A Novel Approach for the Design of Fast-Settling Amplifiers for Biosignal Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Proposed Approach
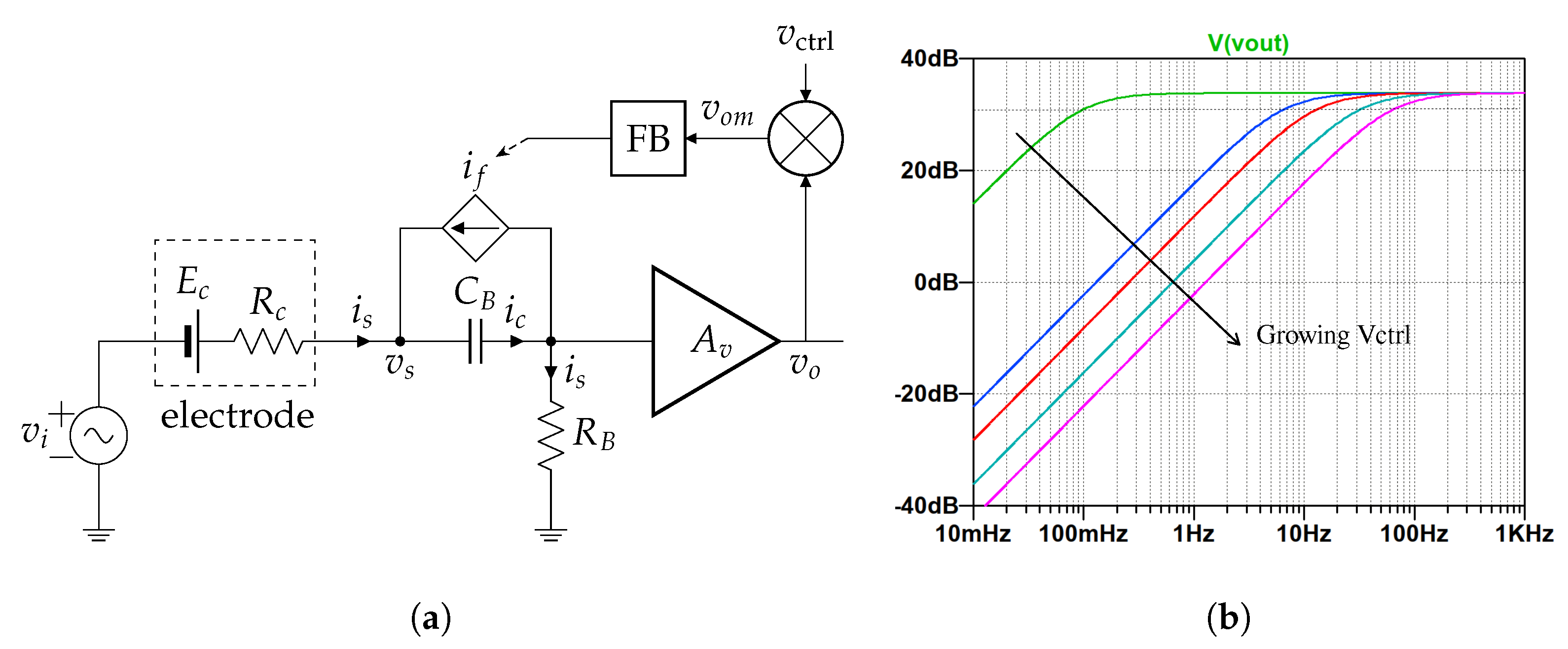
2.1. Single-Ended Amplifier
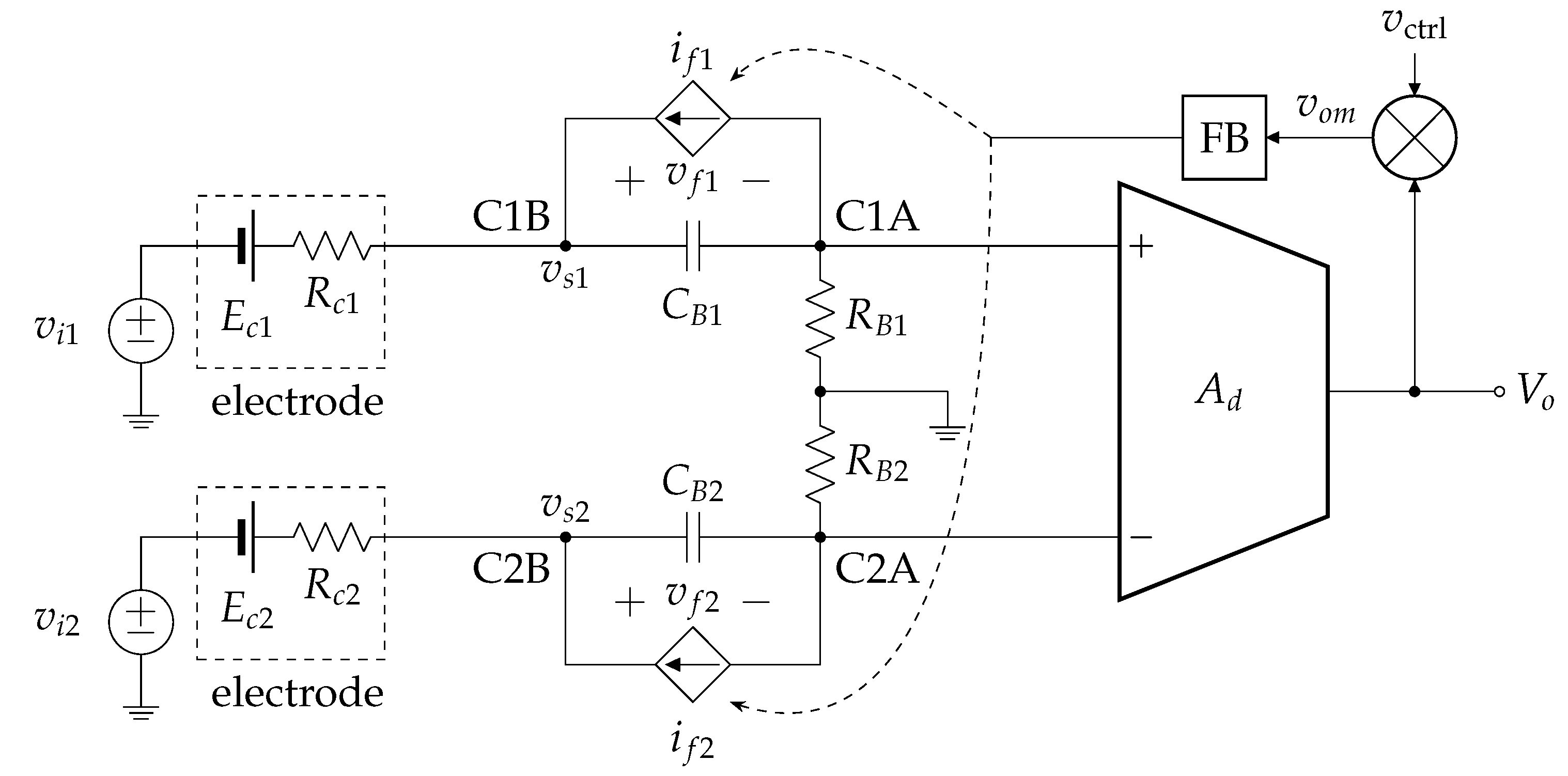
2.2. Extension to a Differential Amplifier
3. Results
3.1. Prototype
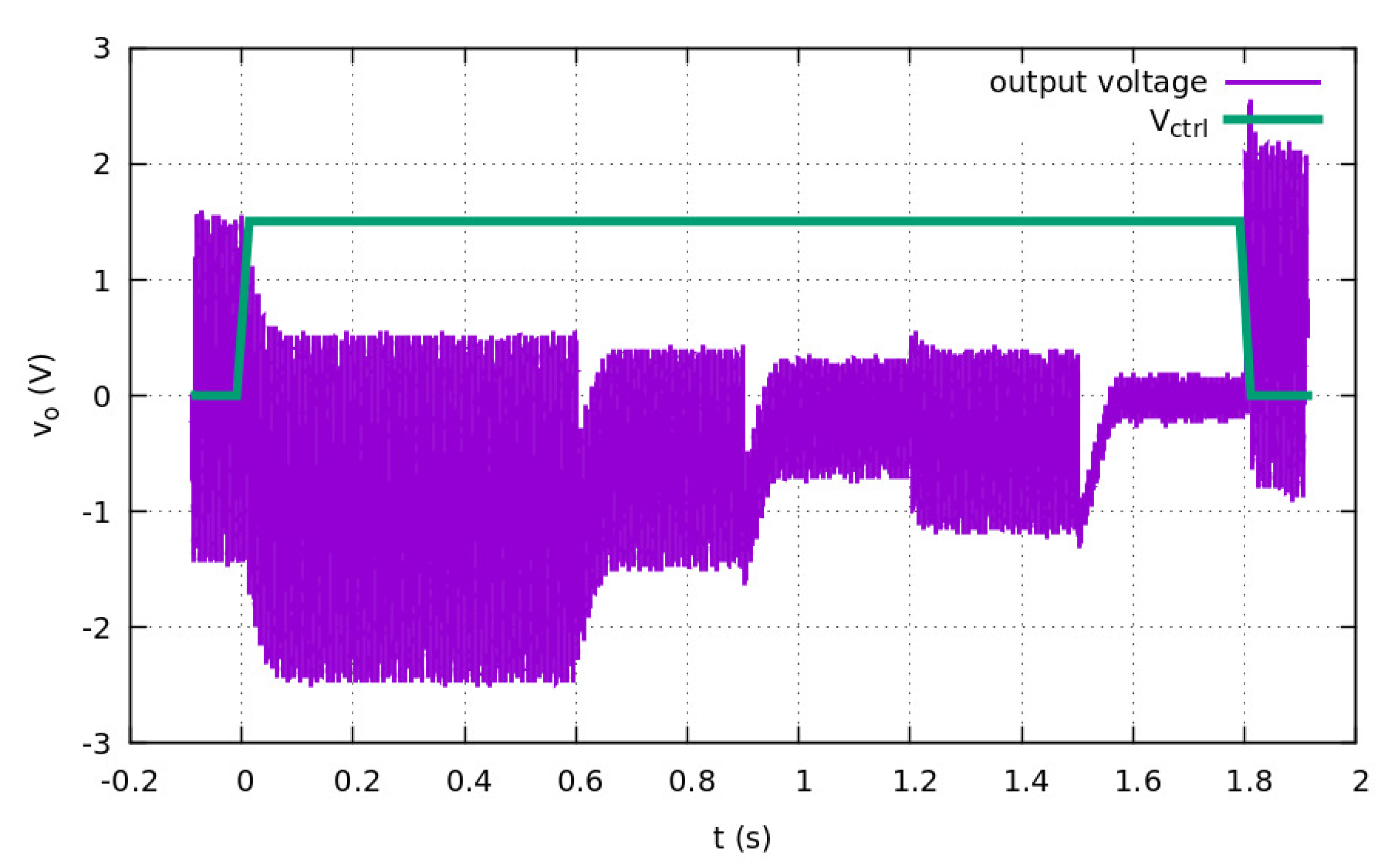
3.2. Measurements on the Prototype
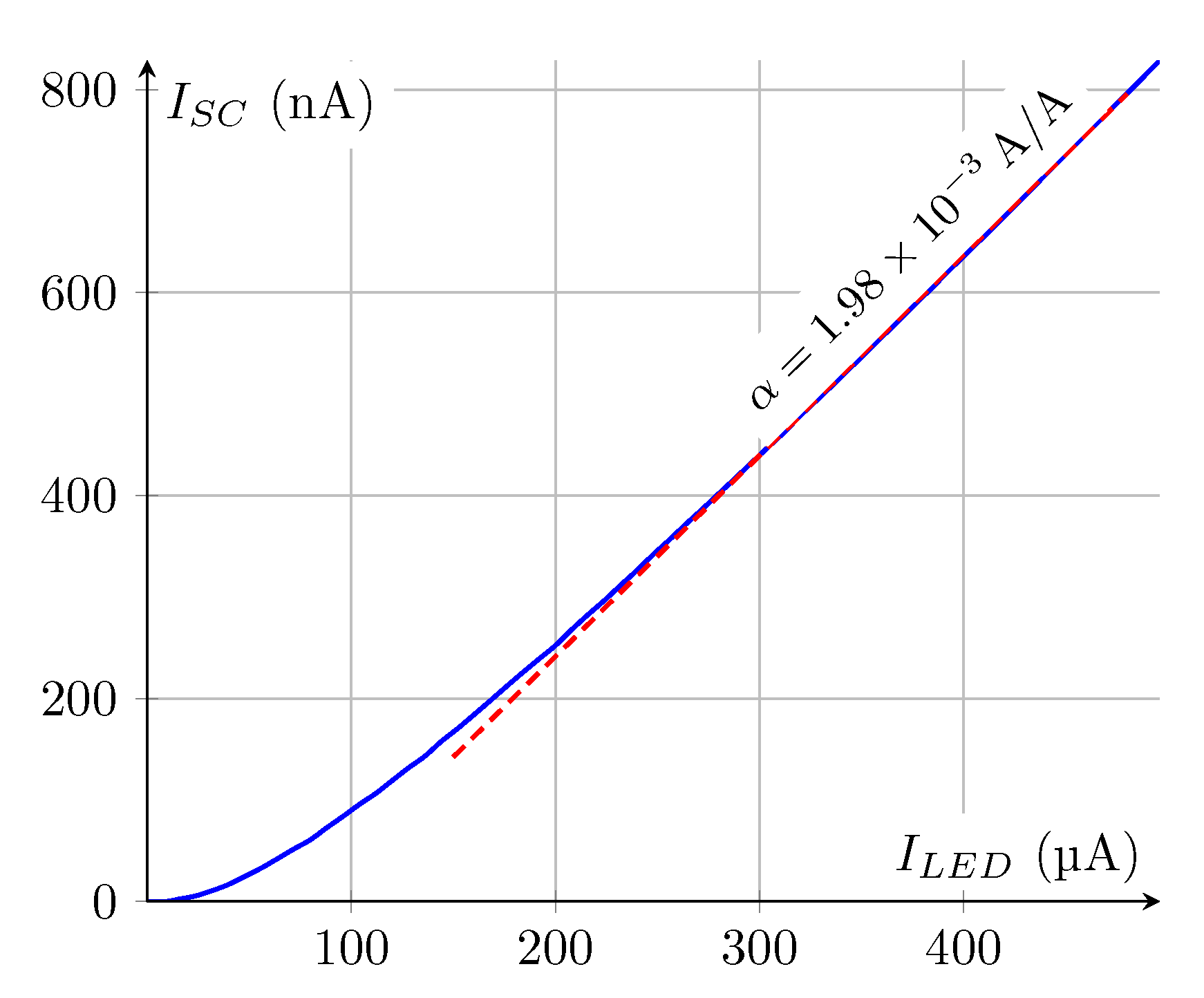
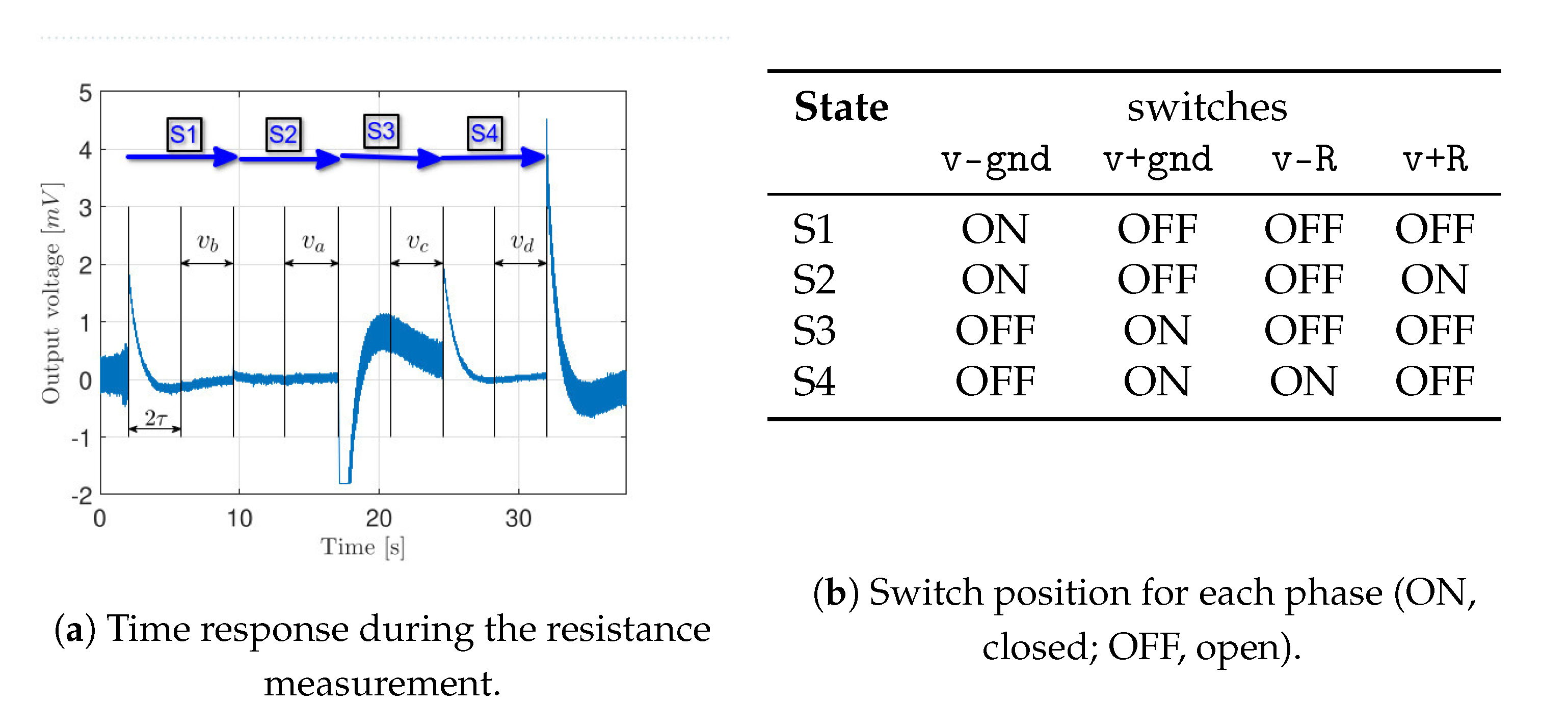
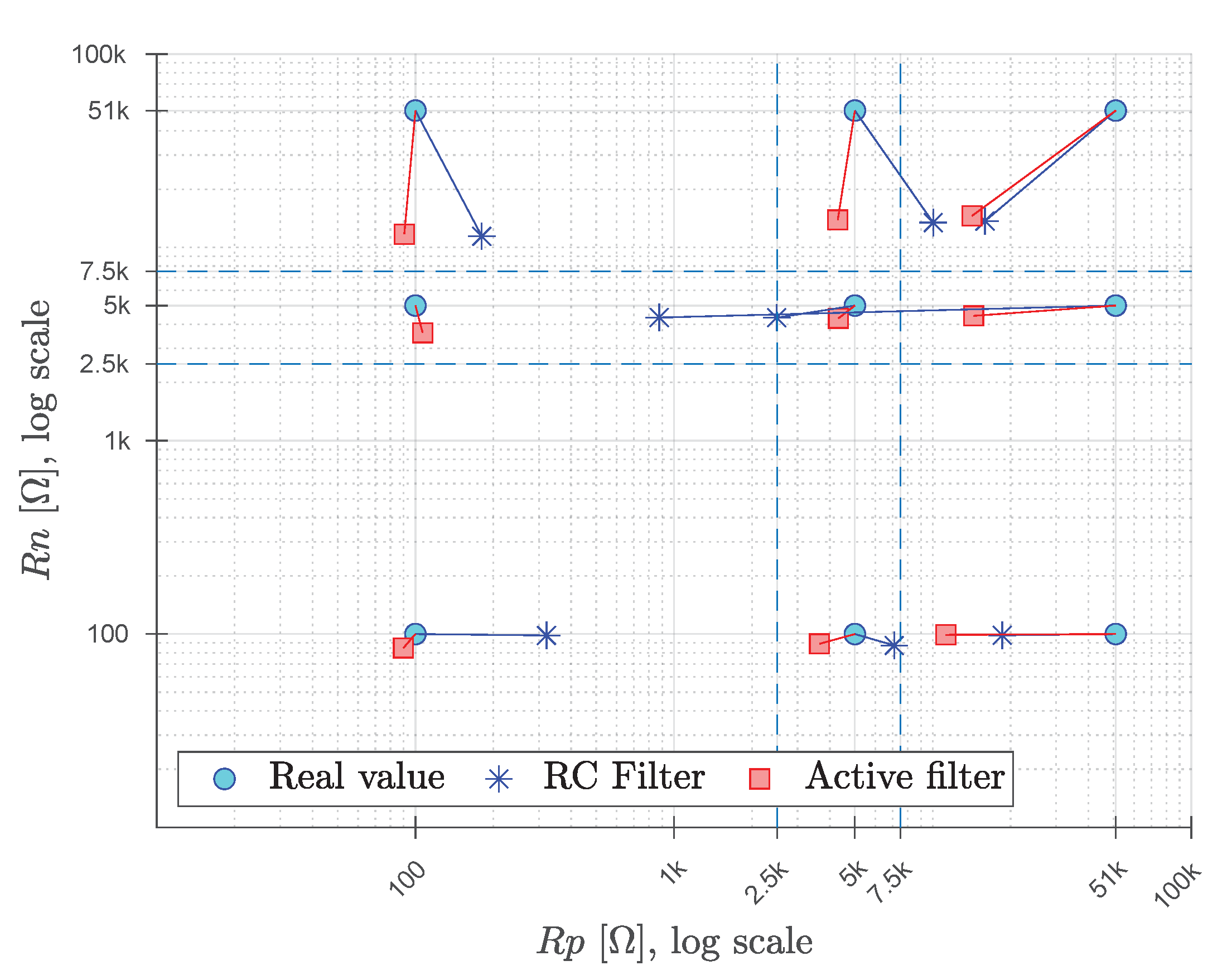
3.3. Application to Resistance Estimation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LNA | Low-noise amplifier |
| RMS | Root mean square |
| HP, HPF | High pass (filter) |
| RC filter | Resistance-capacitor filter |
| FB | Feedback block |
| DC | Direct current (used for continuous signals) |
| AC | Alternating current (used for variable signals) |
References
- Webster, J.G. Medical Instrumentation Application and Design, 4th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Simmich, S.; Bahr, A.; Rieger, R. Noise Efficient Integrated Amplifier Designs for Biomedical Applications. Electronics 2021, 10, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ko, H. A