A Convolutional Neural Network-Based End-to-End Self-Driving Using LiDAR and Camera Fusion: Analysis Perspectives in a Real-World Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preliminaries
2.1.1. Convolutional Neural Network
2.1.2. End-to-End Self-Driving
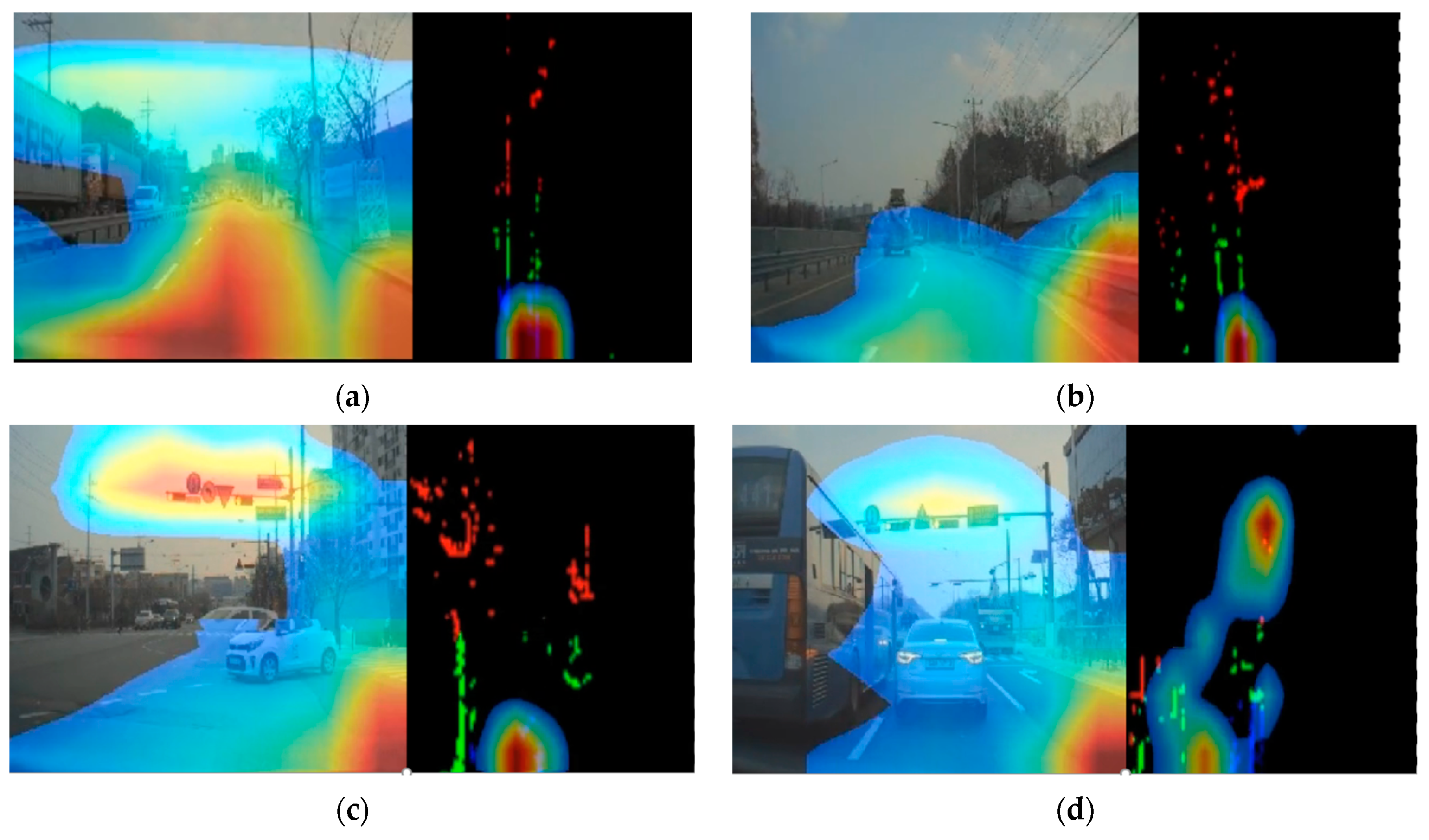
2.1.3. Explainable End-to-End Self-Driving System
2.2. Experiemental Setup
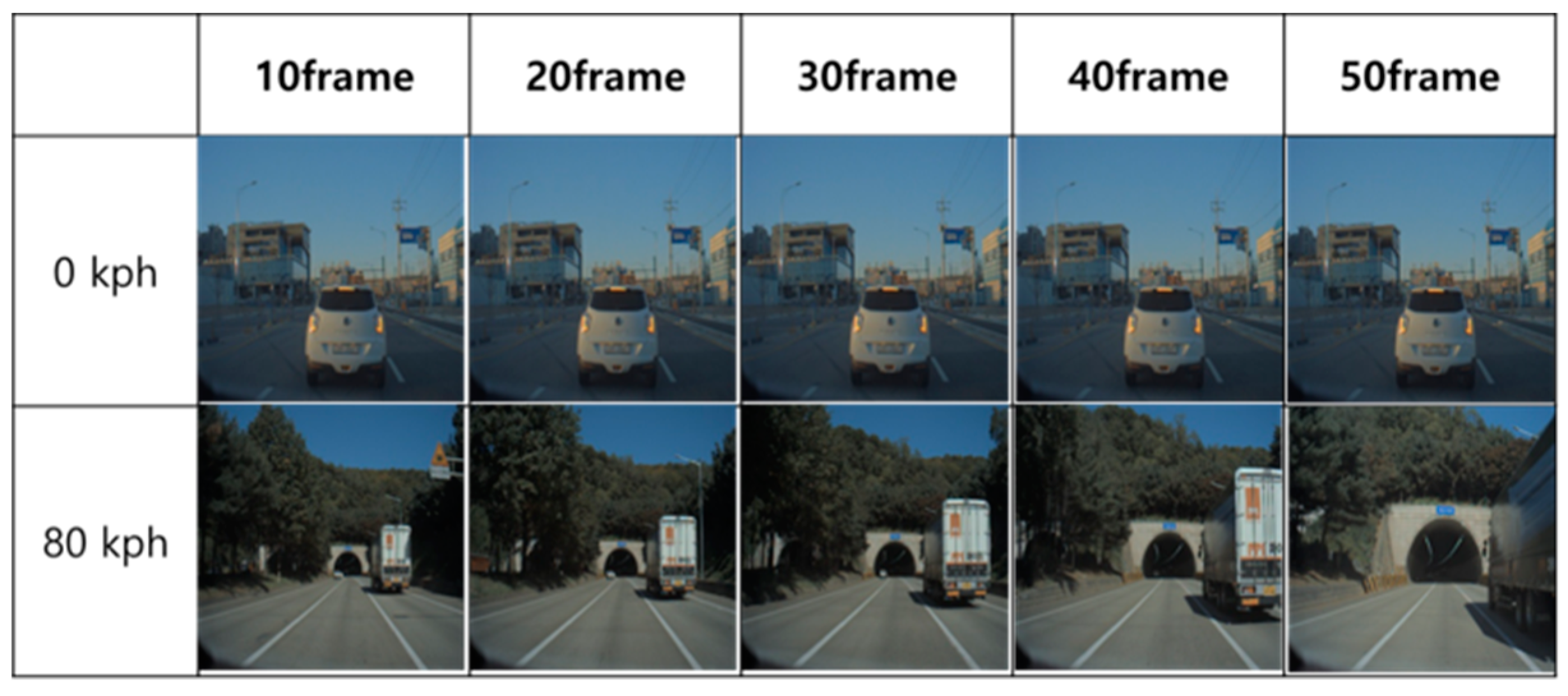
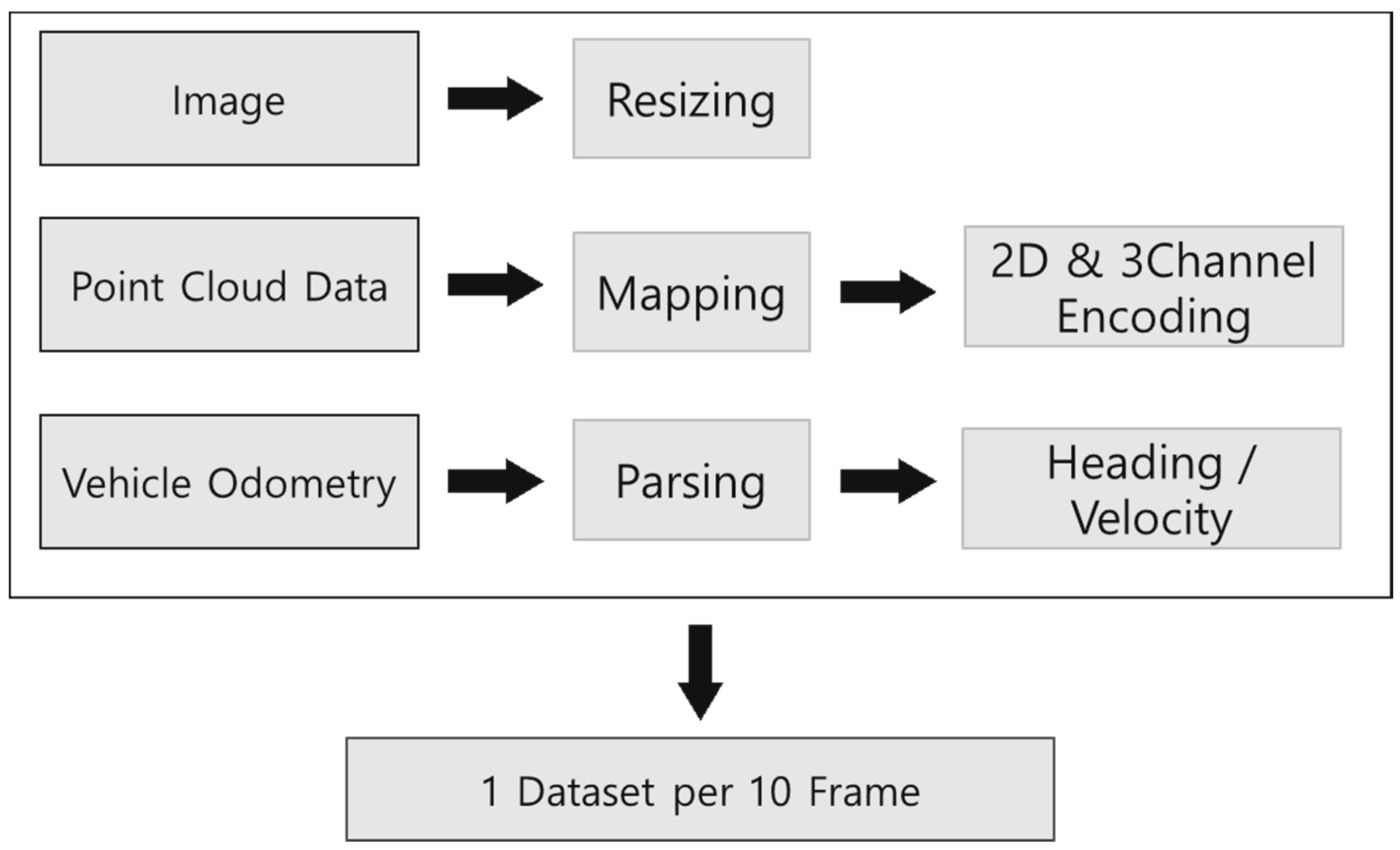
2.3. Data Set
2.4. Convolutional Neural Network for End-to-End Self-Driving
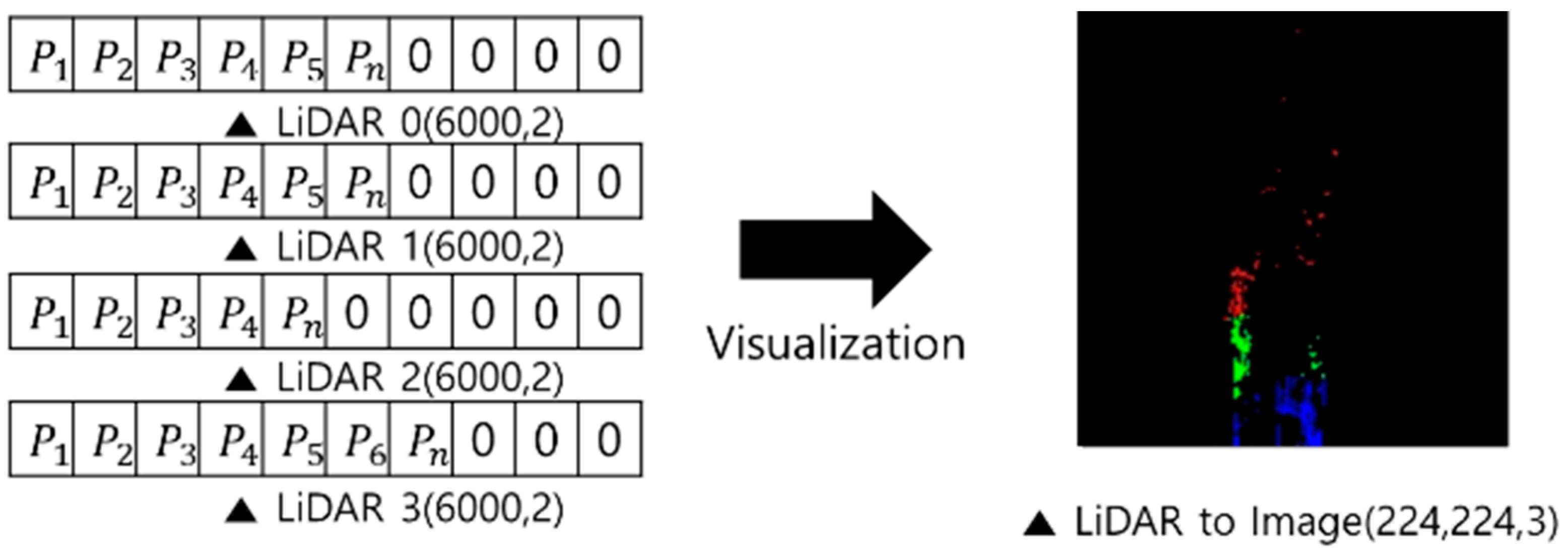
2.4.1. Data Preprocessing
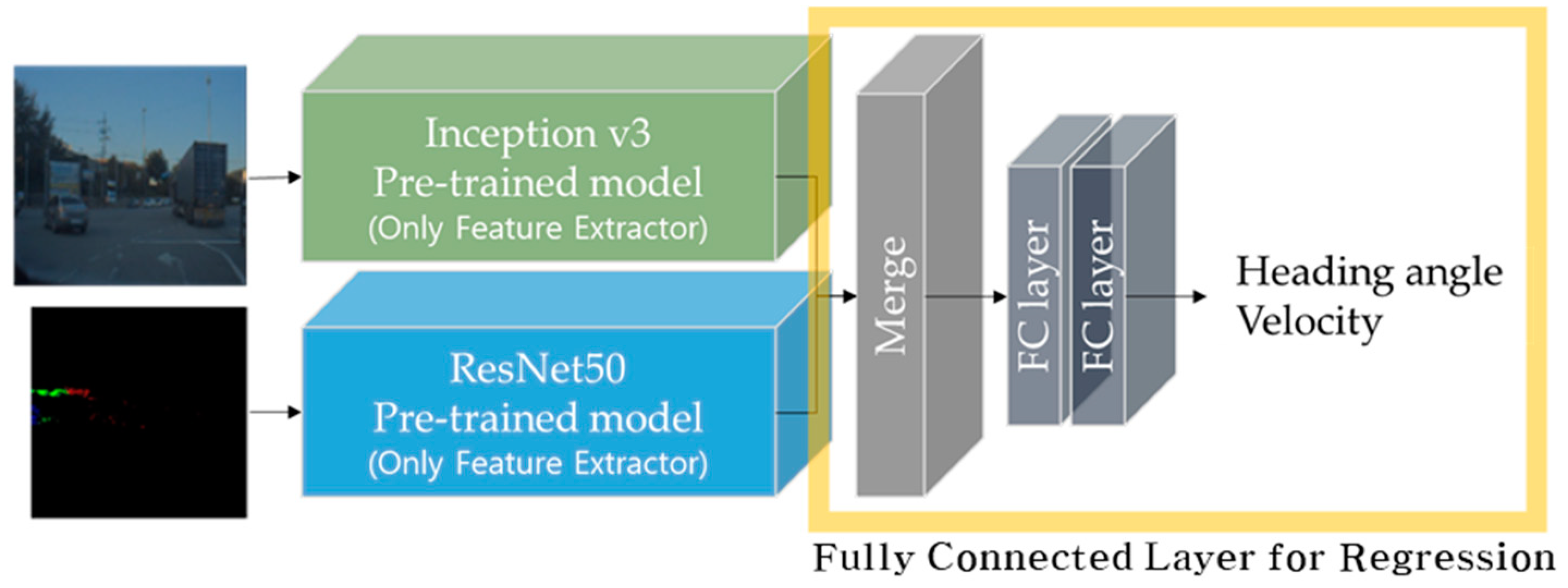
2.4.2. Proposed Network Architecture
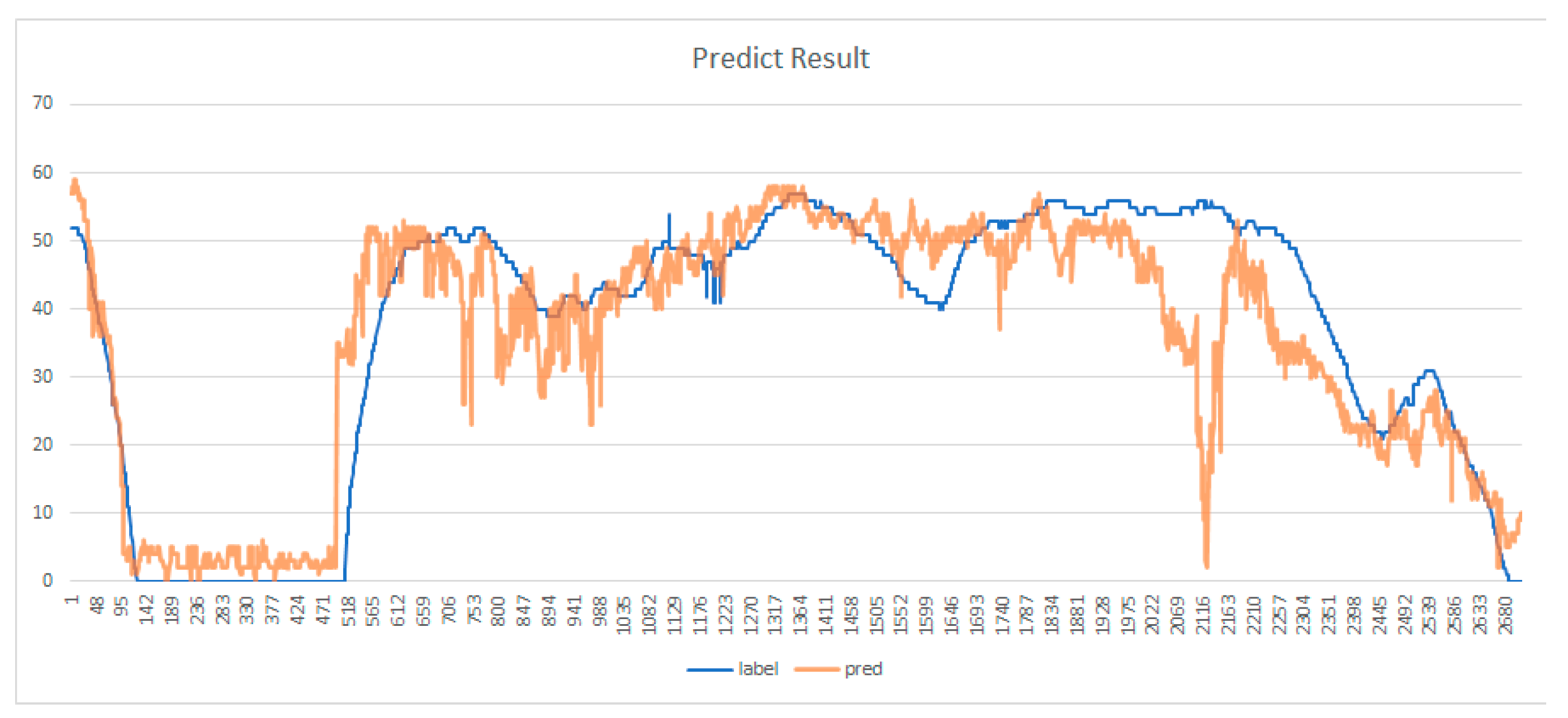
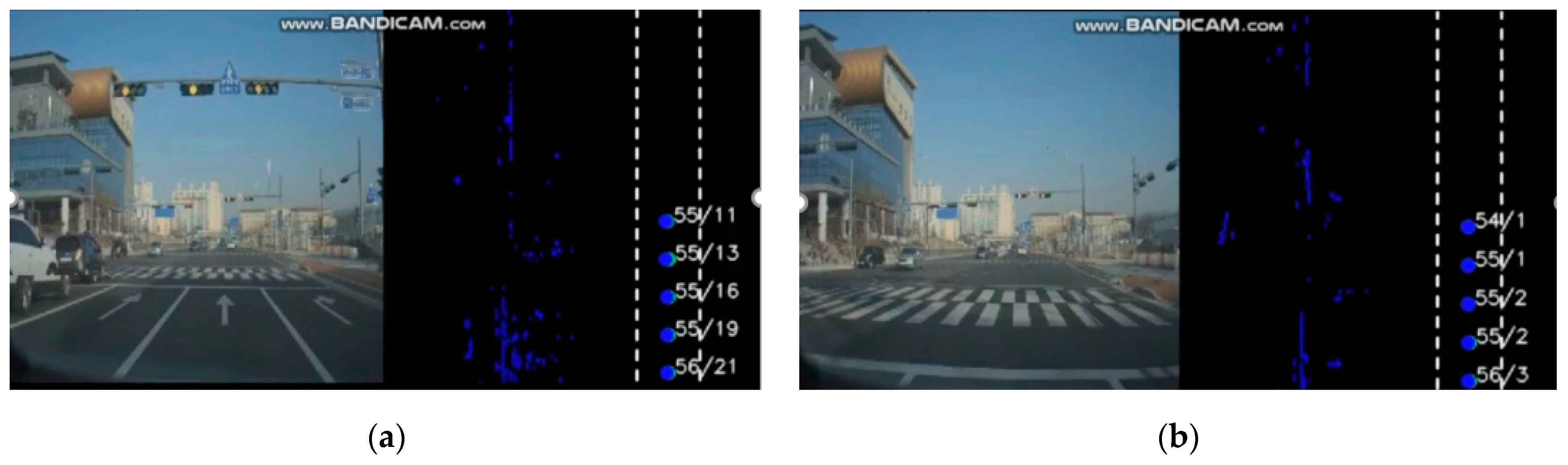
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cho, S.T.; Park, Y.J.; Jung, S. Experimental Setup for Autonomous Navigation of Robotic Vehicle for University Campus. J. Korean Inst. Intell. Syst. 2016, 26, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, H.J.; Kwak, S.W.; Yang, J.