Power System Zone Partitioning Based on Transmission Congestion Identification Using an Improved Spectral Clustering Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We achieve the possibility of decentralized computing in power system by partitioning the power grid into a finite number of smaller zones, which enables a flexible, distributed, and adaptable power system operation and control that utilizes the concept of smart grids [17].
- We identify the potential congested branches before power system zone partitioning for a more reasonable zone partitioning result that can represent regional economic characteristics to support system operation decision-making.
- We improve the spectral clustering algorithm by replacing the traditional k-means algorithm with the k-means++ algorithm for a more stable zone partitioning result without being affected by the selection of the initial values.
2. Related Work
2.1. Zone Partitioning Based on Optimization Algorithm
2.2. Zone Partitioning Based on Clustering Algorithm
2.3. Zone Partitioning Based on Graph Theory
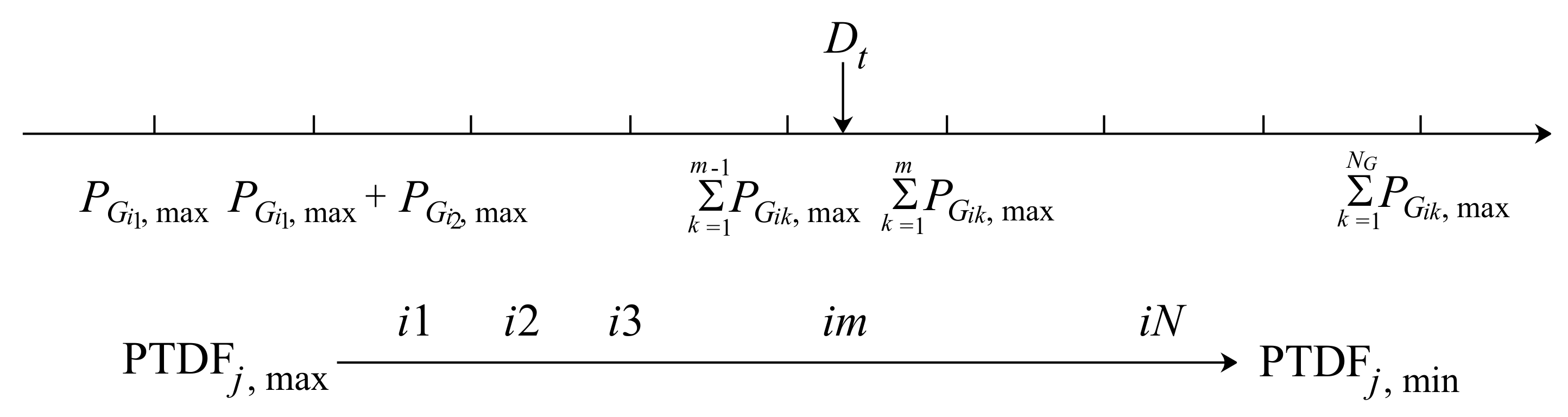
3. Power Transfer Distribution Factor
3.1. Sensitivity Analysis
3.2. Sensitivity Factor
- (1)
- The branch resistance is much less than the branch reactance such that the branch resistance can be ignored in the calculation.
- (2)
- The phase angles at the two ends of the power system branch are basically the same. Since the difference is so small, we have .
- (3)
- The voltage fluctuation of each bus is very small such that the voltage amplitude of all buses is set to 1.
- (4)
- All ground branches are ignored.
