Self-Detection of Early Breast Cancer Application with Infrared Camera and Deep Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
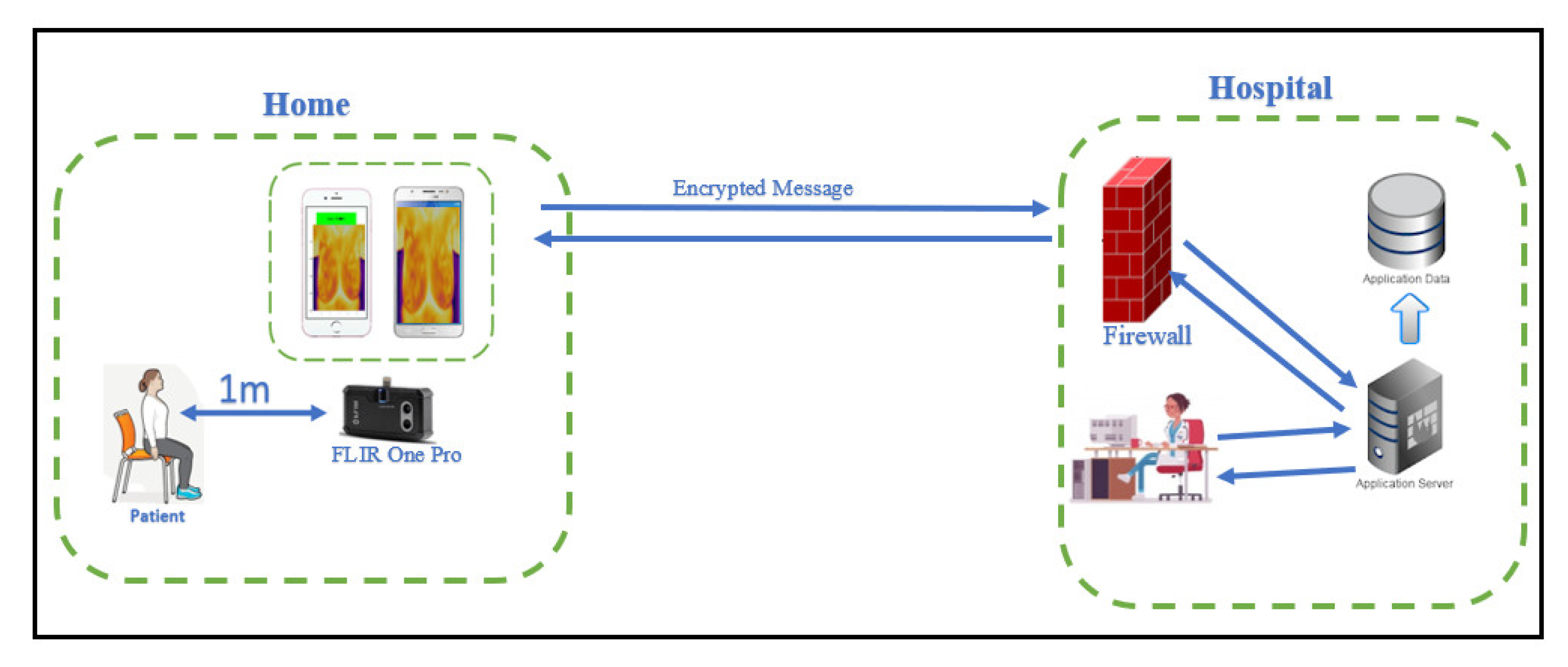
2.1. Framework
2.2. Deep Learning in Matlab
2.3. Graphical User Interface Development Environment (GUIDE)
2.4. Cloud Computing
2.5. Smartphone Health Application
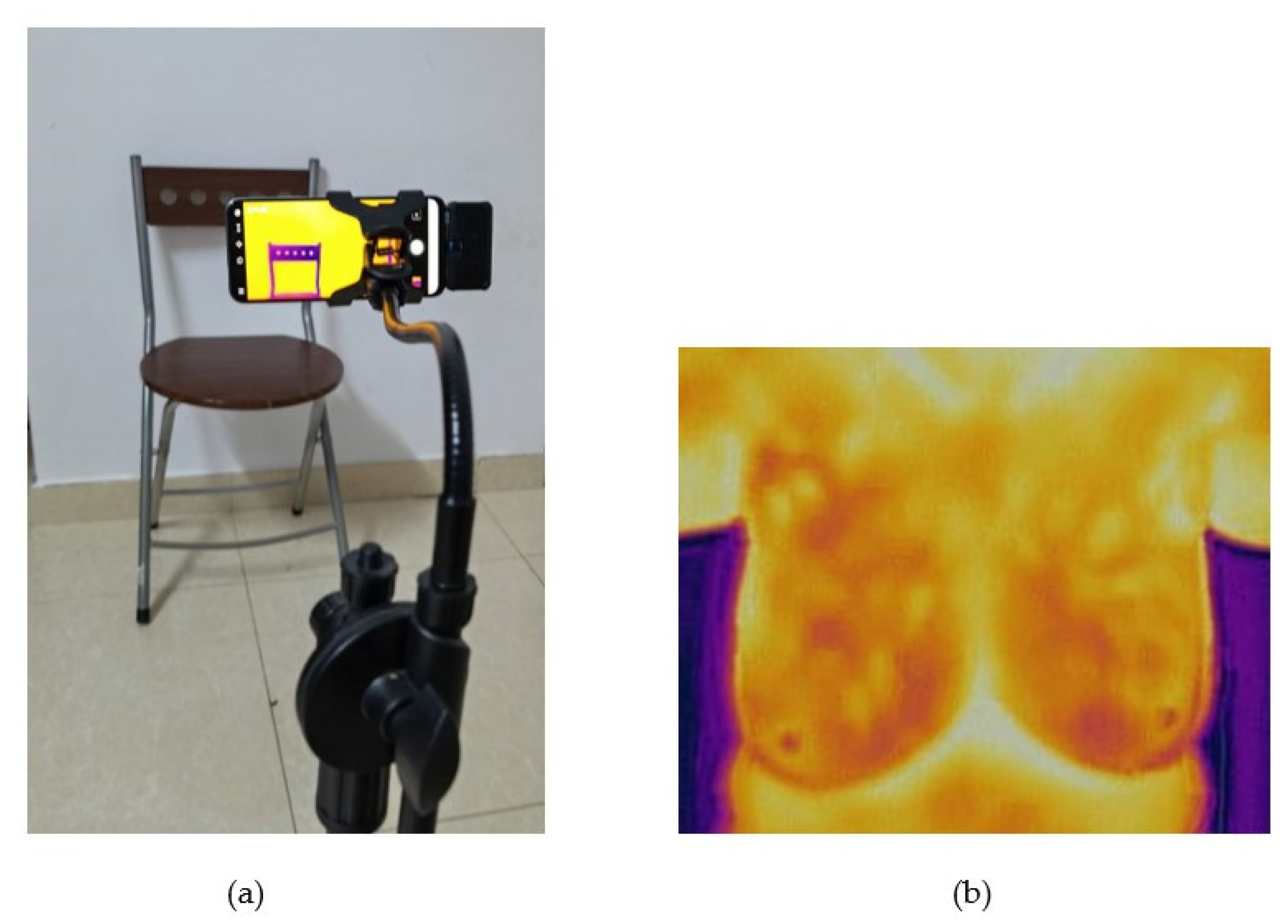
2.6. Experiment Set Up
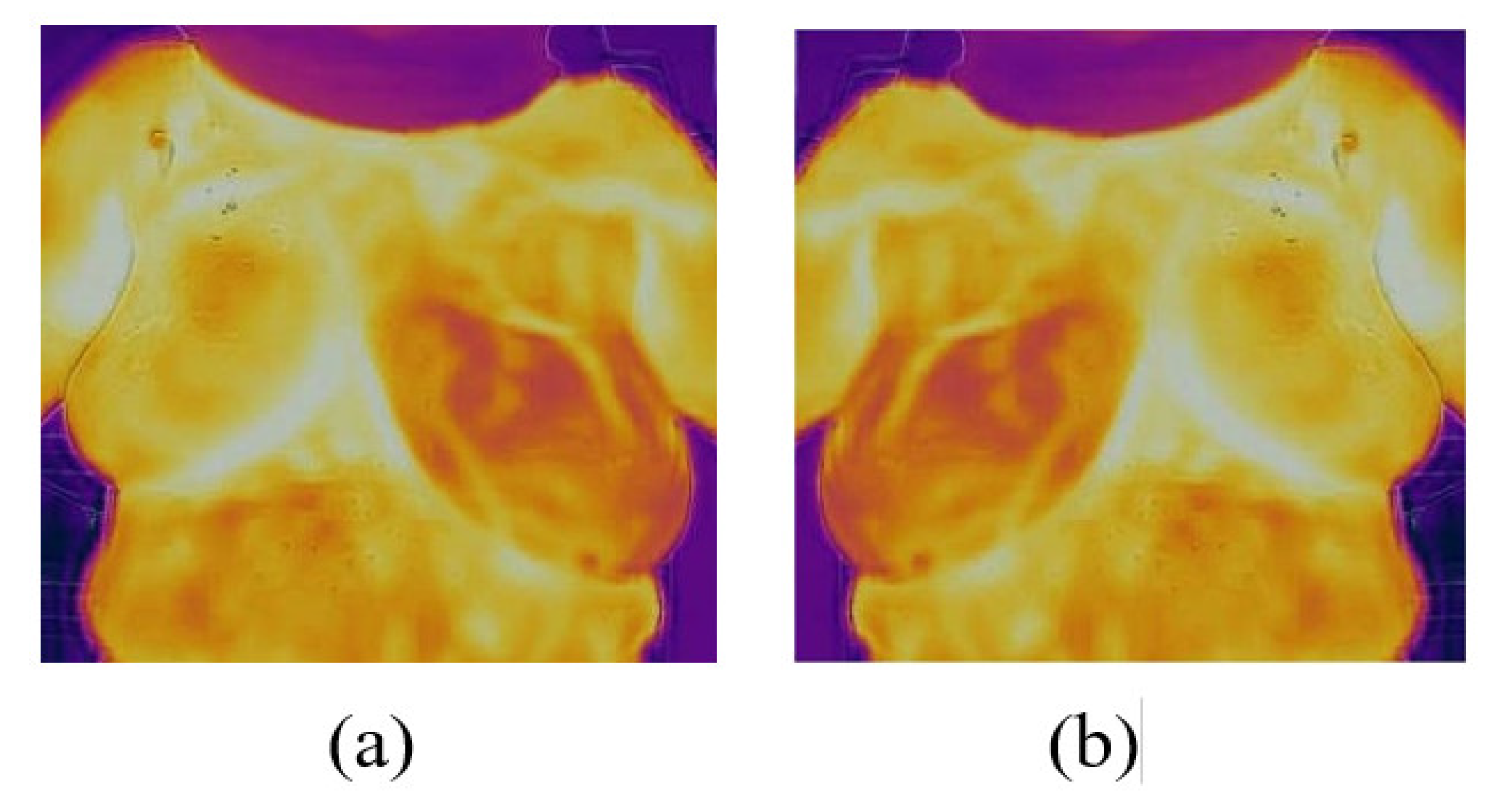
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Houghton, L.C.; Howland, R.E.; McDonald, J.A. Mobilizing Breast Cancer Prevention Research Through Smartphone Apps: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roslidar, R.; Rahman, A.; Muharar, R.; Syahputra, M.R.; Arnia, F.; Syukri, M.; Pradhan, B.; Munadi, K. A Review on Recent Progress in Thermal Imaging and Deep Learning Approaches for Breast Cancer Detection. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 116176–116194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, H.; Holroyd, P.; Burkinshaw, L.; Watten, P.; Zammit, C.; Harris, P.R.; Good, A.; Jenkins, V. A user-centred approach to developing bWell, a mobile app for arm and shoulder exercises after breast cancer treatment. J. Cancer Surviv. 2017, 11, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Uhm, K.E.; Cheong, I.Y.; Yoo, J.S.; Chung, S.H.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Hwang, J.H. Patient Satisfaction with Mobile Health (mHealth) Application for Exercise Intervention in Breast Cancer Survivors. J. Med. Syst. 2018, 42, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akechi, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Uchida, M.; Imai, F.; Momino, K.; Katsuki, F.; Sakurai, N.; Miyaji, T.; Horikoshi, M.; A Furukawa, T.; et al. Smartphone problem-solving and behavioural activation therapy to reduce fear of recurrence among patients with breast cancer (SMartphone Intervention to LEssen fear of cancer recurrence: SMILE project): Protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e024794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Kue, J.; Zhu, X.; Yin, X.; Jiang, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Zeng, L.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.; et al. Effects of Nurse-Led Support Via WeChat, a Smartphone Application, for Breast Cancer Patients After Surgery: A Quasi-Experimental Study. Telemed. e-Health 2020, 26, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyatt, K.D.; Jenkins, S.M.; Plevak, M.F.; Pont, M.R.V.; Pruthi, S. A personalized, web-based breast cancer decision making application: A pre-post survey. