Design and Passive Training Control of Elbow Rehabilitation Robot
Abstract
:1. Introduction
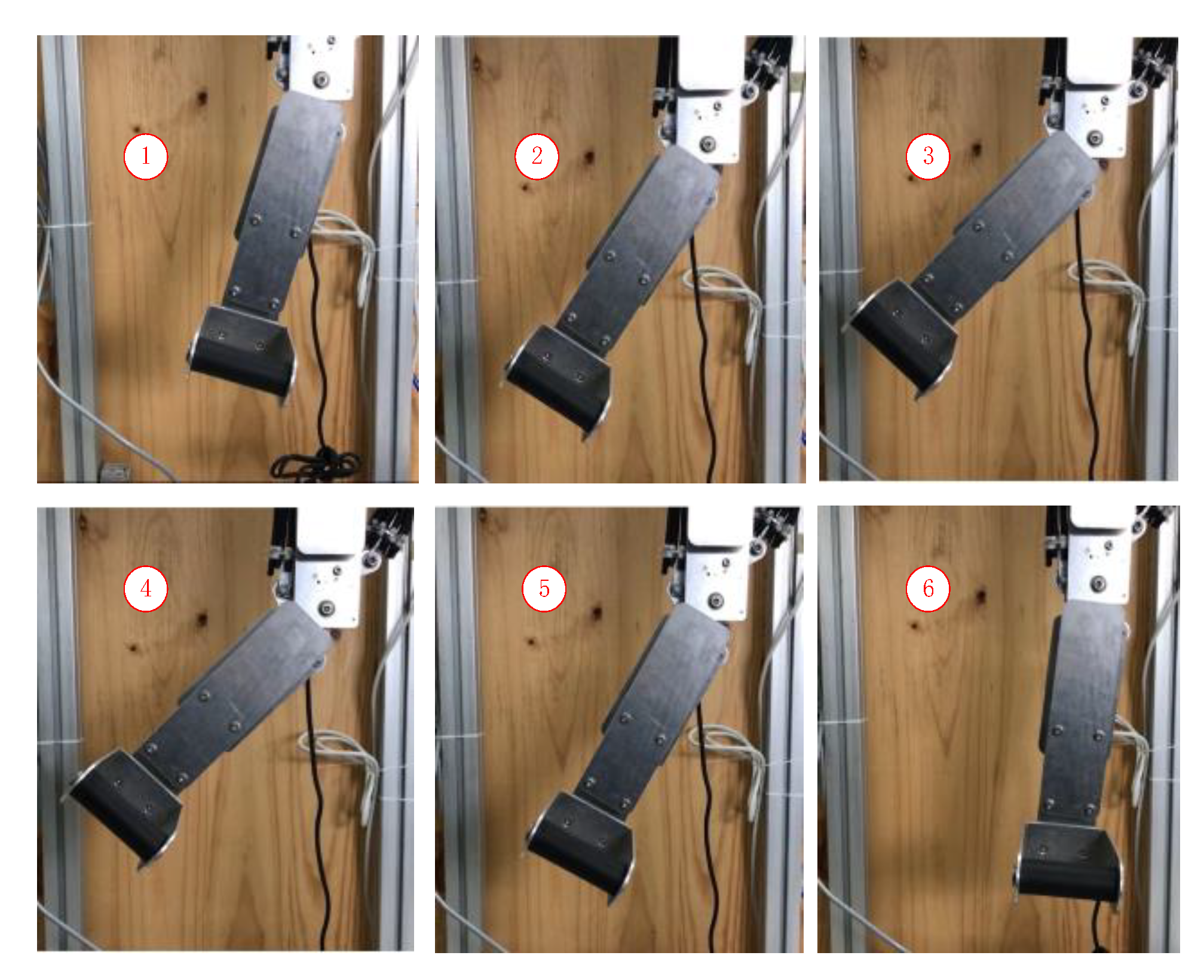
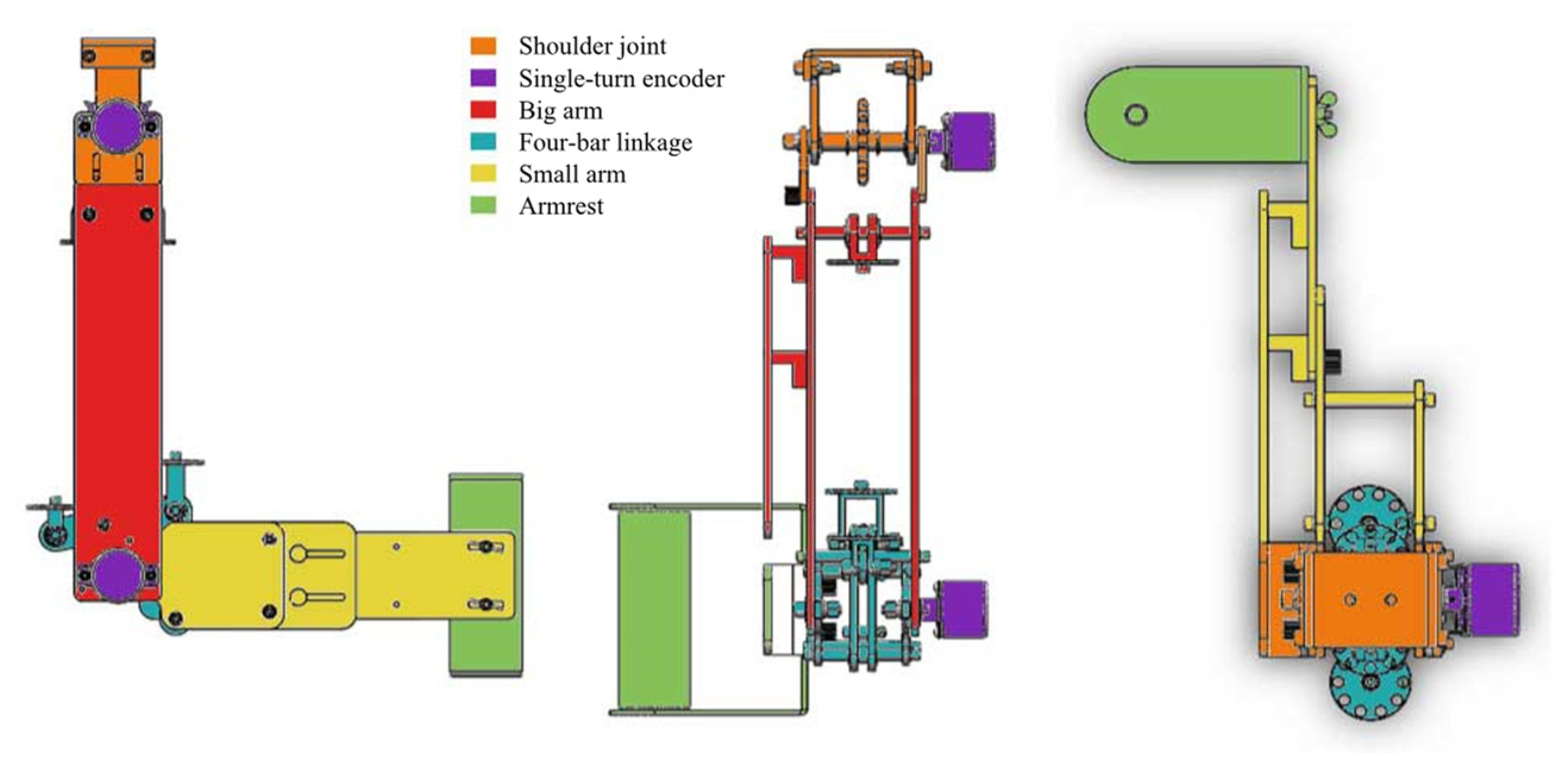
2. Design of Rehabilitation Robot Prototype
3. Elbow Rehabilitation Robot Modeling
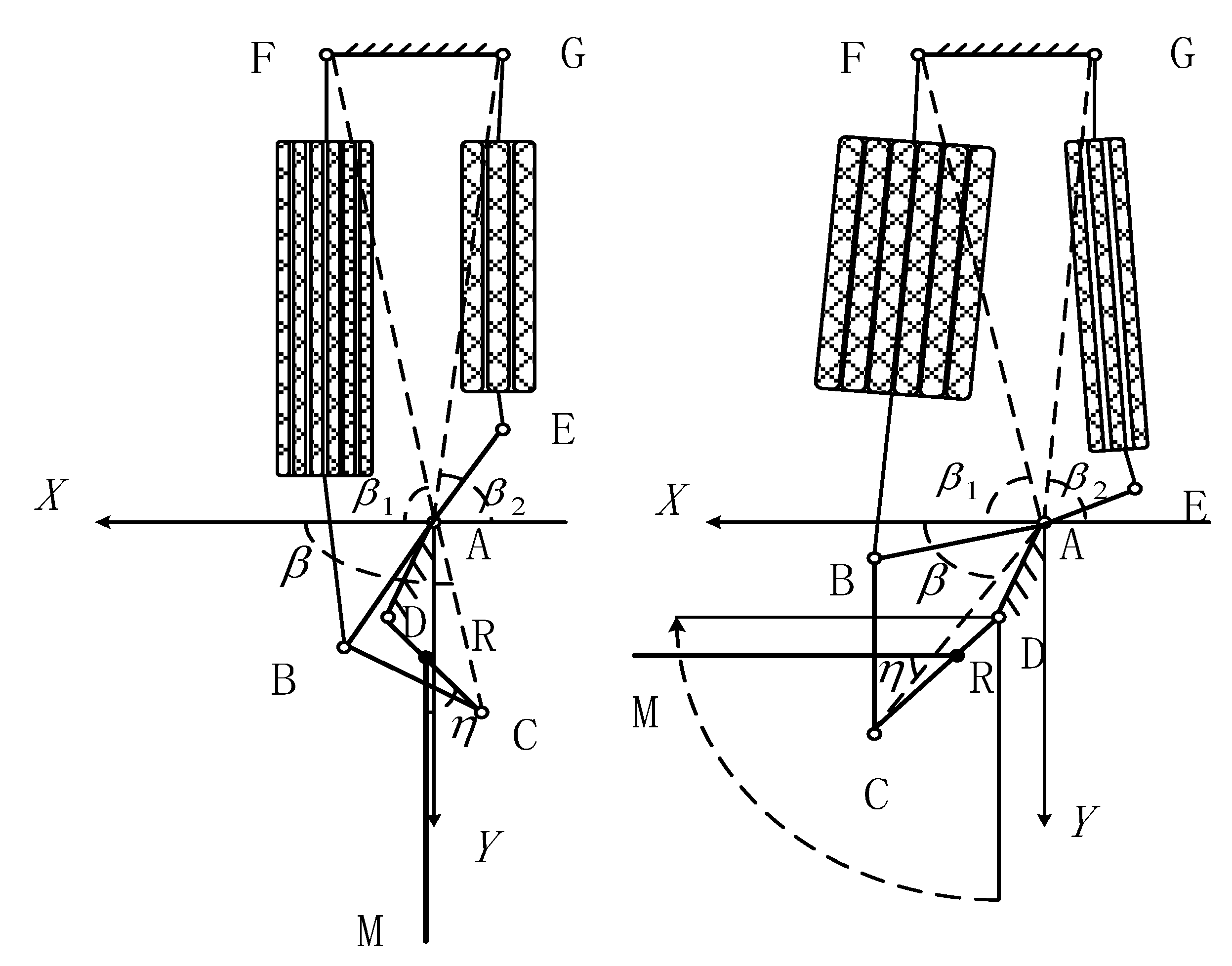
3.1. Kinematic Model
3.2. Joint Model
4. Passive Training Control Algorithms for Elbow Rehabilitation Robot
4.1. Disturbance Sources in Rehabilitation Process
4.2. Active Disturbance Rejection Control of Elbow Rehabilitation Robot
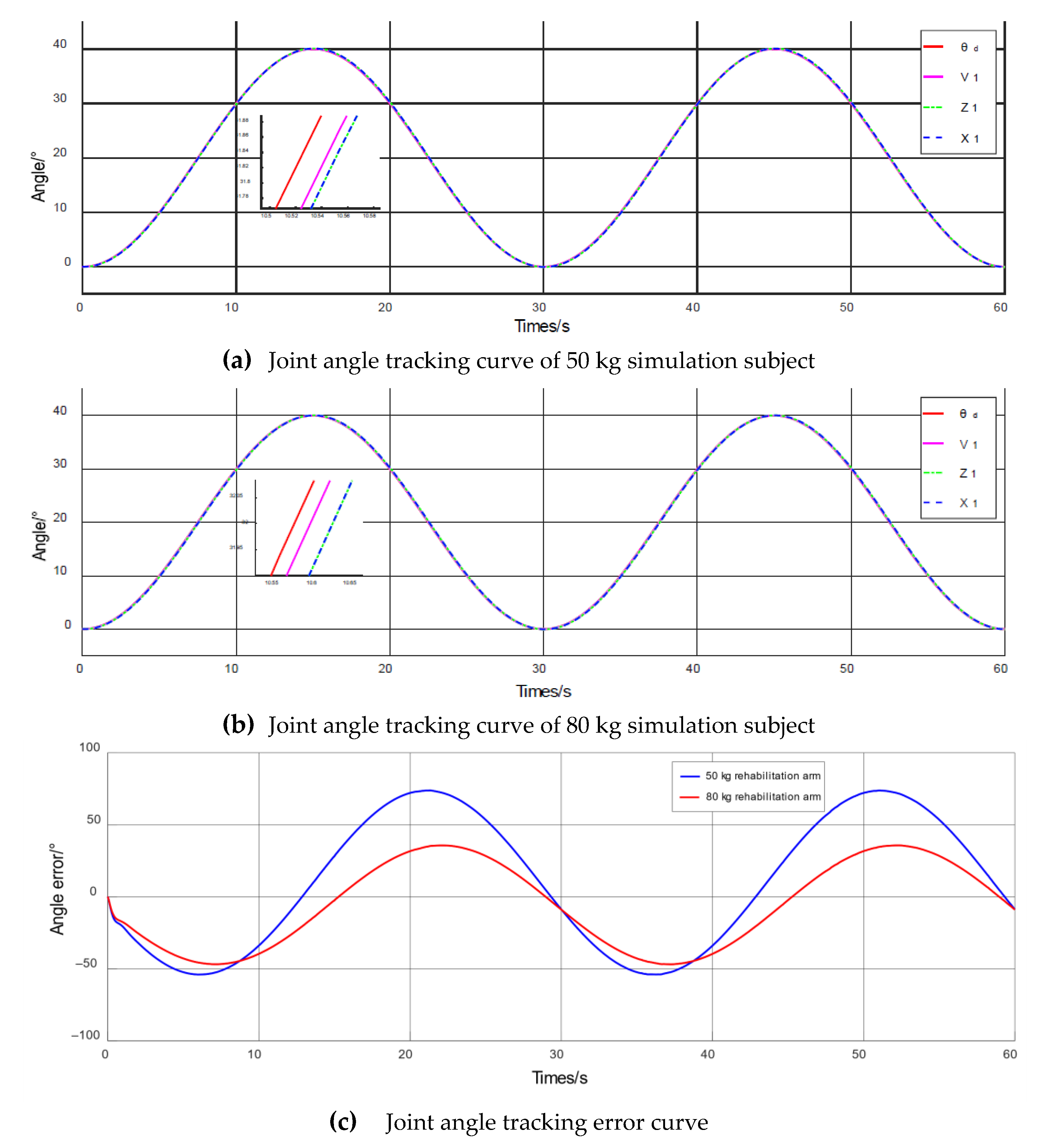
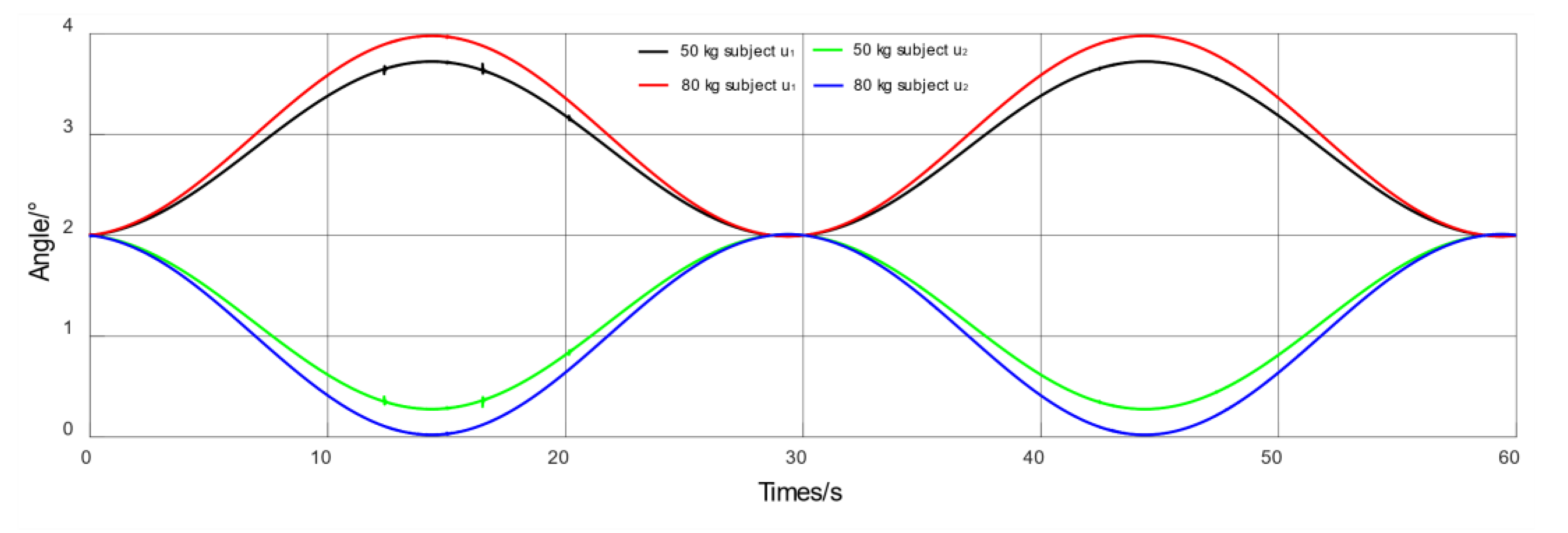
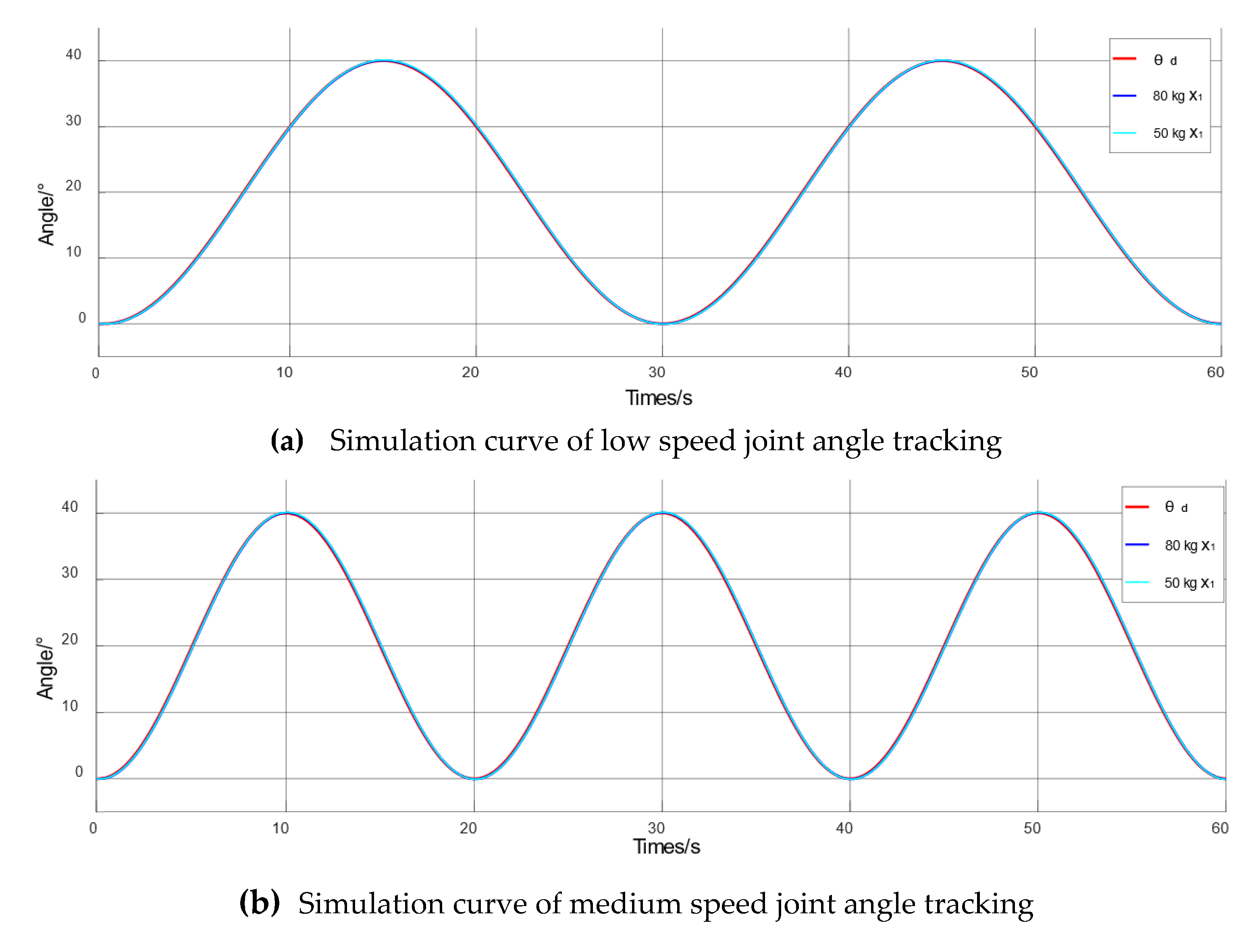
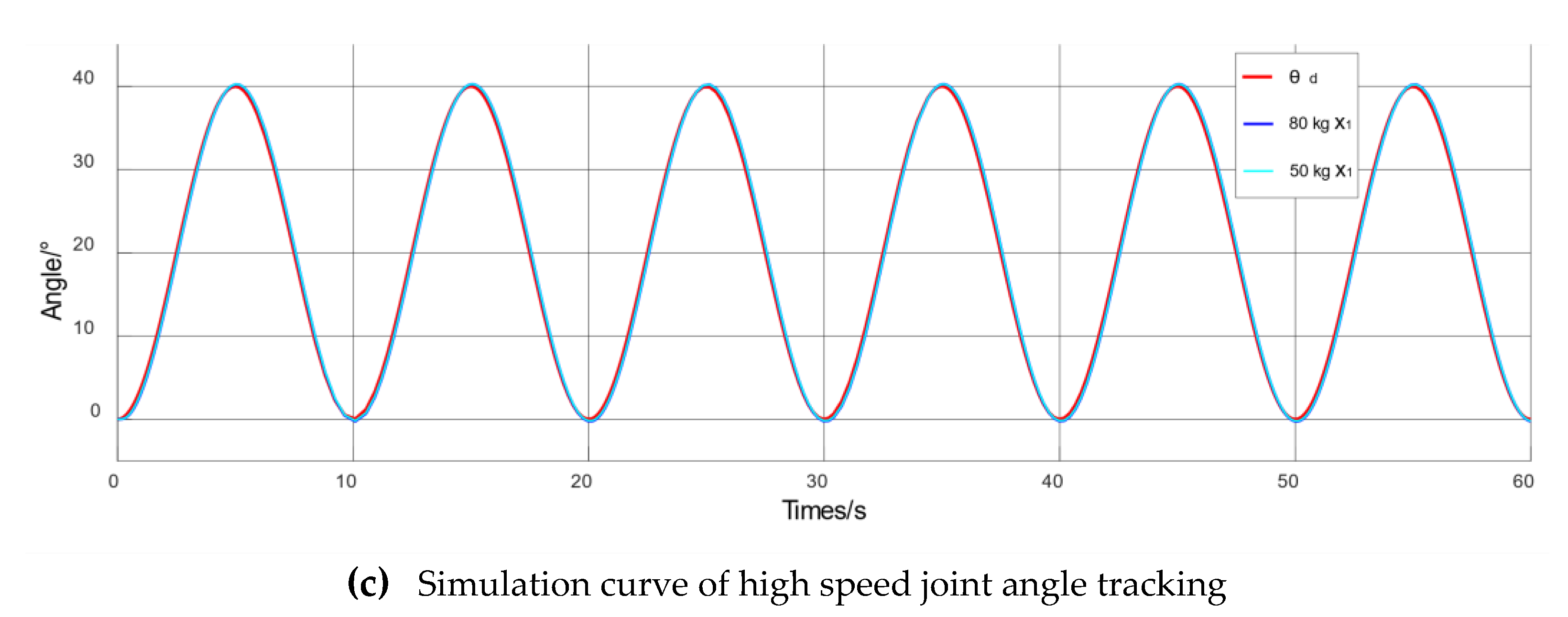
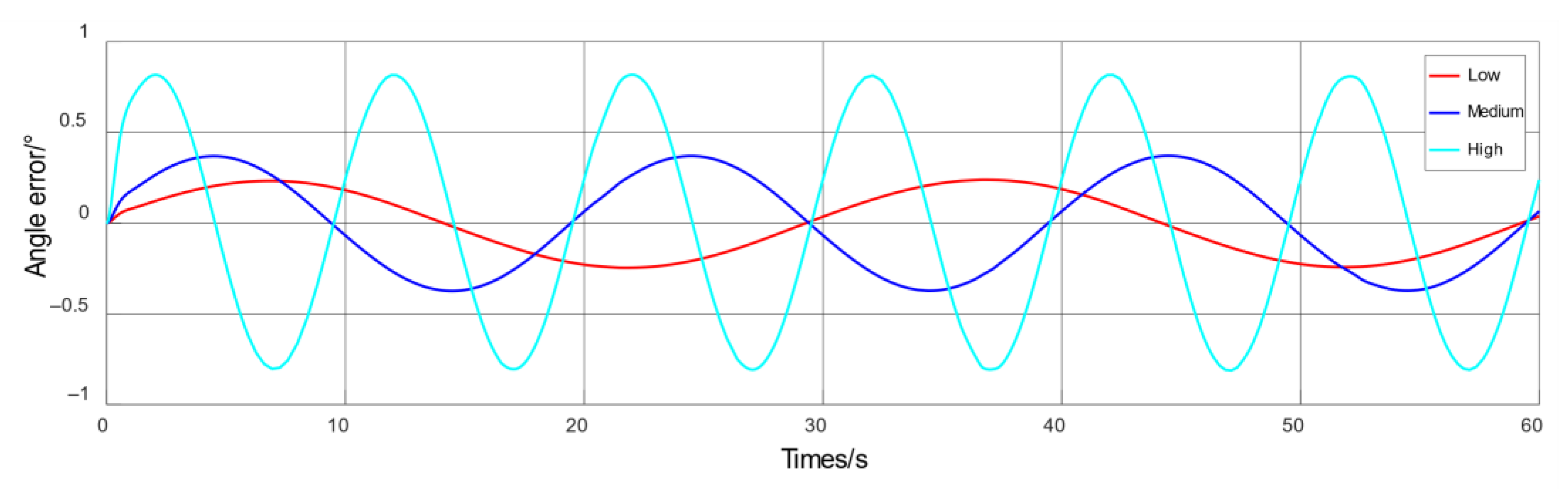
4.3. Simulation of Passive Training Control
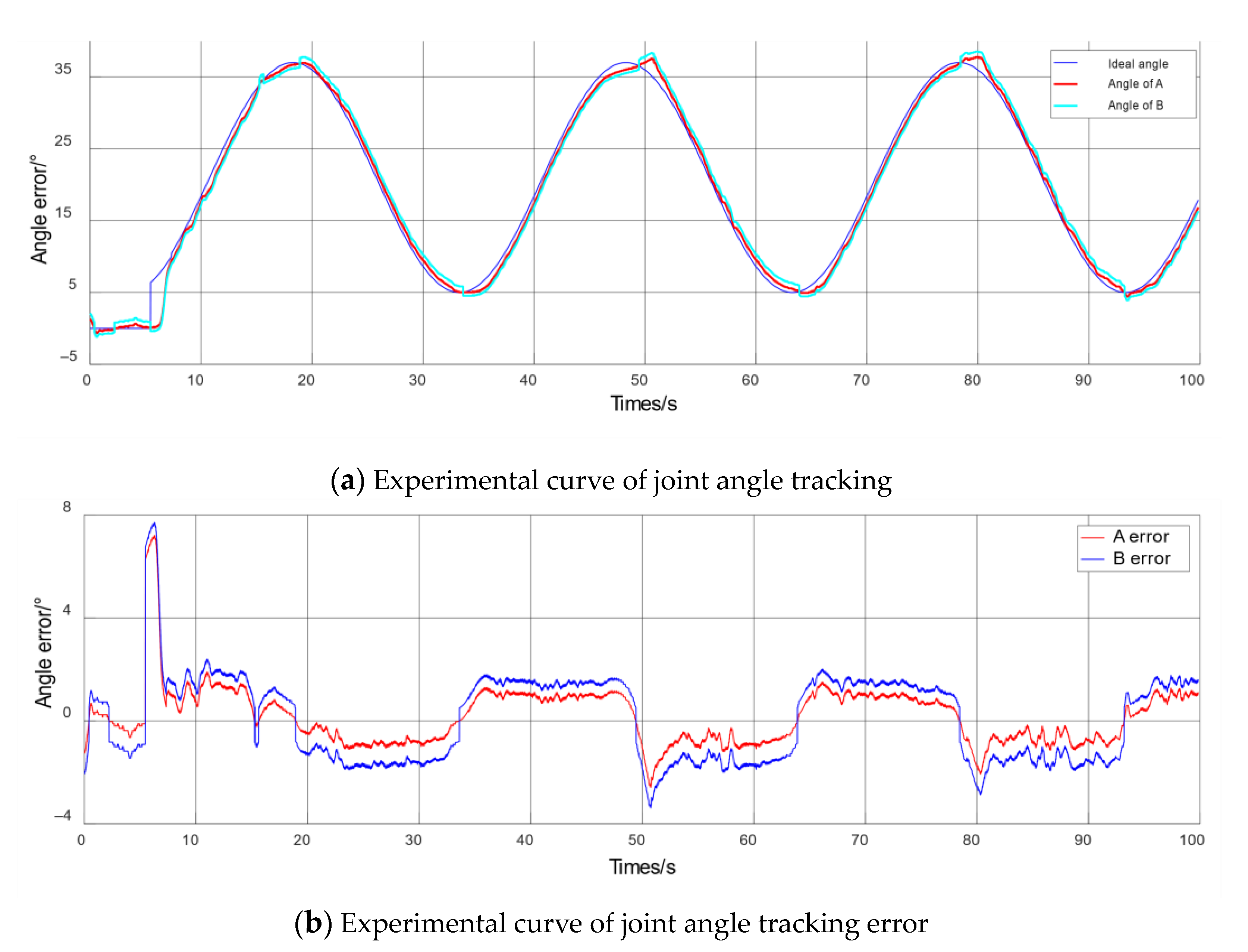
5. Passive Training Experiment of Elbow Rehabilitation Robot
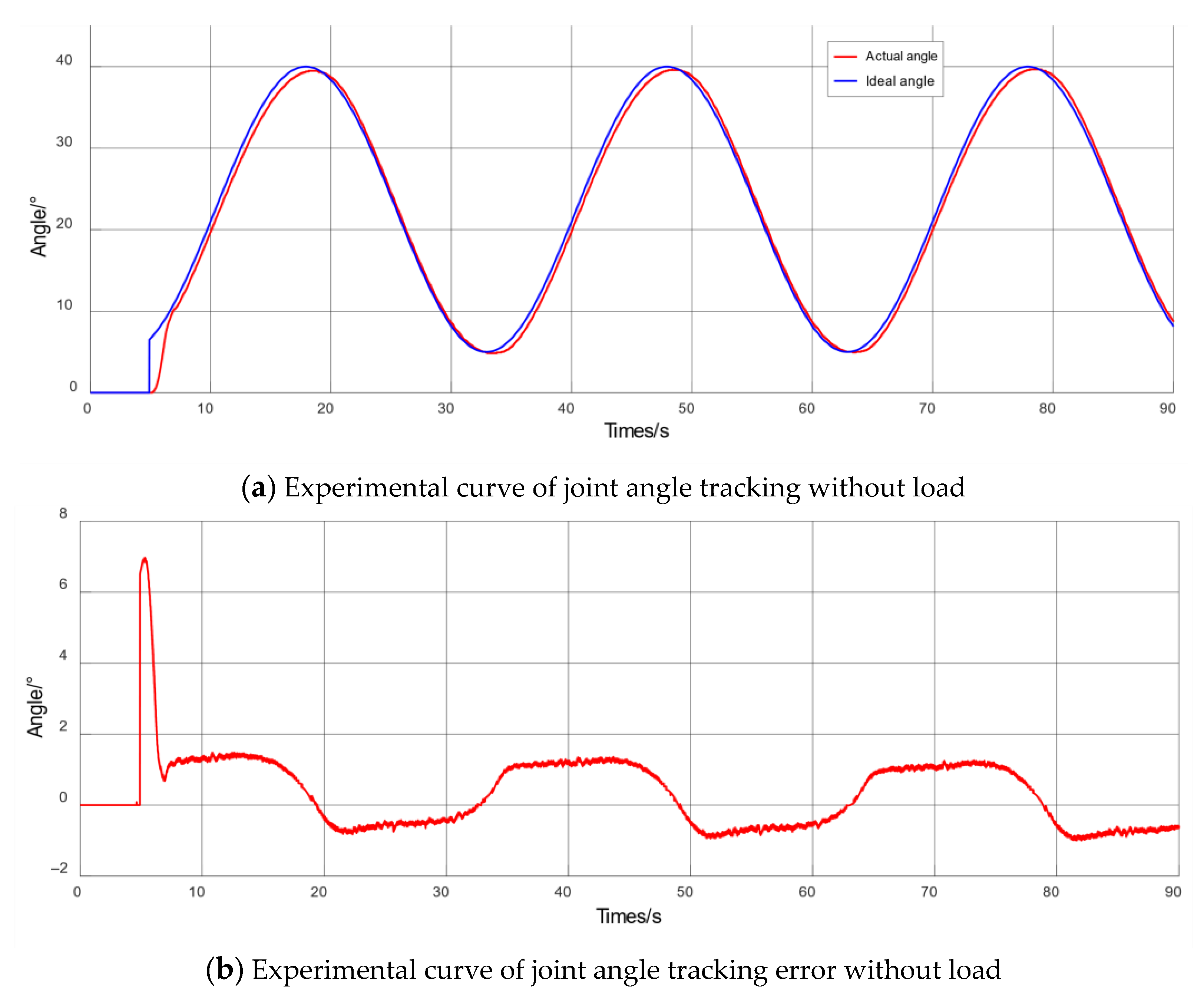
5.1. Experiment on Safety Performance of Passive Training
5.2. Robust Performance of Passive Training and Mechanism Rationality Experiment
