High-Linearity Direct Conversion Receiver with the Transconductance Equalization Technique and DCOC Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. High-Linearity Methods
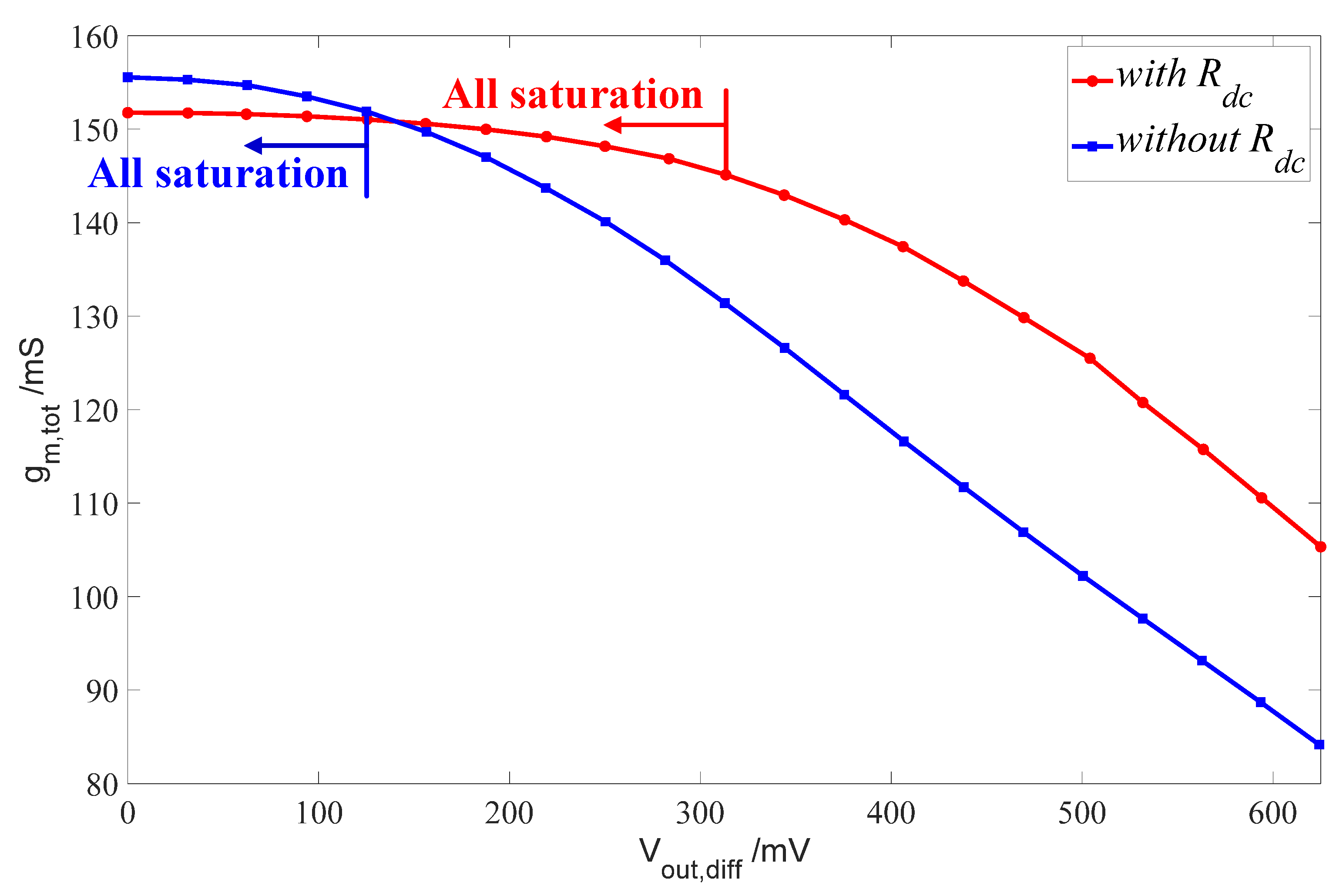
2.1. Transconductance Equalization Technique
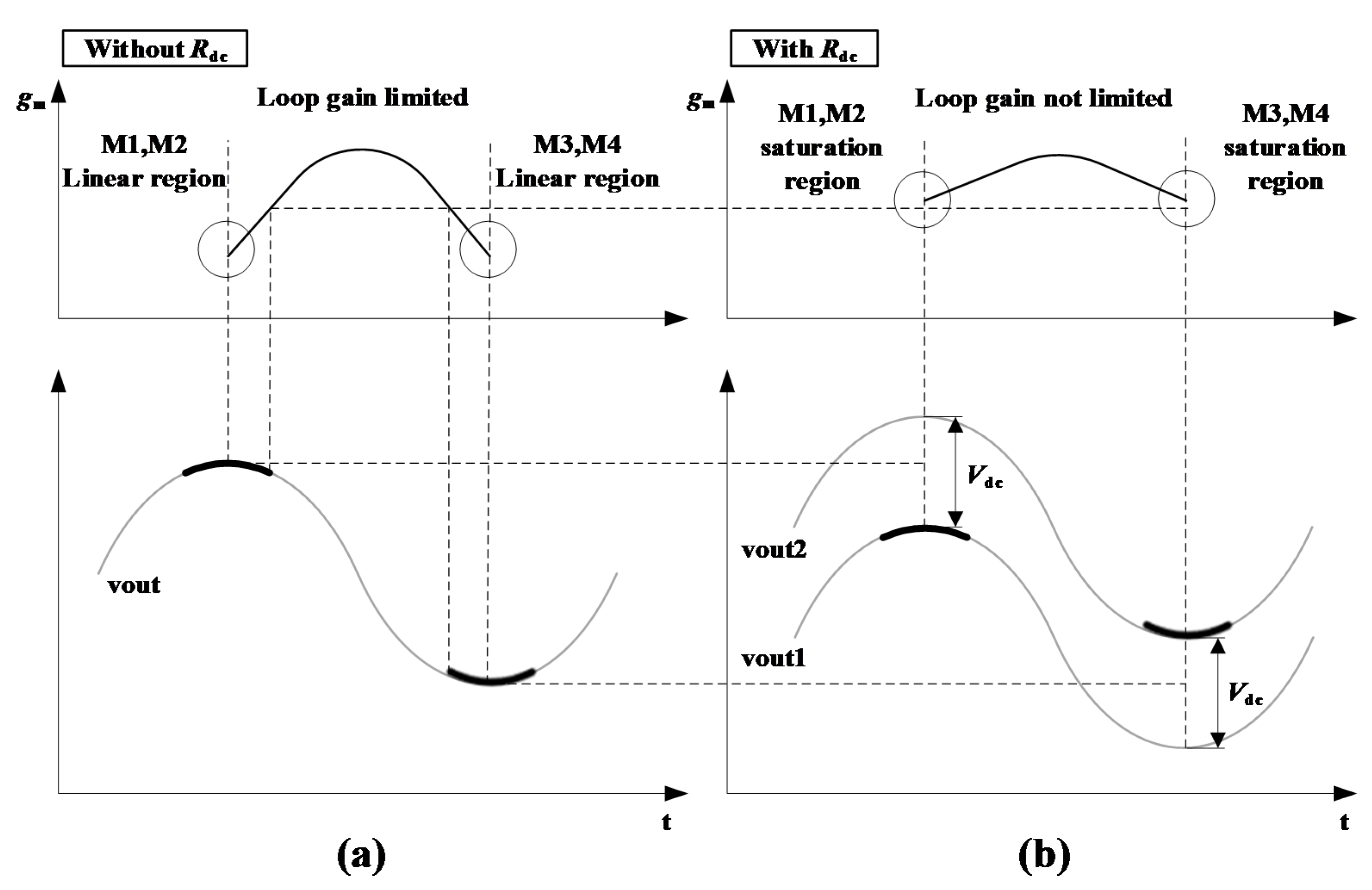
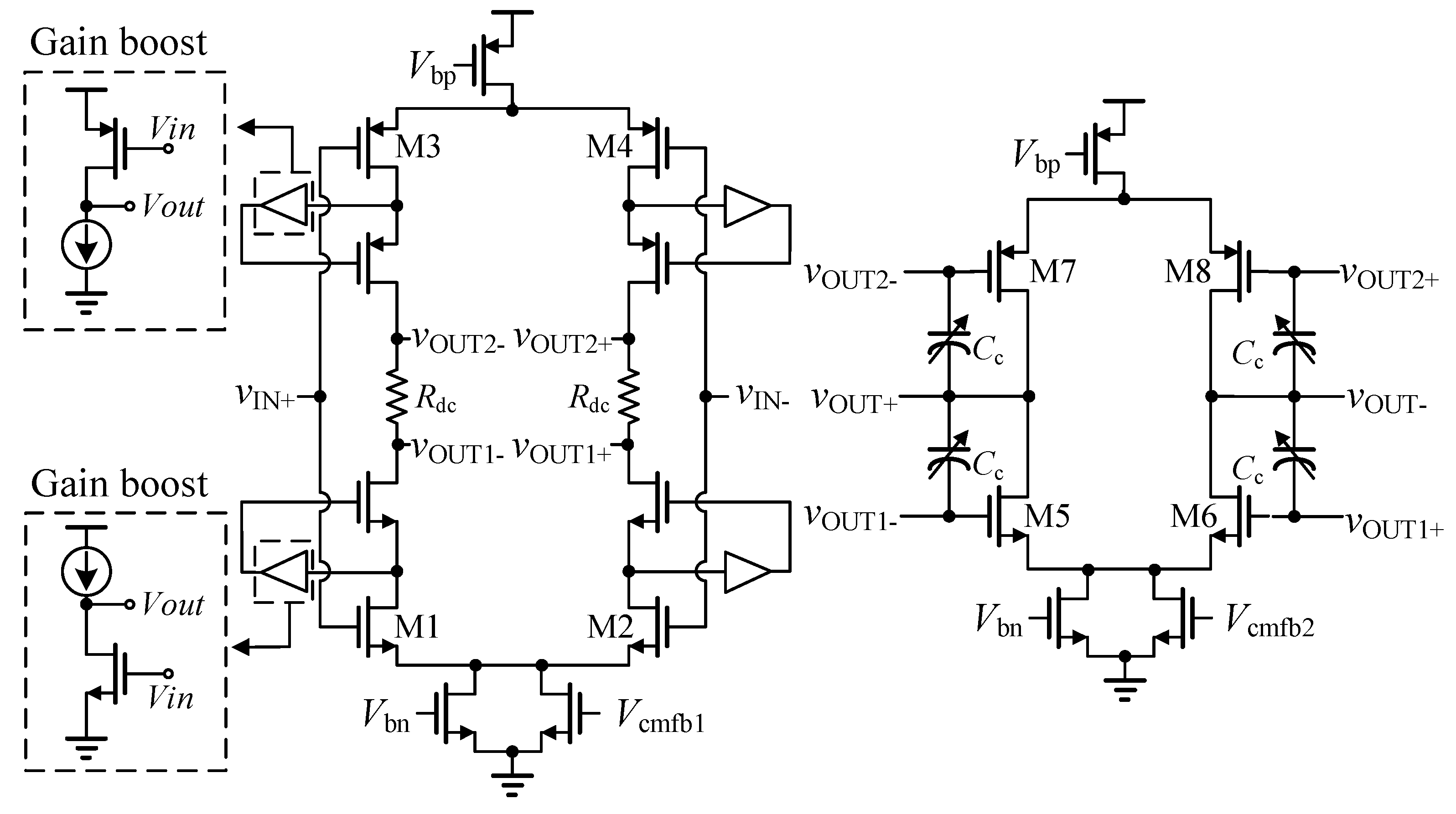
2.2. DCOC Method
3. Circuit Designs
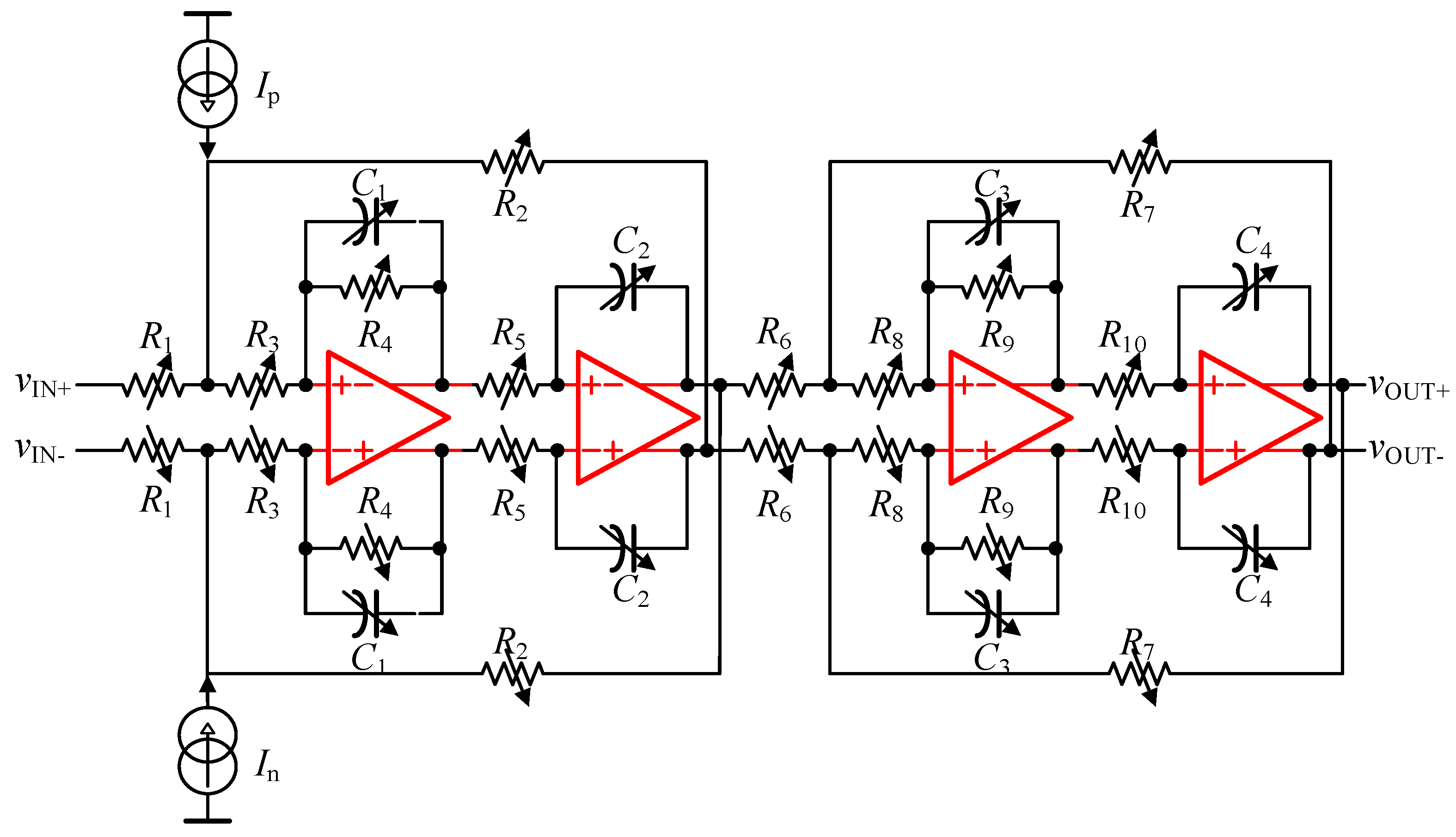
3.1. RC-Active LPF Based on a Complementary OPAMP with the Proposed Transconductance Equalization Technique
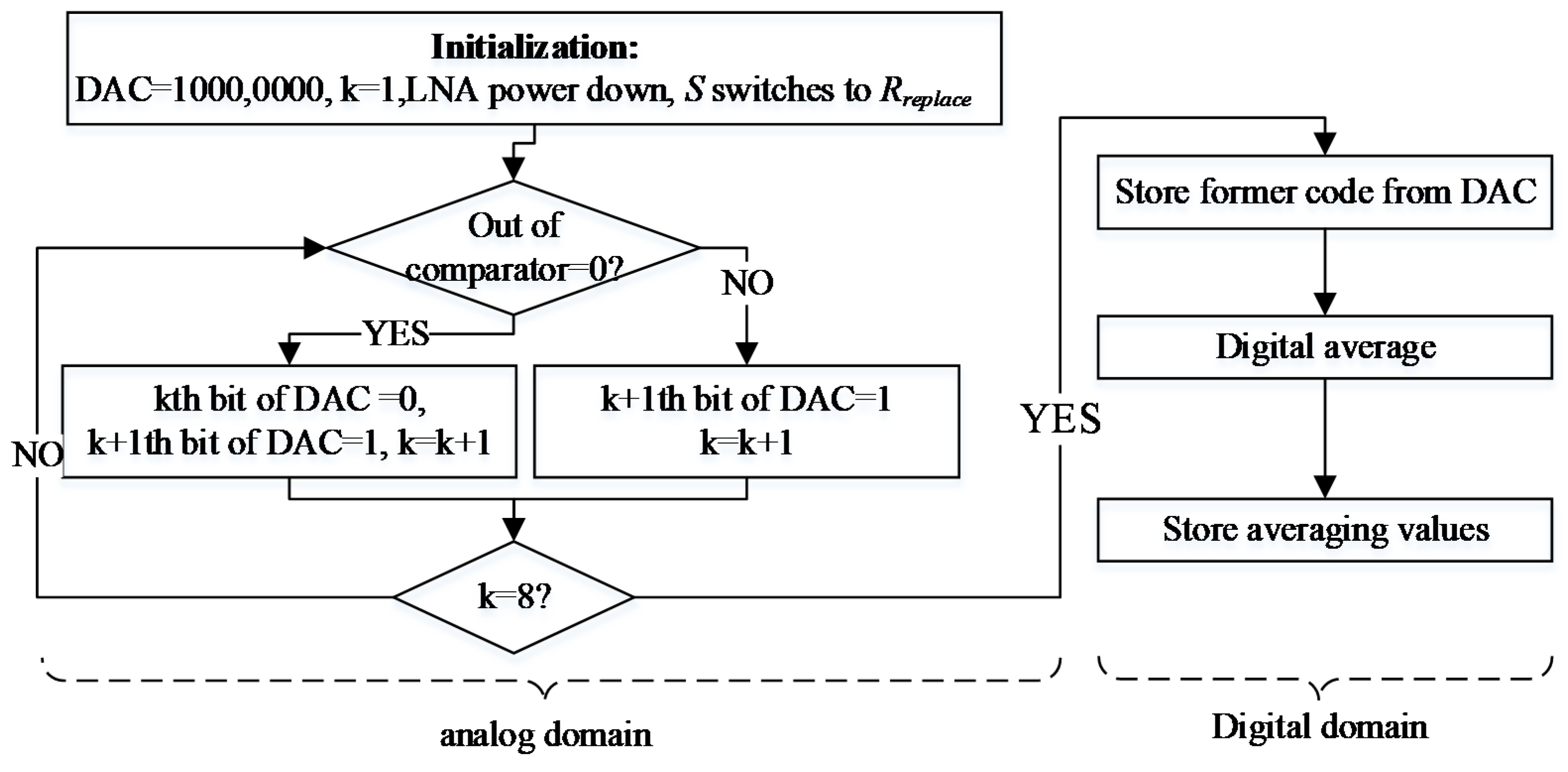
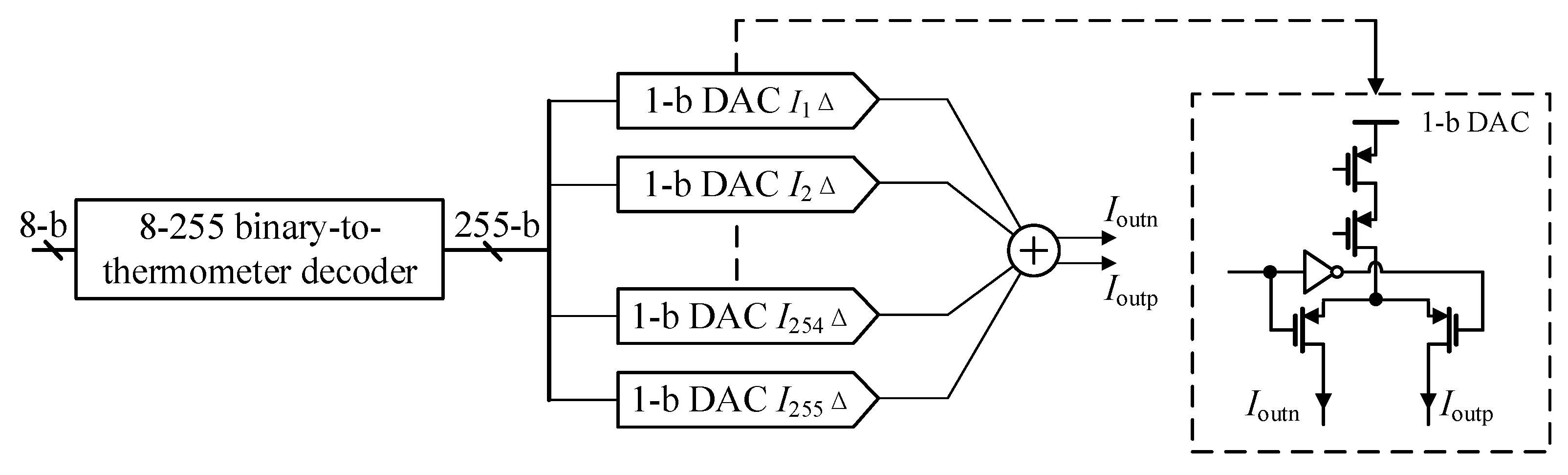
3.2. DCOC Circuits
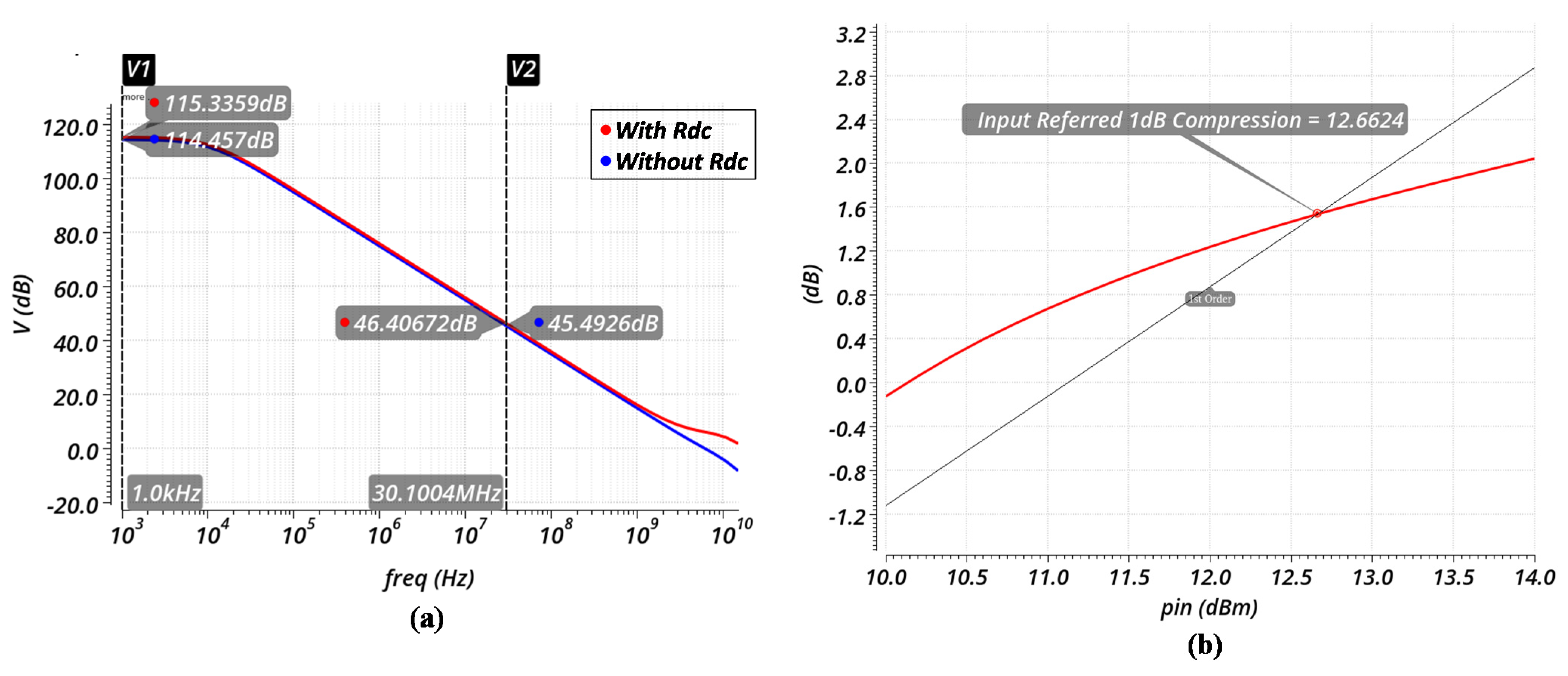
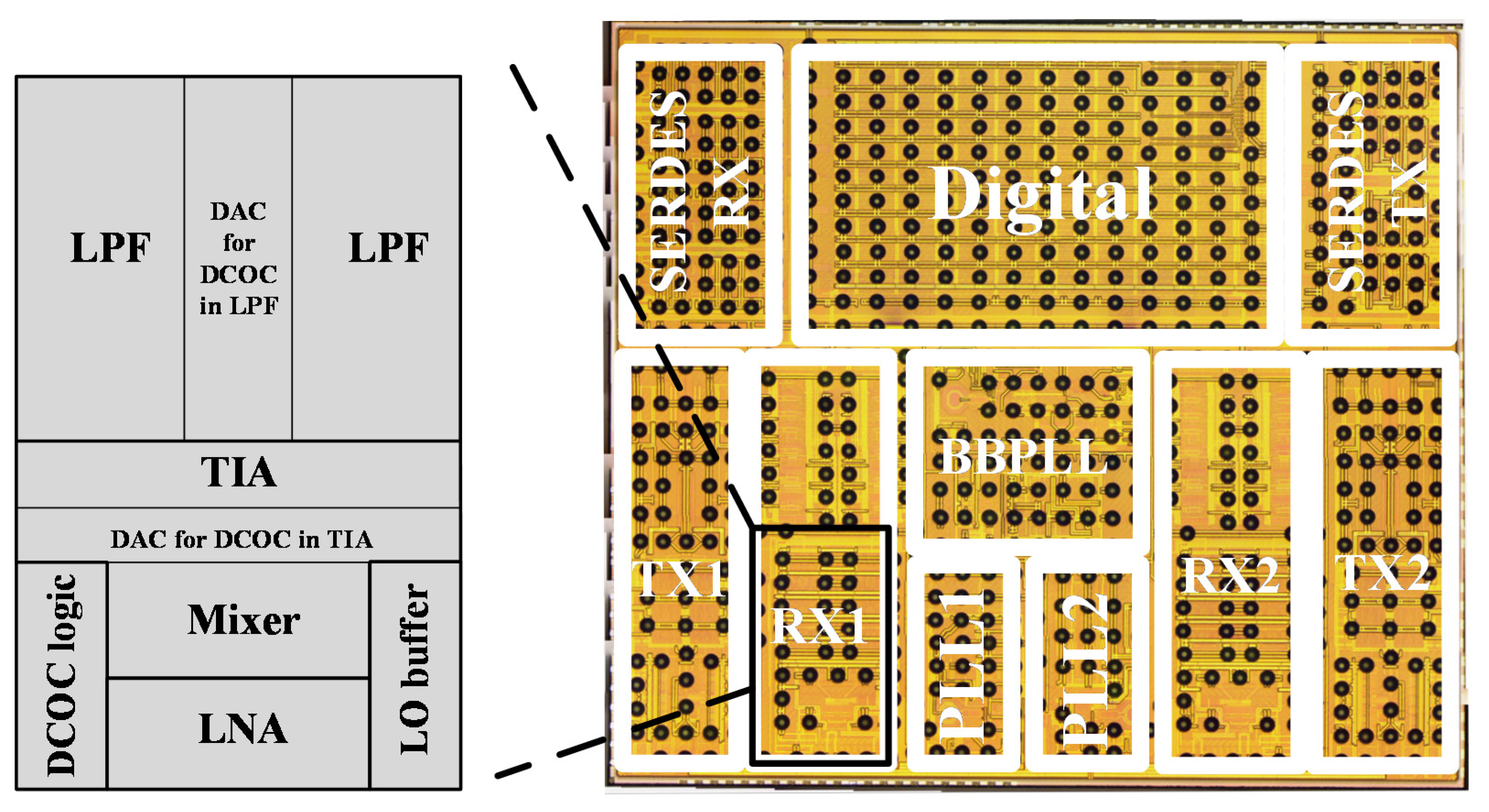
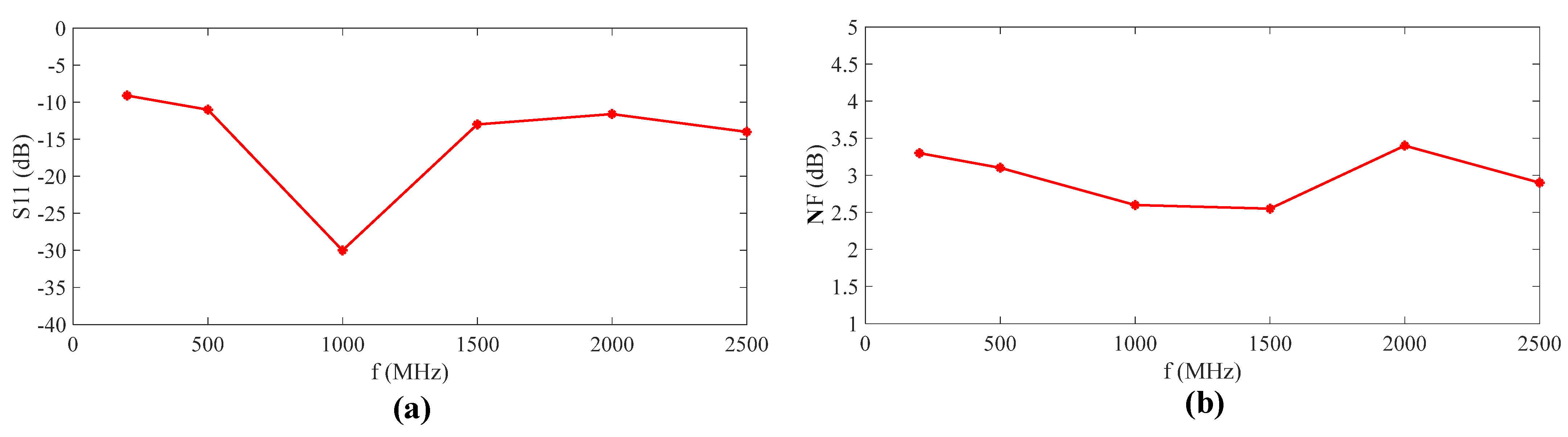
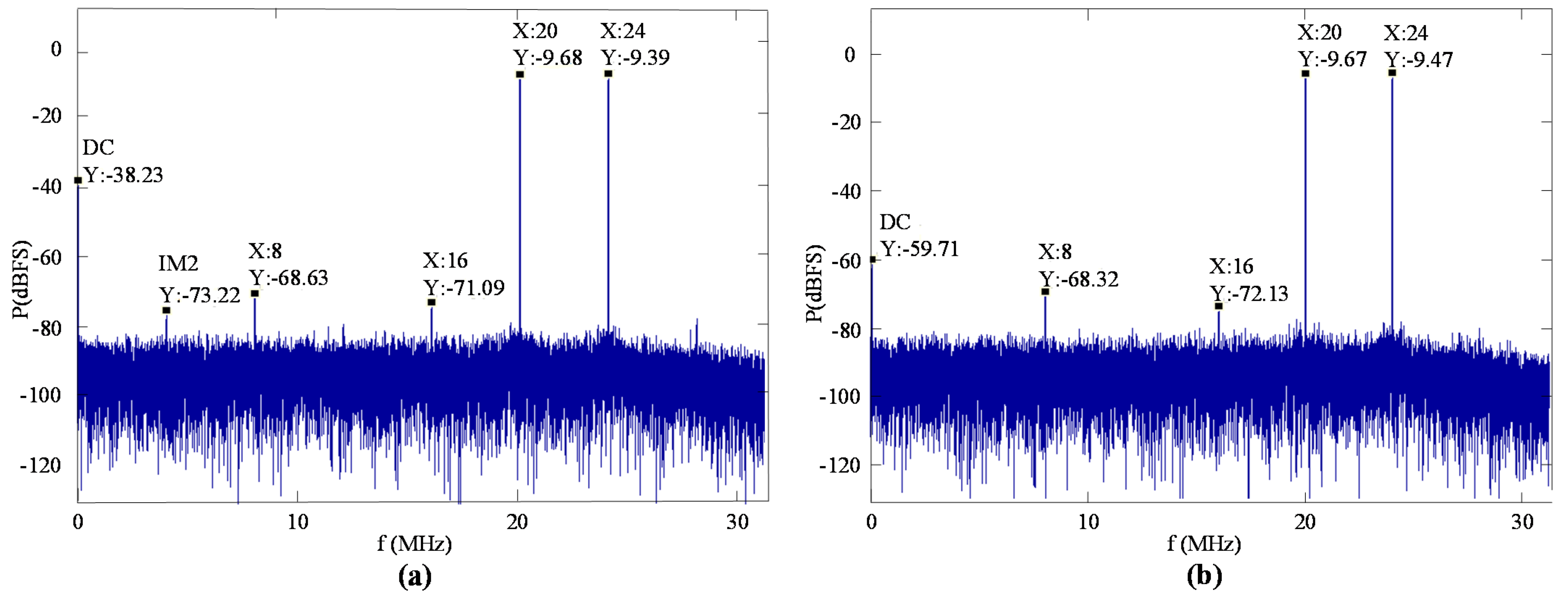
4. Measurement Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Razavi, B. Design considerations for direct-conversion receivers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Analog Digit. Signal Process. 1997, 44, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, J.; Kim, J. A 20-kHz~16-MHz Programmable-Bandwidth 4th Order Active Filter Using Gain-Boosted Opamp With Negative Resistance in 65-nm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2018, 66, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyagarajan, S.V.; Pavan, S.; Sankar, P. Active-RC filters using the Gm-assisted OTA-RC technique. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2011, 46, 1522–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Shi, C.; Liao, H.; Huang, R.; Wang, Y. Highly power-efficient active-RC filters with wide bandwidth-range using low-gain push-pull opamps. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2012, 60, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousai, S.; Hamada, M.; Ito, R.; Itakura, T. A 19.7 MHz, fifth-order active-RC Chebyshev LPF for draft IEEE802. 11n with automatic quality-factor tuning scheme. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2007, 42, 2326–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.; Weste, N. A 500 MHz CMOS anti-alias filter using feed-forward op-amps with local common-mode feedback. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, Digest of Technical Papers, ISSCC 2003, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13 February 2003; pp. 132–483. [Google Scholar]
- Laxminidhi, T.; Prasadu, V.; Pavan, S. Widely programmable high-frequency active RC filters in CMOS technology. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2008, 56, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Mo, T.; Lu, Z. A 180 nm CMOS three stage feedforward compensation op-amp with linearity improvement technique for active RC LPF. In Proceedings of the 2016 10th IEEE International Conference on Anti-counterfeiting, Security, and Identification (ASID), Xiamen, China, 23–25 September 2016; pp. 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Fary, F.; Mangiagalli, L.; Vallicelli, E.; De Matteis, M.; Baschirotto, A. A 28 nm bulk-CMOS 50MHz 18 dBm-IIP3 Active-RC Analog Filter based on 7 GHz UGB OTA. In Proceedings of the ESSCIRC 2019—IEEE 45th European Solid State Circuits Conference (ESSCIRC), Cracow, Poland, 23–26 September 2019; pp. 253–256. [Google Scholar]
