Abstract
A virtual router model with a static and dynamic resource reconfiguration for future internet networking was developed. This technique allows us to create efficient virtual devices with optimal parameters (queue length, queue overflow management discipline, number of serving devices, mode of serving devices) to ensure the required level of quality of service (QoS). An analytical model of a network device with virtual routers is proposed. By means of the mentioned mathematical representation, it is possible to determine the main parameters of the virtual queue system, which are based on the first in, first out (FIFO) algorithm, in order to analyze the efficiency of network resources utilization, as well as to determine the parameters of QoS flows, for a given intensity of packets arrival at the input interface of the network element. In order to research the guaranteed level of QoS in future telecommunications networks, a simulation model of a packet router with resource virtualization was developed. This model will allow designers to choose the optimal parameters of network equipment for the organization of virtual routers, which, in contrast to the existing principle of service, will provide the necessary quality of service provision to end users in the future network. It is shown that the use of standard static network device virtualization technology is not able to fully provide a guaranteed level of QoS to all present flows in the network by the criterion of minimum delay. An approach for dynamic reconfiguration of network device resources for virtual routers has been proposed, which allows more flexible resource management at certain points in time depending on the input load. Based on the results of the study, it is shown that the dynamic virtualization of the network device provides a guaranteed level of QoS for all transmitted flows. Thus, the obtained results confirm the feasibility of using dynamic reconfiguration of network device resources to improve the quality of service for end users.
1. Introduction
Today, businesses are facing increasing demands on the quality and reliability of network infrastructure, as it directly affects the availability of business applications and services. The number of devices connected to the network is growing like an avalanche: PCs, laptops, tablets, smartphones, sensors, surveillance cameras, etc. [1]. This is typical for both commercial organizations and government agencies [2,3]. Many believe that the future of enterprise networking lies in technologies such as software-defined networking, network functions virtualization, and intent-based networking (IBN) [4,5,6,7,8]. These technologies promise to deliver more flexible networks with fewer problems in heterogeneous devices, which in turn benefit from shorter operating systems, continuous performance optimization, better interoperability and improved QoS [9,10,11]. IBN can do this because it manages network configuration automatically, so it can respond and scale faster than a human [12,13,14,15].
Network virtualization is a new technology that is being considered as part of the IBN concept by Cisco, Arista, Dell, Juniper companies which focuses on the ability to share the physical network infrastructure across multiple virtual networks. This issue is also important for the developers of mobile standards [16], in particular the 5–6 G specifications, because the development of mobile networks is characterized by an ever-increasing degree of heterogeneity of telecommunications infrastructure. This, in turn, significantly complicates network infrastructure management for operators. It is worth noting the advantage of virtualization as isolation of logical environments from each other [17]. Resource allocation in network virtualization has been considered in many research works in order to provide better utilization of physical infrastructure [18,19,20,21]. Considerable research has been done on the general infrastructure for QoS networking, but the actual allocation of router resources to QoS flows has received less attention. The partitioning of network router resources between QoS flows is done in such a way that the traffic of one flow minimally affects the traffic of the other flow. Commonly used commercial methods include over-provisioning of routers or using the queuing of shared access to the circuit process, such as prioritized PQ service [22,23].
A virtual machine-based router architecture has been proposed in our work [24], which will be able to increase the resource allocation between different network flows, provides better QoS guarantees. This virtual router architecture consists of a number of virtual machines, each of which allocates a fraction of the machine’s primary physical resources (e.g., CPU time or network bandwidth) [25]. Each virtual machine is called a QoS Routelet and is designed to route a single QoS flow. The primary virtual machine monitor ensures that each QoS flow can only access allocated resources and thus ensures that no other flow can interfere with its flow processing. The end virtual machine routes all traffic and manages the shared router.
This virtualization of router resources can offer a number of advantages given previous approaches to router resource allocation. It allows router resources to be shared between flows, without expensive or inflexible provisioning.
In static allocation, a dedicated virtual router gets a small fraction of each resource and cannot ask for more, even if it is needed. Paper [26] addresses the issue of node allocation in a virtualization network. It was investigated that this allocation should be dynamic to ensure better performance and optimal use of the physical infrastructure. As a result, it is possible to minimize the packet processing latency that occurs when multiple isolated virtual networks use limited resources on a single physical node. Queuing theory provides an interesting mathematical tool for managing queuing problems [27]. It also provides a good model for analyzing a physical router where a packet must be processed by multiple pipeline resources from the router’s input port to the output port.
Most current commercial routers provide a static allocation of physical resources to multiple logical routers, each with its own configuration. This approach does not support any flexibility to configure their resource management. In addition, many researchers did not consider the isolation between parallel virtual routers on the data plane.
That said, the purpose of this work is to develop a new router architecture that offers dynamic changes in resource allocation based on each virtual router’s load evaluation and to ensure QoS guarantees. At the same time, it is necessary to use a dynamic hypervisor, which will allow you to create and run virtual machines of different performance and will manage the work of the virtual routers and allocate physical resources between them.
Considering the above, the following structure of the paper was formed: Section 2 presents the related works; Section 3 presents the proposed solution in the paper, including the proposed static and dynamic virtualization model of router resources for the future internet networking; Section 4 presents the simulation results, and Section 5 presents the conclusions of the study.
2. Related Work
In [28], the use of virtualization technology in industrial control systems to improve their manageability and scalability are considered. To solve the problem of QoS in controller area networks, a hierarchical real-time scheduler and simulator are presented, which allow us to guarantee the requirements of virtual controllers in real time based on the adjustment of the phases of virtual controllers and tasks. Experimental results show that the worst-case end-to-end latency can be reduced to 78.7% from the initial control value by adjusting the phase shifts of virtual controllers and tasks, without considering the priority of data maintenance during virtualization.
The paper [29] deals with the configuration of a software router to ensure the minimum average packet delay in networks. The proposed model for predicting the packet delay uses Erlang-k distribution, and based on that, it presented a measurement system that interacts with the function of virtualization and network function management to improve the efficiency of network management.
In [30], the distribution of physical resources between virtual network elements, in particular routers, which directly affects the quality of service of user applications, is considered. Algorithms for migration of virtual routers to reduce energy consumption in the network are presented. We performed a number of experiments to research their effectiveness but did not take into account the aggregate data flow, which has its own characteristics, and in turn affects the QoS.
The paper [31] is devoted to the use of virtual router (VR) to provide services to end users in the failure of network nodes. The authors propose a robust optimal virtual router selection scheme for dynamic reconfiguration, which is based on a combination of minimum cost selection and balancing bandwidth residuals. Based on the research conducted, it is found that the VR heuristic under consideration has a low overhead when nodes have the ability to support more than one such router in a service. However, the effect of the number of virtual routers on the quality of user service has not been investigated.
In [32], the use of virtualization technology in the area of resource sharing and allocation while ensuring the necessary level of service quality was considered. The authors presented an adaptive virtualized resource allocation system, which carries out the distribution of virtualized resources between workloads, guaranteeing the level of QoS. It is shown that the overall use of resources in accordance with the proposed strategy allows for more accurate QoS control, with no study on the value of the delay in service delivery.
The paper [33] deals with the problem of service-oriented virtual resource allocation in a virtualization environment, which performs a mapping of each configured service. The authors proposed the SerOri framework, which consists of VN SerOri-Class service classification and VN SerOri-Embed embedding. The proposed solution improves resource efficiency and end-user service quality by taking into account different types of services and their features, in particular regarding resource requirements and QoS.
In [34], approaches are considered to effectively respond to the growing performance requirements to provide the required level of quality of service to end users. The authors have proposed a framework for resource management based on an aggressive strategy, which will ensure rapid adaptation during the growth of load, and accordingly provide quality services to users. The main focus of the study was on load balancing.
Paper [35] is devoted to the development of 5G network infrastructure, with virtualization of computing resources is considered as an option for the effective use of computing devices in wireless networks. According to the vision of the authors, the network architecture will be purely service-oriented, according to which the service is provided to the user when he needs it. It is shown that radio resources and computing resources can be effectively, flexibly and efficiently virtualized in services.
Despite the significant amount of works devoted to virtualization of network resources in conditions of intensive load increase, they do not consider the issue QoS of different types of traffic, taking into account the priority of the flow and dynamic reconfiguration of network device resources for virtual routers. These issues will be discussed in this article.
3. Models to Improve QoS Parameters in Future Internet with Regard to Network Nodes Virtualization
3.1. Static and Dynamic Virtualization Model of Router Resources
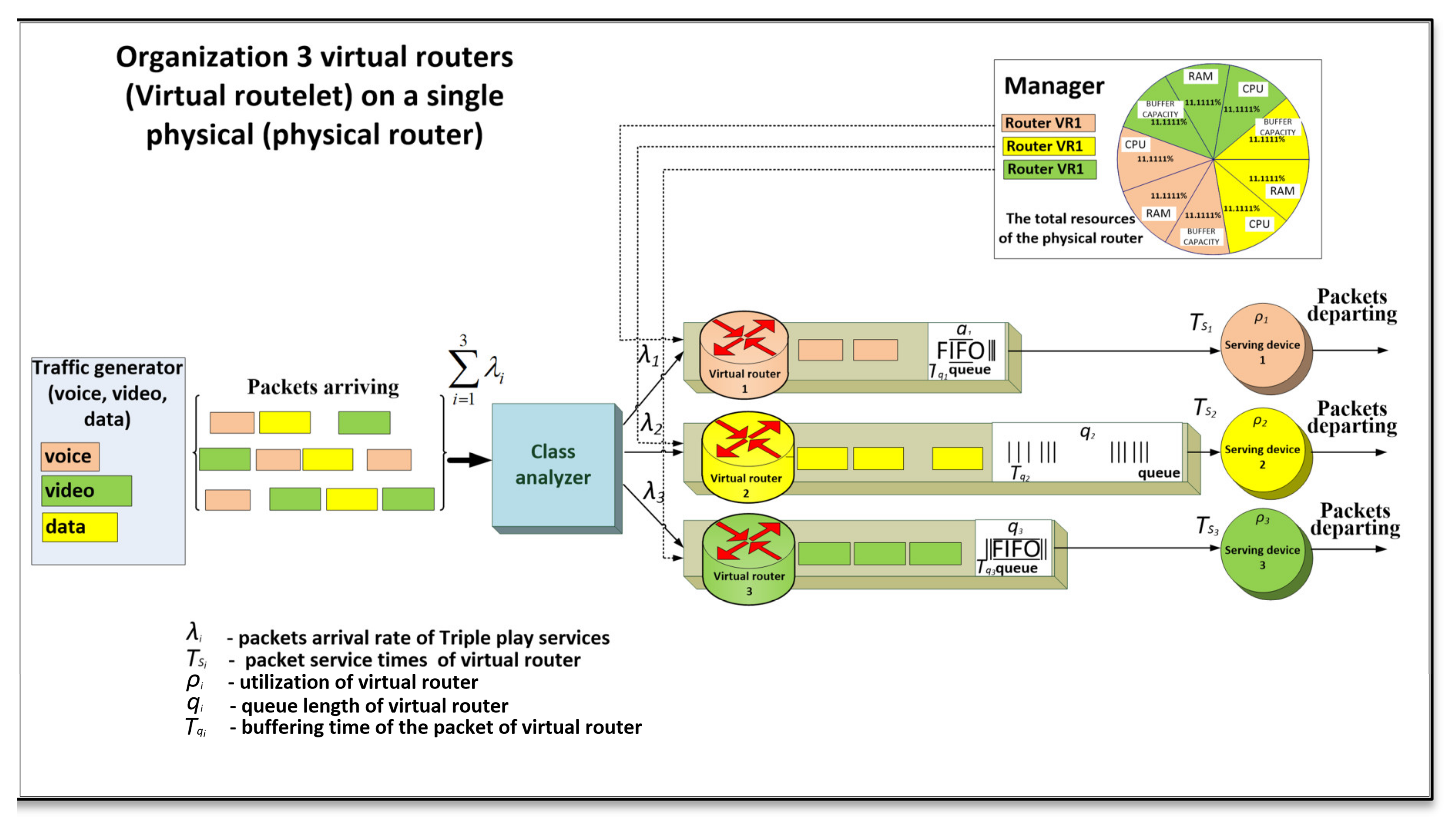
A future internet network with virtualization is a network in which one or more network devices use a virtualized mode of operation. Virtualization of a network device involves the creation of two or more virtualized network machines that act as a router with individual flowing services. In this case, in order to simplify the formalization of the virtual router model, we considered the transmission of three types of services so-called triple play services (voice, video and data). Accordingly, when designing the structure of a network device with virtualization, three virtual routers are deployed, which are designed to individually serve flows of the same type, providing them with the necessary level of QoS in accordance with the requirements (Figure 1). This is ensured by allocating physical hardware device resources to change the required performance of virtual routers serving flows (voice, video and data).
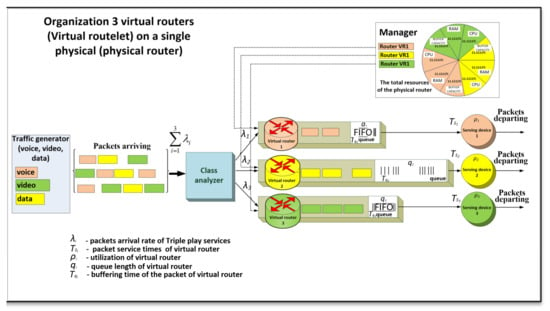
Figure 1.
Conceptual model of a multiple virtual router with dynamic resource allocation.
At the input of the virtual router comes the aggregate flow of packets with the intensity:
The aggregate flow in this case consists of flows, where (voice, video and data), each of which is characterized by its own parameters and distribution. Then the input flow of packets with total intensity arrives to a network device, where it is processed and divided into network virtual devices according to the priority of the service field (ToS), Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP).
Such separation into virtual devices is performed by class analyzer unit, which operates on the basis of IP header analysis, and depending on the content of DSCP or ToS field, it will read the code, which will indicate the appropriate type of service. This allocation principle for routers is similar to the mechanism of packets allocation to the queues of a different priority service system. Then packets will be routed to the virtual routers of the destination class.
Therefore, technically, when virtualizing a network device, the functions of the classification block remain unchanged, they are only applied to a different task. Therefore, when comparing the delay time of the virtual router with the existing router on the principle of priority service, the processing time of the service priority field is the same and constant for all services, while it is much less than the processing time of the application in the router. Thus, this time can be ignored:
where is the packet delay time for processing the priority field, is the packet delay time in the router.
The main factor by degree of influence on the occurrence of queues, which lead to hard-to-predict delays of packet buffering, is the virtual device load factor—the ratio of the average intensity of incoming traffic and the average intensity of packet transmission to the output interface (in the model, this parameter is considered as is the duration of packet -th flow service by virtual router).
The advantage of this model is that by using resource manager block, it is possible to statically and dynamically allocate computing resources of a network device for virtual routers depending on QoS flow requirements. Under computing resources of the device, we will understand hardware resources, the configuration of which significantly affects the ability and performance of packet processing by a virtual node. In turn, the hardware configuration of each node is the amount of its RAM, CPU clock frequency and buffer memory allocated statically and dynamically depending on the prediction of incoming thread load on the node.
Thus, the performance of virtual routers is reconfigured at certain moments of time by allocating the necessary resources to them.