4. Transmission Congestion Identification Scheme
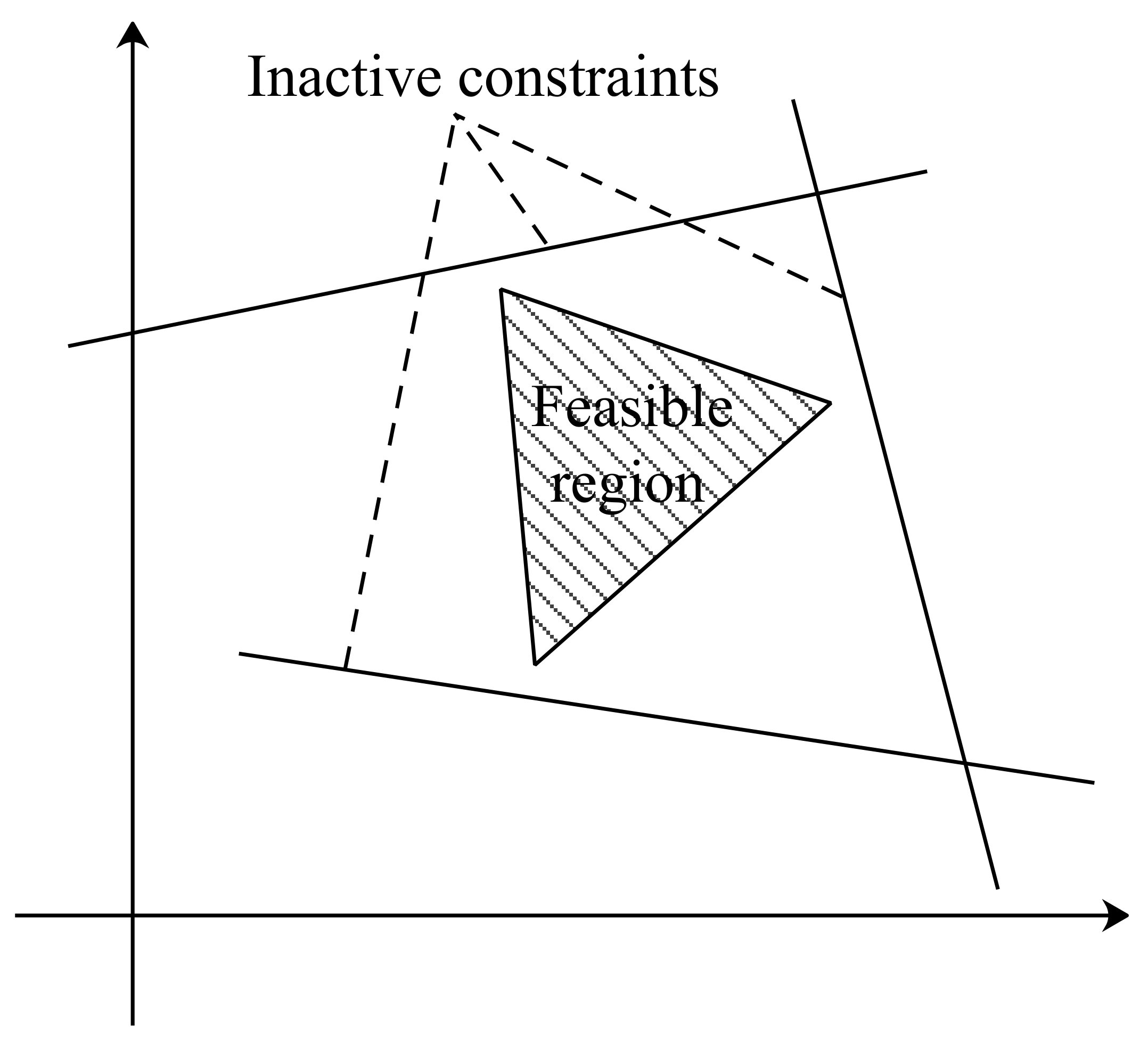
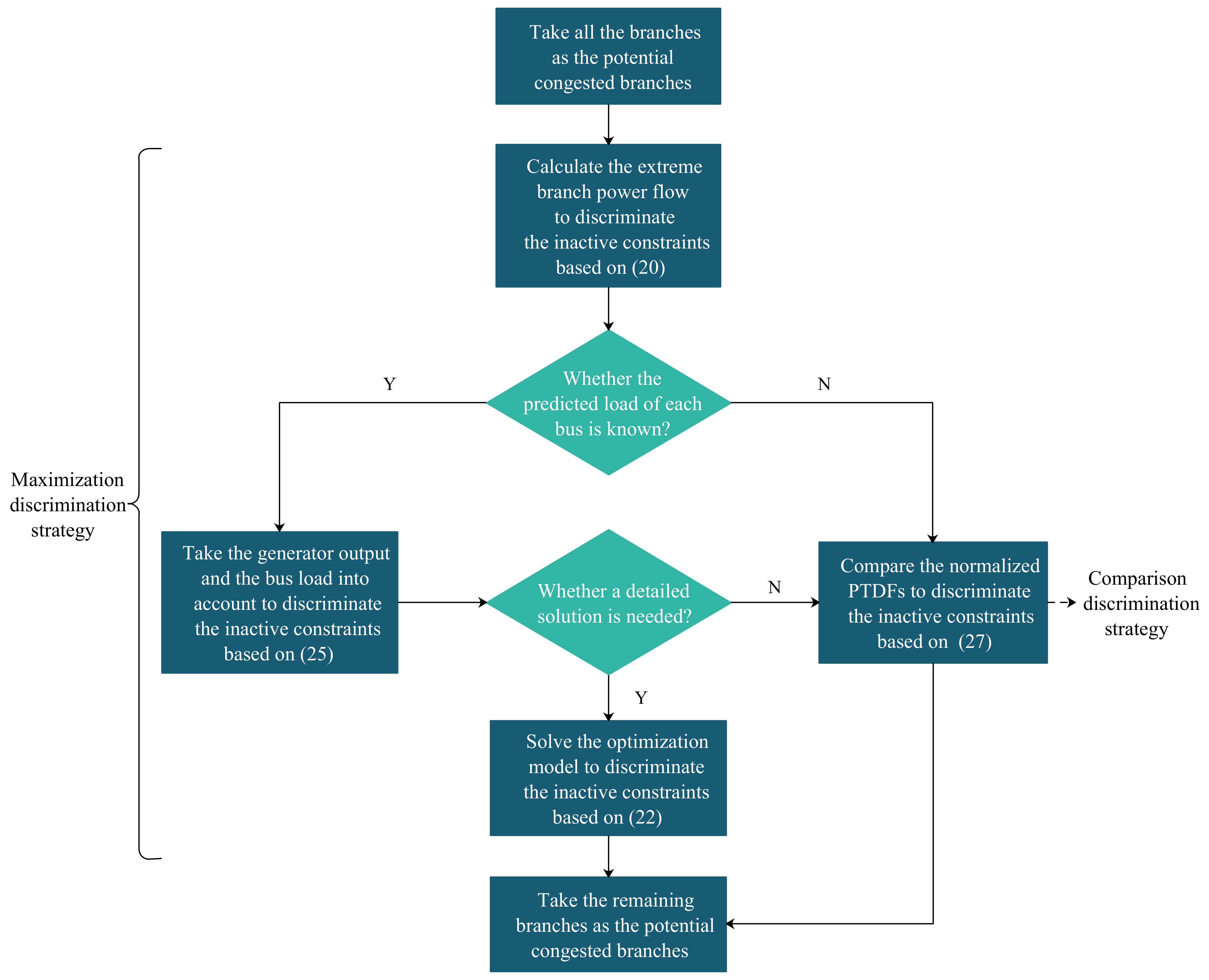
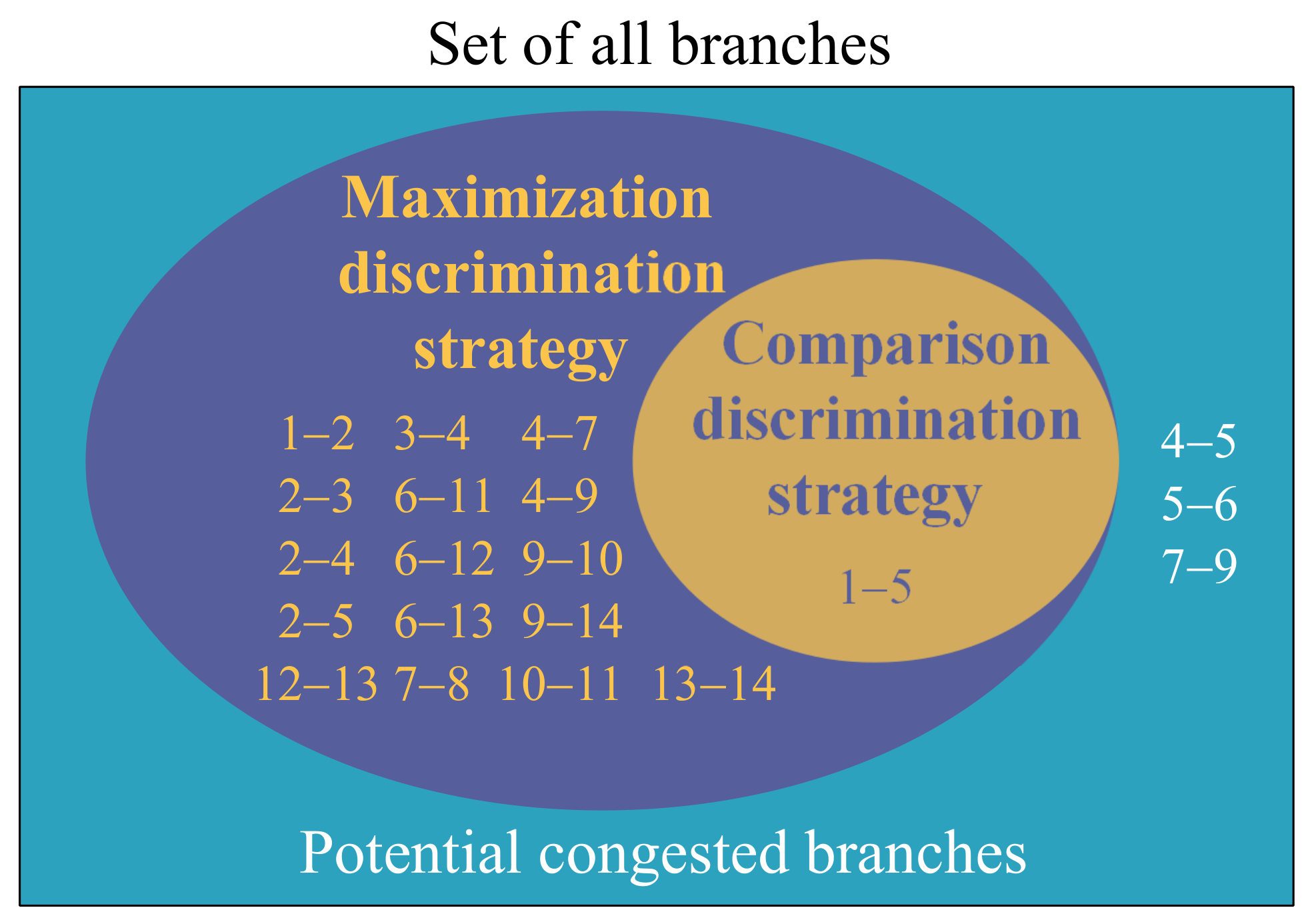
4.1. Congested Branch Identification Strategies
4.1.1. Maximization Discrimination Strategy
4.1.2. Comparison Discrimination Strategy
4.2. Congested Branch Identification Procedure
5. Power System Zone Partitioning Method
5.1. Graph-Based Zone Partitioning Model
- (a)
- , i.e., graph G is undirected and matrix is symmetric.
- (b)
- If , the corresponding branch weight is ; otherwise, .
- (c)
- The diagonal elements of matrix represent the degrees in graph theory, which are denoted as .
5.2. Improved Spectral Clustering Algorithm
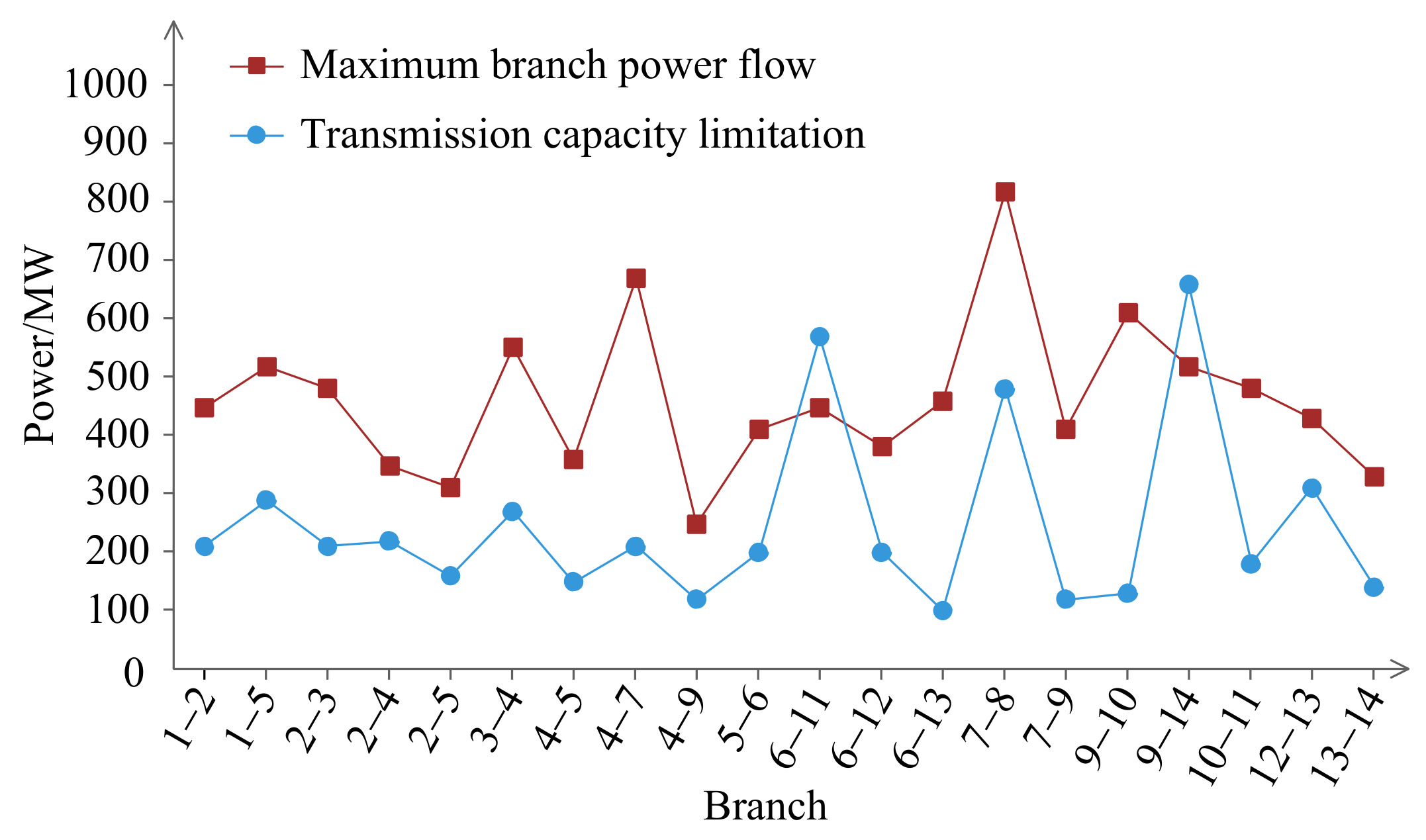
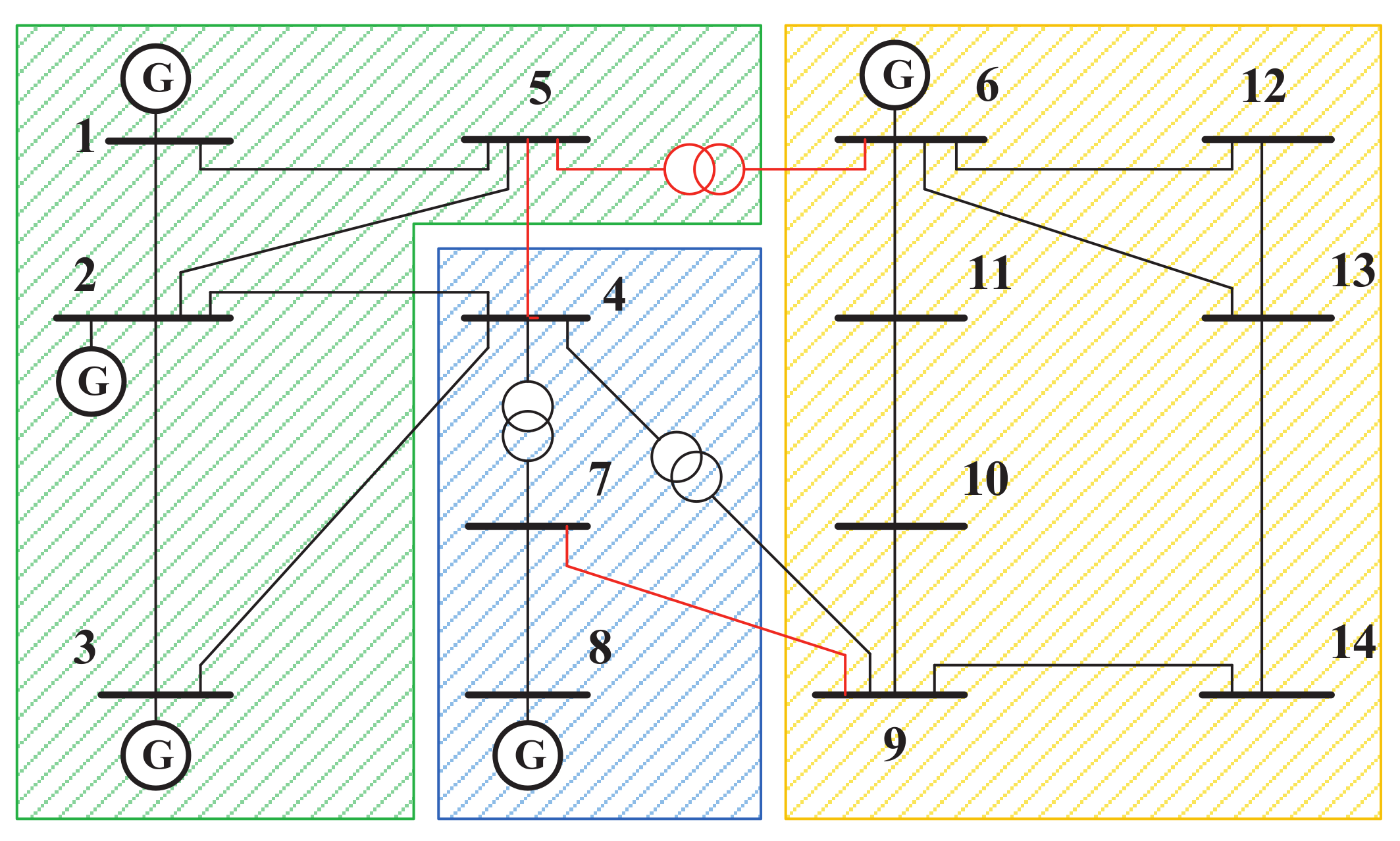
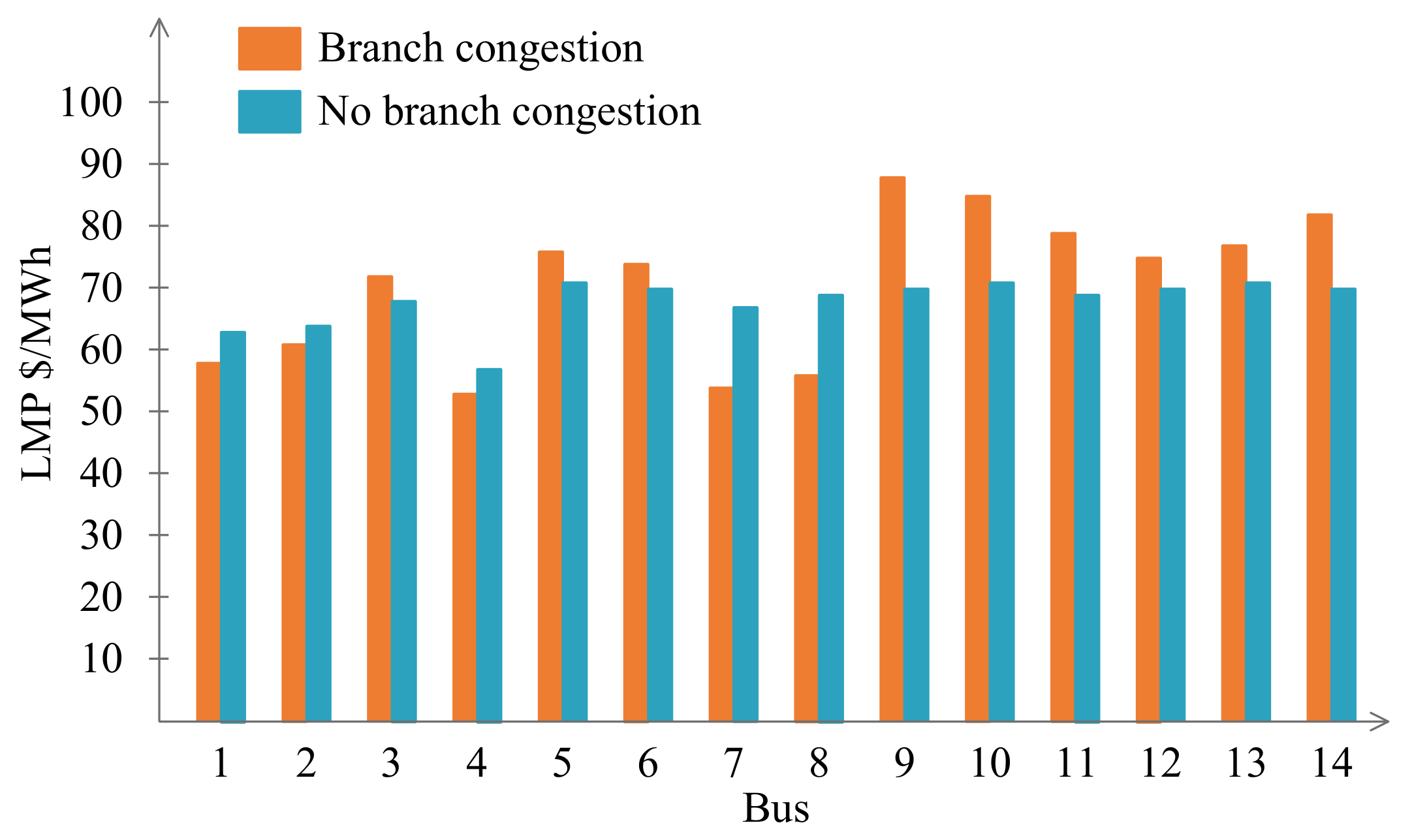
6. Evaluation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Byk, F.; Frolova, Y.; Myshkina, L. The efficiency of distributed and centralized power system integration. In Proceedings of the International Conference of Young Scientists Energy Systems Research 2019, Irkutsk, Russia, 27–30 May 2019; p. 05007. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.k.; Niu, W.j.; Cheng, C.t. China’s large-scale hydropower system: Operation characteristics, modeling challenge and dimensionality reduction possibilities. Renew. Energy 2019, 136, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iris, Ç.; Pacino, D.; Ropke, S.; Larsen, A. Integrated berth allocation and quay crane assignment problem: Set partitioning models and computational results. Trans. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2015, 81, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monteiro, M.R.; Alvarenga, G.F.; Rodrigues, Y.R.; de Souza, A.Z.; Lopes, B.; Passaro, M.C.; Abdelaziz, M. Network partitioning in coherent areas of static voltage stability applied to security region enhancement. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2020, 117, 105623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, L.; Rudnick, H. The future power system: Centralized, distributed, or just integrated?[guest editorial]. IEEE Power Energ. Mag. 2019, 17, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finney, J.D.; Othman, H.A.; Rutz, W.L. Evaluating transmission congestion constraints in system planning. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1997, 12, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Granado, P.C.; Wallace, S.W.; Pang, Z. The value of electricity storage in domestic homes: A smart grid perspective. Energy Syst. 2014, 5, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, J.; He, Z.; Yan, W. Microgrid energy dispatching for industrial zones with renewable generations and electric vehicles via stochastic optimization and learning. Physica A 2018, 501, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Granado, P.C.; Pang, Z.; Wallace, S.W. Synergy of smart grids and hybrid distributed generation on the value of energy storage. Appl. Energy 2016, 170, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iris, Ç.; Lam, J.S.L. A review of energy efficiency in ports: Operational strategies, technologies and energy management systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 112, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iris, Ç.; Lam, J.S.L. Optimal energy management and operations planning in seaports with smart grid while harnessing renewable energy under uncertainty. Omega 2021, 103, 102445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-García, R.J.; Fennelly, M.; Norris, S.; Wright, N.; Niblo, G.; Brodzki, J.; Bialek, J.W. Hierarchical spectral clustering of power grids. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2014, 29, 2229–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Challa, A.; Danda, S.; Sagar, B.D.; Najman, L. Power spectral clustering. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 2020, 62, 1195–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likas, A.; Vlassis, N.; Verbeek, J.J. The global k-means clustering algorithm. Pattern Recognit. 2003, 36, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duthaler, C.; Emery, M.; Andersson, G.; Kurzidem, M. Analysis of the use of Power Transfer Distribution factors (PTDF) in the UCTE transmission grid. In Proceedings of the Power System Computation Conference, Glasgow, UK, 14–18 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Arthur, D.; Vassilvitskii, S. k-means++: The advantages of careful seeding; Technical report; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 6 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- McArthur, S.D.; Taylor, P.C.; Ault, G.W.; King, J.E.; Athanasiadis, D.; Alimisis, V.D.; Czaplewski, M. The