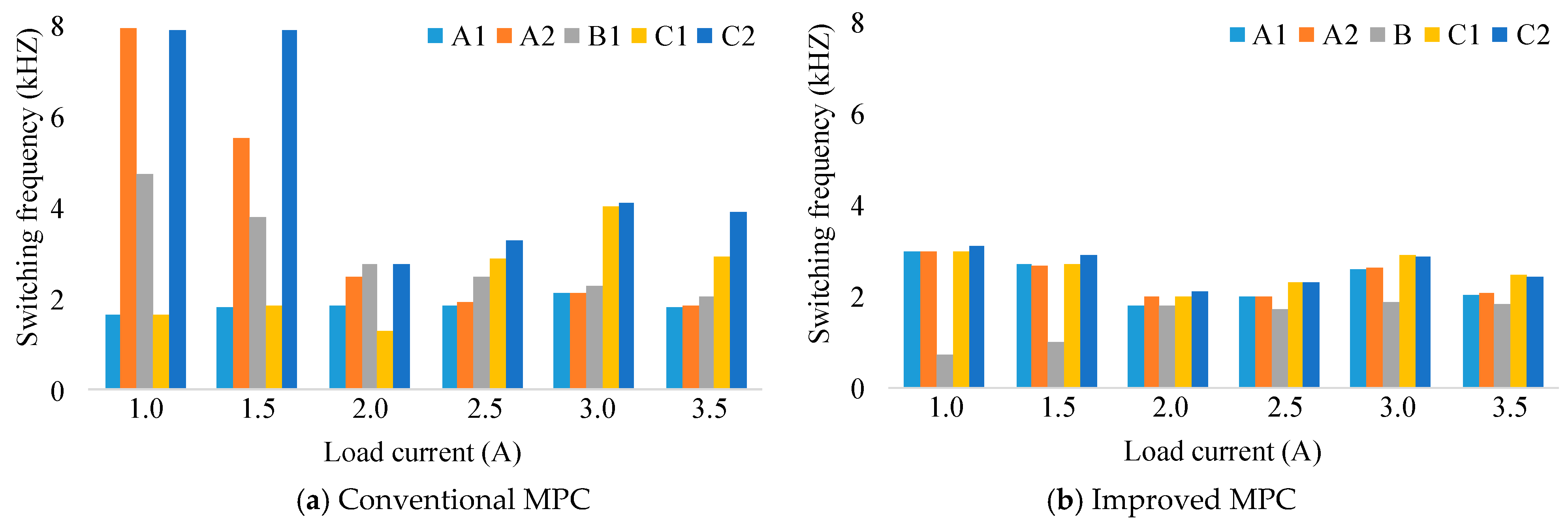Abstract
In this paper, a model predictive control for an asymmetric T-type NPC 3-level inverter is presented. The mathematical model and characteristics of the reduced switching topology are described. An improvement for the predicted strategy with the pre-selected candidate vectors is proposed. The simulation and experimental results are provided and show good efficiency for the proposed control algorithm. The improved algorithm greatly reduces execution time by about 18% and delivers a better load current THD than the conventional model for predictive control. For comparison, similar tests are performed on both 2-level and conventional 3-level inverters. Although the current load quality of the asymmetrical inverter is not as good as the traditional 3-level inverter, it is much better than the 2-level inverter. In addition, it has the benefits of significantly reducing overall costs, simpler hardware system design, and faster predictive processing than the conventional 3-level inverters. Therefore, this asymmetric inverter has advantages for an application with the required output characteristics like the conventional 3-level inverter and with lower cost.
1. Introduction
Three-level voltage source converters have been widely used in industrial applications, which include high-power motor drivers [1], electric vehicles [2], and grid-connected renewable energy conversion systems [3]. Particularly in high-power and medium-voltage applications, they have outstanding advantages compared to 2-level converters, such as lower switching losses, reduced voltage stress in DV/DT across the power devices [4,5,6], and better total harmonic distortion (THD). The most common inverter topologies among them are the flying capacitor (FC), cascaded H-bridge (CHB), and neutral point clamped (NPC). The T-type NPC inverter was more efficient than traditional NPC inverters up to the medium switching frequency range [7,8,9,10].
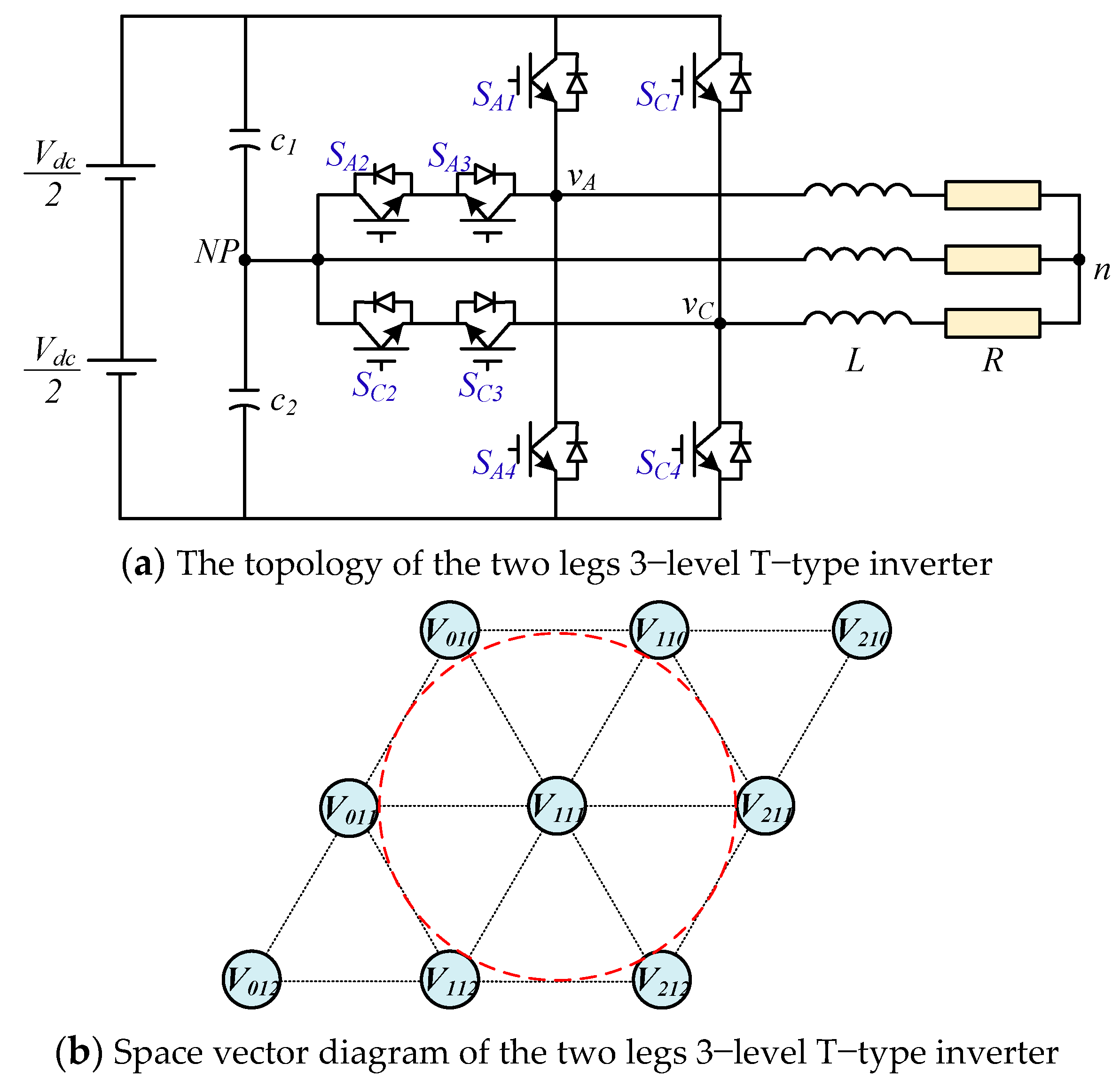
Although 3-level NPC inverters have many advantages compared with 2-level inverters, as mentioned above, their main disadvantages are a higher cost, increased system volume, and reduced reliability because of the increased number of devices. Many recent studies focus on developing reduced switched topologies [11,12,13,14,15,16,17] to reduce cost, with a smaller size and increased system reliability. In [11,12,13], the diode NPC 3-level 2-leg topology was proposed where the required number of switches is reduced from 12 IGBTs and 6 diodes to 8 IGBTs and 4 diodes. A similar structure for T-type has been proposed to eliminate the diodes [17]. These topologies only need two legs for a three-phase 3-level inverter, so the number of components is reduced by one-third, as shown in Figure 1a. However, its drawbacks are that the linear output voltage is limited to half, as shown in Figure 1b.
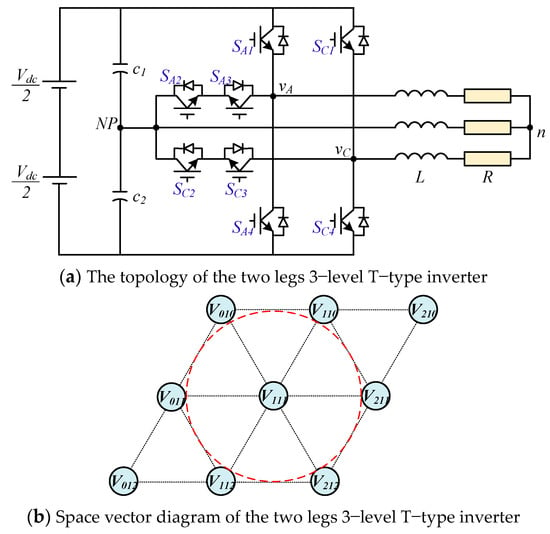
Figure 1.
Structure of the two legs T-type 3-level inverter.
The current control of a three-phase inverter has drawn much attention from researchers in the last decades. The conventional control strategy via proportional-integral (PI) current controllers with pulse width modulation (PWM) [18,19] can gain multiple-objectives, such as the reference current tracking, the reduction of the switching losses, reduced common mode voltage, and DC neutral point balancing. However, this technique suffers from many drawbacks such as a low dynamic response and demanding tuning of PI controller parameters.
With the development of digital signal processors, predictive control strategies have been studied intensively for power electronics converter systems. One of them, deadbeat predictive control [20,21] uses the system model to calculate reference voltage of modulator, which makes the error zero in the next sampling time. The deadbeat control achieves fast dynamic response, but its performance can be degraded caused by measurement noise and parameter variations [22]. Another one, named model predictive control (MPC), is known due to its simplicity of control principle, ease of implementation, ability to integrate multi-object control simultaneously, and excellent dynamic [23,24,25,26,27]. Because of its use of one vector in the sampling period, the MPC leads to high current ripples and variable switching frequency for the converter output. Improvement of the steady state performances demands the MPC to run at a high sampling rate. This difficulty can be avoided by multiple-vector-based model predictive control [28,29,30]. In every sampling period, the control scheme selects the appropriate voltage vector sequence and calculates duty cycles to minimize the cost function. Even if this approach can improve steady state performance, the control complexity is rather high, particularly for multilevel converter topologies.
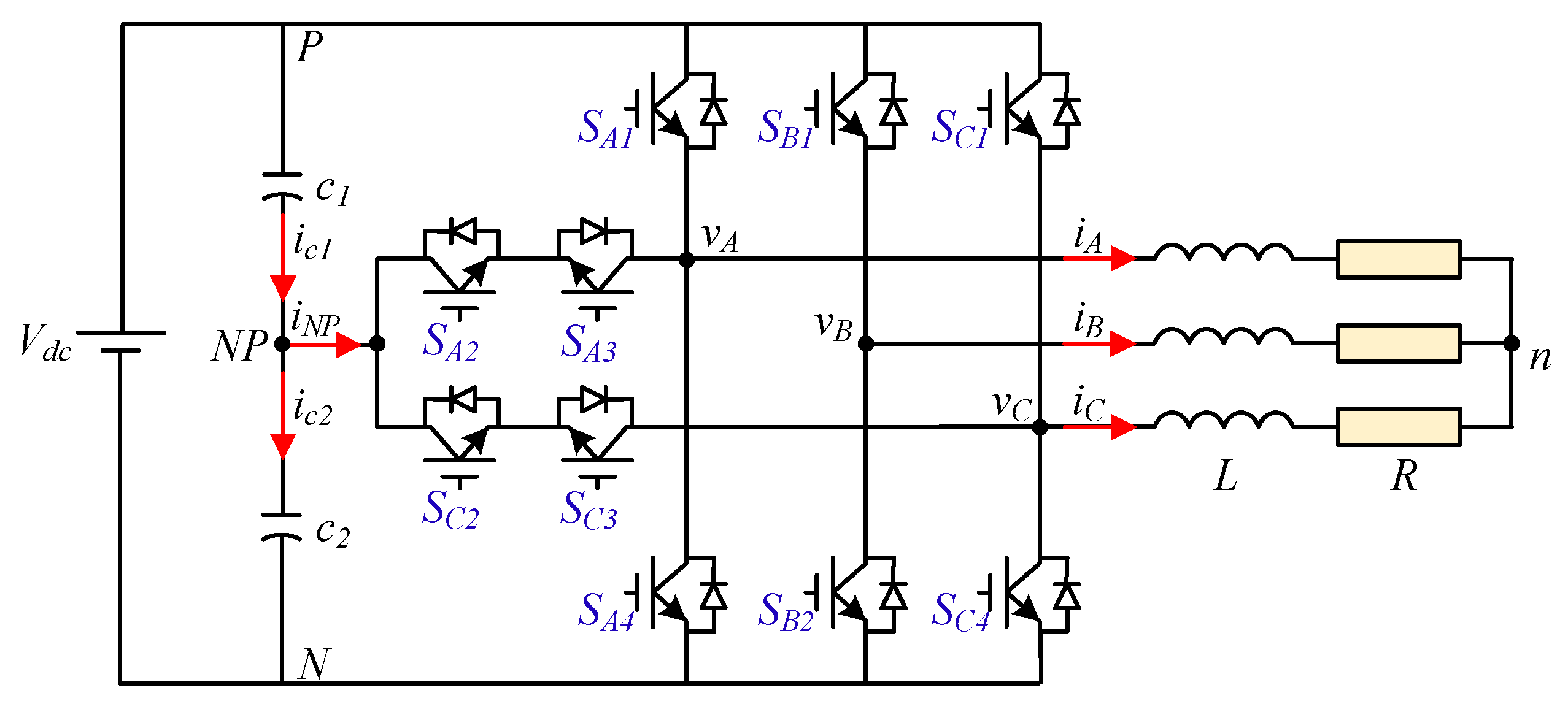
This paper proposes a so-called asymmetric 3-level T-type NPC inverter by adding a half-bridge leg to the 2-leg 3-level NPC inverter. This new configuration, as shown in Figure 2, enables twice the output voltage range compared to Figure 1. An improved model predictive control (IMPC) algorithm for this configuration is proposed for current tracking and capacitor voltage balancing. The candidate vector selection strategy is presented to avoid high voltage jumps in phase legs without designing any additional cost functions. This significantly reduces execution time and switching frequency and improves load current distortion. Simulations and experiments will be performed to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method for asymmetric T-type NPC 3-level inverter.