The essence of the proposed method of quality of service in the nodes of the multiservice network is to control computing resources, depending on the intensity of the incoming packets load of different priority classes, as well as the acceptable quality requirements for their service.
For this purpose, the network node requires management, which will perform the following basic functions:
- Periodic control of the main indicators of the QoS (delays, packet losses of different priority classes);
- Automatic decision-making to change the computing resources of virtual routers, depending on the input load and the corresponding quality of service indicators to the established norms.
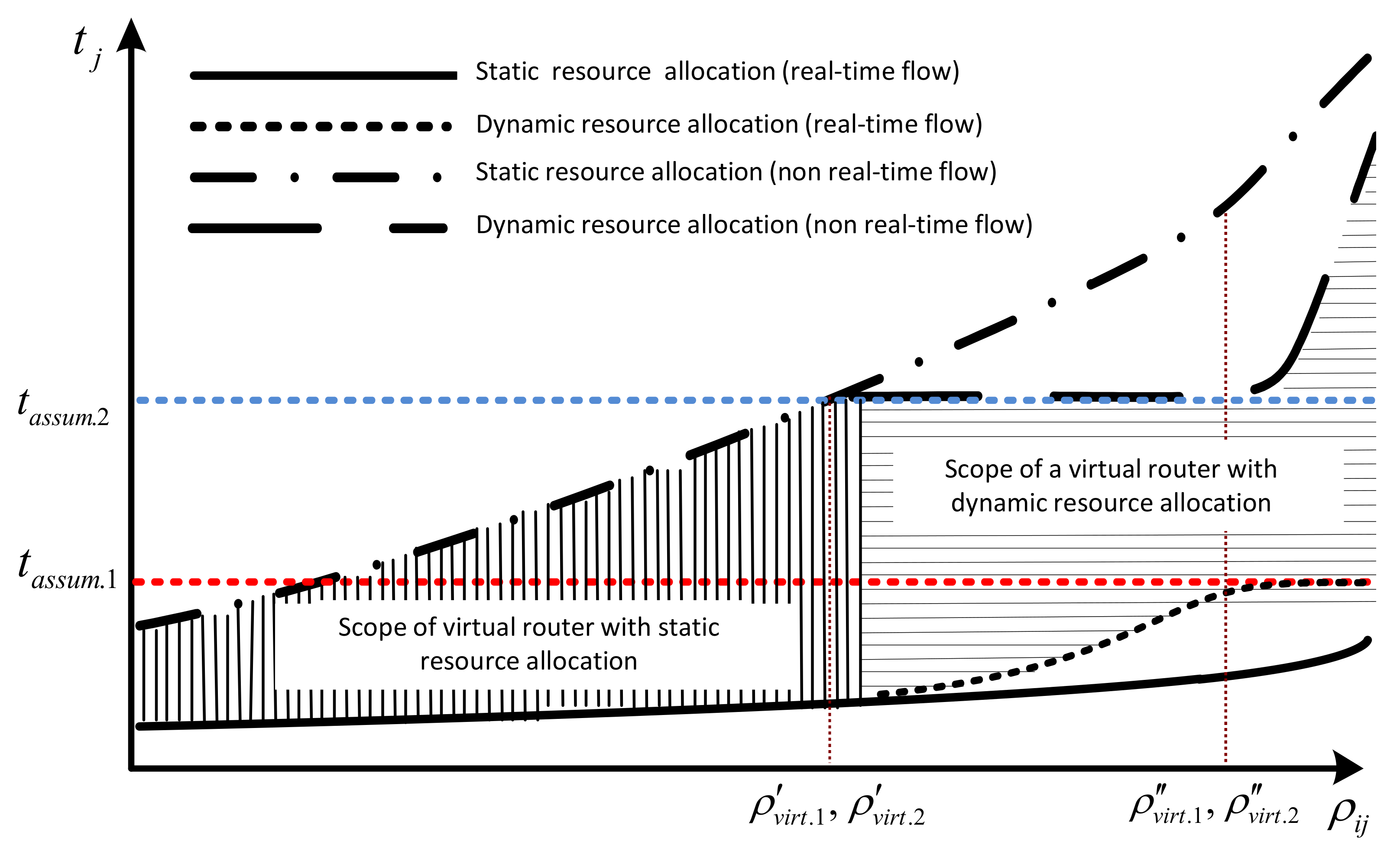
Figure 2 shows the principle of management of computing resources of the network device based on the dependence of the average delay time of packets from the load of virtual routers at static and dynamic resource allocation.
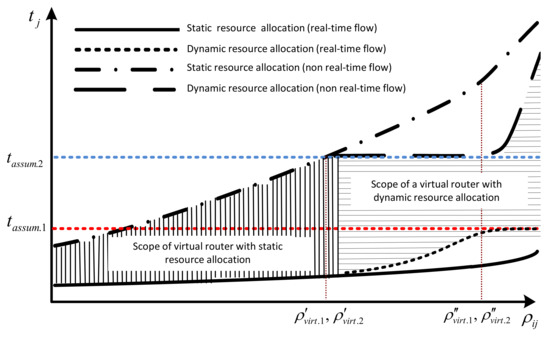
Figure 2.
The principle of static and dynamic allocation of computing resources of a network device in the organization of virtual class-service routers.
Input network traffic can be divided into two types: delay-sensitive and delay-insensitive. Accordingly, for simplicity in formalizing the model, all traffic is divided into two classes of services .
Let the first class packet delay; (delay-sensitive) in the virtual router must not be more than the permissible value , respectively; write the condition of the necessary level of QoS as .
The delay of the second-class packets (not delay-sensitive) must not be higher than ; in this case the condition of the necessary level of QoS in the second virtual router will be as follows: . Then under the conditions of low load on virtual routers of the first and second class at the -th moment in the static allocation of computing resources, all quality-of-service requirements for flows of all priorities are satisfied.
At high load at certain moments of time, there are situations when and . In such a case, it is necessary to use dynamic distribution of computing resources, which will allow balancing packet delays of two classes, avoiding blocking of real-time flows transmission by reconfiguring the performance of virtual routers with respect to QoS requirements.
Based on the results of the current control, QoS parameters are recalculated parameters of computing resources CPU, RAM, buffer capacity, network device between the class virtual routers. As a result, with a further increase in load on the network node in the dynamic resource allocation at certain times, the average delay of non-real-time packets of services is fixed and meets the requirements of , in contrast to the static distribution, where the delay requirements of this flow is not met. In this case, the delay of real-time service packets increases, but .
Under conditions of high load on the network device, when , similarly conducted redistribution of resources between virtual routers of class service in order not to allow it to go beyond the normalized average stay time packets of the first class of real-time services , but in such conditions, it increases the delay of packets for non-real-time services, while not impairing the quality of service perception by end users.
This approach will dynamically create virtual mass service systems (MSS) with optimal parameters (queue length, queue overflow management discipline, number of serving devices, mode of service devices) for a particular type of service with a set of inherent network parameter requirements (loss, delay and jitter).
3.2. Analytical Representation of Virtual Infrastructure Service of Quality Parameters
In this paper, we propose an analytical representation of the quality-of-service parameters of a multiservice infrastructure with resource virtualization. Suppose that the total channel bandwidth of a node in a multiservice network is and the total buffer size is . To simplify the formalization of the model, we use the following notations: is the amount of incoming traffic, is the amount of rejected traffic, is the intensity of service at time .
We also introduce the notion of arrival curve, incoming and outgoing curve for traffic during time interval . The arrival curve and the input curve are defined as
where is the momentary arrival rate of packets at time .
where is the rejection rate of packets at a moment in time.
From formula (4), the difference between the arrival curve and the input curve is the volume of rejected traffic. The output curve characterizes the transmitted traffic during time interval and is defined as
where is the packet service intensity at time .
From this moment on, we will use the following abbreviations to denote arrival curves, input and output at time moments , respectively:
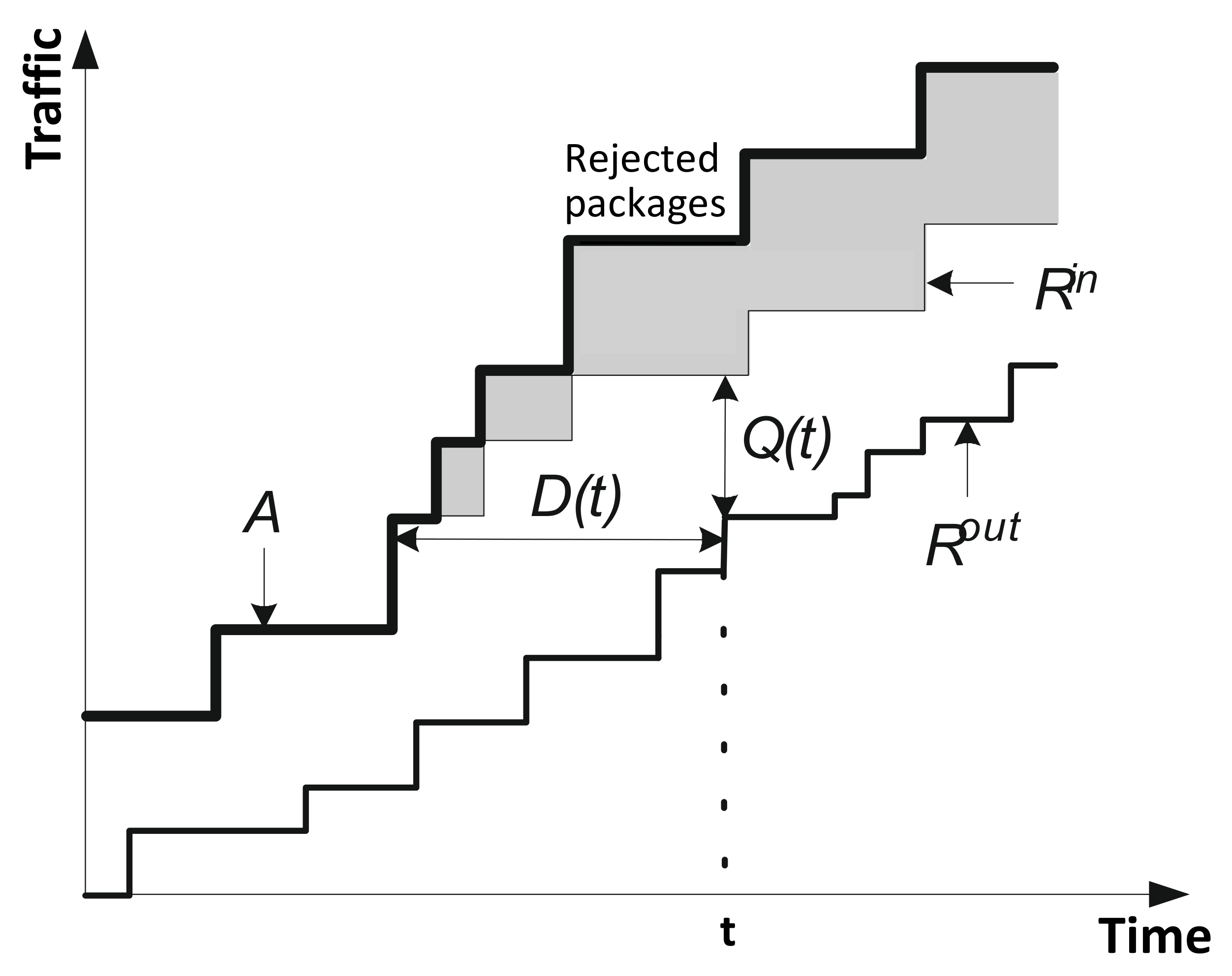
Figure 3 shows the vertical and horizontal distances between the input and output curves characterizing the queue length and the delay in the network device.
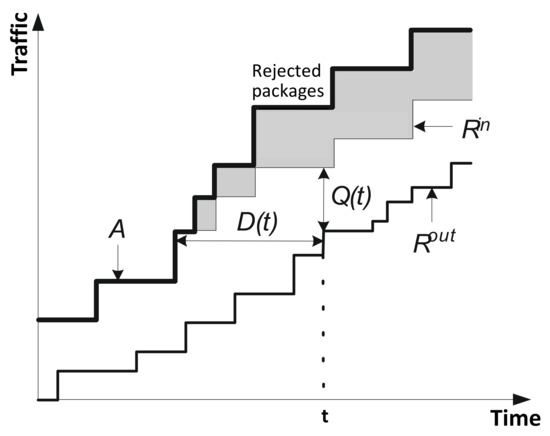
Figure 3.
Queue size, delay and packet loss.
Delay is the duration of packet service of transmitted packets at time . Accordingly, the queue length and delay are determined at time by these formulas:
The average delay can be obtained by averaging the momentary delay over the time window of duration :
Let us denote the loss rate , which represents the fraction of traffic lost since the beginning of the current busy period at time . The busy period is the time interval during which the maximum buffer load of the node occurs. Thus, describes the part of traffic lost in the interval and is defined as
where .
Using the above written expressions, we can formally describe the characteristics of the quality of service of the virtual infrastructure.
3.3. Analytical Model of a Multiple Virtual Routers
For quite a long period of time, it has been generally accepted in theory of telecommunication network analysis that any service device can be described by means of mass service and teletraffic theory. Some of the principles of approaches based on these theories can still be agreed upon today, but more and more often there are situations where the networks calculated in this way at certain moments are in the mode of congestion and are in this state for a very long period of time, which leads to significant losses in the service provider. The analysis has shown that this is due to a discrepancy between the selected models and the actual network traffic before and after service. This, in turn, is explained by differences in the probabilistic characteristics of the random processes adopted for modeling real traffic.
In multiservice telecommunications networks, the input information flows can have constant (CBR), variable (VBR) and mixed bit rate, from which the mathematical model of the flow can be from the simplest Poisson to the complex model of fractal processes (self-similar traffic). The law of the distribution of the time interval between demands in these flows can be arbitrary, and therefore it is logical to investigate the generalized kind of distribution of the random value of this interval in the generalized model. The packet length of each of the services shared by the multiservice network (hence the service duration) may be different—constant for some services and variable for others. In such a case, it is also desirable to investigate the general form of the distribution of the random variable for the service duration.
Real flows in multiservice networks are generated by multiple sources with separate, different load intensities (heterogeneous flows). The process of aggregated flow creation involves sources belonging to different groups of users, services with close load intensities. The value of the resulting flow intensity at each moment depends on which load intensity group the source belongs to and what is the ratio of the number of these sources. A more adequate description of the flow or the distribution of time intervals between packets can be given not by an exponential distribution but by a combination of these, the hyperexponential distribution.
The hyperexponential time interval between packets leads to a distribution of the number of packets per interval in the average service duration that is well approximated by the normal law (Gaussian). For real flows of multiservice communication networks, a mathematical model with a hyperexponential distribution of the time interval between packets, whose number per time interval is approximated by a normal distribution, is adequate.
