Hybrid Deep Learning Model Based Indoor Positioning Using Wi-Fi RSSI Heat Maps for Autonomous Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
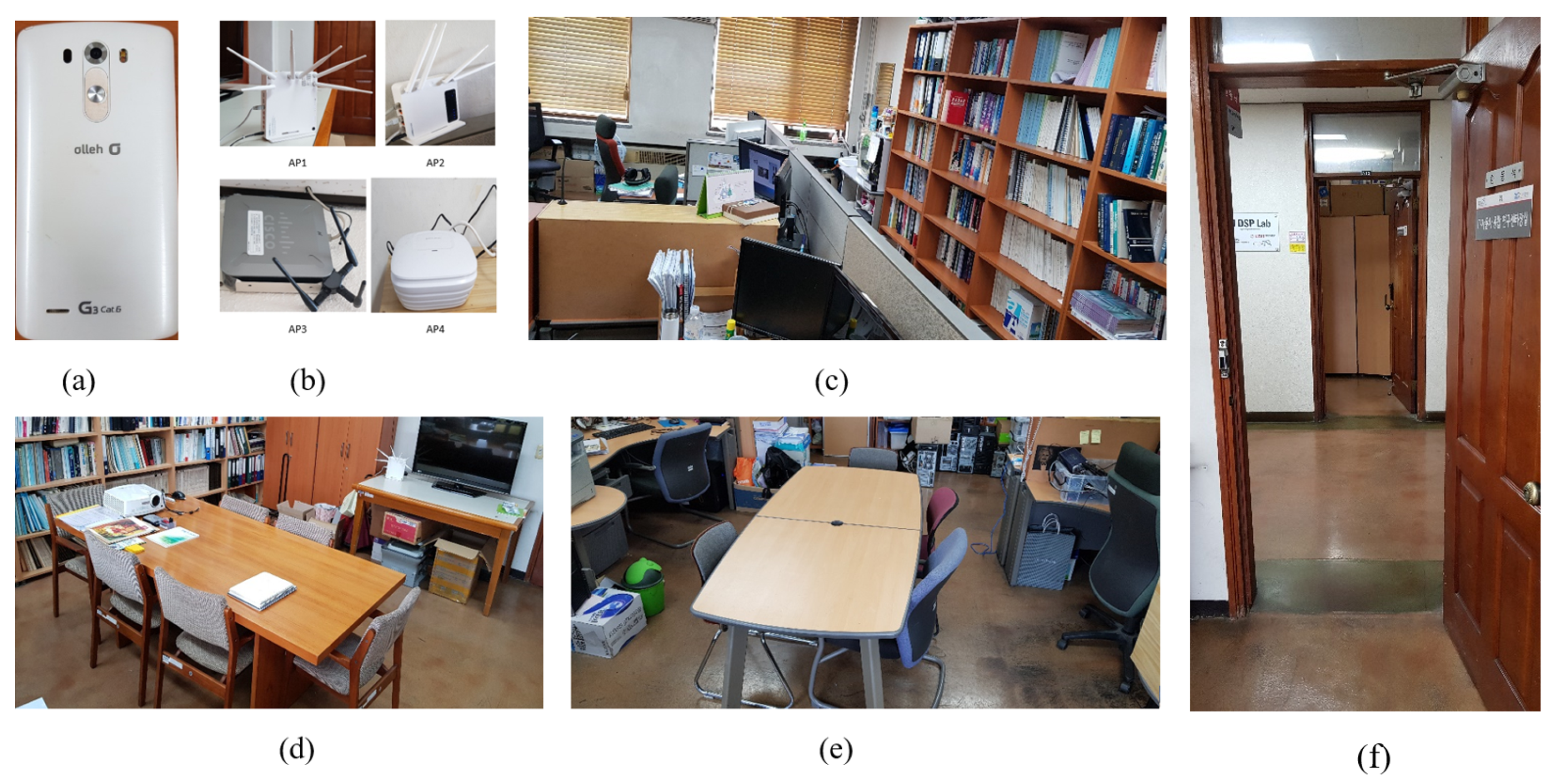
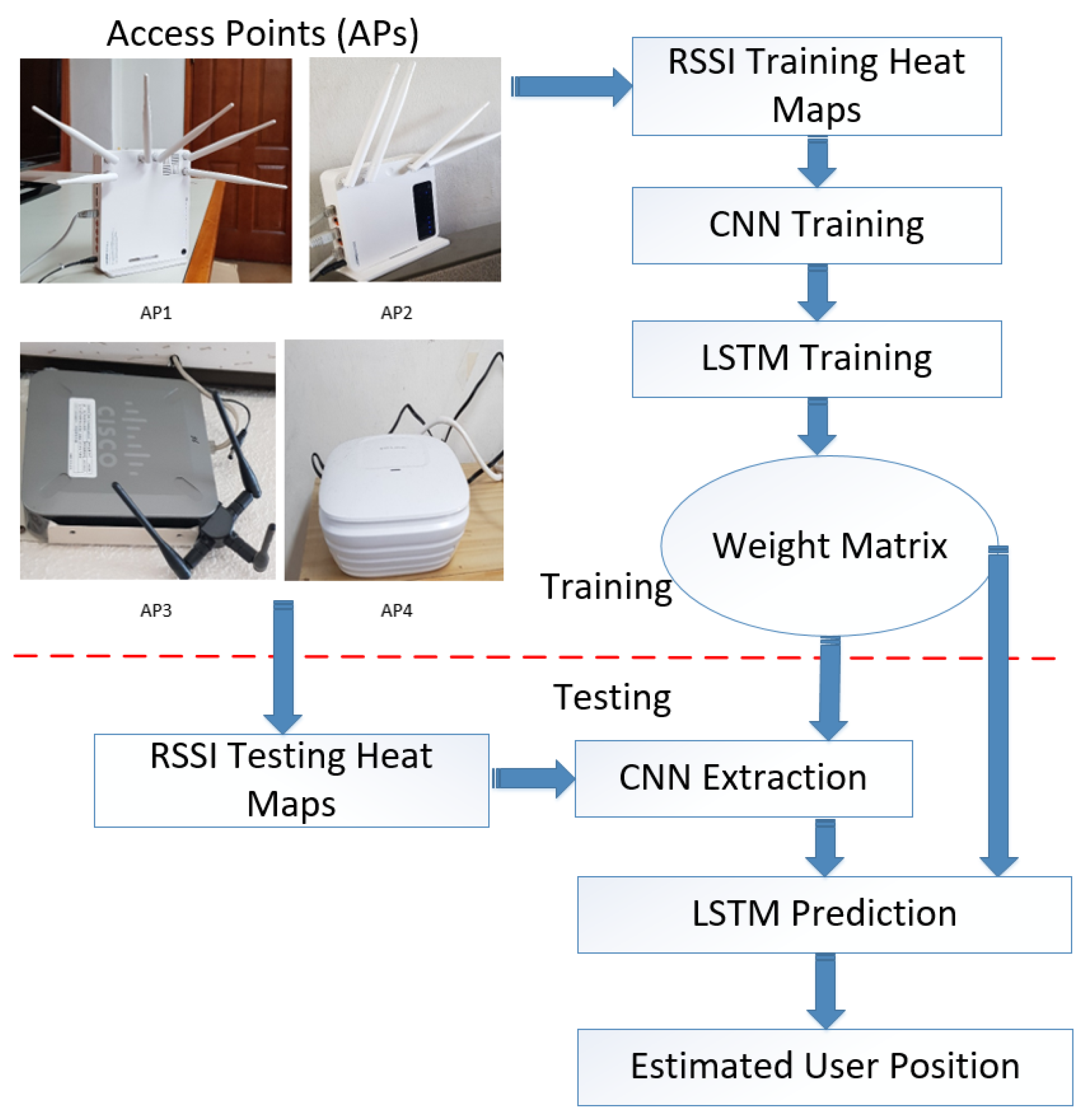
- We formulated a Wi-Fi RSSI signal based positioning system using four APs and collected the RSSI values using an Android based smartphone. The smartphone uses an