High-Frequency and High-Voltage Asymmetric Bipolar Pulse Generator for Electroporation Based Technologies and Therapies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
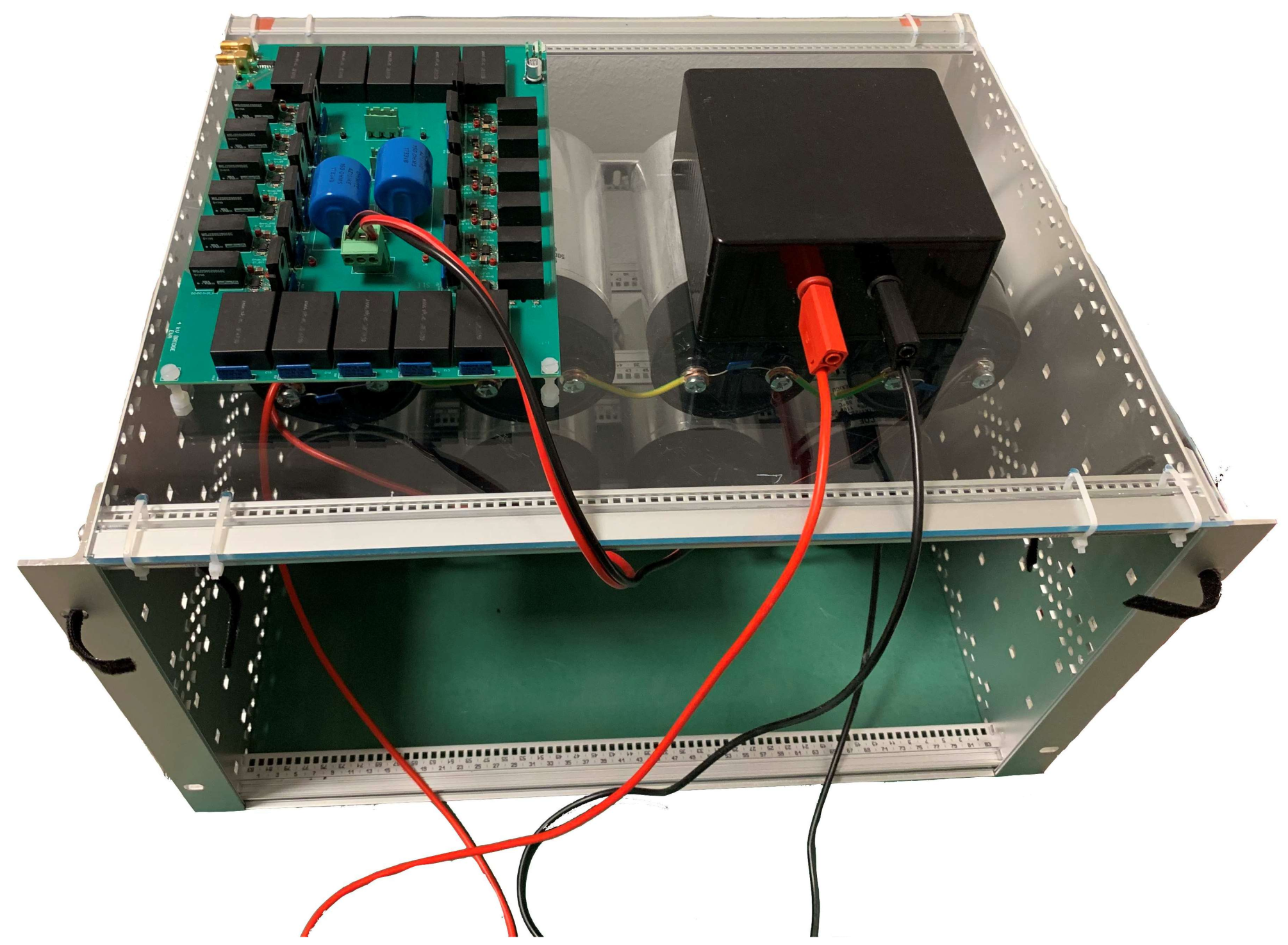
2.1. Prototype Device
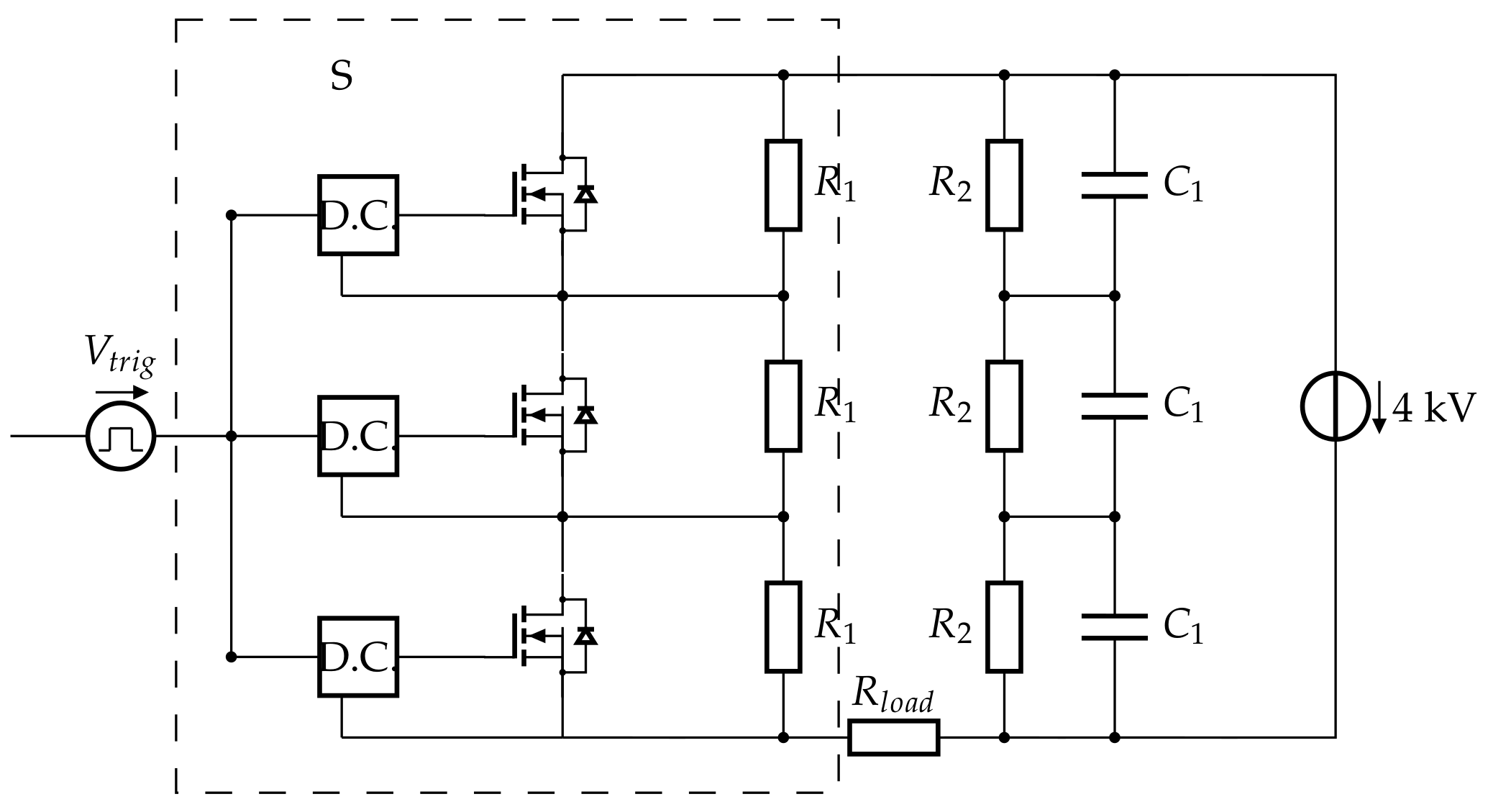
2.1.1. Serial Asymmetric H-Bridge Generator
2.1.2. Triggering of the Pulses
2.1.3. High-Voltage Capacitor Bank
2.1.4. Measurement of the Output Pulses
2.2. In Vivo Experiments
2.2.1. Animals
2.2.2. Treatment Protocol
3. Results
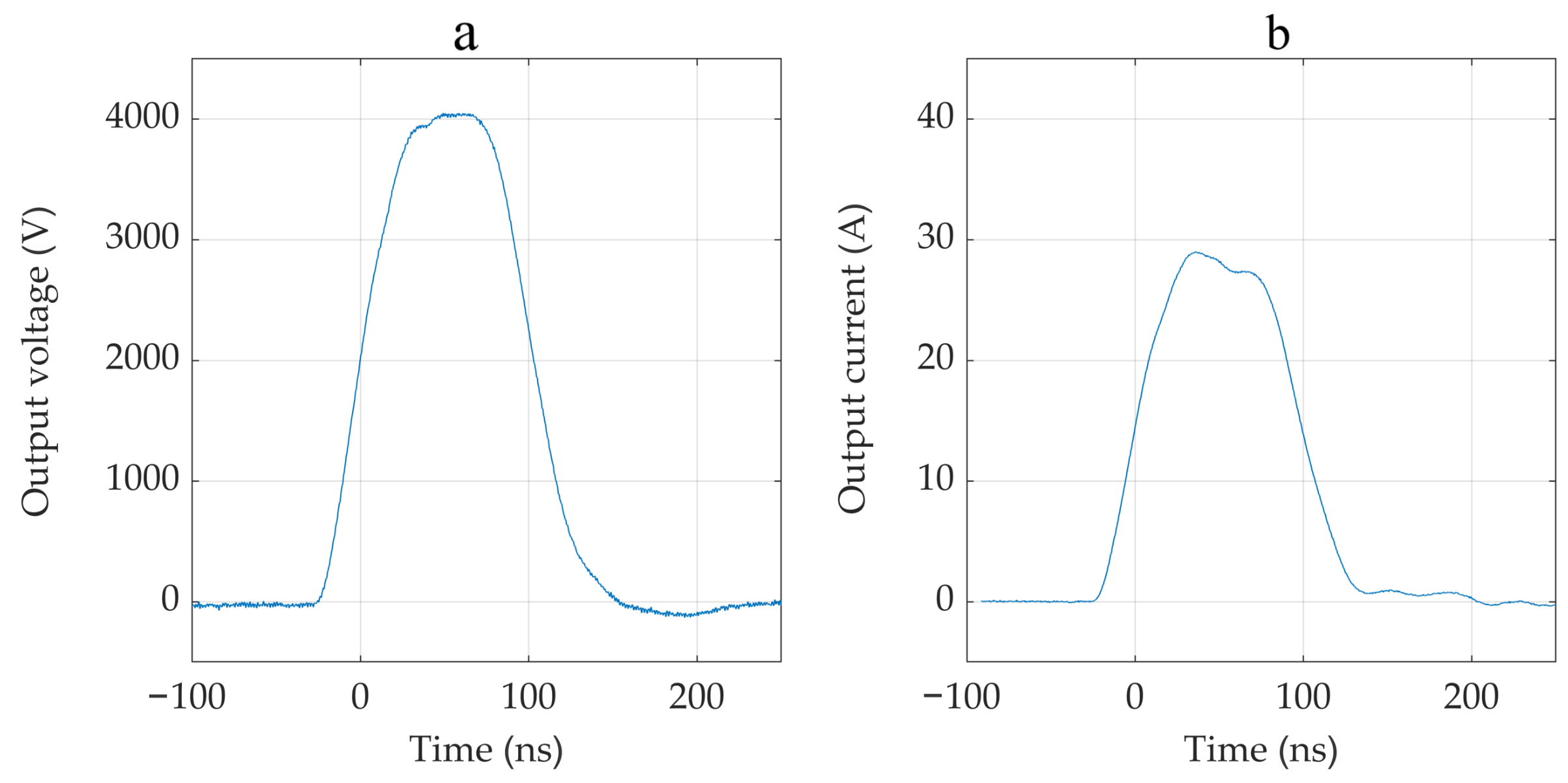
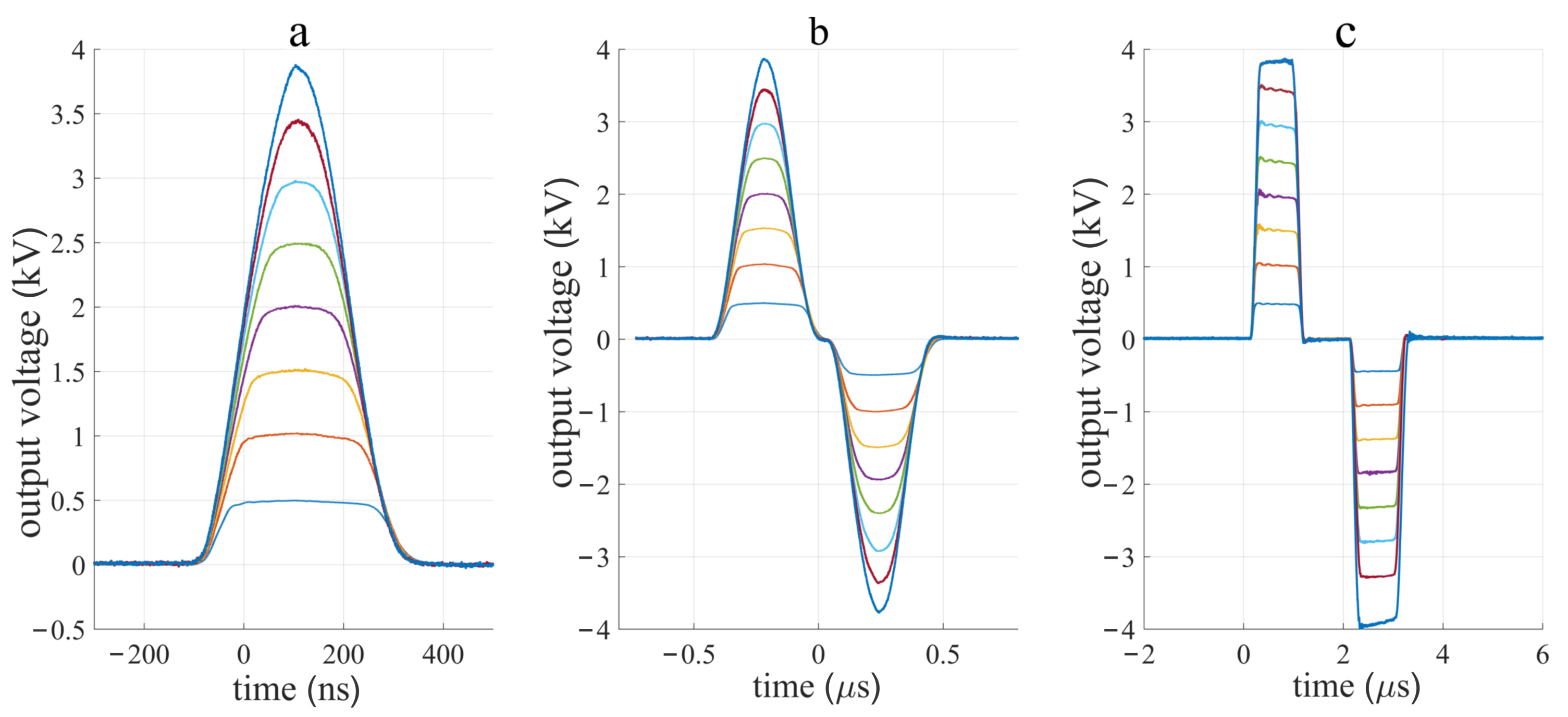
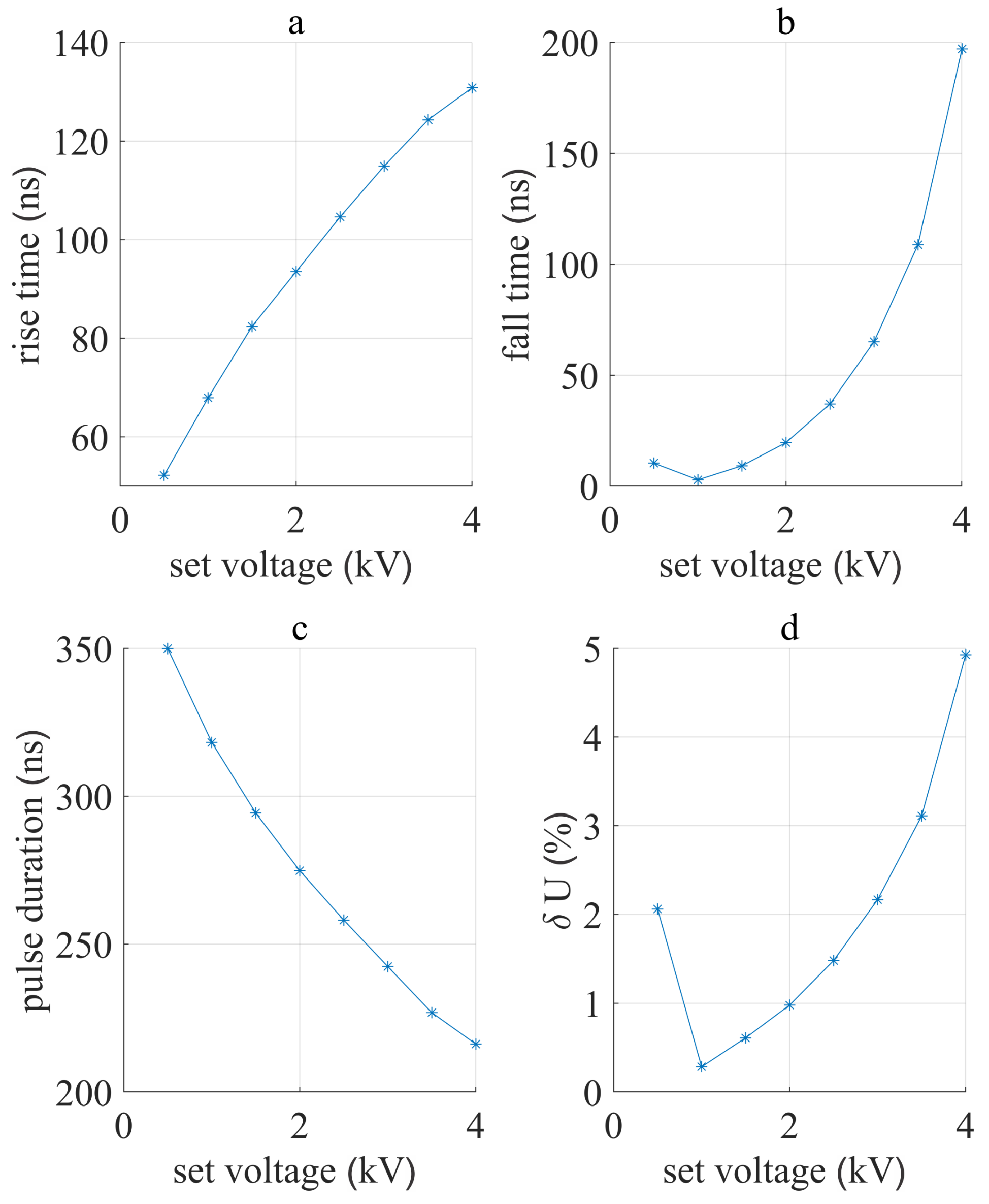
3.1. Device Performance
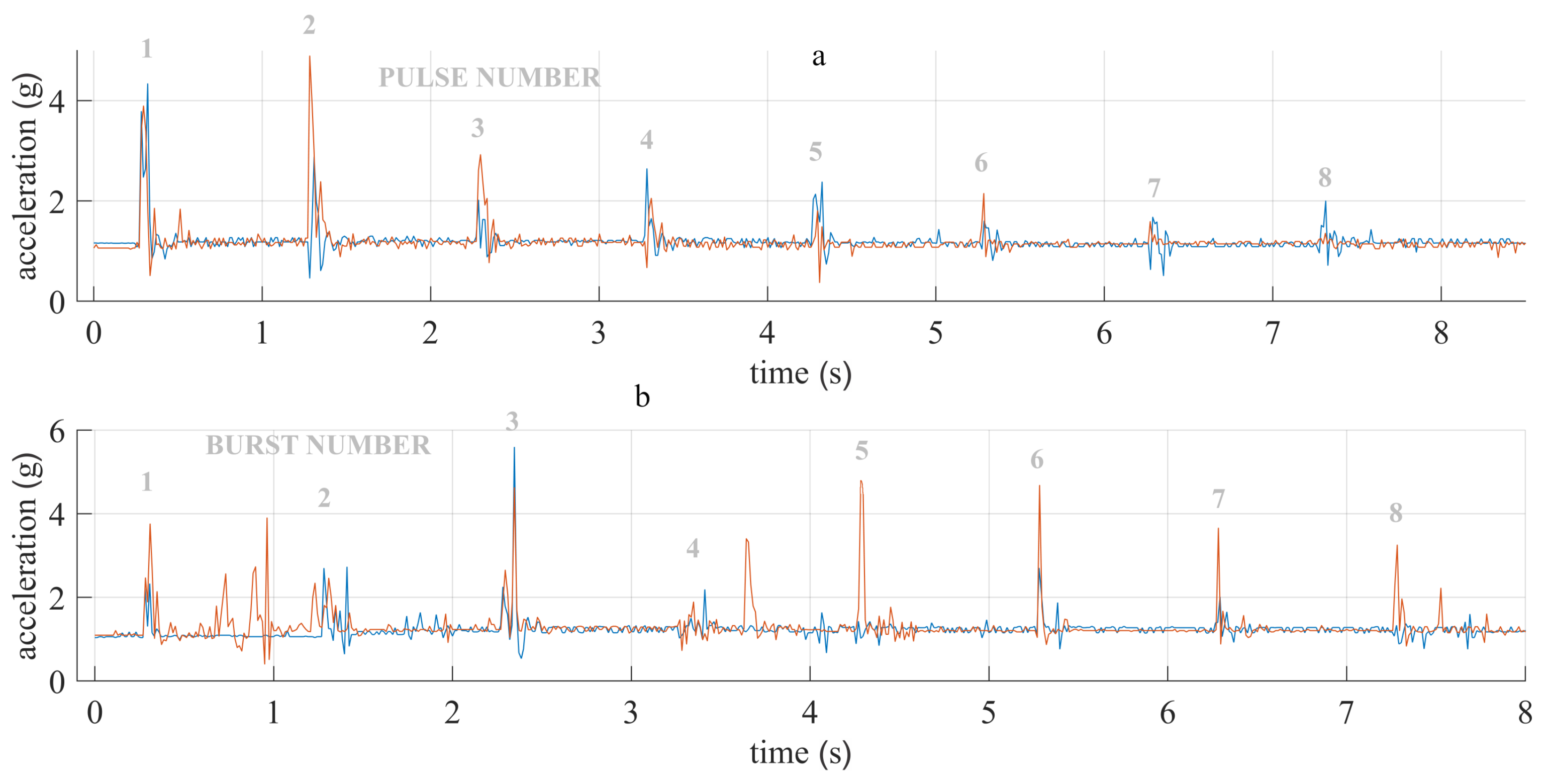
3.2. High-Frequency Electrochemptherapy In Vivo
4. Discussion
4.1. Device Performance
4.2. High-Frequency Electrochemotherapy In Vivo
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IRE | irreversible electroporation |
| ECT | electrochemotherapy |
| BLM | bleomycin |
| CDDP | cisplatin |
| H-FIRE | High-Frequency IRreversible Electroporation |
| HF-EP | high-frequency electroporation |
| AF | atrial fibrillation |
| PFA | pulsed field ablation |
| HF-ECT | high-frequency electrochemotherapy |
| FWHM | Full-Width at Half-Maximum |
Appendix A. Details in Generator Development
Appendix A.1. Driver and Optical Insulation
| Component | Set/Measured Trigger Width (ns) | Output Pulse Width (ns) | Jitter (ns) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HCPL-0723 | 20/19.10 | 18.53 | 1.04 |
| ADuM4223 | 50/49.45 | 40.98 | 0.75 |
| Si826BAD-C-IS | 30/28.65 | 13.84 | 0.29 |
| HFBR 0508Z | 20/19.25 | 30.2 | 0.93 |
| ADuM210N0BRIZ | 20/21.37 | 18.28 | 0.26 |
| Component | Set/Measured Trigger Width (ns) | Output Pulse Width (ns) | Jitter (ns) |
|---|---|---|---|
| IXDN609SI | 20/20.4 | 44.36 | 9.45 |
| ADuM4223 | 70/69.99 | 67.53 | 1.98 |
| UCC27531DBVT | 110/109.23 | 57.27 | 3.8 |
| MIC4422YM | 40/39.82 | 125.26 | 2.55 |
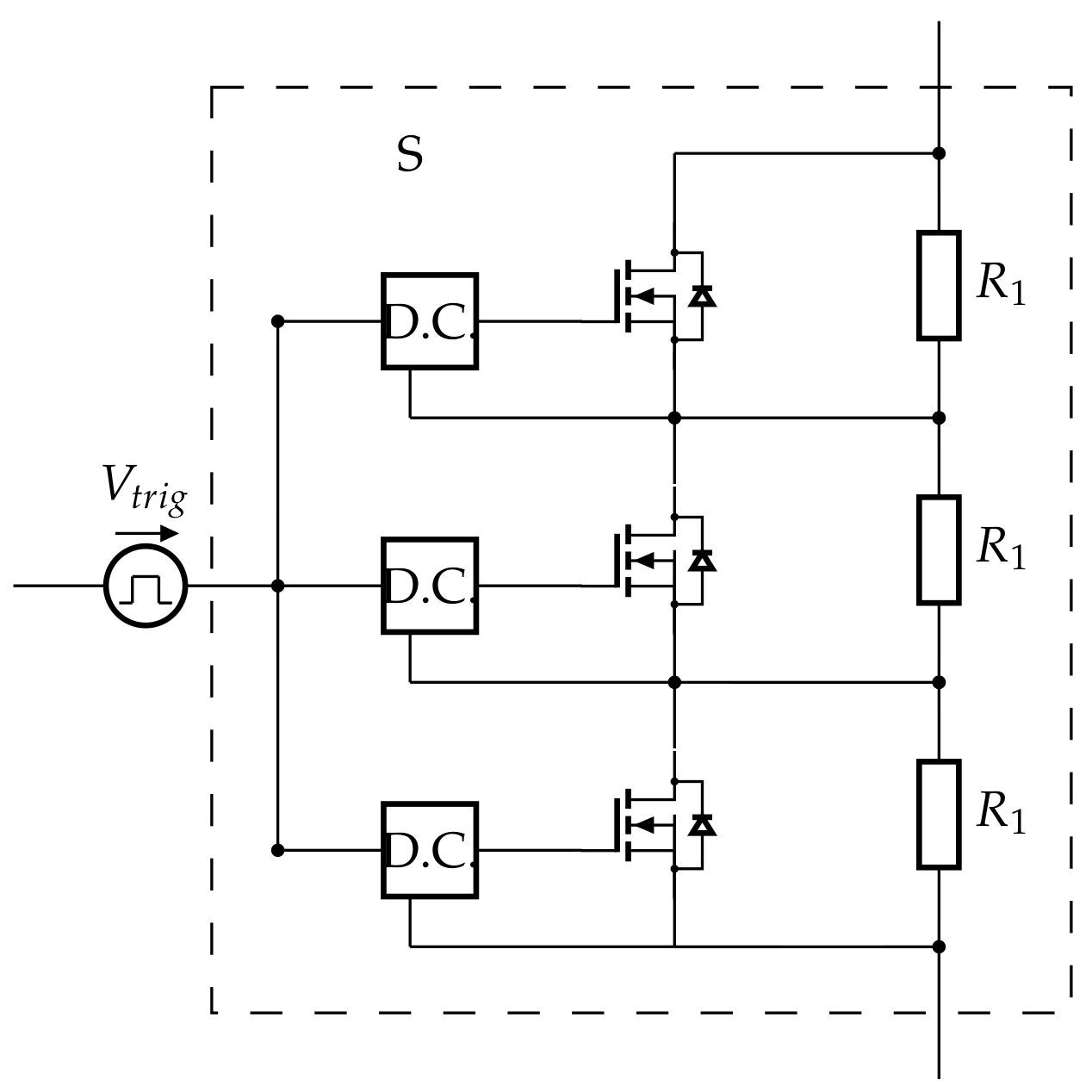
Appendix A.2. Testing MOSFETs in Series
Appendix A.3. Theoretical Maximal Current Calculation
Appendix A.4. Fabrication and Assembly
References
- Kotnik, T.; Rems, L.; Tarek, M.; Miklavčič, D. Membrane Electroporation and Electropermeabilization: Mechanisms and Models. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2019, 48, 63–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Davalos, R.V.; Bischof, J.C. A Review of Basic to Clinical Studies of Irreversible Electroporation Therapy. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haberl, S.; Miklavčič, D.; Serša, G.; Frey, W.; Rubinsky, B. Cell Membrane Electroporation—Part 2: The Applications. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2013, 29, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geboers, B.; Scheffer, H.J.; Graybill, P.M.; Ruarus, A.H.; Nieuwenhuizen, S.; Puijk, R.S.; van den Tol, P.M.; Davalos, R.V.; Rubinsky, B.; de Gruijl, T.D.; et al. High-Voltage Electrical pulses in oncology: Irreversible electroporation, electrochemotherapy, gene electrotransfer, electrofusion, and electroimmunotherapy. Radiology 2020, 295, 254–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golberg, A.; Sack, M.; Teissie, J.; Pataro, G.; Pliquett, U.; Saulis, G.; Töpfl, S.; Miklavčič, D.; Vorobiev, E.; Frey, W. Energy-Efficient Biomass Processing with Pulsed Electric Fields for Bioeconomy and Sustainable Development. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotnik, T.; Frey, W.; Sack, M.; Meglič, S.H.; Peterka, M.; Miklavčič, D. Electroporation-based applications in biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, S.W. Effects of Pulse Length and Strength on Electroporation Efficiency. In Plant Cell Electroporation and Electrofusion Protocols; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Miklavčič, D.; Towhidi, L. Numerical study of the electroporation pulse shape effect on molecular uptake of biological cells. Radiol. Oncol. 2010, 44, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weav, J.C.; Smith, K.C.; Esser, A.T.; Son, R.S.; Gowrishankar, T.R. A brief overview of electroporation pulse strength-duration space: A region where additional intracellular effects are expected. Bioelectrochemistry 2012, 87, 236–243. [Google Scholar]
- Reberšek, M.; Miklavčič, D. Concepts of electroporation pulse generation and overview of electric pulse generators for cell and tissue electroporation. In Advanced Electroporation Techniques in Biology and Medicine; Pakhomov, A.G., Miklavčič, D., Markov, M.S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 323–339. [Google Scholar]
- Reberšek, M.; Miklavčič, D. Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Concepts of Electroporation Pulse Generation. Automatika 2011, 52, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Šel, D.; Cukjati, D.; Batiuskaite, D.; Slivnik, T.; Mir, L.M.; Miklavči, D. Sequential finite element model of tissue electropermeabilization. IEEE Trans. Bio-Med. Eng. 2005, 2, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivorra, A.; Al-Sakere, B.; Rubinsky, B.; Mir, L.M. In Vivo Electrical Conductivity Measurements during and after Tumor Electroporation: Conductivity Changes Reflect the Treatment Outcome. Phys. Med. Biol. 2009, 54, 5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, R.E., 2nd; Garcia, P.A.; Robertson, J.L.; Davalos, R.V. Experimental Characterization and Numerical Modeling of Tissue Electrical Conductivity during Pulsed Electric Fields for Irreversible Electroporation Treatment Planning. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirc, E.; Balosetti, B.; Miklavčič, D.; Reberšek, M. Electronic emulator of biological tissue as an electrical load during electroporation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinert, R.L.; Ramos, A. Applied Electromagnetic Research Group Electroporation threshold, conductivity and memory effect in rat liver. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 64, 102275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, M.F.; Bhonsle, S.P.; Arena, C.B.; Davalos, R.V. Rapid impedance spectroscopy for monitoring tissue impedance, temperature, and treatment outcome during electroporation-based therapies. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 68, 1536–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklavčič, D.; Serša, G.; Brecelj, E.; Gehl, J.; Soden, D.; Bianchi, G.; Ruggieri, P.; Rossi, C.R.; Campana, L.G.; Jarm, T. Electrochemotherapy: Technological advancements for efficient electroporation-based treatment of internal tumors. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2012, 50, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marty, M.; Serša, G.; Garbay, J.R.; Gehl, J.; Collins, C.G.; Snoj, M.; Billarda, V.; Geertsenc, P.F.; Larkind, J.O.; Miklavčič, D.; et al. Electrochemotherapy—An easy, highly effective and safe treatment of cutaneous and subcutaneous metastases: Results of ESOPE (European Standard Operating Procedures of Electrochemotherapy) study. Eur. J. Cancer Suppl. 2006, 4, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, L.M.; Gehl, J.; Serša, G.; Collins, C.G.; Garbay, J.-R.; Billard, V.; Geertsen, P.F.; Rudolf, Z.; O’Sullivan, G.C.; Marty, M. Standard Operating Procedures of the Electrochemotherapy: Instructions for the Use of Bleomycin or Cisplatin Administered Either Systemically or Locally and Electric Pulses Delivered by the CliniporatorTM by Means of Invasive or Non-Invasive Electrodes. EJC Suppl. 2014, 4, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehl, J.; Serša, G.; Wichmann Matthiessen, L.; Muir, T.; Soden, D.; Occhini, A.; Quaglino, P.; Curatolo, P.; Campana, L.G.; Kunte, C.; et al. Updated standard operating procedures for electrochemotherapy of cutaneous tumours and skin metastases. Acta Oncol. 2018, 57, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, L.G.; Edhemovic, I.; Soden, D.; Perrone, A.M.; Scarpa, M.; Campanacci, L.; Čemažar, M.; Valpione, S.; Miklavčič, D.; Mocellin, S.; et al. Electrochemotherapy—Emerging applications technical advances, new indications, combined approaches, and multi-institutional collaboration. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 45, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aycock, K.N.; Davalos, R.V. Irreversible Electroporation: Background, Theory, and Review of Recent Developments in Clinical Oncology. Bioelectricity 2019, 1, 214–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugrue, A.; Vaidya, V.; Witt, C.; DeSimone, C.V.; Yasin, O.; Maor, E.; Killu, A.M.; Kapa, S.; McLeod, C.J.; Miklavčič, D.; et al. Irreversible electroporation for catheter-based cardiac ablation: A systematic review of the preclinical experience. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2019, 55, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Shao, Q.; Bischofet, J. Pulse Timing during Irreversible Electroporation Achieves Enhanced Destruction in a Hindlimb Model of Cancer. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 43, 88795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinsky, B. Irreversible Electroporation in Medicine. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 6, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sakere, B.; Bernat, C.; Andre, F.; Connault, E.; Opolon, P.; Davalos, R.V.; Mir, L.M. A Study of the Immunological Response to Tumor Ablation with Irreversible Electroporation. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 6, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinsky, B.; Onik, G.; Mikus, P. Irreversible Electroporation: A New Ablation Modality—Clinical Implications. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 6, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffer, H.J.; Stam, A.G.M.; Geboers, B.; Vroomen, L.G.P.H.; Ruarus, A.; de Bruijn, B.; van den Tol, M.P.; Kazemier, G.; Meijerink, M.R.; de Gruijl, T.D. Irreversible electroporation of locally advanced pancreatic cancer transiently alleviates immune suppression and creates a window for antitumor T cell activation. OncoImmunology 2019, 8, 1652532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, P.A.; Davalos, R.V.; Miklavčič, D. A numerical investigation of the electric and thermal cell kill distributions in electroporation-based therapies in tissue. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davalos, R.V.; Mir, L.M.; Rubinsky, B. Tissue Ablation with Irreversible Electroporation. Ann Biomed Eng 2005, 33, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, C.; Thomson, K.R.; Kavnoudias, H. Irreversible Electroporation: A New Challenge in Out of Operating Theater Anesthesia. Anesth. Analg. 2010, 110, 13051309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landström, F.J.; Nilsson, C.O.S.; Crafoord, S.; Reizenstein, J.A.; Adamsson, G.-B.M.; Löfgren, L.A. Electroporation Therapy of Skin Cancer in the Head and Neck Area. Dermatol. Surg. 2010, 36, 124550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, B.; Jarm, T.; Jager, F.; Miklavčič, D. An algorithm for synchronization of in vivo electroporation with ECG. J. Med Eng. Technol. 