-M. Vehicle Localization Using Internal Sensors and Low-Cost GPS for Autonomous Driving. J. Korean Inst. Intell. Syst. 2017, 27, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Cho, E.; Choi, H.; Park, S. A Study on the Obstacle Detection and Path Planning of Automobile Using LiDAR. J. Korean Inst. Intell. Syst. 2019, 29, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.; Han, J.; Lee, M.; Kim, D.; Jo, K.; Oh, D.; Yoon, E.; Gwak, M.; Han, K.; Lee, D.; et al. Development of an Autonomous Vehicle: A1. Trans. Korean Soc. Automot. Eng. 2011, 19, 146–154. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, X.; Liang, H.; Yu, B.; Zhao, P.; He, L.; Huang, R. A Scenario-Adaptive Driving Behavior Prediction Approach to Urban Autonomous Driving. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Kee, S.-C. Implementation of Autonomous Driving System in the Intersection Area Equipped with Traffic Lights. Trans. Korean Soc. Automot. Eng. 2019, 27, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.A.; Lee, J.H.; Hwang, J.; Park, J.; Youn, S.H.; Kwon, S. LiDAR and Camera Fusion Approach for Object Distance Estimation in Self-Driving Vehicles. Symmetry 2020, 12, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoang, T.M.; Baek, N.R.; Cho, S.W.; Kim, K.W.; Park, K.R. Road Lane Detection Robust to Shadows Based on a Fuzzy System Using a Visible Light Camera Sensor. Sensors 2017, 17, 2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Su, Y.; Liao, Y. The Path Planning of Mobile Robot by Neural Networks and Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning. Front. Neurorobot. 2020, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojarski, M.; Del Testa, D.; Dworakowski, D.; Firner, B.; Flepp, B.; Goyal, P.; Jackel, L.D.; Monfort, M.; Muller, U.; Zhang, J.; et al. End to End Learning for Self-Driving Cars. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1604.07316. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidhuber, J. Deep learning in neural networks: An overview. Neural Netw. 2015, 61, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Toronto, ON, Canada, 3–8 December 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Lu, C.; Luo, Z.; Xue, H.; Wang, C. Lidar-video driving dataset: Learning driving policies effectively. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 5870–5878. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 652–660. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, P.J.; Miller, L.; Rosique, F.; Fernández-Isla, C.; Gila-Navarro, A. End-to-End Deep Neural Network Architectures for Speed and Steering Wheel Angle Prediction in Autonomous Driving. Electronics 2021, 10, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huch, S.; Ongel, A.; Betz, J.; Lienkamp, M. Multi-Task End-to-End Self-Driving Architecture for CAV Platoons. Sensors 2021, 21, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashanth, V.; Soyeb, N.; Mihir, M.; Manu, M.; Pramod, K.S. End to End Learning based Self-Driving using JacintoNet. In Proceedings of the IEEE 8th International Conference on Consumer Electronics, Berlin, Germany, 2–5 September 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Yang, S.; Gu, W.; Zhang, S. Baidu driving dataset and end-to-end reactive control model. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 11–14 June 2017; pp. 341–345. [Google Scholar]
- Sallab, A.E.; Abdou, M.; Perot, E.; Yogamani, S. End-to-end deep reinforcement learning for lane keeping assist. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.04340. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Khosla, A.; Lapedriza, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Learning deep features for discriminative localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2921–2929. [Google Scholar]
- Bojarski, M.; Yeres, P.; Choromanska, A.; Choromanski, K.; Firner, B.; Jackel, L.; Muller, U. Explaining how a deep neural network trained with end-to-end learning steers a car. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.07911. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]




| Data Set | Sensors | Control Target | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mariusz et al. [10] | Real world | camera | Steering |
| Chen et al. [13] | Real world | LiDAR, camera | Steering, Speed |
| Navarro et al. [15] | Real world | LiDAR, IMU, RGB camera, Depth camera, | Steering, Speed |
| Huch et al. [16] | Simulation | camera, V2V | Steering |