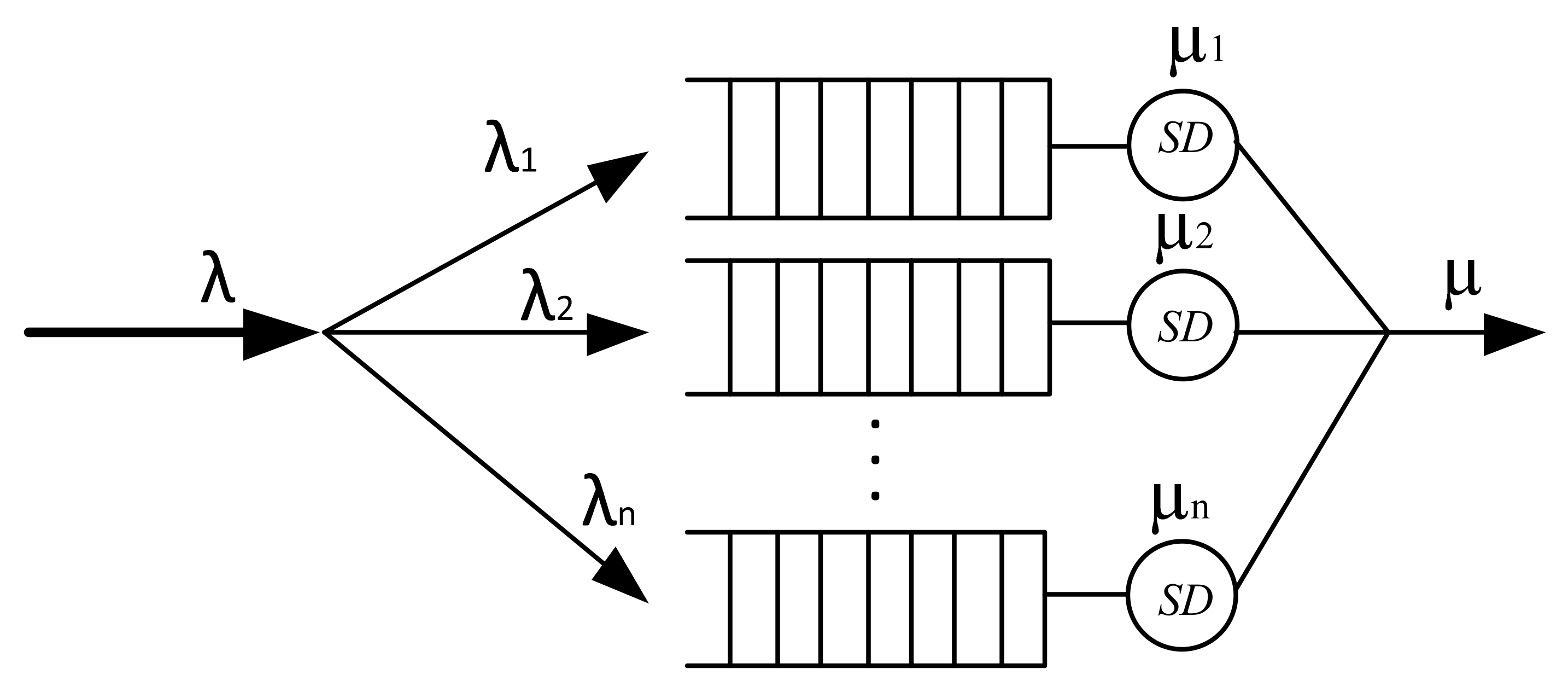
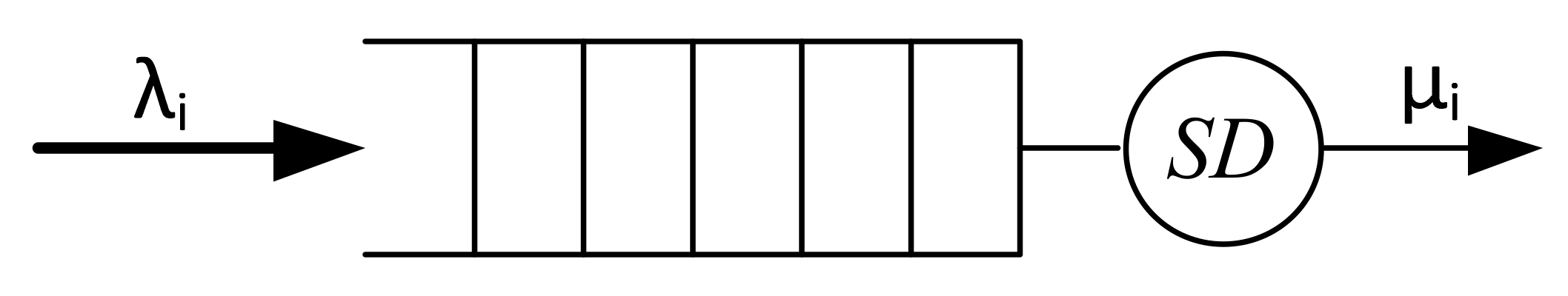
A network device with virtualization according to MSS can be represented by the cascading inclusion of buffer memory and serving devices (SD) (Figure 4). Thus, the traffic behavior of a multiservice IP network is characterized by different distribution laws, and therefore, when a network device is virtualized, each virtual router operates with its own class of services, each of which is described by the corresponding packet interval distribution function and service duration distribution function.
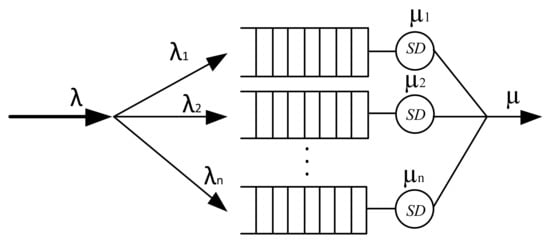
Figure 4.
Model of a multiple virtual routers.
By decomposing the virtualization router model for one type of traffic, we obtain a simplified single-server model, which is shown in Figure 5.
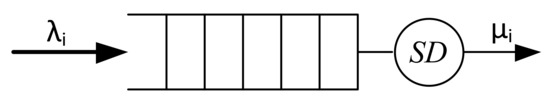
Figure 5.
Router virtual machine model for VoIP traffic.
A random mass-service system can be used to describe such a model. For example, we use the system M/M/1/n, where calls with Poisson distribution law come in, the supercomposing of which forms a multiservice aggregate flow:
For a M/M/1/n system, the loss probability in w -th virtual router is defined as
where is the load factor of the -th virtual router, is the number of places in the buffer of -th virtual router;
where is the packet arrival rate of the -th flow of the -th virtual router, is the intensity of packet service of the -th flow of the -th virtual router.
The average number of packets in the buffer of the -th virtual router:
Thus, the average time that a packet stays in the -th virtual router can be determined based on Little’s formula:
Because the traffic of multiservice packet-switched networks is characterized by the presence of long-term load intensity dependencies, an adequate model of flows in such networks is considered as self-similarity processes, where the input flow is described by a fractal Brownian motion (fBM model). The determination of the predicted buffer size is based on the Norros formula for the average number of packets that are contained in a buffer with infinite size [36].
In this paper, we propose a modified formula for estimating the number of packets of the -th flow in the buffer of the -th virtual router, where each flow is characterized by its properties and with its Hurst parameter:
where is the Hurst parameter of the -th flow arriving at the -th virtual router.
The buffer memory size of the virtual router, required, is determined by the formula:
where is the average packet length.
Calculation of the number of packets waiting for service using the Norros formula is possible for any law of service duration distribution but is valid only for the exponential law of packet interval distribution, for example for models M/G/1, M/D/1, M/M/1.
In the Norros work it was shown that the probability that the number of packets in the system exceeds a given value is determined by the expression
where
Moreover, the estimation of the buffer load was carried out by the Norros formula, but its application for this study is limited by the fact that it is derived for the normal law of Gaussian distribution so that other distributions of incoming traffic may not give reliable results. To determine the buffer load, we write the Norros formula in the following form:
where is the buffer load (bits) in -th virtual router, is the Hurst parameter of the traffic profile in the -th virtual router, is the packet loss probability to be provided by -th virtual router, is the direct channel bandwidth (bits per second (bps)) in -th virtual router, is the packet arrival rate in -th virtual router (bps), is the coefficient of variations for packet arrival rate in -th virtual router (bps).
To date, many works are devoted to the description of incoming flow models. Recent studies of the properties of information flows in multiservice telecommunications systems have shown that the use of self-similar processes (self-similar flows) models allows a more accurate description of the traffic transmitted in these systems. It is now necessary to describe the service device model with virtualization. The resource virtualization router model itself is described above. If we are talking about multiservice networks, even its structure is not uniquely known in advance.
Modeling gives the most accurate results in the case of taking into account as many parameters of the real service system as possible. Important factors are the structure (availability of a certain number of incoming/outgoing interfaces, possibility of parallel processing of data from several interfaces, possibility of priority processing for certain classes of network traffic) and functional parameters (speed of internal incoming/outgoing bus, speed of serving device, speed of switching between interfaces, buffer volume, probability of packets rejection when the given buffer thresholds are exceeded). In order for the serving device model to be adequate, it is necessary to provide verification of the given functional parameters for each element of a particular network node (taking into account possible production tolerances).
The first structural parameter of a node for QoS management is considered a buffer. In virtualization, the total buffer size is shared between virtual routers. Optimal use of the buffer resource by virtual devices will provide the necessary quality to flows with different requirements. A separate aspect of service is to consider the queue behavior model of the information processing system (serving node). The queue state is determined by buffer size, system load and values of packet rejection thresholds for overload control.
The model of the general queue state (without prioritization of traffic classes, it is a separate problem), taking into account the buffer load, can be represented by a number of the following conditions.
The sum of capacities of virtual queues in the critical case cannot exceed the total buffer size at low utilization coefficients of the previous network segment:
where is the length of virtual packet queues, is the total buffer memory capacity.
The paper proposes a model for adaptive control of the total buffer resource for allocation of optimal capacities in virtual queues, in which conditions the required quality of service for information flows is ensured.
where is the current flow buffering delay in -th virtual router, is the allowed flow delay in -th virtual buffer of router according to established recommendations, is the probability of packets rejection in the buffer of the -th virtual router, is the allowed flow loss in -th virtual buffer of router according to established recommendations, is the current flow buffering jitter in -th virtual router, is the allowed flow jitter in -th virtual buffer of router according to established recommendations.
where is the processor frequency of the -th virtual router, is the nominal processor frequency of the physical router, is the operating memory of the physical router, is the operating memory of the -th virtual router.
Depending on the structural and functional type of the network node it is possible to change the structure of the outgoing traffic compared to the incoming one. Therefore, it is necessary to apply methods for selecting a mathematical model (distribution density) of the outgoing traffic to be able to analyze the input impact on the subsequent service node. Accordingly, it is necessary to write down a traffic model.
The greatest difficulty is the analysis of self-similar processes, because, apart from Pareto’s law, it is almost impossible to select a mathematical model of such traffic through its antipersistence. The traffic transmitted in multiservice packet-switched networks has a long-term dependence on the intensity, and even more significantly differs from the Poisson flow and even any other flows, which are determined by a one-dimensional probability distribution function of the time interval between the moments of packets arrival.
A more adequate model of flows in such networks is self-similar processes, but the study of the characteristics of the quality of service of information distribution systems in these conditions is a very complex mathematical problem. In multiservice packet networks, the traffic is heterogeneous and with certain QoS requirements. Here, the transmission of flows of different services is provided by the same network with unified protocols and control laws. Because the sources of each service can have different information transmission rates and can change it during the communication session (maximum and average speed), the combined packet flow is characterized by the so-called “burstiness” of the traffic, measured by the bursting factor. This burstiness causes even greater traffic irregularity, in which the variance of traffic intensity exceeds its mathematical expectation from 20 to 60 times or more.
When deploying virtual routers, the topology of the physical multiservice network becomes a virtual monoservice network. This, in turn, simplifies the problem of building an adequate mathematical model of the input flow in monoservice networks with homogeneous traffic—such, for example, are purely telephone networks with a single telephone service, which causes homogeneity of traffic. The simplest Poisson flow model basically corresponds to such conditions, and the value of traffic intensity and its dispersion coincide or are close enough.
The most important is the question of ensuring the service quality parameters by a node. By changing the parameters of the structural-functional model of the serving node, we can observe the changes in the quantitative and temporal parameters of quality of service. The problem of resource planning comes down to the selection of the parameters of the structural-functional model of the service node, ensuring compliance with the desired (specified, necessary) temporal and quantitative parameters of QoS.
4. Simulation Results
4.1. Modeling and Comparison of Information Flow Service Systems with Static Reconfiguration of Router Resources and Queued Packet Processing
To verify the proposed technical solutions to improve and ensure a guaranteed level of quality of service for information flows in the multiservice network, a simulation of the developed model with static virtualization of router resources was performed.
The simulation process generates voice, video, and data services, each of which is characterized by its allowable QoS according to ITU-T recommendations. Moreover, the model must take into account that in the deployment of virtual routers as well as in the deployment of virtual machines, the total resources of RAM, CPU and buffer memory are divided according to the number of allocated independent machines (routers) and the static configuration of the proportions provided for the use of resources.
The model compares the performance of the router with the time it takes to serve a packet or the time it takes to fire the CPU resource. Because the nominal CPU frequency of the router is the most weighted performance indicator, according to the analysis of router manufacturers’ data sheets, the average packet service time depending on the CPU is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Dependence of packet service time on router processor frequency.
Therefore, under the conditions of deploying three virtual routers on one physical router, we obtain this distribution of resources during static allocation (Table 2).

Table 2.
Source block parameters for three virtual routers (CPU-450 MHz) and one physical router without virtualization (CPU-1400 MHz) for a service time 30 µs.
Multiservice flow generation occurs from three independent sources with different packet intensities and with an exponential distribution of interpacket distance (Table 3). Accordingly, at the output of the network device we obtain an aggregated hyperexponential distribution of interpacket distance intervals, which is characteristic of real multiservice network flows.

Table 3.
Time-based entity generator parameters.