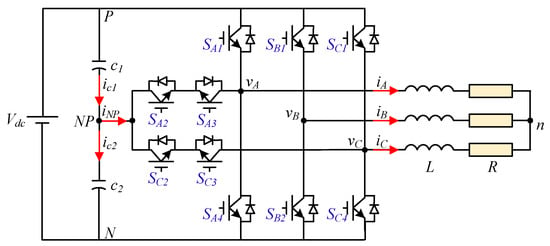
Figure 2.
The topology of asymmetric T-type NPC 3-level Inverter.
2. Mathematical Model of Asymmetric 3-Level T-Type NPC Inverter
The asymmetric inverter topology is shown in Figure 2. The phases A and C are 3-level T-type legs; phase leg B is a half-bridge. Two DC-bus voltages are supplied via DC-link capacitors () in series. Three-phase load R-L is connected to the output terminals of the converter.
Under the condition of balanced DC-link capacitor voltages, the phase leg voltage ) can be expressed as follows:
where ; is the phase switching state.
The switching states of three phases legs are described in Table 1. For 3-level legs phase A, C; can be 0, 1, 2. For 2-level legs phase B; can be 0, 2.

Table 1.
Switching states and output voltages of the asymmetric inverter.
The Clarke formula transforms three phase leg voltages in the to coordinate system as follows:
Similar for three phase currents:
Applying (1) and (2) to all switching states, the voltage vectors of the asymmetric T-type NPC 3-level inverter can be deduced. The converter generates 18 voltage vectors 17, including 6 large voltage vectors (LV), 4 medium voltage vectors (MV), 6 small voltage vectors (SV), and 2 redundant zero voltage vectors (ZV), as illustrated in Table 2.

Table 2.
Switching states and output voltage vectors for proposed inverter.
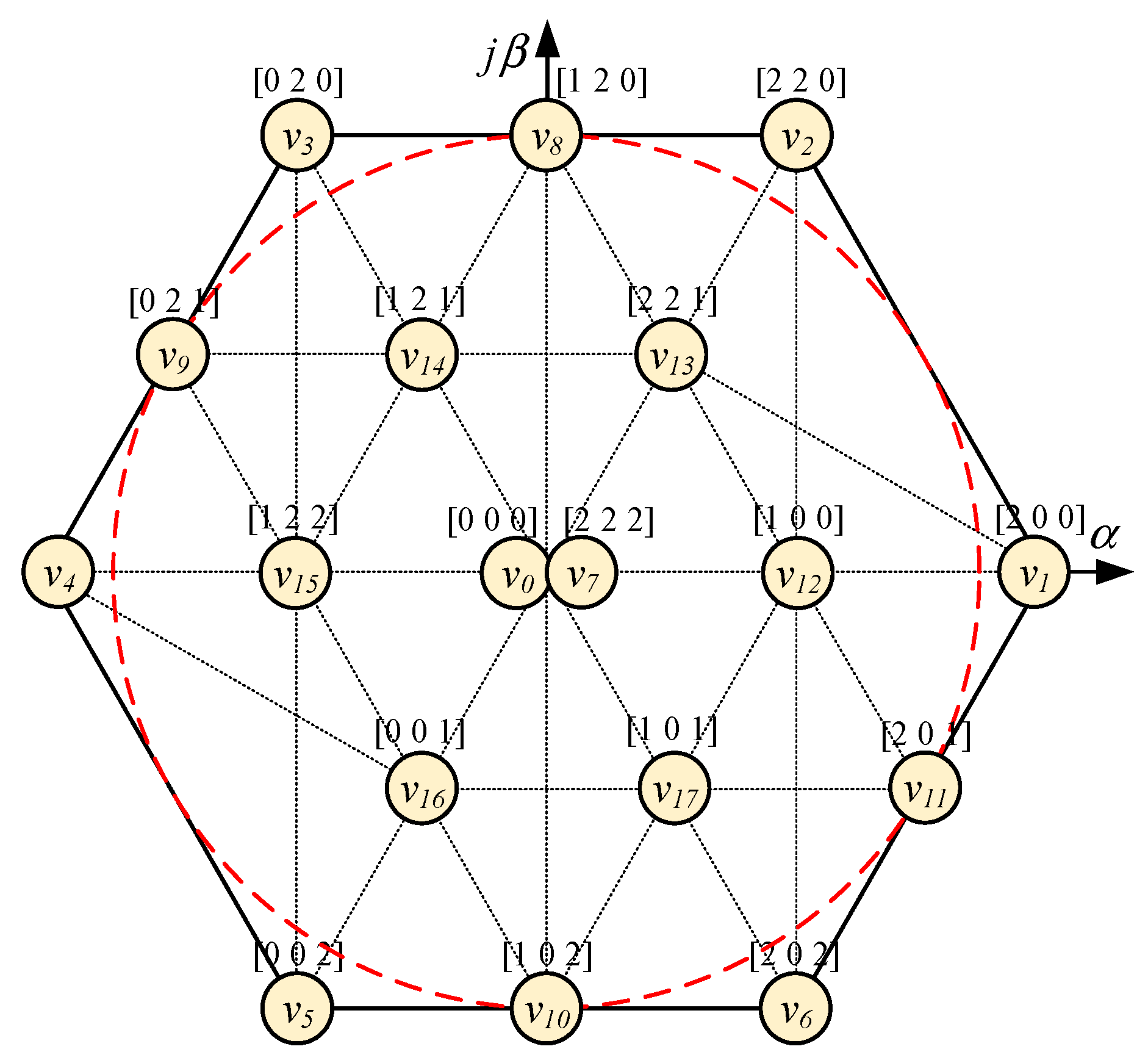
The space vector diagram of the asymmetric T-type 3-level inverter is shown in Figure 3. The linear modulation range, corresponding to the radius of the largest circle inscribed in the hexagon, of this topology is extended to twice that of the NPC 3-level 2-leg asymmetric inverter [14,15,16,17].
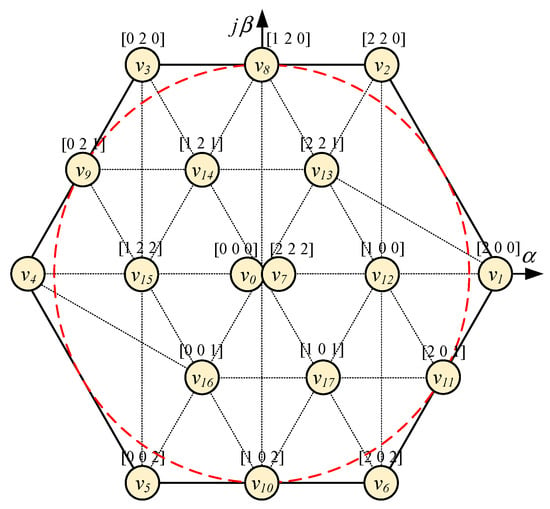
Figure 3.
Space vector diagram of asymmetric T-type 3-level NPC inverter.
The specific characteristics of an asymmetric inverter compared with conventional 2-level and 3-level inverters are reported in Table 3. The asymmetric topology can generate line voltages at 5 voltage levels , and similarly to the traditional 3-level inverter. Furthermore, the different voltage vectors of the asymmetric inverter are 17, only two less than the space vector diagram of a traditional 3-level inverter. Therefore, it would be expected that the performance of the asymmetric inverter be as good as the 3-level NPC inverter.

Table 3.
Typical properties comparison of conventional 2-level, 3-level, and asymmetric 3-level inverter.
3. Proposed MPC for Asymmetric T-Type NPC 3-Level Inverter
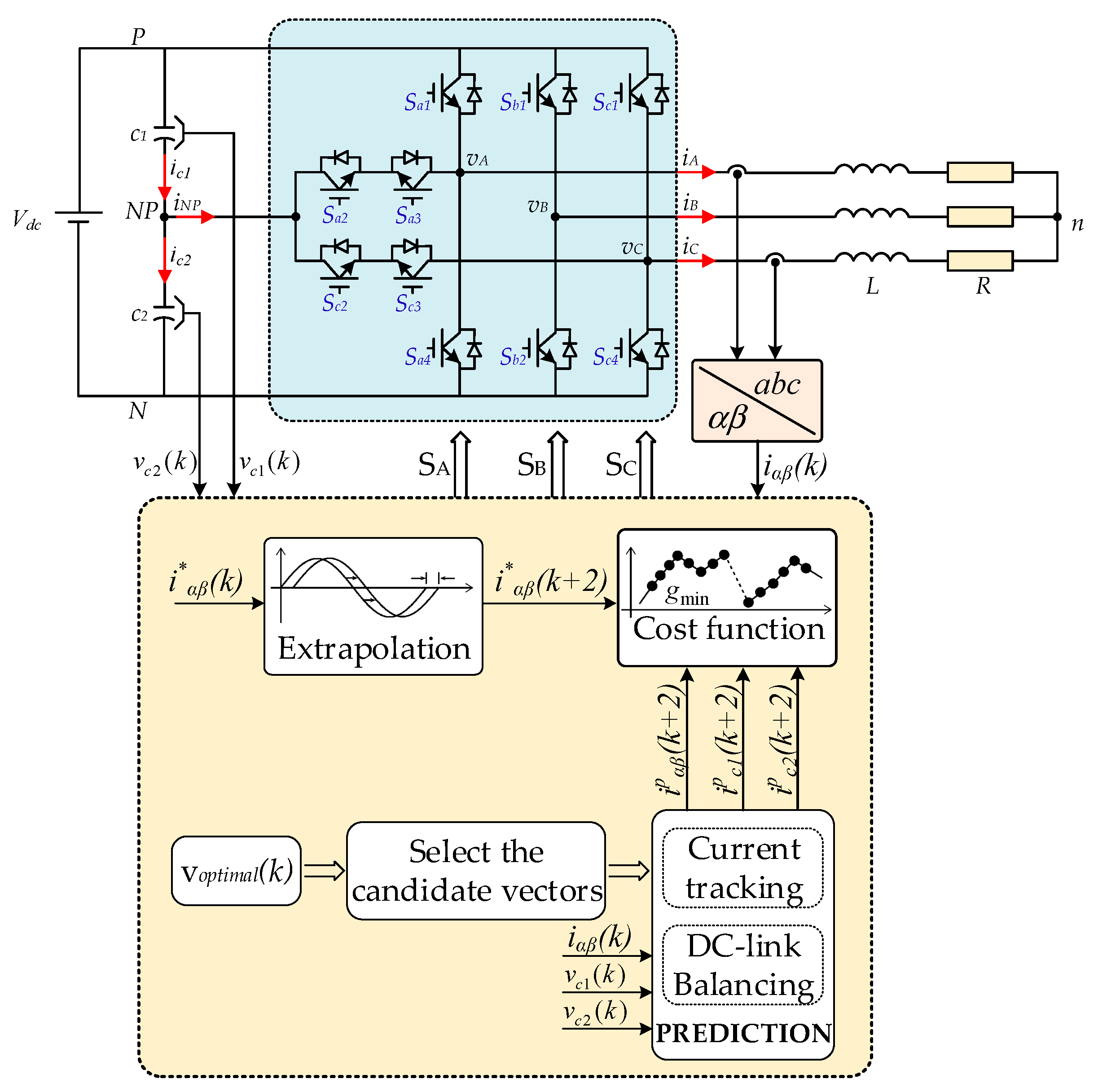
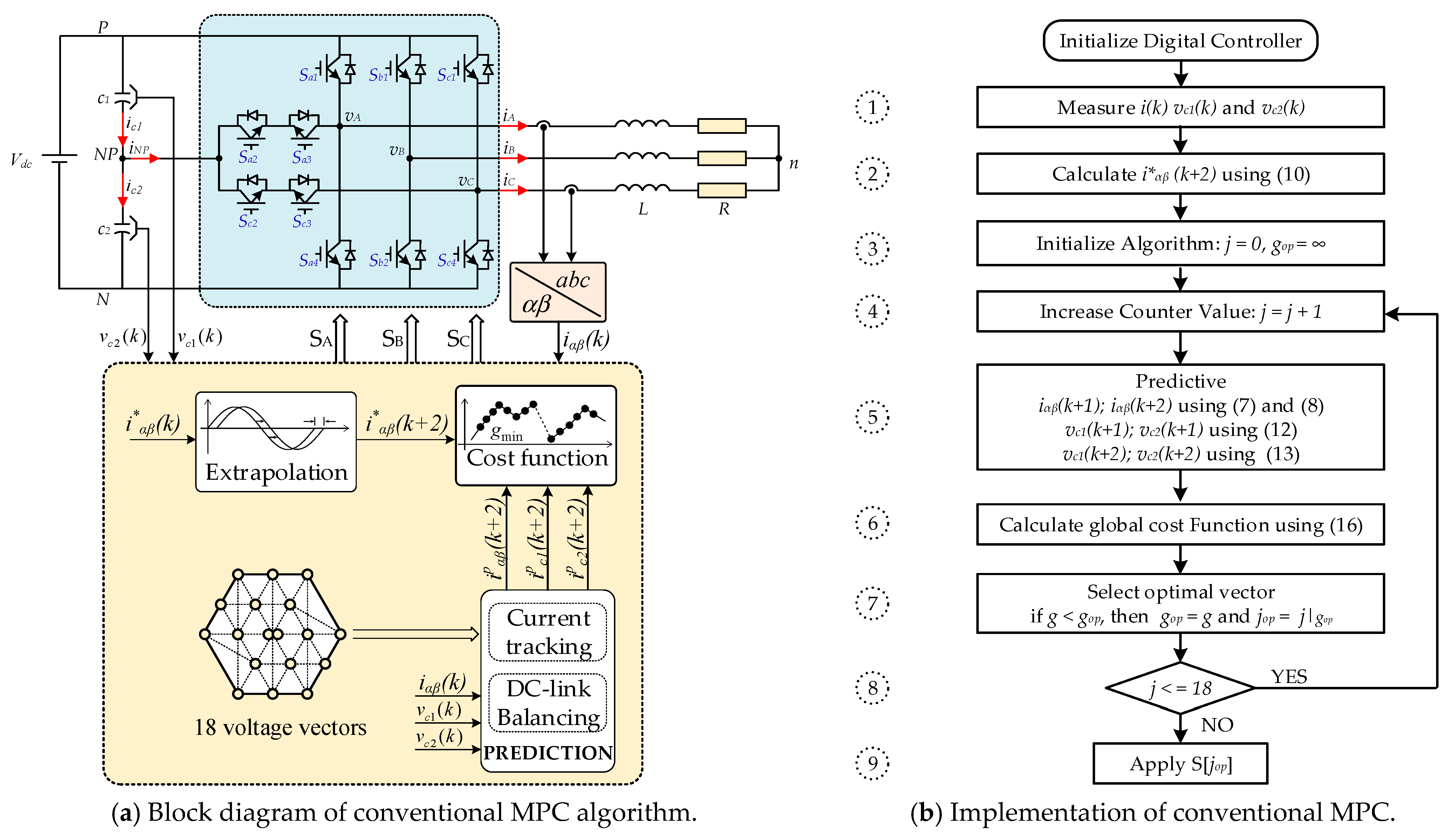
The block diagram of the improved MPC algorithm for the asymmetric T-type NPC inverter to achieve the two main goals of current tracking and voltage capacitor balancing is shown in Figure 4. The algorithm consists of the following stages: establishment of cost functions for current tracking and capacitor voltage balancing based on a mathematical model, design of the global cost function and candidate vector pre-selection strategy to optimize execution time, and improvement of THD of load current.