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2019, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stubbins, R.; He, T.; Yu, X.; Puppala, M.; Ezeana, C.F.; Chen, S.; Alvarado, M.V.Y.; Ensor, J.; Rodriguez, A.; Niravath, P.; et al. A Behavior-Modification, Clinical-Grade Mobile Application to Improve Breast Cancer Survivors’ Accountability and Health Outcomes. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2018, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buscemi, J.; Buitrago, D.; Iacobelli, F.; Penedo, F.; Maciel, C.; Guitleman, J.; Balakrishnan, A.; Corden, M.; Adler, R.F.; Bouchard, L.C.; et al. Feasibility of a Smartphone-based pilot intervention for Hispanic breast cancer survivors: A brief report. Transl. Behav. Med. 2018, 9, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, I.Y.; Jung, M.; Park, Y.R.; Cho, D.; Chung, H.; Min, Y.H.; Park, H.J.; Lee, M.; Lee, S.B.; Chung, S.; et al. Exercise Promotion and Distress Reduction Using a Mobile App-Based Community in Breast Cancer Survivors. Front. Oncol. 2020, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, A.; Nambisan, P.; Baker, E. Mobile applications for breast cancer survivorship and self-management: A systematic review. Health Inform. J. 2020, 26, 2892–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Ebert, L.; Liu, X.; Chan, S.W.-C. A mobile application of breast cancer e-support program versus routine Care in the treatment of Chinese women with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Shang, P.; Lu, C.; Meraghni, S.; Benaggoune, K.; Zuluaga, J.; Zerhouni, N.; Devalland, C.; Al Masry, Z. A portable breast cancer detection system based on smartphone with infrared camera. Vibroengineering Procedia 2019, 26, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, B.; Iqbal, H.T.; Khan, U.; Bin Altaf, M.A. A Portable Thermogram Based Non-Contact Non-Invasive Early Breast-Cancer Screening Device. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), Cleveland, OH, USA, 17–19 October 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Al Husaini, M.A.S.; Habaebi, M.H.; Gunawan, T.S.; Islam, R.; Elsheikh, E.A.A.; Suliman, F.M. Thermal-based early breast cancer detection using inception V3, inception V4 and modified inception MV4. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namasudra, S. Data Access Control in the Cloud Computing Environment for Bioinformatics. Int. J. Appl. Res. Bioinform. 2021, 11, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbostad, J.L.; Vereijken, B.; Becker, C.; Todd, C.; Taraldsen, K.; Pijnappels, M.; Aminian, K.; Mellone, S. Mobile Health Applications to Promote Active and Healthy Ageing. Sensors 2017, 17, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Chady, T.; Tian, G.Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, S. CFRP Impact Damage Inspection Based on Manifold Learning Using Ultrasonic Induced Thermography. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 15, 2648–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.K.; Borgen, R.; Kelly, J.; Millington, S.; Hilton, B.; Aspin, R.; Lança, C.; Hogg, P. Blurred digital mammography images: An analysis of technical recall and observer detection performance. Br. J. Radiol. 2017, 90, 20160271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaster, B.R.; Howes, L.; Kaeli, D.R.; Mistry, P.; Schaa, D. Introduction to Parallel Programming. In Heterogeneous Computing with OpenCL; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.G. Some improvements on deep convolutional neural network based image classification. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2014, Banff, AB, Canada, 14–16 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, T.; Park, J.; Seshadrinathan, K.; Lee, S.; Bovik, A.C. No-Reference Sharpness Assessment of Camera-Shaken Images by Analysis of Spectral Structure. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 5428–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glowacz, A. Ventilation Diagnosis of Angle Grinder Using Thermal Imaging. Sensors 2021, 21, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Configuration | Inception V3 | Inception V4 | Inception MV4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters of Augmentation | randomly flip the training images along the vertical axis and randomly translate them up to 30 pixels and scale them up to 10% horizontally and vertically | randomly flip the training images along the vertical axis and randomly translate them up to 30 pixels and scale them up to 10% horizontally and vertically | randomly flip the training images along the vertical axis and randomly translate them up to 30 pixels and scale them up to 10% horizontally and vertically |