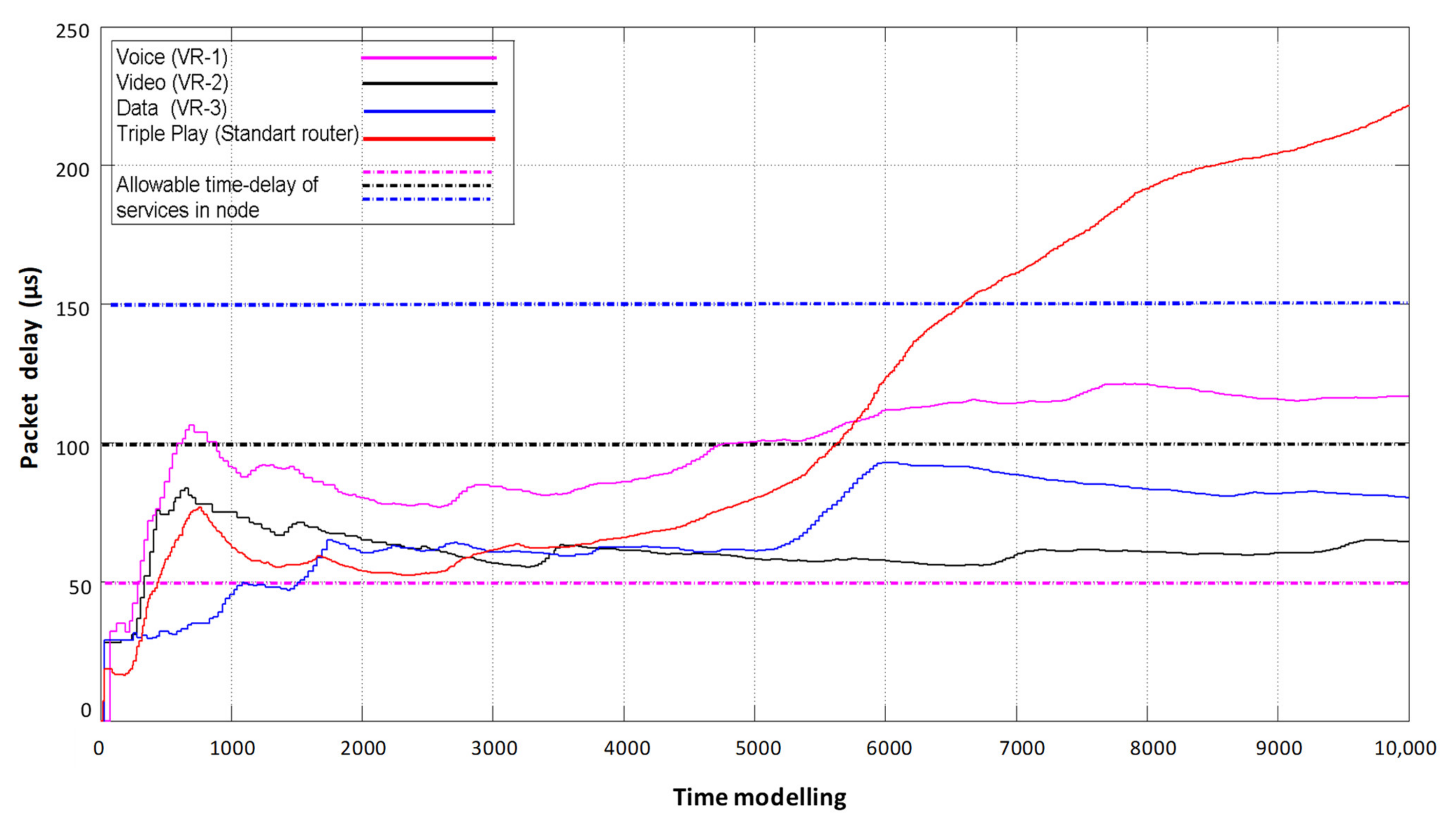
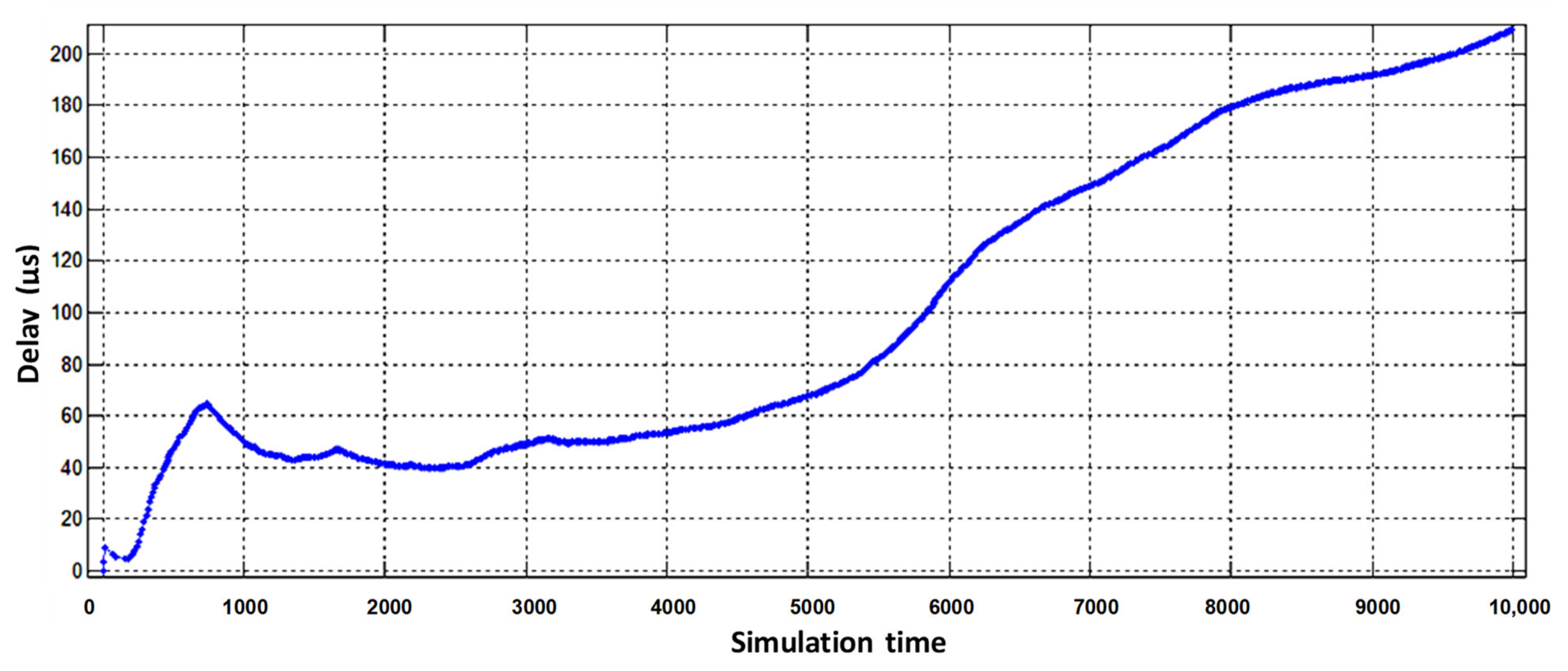
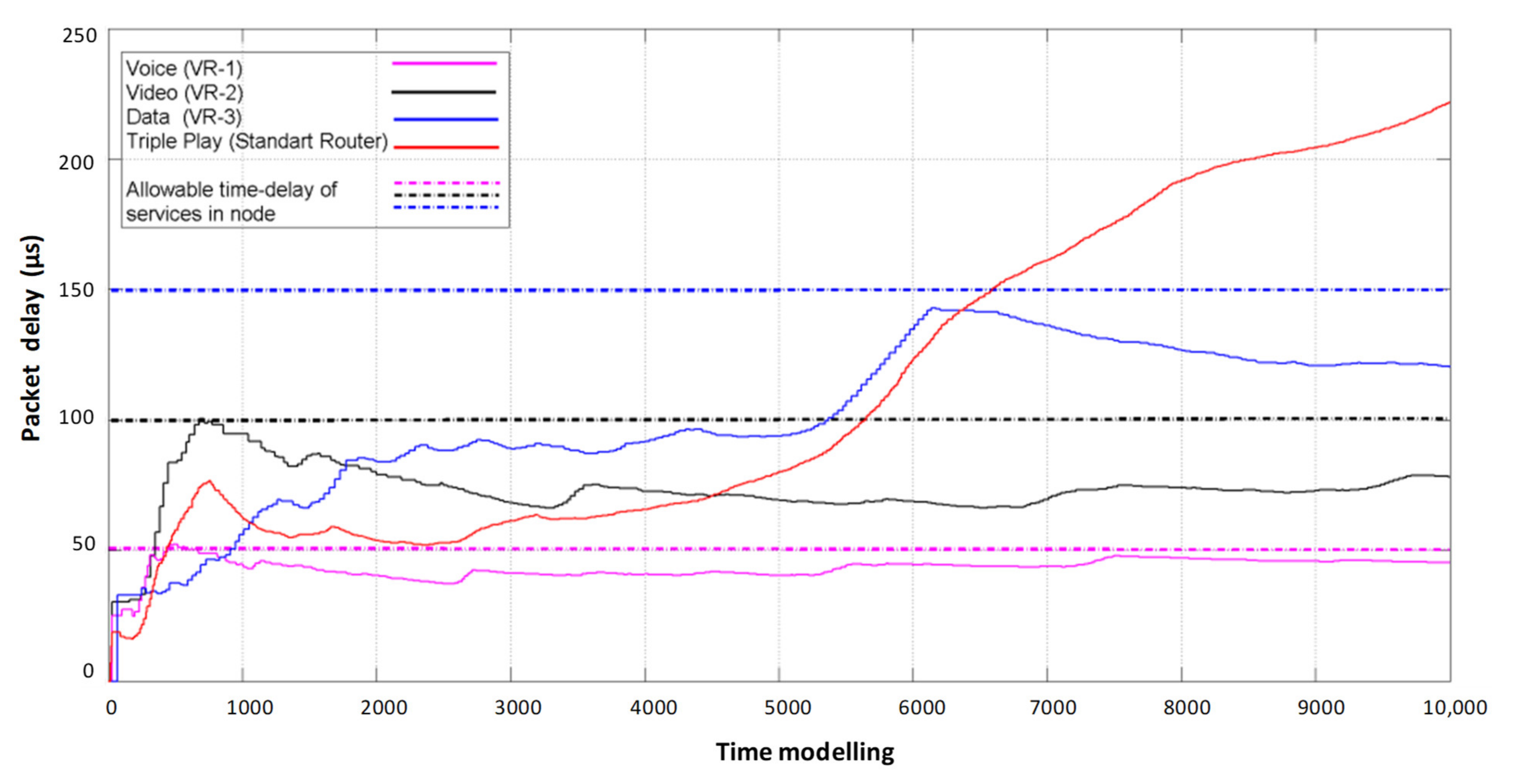
The final result of the proposed simulation model is a comparison of packet delay results of information flow service systems with static reconfiguration of router resources (organization of three virtual routers) and FIFO queue processing in one physical router (Figure 6).
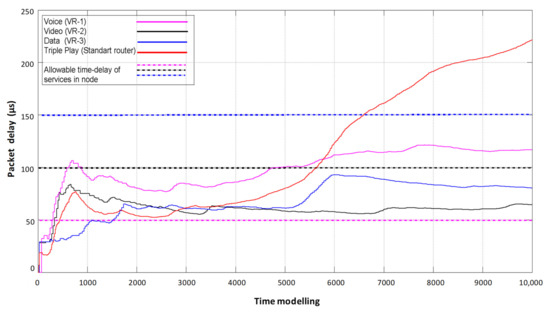
Figure 6.
Comparison of packet delay times in a router without virtualization and with static virtualization of network device resources.
Figure 6 shows the delays occurring on each of the virtual routers when serving its type of traffic. Accordingly, each of the flows has its own allowable duration of a packet staying in the node, depending on the sensitivity of the service to latency according to IT-UT recommendations.
In the case of exceeding the allowable delay by the flows in the node, it is considered that the service experiences a degradation in the quality of service according to the minimum delay criterion. The PR curve reflects the delay of Triple Play flows that occurs in conventional routers without using FIFO queue maintenance virtualization. The disadvantage is that with this flow servicing system, it is not known which packet of which service is experiencing latency at which point in time, and it is difficult to know if the permissible limit is exceeded. In contrast to the previous system, the flow service system with network device virtualization allows fixing delay for each flow separately during the whole model time and to determine at what points of time the exceeding of allowable delay limits occurs.
According to the simulation results, we see that starting from 6600 model time of multiservice flows service by a physical router without virtualization does not provide a proper QoS level because the final delay exceeds the allowable norms of each of the flows. Therefore, the advantages of static virtualization of router resources, where video flows (curve—VR1) and data flows (curve—VR3) are provided with acceptable delay, are clearly seen. However, voice flow delay is also fixed, which is introduced by the VR2 virtual router, in which the moments of exceeding the allowable delay are fixed. As we see, the use of a static virtualization technology network device is not able to fully provide a guaranteed level of QoS to all present flows in the network on the criterion of minimum delay.
The solution to this problem is proposed by using dynamic reconfiguration of the network device resources to organize virtual routers, which allows a flexible management of resources at certain moments of time depending on the input load.
4.2. Modeling and Comparison of Information Flow Service Systems with Dynamic Reconfiguration of Router Resources and Queued Packet Processing
To organize dynamic resource allocation of a physical network device between virtual routers, it is necessary in the simulation model to change the average packet service time, which depends on the nominal CPU frequency. Because the virtual router, which is responsible for voice packet processing, did not provide the proper level of quality of service according to the minimum latency criterion during static resource allocation, the resource manager block will increase the virtual CPU frequency for this machine during dynamic resource allocation, thus reducing the average duration of a packet staying in a virtual node, as its service intensity increases. In practice, this is done by allocating more time to use the total CPU resource of a particular virtual machine.
Consequently, it is theoretically possible to achieve different virtual router performance on a single network device with one physical 1400 MHz processor. This is done by changing the virtual CPU usage time, which would almost match the performance of routers with different nominal CPU frequency, for example 350 MHz, 760 MHz, 240 MHz (Table 4). Thus, virtualization provides the performance of virtual routers, which in practice can be compared to the performance of a nonvirtualized router with a lower processor frequency, which gives virtualization an opportunity for practical use and contributes to its wide dissemination in telecommunications networks.

Table 4.
Source block parameters for three virtual routers (one router—CPU 450 MHz, two router—CPU 760 MHz, three router—CPU 240 MHz) and one physical router without virtualization (CPU 1400 MHz) for a service time 32.5 µs.