- Ballo, A.; Grasso, A.D.; Pennisi, S. Active load with cross-coupled bulk for high-gain high-CMRR nanometer CMOS differential stages. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2019, 47, 1700–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballo, A.; Grasso, A.D.; Pennisi, S.; Venezia, C. High-Frequency Low-Current Second-Order Bandpass Active Filter Topology and Its Design in 28-nm FD-SOI CMOS. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2020, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Zheng, Y.; Garg, H. A novel algorithm for DC offsets and flicker noise cancellation in direct conversion receivers. In Proceedings of the 2004 Ninth International Conference onCommunications Systems, ICCS 2004, Singapore, 7 September 2004; pp. 441–445. [Google Scholar]
- Namgoong, W. DC-offset and 1/f noise effects on AC-coupled direct-conversion receiver. In Proceedings of the 44th IEEE 2001 Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems. MWSCAS 2001 (Cat. No. 01CH37257), Dayton, OH, USA, 14–17 August 2001; pp. 886–889. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, M.-C.; Kao, S.-W.; Chen, C.-H.; Hung, T.-S.; Shih, Y.-S.; Yang, T.-Y.; Kuo, C.-N. A 1.2 V 114 mW Dual-Band Direct-Conversion DVB-H Tuner in 0.13 μm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2009, 44, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Lin, M.; Gong, Z.; Shi, Y.; Dai, F.F. A CMOS programmable gain amplifier with a novel DC-offset cancellation technique. In Proceedings of the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference 2010, San Jose, CA, USA, 19–22 September 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Liao, H.; Song, F.