application which shows the RSSI signal strengths of the particular location in the experiment area.
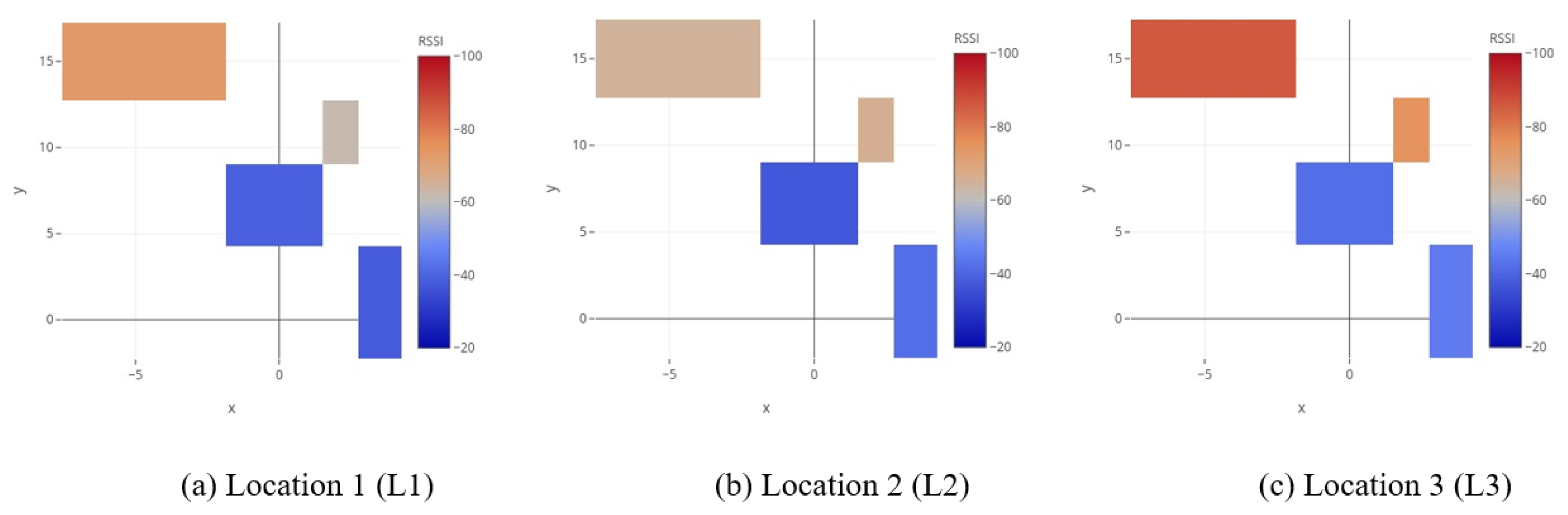
- We generated a database of Wi-Fi RSSI heat maps from the RSSI data. The heat maps indicate the RSSI signal strength from APs to the receiver for a particular location in the experiment area. The proposed HDLM uses the generated heat maps for localization.