| Configuration | Global Average Pooling + Full Connected Layer (2048) + SoftMax | Global Average Pooling + Dropout (0.8) + Full Connected Layer (1536) + SoftMax | Global Average Pooling + Dropout (0.8) + Full Connected Layer (1536) + SoftMax |
| first 10 convolution layers frozen | first 10 convolution layers frozen | first 10 convolution layers frozen | |
| Number of parameters | 21,806,882 | 156,042,082 | 128,174,466 |
| Optimization method | ADAM | SGDM | SGDM |
| Database | 1874 thermal images from DMR-IR (70% training &30% Testing) | 1874 thermal images from DMR-IR (70% training &30% Testing) | 1874 thermal images from DMR-IR (70% training &30% Testing) |
| Learning rate | 1e−4 | 1e−4 | 1e−4 |
| Software | MATLAB | MATLAB | MATLAB |
| Accuracy | Average 98.104% | Average 99.712% | Average 99.748 % |
| Error | ±1.52% | ±0.27% | ±0.18% |
| Training Time epoch 3 | 6.376 min with error ±0.015 min | 9.554 min with error ±0.145 min | 7.704 min with error ±0.01 min |
| Method | Sub Method | DMR-IR Database | Image 1 | Image 2 | Image 3 | Image 4 | Image 5 | Image 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classification | Health Images | Cancer Images | ||||||
| Cable/ Data | 1. MSE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2. PSNR | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | ||
| 3. AD | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 4. SC | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 5 NK | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 6. MD | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 7 LMSE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 8. NAE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Accuracy % | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.9998 | 99.9998 | 99.9999 | ||
| WiFi | 1 m/5 m/7 m /One Wall/ Two walls/ Roof/ Roof and one wall/ Roof and two walls | 1. MSE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2. PSNR | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | ||
| 3. AD | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 4. SC | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 5 NK | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 6. MD | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 7 LMSE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 8. NAE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Accuracy % | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.9998 | 99.9998 | 99.9999 | ||
| Method | Sub Method | FLIR ONE PRO | Image 1 | Image 2 | Image 3 | Image 4 | Image 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classification | Cancer Images | ||||||