Autonomic Power System-Network operation and control beyond smart grids. In Proceedings of the 2012 3rd IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Europe (ISGT Europe), Berlin, Germany, 14–17 October 2012; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, H.; Takeda, K. Parallel simulated annealing for power system decomposition. In Proceedings of the Conference Proceedings Power Industry Computer Application Conference, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 4–7 May 1993; pp. 366–372. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.C.; Wang, X.F.; Wang, X.L.; Chen, H.Y. A two-layered network partitioning approach for optimal reactive power dispatching. Power Syst. Technol. 2005, 29, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.; Lu, L.; Wen, F. Power system network partitioning using tabu search. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 1999, 49, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Tang, G. Tabu search based network partitioning for voltage control. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2002, 26, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.; Gao, F.; Wang, F. An optimal network partitioning algorithm for reactive power and voltage control considering subareaal reactive power margin. Power Syst. Technol. 2015, 39, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, H.G.; Cheng, H.Z.; Kong, T. Network partitioning for reactive power/voltage control based on immune-ventral point clustering algorithm. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2007, 31, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.L.; Sun, H.B.; Zhang, B.M.; Wu, W.C. Power network partitioning based on clustering analysis in Mvar control space. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2005, 29, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, F.; Deng, Y.; Li, K.; Fang, Z.; Huang, W. Network partitioning for reactive power/voltage control based on a mapping division algorithm. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2010, 34, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.H.; Yun, Y.Z.; Xing, W.Y.; Hu, X. A novel strategy of network partitioning for load node in power systems using spectral clustering. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2013, 41, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.I.; Zihao, F.U.; Sun, L.; Yang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Lin, Z.; Wen, F. Black-start zoning strategy based semi-supervised spectral clustering algorithm. Electr. Power Constr. 2017, 38, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, D.; Yun, W.Y. Power-grid-partitioning model and its tabu-search-embedded algorithm for zonal pricing. IFAC Proc. Volumes 2008, 41, 15927–15932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.R.; Kang, C.Q.; Xia, Q.; Jiang, J.J. Dynamic zonal pricing of power grid based on graph theory. Proc. CSEE 2005, 25, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, S.; Mokhlis, H.; Arof, H.; Laghari, J.; Mohamad, H. A sensitivity analysis of different power system parameters on islanding detection. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2015, 7, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyya, R.; Vazhkudai, S. Compute power market: Towards a market-oriented grid. In Proceedings of the Proceedings First IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster Computing and the Grid, Brisbane, Australia, 15–18 May 2001; pp. 574–581. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, H.; Hao, S.; Papalexopoulos, A. Transmission congestion management in competitive electricity markets. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1998, 13, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musicant, D.R.; Feinberg, A. Active set support vector regression. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 2004, 15, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conejo, A.J.; Castillo, E.; Mínguez, R.; Milano, F. Locational marginal price sensitivities. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2005, 20, 2026–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Peng, G.; Sun, D.; Xie, X. Active contours driven by Gaussian function and adaptive-scale local correntropy-based K-means clustering for fast image segmentation. Signal Process. 2020, 174, 107625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.S.; Lai, C.Y.; Lin, C.Y. A robust EM clustering algorithm for Gaussian mixture models. Pattern Recognit. 2012, 45, 3950–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meila, M.; Xu, L. Multiway Cuts and Spectral Clustering. 2003. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.142.8591 (accessed on 4 August 2021).
