Advancing Stress Detection Methodology with Deep Learning Techniques Targeting UX Evaluation in AAL Scenarios: Applying Embeddings for Categorical Variables
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Description of Employed Datasets
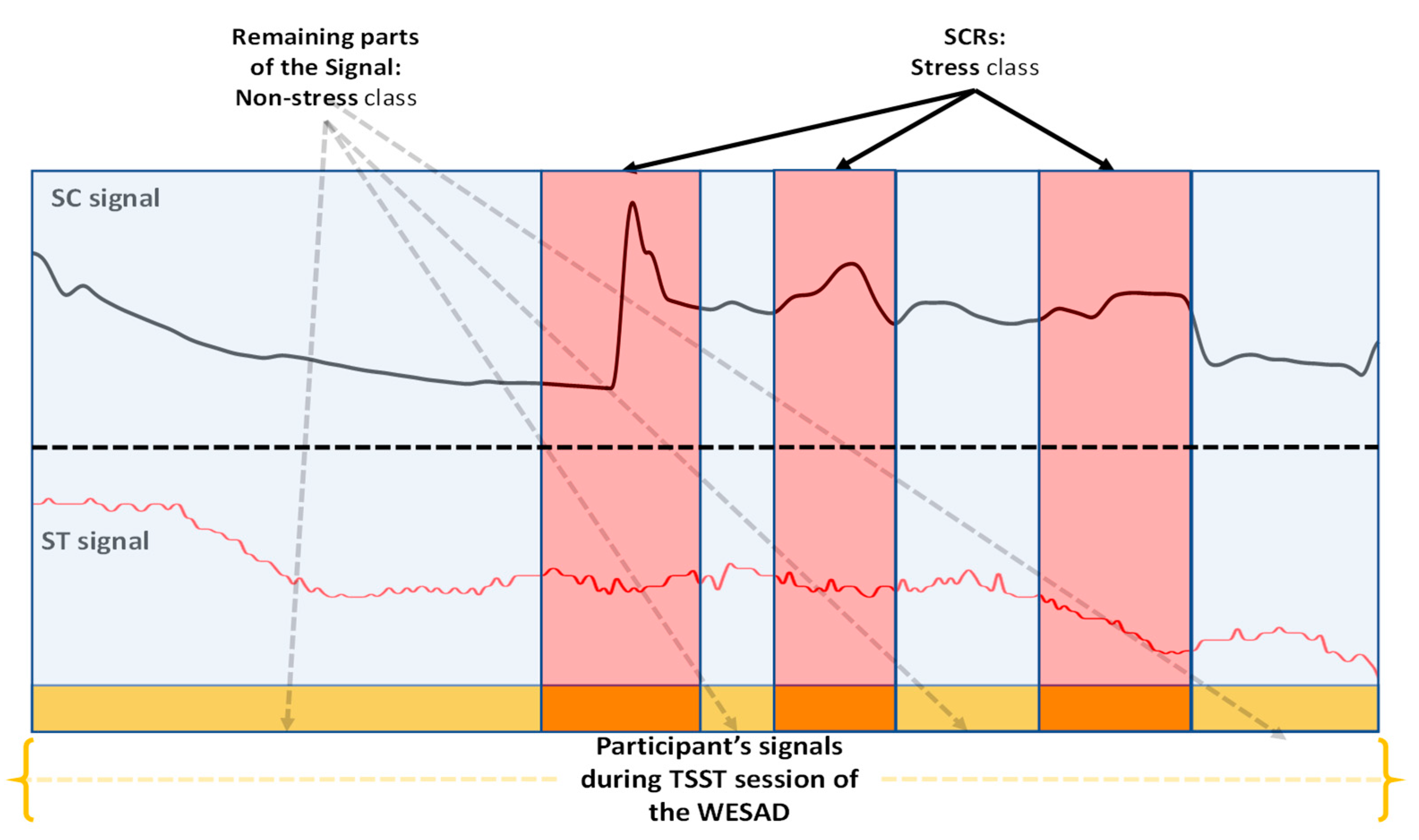
2.1. Wearable Stress and Affect Detection (WESAD) Dataset
3. Training and Results
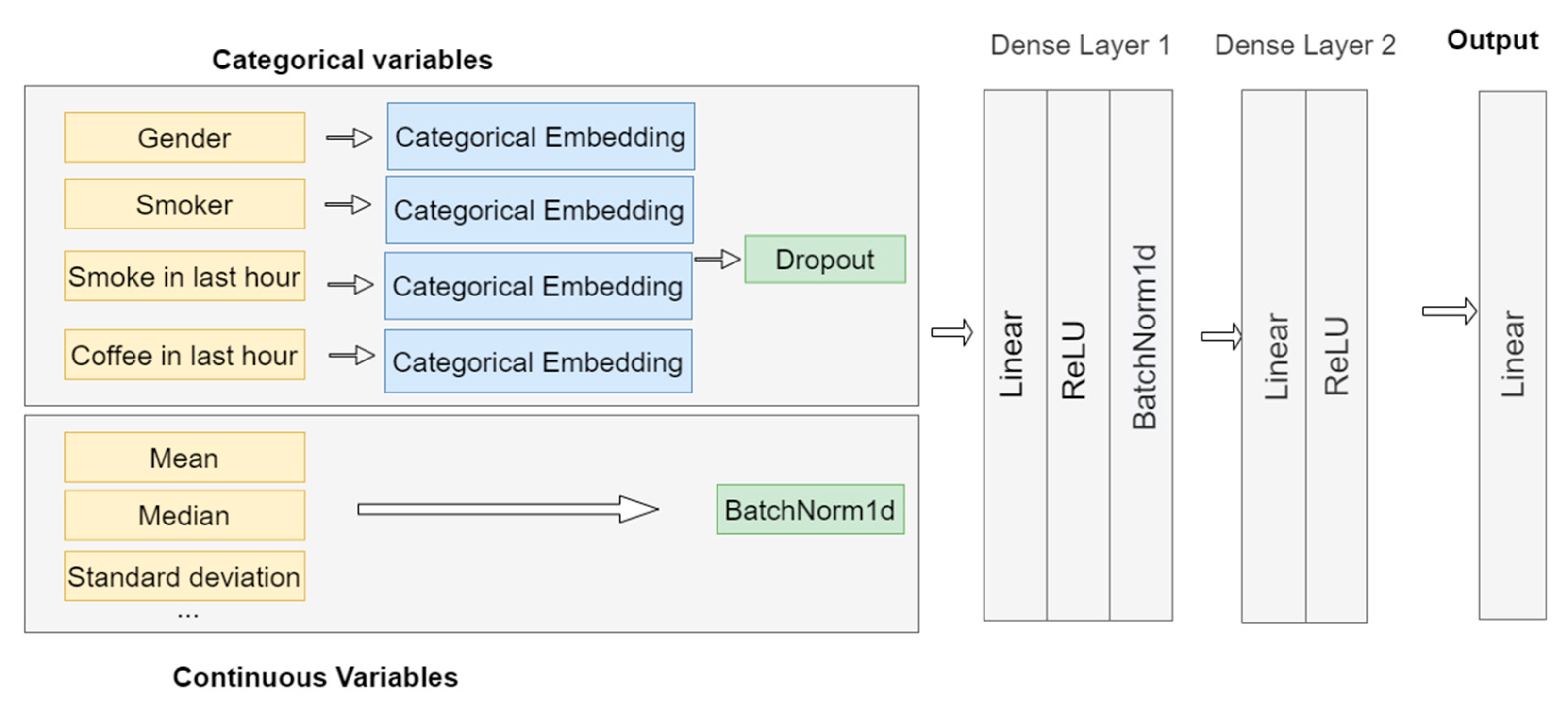
3.1. Training a Deep Learning Model by Combining Continues Variables and Entity Embeddings
3.2. Training Dataset Creation
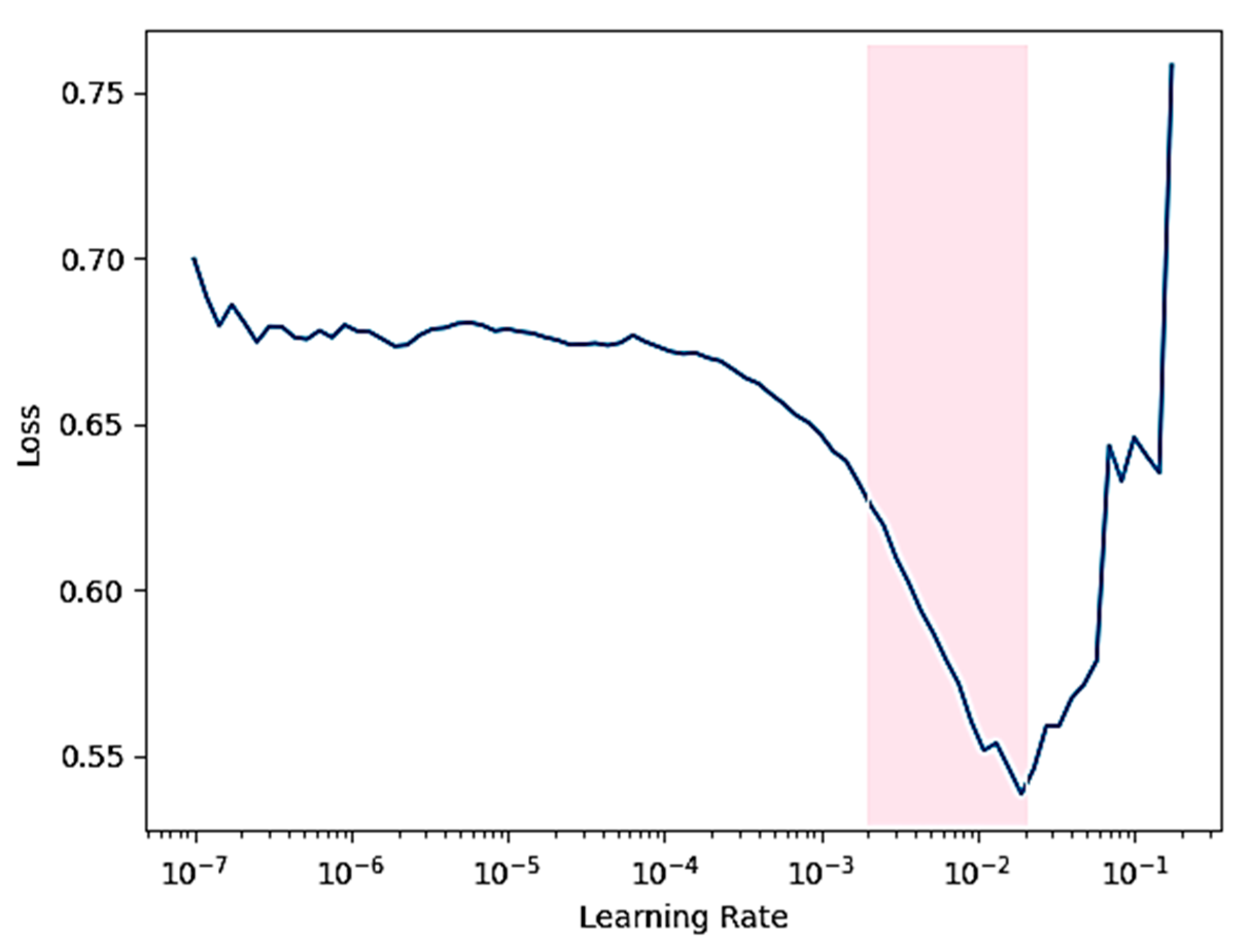
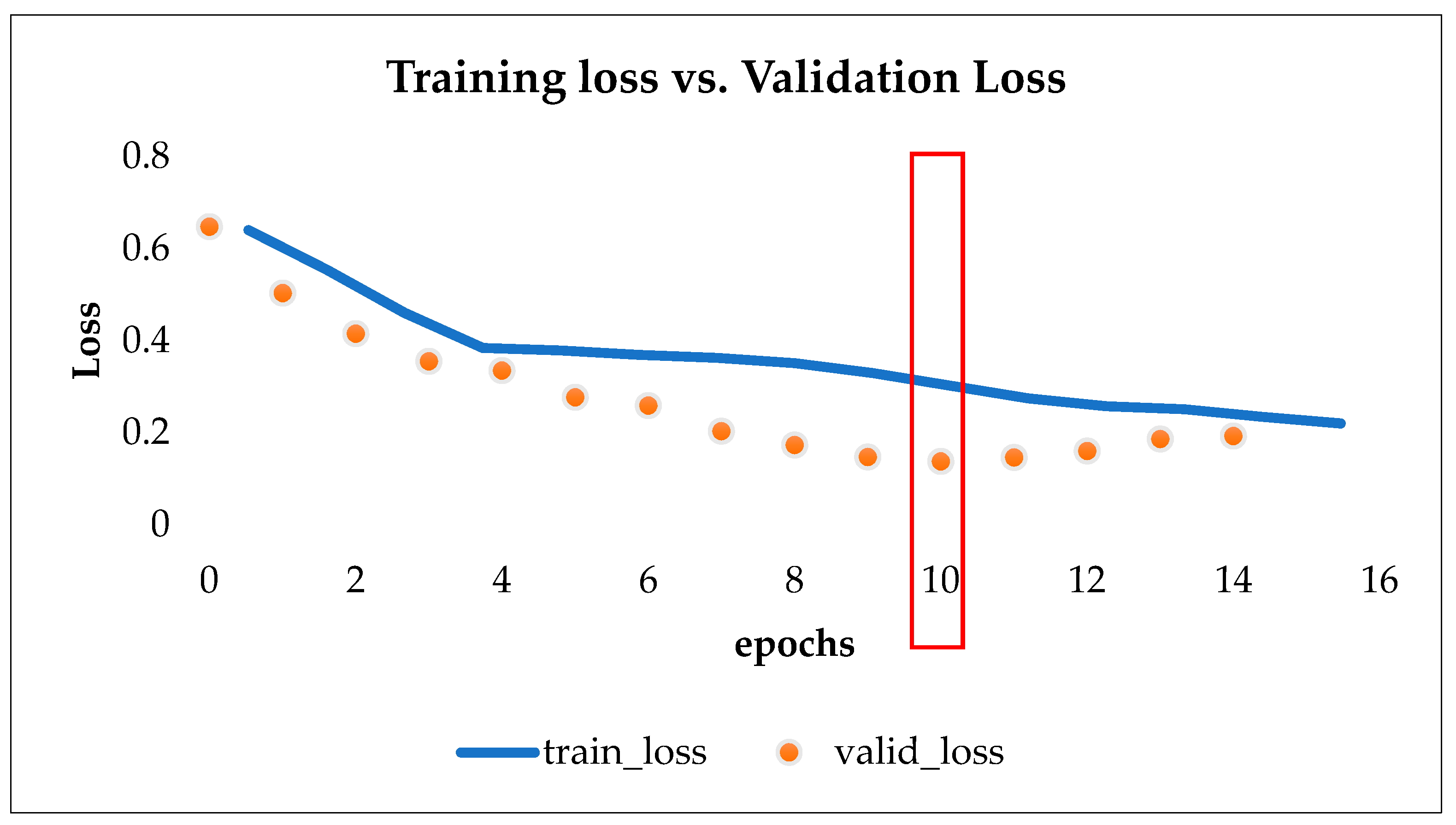
3.3. Training and Classification
4. Testing the Models in Another Context
4.1. Ground Truth Physiological Dataset—UX Context
4.2. Evaluation of Classifiers
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarsenbayeva, Z.; Marini, G.; van Berkel, N.; Luo, C.; Jiang, W.; Yang, K.; Wadley, G.; Dingler, T.; Kostakos, V.; Goncalves, J. Does Smartphone Use Drive Our Emotions or Vice Versa? A Causal Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 April 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Remy, C.; Bates, O.; Dix, A.; Thomas, V.; Hazas, M.; Friday, A.; Huang, E.M. Evaluation Beyond Usability: Validating Sustainable HCI Research. In Proceedings of the 2018 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–26 April 2018; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 216:1–216:14. [Google Scholar]
- Silvennoinen, J.M.; Jokinen, J.P.P. Aesthetic Appeal and Visual Usability in Four Icon Design Eras. In Proceedings of the 2016 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, San Jose, CA, USA, 7–12 May 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: San Jose, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 4390–4400. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Oreiro, I.; López, G.; Quesada, L.; Guerrero, L.A. Standardized Questionnaires for User Experience Evaluation: A Systematic Literature Review. Proceedings 2019, 31, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarnowski, P.; Kołodziej, M.; Majkowski, A.; Rak, R.J. Emotion Recognition Using Facial Expressions. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 108, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathour, N.; Alshamrani, S.S.; Singh, R.; Gehlot, A.; Rashid, M.; Akram, S.V.; AlGhamdi, A.S. IoMT Based Facial Emotion Recognition System Using Deep Convolution Neural Networks. Electronics 2021, 10, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Dong, M.; Huang, Z.; Zhan, Y. Learning Salient Features for Speech Emotion Recognition Using Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2014, 16, 2203–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikadar, S.; Bhattacharya, S. A Novel Method to Build and Validate an Affective State Prediction Model from Touch-Typing. In Proceedings of the Human-Computer Interaction—INTERACT 2019, Paphos, Cyprus, 2–6 September 2019; Lamas, D., Loizides, F., Nacke, L., Petrie, H., Winckler, M., Zaphiris, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 99–119. [Google Scholar]
- Tikadar, S.; Kazipeta, S.; Ganji, C.; Bhattacharya, S. A Minimalist Approach for Identifying Affective States for Mobile Interaction Design. In Proceedings of the Human-Computer Interaction—INTERACT 2017, Mumbai, India, 25–29 September 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, M.; Marouane, C.; Elsner, D. DeepFlow: Detecting Optimal User Experience From Physiological Data Using Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and MultiAgent Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 13–17 May 2019; International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2019; pp. 2108–2110. [Google Scholar]