| Cable/Data | 1. MSE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2. PSNR | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | ||
| 3. AD | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 4. SC | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 5 NK | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 6. MD | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 7 LMSE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 8. NAE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Accuracy % | 99.9451 | 99.2805 | 99.9593 | 99.4079 | 97.6108 | ||
| WiFi | 1 m/5 m/7 m /One Wall/ Two walls/ Roof/ Roof and one wall/ Roof and two walls | 1. MSE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2. PSNR | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | Inf | ||
| 3. AD | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 4. SC | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 5 NK | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 6. MD | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 7 LMSE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 8. NAE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Accuracy % | 99.9451 | 99.2805 | 99.9593 | 99.4079 | 97.6108 | ||
| Quality Parameters | DMR-IR | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy | Cancer | |||||
| Sample 1 | Sample2 | Sample 3 | Sample 1 | Sample 2 | ||
| Compressed 5% | MSE | 21.154531 | 20.738177 | 22.212344 | 11.707760 | 13.383073 |
| PSNR | 34.876770 | 34.963098 | 34.664860 | 37.446065 | 36.865245 | |
| AD | −0.074635 | −0.101302 | −0.099323 | 0.006406 | −0.029844 | |
| SC | 0.994841 | 0.995139 | 0.994897 | 0.996824 | 0.996018 | |
| NK | 1.002299 | 1.002157 | 1.002257 | 1.001439 | 1.001821 | |
| MD | 29 | 34 | 29 | 22 | 24 | |
| LMSE | 0.050918 | 0.049811 | 0.050031 | 0.033628 | 0.034838 | |
| NAE | 0.018818 | 0.018412 | 0.019231 | 0.012792 | 0.013845 | |
| Accuracy | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| Compressed 15% | MSE | 21.154531 | 20.738177 | 22.212344 | 20.570000 | 21.878854 |
| PSNR | 34.876770 | 34.963098 | 34.664860 | 34.998461 | 34.730558 | |
| AD | −0.074635 | −0.101302 | −0.099323 | −0.050521 | 0.011979 | |
| SC | 0.994841 | 0.995139 | 0.994897 | 0.997278 | 0.998356 | |
| NK | 1.002299 | 1.002157 | 1.002257 | 1.001094 | 1.000533 | |
| MD | 29 | 34 | 29 | 29 | 36 | |
| LMSE | 0.050918 | 0.049811 | 0.050031 | 0.044961 | 0.046356 | |