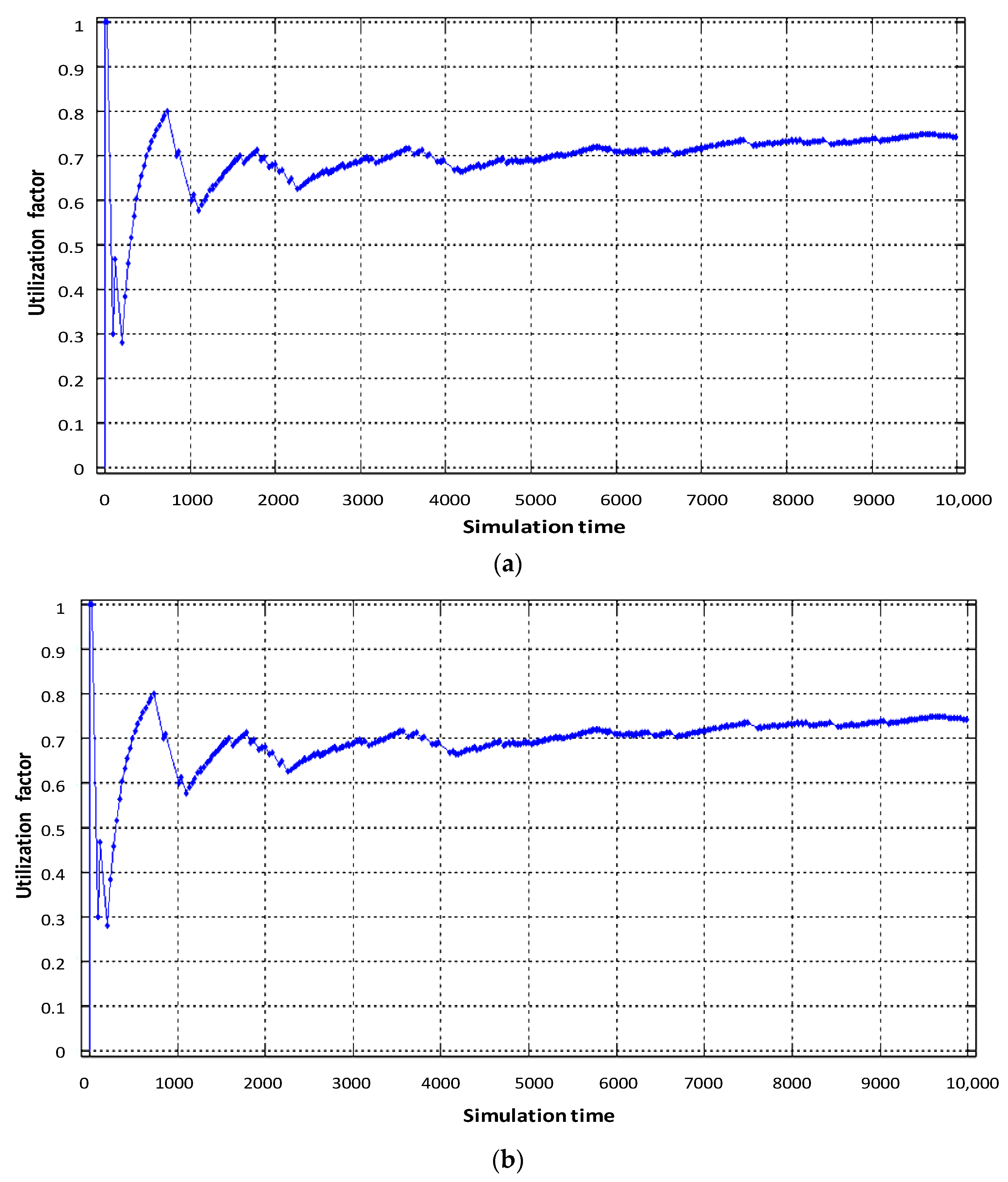
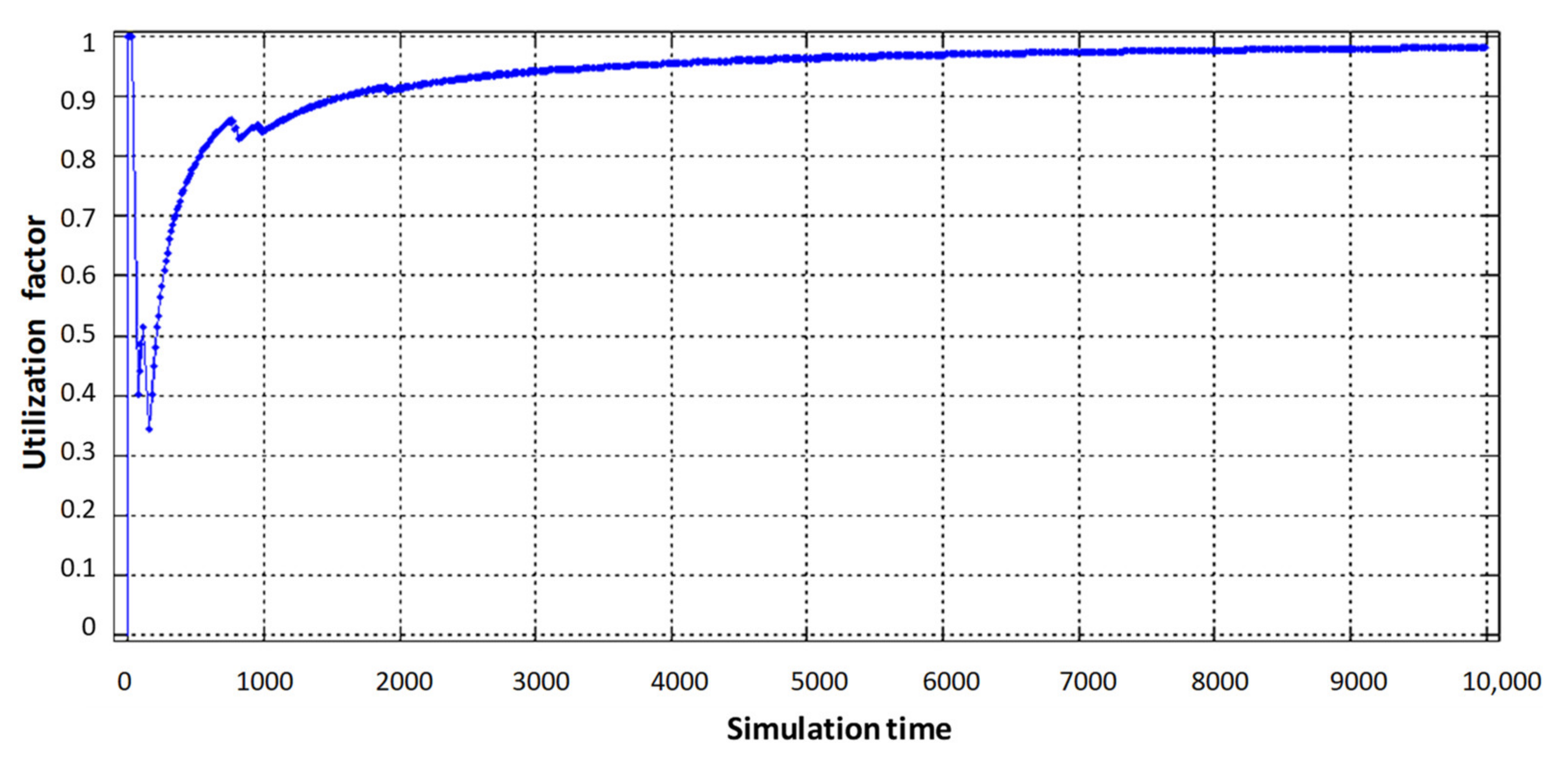
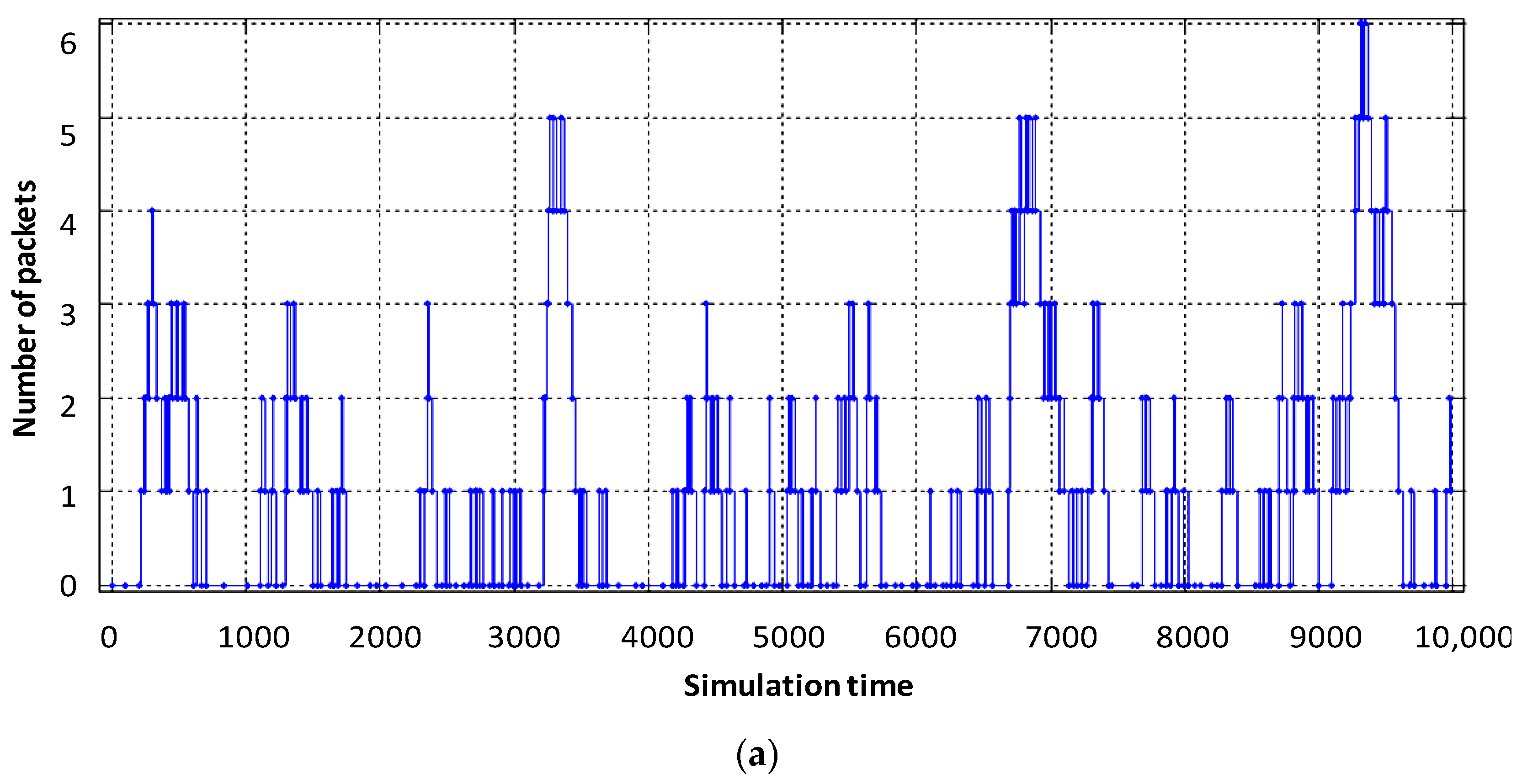
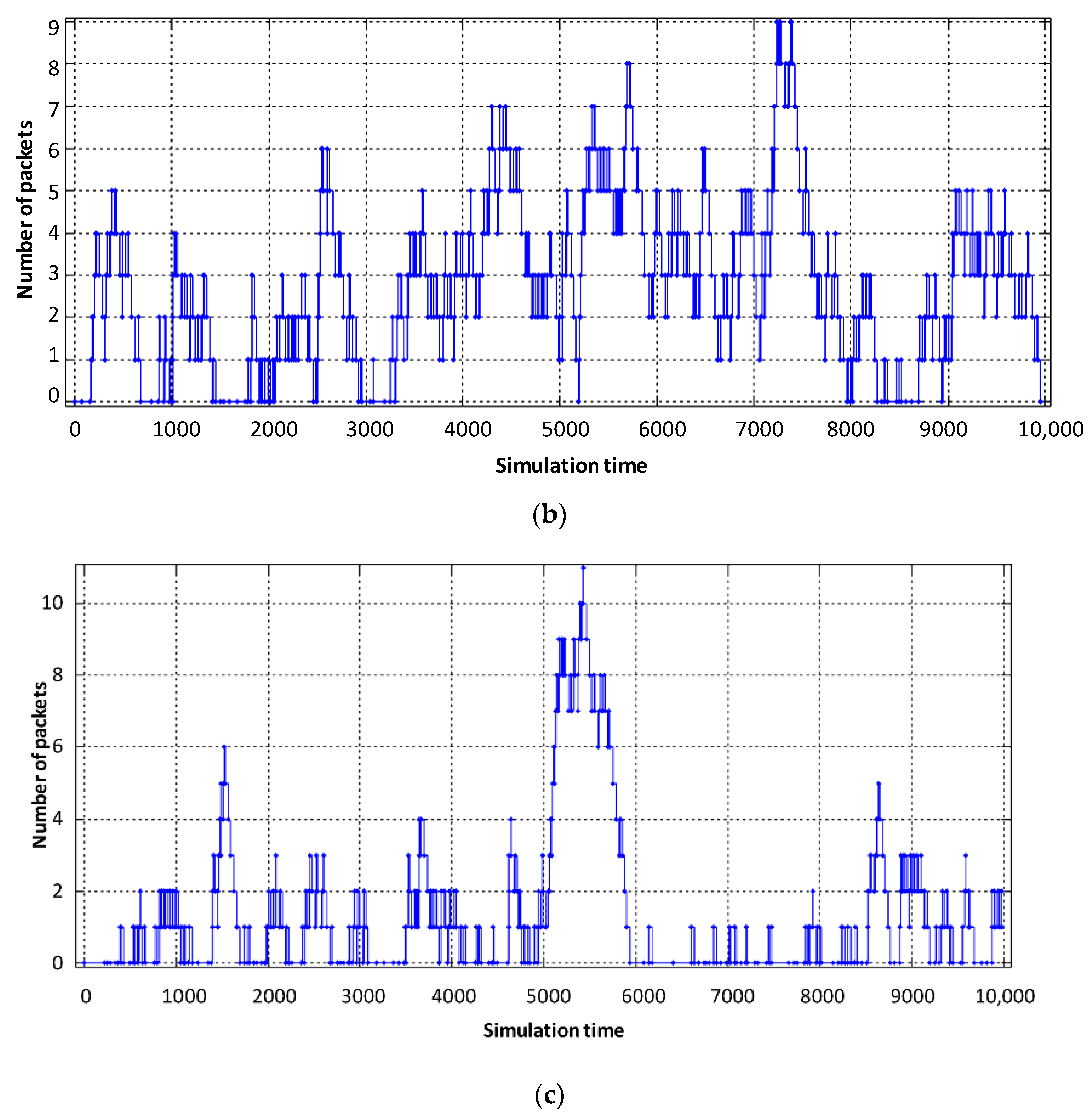
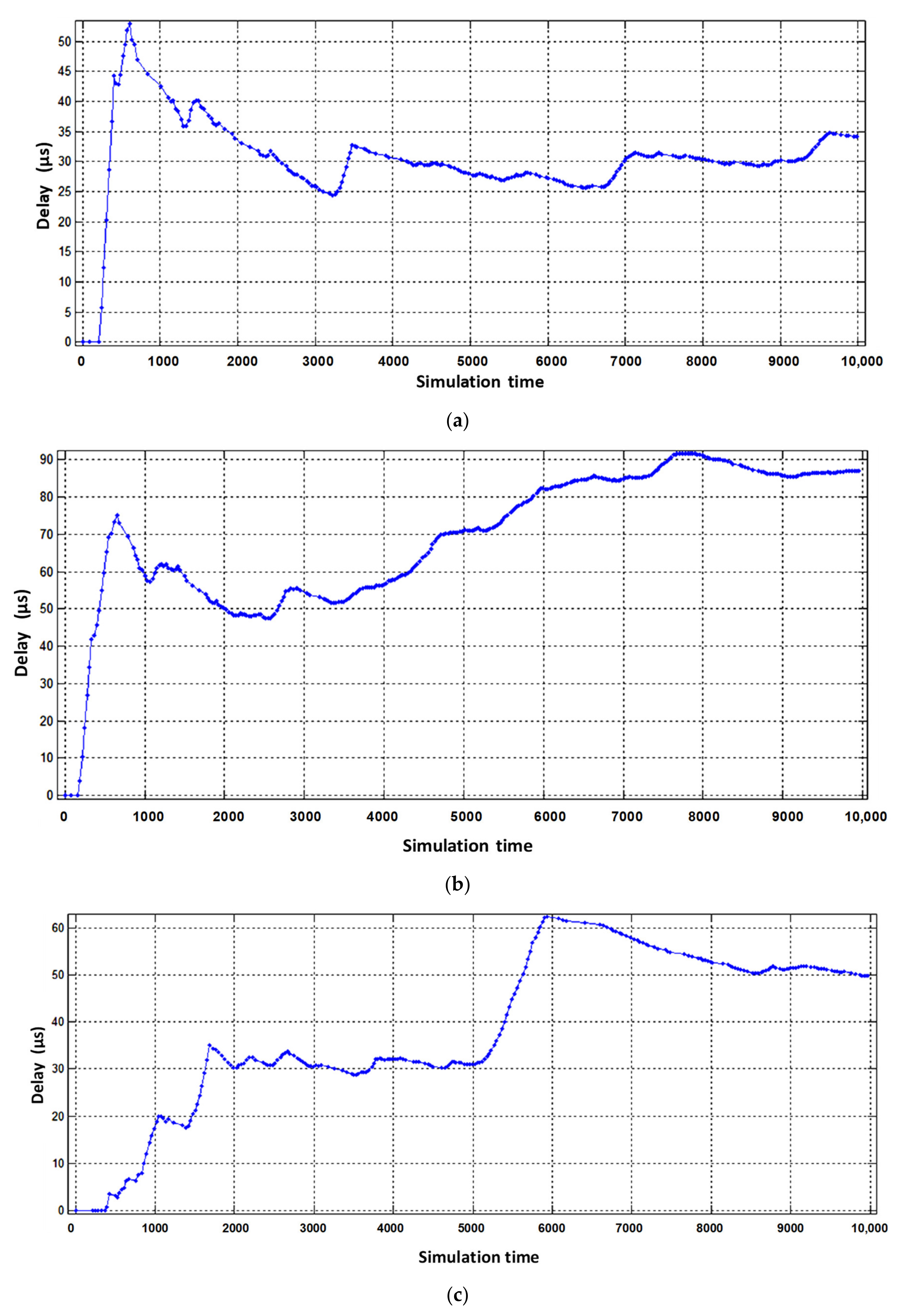
Figure 7 shows load diagrams for each virtual router, depending on the intensity of incoming traffic when dynamically allocating router computing resources.