| Prashanth et al. [17] | Simulation | camera | Steering |
| Yu et al. [18] | Simulation | camera | Steering, Speed |
| Sallab et al. [19] | Real world | camera | Steering |
| Component | Training Environment | Embedded PC on Vehicle |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | Intel Xeon E5 | Intel i7-6820EQ |
| GPU | NVIDIA GTX 1080TI 2ea | Nvidia Jetson Xavier |
| SSD/HDD | SSD: 512 GB HDD: 10 TB | SSD: 250 GB HDD: 4 TB |
| RAM | 64 GB | 32 GB |
| LiDAR |  | |
| Model | IBEO LUX2010 | |
| Range | 200 m/560 ft | |
| FOV | 2 layers: 110° | |
| 4 layers: 85° | ||
| Interface | Ethernet/CAN/RS232 | |
| Camera |  | |
| Model | BFLY-PGE-23S6C | |
| FOV | 90° | |
| Sensor format | 1/1.2″ | |
| FPS | 41 | |
| Interface | Giga Ethernet |
| Data Set | Number of Data (Frame) | Number of Data (Frame) |
|---|---|---|
| With No Down Sampling | With Down Sampling | |
| Training | 134,208 | 10,6251 |
| Validation | 7063 | 7063 |
| Test | 4656 | 4656 |
| Type | Filters/Activation | Size | Output | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layer 1 | Concatenate | Merge | ||