| NAE | 0.018818 | 0.018412 | 0.019231 | 0.017210 | 0.018037 | |
| Accuracy | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.9999 | 99.9999 | |
| Compressed 26% | MSE | 56.750885 | 52.876302 | 56.055312 | 20.570000 | 21.878854 |
| PSNR | 30.591077 | 30.898193 | 30.644636 | 34.998461 | 34.730558 | |
| AD | −0.084948 | −0.159635 | −0.147604 | −0.050521 | 0.011979 | |
| SC | 0.995986 | 0.995805 | 0.996534 | 0.997278 | 0.998356 | |
| NK | 1.001228 | 1.001378 | 1.000963 | 1.001094 | 1.000533 | |
| MD | 65 | 46 | 58 | 29 | 36 | |
| LMSE | 0.106175 | 0.095837 | 0.098707 | 0.044961 | 0.046356 | |
| NAE | 0.030304 | 0.029065 | 0.029868 | 0.017210 | 0.018037 | |
| Accuracy | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.9999 | 99.9999 | |
| Quality Parameters | FLIR One Pro | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cancers | ||||||
| Sample 1 | Sample2 | Sample 3 | Sample 4 | Sample 5 | ||
| Compressed 5% | MSE | 0.649030 | 0.675719 | 0.585162 | 0.829629 | 2.590069 |
| PSNR | 50.008153 | 49.833142 | 50.458039 | 48.941965 | 43.997690 | |
| AD | 0.001027 | −0.003398 | −0.004354 | 0.002947 | −0.017099 | |
| SC | 0.999920 | 0.999845 | 0.999872 | 0.999974 | 0.999875 | |
| NK | 1.000030 | 1.000067 | 1.000055 | 1.000004 | 1.000037 | |
| MD | 6 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 13 | |
| LMSE | 0.069368 | 0.246863 | 0.075993 | 0.176870 | 0.226512 | |
| NAE | 0.002163 | 0.002171 | 0.001914 | 0.002665 | 0.005469 | |
| Accuracy | 99.95 | 99.3311 | 99.9608 | 99.4006 | 97.469 | |
| Compressed 15% | MSE | 0.649030 | 0.675719 | 0.585162 | 1.988979 | 2.590069 |
| PSNR | 50.008153 | 49.833142 | 50.458039 | 45.144501 | 43.997690 | |
| AD | 0.001027 | −0.003398 | −0.004354 | 0.001004 | −0.017099 | |
| SC | 0.999920 | 0.999845 | 0.999872 | 0.999964 | 0.999875 | |
| NK | 1.000030 | 1.000067 | 1.000055 | 0.999996 | 1.000037 | |
| MD | 6 | 6 | 7 | 11 | 13 | |
| LMSE | 0.069368 | 0.246863 | 0.075993 | 0.301946 | 0.226512 | |
| NAE | 0.002163 | 0.002171 | 0.001914 | 0.004966 | 0.005469 | |
| Accuracy | 99.95 | 99.3311 | 99.9608 | 99.4275 | 97.469 | |
| Compressed 26% | MSE | 0.716193 | 0.675719 | 0.585162 | 2.520331 | 3.415912 |
| PSNR | 49.580501 | 49.833142 | 50.458039 | 44.116228 | 42.795737 | |
| AD | 0.001384 | −0.003398 | −0.004354 | 0.000240 | −0.008514 | |
| SC | 0.999915 | 0.999845 | 0.999872 | 0.999955 | 0.999934 | |
| NK | 1.000031 | 1.000067 | 1.000055 | 0.999995 | 1 | |
| MD | 6 | 6 | 7 | 13 | 15 | |
