Abstract
Sensor–artery alignment has always been a significant problem in arterial tonometry devices and prevents their application to wearable continuous blood pressure (BP) monitoring. Traditional solutions are to use a complex servo system to search for the best measurement position or to use an inefficient pressure sensor array. In this study, a novel solid–liquid mixture pressure sensing module is proposed. A flexible film with unique liquid-filled structures greatly reduces the pulse measurement error caused by sensor misplacement. The ideal measuring location was defined as −2.5 to 2.5 mm from the center of the module and the pressure variation was within 5.4%, which is available in the real application. Even at a distance of ±4 mm from the module center, the pressure decays by 23.7%, and its dynamic waveform is maintained. In addition, the sensing module is also endowed with the capability of measuring the pulse wave transmit time as a complementary method for BP measuring. The capability of the developed alignment-free sensing module in BP measurement was been validated. Twenty subjects were selected for the BP measurement experiment, which followed IEEE standards. The experimental results showed that the mean error of SBP is −4.26 mmHg with a standard deviation of 7.0 mmHg, and the mean error of DBP is 2.98 mmHg with a standard deviation of 5.07 mmHg. The device is expected to provide a new solution for wearable continuous BP monitoring.
1. Introduction
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the world [1]. It is estimated that about 270 million people suffer from hypertension in China and nearly 1.13 billion people worldwide [2,3]. Hypertension at any age is associated with a cognitive decline in different abilities [4]. However, prehypertension has few noticeable symptoms, and it is difficult to recognize when lacking frequent blood pressure (BP) examinations because there are many considerable influences on human BP, such as circadian rhythm and the environment. Compared to intermittent BP measurement, continuous BP monitoring is of great significance by providing more comprehensive information for the clinical diagnosis and control of hypertension [5].
As a result of the expansion of health care, commercial wearable BP monitoring devices are already available on the market. For example, Bpump Inc. launched a BP measurement watch (WF1610B) in 2017, and Omron Inc. launched ‘HeartGuide’ in 2019. However, their measurement principle is still based on the traditional oscillometric method, which cannot meet the requirements of continuous BP monitoring. The clinical available continuous BP monitoring devices include Finometer PRO (Finapres Medical Systems BV, Amsterdam, The Netherlands), BP-8800 (Omron, Colin Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), TL-200 (Tensys Medical Inc., CA, USA), and BPro (Healthstats International Pte. Ltd., Singapore). Their servo-mechanism makes them bulky and prevents their application in daily life.
Research on noninvasive wearable continuous BP measurement is ongoing. For measuring methods, photoplethysmogram (PPG), arterial tonometry, and pulse wave transit time (PWTT) methods have been widely studied [6]. Several scholars have contributed to modern BP measurements from theoretical and algorithmic perspectives, such as the establishment of multifactor mathematical models [7,8,9], the use of the adaptive filter to reduce motion artifacts [10,11], and the application of machine learning to assist in calculations [12,13,14]. Another research field is the enhancement of the sensing device. Nonetheless, a miniaturized, alignment-free, and high sensitivity sensor has always been desired [15]. However, noninvasive BP monitoring is still difficult to accomplish with current sensors. In addition, the sensors are generally specialized, so it is not easy to combine different measurement methods. Specifically, the PPG method is always matched with a photoelectric sensor, which is energy intensive; sensors for the PWTT method mostly use a distributed placement and are challenging to integrate; and for arterial tonometry, a pressure sensor is commonly used. Some scholars have presented excellent solutions with developing technologies, such as liquid capsule structures [16], ultrasonic patch devices [17], and a smartphone-based oscillometric finger-pressing method [18]. In the areas of noninvasive, portable, and continuous measurement, there is still much space for progress.
In this study, the authors proposed an alignment-free compact sensing module. The main obstacle to arterial tonometry is the rigorous placement of the sensor. Therefore, the sensing module was designed as a solid–liquid composite structure, which aims at reducing the pressure measurement error caused by misplacement. Furthermore, it has the potential to combine the PWTT method with arterial tonometry. In order to demonstrate its BP monitoring capability in daily life, the sensing module was integrated into a wearable BP device. The performance of the device was systematically verified by simulation and experiment.