- Lazar, J.; Feng, J.H.; Hochheiser, H. Research Methods in Human-Computer Interaction; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-470-72337-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, J.; Paredes, P.; Roseway, A.; Czerwinski, M. Under Pressure: Sensing Stress of Computer Users. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Boucsein, W. Electrodermal Activity, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA; Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Heidelberg, Germany; London, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-1-4614-1125-3. [Google Scholar]
- Quazi, M.T.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Suryadevara, N.K.; Huang, Y.M. Towards the Smart Sensors Based Human Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Proceedings, Graz, Austria, 13–16 May 2012; pp. 2365–2370. [Google Scholar]
- Kaklauskas, A. Web-based Biometric Computer Mouse Advisory System to Analyze a User’s Emotions and Work Productivity. In Biometric and Intelligent Decision Making Support; Kaklauskas, A., Ed.; Intelligent Systems Reference Library; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 137–173. ISBN 978-3-319-13659-2. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, D.; Ham, J.; Oh, J.; Park, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, N.-K.; Lee, B. Detection of Stress Levels from Biosignals Measured in Virtual Reality Environments Using a Kernel-Based Extreme Learning Machine. Sensors 2017, 17, 2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, T.K.L.; Sherratt, R.S. Coverage of Emotion Recognition for Common Wearable Biosensors. Biosensors 