Dynamic Instrumentation Amplifier for Low-Power and Low-Noise Biopotential Acquisition. Sensors 2016, 16, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chebli, R.; Ali, M.; Sawan, M. High-CMRR Low-Noise Fully Integrated Front-End for EEG Acquisition Systems. Electronics 2019, 8, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Amaya, J.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.; Delgado-Restituto, M. A Low Noise Amplifier for Neural Spike Recording Interfaces. Sensors 2015, 15, 25313–25335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bansal, M.; Srivastava, G. Design and Implementation of LNA for Biomedical Applications. In Intelligent Computing, Information and Control Systems; Pandian, A.P., Ntalianis, K., Palanisamy, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 154–167. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Amaya, J.; Rodríguez-Pérez, A.; Delgado-Restituto, M. A review of low-noise amplifiers for neural applications. In Proceedings of the 2010 2nd Circuits and Systems for Medical and Environmental Applications Workshop (CASME), Merida, Mexico, 13–15 December 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Portelli, A.J.; Nasuto, S.J. Design and Development of Non-Contact Bio-Potential Electrodes for Pervasive Health Monitoring Applications. Biosensors 2017, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alimisis, V.; Dimas, C.; Pappas, G.; Sotiriadis, P.P. Analog Realization of Fractional-Order Skin-Electrode Model for Tetrapolar Bio-Impedance Measurements. Technologies 2020, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.M.; Jung, T.p.; Cauwenberghs, G. Dry-Contact and Noncontact Biopotential Electrodes. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 3, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kappenman, E.S.; Luck, S.J. The effects of electrode impedance on data quality and statistical significance in ERP recordings. Psychophysiology 2010, 47, 888–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buxi, D.; Kim, S.; Van Helleputte, N.; Altini, M.; Wijsman, J.; Yazicioglu, R.F.; Penders, J.; Van Hoof, C. Correlation between electrode-tissue impedance and motion artifact in biopotential recordings. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 3373–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taji, B.; Shirmohammadi, S.; Groza, V.; Batkin, I. Impact of skin-electrode interface on electrocardiogram measurements using conductive textile electrodes. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2014, 63, 1412–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musteata, M.; Borcea, D.G.; Ștefănescu, R.; Solcan, G.; Lăcătuș, R. Influence of Stainless Needle Electrodes and Silver Disk Electrodes over the Interhemispheric Cerebral Coherence Value in Vigil Dogs. Sensors 2018, 18, 3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Y.; Wang, X. Dry Electrodes for Human Bioelectrical Signal Monitoring. Sensors 2020, 20, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, G.; Ozturk, O.; Golparvar, A.J.; Elboshra, T.A.; Böhringer, K.; Yapici, M.K. Wearable and Flexible Textile Electrodes for Biopotential Signal Monitoring: A review. Electronics 2019, 8, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sundarasaradula, Y.; Thanachayanont, A. A Low-Noise, Low-Power, Wide Dynamic Range Logarithmic Amplifier for Biomedical Applications. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2018, 27, 1850104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. A low-noise integrated bioamplifier with active DC offset suppression. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference, Beijing, China, 26–28 November 2009; pp. 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, B.; Schoukens, J.; Bragos, R. Novel Estimation of the Electrical Bioimpedance Using the Local Polynomial Method. Application to In Vivo Real-Time Myocardium Tissue Impedance Characterization During the Cardiac Cycle. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 3376–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guermandi, M.; Cardu, R.; Scarselli, E.F.; Guerrieri, R. Active Electrode IC for EEG and Electrical Impedance Tomography with Continuous Monitoring of Contact Impedance. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2015, 9, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dardé, J.; Hyvönen, N.; Kuutela, T.; Valkonen, T. Electrodeless electrode model for electrical impedance tomography. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.01926. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, E.; Giannetti, R.; Rodríguez-Morcillo, C.; Matanza, J.; Muñoz-Frías, J.D. A Novel Passive Method for the Assessment of Skin-Electrode Contact Impedance in Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring Systems. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jimenez-Carles Gil-Delgado, E. Intraoperative Monitoring System. Patent Application WO 2018/011439 Al, 18 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ferree, T.C.; Luu, P.; Russell, G.S.; Tucker, D.M. Scalp electrode impedance, infection risk, and EEG data quality. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2001, 112, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tautan, A.M.; Mihajlovic, V.; Chen, Y.H.; Grundlehner, B.; Penders, J.; Serdijn, W. Signal Quality in Dry Electrode EEG and the Relation to Skin-electrode Contact Impedance Magnitude. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices (BIOSTEC 2014), Loire Valley, France, 3–6 March 2014; pp. 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teplan, M. Fundamentals of EEG Measurement. Meas. Sci. Rev. 2002, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Scandurra, G.; Cannatà, G.; Giusi, G.; Ciofi, C. A new approach to DC removal in high gain, low noise voltage amplifiers. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Noise and Fluctuations (ICNF), Vilnius, Lithuania, 20–23 June 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alonso Rivas, E.; Scandurra, G.; Ciofi, C.; Rodríguez-Morcillo García , C.; Giannetti, R. A Novel Approach for the Design of Fast-Settling Amplifiers for Biosignal Detection. Electronics 2021, 10, 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10212631
Alonso Rivas E, Scandurra G, Ciofi C, Rodríguez-Morcillo García C, Giannetti R. A Novel Approach for the Design of Fast-Settling Amplifiers for Biosignal Detection. Electronics. 2021; 10(21):2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10212631
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlonso Rivas, Eduardo, Graziella Scandurra, Carmine Ciofi, Carlos Rodríguez-Morcillo García , and Romano Giannetti. 2021. "A Novel Approach for the Design of Fast-Settling Amplifiers for Biosignal Detection" Electronics 10, no. 21: 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10212631
APA StyleAlonso Rivas, E., Scandurra, G., Ciofi, C., Rodríguez-Morcillo García , C., & Giannetti, R. (2021). A Novel Approach for the Design of Fast-Settling Amplifiers for Biosignal Detection. Electronics, 10(21), 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10212631