2005, 29, 28896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arena, C.B.; Sano, M.B.; Rossmeisl, J.H., Jr.; Caldwell, J.L.; Garcia, P.A.; Rylander, M.N.; Davalos, R.V. High-Frequency Irreversible Electroporation (H-FIRE) for Non-Thermal Ablation without Muscle Contraction. BioMedical Eng. OnLine 2012, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arena, C.B.; Davalos, R.V. Advances in Therapeutic Electroporation to Mitigate Muscle Contractions. J. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sweeney, D.C.; Reberšek, M.; Dermol, J.; Rems, L.; Miklavčič, D.; Davalos, R.V. Quantification of cell membrane permeability induced by monopolar and high-frequency bipolar bursts of electrical pulses. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 2689–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scuderi, M.; Reberšek, M.; Miklavčič, D.; Dermol-Černe, J. The use of high-frequency short bipolar pulses in cisplatin electrochemotherapy in vitro. Radiol. Oncol. 2019, 53, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lavee, J.; Onik, G.; Mikus, P.; Rubinsky, B. A novel nonthermal energy source for surgical epicardial atrial ablation: Irreversible electroporation. Heart Surg. Forum. 2007, 10, E162–E167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.Y.; Neuzil, P.; Koruth, J.S.; Petru, J.; Funosako, M.; Cochet, H.; Sediva, L.; Chovanec, M.; Dukkipati, S.R.; Jais, R. Pulsed Field Ablation for Pulmonary Vein Isolation in Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, F.D.; Reddy, V.Y.; Viswanathan, R.; Hocini, M.; Jaïs, P. Emerging Technologies for Pulmonary Vein Isolation. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.T.; Haines, D.E.; Miklavčič, D.; Kos, B.; Kirchhof, N.; Barka, N.; Mattison, L.; Martien, M.; Onal, B.; Howard, B.; et al. Safety and chronic lesion characterization of pulsed field ablation in a Porcine model. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2021, 32, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golberg, A.; Rubinsky, B. Towards Electroporation Based Treatment Planning Considering Electric Field Induced Muscle Contractions. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 11, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pakhomova, O.N.; Gregory, B.W.; Khorokhorina, V.A.; Bowman, A.M.; Xiao, S.; Pakhomov, A.G. Electroporation-Induced Electrosensitization. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pakhomova, O.N.; Gregory, B.W.; Pakhomov, A.G. Facilitation of Electroporative Drug Uptake and Cell Killing by Electrosensitization. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2013, 17, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhomov, A.G.; Semenov, I.; Xiao, S.; Pakhomova, O.N.; Gregory, B.; Schoenbach, K.H.; Ullery, J.C.; Beier, H.T.; Rajulapati, S.R.; Ibey, B.L. Cancellation of Cellular Responses to Nanoelectroporation by Reversing the Stimulus Polarity. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2014, 71, 443141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibey, B.L.; Ullery, J.; Pakhomova, O.N.; Roth, C.C.; Semenov, I.; Beier, H.T.; Tarango, M.; Xiao, S.; Schoenbach, K.; Pakhomov, A.G. Bipolar nanosecond electric pulses are less efficient at electropermeabilization and killing cells than monopolar pulses. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 568573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dermol, J.; Pakhomova, O.N.; Pakhomov, A.G.; Miklavčič, D. Cell Electrosensitization Exists Only in Certain Electroporation Buffers. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polajžer, T.; Dermol-Černe, J.; Reberšek, M.; O’Connor, R.; Miklavčič, D. Cancellation effect is present in high-frequency reversible and irreversible electroporation. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 132, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Es, R.; Konings, M.K.; Du Pré, M.C.; Neven, K.; van Wessel, H.; van Driel, V.J.H.M.; Westra, A.H.; Doevendans, P.A.F.; Wittkampf, F.H.M. High-frequency irreversible electroporation for cardiac ablation using an asymmetrical waveform. BioMed Eng. OnLine 2019, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novickij, V.; Grainys, A.; Butkus, P.; Tolvaišienė, S.; Švedienė, J.; Paškevičius, A.; Novickij, J. High-frequency submicrosecond electroporator. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2016, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redon, L.M.; Zahyka, M.; Kandratsyeu, A. Solid-State Generation of High-Frequency Burst of Bipolar Pulses for Medical Applications. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2019, 47, 4091–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovšek, M.; Nastran, J.; Vončina, D.; Zajec, P.; Miklavčič, D.; Serša, G. High Voltage Pulse Generation [Electroporation]. Electron. Lett. 2002, 38, 680–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grainys, A.; Novickij, V.; Novickij, J. High-power bipolar multilevel pulsed electroporator. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2016, 44, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirc, E.; Reberšek, M.; Miklavčič, D. Dosimetry in Electroporation-Based Technologies and Treatments. In Dosimetry in Bioelectromagnetics; Markov, M., Ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 233–268. [Google Scholar]
