Multi-Level Control of Resistive RAM (RRAM) Using a Write Termination to Achieve 4 Bits/Cell in High Resistance State
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A MLC architecture based on compliance current control during the RST operation, allowing a tight control of post-programming resistances for optimal robustness. The compliance current being defined as the minimal current allowed during the RST operation.
- An implementation at the circuit level with a minimal area overhead (i.e., dozens of transistors per bit-line) as no specialized read verification circuits are required.
- A minimal energy consumption as high resistance levels (i.e., HRS RRAM states) are targeted.
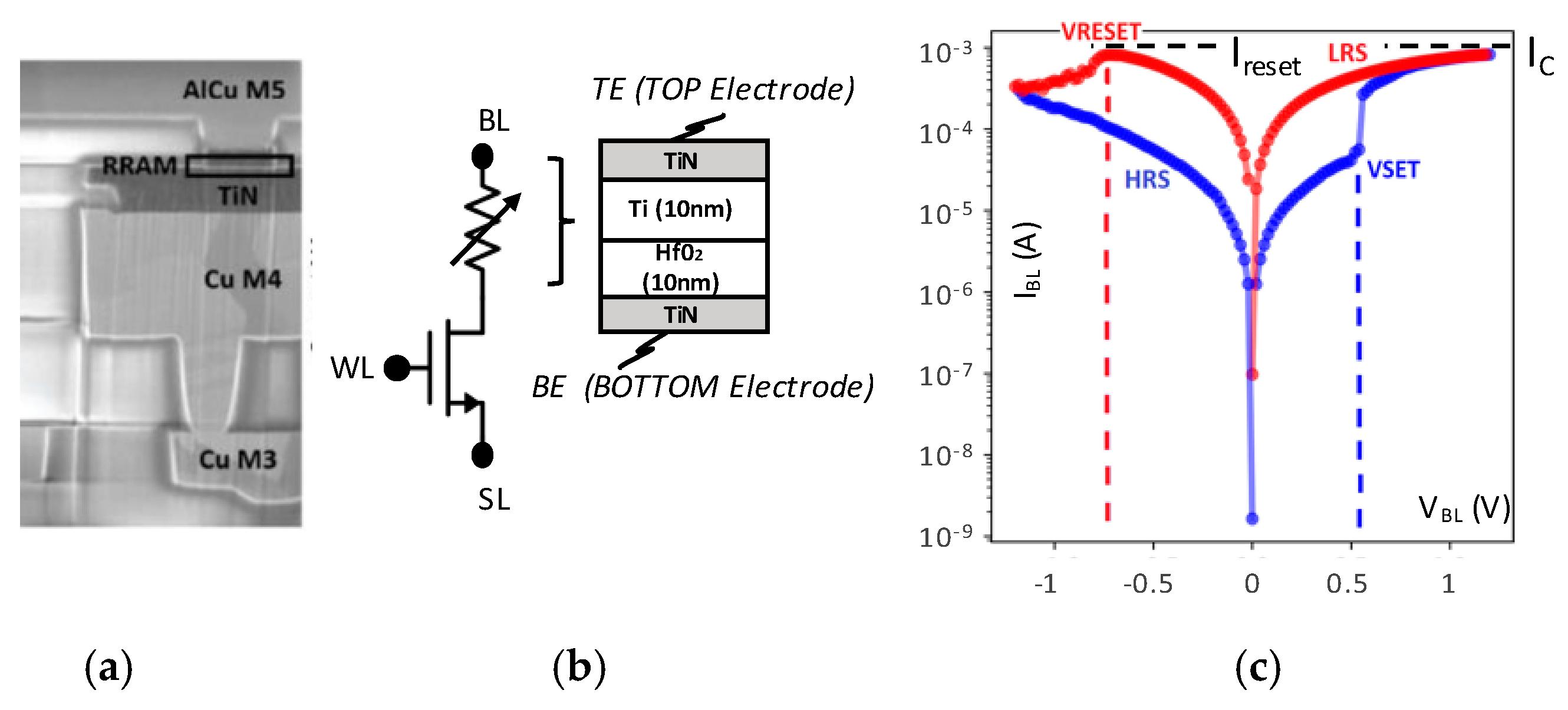
2. OxRAM Technology vs. MLC Modes
2.1. OxRAM Variability
2.2. OxRAM Model
3. MLC Design Scheme
3.1. High Level Architecture Implementation
3.2. Low Level Architetcure Implementation
4. Circuit Level Evaluation
4.1. MLC Concept
4.2. Simulation Setup
4.3. Transient Simulations
4.4. Monte Carlo (MC) Analysis
4.4.1. Quad-Level Cell (4 Bits/Cell)
4.4.2. Projections beyond Quad-Level Cell
5. Discussion
5.1. Performance Metrics
5.2. Comparison with State-of-the-Art MLC Approaches
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aziza, H. Embedded Memories. In Silicon Systems for Wireless Lan; Stamenković, Z., Leger, G., Bosio, A., Eds.; World Scientific: Singapore, 2020; Volume 22, pp. 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-L.; Tsung, P.-K.; Wu, M. Techology trend of edge AI. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Symposium on VLSI Design, Automation and Test (VLSI-DAT), Hsinchu, Taiwan, 16–19 April 2018; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Chen, P.-Y. Emerging Memory Technologies: Recent Trends and Prospects. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Mag. 2016, 8, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielmini, D. Resistive switching memories based on metal oxides: Mechanisms, reliability and scaling. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2016, 31, 063002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Niu, D.; Muralimanohar, N.; Jouppi, N.P.; Xie, Y. Understanding the trade-offs in multi-level cell ReRAM memory design. In Proceedings of the 50th Annual Design Automation Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 29 May–7 June 2013; p. 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wong, H.-S.P. Cross-Point Memory Array without Cell Selectors—Device Characteristics and Data Storage Pattern Dependencies. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2010, 57, 2531–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Lei, D.; He, Z.; En, Y.; Huang, Y. Layer-dependent resistance variability assessment on 2048 8-layer 3D vertical RRAMs. Electron. Lett. 2019, 55, 955–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.R.; Kim, Y.-B.; Chang, M.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, C.B.; Hur, J.H.; Park, G.-S.; Lee, D.; Lee, M.-J.; Kim, C.J.; et al. Multi-level switching of triple-layered TaOx RRAM with excellent reliability for storage class memory. In Proceedings of the 2012 Symposium on VLSI Technology (VLSIT), Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–14 June 2012; pp. 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Lin, Y.-H.; Lee, F.-M.; Lee, D.-Y.; Hsieh, K.-Y. Studies on ReRAM Conduction Mechanism and the Varying-bias Read Scheme for MLC and Wide Temperature Range TMO ReRAM. In Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology (ICSICT), Qingdao, China, 31 October–3 November 2018; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Su, W.; Liu, Y.; Hu, B.; Pan, L.; Lu, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, R.-W. Observation of Conductance Quantization in Oxide-Based Resistive Switching Memory. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3941–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, B.; Galatage, R.V.; Vogel, E.M. Multilevel Switching in Forming-Free Resistive Memory Devices with Atomic Layer Deposited HfTiOx Nanolaminate. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2013, 34, 867–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, H.-Y.; Wu, S.-C.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, S.; Hou, T.-H.; Wong, H.-S.P.; Nishi, Y.; Shimeng, Y. Improved multi-level control of RRAM using pulse-train programming. In Proceedings of the Technical Program—2014 International Symposium on VLSI Technology, Systems and Application (VLSI-TSA), Hsinchu, Taiwan, 28–30 April 2014; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Long, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Zuo, Q.; Yang, J.; et al. Investigation of resistive switching in Cu-doped HfO2thin film for multilevel non-volatile memory applications. Nanotechnol. 2009, 21, 045202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziza, H.; Hamdioui, S.; Fieback, M.; Taouil, M.; Moreau, M. Density Enhancement of RRAMs using a RESET Write Termination for MLC Operation. In Proceedings of the Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Grenoble, France, 1–5 February 2021; pp. 1877–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangeneh, M.; Joshi, A. Design and Optimization of Nonvolatile Multibit 1T1R Resistive RAM. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2013, 22, 1815–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Xu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Li, Q. Practical considerations of read-out circuits for passive, multi-level ReRAM arrays. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Manipulation, Manufacturing and Measurement on the Nanoscale (3M-NANO), Chongqing, China, 18–22 July 2016; pp. 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuben, J.; Fey, D. A Time-based Sensing Scheme for Multi-level Cell (MLC) Resistive RAM. In Proceedings of the IEEE Nordic Circuits and Systems Conference (NORCAS): NORCHIP and International Symposium of System-on-Chip (SoC), Helsinki, Finland, 29–30 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zahoor, F.; Zulkifli, T.Z.A.; Khanday, F.A. Resistive Random Access Memory (RRAM): An Overview of Materials, Switching Mechanism, Performance, Multilevel Cell (mlc) Storage, Modeling, and Applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlas, M.; Grossi, A.; Grenouillet, L.; Vianello, E.; Nolot, E.; Vaxelaire, N.; Blaise, P.; Traore, B.; Coignus, J.; Perrin, F.; et al. Improvement of HfO2 based RRAM array performances by local Si implantation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–6 December 2017; pp. 14.6.1–14.6.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, A.; Nowak, E.; Zambelli, C.; Pellissier, C.; Bernasconi, S.; Cibrario, G.; El Hajjam, K.; Crochemore, R.; Nodin, J.; Olivo, P.; et al. Fundamental variability limits of filament-based RRAM. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–7 December 2016; pp. 4.7.1–4.7.4. [Google Scholar]
- Bocquet, M.; Aziza, H.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Onkaraiah, S.; Muller, C.; Reyboz, M.; Deleruyelle, D.; Clermidy, F.; Portal, J.-M. Compact Modeling Solutions for Oxide-Based Resistive Switching Memories (OxRAM). J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2014, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajri, B.; Mansour, M.M.; Chehab, A.; Aziza, H. Oxide-based RRAM models for circuit designers: A comparative analysis. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Design & Technology of Integrated Systems in Nanoscale Era (DTIS), Palma de Mallorca, Spain, 4–6 April 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banba, H.; Shiga, H.; Umezawa, A.; Miyaba, T.; Tanzawa, T.; Atsumi, S.; Sakui, K. A CMOS bandgap reference circuit with sub-1-V operation. IEEE J. Solid-state Circuits 1999, 34, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziza, H.; Canet, P.; Postel-Pellerin, J.; Moreau, M.; Portal, J.