2. Device Development
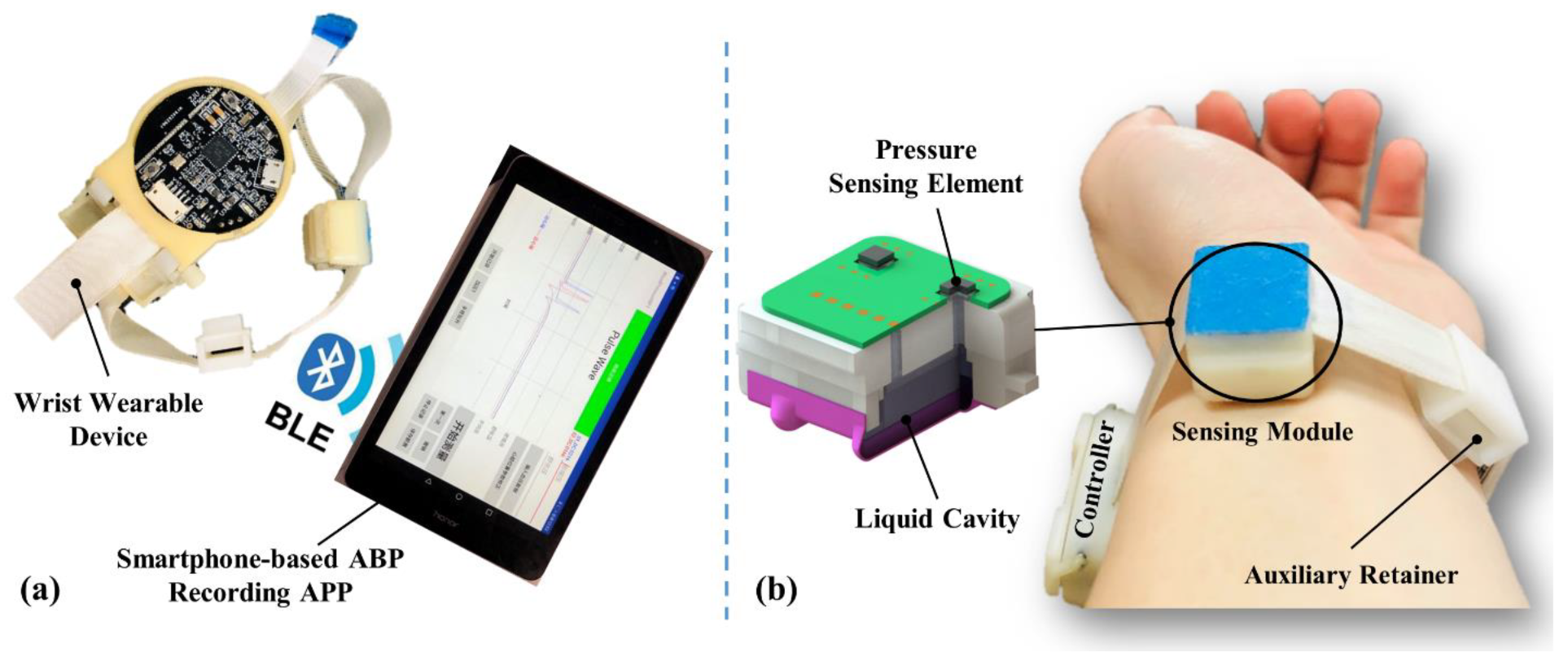
The radial artery BP measurement device includes a wrist wearable device and a smartphone-based arterial blood pressure (ABP) recording APP, as shown in Figure 1. Data transmission between the wearable device and the recording APP is via Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), which removes the need for an enormous data acquisition system, and satisfying the need for the portability of continuous BP measurement in daily life. The measuring principle of the device is mainly based on that of arterial tonometry, combined with the PWTT measurement.
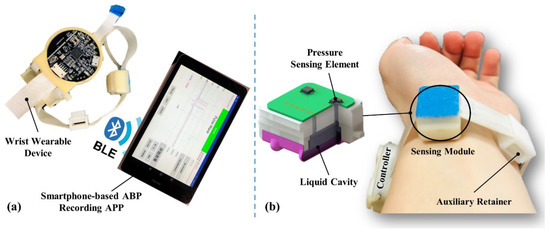
Figure 1.
The radial artery BP measurement device: (a) BP measurement device and smartphone-based recording APP; (b) photo of the device worn on the wrist.