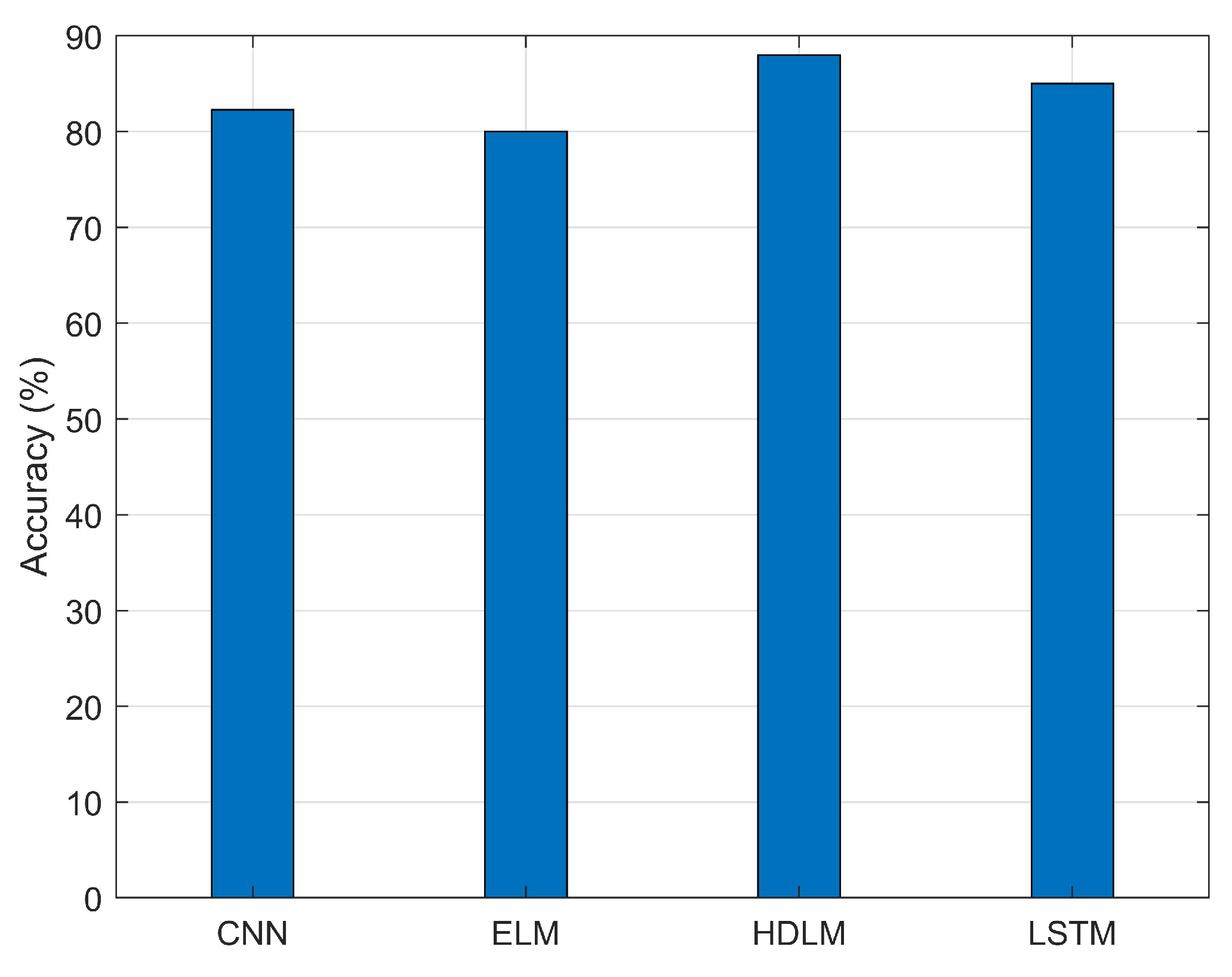
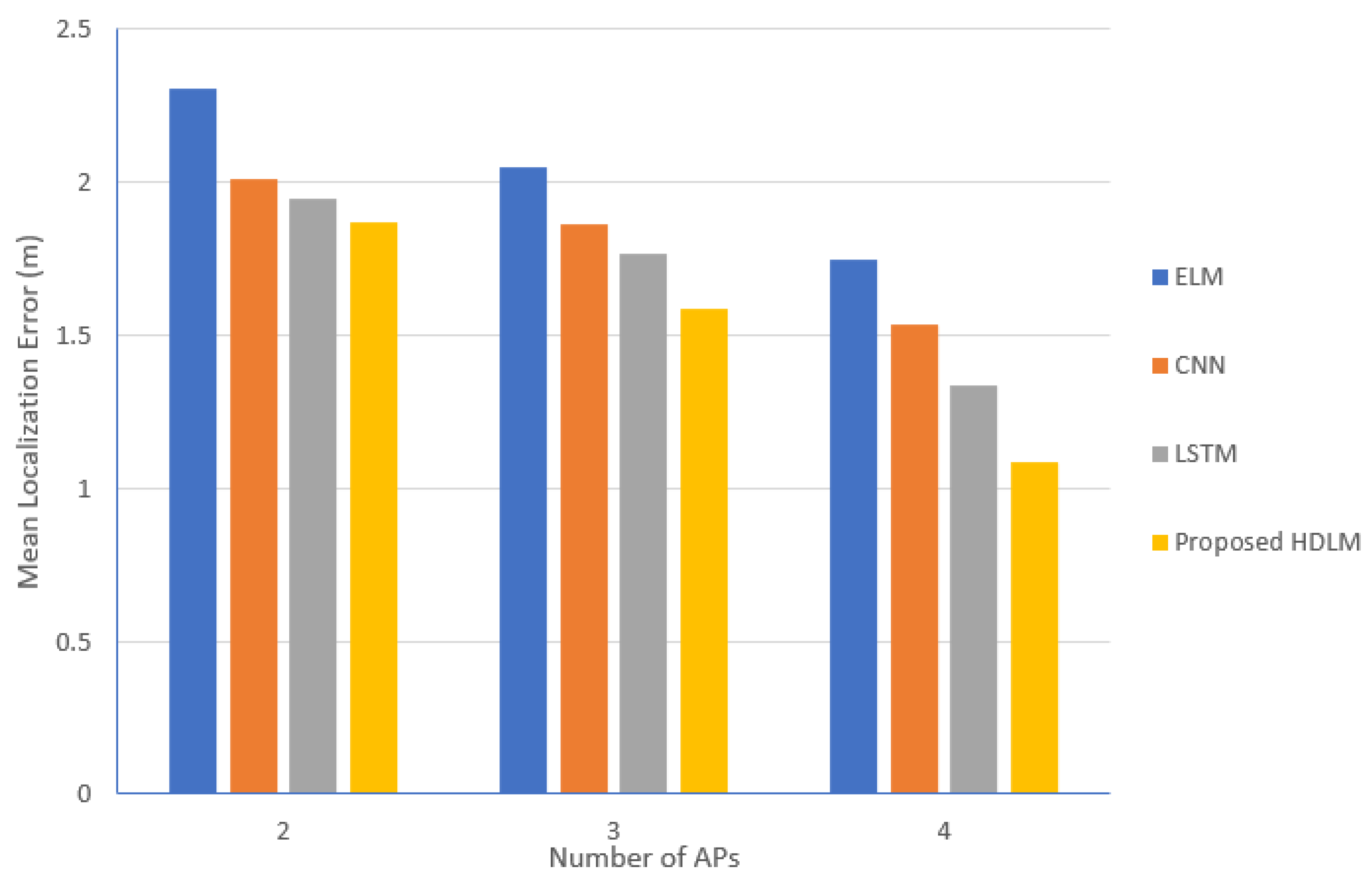
- We implemented HDLM using CNN-LSTM. The model takes RSSI heat maps as the input and predicts the user positions. The results from the proposed HDLM approach have better localization accuracy and less error for localization compared to conventional localization approaches.