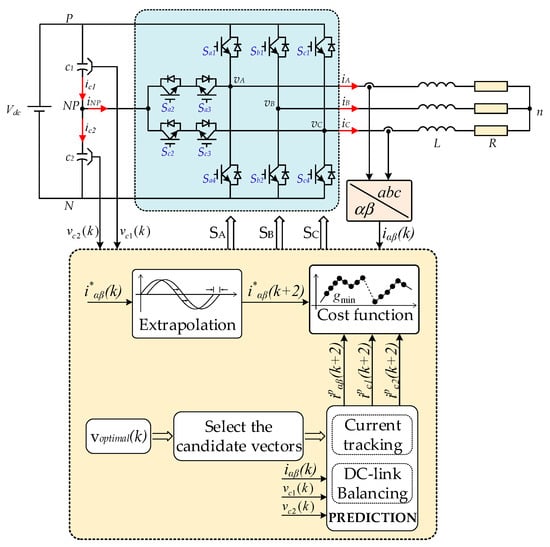
Figure 4.
Block diagram of improved MPC algorithm for the asymmetric T-type NPC inverter.
3.1. Current Tracking Control
The mathematical model of the asymmetric configuration is described as follows:
where is the offset voltage between the neutral-point of load and the negative of the DC-bus.
Using (2) and (3), the Equation (4) can be rewritten in the coordinate system as follows:
Euler’s forward approximation to convert the continuous domain to the discrete domain with sampling period is as follows:
Substituting (6) into (5), the predicted current is obtained in the discrete domain as:
where is the predicted current at time (k + 1); is the current feedback at time (k); is the voltage vector corresponding to the switching states of the inverter.
To obtain delay compensation due to algorithm calculations and analog-to-digital converters, the discrete-time equation of the model (7) is shifted one step forward as:
The cost function for current tracking can be expressed as [26,27,31]:
where is the reference current at time . It can be determined by the Lagrange extrapolation formula as follows:
3.2. DC-Link Capacitor Voltage Balancing
Assuming that , the DC-link capacitor voltages are described as follows [32]:
where is the neutral point current, as shown in Figure 2.
Using Equation (6), the predicted voltage of the capacitor is written in the discrete-time domain as follows:
The delay is compensated by shifting in (12) forward one step as follows:
The current is calculated in relation to the switching states as below:
where with are defined as Table 1; and are the measurement currents at time on phases A and C, respectively.
The cost function for the DC-link capacitor voltage balance is defined as follows:
3.3. Global Cost Function
The global cost function for current tracking and capacitor voltage balancing is defined as follows:
where is the weighting factor to adjust the balance of the capacitor voltages.
The block diagram of the conventional MPC algorithm is presented in Figure 5a. The implementation flowchart, as shown in Figure 5b, consists of 9 steps:
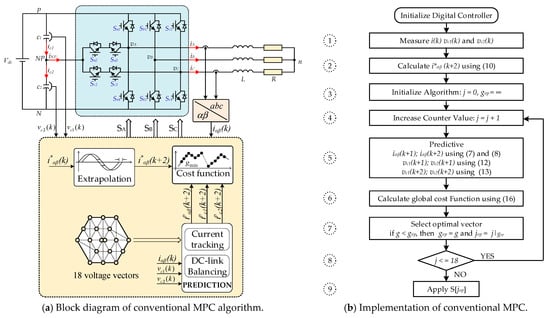
Figure 5.
Normal MPC algorithm for the asymmetric T-type NPC inverter.
- ➀
- Measure current, capacitor voltages from sensor feedback signals;
- ➁
- The reference current at the time is calculated by extrapolation;
- ➂
- Initialize the initial values;
- ➃
- Enter the loop, where the counter increases j value in steps;
- ➄
- The output current and DC capacitor voltages are predicted to time corresponding to each candidate vector;
- ➅
- Calculate the global cost function;
- ➆
- During any iteration, if , the minimum of value is stored as an optimal value and the corresponding position is stored as ;
- ➇
- Check the loop condition, if 18 is true then return to execute the tasks from step 4, if false, exit the loop and continue to step 9;
- ➈
- Apply the switching states based on the value.
The conventional MPC for an asymmetric T-type 3-level NPC inverter uses 18 switching states for the prediction. The execution time is obviously reduced compared to the traditional 3-level inverter with 27 switching states. The MPC algorithm in this paper is designed to prioritize the current tracking and balance the capacitor voltage by adjusting the weighting factor .
3.4. Improved Algorithm
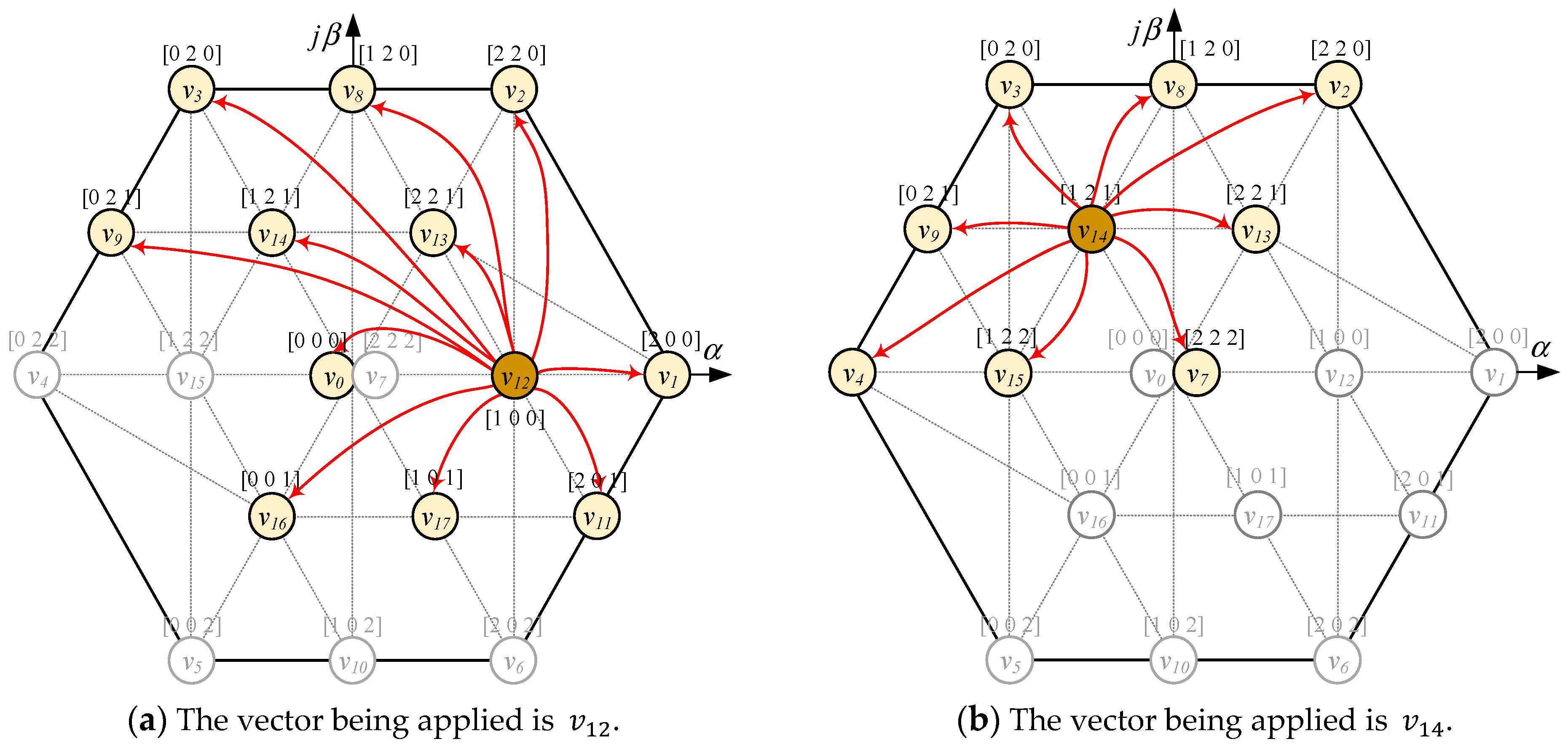
Although the conventional MPC algorithm satisfies the design requirements, it may have associated adverse effects. For example, when vector is being used at time , the optimal vector at the time is . At phase leg C, the switching from 2 to 0 causes a high voltage jump with amplitude . In addition, all four IGBTs of the phase C switch state cause large switching frequency. The candidate vector pre-selection strategy is proposed to overcome the issues without the need to design any additional cost functions. Based on the vector being applied at instant , vectors that cause switching 0 to 2 or 2 to 0 will not be included in the predictive model for time .
For example, in the case the vector applies at instant k, there are 12 voltage vectors (, , , , , , , , , , , ) that are suitable which do not cause a high voltage jump on phase leg A and C, as shown in Figure 6a. These switching states are considered as candidates for the prediction model to select the optimal vector applied at time (k + 1). Another example is at instant k as shown in Figure 6b, where all states are satisfied for phases A and C. In this situation, vectors that do not cause a high voltage jump in phase leg B will be chosen as candidate vectors, including (, , , , , , , ).
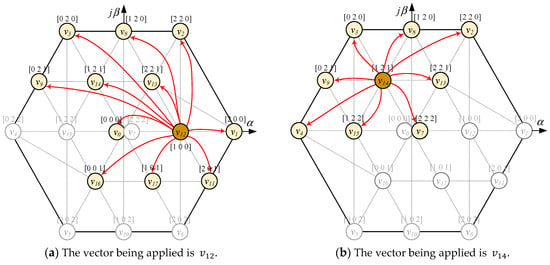
Figure 6.
The strategy for selecting candidate vectors.
Similarity analysis applies for the remaining vectors, and preselected candidate vectors are listed as shown in Table 4. The improved algorithm uses a maximum 12 vectors for each prediction, so it greatly reduces the computational burden compared to the conventional MPC algorithm.

Table 4.
The candidate vector pre-selection strategy based on the vector applied at time k.
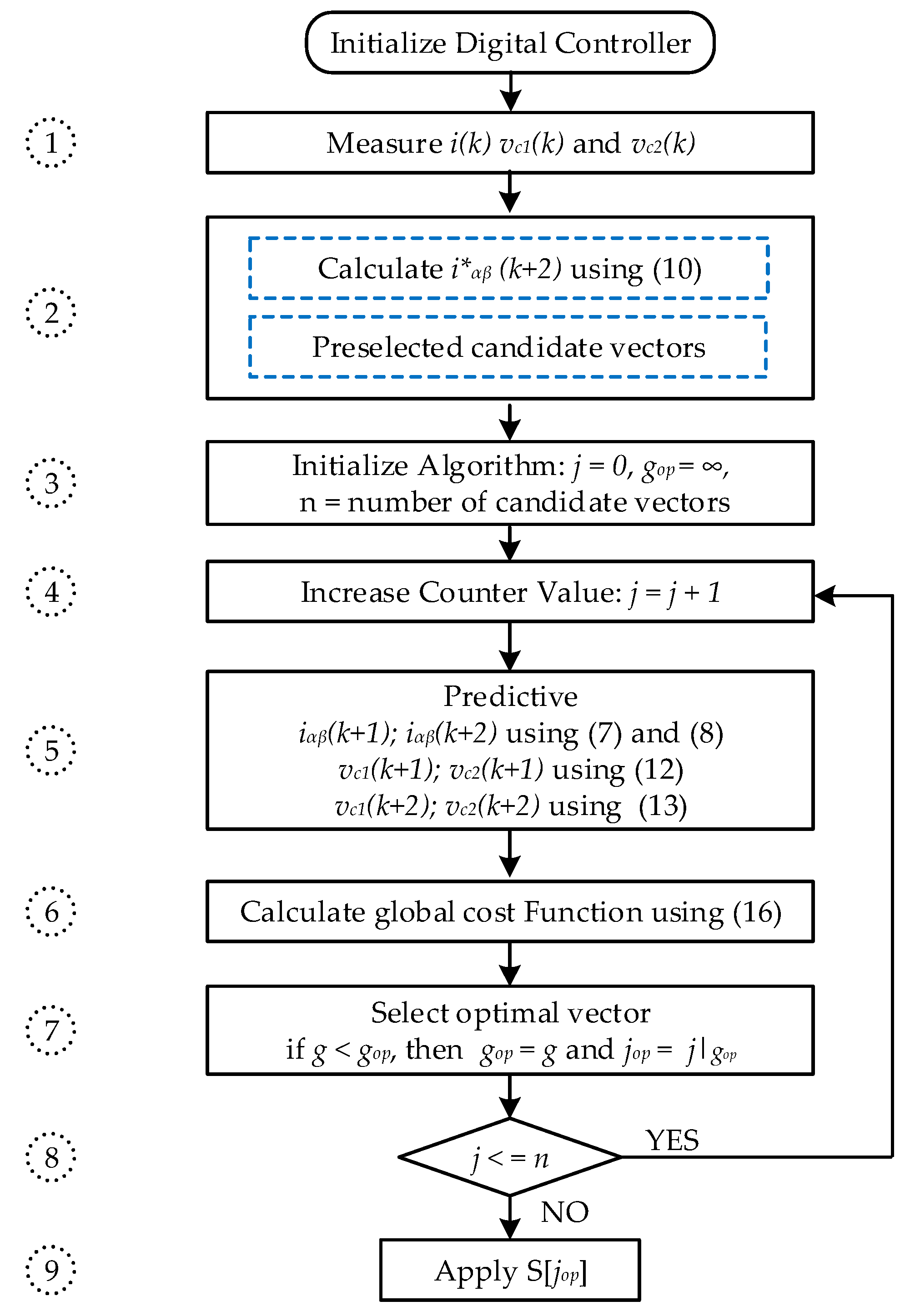
The digital implementation diagram of the improved MPC algorithm is shown in Figure 7, consisting of 9 steps similar to that of the conventional MPC algorithm. However, step 2 incorporates an additional task of selecting candidate vectors. The number of loop executions is equal to the number of candidate vectors, instead of 18 as in the conventional MPC algorithm.
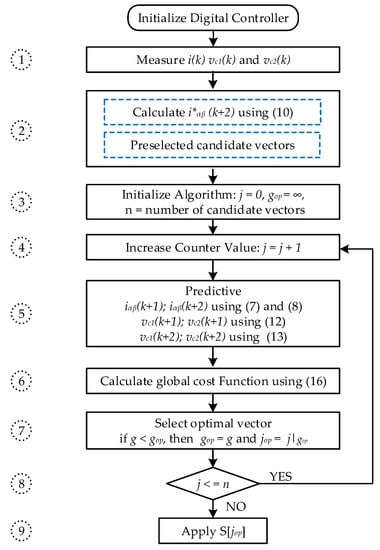
Figure 7.