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scalera, L.; Gasparetto, A.; Zanotto, D. Design and experimental validation of a 3-dof underactuated pendulum-like robot. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 25, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, S.J.; Brown, I.E.; Scott, S.H. MEDARM: A rehabilitation robot with 5DOF at the shoulder complex. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE/ASME international conference on Advanced intelligent mechatronics, Zurich, Switzerland, 4–7 September 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Kim, W.; Han, J.; Han, C. The technical trend of the exoskeleton robot system for human power assistance. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2012, 13, 1491–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Guo, S.; Xiao, N.; Gao, B.; Shi, L. Implementation of human-machine synchronization control for active rehabilitation using an inertia sensor. Sensors 2012, 12, 16046–16059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Guo, S.; Pang, M.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, N.; Gao, B.; Shi, L. Implementation of resistance training using an upper-limb exoskeleton rehabilitation device in elbow joint. J. Med Biol. Eng. (JMBE) 2013, 34, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Yang, Q.; Chen, G.; Song, R. Nonlinear disturbance observer based sliding mode control of a cable-driven rehabilitation robot. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), London, UK, 17–20 July 2017; pp. 664–669. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, G.; Ye, W.; Xie, Q. PID control for the robotic exoskeleton arm: Application to rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 31st Chinese Control Conference, Hefei, China, 25–27 July 2012; pp. 4496–4501. [Google Scholar]
- Pietrala, D. The characteristics of a pneumatic muscle. In Proceedings of the EPJ Web of Conferences, Hobart, Australia, 20–24 February 2017; Volume 143, pp. 2093–2102. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, D.B.; Repperger, D.W.; Phillips, C.A. Modeling the dynamic characteristics of pneumatic muscle. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2003, 31, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takosoglu, J.E.; Laski, P.A.; Blasiak, S.; Bracha, G.; Pietrala, D. Determining the static characteristics of pneumatic muscles. Meas. Control 2016, 49, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugar, T.G.; He, J.; Koeneman, E.J.; Koeneman, J.B.; Herman, R.; Huang, H.; Schultz, R.S.; Herring, D.E.; Wanberg, J.; Balasubramanian, S.; et