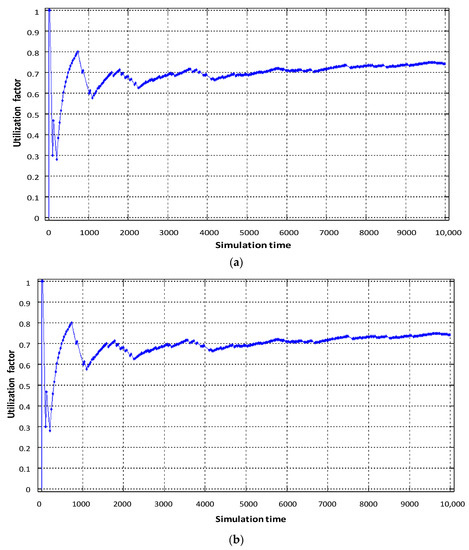
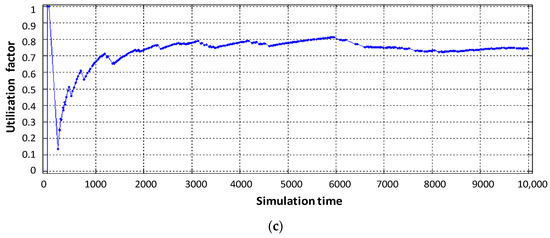
Figure 7.
Service device loading of the virtual router with flows: (a) video, (b) voice, (c) data.
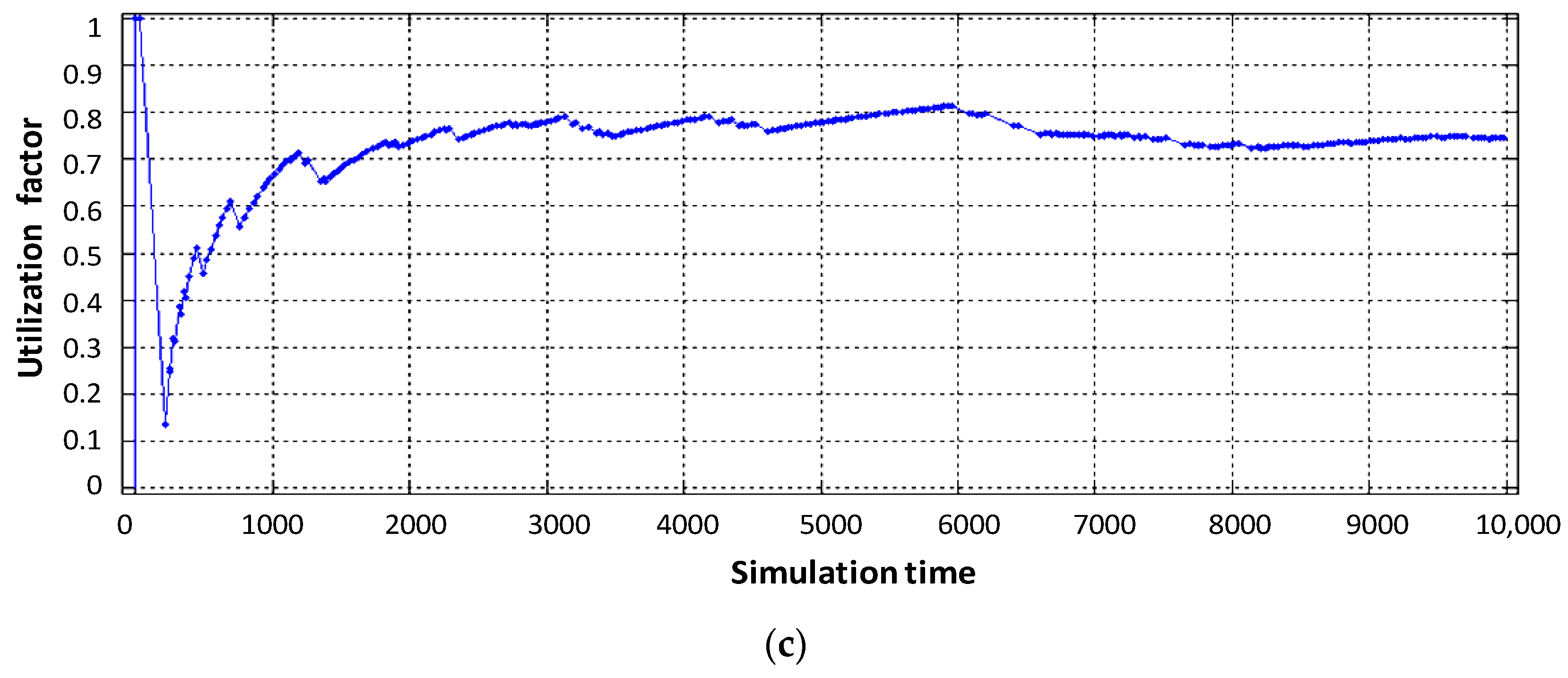
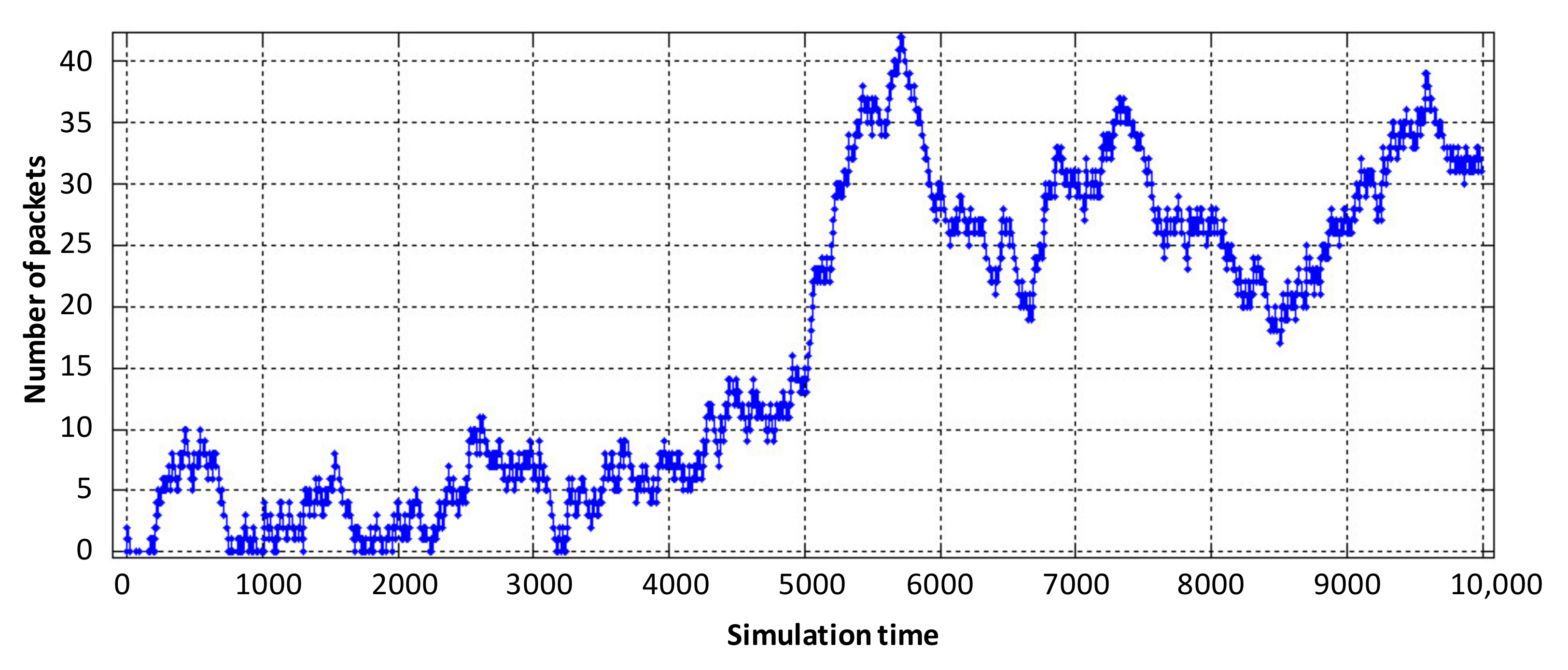
As can be seen in Figure 7b, the utilization factor of the virtual router when serving voice traffic decreased from 0.9 (static virtualization) to 0.7 (dynamic virtualization). This is explained by the fact that with dynamic allocation of computing resources, the performance of the virtual router, which processes voice traffic, has increased due to the fact that the intensity of traffic servicing by the device has increased, by allocating a larger access time window to the router’s CPU space. Accordingly, this situation leads to a decrease in the performance of the virtual router dedicated to data flow. With the same load on the virtual router serving device (data flow), the allocated CPU usage time in dynamic virtualization is less compared to static virtualization. Therefore, the load factor of the virtual router when serving the data flow increased from 0.75 to 0.85 (Figure 7c). Service device loading of the physical router with Triple Play flows is depicted in Figure 8. The impact of virtual router buffer utilization during dynamic virtualization is shown in Figure 9 and physical router utilization in Figure 10.
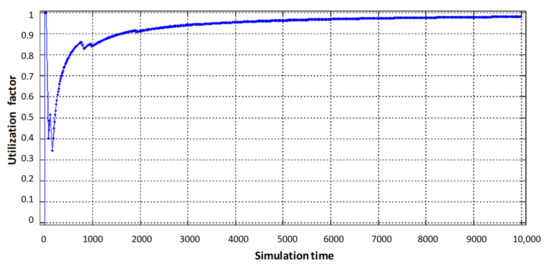
Figure 8.
Service device loading of the physical router with Triple Play flows.
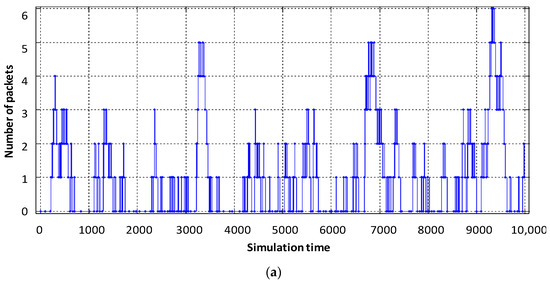
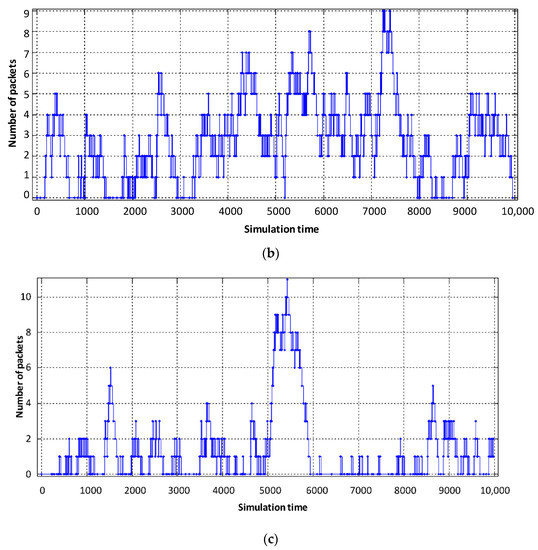
Figure 9.
Loading the virtual router buffer with flows: (a) video, (b) voice, (c) data.
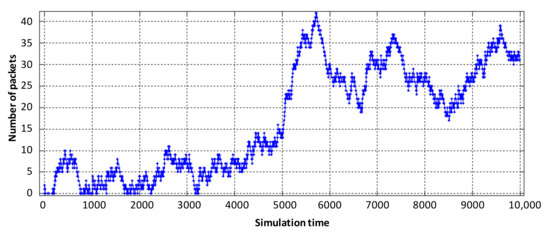
Figure 10.
Loading the physical router buffer with Triple Play flows.
From the obtained results it can be seen that the average number of packets in the buffer of the virtual router, designed to serve voice flows, decreased from six to three (Figure 9b). The obtained result is explained by the fact that the intensity of packets serviced by the virtual router when servicing voice traffic has increased. However, for the other two virtual routers, the average number of packets in the buffer increased by 2–3 packets (Figure 9a,c). The delay caused by buffering is shown in Figure 11 and Figure 12.
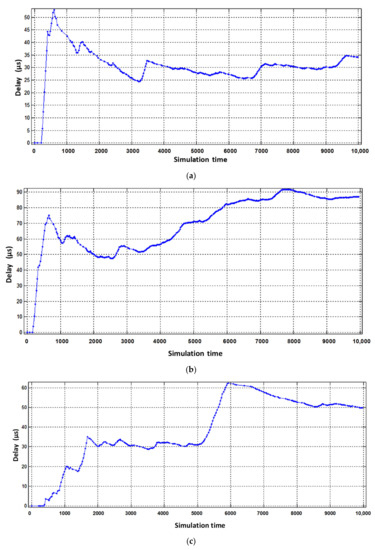
Figure 11.
Delay of virtual router buffering when serving (a) video, (b) voice, (c) data.
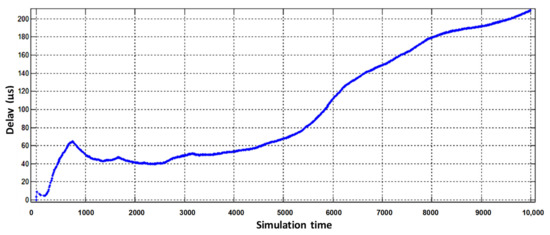
Figure 12.
Delay of physical router buffering when serving aggregated flow.
From the obtained simulation results, we see that the average value of voice traffic buffering delay decreased from 75 µs to 25 µs. For the other two virtual routers, the buffering delay compared to the static virtualization increased within the allowable value of Figure 11c.