Implementation of improved MPC for the asymmetric T-type NPC inverter.
4. Simulation and Experimental Results
4.1. Simulation Results
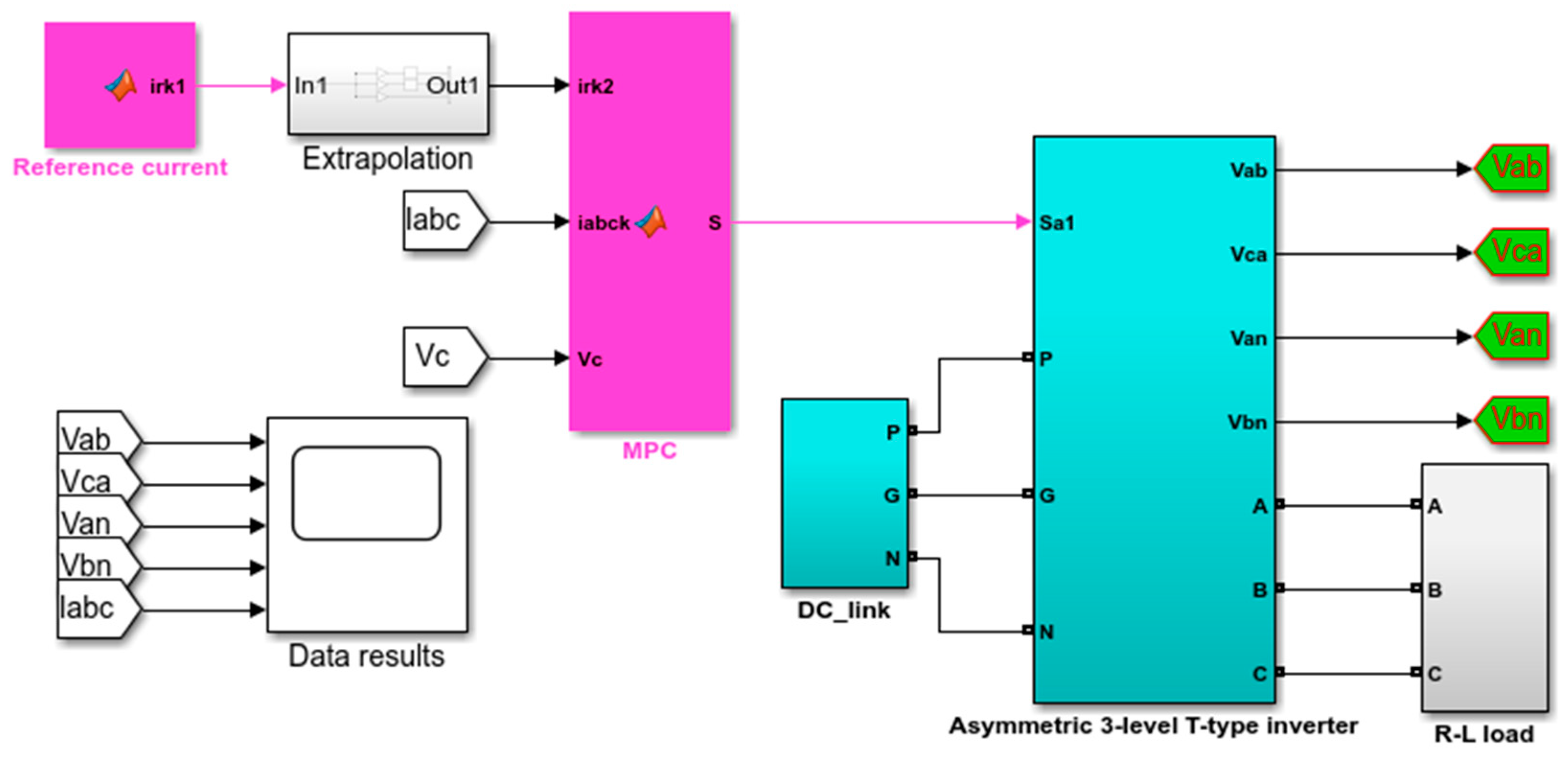
To validate the improved MPC algorithm for an asymmetric T-type NPC inverter, simulations were performed using MATLAB/Simulink software with version 2018a, as shown in Figure 8. The system parameters are shown in Table 5.
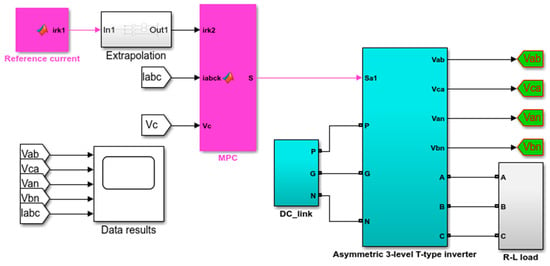
Figure 8.
Simulation diagram of the improved MPC algorithm for asymmetric T-type NPC inverter.

Table 5.
System parameters for simulation and experimental.
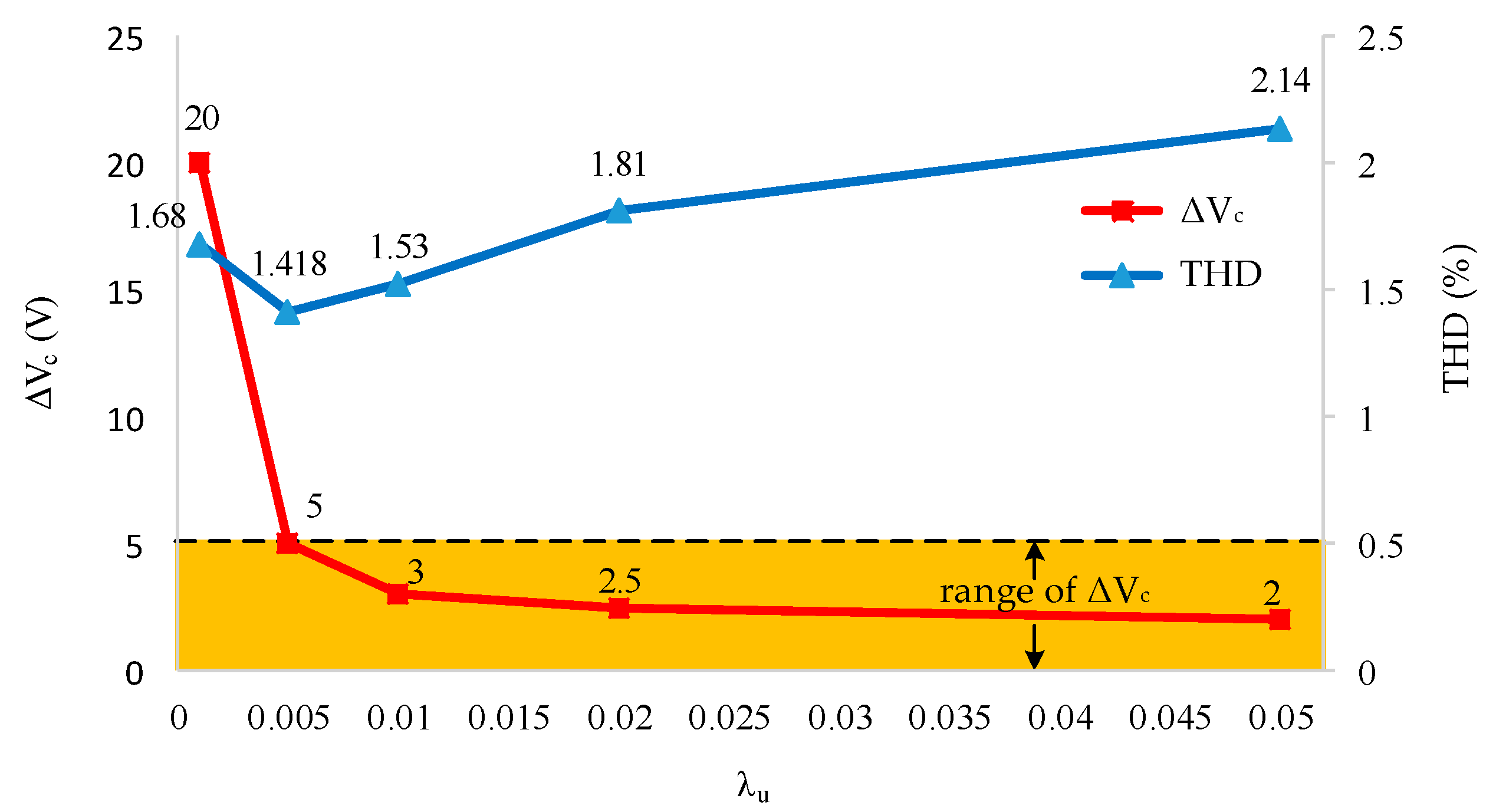
The first simulation is performed with the improved MPC algorithm at reference current 15 A, and the parameter is weighting factor. The influence of the weighting factor on the THD load current and the voltage difference between the capacitors is described in Figure 9. The higher , the smaller , but THD tends to be increased. From the figure, for example, the requirement (i.e., ) can be obtained if . Therefore, for the best THD is selected in the following studies.
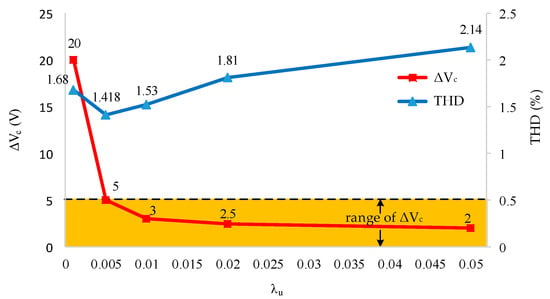
Figure 9.
Effect of weighting coefficient on THD and ΔVdc characteristics.
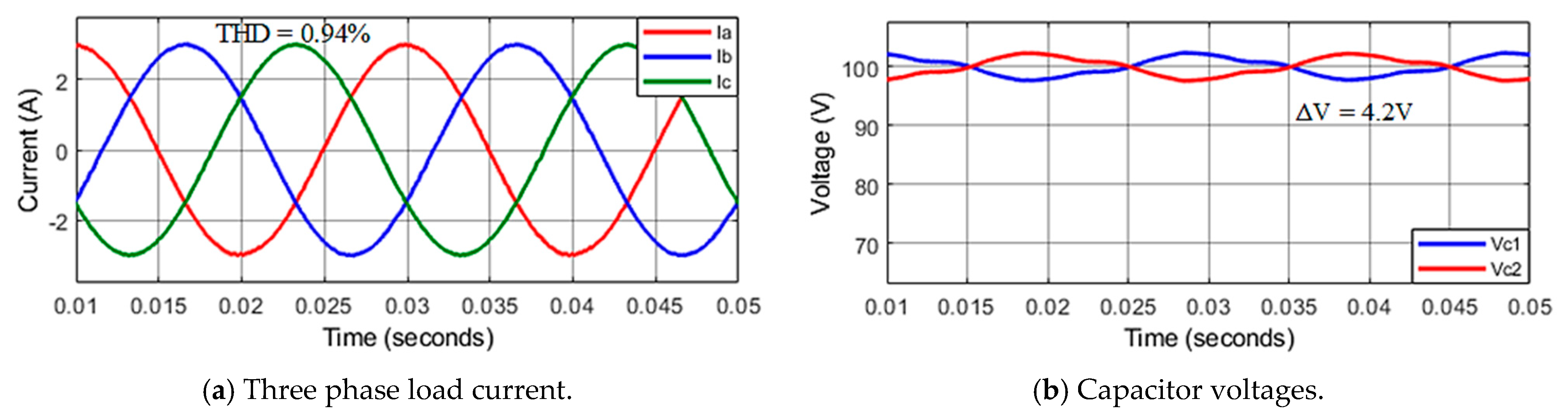
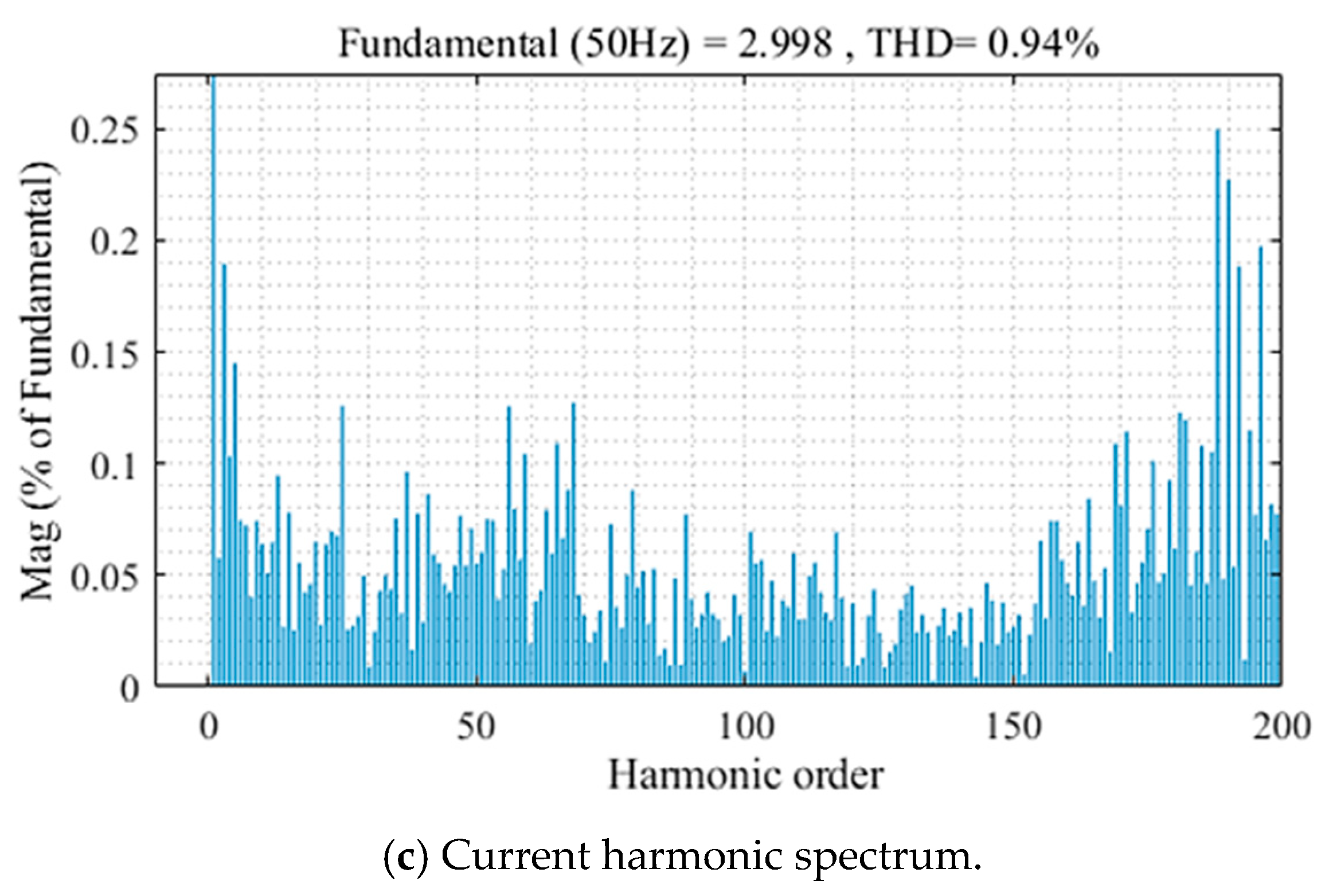
Steady-state responses at reference current 3 A of the improved method for the asymmetric T-type NPC inverter are illustrated in Figure 10. Load currents are sinusoidal and stable at the set values with THD about 0.94%, as in Figure 10a,c. The capacitor voltages are maintenance balanced with ΔV about 4 V, as shown in Figure 10b.