2. Related Work
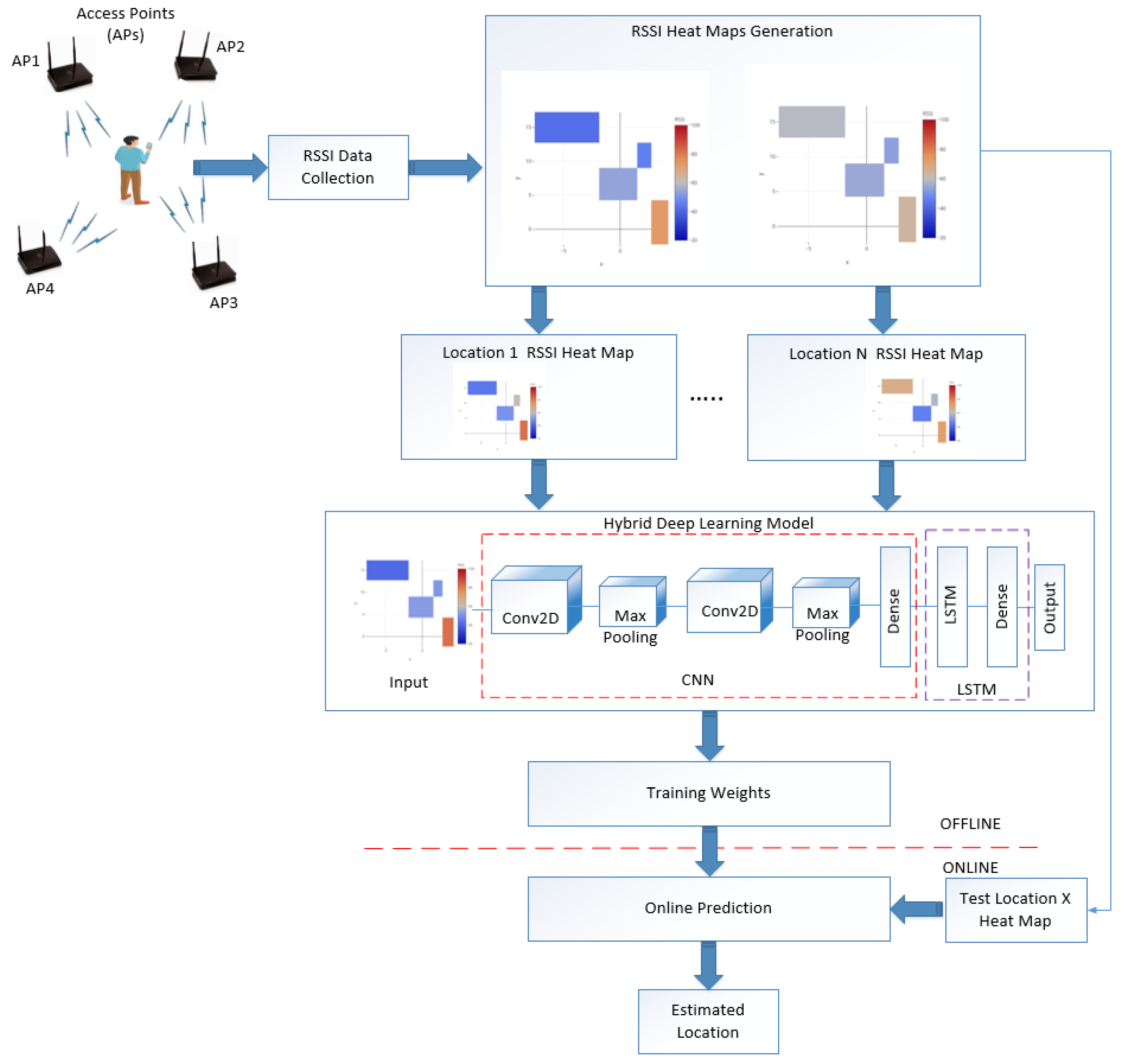
3. Proposed Hybrid Deep Learning Model Based Indoor Positioning System
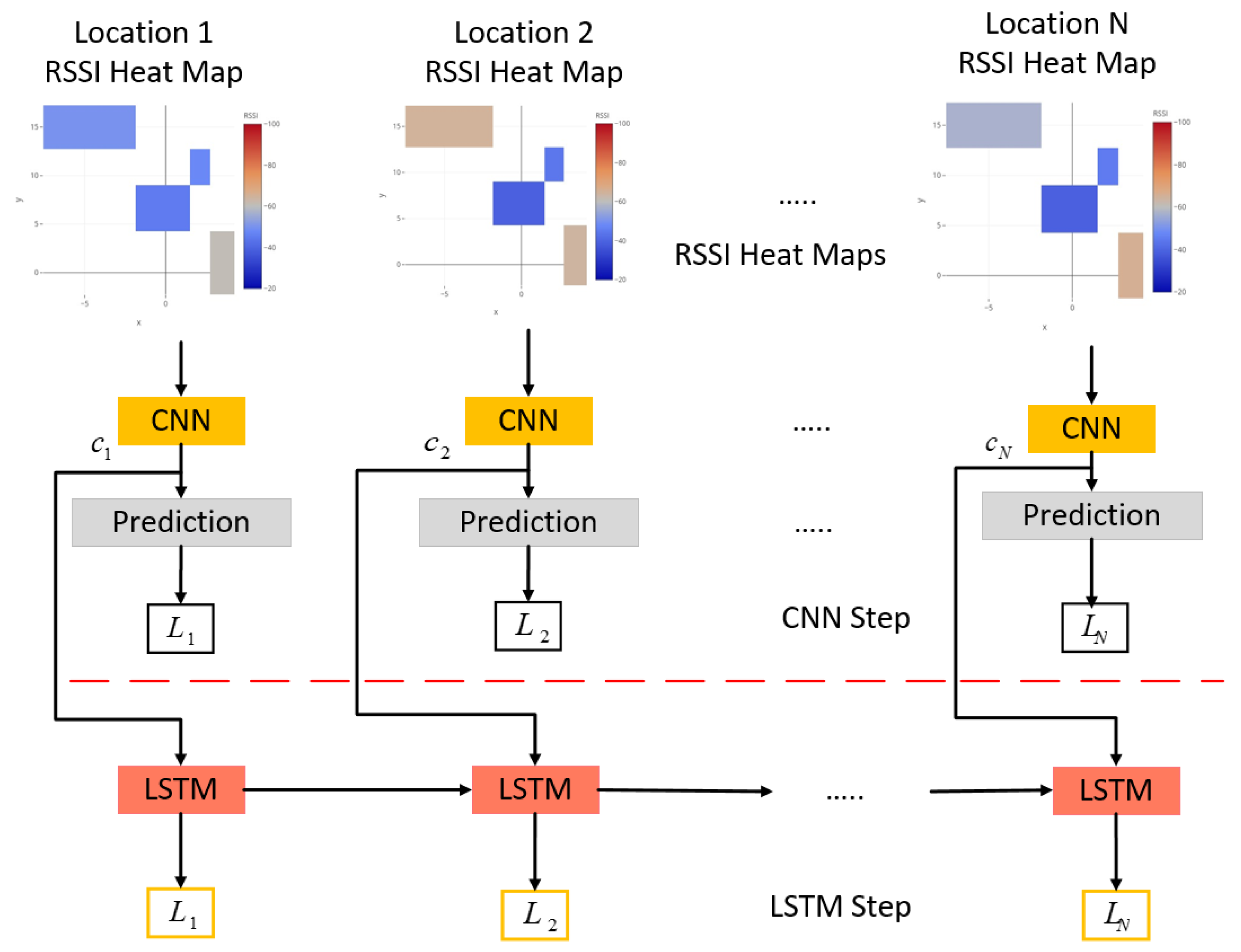
3.1. Proposed HDLM Model
3.2. Localization Process
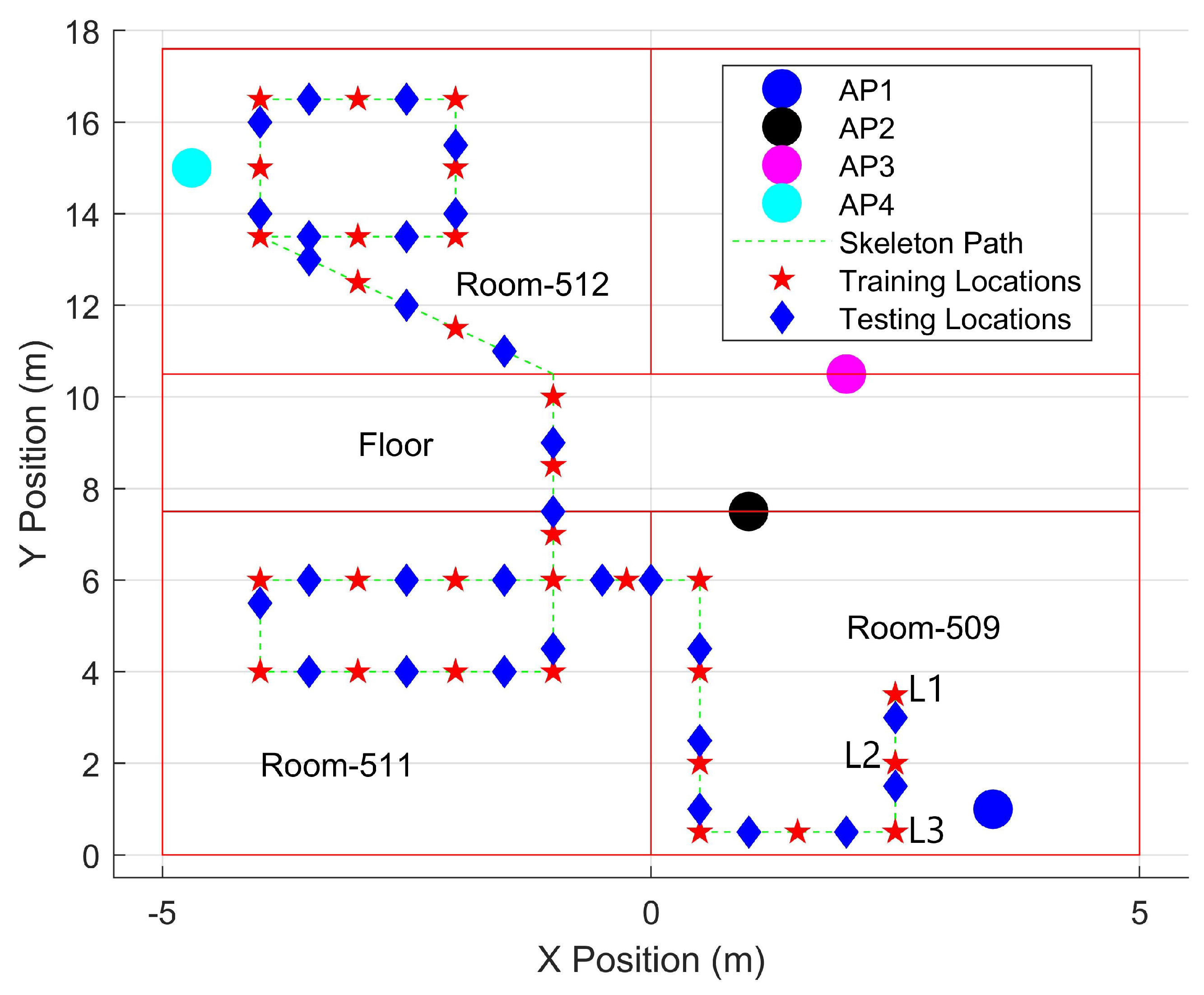
4. Experiment Setup and Result Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poulose, A.; Eyobu, O.S.; Han, D.S. An indoor position-estimation algorithm using smartphone IMU sensor data. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 11165–11177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulose, A.; Han, D.S. Hybrid Indoor Localization Using IMU Sensors and Smartphone Camera. Sensors 2019, 19, 5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shchekotov, M. In Indoor localization method based on Wi-Fi trilateration technique. In Proceedings of the 16th conference of Fruct Association, Oulu, Finland, 27–31 October 2014; pp. 177–179. [Google Scholar]
- Poulose, A.; Eyobu, O.S.; Han, D.S. A combined PDR and Wi-Fi trilateration algorithm for indoor localization. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC), Okinawa, Japan, 11–13 February 2019; pp. 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zegeye, W.K.; Amsalu, S.B.; Astatke, Y.; Moazzami, F. WiFi RSS fingerprinting indoor localization for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 7th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), New York, NY, USA, 20–22 October 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Poulose, A.; Han, D.S. Indoor Localization using PDR with Wi-Fi Weighted Path Loss Algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju Island, South Korea, 16–18 October 2019; pp. 689–693. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, S.; van den Hengel, A.; Wu, Q. Object-and-Action Aware Model for Visual Language Navigation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, Scotland, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.; Wu, Q.; Teney, D.; Bruce, J.; Johnson, M.; Sünderhauf, N.; Reid, I.; Gould, S.; van den Hengel, A. Vision-and-language navigation: Interpreting visually-grounded navigation instructions in real environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3674–3683. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Wu, Q.; Anderson, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.Y.; Shen, C.; Hengel, A.v.d. REVERIE: Remote Embodied Visual Referring Expression in Real Indoor Environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9982–9991. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Qin, L.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Q.; Yao, H. Robust visual tracking via scale-and-state-awareness. Neurocomputing 2019, 329, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, F.; Zhou, H.; Tao, D.; Li, X. Siamese local and global networks for robust face tracking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 9152–9164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Qi, Y.; Huang, Q. Release the Power of Online-Training for Robust Visual Tracking. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 12645–12652. [Google Scholar]