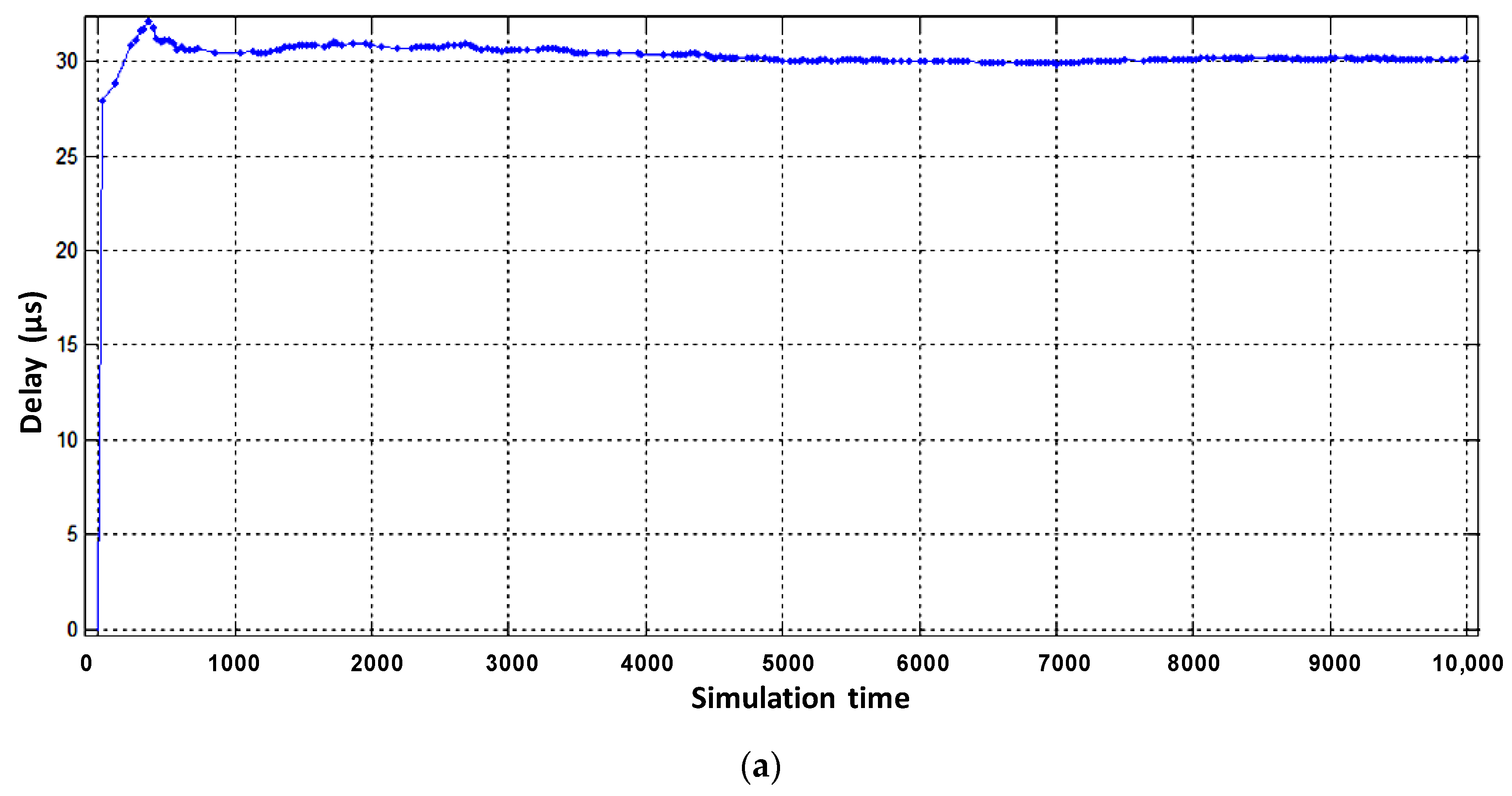
Figure 13 and Figure 14 shows the sum of processor and interface packet latency for the virtual and physical router, respectively.
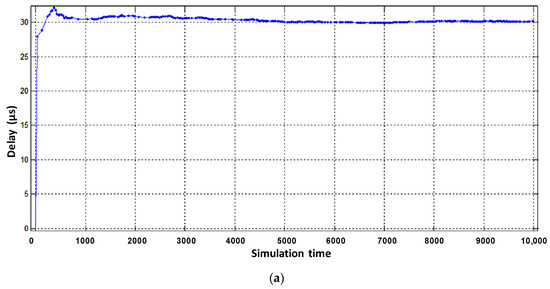
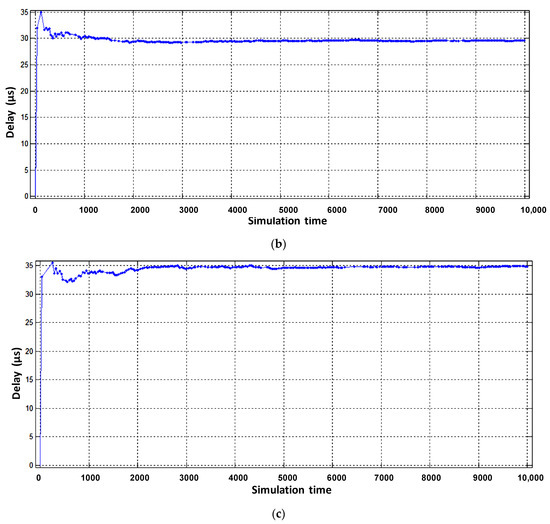
Figure 13.
The sum of processor and interface packet latency of the virtual router when serving flow: (a) video, (b) voice, (c) data.
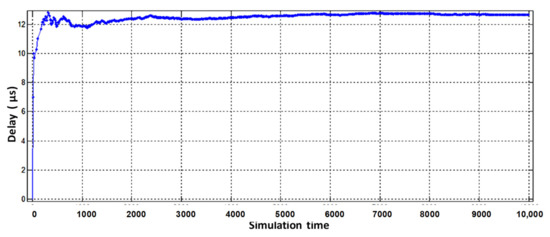
Figure 14.
The sum of processor and interface packet latency of the physical router when serving aggregate flow.
The final result of the proposed simulation model is a comparison of the results of packet delay of information flow service systems with dynamic reconfiguration of router resources (organization of three virtual routers) and the processing of packets in FIFO order in one physical router (Figure 15).
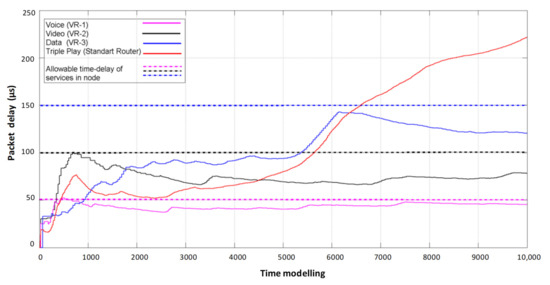
Figure 15.
Comparison of packet delay times in a router without virtualization and with dynamic virtualization of network device resources.
By analyzing the obtained results, we see that the duration of packet delay in all virtual nodes of the class destination do not exceed permissible values by dynamically balancing the computing resources between them. Therefore, based on the results obtained, it is proved that the dynamic virtualization of the network device provides a guaranteed level of quality of service for all transmitted flows in the multiservice network.
4.3. Modeling of Incoming Flows Service Systems with Static and Dynamic Reconfiguration of Node Resources and Comparison with Priority Packet Processing
When comparing the performance of an information flow service system with resource virtualization to a system without virtualization using the FIFO queue service algorithm, network device virtualization technology offers a gain. This gain relates to the flexibility of resource management, which allows the providing of a guaranteed level of service for multiservice flows.
Therefore, the next step of this research is to compare the virtualization technology of the router with the standard router, which is configured according to the principle of priority processing of queues. For this purpose, in the developed simulation model, the Fifo Queue4 block in the physical router under number four should be changed to Priority Queue block, in which case packets will be served in the order of priorities. To do this, in the Time-Based Entity Generator, Time-Based Entity Generator1, Time-Based Entity Generator2 blocks, which are responsible for generating flows in the Generation event priority window, you should set the flow priority: data-1, video-2 and voice-3. A larger value means a higher priority and is served first. In order to divide the total delay of packets between the transmitted flows, the original schedule priority flow delay block is proposed by writing program code that reads its priority when analyzing a packet. Then it forms an appropriate array of delay values and sends them to the Mux2 block to visually and graphically display the delays for each flow separately.
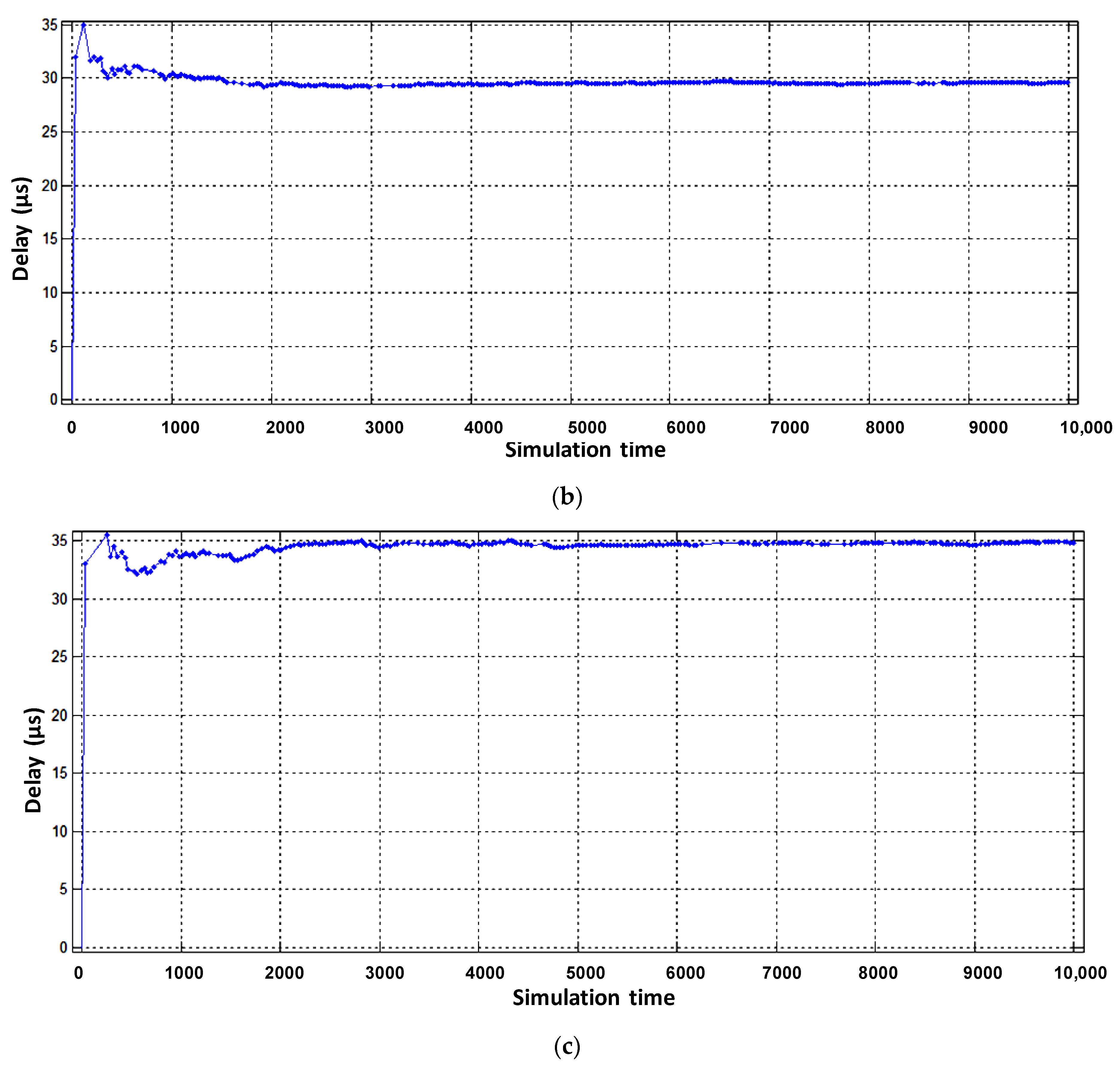
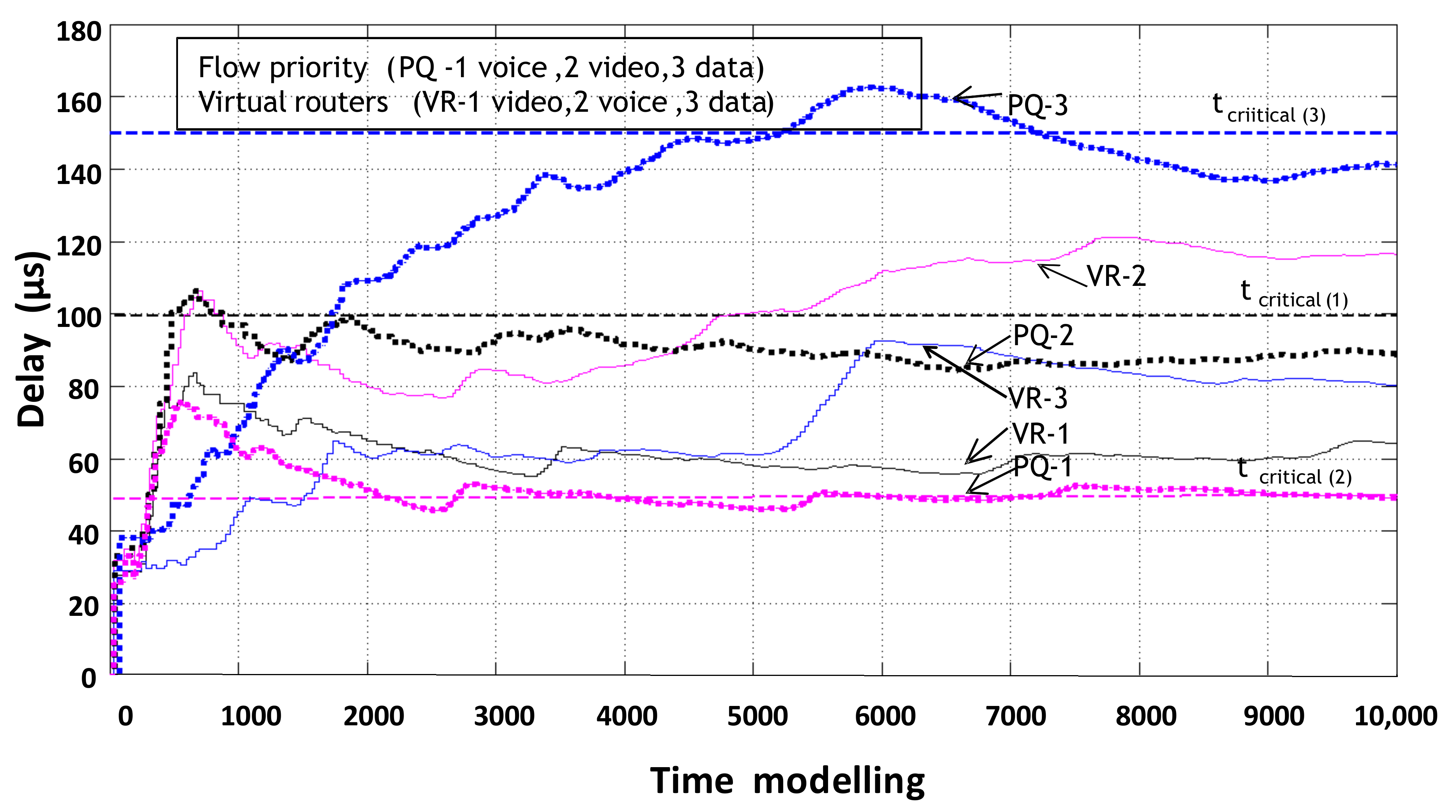
The final result of this simulation model is a comparison of packet delay results of information flow service systems with static reconfiguration of router resources (organization of three virtual routers) and processing of packets in PQ priority queuing order priority service in one physical router (Figure 16).