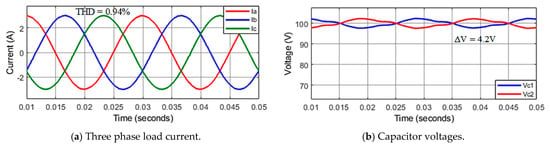
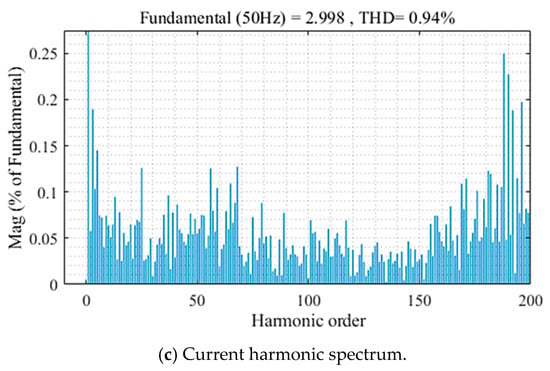
Figure 10.
The steady−state response of asymmetric inverter using improved MPC algorithm.
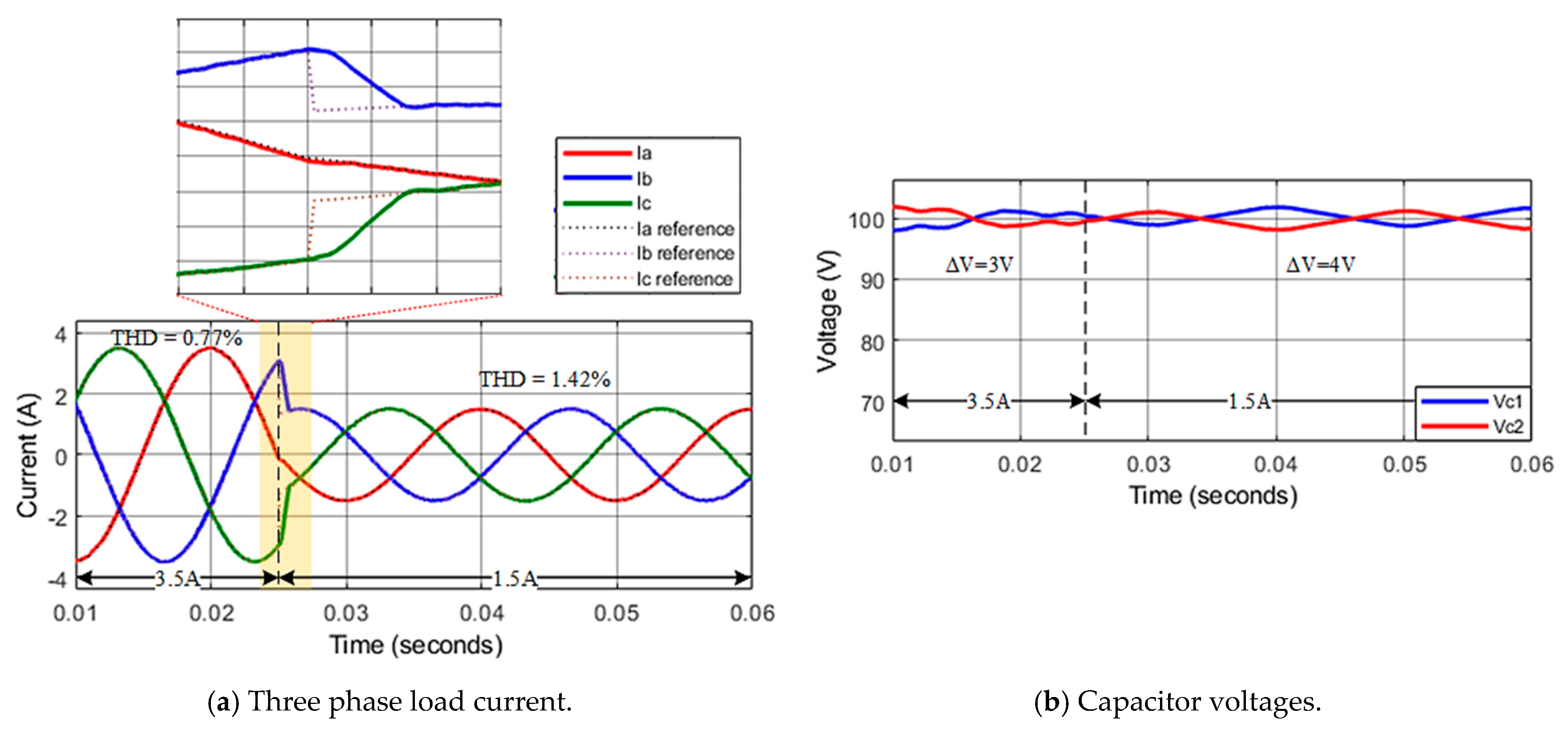
To check the system’s dynamic response, a simulation is performed with an abrupt change of reference current from to at time . The load current quickly tracks and stabilizes at the set value after about of the fundamental period, and THD increases from 0.77% to 1.42%, as shown in Figure 11a. The capacitor voltages are maintained in balance, as shown in Figure 11b.
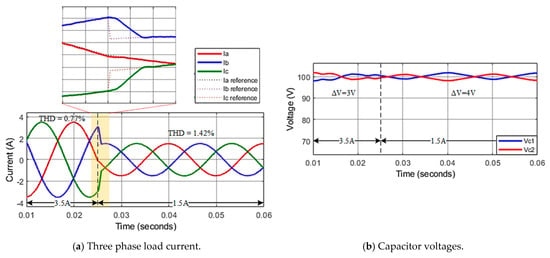
Figure 11.
Transient response of asymmetric inverter using improved MPC algorithm.
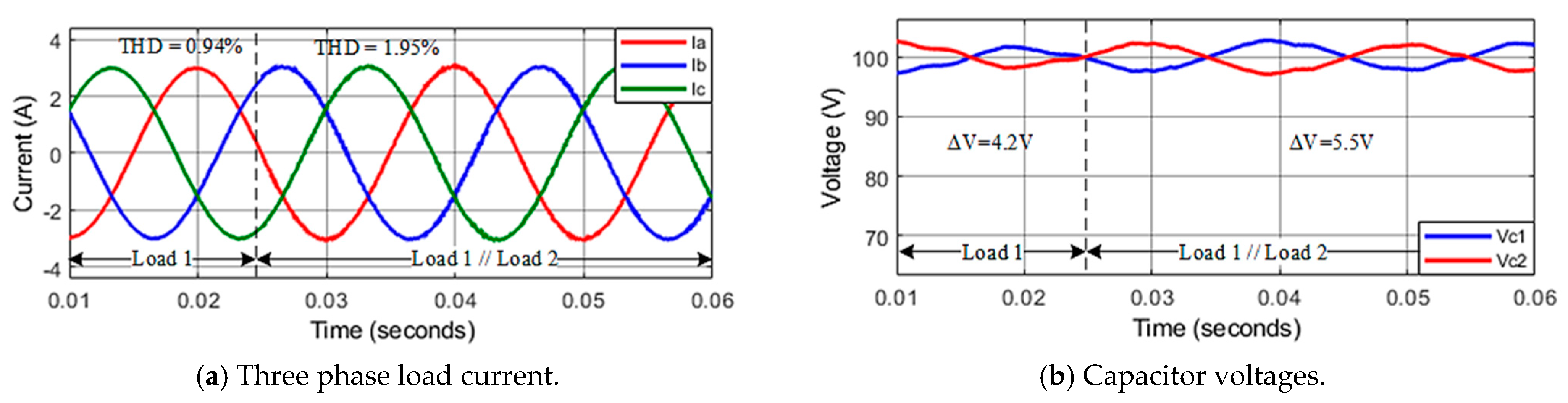
Another simulation scenario is performed under changing load parameters. A short time after connecting the second load ( in parallel with at t = 0.025 s, the reference current is maintained at 3 A. The results show that the current is stable at a set value, and THD increases from 0.94% to 1.95%, as illustrated in Figure 12a. The capacitor voltages are well balanced, as shown in Figure 12b. In the previous transient investigation, the improved MPC algorithm applying to asymmetric T-type inverter proves to have good performance during load changing.
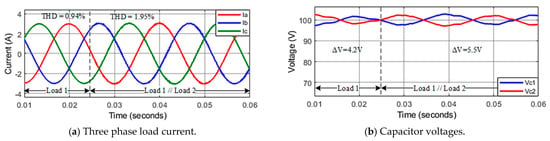
Figure 12.
Response of the system in conditions of changing load parameters.
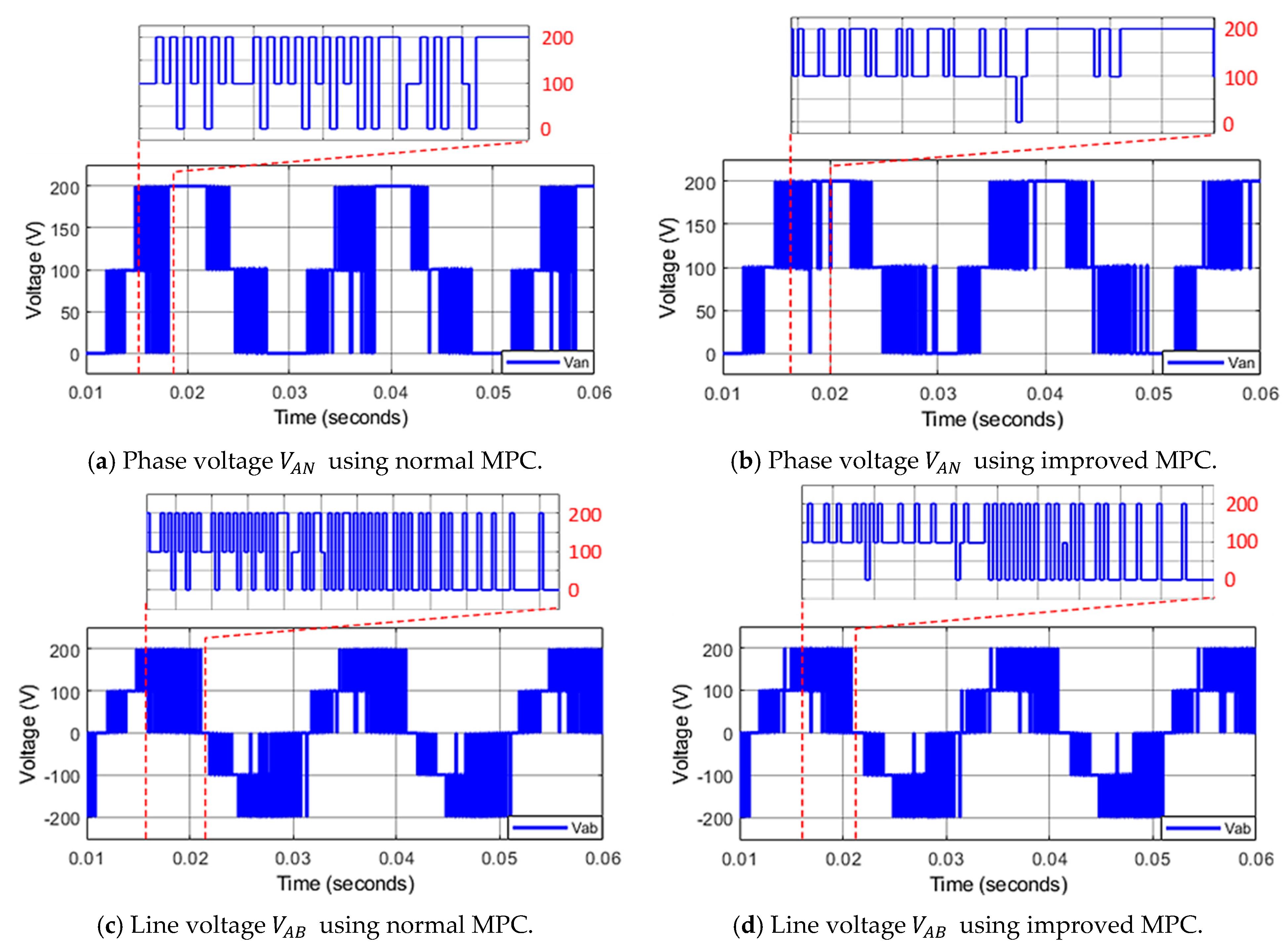
A comparison between a conventional MPC and the improved MPC is carried out to prove the effectiveness of the proposed method. Figure 13a,c shows phase voltage and line voltage while using the conventional MPC method. These voltages attain a high voltage jump with amplitude in their waveforms. In contrast, when applying the improved MPC algorithm, the voltage slope steepness of phase voltage reduces its maximum value to , a half of the previous case, as shown in Figure 13b. The improvement can be also seen in the line-to-line voltage, as shown in Figure 13d.
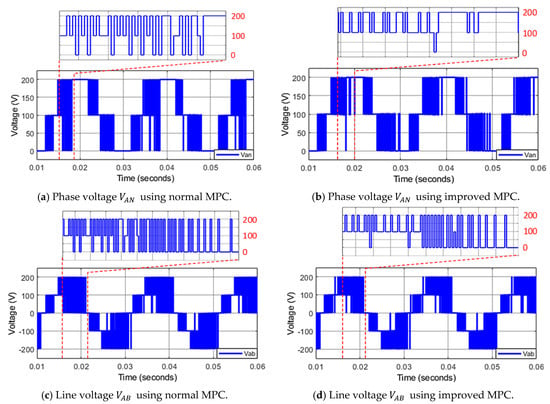
Figure 13.
The phase voltage and line voltage using normal MPC and improved MPC for asymmetric 3-level inverter.