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Zhao, J.; Liu, R.; Wang, C.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. A single-chip CMOS UHF RFID reader transceiver for Chinese mobile applications. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2010, 45, 1316–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moezzi, M.; Mousavi, S.F.; Ashtari, P. An area-efficient DC offset cancellation architecture for zero-IF DVB-H receivers. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2018, 28, 813–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpe, P.; Zhou, C.; Philips, K.; de Groot, H. A 1.6 mW 0.5 GHz open-loop VGA with fast startup and offset calibration for UWB radios. In Proceedings of the 2011 Proceedings of the ESSCIRC (ESSCIRC), Helsinki, Finland, 12–16 September 2011; pp. 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.-M.; Park, K.-S.; Yoo, H.-H.; Na, Y.-S.; Kim, T.-S. A design of DC offset canceller using parallel compensation. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 27–30 May 2007; pp. 1685–1688. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, H.; Tsurumi, H.; Suzuki, Y. DC offset canceller in a direct conversion receiver for QPSK signal reception. In Proceedings of the Ninth IEEE International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (Cat. No. 98TH8361), Boston, MA, USA, 8–11 September 1998; pp. 1314–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, F.; Guo, Q.; Liu, J.; Tan, X.; Min, H. A new DC cancellation technique for a mixer-first receiver in UHF RFID reader. In Proceedings of the 2016 13th IEEE International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology (ICSICT), Hangzhou, China, 25–28 October 2016; pp. 1564–1566. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Tan, X.; Min, H. An area-efficient digitally-assisted DC canceling loop for high sensitivity UHF RFID receiver. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on RFID Technology and Applications (RFID-TA), Foshan, China, 21–23 September 2016; pp. 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, S.J.; Lee, S.T.; Allstot, D.J.; Bellaouar, A. A 2 GHz CMOS even harmonic mixer for direct conversion receivers. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (Cat. No. 02CH37353), Phoenix-Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 26–29 May 2002; p. IV. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Hu, S.; Xie, R.; Li, X.; Fu, J.; Sun, Y.; Pan, Y.; Chen, H.; Jiang, C. A High-Linearity WCDMA/GSM Reconfigurable Transceiver in 0.13-μm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2012, 61, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crols, J.; Steyaert, M.S. A 1.5 GHz highly linear CMOS downconversion mixer. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 1995, 30, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Jiang, C.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; Hong, Z. A dual-mode analog baseband utilizing digital-assisted calibration for WCDMA/GSM receivers. In Proceedings of the 2011 9th IEEE International Conference on ASIC, Xiamen, China, 25–28 October 2011; pp. 1058–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Valla, M.; Montagna, G.; Castello, R.; Tonietto, R.; Bietti, I. A 72-mW CMOS 802.11 a direct conversion front-end with 3.5-dB NF and 200-kHz 1/f noise corner. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2005, 40, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redman-White, W.; Leenaerts, D. 1/f noise in passive CMOS mixers for low and zero IF integrated receivers. In Proceedings of the 27th European Solid-State Circuits Conference, Villach, Austria, 18–20 September 2001; pp. 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi, E.; Bietti, I.; Erba, S.; Tee, L.; Vilmercati, P.; Castello, R. A 15 mW, 70 kHz 1/f corner direct conversion CMOS receiver. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2003 Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 24 September 2003; pp. 459–462. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Fan, L.; Shen, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Yu, F. An effective DC offset calibration method combined with analog and digital circuits for direct conversion receivers. IEICE Electron. Express 2019, 16, 20190518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vassiliou, I.; Vavelidis, K.; Georgantas, T.; Plevridis, S.; Haralabidis, N.; Kamoulakos, G.; Kapnistis, C.; Kavadias, S.; Kokolakis, Y.; Merakos, P. A single-chip digitally calibrated 5.15–5.825-GHz 0.18-μm CMOS transceiver for 802.11 a wireless LAN. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2003, 38, 2221–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, H.-Y.; Kuo, C.-N.; Chen, W.-H.; Yang, T.-Y.; Juang, K.-C. A 250 MHz 14 dB-NF 73 dB-gain 82 dB-DR analog baseband chain with digital-assisted DC-offset calibration for ultra-wideband. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2010, 45, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, F.A.; Murad, S.A.Z.; Ismail, R.C.; Saari, V.; Halonen, K. A 9-bit current-steering Digital to Analog Converter for differential dc-offset compensation of a baseband chain. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Student Conference on Research and Development, Penang, Malaysia, 16–17 December 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.; Shin, H. 2.4-GHz CMOS Bluetooth RF Receiver With Improved IM2 Distortion Tolerance. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2020, 68, 4589–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y. A PVT-robust analog baseband with DC offset cancellation for FMCW automotive radar. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 43249–43257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaei, M.A.; Golabighezelahmad, S.; de Boer, P.-T.; van Vliet, F.E.; Klumperink, E.A.; Kokkeler, A.B. Interference Mitigation by Adaptive Analog Spatial Filtering for MIMO Receivers. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Transconductance Amplifier of the Mixer | First-Stage OPAMP of the LPF | Second-Stage OPAMP of the LPF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gain | (Ω) | Gain | (Ω) | Gain | (Ω) |
| 15–27 dB | 500–2700 Max BW | 0–18 dB | 100–800 Max BW | 0–5 dB | 340–600 Max BW |
| 400–3200 Min BW | 1360–2400 Min BW | ||||
| [34] | [35] | [36] | This Work | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | 65 nm CMOS | 65 nm CMOS | 22 nm FD-SOI | 40 nm CMOS |