- Turgut, Z.; Ustebay, S.; Aydın, G.Z.G.; Sertbas, A. Deep learning in indoor localization using WiFi. In Proceedings of the International Telecommunications Conference (ITelCon 2017), Istanbul, Turkey, 28–29 December 2017; pp. 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Khatab, Z.E.; Hajihoseini, A.; Ghorashi, S.A. A fingerprint method for indoor localization using autoencoder based deep extreme learning machine. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2017, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Luof, H.; Zhao, F.; Wang, C.; Crivello, A.; Tunio, M.Z. DePos: Accurate orientation-free indoor positioning with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 Ubiquitous Positioning, Indoor Navigation and Location Based Services (UPINLBS), Wuhan, China, 22–23 March 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, A.; Tiku, S.; Pasricha, S. Adapting convolutional neural networks for indoor localization with smart mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 2018 on Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI, Chicago, IL, USA, 23–25 May 2018; pp. 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, S.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, G.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Z. Indoor fingerprint positioning based on Wi-Fi: An overview. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Xiu, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, D. WiFi indoor localization with CSI fingerprinting based random forest. Sensors 2018, 18, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Park, J.G. A Novel Indoor Ranging Algorithm Based on a Received Signal Strength Indicator and Channel State Information Using an Extended Kalman Filter. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Qi, H.; Hu, X. Indoor Positioning Tightly Coupled Wi-Fi FTM Ranging and PDR Based on the Extended Kalman Filter for Smartphones. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 49671–49684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayekh, S.; Affes, S.; Kandil, N.; Nerguizian, C. Cooperative localization in mines using fingerprinting and neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Wireless Communication and Networking Conference. Sydney, NSW, Australia, 18–21 April 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.S.; Lee, S.; Huang, K. A scalable deep neural network architecture for multi-building and multi-floor indoor localization based on Wi-Fi fingerprinting. Big Data Anal. 2018, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adege, A.B.; Lin, H.