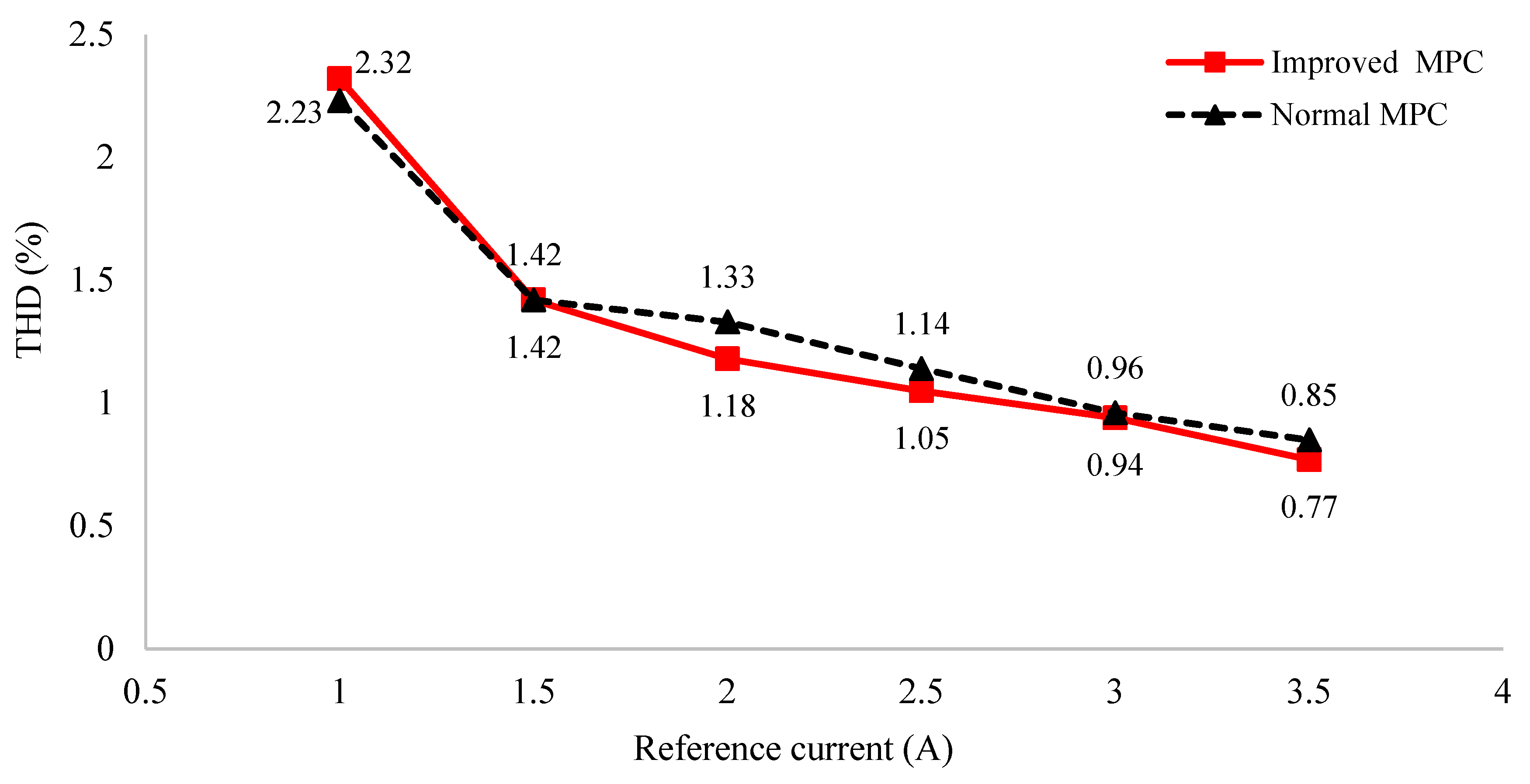
For evaluation of output quality, the graph comparing the THD curve of the load current between the conventional MPC and the improved MPC is illustrated in Figure 14. The proposed algorithm produces output line voltages with lower THD than that of the normal MPC. For example, at , the THD value of the improved MPC is 1.18% and 1.33% for the normal MPC. This translates to a more than an 11% improvement of load current THD. Likewise, at , the THD values are 0.77% and 0.85% for improved MPC and normal PMC, respectively.
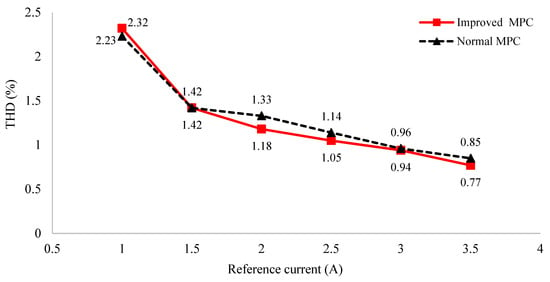
Figure 14.
Graph of THD comparison of normal MPC and improved MPC for asymmetric 3-level inverter.
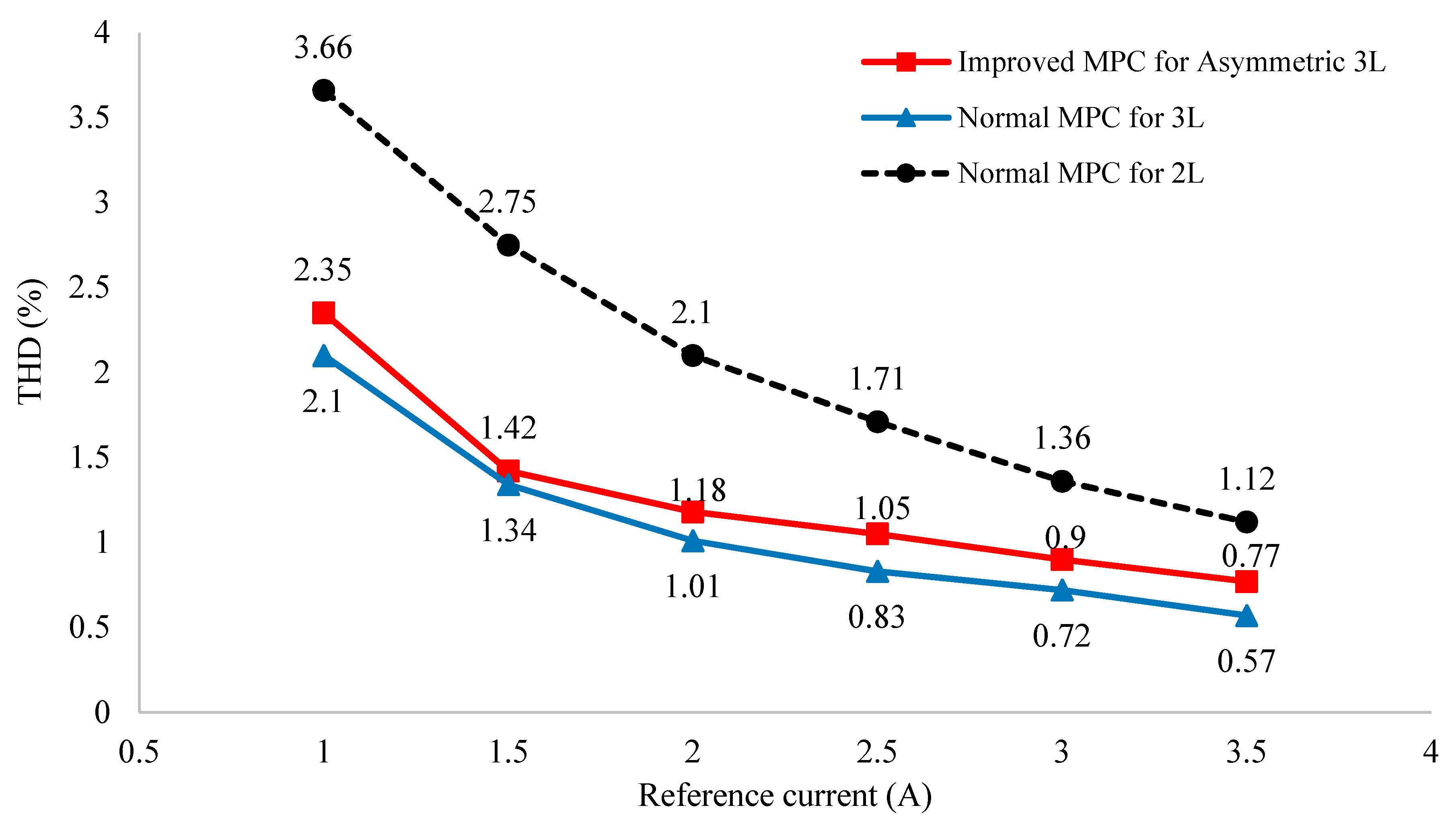
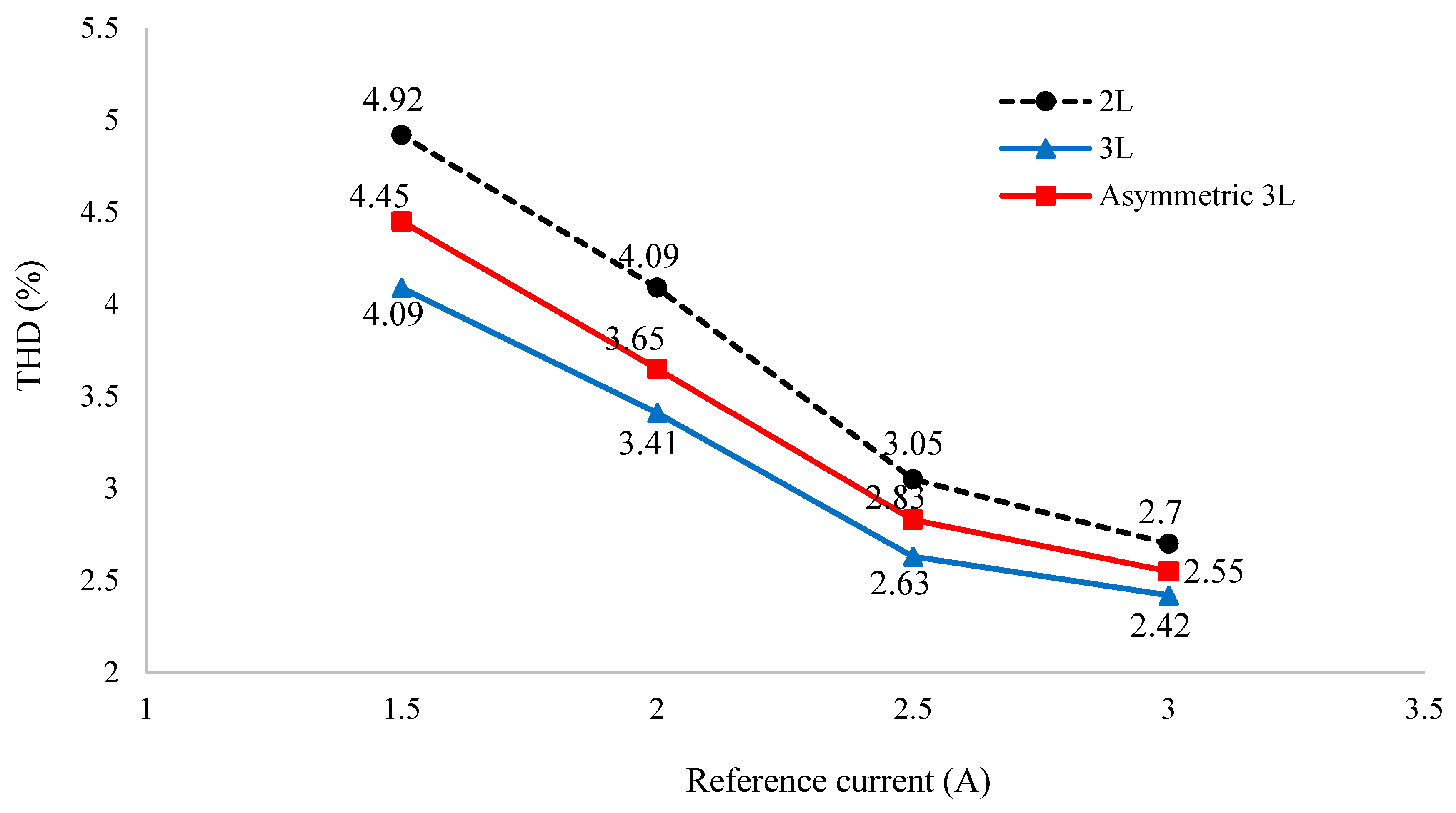
For a better view, the total harmonic distortion performance of the asymmetric T NPC 3-level inverter is also compared with traditional 3-level and 2-level inverters. Figure 15 clearly shows that the load current THD of the asymmetric T-type NPC inverter is much better than that of the 2-level inverter, but slightly worse than that of the conventional 3-level inverter.
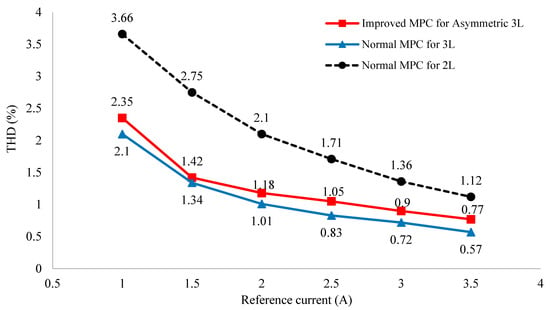
Figure 15.
Graph of THD comparison of asymmetric 3-level, conventional 3-level, and 2-level inverter.
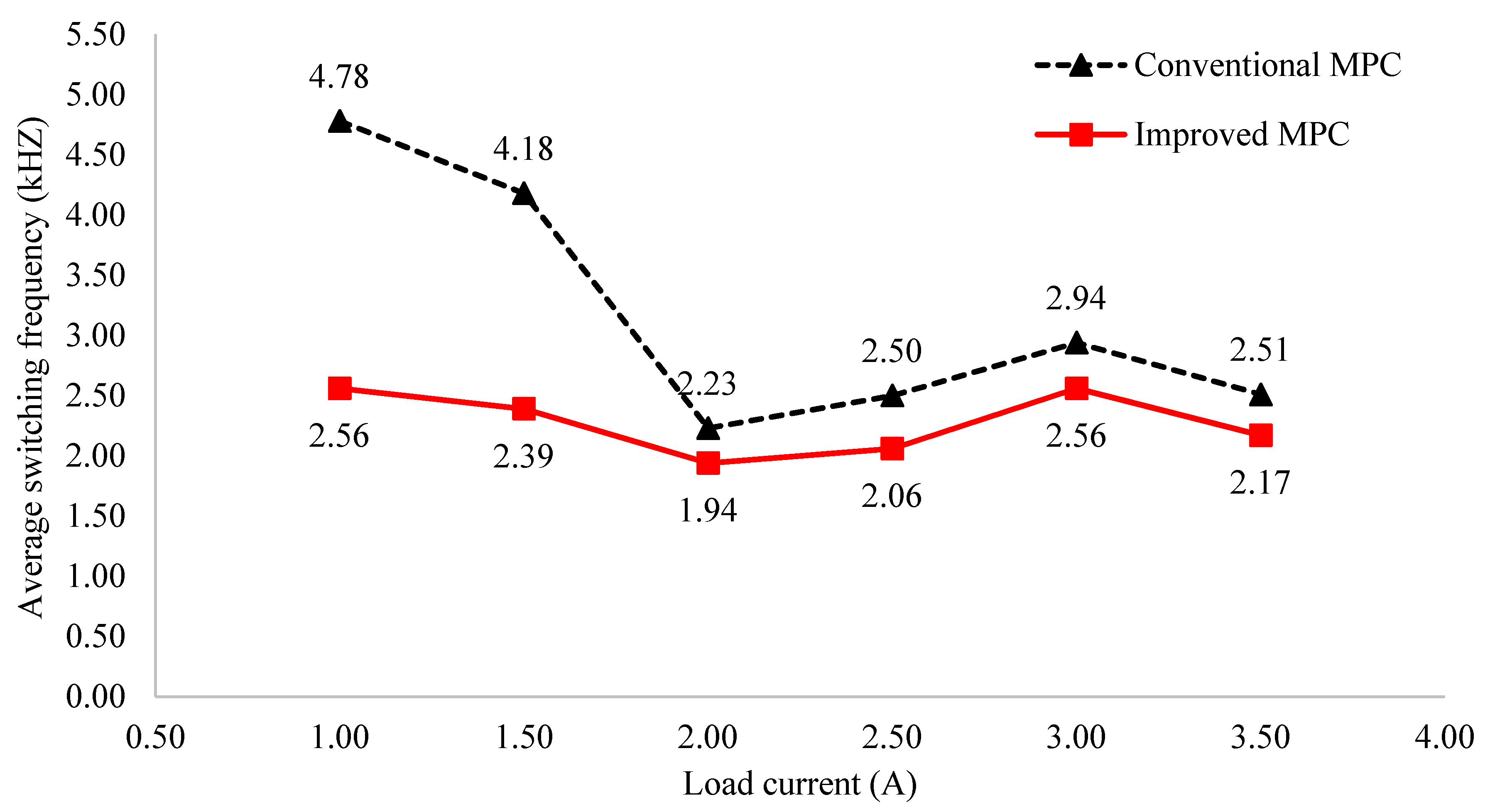
Another benefit of the proposed MPC can be demonstrated in switching frequency. Figure 16 shows the average switching frequency curves of the conventional MPC algorithm and the improved MPC for the asymmetric inverter configuration. For example, at , the average switching frequency of the improved MPC algorithm is 2.56 kHz, while that of the normal MPC algorithm is 2.94 kHz. It gives a reduction of about 13% switching frequency. Similar results are also obtained for the remaining load currents. For more detail, Figure 17a illustrates the switching frequency distribution among switching devices of the conventional MPC method, which is less uniformly distributed than that of the improved MPC algorithm, as shown in Figure 17b, which possibly leads to failures in some switching devices that have to experience a considerable amount of switching frequency over a long-term operation [33].