al. Design and control of RUPERT: A Device for Robotic Upper Extremity Repetitive Therapy. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2007, 15, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Koeneman, E.J.; Schultz, R.S.; Herring, D.E.; Wanberg, J.; Huang, H.; Sugar, T.; Herman, R.; Koeneman, J.B. RUPERT: A Device for Robotic Upper Extremity Repetitive Therapy. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conference, Shanghai, China, 1–4 September 2005; pp. 6844–6847. [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Wei, R.; Perez, M.; Shepard, B.; Koeneman, E.; Koeneman, J.; He, J. RUPERT: An exoskeleton robot for assisting rehabilitation of arm functions. In Proceedings of the 2008 Virtual Rehabilitation, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 25–27 August 2008; pp. 163–167. [Google Scholar]
- Ghobj, S.; Akl, A.; El-Farr, A.; Ayyash, M.; Abu-Khalaf, J. Mechanical design for a cable driven upper limb exoskeleton prototype actuated by pneumatic rubber muscles. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Research and Education in Mechatronics (REM), Wolfenbuettel, Germany, 14–15 September 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Xing, K.X.; Xu, Q. Fuzzy PID control of a wearable rehabilitation robotic hand driven by pneumatic muscles. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Symposium on Micro-NanoMechatronics and Human Science, Nagoya, Japan, 9–11 November 2009; pp. 408–413. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Xing, K.X. RLSESN-based PID adaptive control for a novel wearable rehabilitation robotic hand driven by PM-TS actuators. Int. J. Intell. Comput. Cybern. 2012, 5, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurumaya, S.; Nabae, H.; Endo, G. Design of thin McKibben muscle and multifilament structure. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 261, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakimoto, S.; Suzumori, K.; Takeda, J. Flexible artificial muscle by bundle of McKibben fiber actuators. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Budapest, Hungary, 3–7 July 2011; pp. 457–462. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.; Gao, Z. An energy saving, factory-validated disturbance decoupling control design for extrusion processes. In Proceedings of the 10th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Beijing, China, 6–8 July 2012; pp. 2891–2896. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, Z. A practical solution to some problems in flight control. In Proceedings of the 48th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC) held jointly with 2009 28th Chinese Control Conference, Shanghai, China, 15–18 December 2009; pp. 654–659. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Kou, C.H. Stabilization of an Orr-Sommerfeld equation cascaded by both the Squire equation and ODE subject to boundary control matched disturbance via active disturbance. IMA J. Math. Control Inf. 2020, 37, 120–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Castellanos, J.F.; Rifaï, H.; Arnez-Paniagua, V.; Linares-Flores, J.; Saynes-Torres, L.; Mohammed, S. Robust active disturbance rejection control via control Lyapunov functions: Application to actuated-ankle–foot-orthosis. Control Eng. Pract. 2018, 80, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujana-Arrese, A.; Mendizabal, A.; Arenas, J.; Prestamero, R.; Landaluze, J. Modelling in Modelica and position control of a 1-DoF set-up powered by pneumatic muscles. Mechatronics 2010, 20, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J. Active Disturbance Rejection Control Technology. Front. Sci. 2007, 1, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin, B.; Warren, H.; Spinks, G.M. A comprehensive test method for measuring actuation performance of McKibben artificial muscles. Smart Mater. Struct. 2021, 30, 045016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Song, M. Ergonomics; Basic Textbook for Art Design Majors in Colleges and Universities; Chongqing University Press: Chongqing, China, 2014; Volume 9, p. 199. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, D.; Khan, A.M.; Yan, R.J.; Ji, Y.; Jang, H.; Iqbal, J.; Han, C. Handling subject arm uncertainties for upper limb rehabilitation robot using robust sliding mode control. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2016, 17, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | ||||||
| Value | 10,000 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Parameters | - | |||||
| Value | 1000 | 1400 | 500 | 20,000 | 2000 | - |
| Parameters | P | I | D |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter 1 | 50 | 300 | 3 |
| Parameter 2 | 20 | 0 | 5 |
| Parameters | ||||||
| Value | 2000 | 0.01 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Parameters | - | |||||
| Value | 50 | 3000 | 13,000 | 50 | 300 | - |
| Subjects | A | B |
|---|---|---|
| Height (m) | 1.60 | 1.82 |
| Weight (kg) | 48 | 82 |
| Arm length (m) | 0.4 | 0.53 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, X.; Wang, B.; Lu, H.; Chen, J. Design and Passive Training Control of Elbow Rehabilitation Robot. Electronics 2021, 10, 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10101147
Cui X, Wang B, Lu H, Chen J. Design and Passive Training Control of Elbow Rehabilitation Robot. Electronics. 2021; 10(10):1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10101147
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Xiaohong, Binrui Wang, Han Lu, and Jiayu Chen. 2021. "Design and Passive Training Control of Elbow Rehabilitation Robot" Electronics 10, no. 10: 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10101147
APA StyleCui, X., Wang, B., Lu, H., & Chen, J. (2021). Design and Passive Training Control of Elbow Rehabilitation Robot. Electronics, 10(10), 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10101147