2018, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suoja, K.; Liukkonen, J.; Jussila, J.; Salonius, H.; Venho, N.; Sillanpää, V.; Vuori, V.; Helander, N. Application for pre-processing and visualization of electrodermal activity wearable data. In EMBEC & NBC 2017; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Kleinsmith, A. Public Speaking Anxiety in a Real Classroom: Towards Developing a Reflection System. In Proceedings of the Extended Abstracts of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Glasgow, UK, 4–9 May 2019; Association for Computing Machinery: Glasgow, UK, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Betella, A.; Zucca, R.; Cetnarski, R.; Greco, A.; Lanatà, A.; Mazzei, D.; Tognetti, A.; Arsiwalla, X.D.; Omedas, P.; De Rossi, D. Inference of Human Affective States from Psychophysiological Measurements Extracted under Ecologically Valid Conditions. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowley, B.; Filetti, M.; Lukander, K.; Torniainen, J.; Henelius, A.; Ahonen, L.; Barral, O.; Kosunen, I.; Valtonen, T.; Huotilainen, M. The Psychophysiology Primer: A Guide to Methods and a Broad Review with a Focus on Human–Computer Interaction. Found. Trends Hum. Comput. Interact. 2016, 9, 151–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koelstra, S.; Muhl, C.; Soleymani, M.; Lee, J.-S.; Yazdani, A.; Ebrahimi, T.; Pun, T.; Nijholt, A.; Patras, I. DEAP: A Database for Emotion Analysis; Using Physiological Signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2012, 3, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koldijk, S.; Sappelli, M.; Verberne, S.; Neerincx, M.A.; Kraaij, W. The SWELL Knowledge Work Dataset for Stress and User Modeling Research. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Istanbul, Turkey, 12–16 November 2014; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 291–298. [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian, R.; Wache, J.; Abadi, M.K.; Vieriu, R.L.; Winkler, S.; Sebe, N. ASCERTAIN: Emotion and Personality Recognition Using Commercial Sensors. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2018, 9, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberdi, A.; Aztiria, A.; Basarab, A. Towards an Automatic Early Stress Recognition System for Office Environments Based on Multimodal Measurements: A Review. J. Biomed. Inform. 2016, 59, 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, P.; Reiss, A.; Duerichen, R.; Marberger, C.; Van Laerhoven, K. Introducing WESAD, a Multimodal Dataset for Wearable Stress and Affect Detection. In Proceedings of the 20th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Boulder, CO, USA, 16–20 October 2018; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 400–408. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, J.; Gugger, S. Fastai: A Layered API for Deep Learning. Information 2020, 11, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liapis, A.; Katsanos, C.; Karousos, N.; Xenos, M.; Orphanoudakis, T. User Experience Evaluation: A Validation Study of a Tool-Based Approach for Automatic Stress Detection Using Physiological Signals. Int. J. Hum.–Comput. Interact. 2021, 37, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, C.; Gedeon, T. Evaluating Crowdsourced Relevance Assessments Using Self-Reported Traits and Task Speed. In Proceedings of the 29th Australian Conference on Computer-Human Interaction; Association for Computing Machinery: Brisbane, Qld, Australia, 2017; pp. 407–411. [Google Scholar]