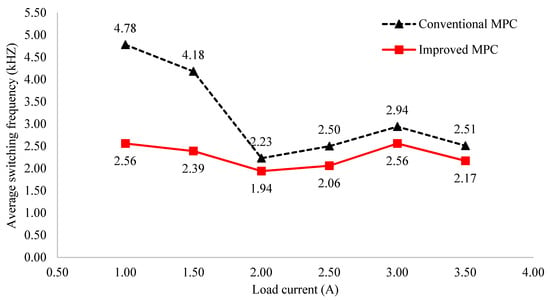
Figure 16.
Average switching frequency comparison of normal MPC and improved MPC for asymmetric 3-level inverter.
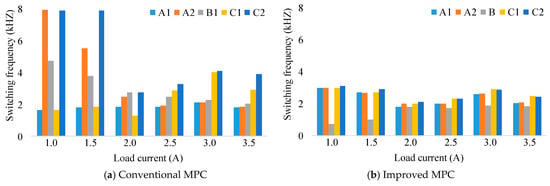
Figure 17.
The switching frequency distribution among switching devices.
4.2. Experimental Results
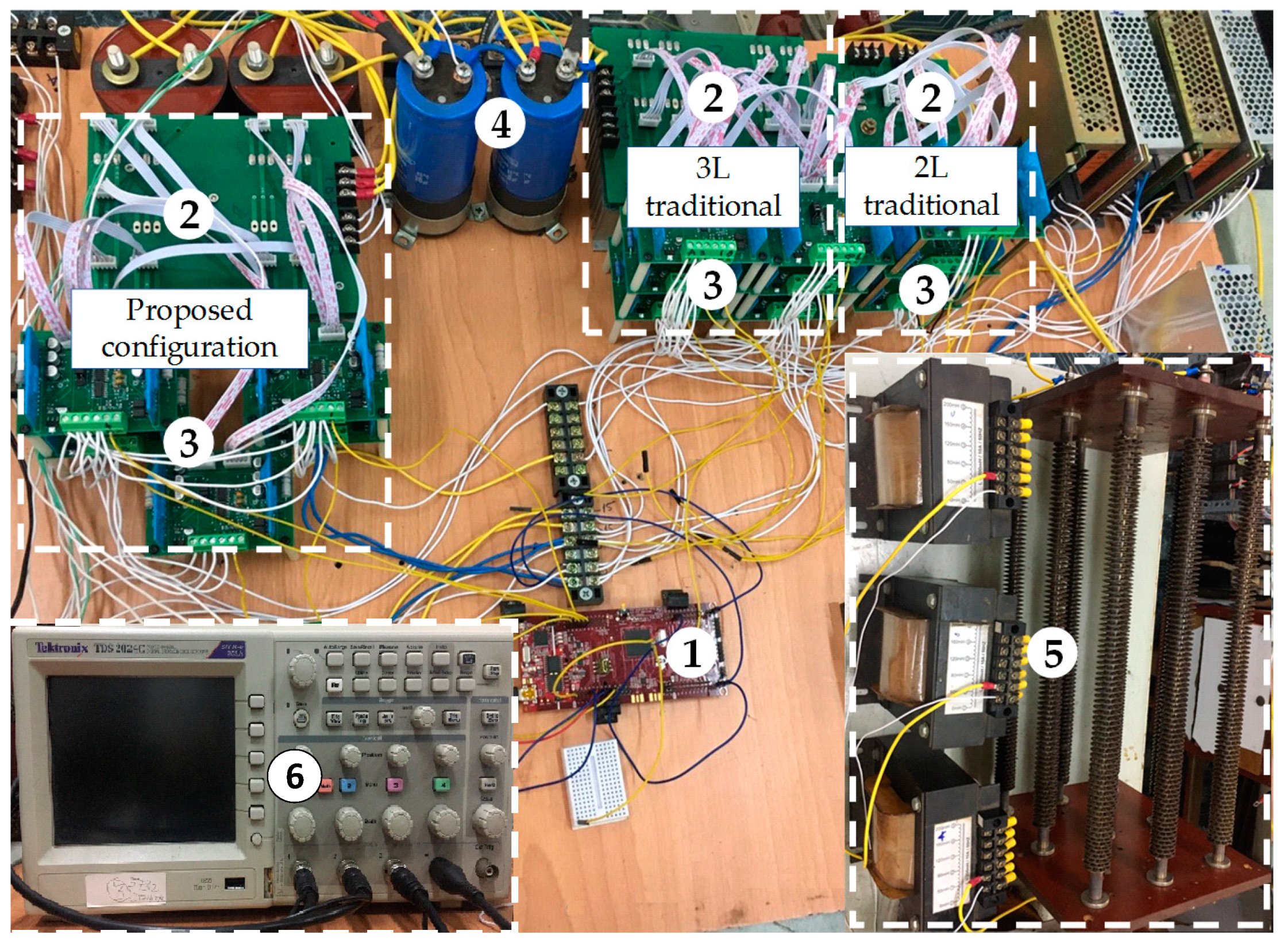
To verify the effectiveness of the asymmetric T-type NPC inverter when applying the improved MPC algorithm, experiments are performed for both transient and steady-state conditions. A laboratory model was built, as shown in Figure 18, including: ➀ a digital signal processor TMS320F28379D to perform algorithms built-in Matlab/Simulink environment with Embedded Coder Support Package for TI C2000 Processors; ➁ the inverter is made from TOSHIBA’s IGBT GT50J325-type; ➂ IGBT driver circuit uses QP12W08S-37 type; ➃ DC-bus voltage is fed from 2 capacitors 1200μf-450VDC; ➄ the load R = 25 Ω, L = 50 mH; ➅ Tektronix TDS2024C oscilloscope. The detailed parameters are listed in Table 5.
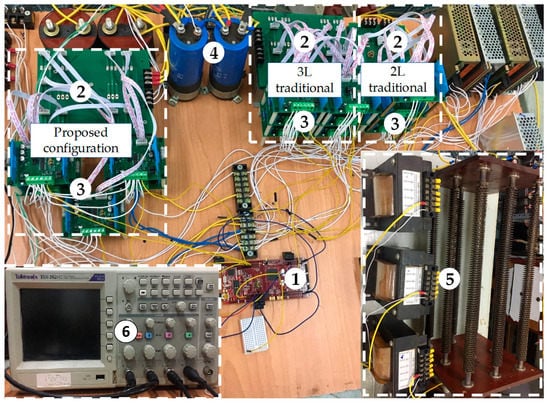
Figure 18.
Experimental model in the laboratory.
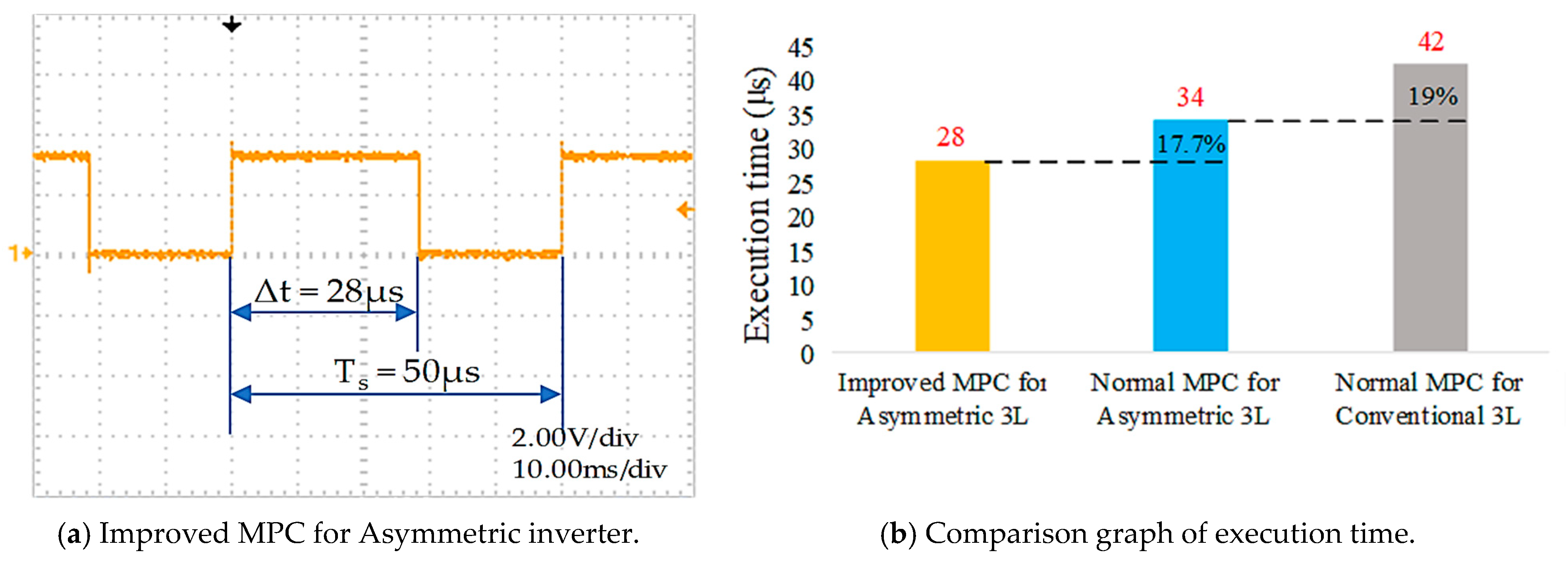
The digital signal processing (DSP) generates the signals for switching devices of the inverter via general-purpose input/output (GPIO) outputs at sampling time 50 µs and DC-bus voltage at 200 V. The execution time efficiency of the improved MPC algorithm for the asymmetric inverter configuration has been demonstrated by the results shown in Figure 19. It can be seen that the conventional MPC algorithm for asymmetric 3-level inverter takes about 34 µs, which is about 19% less compared with a conventional 3-level inverter, as presented in Figure 19b. Meanwhile, the improved MPC method takes about 28 µs, as shown in Figure 19a, improving by about 17.7% compared to a conventional MPC.
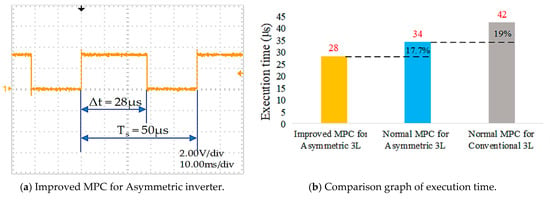
Figure 19.
Execution time.
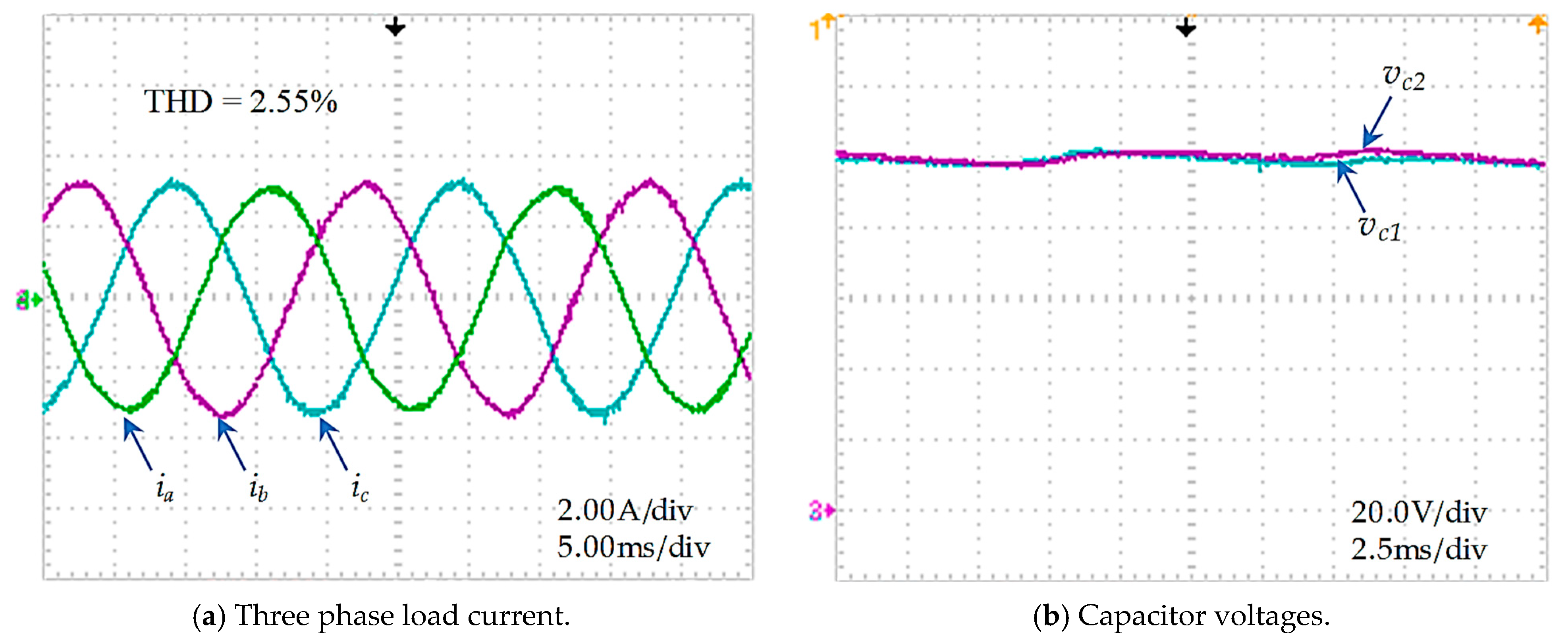
The steady-state current responses are sinusoidal and stable at a set-value 3 A with THD about 2.55%, as illustrated in Figure 20a. The capacitor voltages are maintained in good balance, as shown in Figure 20b.