| LMSE | 0.073986 | 0.246863 | 0.075993 | 0.441004 | 0.386388 | |
| NAE | 0.002374 | 0.002171 | 0.001914 | 0.005745 | 0.006382 | |
| Accuracy | 99.9491 | 99.3311 | 99.9608 | 99.4223 | 97.5137 | |
| DMR-IR Database | Image 1 | Image 2 | Image 3 | Image 4 | Image 5 | Image 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image Effects | Classification | Healthy | Healthy | Healthy | Cancer | Cancer | Cancer |
| Blurry images | Accuracy % | 99.8514 | 99.742 | 99.9156 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Tilted images | Accuracy % | 98.6175 | 98.4814 | 98.786 | 88.7197 | 90.3664 | 90.9845 |
| Shaken images | Accuracy % | 99.9988 | 99.9999 | 99.9995 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Flipped image | Accuracy % | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.9998 | 99.9998 | 99.9999 |
| FLIR ONE PRO | Image 1 | Image 2 | Image 3 | Image 4 | Image 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image Effects | Classification | Cancer | Cancer | Cancer | Cancer | Cancer |
| Blurry images | Accuracy % | 99.981 | 99.6775 | 99.974 | 99.6294 | 97.8939 |
| Tilted images | Accuracy % | 99.8634 | 98.173 | 99.5872 | 99.9466 | 99.0886 |
| Shaken images | Accuracy % | 99.9582 | 99.4484 | 99.9594 | 99.5151 | 97.9629 |
| Flipped image | Accuracy % | 99.9933 | 99.6179 | 99.9967 | 99.8228 | 98.7214 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Husaini, M.A.S.; Hadi Habaebi, M.; Gunawan, T.S.; Islam, M.R. Self-Detection of Early Breast Cancer Application with Infrared Camera and Deep Learning. Electronics 2021, 10, 2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202538
Al Husaini MAS, Hadi Habaebi M, Gunawan TS, Islam MR. Self-Detection of Early Breast Cancer Application with Infrared Camera and Deep Learning. Electronics. 2021; 10(20):2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202538
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Husaini, Mohammed Abdulla Salim, Mohamed Hadi Habaebi, Teddy Surya Gunawan, and Md Rafiqul Islam. 2021. "Self-Detection of Early Breast Cancer Application with Infrared Camera and Deep Learning" Electronics 10, no. 20: 2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202538
APA StyleAl Husaini, M. A. S., Hadi Habaebi, M., Gunawan, T. S., & Islam, M. R. (2021). Self-Detection of Early Breast Cancer Application with Infrared Camera and Deep Learning. Electronics, 10(20), 2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202538







