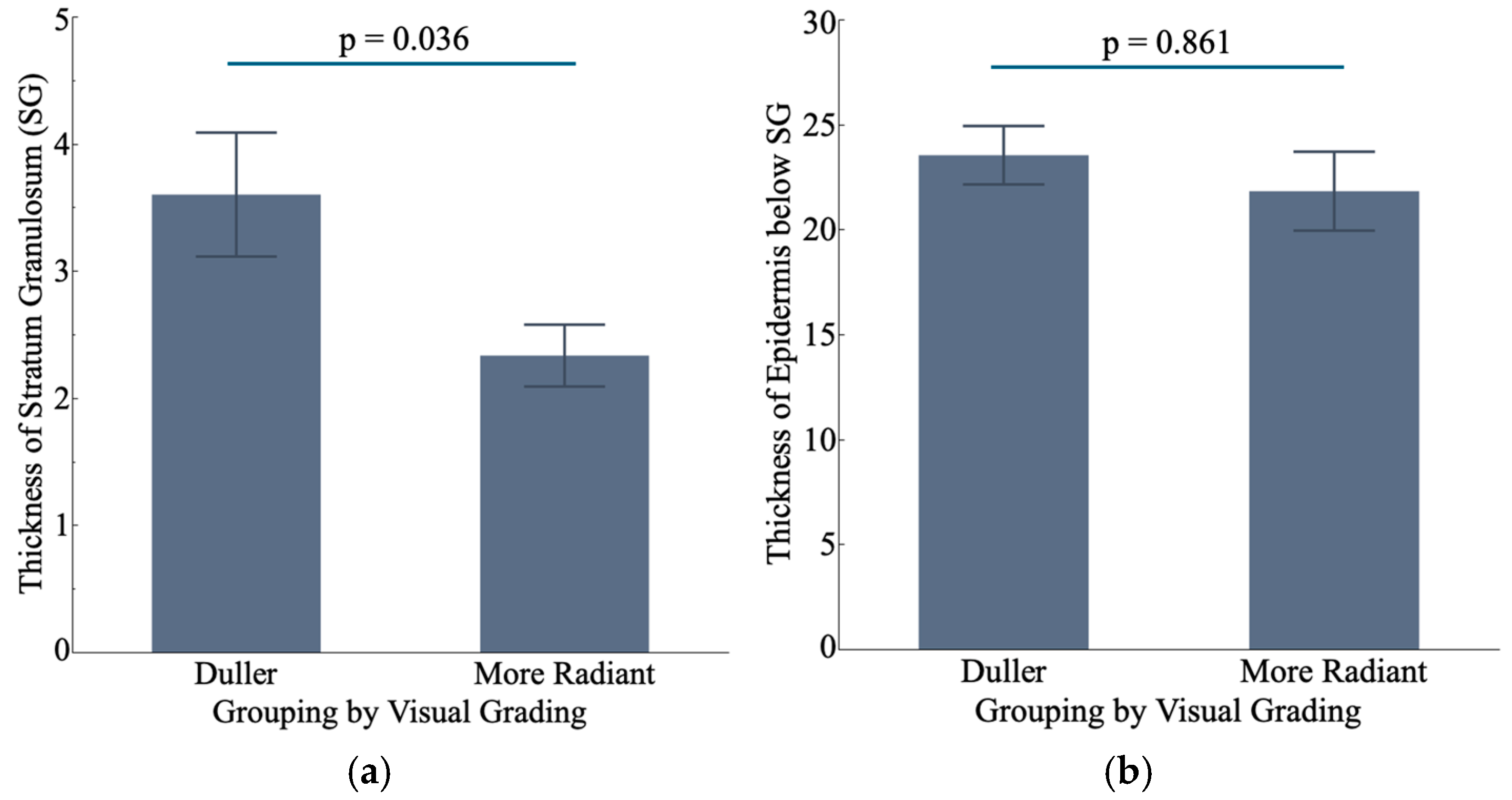
3.2. Duller Skin Exhibits Altered Cornification Process
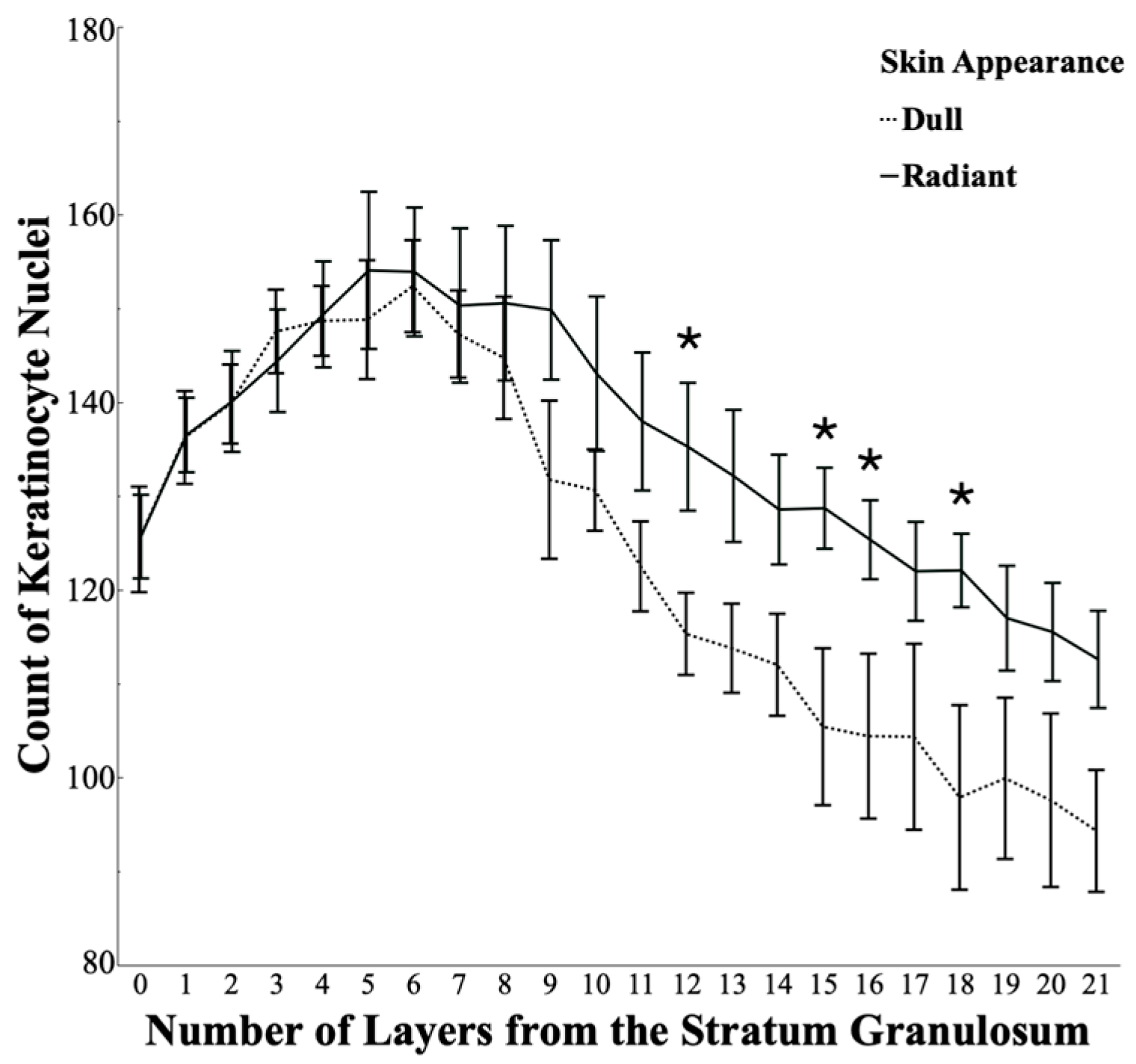
3.3. Keratinocytes Are Less Densely Packed in Dull Skin than in Radiant Skin
3.4. Molecular Differences Between Radiant and Dull Skin via Biochemical Analysis
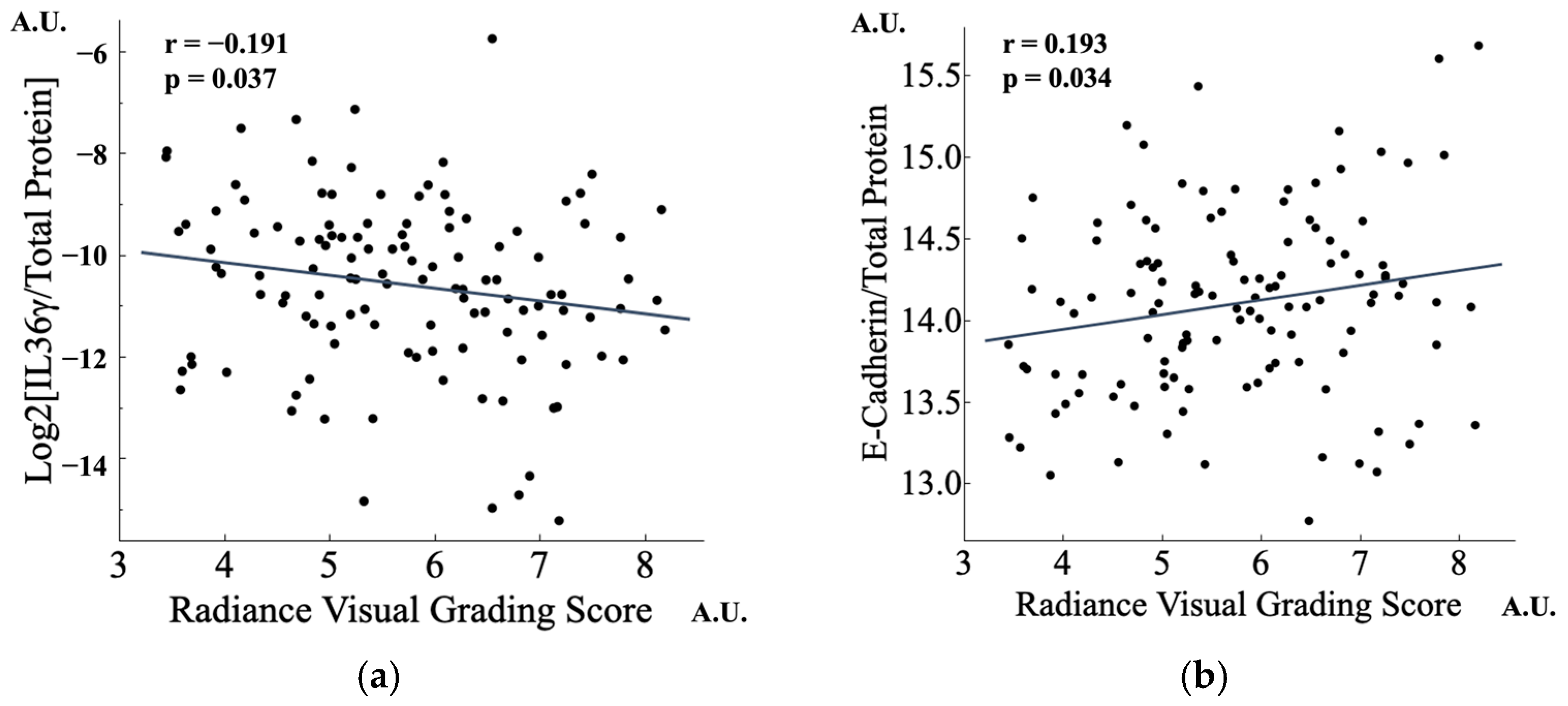
3.4.1. Lower IL-36γ and Higher CDH1 Were Found in Radiant Skin
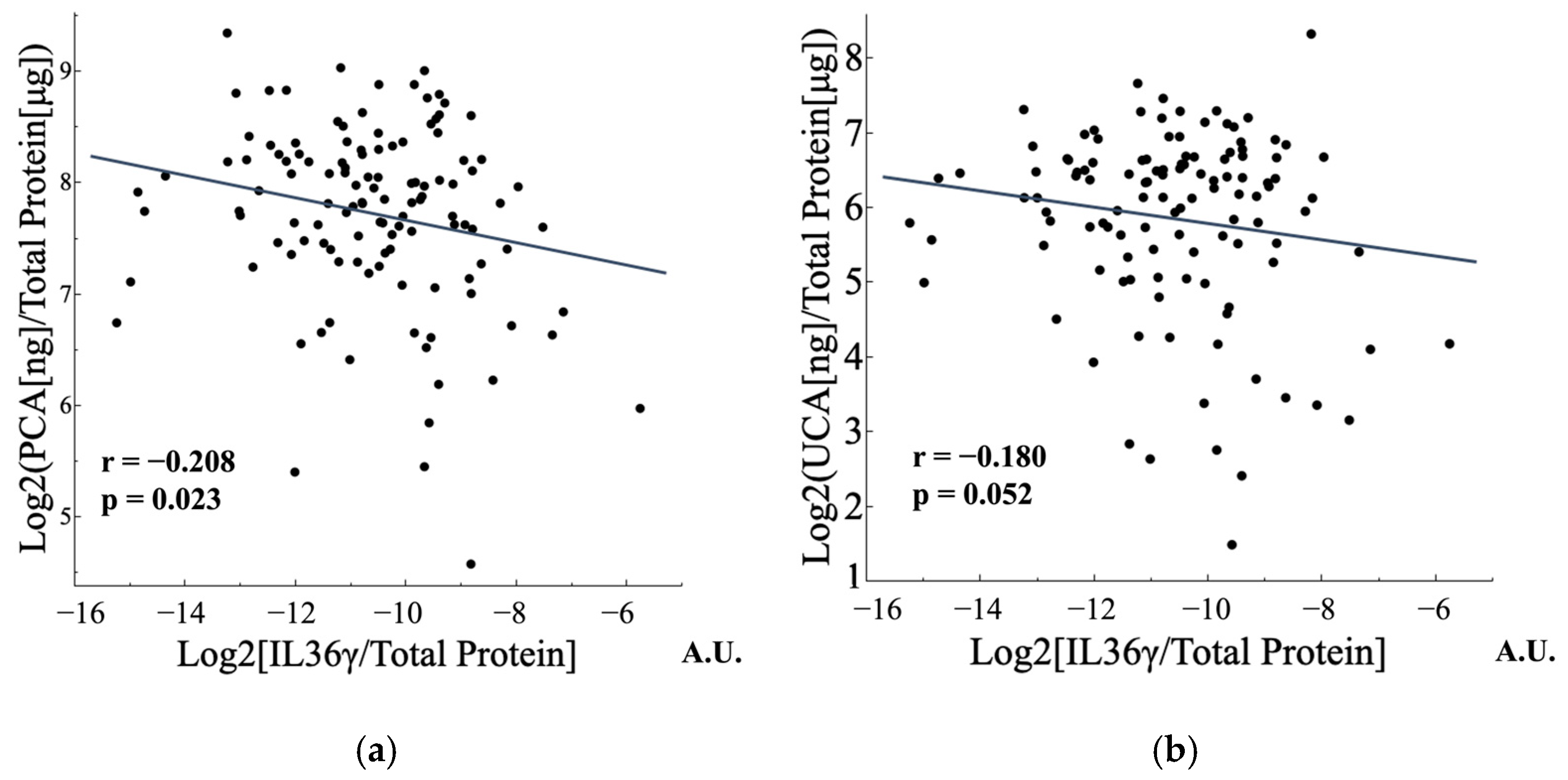
3.4.2. FLG Metabolites and IL-36γ Were Negatively Correlated
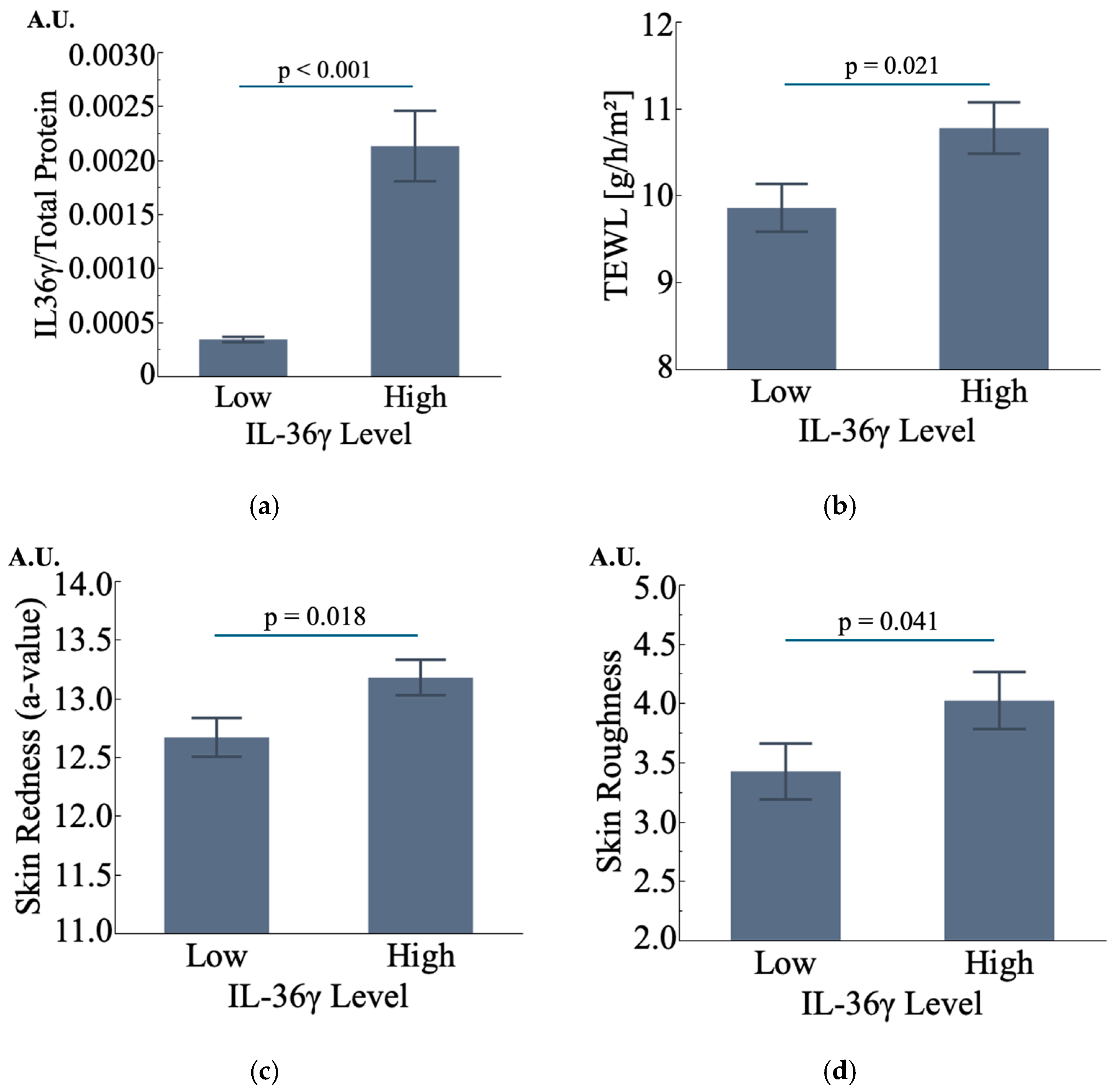
3.4.3. IL-36γ Is Also Potentially Associated with Changes in Skin Condition
3.5. Effect of Skincare Materials on Identified Biomarkers
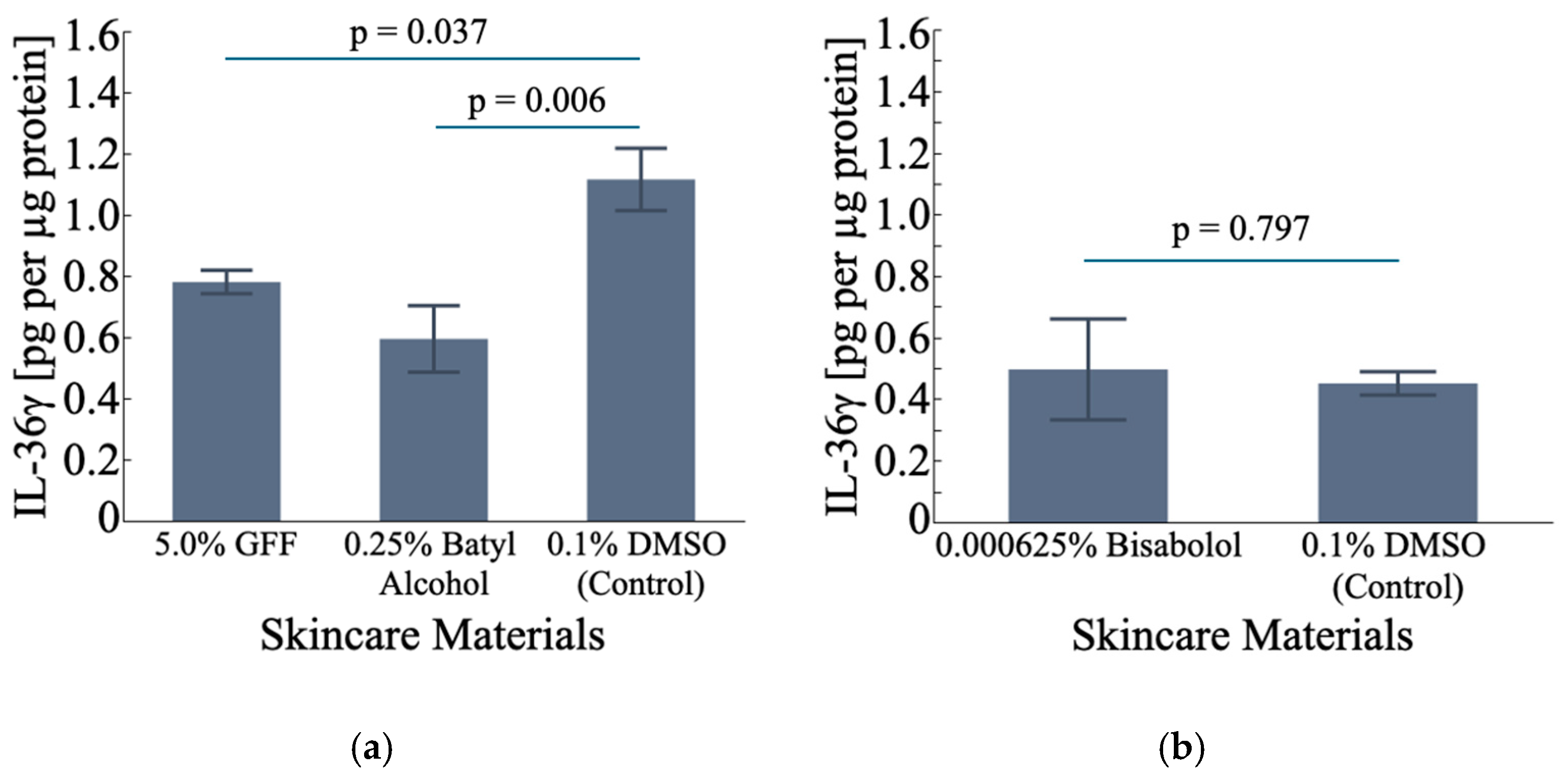
3.5.1. Effect on IL-36γ
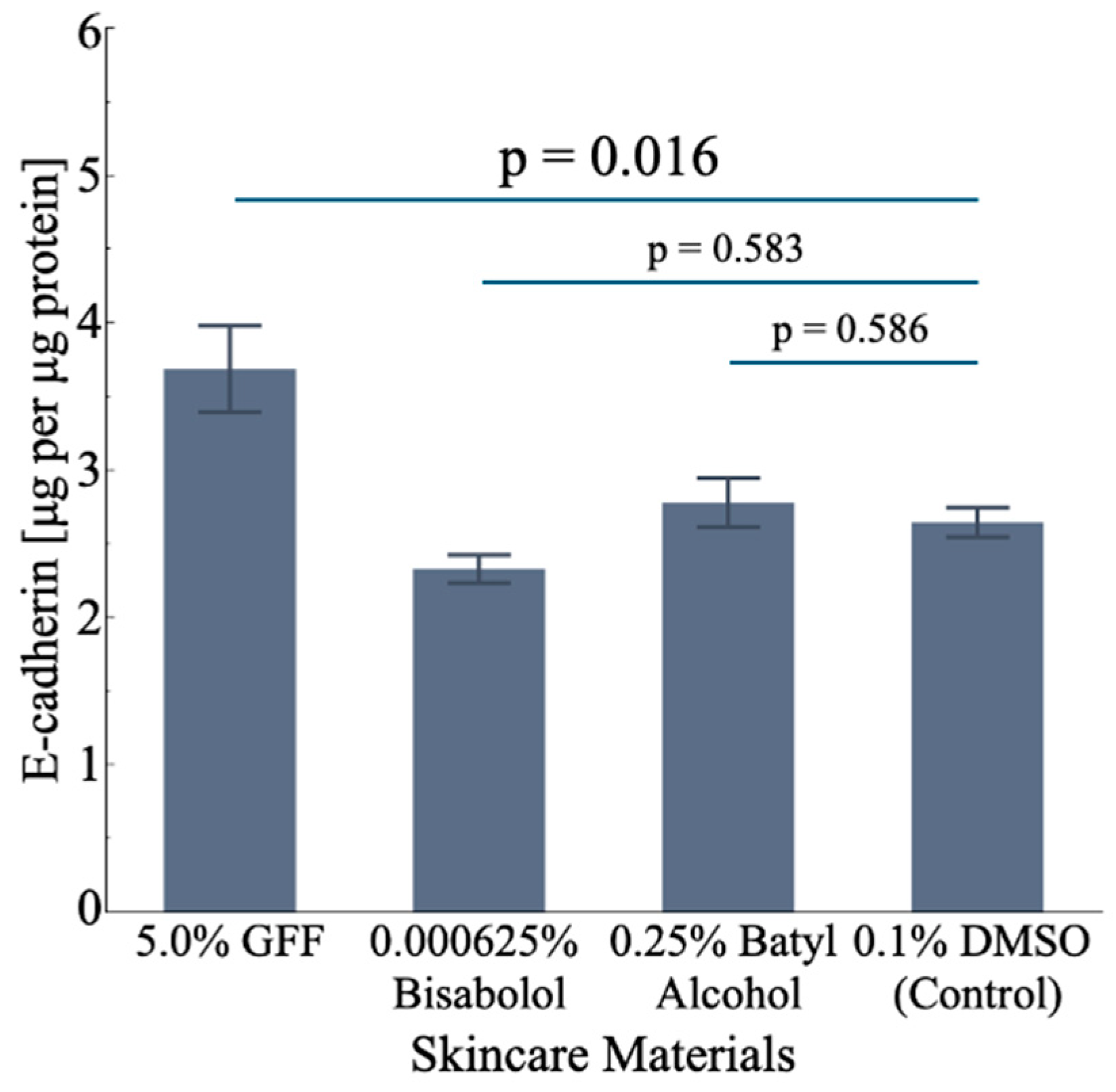
3.5.2. Effect on CDH1
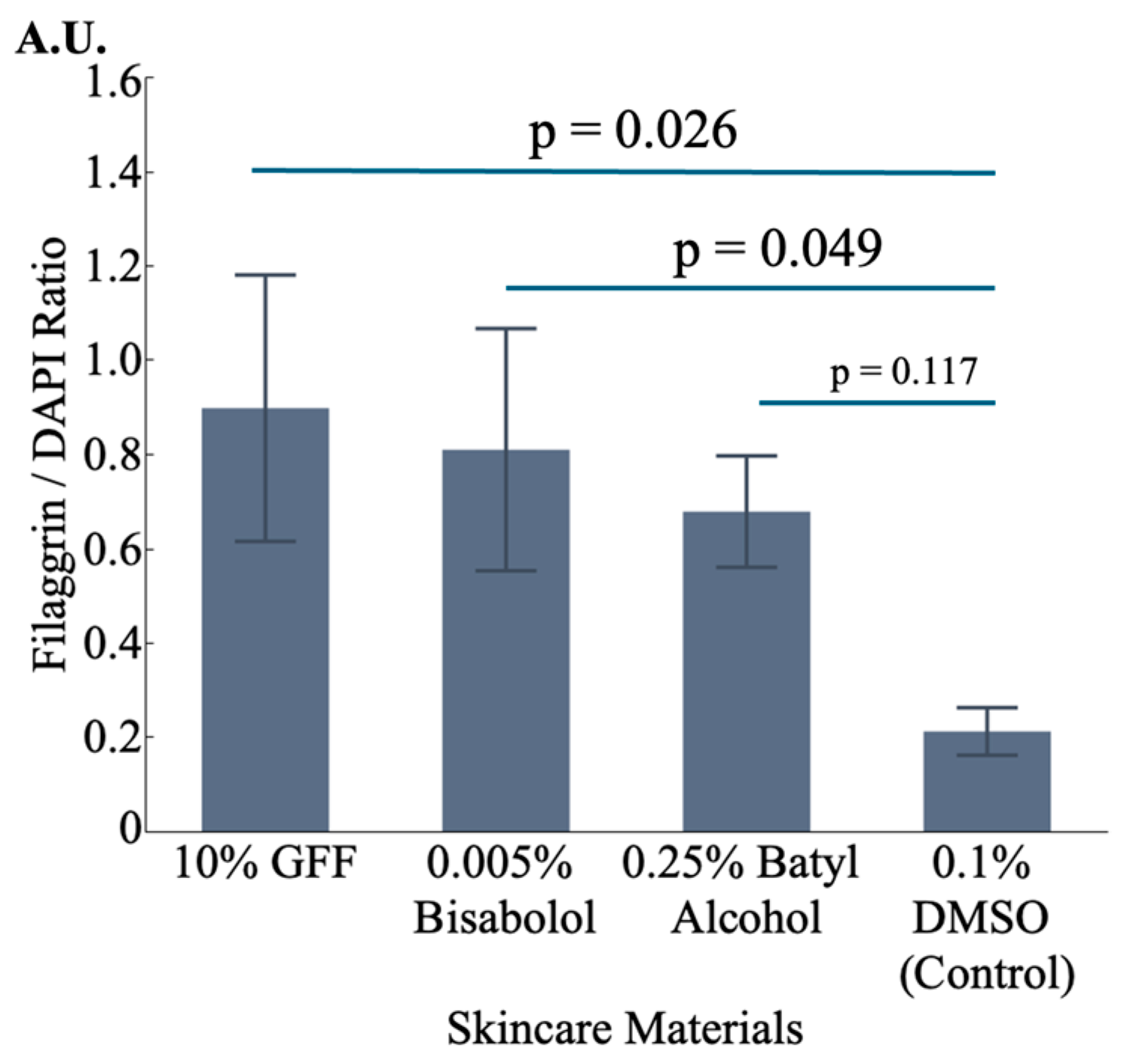
3.5.3. Effect on FLG
4. Discussion
Limitation of Our Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsubara, A.; Liang, Z.; Sato, Y.; Uchikawa, K. Analysis of Human Perception of Facial Skin Radiance by Means of Image 612 Histogram Parameters of Surface and Subsurface Reflections from the Skin. Skin Res. Technol. 2012, 18, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeudy, A.; Ecarnot, V.; Humbert, P. Measurement of Skin Radiance. In Agache’s Measuring the Skin; Humbert, P., Maibach, H., Fanian, F., Agache, P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martschin, C.; Bahhady, R.; Li, J.; Loureiro, W.; Mansour, W.; Metelitsa, A.; Minocha, K.; Somenek, M.; Taghetchian, K.; Tienthavorn, T. Development and Validation of a Novel Holistic Skin Quality Assessment Scale. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, B.; Matts, P.J.; Brauckmann, C.; Gundlach, S. The effect of skin surface topography and skin colouration cues on perception of male facial age, health and attractiveness. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2018, 40, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, H.; Saheki, Y.; Sakano, Y.; Wada, A.; Ando, H.; Tagai, K. Facial radiance influences facial attractiveness and affective impressions of faces. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2021, 43, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Souza, I.D.; Lampe, L.; Winn, D. New topical tranexamic acid derivative for the improvement of hyperpigmentation and inflammation in the sun-damaged skin. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarshish, E.; Hermoni, K. Beauty from within: Improvement of skin health and appearance with Lycomato a tomato-derived oral supplement. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 1786–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rigal, J.; Des Mazis, I.; Diridollou, S.; Querleux, B.; Yang, G.; Leroy, F.; Barbosa, V.H. The effect of age on skin color and color heterogeneity in four ethnic groups. Skin Res. Technol. 2010, 16, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, O.; Tsukada, H.; Ishikawa, Y.; Kawaguchi, Y. Measuring Apparent Darkening of the Skin (First Report): Factors Inherent in Light Reflected from the Skin. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. Jpn. 1997, 31, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, O.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Ishikawa, Y.; Inagaki, K. Measuring Apparent Darkening of the Skin (Second Report): Relationship between Age-associated Changes in Physical Properties of the Skin and Apparent Darkening. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. Jpn. 1997, 31, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitjean, A.; Sainthillier, J.M.; Mac-Mary, S.; Muret, P.; Closs, B.; Gharbi, T.; Humbert, P. Skin Radiance: How to Quantify? Validation of an Optical Method. Skin Res. Technol. 2007, 13, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurani, A.M.; Kikuchi, K.; Iino, M.; Shirasugi, Y.; Sonoki, A.; Fujimura, T.; Hasegawa, K.; Shibata, T. Development of a Method for Evaluating Skin Dullness: A Mathematical Model Explaining Dullness by the Color, Optical Properties, and Microtopography of the Skin. Skin Res. Technol. 