- Colombo, G.L.; Di Matteo, S.; Mir, L.M. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Electrochemotherapy with the Cliniporatortrade Mark vs Other Methods for the Control and Treatment of Cutaneous and Subcutaneous Tumors. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pirc, E.; Federici, C.; Bošnjak, M.; Perić, B.; Reberšek, M.; Pecchia, L.; Glumac, N.; Čemažar, M.; Snoj, M.; Serša, G.; et al. Early cost-effectiveness analysis of electrochemotherapy as a prospect treatment modality for skin melanoma. Clin. Ther. Accept. Publ. 2020, 42, 1535–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health. Irreversible Electroporation for Tumors of the Pancreas or Liver: Review of Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness; Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, C.; Dong, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lv, Y.; Liu, H.; Gong, L.; Ma, J.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y. Bipolar Microsecond Pulses and Insulated Needle Electrodes for Reducing Muscle Contractions During Irreversible Electroporation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 2924–2937. [Google Scholar]
- Sano, M.B.; Arena, C.B.; Bittleman, K.B.; De Witt, M.R.; Cho, H.J.; Szot, C.S.; Saur, D.; Cissell, J.M.; Robertson, J.; Lee, Y.W.; et al. Bursts of Bipolar Microsecond Pulses Inhibit Tumor Growth. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pirc, E.; Miklavčič, D.; Reberšek, M. Nanosecond Pulse Electroporator With Silicon Carbide mosfets: Development and Evaluation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 66, 3526–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, L.G.; Cesari, M.; Dughiero, F.; Forzan, M.; Rastrelli, M.; Rossi, C.R.; Sieni, E.; Tosi, A.L. Electrical resistance of human soft tissue sarcomas: An ex vivo study on surgical specimens. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2016, 54, 773–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, M.B.; Arena, C.B.; De Witt, M.R.; Saur, D.; Davalos, R.V. In-vitro bipolar nano—And microsecond electro-pulse bursts for irreversible electroporation therapies. Bioelectrochemistry 2014, 100, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, M.B.; Fan, R.E.; Cheng, K.; Saenz, Y.; Sonn, G.A.; Hwang, G.L.; Xing, L. Reduction of Muscle Contractions during Irreversible Electroporation Therapy Using High-Frequency Bursts of Alternating Polarity Pulses: A Laboratory Investigation in an Ex Vivo Swine Model. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 29, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, J.D.; Fesmire, C.C.; Petrella, R.A.; Fogle, C.A.M.; Xing, L.; Gerber, D.; Sano, M.B. High-Frequency Irreversible Electroporation Using 5000-V Waveforms to Create Reproducible 2-and 4-cm Ablation Zones—A Laboratory Investigation Using Mechanically Perfused Liver. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhonsle, S.P.; Arena, C.B.; Sweeney, D.C.; Davalos, R.V. Mitigation of impedance changes due to electroporation therapy using bursts of high-frequency bipolar pulses. Biomed. Eng. Online 2015, 14, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, S.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yao, C. First human trial of high-frequency irreversible electroporation therapy for prostate cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirai Medical. Available online: https://www.mirai-medical.com/ (accessed on 25 December 2019).