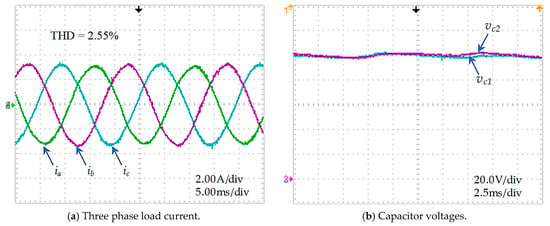
Figure 20.
Steady−state of the improved PMC method for an asymmetric T-type NPC inverter.
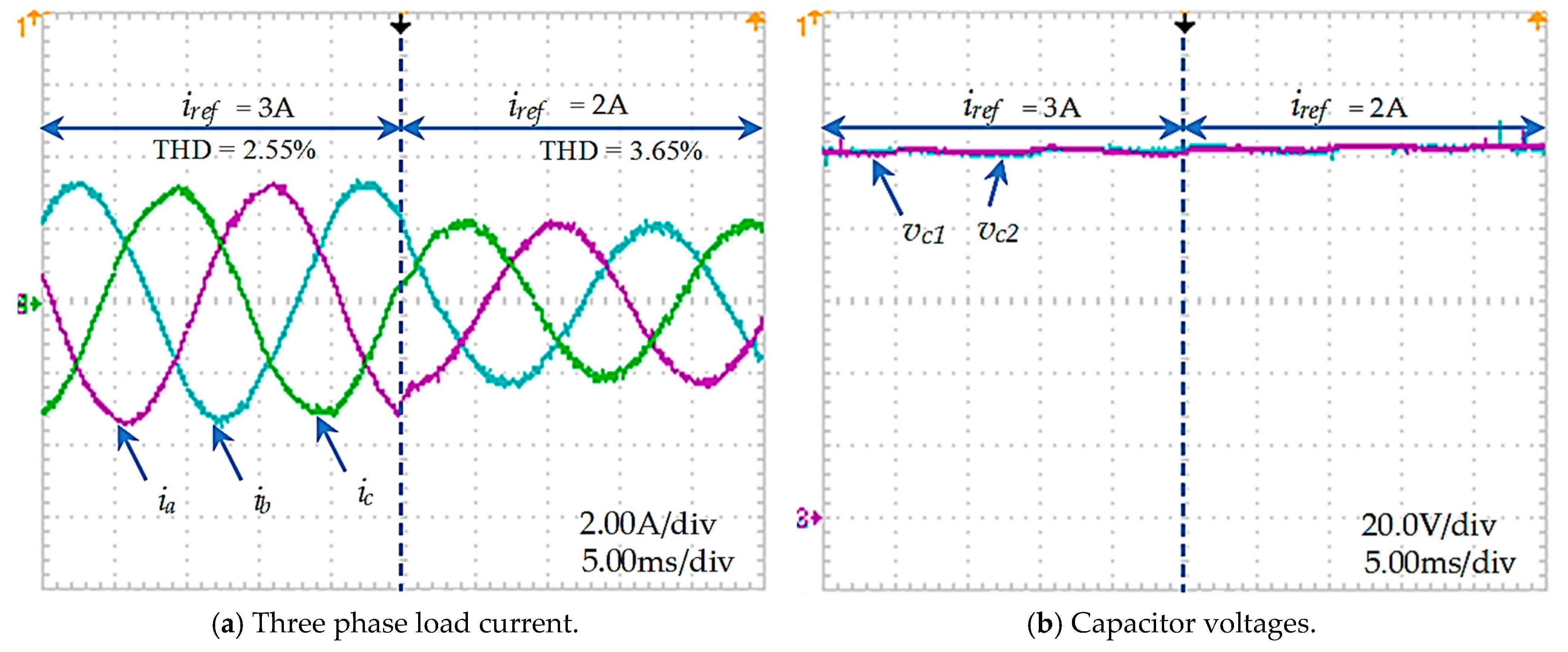
Another experiment on changing the reference current was also performed. The reference current is initially set at 3 A, then suddenly changed to 2 A. The capacitor voltages are stable at balance, as shown in Figure 21b. The current response quickly reached a steady state at the reference value, with THD increasing from 2.55% to 3.65%, as presented in Figure 21a.
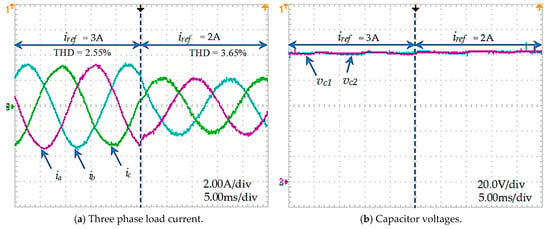
Figure 21.
Transient response of the improved PMC for an asymmetric T-type NPC inverter.
Similar experiments were also carried out on 2-level and conventional 3-level inverters for comparison, and the results are shown in Figure 22. For example, at , the current load THD of the asymmetric inverter is 2.55% compared with 2.7% of the 2-level inverter and 2.42% of the 3-level inverter. The THD increased to 4.45% at for the asymmetric inverter, compared with 4.92% and 4.09% of the 2-level inverter and 3-level inverter, respectively. The load current THD of the asymmetrical T-type NPC inverter was not as good as the 3-level inverter although better than the 2-level inverter. The characteristics in Figure 22 are similar to those of the simulation shown in Figure 15.
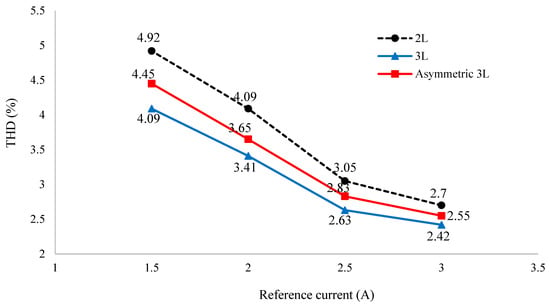
Figure 22.
Experimental results of THD comparison of asymmetric 3-level, conventional 3-level, and 2-level inverter.
5. Conclusions
This paper presented the asymmetric T-type NPC inverter topology. An improved predictive control strategy is proposed to control this configuration. A comparative evaluation of output current performances between asymmetric 3-level T-type, conventional 3-level, and 2-level inverters was performed. Simulation and experimental results have demonstrated the benefits of the asymmetric inverter when controlled by the improved MPC algorithm. The proposed MPC also proves to be better than the conventional MPC for a shorter execution time. Applying the proposed MPC method, the load current THD of the asymmetric inverter is obviously better than the 2-level inverter, and its quality is close to that of the traditional 3-level inverter. Therefore, the asymmetric 3-level inverter is shown to be attractive for applications that require the full range of output voltage and low harmonic distortion like the traditional 3-level inverter, but at a lower cost. Furthermore, in another application, control of this topology can be applied for a conventional 3-level NPC in faulty situations where one T-leg connected to the neutral point is faulty and open. For simplicity, the paper presents the improved MPC method for RL load. In order to ensure its use in real-life applications such as electrical motor drives and utility converter systems, further studies are needed such as analysis and modeling of the whole system fed by asymmetrical inverter and control design with IMPC algorithm and system stability issue. In addition, the overall performance of IMPC will be further assessed by executing a comparative study with linear controllers based on PWM.
Author Contributions
Formal Analysis by N.V.N., Investigation by N.X.D., Software by N.X.D., Supervision by N.V.N., Validation by N.V.N., Writing—Original Draft by N.X.D., Writing—Review and Editing by N.V.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number 103.99-2019.369.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Davoodnezhad, R.; Holmes, D.G.; McGrath, B.P. A Novel Three-Level Hysteresis Current Regulation Strategy for Three-Phase Three-Level Inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 29, 6100–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Giri, S.K.; Kundu, S.; Banerjee, S. A Generalized Discontinuous PWM Scheme for Three-Level NPC Traction Inverter With Minimum Switching Loss for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Bansal, R.C.; Singh, A.R.; Naidoo, R. Multi-Objective Optimization of Hybrid Renewable Energy System Using Reformed Electric System Cascade Analysis for Islanding and Grid Connected Modes of Operation. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 47332–47354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Pillay, P.; Williamson, S.S. Comparative Analysis Between Two-Level and Three-Level DC/AC Electric Vehicle Traction Inverters Using a Novel DC-Link Voltage Balancing Algorithm. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2014, 2, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annoukoubi, M.; Essadki, A.; Laghridat, H.; Nasser, T. Comparative study between the performances of a three-level and two-level converter for a Wind Energy Conversion System. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Wireless Technologies, Embedded and Intelligent Systems (WITS), Fez, Morocco, 3–4 April 2019; IEEE: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Teichmann, R.; Bernet, S. A Comparison of Three-Level Converters Versus Two-Level Converters for Low-Voltage Drives, Traction, and Utility Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2005, 41, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, U.M.; Blaabjerg, F.; Lee, K.-B. Reliability Improvement of a T-Type Three-Level Inverter With Fault-Tolerant Control Strategy. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 2660–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemi, P.; Jeung, Y.C.; Lee, D.C. DC-Link Capacitance Minimization in T-Type Three-Level AC/DC/AC PWM Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 1382–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, M.; Friedli, T.; Kolar, J.W. Comparative Evaluation of Advanced Three Phase Three-Level Inverter/Converter Topologies against Two-Level Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 5515–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemi, P.; Lee, D.C. Comparative Analysis of Power Losses for Three-Level T-Type and NPC PWM Inverters. Trans. Korean Inst. Power Electron. 2014, 19, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patsakis, G.; Karamanakos, P.; Stolze, P.; Manias, S.; Kennel, R.; Mouton, H.D.T. Variable switching point predictive torque control for the four-switch three-phase inverter. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Sensorless Control for Electrical Drives and Predictive Control of Electrical Drives and Power Electronics (SLED/PRECEDE), Munich, Germany, 17–19 October 2013; IEEE: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sefa, I.; Komurcugil, H.; Demirbas, S.; Altin, N.; Ozdemir, S. Three-phase three-level inverter with reduced number of switches for stand-alone PV systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 6th International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Applications (ICRERA), San Diego, CA, USA, 5–8 November 2017; IEEE: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1119–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Tarek, G.; Badii, B.; Ahmed, M. DTC of reconfigured three level inverter fed IM drives following a leg failure. COMPEL Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. 2016, 35, 764–781. [Google Scholar]
- Ozdemir, S.; Altin, N.; Komurcugil, H.; Sefa, I. Sliding Mode Control of Three-Phase Three-Level Two-Leg NPC Inverter with LCL Filter for Distributed Generation Systems. In Proceedings of the IECON 2018—44th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Washington, DC, USA, 21–23 October 2018; IEEE: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 3895–3900. [Google Scholar]
- Heydari, M.; Fatemi, A.; Varjani, A.Y. A Reduced Switch Count Three-Phase AC/AC Converter With Six Power Switches: Modeling, Analysis, and Control. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2017, 5, 1720–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidhya, V.; Balamurugan, C.R.; Natarajan, S.P. Investigation on symmetrical three phase hybrid cascaded multilevel inverter with reduced number of switches. In Proceedings of the DST Sponsored International Conference on Power and Energy System ICPES’12, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 12–14 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Altin, N.; Sefa, I.; Komurcugil, H.; Ozdemir, S. Three-phase three-level T-type grid-connected inverter with reduced number of switches. In Proceedings of the 2018 6th International Istanbul Smart Grids and Cities Congress and Fair (ICSG), Istanbul, Turkey, 25–26 April 2018; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Manhattan, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Nachiappan, A.; Sundararajan, K.; Malarselvam, V. Current controlled voltage source inverter using Hysteresis controller and PI controller. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Power, Signals, Controls and Computation, Thrissur, Kerala, 3–6 January 2012; IEEE: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, T.-S.; Sul, S.-K. Novel Antiwindup of a Current Regulator of a Surface-Mounted Permanent-Magnet Motor for Flux-Weakening Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2006, 42, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, T.; Miyashita, T.; Yamamoto, Y. Dead beat control of three phase PWM inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1990, 5, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukrer, O. Discrete-time current control of voltage-fed three-phase PWM inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1996, 11, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-C.; Sul, S.-K.; Park, M.-H. Comparison of AC current regulators for IGBT inverter. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the Power Conversion Conference, Yokohama, Japan, 9–12 April 1993; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Manhattan, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 206–212. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, V.-Q.-B.; Nguyen, M.-K.; Tran, T.-T.; Lim, Y.-C.; Choi, J.-H. A Simplified Model Predictive Control for T-Type Inverter with Output LC Filter. Energies 2019, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortes, P.; Rodriguez, J.; Silva, C.; Flores, A. Delay Compensation in Model Predictive Current Control of a Three-Phase Inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 1323–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatani, M.; Hovd, M.; Molinas, M. Finite Control Set Model Predictive Control of a shunt active power filter. In Proceedings of the 2013 Twenty-Eighth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, 17–21 March 2013; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Manhattan, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 2156–2161. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, C.; Zhou, D.; Li, Y. Finite-Control-Set Model Predictive Control for Three-Level NPC Inverter-Fed PMSM Drives With LC Filter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 11980–11991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, P.; Kazmierkowski, M.P.; Kennel, R.M.; Quevedo, D.E.; Rodriguez, J. Predictive Control in Power Electronics and Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 4312–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurtenechea, S.; Rodríguez, M.A.; Oyarbide, E.; Torrealday, J.R. Predictive control strategy for dc/ac converters based on direct power control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar]
- Aurtenechea, S.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Oyarbide, E.; Torrealday, J.R. Predictive direct power control—A new control strate-gy for DC/AC converters. In Proceedings of the IECON 2006-32nd Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics, Paris, France, 7–10 November 2006; pp. 1661–1666. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Fang, H.; Gao, F.; Rodriguez, J.; Kennel, R. Multiple-Vector Model Predictive Power Control for Grid-Tied Wind Turbine System With Enhanced Steady-State Control Performance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 6287–6298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaramasu, V.; Wu, B. Model Predictive Control of Wind Energy Conversion Systems; Wiley-IEEE Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-118-98858-9. [Google Scholar]
- Calle-Prado, A.; Alepuz, S.; Bordonau, J.; Nicolas-Apruzzese, J.; Cortes, P.; Rodriguez, J. Model Predictive Current Control of Grid-Connected Neutral-Point-Clamped Converters to Meet Low-Voltage Ride-Through Requirements. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruckner, T.; Bernet, S.; Guldner, H. The Active NPC Converter and Its Loss-Balancing Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2005, 52, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).