2023, 29, e13407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lua, B.L.; Robic, J. Yellowness in skin complexion: Analysis of self-perception of women in China evaluated against clinical parameters of yellowness. Skin Res. Technol. 2024, 30, e13831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, K.; Yoshikawa, H.; Saruwatari, K.; Akazawa, Y.; Inoue, T.; Kuze, T.; Sayo, T.; Uchida, N.; Sugiyama, Y. The presence of N(ε)-(Carboxymethyl) lysine in the human epidermis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1814, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laughlin, T.; Tan, Y.; Jarrold, B.; Chen, J.; Li, L.; Fang, B.; Zhao, W.; Tamura, M.; Matsubara, A.; Deng, G.; et al. Autophagy activators stimulate the removal of advanced glycation end products in human keratinocytes. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34 (Suppl. 3), 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.A.; Kim, E.J.; Kang, B.Y.; Lee, H.K. The Effects of Sleep Deprivation on the Biophysical Properties of Facial Skin. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. Sci. Appl. 2017, 7, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.S.; Apolinar, M.A.; Ma, L. Perception, understanding, and association between psychological stress and skin aging: Quantitative surveys of Asian women aged 18–34 years, dermatologists, and psychologists in China and Japan. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 2297–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, M.R.; Olmstead, R.; Carrol, J.E. Sleep Disturbance, Sleep Duration, and Inflammation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies and Experimental Sleep Deprivation. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 80, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, M.R.; Wang, M.; Campomayor, C.O.; Collado-Hidalgo, A.; Cole, S. Sleep Deprivation and Activation of Morning Levels of Cellular and Genomic Markers of Inflammation. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 1756–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K.; Kudoh, H. Quantification and visualization of cellular NAD(P)H in young and aged female facial skin with in vivo two-photon tomography. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169 (Suppl. 2), 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, B.P.; Chada, N.; Sanganna Gari, R.R.; Sigdel, K.P.; King, G.M. The Hessian Blob Algorithm: Precise Particle Detection in Atomic Force Microscopy Imagery. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcomb, J.D. Helium plasma dermal resurfacing: VISIA CR assessment of facial spots, pores, and wrinkles-Preliminary findings. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 1668–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, K.; Takiwaki, H.; Hillebrand, G.G.; Arase, S. Development of a Digital Imaging System for Objective Measurement of Hyperpigmented Spots on the Face. Skin Res. Technol. 2002, 8, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dissanayake, B.; Miyamoto, K.; Purwar, A.; Chye, R.; Matsubara, A. New Image Analysis Tool for Facial Pore Characterization and Assessment. Skin Res. Technol. 2019, 25, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, K.; Dissanayake, B.; Omotezako, T.; Takemura, M.; Tsuji, G.; Furue, M. Daily Fluctuation of Facial Pore Area, Roughness and Redness among Young Japanese Women; Beneficial Effects of Galactomyces Ferment Filtrate Containing Antioxidative Skin Care Formula. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 5, 10–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omotezako, T.; Neo, E.; Zhu, H.; Ehrman, M. Disordered spatial pattern of redness signal on facial skin and visual perception of health, stress, and hidden aging. Skin Res. Technol. 2024, 30, e13628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omotezako, T.; Zhao, W.; Rodrigues, M.; Ehrman, M.; Deng, D.; Lau, H.; Hakozaki, T. Skin inflammatory signatures, as measured by disordered spatial redness patterns, predict current and future skin ageing attributes. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 33, e15163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paepe, K.; Houben, E.; Adam, R.; Wiesemann, F.; Rogiers, V. Validation of the VapoMeter, a closed unventilated chamber system to assess transepidermal water loss vs. the open chamber Tewameter. Skin Res. Technol. 2005, 11, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleja, P.; Emmert, H.; Gerstel, U.; Weidinger, S.; Tholey, A. Evaluation and improvement of protein extraction methods for analysis of skin proteome by noninvasive tape stripping. J. Proteomics. 2020, 15, 217–103678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakozaki, T.; Wang, J.; Laughlin, T.; Jarrold, B.; Zhao, W.; Furue, M. Role of interleukin-6 and endothelin-1 receptors in enhanced melanocyte dendricity of facial spots and suppression of their ligands by niacinamide and tranexamic acid. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 38 (Suppl. 2), 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadially, R.; Reed, J.T.; Elias, P.M. Stratum Corneum Structure and Function Correlates with Phenotype in Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1996, 107, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, R.; Orion, E.; Ruocco, E.; Ruocco, V. Abnormal Epidermal Barrier in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. Clin. Dermatol. 2012, 30, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shutova, M.S.; Borowczyk, J.; Russo, B.; Sellami, S.; Drukala, J.; Wolnicki, M.; Brembilla, N.C.; Kaya, G.; Ivanov, A.I.; Boehncke, W.-H. Inflammation Modulates Intercellular Adhesion and Mechanotransduction in Human Epidermis via ROCK2. iScience 2023, 26, 106195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachen, K.L.; Greving, C.N.A.; Towne, J.E. Role of IL-36 Cytokines in Psoriasis and Other Inflammatory Skin Conditions. Cytokine 2022, 156, 155897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Erme, A.M.; Wilsmann-Theis, D.; Wagenpfeil, J.; Hölzel, M.; Ferring-Schmitt, S.; Sternberg, S.; Wittmann, M.; Peters, B.; Bosio, A.; Bieber, T.; et al. IL-36γ (IL-1F9) Is a Biomarker for Psoriasis Skin Lesions. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 135, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macleod, T.; Ainscough, J.S.; Hesse, C.; Konzok, S.; Braun, A.; Buhl, A.; Wenzel, J.; Bowyer, P.; Terao, Y.; Herrick, S.; et al. The Proinflammatory Cytokine IL-36γ Is a Global Discriminator of Harmless Microbes and Invasive Pathogens within Epithelial Tissues. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhl, A.; Wenzel, J. Interleukin-36 in Infectious and Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queen, D.; Ediriweera, C.; Liu, L. Function and Regulation of IL-36 Signaling in Inflammatory Diseases and Cancer Development. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendon, A.; Schäkel, K. Psoriasis Pathogenesis and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Vilchez, T.; Segura-Fernández-Nogueras, M.V.; Pérez-Rodríguez, I.; Soler-Gongora, M.; Martinez-Lopez, A.; Fernández-González, A.; Molina-Leyva, A.; Arias-Santiago, S. Skin Barrier Function in Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis: Transepidermal Water Loss and Temperature as Useful Tools to Assess Disease Severity. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Xu, X.; Li, F.; Lu, L.; Li, W.; Su, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Xie, Z.; et al. Loss-of-Function Mutations in Filaggrin Gene Associate with Psoriasis Vulgaris in Chinese Population. Hum. Genet. 2012, 131, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.; Skov, L. Filaggrin in Psoriasis. In Filaggrin; Thyssen, J., Maibach, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, C.R.; Aho, S.; Bosko, C.A. Filaggrin-Revisited. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 35, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yu, X.; Wu, C.; Jin, H. IL-36γ Inhibits Differentiation and Induces Inflammation of Keratinocyte via Wnt Signaling Pathway in Psoriasis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 14, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, E.; Cook, P.W.; Parkos, C.A.; Park, Y.; Pittelkow, M.R.; Coffey, R.J. Amphiregulin Causes Functional Downregulation of Adherens Junctions in Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berekméri, A.; Latzko, A.; Alase, A.; Macleod, T.; Ainscough, J.S.; Laws, P.; Goodfield, M.; Wright, A.; Helliwell, P.; Edward, S.; et al. Detection of IL-36γ through Noninvasive Tape Stripping Reliably Discriminates Psoriasis from Atopic Eczema. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 988–991.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madonna, N.; Girolomoni, G.; Dinarello, C.A.; Albanesi, C. The Significance of IL-36 Hyperactivation and IL-36R Targeting in Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajinov, Z.A.; Matić, M.; Prćić, S.; Đuran, V. Optical Properties of the Human Skin. Serb. J. Dermatol. Venereol. 2010, 2, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takehana, S. Vascular Imaging Using Image-Enhanced Endoscopy with Optical-Digital Method and the Application to Portal Hypertension. Jpn. J. Portal Hypertens. 2008, 14, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourant, J.R.; Canpolat, M.; Brocker, C.; Esponda-Ramos, O.; Johnson, T.M.; Matanock, A.; Stetter, K.; Freyer, J.P. Light Scattering from Cells: The Contribution of the Nucleus and the Effects of Proliferative Status. J. Biomed. Opt. 2000, 5, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wu, T.T.; Qu, J.Y. Unified Mie and Fractal Scattering by Cells and Experimental Study on Application in Optical Characterization of Cellular and Subcellular Structures. J. Biomed. Opt. 2008, 13, 024015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.X.; DeLaCruz, J. Appearance Benefits of Skin Moisturization. Skin Res. Technol. 2011, 17, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Experiment No. (Sample Size, Treatment Duration) | Cultured Cell Tissue | Treatment | Concentration | Manufacturer | Endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (n = 3, 24 h) | 2D HEKn * | Vehicle (DMSO **) GFF *** Batyl alcohol | 0.1% 5.0% 0.25% | Sigma Aldrich P&G IGK Sigma Aldrich | IL-36γ |