| Layer 2 | Dense | ReLU | 1024 | 1024 |
| Layer 3 | Dense | ReLU | 256 | 256 |
| Layer 4 | Dense | ReLU | 128 | 128 |
| Layer 5 | Regression | Linear | 10 | 10 |
| Frame | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| Time (ms) | 250 | 500 | 750 | 1000 | 1250 |
| Angle < 5° | 3.83 | 3.62 | 2.99 | 2.83 | 2.93 |
| Angle 5° | 5.14 | 5.22 | 5.31 | 5.54 | 5.62 |
| Speed < 10 kph | 16.05 | 15.57 | 14.64 | 13.70 | 13.10 |
| Speed 10 kph | 5.67 | 5.73 | 5.66 | 5.89 | 6.11 |
| Frame | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| Time (ms) | 250 | 500 | 750 | 1000 | 1250 |
| Angle < 5° | 4.07 | 3.66 | 2.96 | 2.93 | 3.10 |
| Angle 5° | 4.82 | 5.43 | 5.40 | 5.42 | 5.83 |
| Speed < 10 kph | 7.75 | 6.29 | 4.74 | 3.67 | 2.90 |
| Speed 10 kph | 5.98 | 5.93 | 5.96 | 6.06 | 6.26 |
| Frame | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| Time (ms) | 250 | 500 | 750 | 1000 | 1250 |
| Down sampling data | 7.75 | 6.29 | 4.74 | 3.67 | 2.90 |
| Original data | 16.05 | 15.57 | 14.64 | 13.70 | 13.10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, M.; Kim, H.; Park, S. A Convolutional Neural Network-Based End-to-End Self-Driving Using LiDAR and Camera Fusion: Analysis Perspectives in a Real-World Environment. Electronics 2021, 10, 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10212608
Park M, Kim H, Park S. A Convolutional Neural Network-Based End-to-End Self-Driving Using LiDAR and Camera Fusion: Analysis Perspectives in a Real-World Environment. Electronics. 2021; 10(21):2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10212608
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Mingyu, Hyeonseok Kim, and Seongkeun Park. 2021. "A Convolutional Neural Network-Based End-to-End Self-Driving Using LiDAR and Camera Fusion: Analysis Perspectives in a Real-World Environment" Electronics 10, no. 21: 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10212608
APA StylePark, M., Kim, H., & Park, S. (2021). A Convolutional Neural Network-Based End-to-End Self-Driving Using LiDAR and Camera Fusion: Analysis Perspectives in a Real-World Environment. Electronics, 10(21), 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10212608