- Khorram, S.; Jaiswal, M.; Gideon, J.; McInnis, M.; Mower Provost, E. The PRIORI Emotion Dataset: Linking Mood to Emotion Detected In-the-Wild. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2018, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; ISCA: Hyderabad, India, 2018; pp. 1903–1907. [Google Scholar]
- Pakarinen, T.; Pietilä, J.; Nieminen, H. Prediction of Self-Perceived Stress and Arousal Based on Electrodermal Activity*. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 2191–2195. [Google Scholar]
- Bruun, A. It’s Not Complicated: A Study of Non-Specialists Analyzing GSR Sensor Data to Detect UX Related Events. In Proceedings of the 10th Nordic Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Oslo, Norway, 29 September–3 October 2018; ACM: Oslo, Norway, 2018; pp. 170–183. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Du, S. Psychological Stress Level Detection Based on Electrodermal Activity. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 341, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jussila, J.; Venho, N.; Salonius, H.; Moilanen, J.; Liukkonen, J.; Rinnetmäki, M. Towards Ecosystem for Research and Development of Electrodermal Activity Applications. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Academic Mindtrek Conference, Tampere, Finland, 10–11 October 2018; Association for Computing Machinery: Tampere, Finland, 2018; pp. 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and Regression Trees. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth. Int. Group 1984, 432, 151–166. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; He, T.; Benesty, M.; Khotilovich, V.; Tang, Y.; Cho, H. Xgboost: Extreme Gradient Boosting. R Package Version 0.4-2. 2015, Volume 1. Available online: https://mran.microsoft.com/web/packages/xgboost/vignettes/xgboost.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2021).