-P.; Tarekegn, G.B.; Munaye, Y.Y.; Yen, L. An indoor and outdoor positioning using a hybrid of support vector machine and deep neural network algorithms. J. Sens. 2018, 2018, 1253752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, K.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, J. Deep neural networks for wireless localization in indoor and outdoor environments. Neurocomputing 2016, 194, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adege, A.B.; Lin, H.-P.; Tarekegn, G.B.; Jeng, S.-S. Applying deep neural network (DNN) for robust indoor localization in multi-building environment. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, M.; Torki, M.; ElNainay, M. CNN based indoor localization using RSS time-series. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC), Natal, Brazil, 25–28 June 2018; pp. 01044–01049. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J. ime-Series Laplacian Semi-Supervised Learning for Indoor Localization. Sensors 2019, 19, 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Jiang, X. Semi-supervised deep extreme learning machine for Wi-Fi based localization. Neurocomputing 2015, 166, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Lu, X.; Jiang, H.; Xie, L. A fast and precise indoor localization algorithm based on an online sequential extreme learning machine. Sensors 2015, 15, 1804–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukito, Y.; Chrismanto, A.R. Recurrent neural networks model for WiFi based indoor positioning system. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Smart Cities, Automation & Intelligent Computing Systems (ICON-SONICS), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 8–10 November 2017; pp. 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zou, H.; Yang, J.; Jiang, H.; Xie, L. WiFi fingerprinting indoor localization using local feature based deep LSTM. IEEE Syst. J. 2019, 14, 3001–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahar, A.; Han, D. An LSTM based indoor positioning method using Wi-Fi signals. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Vision, Image and Signal Processing, Las Vegas, CA, USA, 27–29 July 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, C.-H.; Chen, J.-Y.; Nien, B.-H. Deep learning based indoor localization using received signal strength and channel state information. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 33256–33267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MATLAB R2020a; The MathWorks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2020.