- Zimmerman, R.D.; Murillo-Sánchez, C.E.; Gan, D. MATPOWER: A MATLAB Power System Simulation Package; Manual, Power Systems Engineering Research Center: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]



| Branch | 1–2 | 1–5 | 2–3 | 2–4 | 2–5 | 3–4 | 4–5 | 4–7 | 4–9 | 5–6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward power flow | 181.24 | 75.65 | 104.54 | 101.52 | 77.47 | 173.78 | −17.05 | 98.37 | 58.14 | 93.57 |
| Reverse power flow | 61.45 | 41.28 | 58.78 | 41.45 | 35.15 | −31.76 | −59.75 | −183.39 | −35.21 | 42.37 |
| Branch | 6–11 | 6–12 | 6–13 | 7–8 | 7–9 | 9–10 | 9–14 | 10–11 | 12–13 | 13–14 |
| Forward power flow | 71.34 | 16.52 | 48.68 | 0 | 8.83 | −11.36 | −1.96 | −22.64 | 12.04 | 46.79 |
| Reverse power flow | 25.15 | 11.43 | 25.31 | −340.13 | −39.85 | −60.04 | −32.86 | −69.42 | 5.24 | 18.72 |
| Class | Branch |
|---|---|
| I | 1–2, 1–5, 5–6 |
| II | 2–3, 2–4, 2–5 |
| III | 3–4, 4–7, 4–9 |
| IV | 4–5, 7–9, 9–10, 9–14, 10–11 |
| V | 6–11, 6–13, 13–14 |
| Class | K-Means++ | K-Means (Solution 1) | K-Means (Solution 2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | 4,5,6,7,8,10,11, 12,13,14,31,32 | 4,5,6,7,8,10,11, 12,13,14,31,32 | 4,5,6,7,8,10,11, 12,13,14,31,32 |
| II | 2,3,17,18,25,26 27,28,29,30,37,38 | 2,3,18,25,26 27 28,29,30,37,38 | 2,3,17,18,25,26 27,28,29,30,37,38 |
| III | 15,16,19,20,21,22 23,24,33,34,35,36 | 16,19,20,21,22,23 24,33,34,35,36 | 16,19,20,21,22,23 24,33,34,35,36 |
| IV | 1,9,39 | 1,9,15,17,39 | 1,9,15,39 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Xun, P.; Kang, W.; Zhu, P.; Xiong, Y.; Shi, W. Power System Zone Partitioning Based on Transmission Congestion Identification Using an Improved Spectral Clustering Algorithm. Electronics 2021, 10, 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10172126
Hu Y, Xun P, Kang W, Zhu P, Xiong Y, Shi W. Power System Zone Partitioning Based on Transmission Congestion Identification Using an Improved Spectral Clustering Algorithm. Electronics. 2021; 10(17):2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10172126
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yifan, Peng Xun, Wenjie Kang, Peidong Zhu, Yinqiao Xiong, and Weiheng Shi. 2021. "Power System Zone Partitioning Based on Transmission Congestion Identification Using an Improved Spectral Clustering Algorithm" Electronics 10, no. 17: 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10172126
APA StyleHu, Y., Xun, P., Kang, W., Zhu, P., Xiong, Y., & Shi, W. (2021). Power System Zone Partitioning Based on Transmission Congestion Identification Using an Improved Spectral Clustering Algorithm. Electronics, 10(17), 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10172126