- Joachims, T. Training Linear SVMs in Linear Time. In Proceedings of the 12th ACM SIGKDD on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 20–23 August 2006; pp. 217–226. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Berkhahn, F. Entity Embeddings of Categorical Variables. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1604.06737. [Google Scholar]
- Mandryk, R.L.; Atkins, M.S. A Fuzzy Physiological Approach for Continuously Modeling Emotion during Interaction with Play Technologies. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 2007, 65, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, J.; Picard, R. Detecting Stress during Real-World Driving Tasks Using Physiological Sensors. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2005, 6, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heaton, J. Introduction to Neural Networks for Java, 2nd ed.; Heaton Research, Inc.: Chesterfield, UK, 2008; ISBN 978-1-60439-008-7. [Google Scholar]
- Sewak, M.; Sahay, S.K.; Rathore, H. An Overview of Deep Learning Architecture of Deep Neural Networks and Autoencoders. J.Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2020, 17, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liapis, A.; Karousos, N.; Katsanos, C.; Xenos, M. Evaluating user’s emotional experience in HCI: The physiOBS approach. In Human-Computer Interaction. Advanced Interaction Modalities and Techniques; Kurosu, M., Ed.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 758–767. ISBN 978-3-319-07229-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bruun, A.; Law, E.L.-C.; Heintz, M.; Alkly, L.H.A. Understanding the Relationship between Frustration and the Severity of Usability Problems: What Can Psychophysiological Data (Not) Tell Us? In Proceedings of the 2016 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, San Jose, CA, USA, 7–12 May 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 3975–3987. [Google Scholar]
- Liapis, A.; Katsanos, C.; Karousos, N.; Xenos, M.; Orphanoudakis, T. UDSP+: Stress Detection Based on User-Reported Emotional Ratings and Wearable Skin Conductance Sensor. In Proceedings of the Adjunct Proceedings of the 2019 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing and Proceedings of the 2019 ACM International Symposium on Wearable Computers, London, UK, 9–13 September 2019; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.N. A Disciplined Approach to Neural Network Hyper-Parameters: Part 1—Learning Rate, Batch Size, Momentum, and Weight Decay. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.09820. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, S.; Giles, C.L. Overfitting and Neural Networks: Conjugate Gradient and Backpropagation. In Proceedings of the IEEE-INNS-ENNS International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. IJCNN 2000. Neural Computing: New Challenges and Perspectives for the New Millennium, Como, Italy, 27 July 2000; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2000; Volume 1, pp. 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. A Coefficient of Agreement for Nominal Scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| C-SVM | L-SVM | Q-SVM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | SC | 89.7% | 92.6% | 92.4% |
| ST | 37.1% | 25.0% | 33.3% | |
| Recall | SC | 89,7% | 91.5% | 88.5% |
| ST | 31.5% | 03.6% | 22.4% | |
| Accuracy | SC | 91.1% | 93.2% | 91.8% |
| ST | 47.1% | 53.4% | 46.8% | |
| F1-Score | SC | 89.7% | 92.1% | 90.4% |
| ST | 34.1% | 06.3% | 26.8% |
| Without Categorical Variables | With Categorical Variables | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Train loss | SC | 48.2 | 27.5 |
| ST | 54 | 52.1 | |
| SC_ST | 48.6 | 26.9 | |
| Valid loss | SC | 29.1 | 13.8 |
| ST | 48.7 | 44.3 | |
| SC_ST | 28.8 | 14.4 | |
| Accuracy | SC | 94.7 | 97.4 |
| ST | 78,9 | 83.2 | |
| SC_ST | 94.7 | 97.3 | |
| F1-Score | SC | 92.8 | 97.7 |
| ST | 60 | 67.1 | |
| SC_ST | 92.9 | 97.6 |
| Trained Model | Kappa Value | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|
| C-SVM | −0.02 | [−0.20, 0.16] |
| L-SVM | 0.02 | [−0.16, 0.20] |
| Q-SVM | 0.17 | [−0.01, 0.35] |
| NN model | 0.27 | [0.09, 0.45] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liapis, A.; Faliagka, E.; Antonopoulos, C.P.; Keramidas, G.; Voros, N. Advancing Stress Detection Methodology with Deep Learning Techniques Targeting UX Evaluation in AAL Scenarios: Applying Embeddings for Categorical Variables. Electronics 2021, 10, 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10131550
Liapis A, Faliagka E, Antonopoulos CP, Keramidas G, Voros N. Advancing Stress Detection Methodology with Deep Learning Techniques Targeting UX Evaluation in AAL Scenarios: Applying Embeddings for Categorical Variables. Electronics. 2021; 10(13):1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10131550
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiapis, Alexandros, Evanthia Faliagka, Christos P. Antonopoulos, Georgios Keramidas, and Nikolaos Voros. 2021. "Advancing Stress Detection Methodology with Deep Learning Techniques Targeting UX Evaluation in AAL Scenarios: Applying Embeddings for Categorical Variables" Electronics 10, no. 13: 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10131550
APA StyleLiapis, A., Faliagka, E., Antonopoulos, C. P., Keramidas, G., & Voros, N. (2021). Advancing Stress Detection Methodology with Deep Learning Techniques Targeting UX Evaluation in AAL Scenarios: Applying Embeddings for Categorical Variables. Electronics, 10(13), 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10131550