-M.; Bocquet, M. ReRAM ON/OFF resistance ratio degradation due to line resistance combined with device variability in 28 nm FDSOI technology. In Proceedings of the Joint International EUROSOI Workshop and International Conference on Ultimate Integration on Silicon (EUROSOI-ULIS), Athens, Greece, 3–5 April 2017; pp. 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Yeh, S.; Wong, S.S.; Wong, H.-S.P. Effect of Wordline/Bitline Scaling on the Performance, Energy Consumption, and Reliability of Cross-Point Memory Array. ACM J. Emerg. Technol. Comput. Syst. 2013, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziza, H.; Moreau, M.; Fieback, M.; Taouil, M.; Hamdioui, S. An Energy-Efficient Current-Controlled Write and Read Scheme for Resistive RAMs (RRAMs). IEEE Access 2020, 8, 137263–137274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajri, B.; Aziza, H.; Mansour, M.M.; Chehab, A. RRAM Device Models: A Comparative Analysis with Experimental Validation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 168963–168980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, Y.; Lopez, L.; Portal, J.-M.; Aziza, H.; Bert, Y.; Julien, F.; Fornara, P. Impact of hump effect on MOSFET mismatch in the sub-threshold area for low power analog applications. In Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology, Shanghai, China, 1–4 November 2010; pp. 1817–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, Y.; Lopez, L.; Truphemus, L.; Portal, J.-M.; Aziza, H.; Julien, F.; Fornara, P.; Masson, P.; Ogier, J.-L.; Bert, Y. Gate Voltage Matching Investigation for Low-Power Analog Applications. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2013, 60, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziza, H.; Bocquet, M.; Portal, J.-M.; Muller, C. Evaluation of OxRAM cell variability impact on memory performances through electrical simulations. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual Non-Volatile Memory Technology Symposium Proceeding, Shanghai, China, 7–9 November 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Jian, W.; Yang, J.; Xiao, F.; Chen, G.; Xu, S.; Xie, Y.; Lin, Y.; Huang, R.; Zou, Q.; et al. A 0.13 µm 8 Mb Logic-Based CuxSiyO ReRAM with Self-Adaptive Operation for Yield Enhancement and Power Reduction. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 48, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-H.; Lin, W.-J.; Lai, L.-Y.; Li, S.; Hsu, C.-H.; Lin, H.-T.; Lee, H.-Y.; Su, J.-W.; Xie, Y.; Sheu, S.-S.; et al. A 16Mb dual-mode ReRAM macro with sub-14ns computing-in-memory and memory functions enabled by self-write termination scheme. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–6 December 2017; pp. 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.-F.; Wu, J.-J.; Chien, T.-F.; Liu, Y.-C.; Yang, T.-C.; Shen, W.-C.; King, Y.-C.; Lin, C.J.; Lin, K.-F.; Chih, Y.-D.; et al. Low VDDmin Swing-Sample-and-Couple Sense Amplifier and Energy-Efficient Self-Boost-Write-Termination Scheme for Embedded ReRAM Macros Against Resistance and Switch-Time Variations. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2015, 50, 2786–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziza, H.; Postel-Pellerin, J.; Bazzi, H.; Canet, P.; Moreau, M.; Della Marca, V.; Harb, A. True Random Number Generator Integration in a Resistive RAM Memory Array Using Input Current Limitation. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2020, 19, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portal, J.-M.; Bocquet, M.; Onkaraiah, S.; Moreau, M.; Aziza, H.; Deleruyelle, D.; Torki, K.; Vianello, E.; Levisse, A.; Giraud, B.; et al. Design and Simulation of a 128 kb Embedded Nonvolatile Memory Based on a Hybrid RRAM (HfO2)/28 nm FDSOI CMOS Technology. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2017, 16, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaz, P.I.; Girard, P.; Virazel, A.; Aziza, H. Improving TID Radiation Robustness of a CMOS OxRAM-Based Neuron Circuit by Using Enclosed Layout Transistors. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2021, 29, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziza, H.; Moreau, M.; Perez, A.; Virazel, A.; Girard, P. A Capacitor-Less CMOS Neuron Circuit for Neuromemristive Networks. In Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International New Circuits and Systems Conference (NEWCAS), Munich Germany, 23–26 June 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, T.; Song, B.; Kim, J.P.; Kang, S.H.; Jung, S.-O. Offset-Canceling Current-Sampling Sense Amplifier for Resistive Nonvolatile Memory in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2017, 52, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, H.-Y.; Wu, S.-C.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, S.; Hou, T.-H.; Wong, H.-S.P.; Nishi, Y. Multi-level control of conductive nano-filament evolution in HfO2 ReRAM by pulse-train operations. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 5698–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.; Menzel, S.; Wouters, D.J.; Waser, R.; Rana, V. 3-Bit Multilevel Switching by Deep Reset Phenomenon in Pt/W/TaOX/Pt-ReRAM Devices. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2016, 37, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| FMG | RST | SET | READ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WL | 2 V | 2.5 V | 2 V | 2.5 V |
| BL | 3.3 V | 0 V | 1.2 V | 0.2 V |
| SL | 0 V | 1.2 V | 0 V | 0 V |
| State | 1111 | 1110 | 1011 | 1100 | 1011 | 1010 | 1001 | 1000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IrefR | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 |
| RHRS | 267 | 185 | 153 | 125 | 106 | 92 | 81 | 72.4 |
| State | 0111 | 0110 | 0101 | 0100 | 0011 | 0010 | 0001 | 0000 |
| IrefR | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 30 | 32 | 34 | 36 |
| RHRS | 65.3 | 59.4 | 54.5 | 50.3 | 46.6 | 43.45 | 40.65 | 38.17 |
| Mlc Levels | 4 Bits/Cell | 5 Bits/Cell | 6 Bits/Cell |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimal ∆R | 2.5 kΩ | 1.24 kΩ | 620 Ω |
| Worst case ∆R | 2.1 kΩ | 490 Ω | 90 Ω |
| RRAM Device | States Number | MLC Mode | Design Level | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [8] | Pt/TaOx/Ta2O5/Pt | 4 HRS | VRST | Device |
| [11] | TiN/HfTiO2/TiN | 3 LRS/1 HRS | IC SET | Device |
| [39] | TiN/HfOx/Pt | 8 HRS | VRST | Device |
| [13] | Cu/HfO2/Cu/Pt | 3 LRS/1 HRS | IC SET | Device |
| [17] | Ti/HfOx/Ti/TiN | 3 LRS/1 HRS | IC SET | Circuit |
| [12] | TiN/HfOx/Pt | 8 HRS | VRST | Device |
| [40] | Pt/W/ TaOx/Pt | 7 HRS/1 LRS | VRST | Device |
| [14] | TiN/Ti/HfOx/TiN | 8 HRS | IC RST | Circuit |
| Work | TiN/Ti/HfOx/TiN | 16 HRS | IC RST | Circuit |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aziza, H.; Hamdioui, S.; Fieback, M.; Taouil, M.; Moreau, M.; Girard, P.; Virazel, A.; Coulié, K. Multi-Level Control of Resistive RAM (RRAM) Using a Write Termination to Achieve 4 Bits/Cell in High Resistance State. Electronics 2021, 10, 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10182222
Aziza H, Hamdioui S, Fieback M, Taouil M, Moreau M, Girard P, Virazel A, Coulié K. Multi-Level Control of Resistive RAM (RRAM) Using a Write Termination to Achieve 4 Bits/Cell in High Resistance State. Electronics. 2021; 10(18):2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10182222
Chicago/Turabian StyleAziza, Hassan, Said Hamdioui, Moritz Fieback, Mottaqiallah Taouil, Mathieu Moreau, Patrick Girard, Arnaud Virazel, and Karine Coulié. 2021. "Multi-Level Control of Resistive RAM (RRAM) Using a Write Termination to Achieve 4 Bits/Cell in High Resistance State" Electronics 10, no. 18: 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10182222
APA StyleAziza, H., Hamdioui, S., Fieback, M., Taouil, M., Moreau, M., Girard, P., Virazel, A., & Coulié, K. (2021). Multi-Level Control of Resistive RAM (RRAM) Using a Write Termination to Achieve 4 Bits/Cell in High Resistance State. Electronics, 10(18), 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10182222