- Yamashita, R.; Nishio, M.; Do, R.K.G.; Togashi, K. Convolutional neural networks: An overview and application in radiology. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emeršič, Ž.; Gabriel, L.L.; Štruc, V.; Peer, P. Convolutional encoder–decoder networks for pixel-wise ear detection and segmentation. IET Biom. 2018, 7, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njima, W.; Ahriz, I.; Zayani, R.; Terre, M.; Bouallegue, R. Deep CNN for Indoor Localization in IoT-Sensor Systems. Sensors 2019, 19, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferraz, P.A.P.; de Oliveira, B.A.G.; Ferreira, F.M.F.; da Silva Martins, C.A.P. Three-stage RGBD architecture for vehicle and pedestrian detection using convolutional neural networks and stereo vision. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 14, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jolfaei, A.; Alazab, M. A face emotion recognition method using convolutional neural network and image edge computing. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 159081–159089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dai, W. Bitcoin price forecasting method based on CNN-LSTM hybrid neural network model. J. Eng. 2020, 2020, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, F.; Majumdar, S.; Darabi, H.; Chen, S. LSTM fully convolutional networks for time series classification. IEEE Access 2017, 6, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, M.T.; Yuen, B.; Ren, K.; Dong, X.; Lu, T.; Westendorp, R.; Reddy, K. A CNN-LSTM Quantifier for Single Access Point CSI Indoor Localization. arXiv 2005, arXiv:2005.06394 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Fan, X.; Xiang, C.; Ye, Q.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; He, X.; Yang, N.; Fang, G. A novel convolutional neural network based indoor localization framework with WiFi fingerprinting. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 110698–110709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, H. An efficient indoor localization method based on the long short-term memory recurrent neuron network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 123912–123921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, D.; Gu, Y.; Chen, Z. Real-time and accurate indoor localization with fusion model of Wi-Fi fingerprint and motion particle filter. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 545792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Xu, J.; Yang, Z.; Lane, N.D.; Yin, Z. Gain without pain: Accurate WiFi based localization using fingerprint spatial gradient. Proc. ACM Interact. Mobile Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2017, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulose, A.; Kim, J.; Han, D.S. A sensor fusion framework for indoor localization using smartphone sensors and Wi-Fi RSSI measurements. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Kernel size for convolution | 3 × 3 |
| Pooling size | 2 × 2 |
| Activation function | ReLU (rectified liner unit) |
| Number of epochs | 150 |
| Batch size | 5 |
| learning rate | 0.001 |
| Hidden nodes | 32 |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Loss | Mean squared error (MSE) |
| Time | CNN | ELM | LSTM | HDLM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training time (s) | 105.33 | 1.61 | 127.52 | 145.43 |
| Testing time (s) | 0.39 | 0.05 | 0.42 | 0.50 |
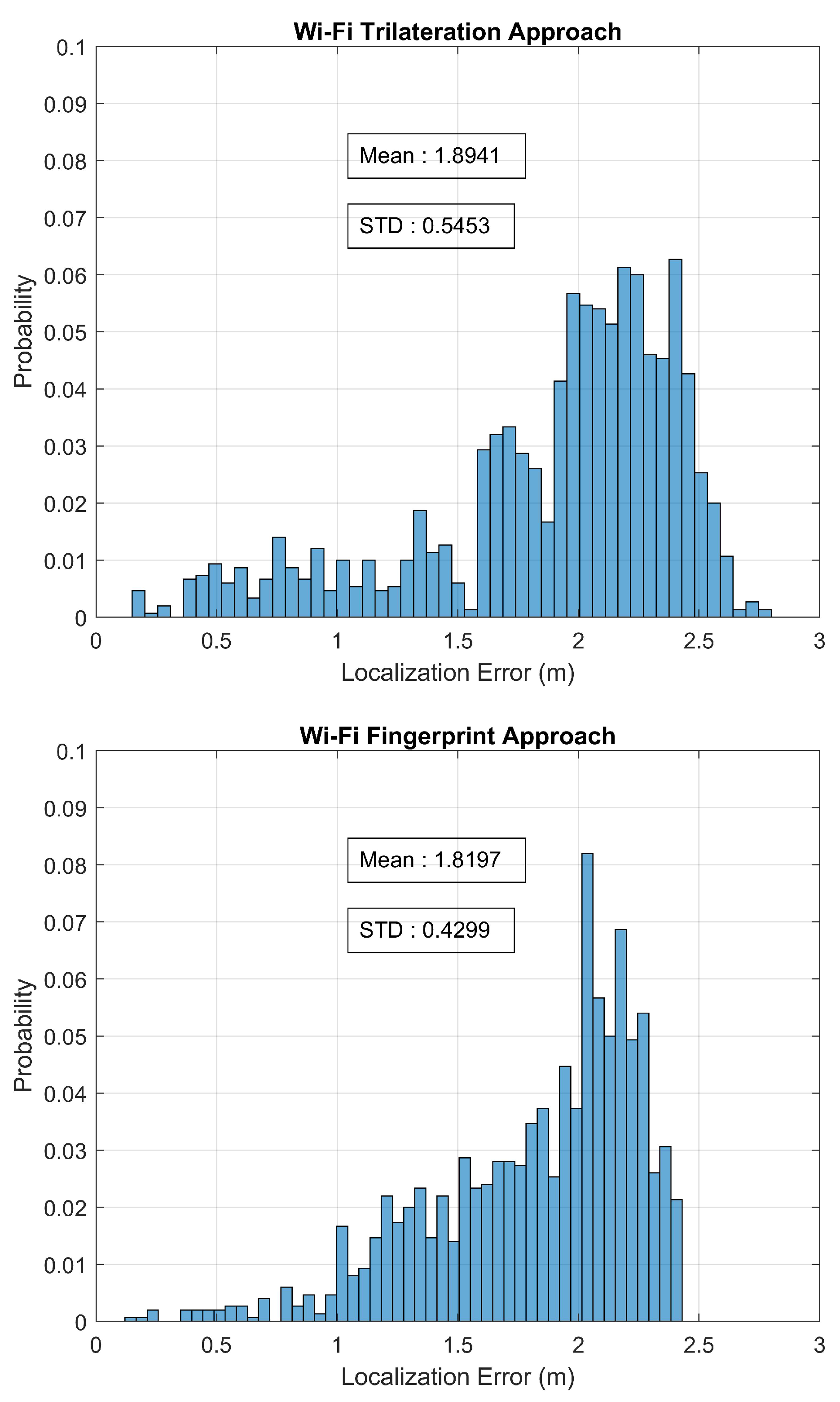
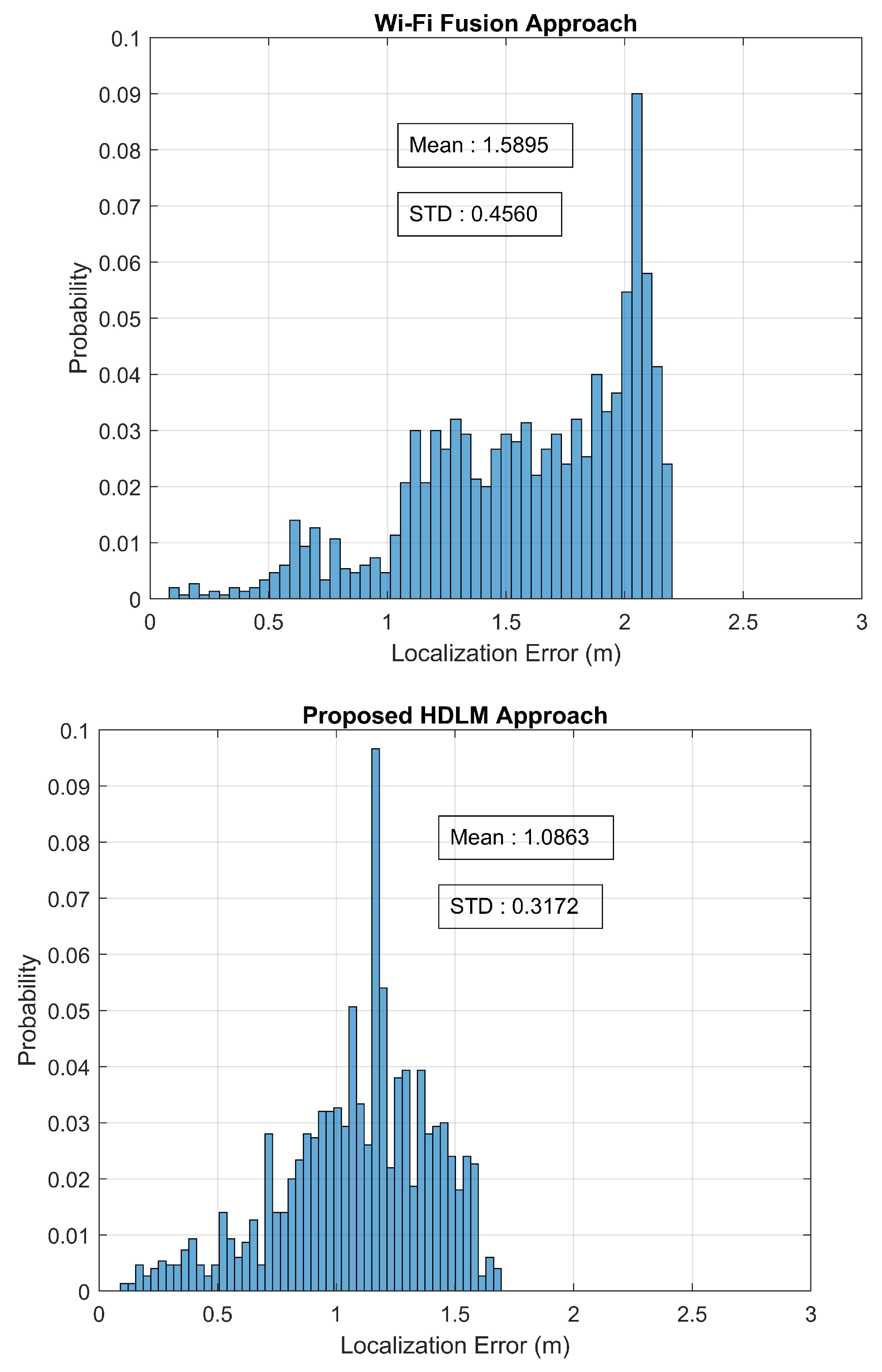
| Localization Method | Mean Error (m) | Max. Error (m) | Min. Error (m) | Standard Deviation of Error (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi Trilateration Approach | 1.8941 | 2.7727 | 0.1667 | 0.5453 |
| Wi-Fi Fingerprint Approach | 1.8197 | 2.4280 | 0.1214 | 0.4299 |
| Wi-Fi Fusion Approach | 1.5895 | 2.1993 | 0.1078 | 0.4560 |
| Proposed HDLM Approach | 1.0863 | 1.6901 | 0.1124 | 0.3172 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poulose, A.; Han, D.S. Hybrid Deep Learning Model Based Indoor Positioning Using Wi-Fi RSSI Heat Maps for Autonomous Applications. Electronics 2021, 10, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10010002
Poulose A, Han DS. Hybrid Deep Learning Model Based Indoor Positioning Using Wi-Fi RSSI Heat Maps for Autonomous Applications. Electronics. 2021; 10(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10010002
Chicago/Turabian StylePoulose, Alwin, and Dong Seog Han. 2021. "Hybrid Deep Learning Model Based Indoor Positioning Using Wi-Fi RSSI Heat Maps for Autonomous Applications" Electronics 10, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10010002
APA StylePoulose, A., & Han, D. S. (2021). Hybrid Deep Learning Model Based Indoor Positioning Using Wi-Fi RSSI Heat Maps for Autonomous Applications. Electronics, 10(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10010002