| Supply (V) | 1.0 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 1.3 |
| RF (MHz) | 2400 | N/A | 700–5700 | 200–2500 |
| IF (MHz) | N/A | 0.07–10 | N/A | 1–32 |
| Gain Range (dB) | 2–62 | 18.2–70.6 | 41 | 0–60 |
| IM2 (dBc) | 31.1 | N/A | N/A | >70 |
| OIP3 (dBm) | N/A | 7.8 | 22 | 28 |
| DC Remaining (dBm) | N/A | N/A | N/A | −53.2 |
| Noise Figure (dB) | 3.0 | N/A | 6.8–9.2 | 2.6–3.5 |
| Total Area (mm2) | 0.75 | N/A | 0.52 | 1.15 |
| Total Power (mW) | 3.55 | N/A | 19.25–34.75 | 160 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Yu, F. High-Linearity Direct Conversion Receiver with the Transconductance Equalization Technique and DCOC Method. Electronics 2021, 10, 1966. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10161966
Han Y, Wang F, Liu J, Wang Z, Yu F. High-Linearity Direct Conversion Receiver with the Transconductance Equalization Technique and DCOC Method. Electronics. 2021; 10(16):1966. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10161966
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yiming, Fengjie Wang, Jiarui Liu, Zhiyu Wang, and Faxin Yu. 2021. "High-Linearity Direct Conversion Receiver with the Transconductance Equalization Technique and DCOC Method" Electronics 10, no. 16: 1966. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10161966
APA StyleHan, Y., Wang, F., Liu, J., Wang, Z., & Yu, F. (2021). High-Linearity Direct Conversion Receiver with the Transconductance Equalization Technique and DCOC Method. Electronics, 10(16), 1966. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10161966