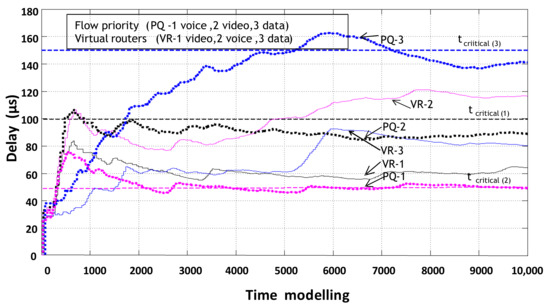
Figure 16.
Comparison of packet delay times in a router with prioritized service and with static virtualization of network device resources.
When compared with prioritized packet services, static virtualization for voice flow gives the worst latency result. This is because of prioritized services; voice packets have the highest priority and are served first. However, the other two flows at some points in the model time exceed the allowable latency norm and are large compared to the latency that static virtualization provides. Therefore, neither service system is able to guarantee the quality of service of the threads.
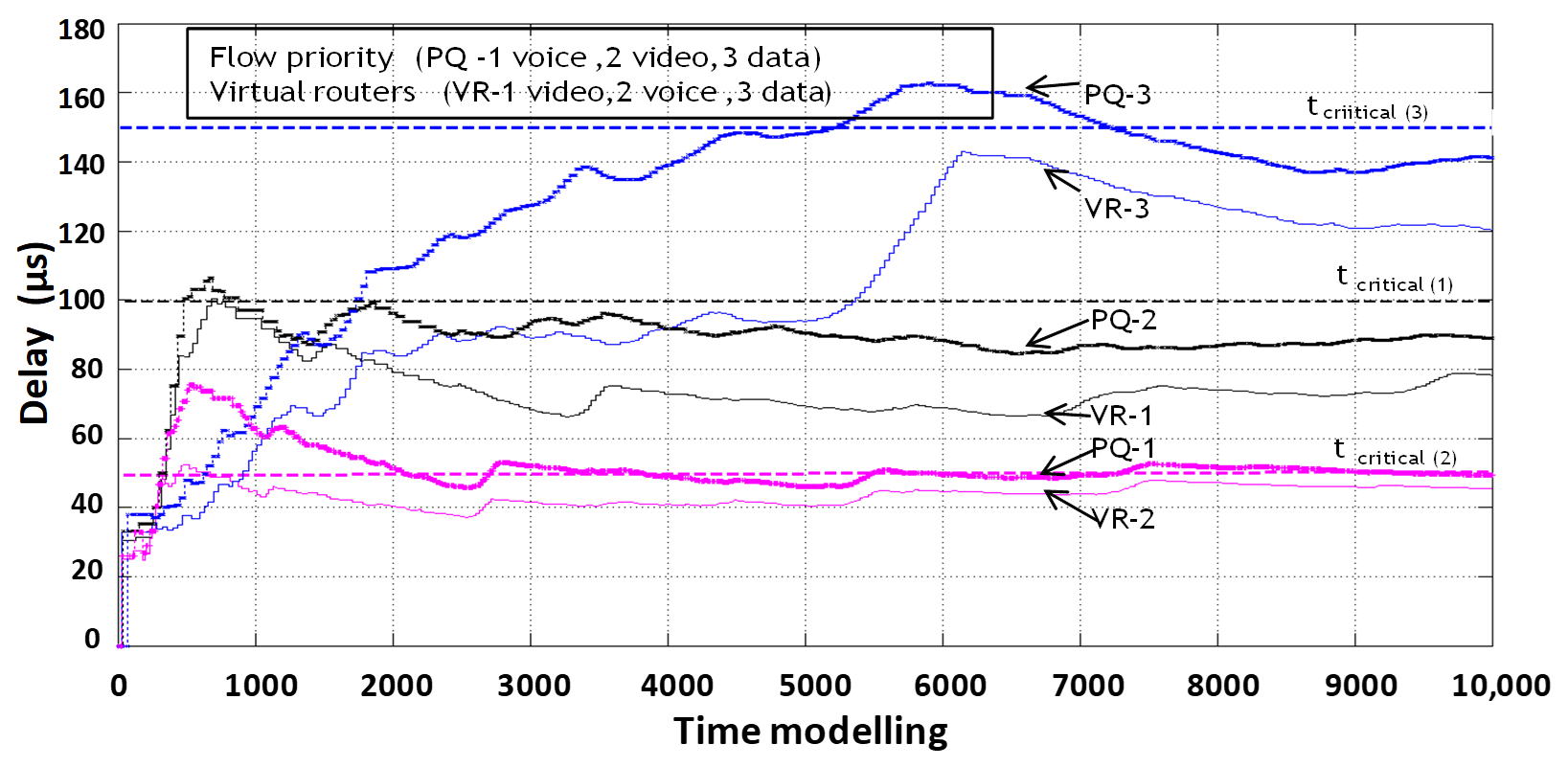
The next step of the research is to compare the results of packet delay of information flow service systems with dynamic reconfiguration of router resources (organization of three virtual routers) and packet processing in the order of PQ in a physical router (Figure 17).
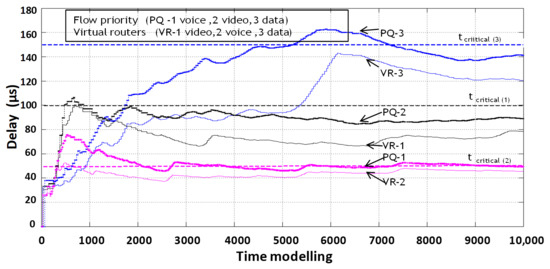
Figure 17.
Comparison of packet delay times in a router with prioritized service and with dynamic virtualization of network device resources.
From the simulation results (Figure 16 and Figure 17), it can be seen that the system of priority service of information flows is not able to provide all flows a guaranteed level of QoS on the criterion of minimum delay and is less efficient compared to the system of dynamic virtualization of computing resources of the router.
5. Conclusions
A simulation model of a packet router with resource virtualization has been developed for future internet networking. The model will allow designers to choose optimal parameters of network equipment for the organization of virtual routers, which, unlike the existing principle of service, will provide the necessary quality of service provision to end users. We have compared the system of information flow service with static virtualization of router computing resources with the system, functioning in the existing standard routers to the FIFO queue service algorithm. We have established the effectiveness area of virtual routers with static allocation of resources by the criterion of minimum delay required to ensure a guaranteed level of service quality.
Because the use of static network device virtualization technology is not able to fully provide a guaranteed level of QoS to all present flows in the network by the criterion of minimum delay, we proposed a model of dynamic reconfiguration of network device resources for virtual routers, which allows more flexible management of resources at certain times depending on the input load. It is proved that the dynamic virtualization of the network device provides a guaranteed level of quality of service for all transmitted flows in the multiservice network. The investigation and comparison of the results of the packet delay of the information flows service systems with static and dynamic reconfiguration of the router resources (organization of three virtual routers) with the system of priority service in one physical router have been made. From the simulation results, it can be seen that the priority service system of information flows is not able to provide all the flows of the guaranteed level of QoS by the criterion of minimum delay and is less effective in comparison with the system of dynamic virtualization of computing router resources.
In this paper, we simulate and investigate the impact of the method of managing the structural parameters of the router with resource virtualization on the quality of service of information flows.
The obtained results were used to formulate recommendations for the selection of necessary structural and functional parameters of such a system, as well as to study the dependence of service quality parameters on changes in the service system parameters and the intensity of incoming flows. It was found that with the growth of the network node utilization factor, the buffer size grows exponentially, and at high values of this factor increases linearly. A model was developed that allows us to choose the optimal parameters of virtual service systems according to the given delay and losses. Moreover, the inverse problem can be solved. This approach can be used at the design stage, as well as to improve the efficiency of network operation.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Methodology, M.B. and H.B. Formal analysis and investigation, O.Y. and H.B. Writing of the original draft preparation N.K. and H.B. Writing of review and editing, M.B. and J.P. Funding acquisition N.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Ukrainian project No 0120U100674 “Development of the novel decentralized mobile network based on blockchain-architecture and artificial intelligence for 5G/6G development in Ukraine”. This work was supported by the Ukrainian project No. 0120U102201 “Development the methods and unified software-hardware means for the deployment of the energy efficient intent-based multi-purpose information and communication networks”, and by the Faculty of Management of Comenius University in Bratislava, Slovakia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Erjavec, H.; Dmitrovic, T.; Povalej, P. Drivers of Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty in Service Industries. J. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2016, 17, 810–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakabitze, A.A.; Barman, N.; Ahmad, A.; Zadtootaghaj, S.; Sun, L.; Martini, M.G.; Atzori, L. QoE Management of Multimedia Streaming Services in Future Networks: A Tutorial and Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 526–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewage, C.; Ekmekcioglu, E. Multimedia Quality of Experience (QoE): Current Status and Future Direction. Future Internet 2020, 12, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-J.; Hwang, P.-C.; Hwang, W.-S.; Cheng, M.-H. Artificial Intelligence Enabled Routing in Software Defined Networking. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujcich, B.E.; Bates, A.; Sanders, W.H. Provenance for Intent-Based Networking. In Proceedings of the 2020 6th IEEE Conference on Network Softwarization (NetSoft), Ghent, Belgium, 29 June–3 July 2020; pp. 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.; Shah, N.; Tahir, A. Graph-Based Policy Change Detection and Implementation in SDN. Electronics 2019, 8, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraz, M.; Ismail, M. INMTD: Intent-based Moving Target Defense Framework using Software Defined Networks. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2020, 10, 5142–5147. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Song, L. Analysis of an SDN-Based Cooperative Caching Network with Heterogeneous Contents. Electronics 2019, 8, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, K.; Afaq, M.; Ahmed Khan, T.; Rafiq, A.; Song, W.-C. Slicing the Core Network and Radio Access Network Domains through Intent-Based Networking for 5G Networks. Electronics 2020, 9, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Yang, C.; Chen, D.; Song, Y.; Guizani, M. A survey on intent-driven networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 22862–22873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrus, R.; Sallent, O.; Pérez-Romero, J.; Agusti, R. On 5G radio access network slicing: Radio interface protocol features and configuration. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshley, M.; Veselý, P.; Pryslupskyi, A.; Beshley, H.; Kyryk, M.; Romanchuk, V.; Kahalo, I. Customer-Oriented Quality of Service Management Method for the Future Intent-Based Networking. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshley, M.; Pryslupskyi, A.; Panchenko, O.; Beshley, H. SDN/Cloud Solutions for Intent-Based Networking. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Advanced Information and Communications Technologies (AICT), Lviv, Ukraine, 2–6 July 2019; pp. 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Beshley, M.; Pryslupskyi, A.; Panchenko, O.; Seliuchenko, M. Dynamic Switch Migration Method Based on QoE- Aware Priority Marking for Intent-Based Networking. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 15th International Conference on Advanced Trends in Radioelectronics, Telecommunications and Computer Engineering (TCSET), Lviv-Slavske, Ukraine, 20–23 February 2020; pp. 864–868. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiq, A.; Mehmood, A.; Ahmed Khan, T.; Abbas, K.; Afaq, M.; Song, W.-C. Intent-Based End-to-End Network Service Orchestration System for Multi-Platforms. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agiwal, M.; Kwon, H.; Park, S.; Jin, H. A Survey on 4G-5G Dual Connectivity: Road to 5G Implementation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 16193–16210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-B.; Tseng, C.-C.; Wang, M.-H. Effects of Transport Network Slicing on 5G Applications. Future Internet 2021, 13, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Wei, Y. A Virtual Network Resource Allocation Framework Based on SR-IOV. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, L.; Lo Bello, L.; Aglianò, S. Priority-Based Bandwidth Management in Virtualized Software-Defined Networks. Electronics 2020, 9, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliwal, M.; Shrimankar, D. Effective Resource Management in SDN Enabled Data Center Network Based on Traffic Demand. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 69698–69706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blenk, A.; Basta, A.; Reisslein, M.; Kellerer, W. Survey on Network Virtualization Hypervisors for Software Defined Networking. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 655–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monowar, M.M.; Rahman, M.O.; Hong, C.S.; Lee, S. MQ-MAC: A Multi-Constrained QoS-Aware Duty Cycle MAC for Heterogeneous Traffic in Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2010, 10, 9771–9798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klymash, M.; Beshley, M.; Stryhaluk, B. System for Increasing Quality of Service of Multimedia Data in Convergent Networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 First International Scientific-Practical Conference Problems of Infocommunications Science and Technology, Kharkov, Ukraine, 22 December 2014; pp. 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Beshley, M.; Romanchuk, V.; Seliuchenko, M.; Masiuk, A. Investigation the Modified Priority Queuing Method Based on Virtualized Network Test Bed. In Proceedings of the Experience of Designing and Application of CAD Systems in Microe-lectronics, Lviv, Ukraine, 24–27 February 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Romanchuk, V.; Beshley, M.; Panchenko, O.; Arthur, P. Design of Software Router with a Modular Structure and Automatic Deployment at Virtual Nodes. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conference on Advanced Information and Communication Technologies (AICT), Lviv, Ukraine, 4–7 July 2017; pp. 295–298. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Hong, C.-H.; Hwang, J.; Yoo, C. Dynamic Network Scheduling for Virtual Routers. IEEE Syst. J. 2020, 14, 3618–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efrosinin, D.; Stepanova, N.; Sztrik, J.; Plank, A. Approximations in Performance Analysis of a Controllable Queueing System with Heterogeneous Servers. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kim, J.-S.; Seok, J.-S.; Jin, H.-W. Virtualization of Industrial Real-Time Networks for Containerized Controllers. Sensors 2019, 19, 4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suksomboon, K.; Matsumoto, N.; Okamoto, S.; Hayashi, M.; Ji, Y. Configuring a Software Router by the Erlang- k -Based Packet Latency Prediction. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2018, 36, 422–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.; Alkmim, G.P.; Fonseca, N.L.S.; Batista, D.M. Energy-Aware Mapping and Live Migration of Virtual Networks. IEEE Syst. J. 2017, 11, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Medhi, D. Optimally Selecting Standby Virtual Routers for Node Failures in a Virtual Network Environment. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2017, 14, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Yao, J.; Guan, H.; Gao, P. gQoS: A QoS-Oriented GPU Virtualization with Adaptive Capacity Sharing. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2020, 31, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Xiao, A.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wu, S.; Yang, L. On Virtual Resource Allocation of Heterogeneous Networks in Virtualization Environment: A Service Oriented Perspective. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2020, 7, 2468–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, H. Aggressive Resource Provisioning for Ensuring QoS in Virtualized Environments. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2015, 3, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, S.; Chen, T.; Ristaniemi, T. Towards Service-Oriented 5G: Virtualizing the Networks for Everything-as-a-Service. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouvatsos, D.; Assi, S.A. Notice of Violation of IEEE Publication Principles: On the Analysis of Queues with Long Range Dependent Traffic: An Extended Maximum Entropy Approach. In Proceedings of the Next Generation Internet Networks, Trondheim, Norway, 21–23 May 2007; pp. 226–233. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).