| 2 (n = 4, 24 h) | 2D HEKn | Vehicle (DMSO) Bisabolol | 0.1% 0.000625% | Sigma Aldrich Symrise | IL-36γ |
| 3 (n = 4, 24 h) | 2D HEKn | Vehicle (DMSO) GFF Bisabolol Batyl alcohol | 0.1% 5.0% 0.000625% 0.25% | Sigma Aldrich P&G IGK Symrise Sigma Aldrich | CDH1 |
| 4 (n = 6, 5 days) | 3D skin equivalent | Vehicle (DMSO) GFF Bisabolol Batyl alcohol | 0.1% 10.0% 0.005% 0.25% | Sigma Aldrich P&G IGK Symrise Sigma Aldrich | FLG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsubara, A.; Omotezako, T.; Xu, Y.; Evdokiou, A.; Li, L.; Zhao, W.; Braga, C.P.; Swift, D.; Nagasawa, H.; Byrd, J.I.; et al. Insights from Biophotonic Imaging and Biochemical Analysis on Cellular and Molecular Alterations Exhibited in Dull Skin. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11060219
Matsubara A, Omotezako T, Xu Y, Evdokiou A, Li L, Zhao W, Braga CP, Swift D, Nagasawa H, Byrd JI, et al. Insights from Biophotonic Imaging and Biochemical Analysis on Cellular and Molecular Alterations Exhibited in Dull Skin. Cosmetics. 2024; 11(6):219. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11060219
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsubara, Akira, Tatsuya Omotezako, Ying Xu, Anna Evdokiou, Lijuan Li, Wenzhu Zhao, Camila Pereira Braga, Dionne Swift, Hitomi Nagasawa, Jennifer I. Byrd, and et al. 2024. "Insights from Biophotonic Imaging and Biochemical Analysis on Cellular and Molecular Alterations Exhibited in Dull Skin" Cosmetics 11, no. 6: 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11060219
APA StyleMatsubara, A., Omotezako, T., Xu, Y., Evdokiou, A., Li, L., Zhao, W., Braga, C. P., Swift, D., Nagasawa, H., Byrd, J. I., Jarrold, B., Deng, G., Wang, J., & Hakozaki, T. (2024). Insights from Biophotonic Imaging and Biochemical Analysis on Cellular and Molecular Alterations Exhibited in Dull Skin. Cosmetics, 11(6), 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11060219