- Novickij, V.; Zinkevičienė, A.; Perminaitė, E.; Čėsna, R.; Lastauskienė, E.; Paškevičius, A.; Švedienė, J.; Markovskaja, S.; Novickij, J.; Girkontaitė, I. Non-invasive nanosecond electroporation for biocontrol of surface infections: an in vivo study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ringel-Scaia, V.M.; Beitel-White, N.; Lorenzo, M.F.; Brock, R.M.; Huie, K.E.; Coutermarsh-Ott, S.; Eden, K.; McDaniel, D.K.; Verbridge, S.S.; Rossmeisl, J.H.; et al. High-frequency irreversible electroporation is an effective tumor ablation strategy that induces immunologic cell death and promotes systemic anti-tumor immunity. EBioMedicine 2019, 44, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stevanovic, L.D.; Matocha, K.S.; Losee, P.A.; Glaser, J.S.; Nasadoski, J.J.; Arthur, S.D. Recent advances in silicon carbide MOSFET power devices. In Proceedings of the 2010 Twenty-Fifth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Palm Springs, CA, USA, 21–25 February 2010; pp. 401–407. [Google Scholar]





| Method Used | s.c. TC | i.t. BLM | i.t. CDDP | EP | HF-EP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp. Group | ||||||
| Control | x | |||||
| BLM | x | x | ||||
| CDDP | x | x | ||||
| ECT pulses | x | x | ||||
| HF-ECT pulses | x | x | ||||
| BLM/ECT | x | x | x | |||
| BLM/HF-ECT | x | x | x | |||
| CDDP/ECT | x | x | x | |||
| CDDP/HF-ECT | x | x | x | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pirc, E.; Miklavčič, D.; Uršič, K.; Serša, G.; Reberšek, M. High-Frequency and High-Voltage Asymmetric Bipolar Pulse Generator for Electroporation Based Technologies and Therapies. Electronics 2021, 10, 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10101203
Pirc E, Miklavčič D, Uršič K, Serša G, Reberšek M. High-Frequency and High-Voltage Asymmetric Bipolar Pulse Generator for Electroporation Based Technologies and Therapies. Electronics. 2021; 10(10):1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10101203
Chicago/Turabian StylePirc, Eva, Damijan Miklavčič, Katja Uršič, Gregor Serša, and Matej Reberšek. 2021. "High-Frequency and High-Voltage Asymmetric Bipolar Pulse Generator for Electroporation Based Technologies and Therapies" Electronics 10, no. 10: 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10101203
APA StylePirc, E., Miklavčič, D., Uršič, K., Serša, G., & Reberšek, M. (2021). High-Frequency and High-Voltage Asymmetric Bipolar Pulse Generator for Electroporation Based Technologies and Therapies. Electronics, 10(10), 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10101203