2.1. Theory
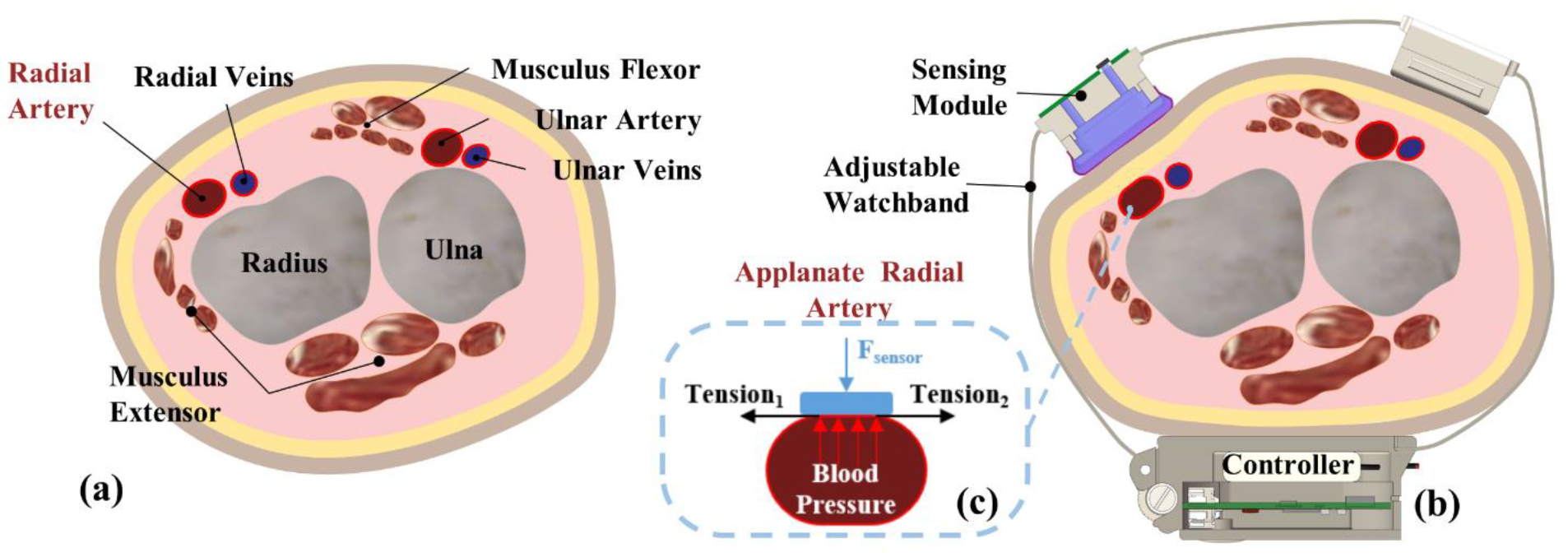
Arterial tonometry is a noninvasive BP measurement method proposed by Pressman and Newgard in 1963 [19]. A cross-sectional view of the human wrist is shown in Figure 2a. The radial artery is located between the epidermal tissue and the radius, flanked by the flexor and extensor muscles. After wearing the measurement device, the changes in the radial artery are shown in Figure 2b. Due to the squeezing of the wearable device, the sensor puts external pressure on the radial artery. As a result, the epidermal tissue, radial artery, and radius are close to each other, leading to deformation of the radial artery. When the external pressure is appropriate, the radial artery section will become flat, as shown in Figure 2c. In this case, the tension of the arterial wall is completely horizontal; thus, pressure measured by the sensing module will be equal to the pressure in the artery (BP) if the elastic attenuation of the epidermal tissue is neglected.
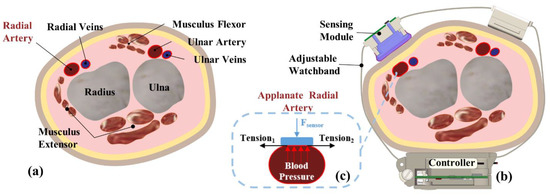
Figure 2.
Schematic of arterial tonometry: (a) cross section of the human wrist; (b) device wearing schematic; (c) applanate radial artery.
According to the principle of arterial tonometry, the module has to be directly above the radial artery and remain fixed during measurement. Otherwise, it is possible to introduce considerable measuring errors. However, it is relatively difficult to align the center of the module to the central line of underneath the vascular vessel, whose diameter is relatively small (about 3 mm). Usually, the sensor alignment can only be roughly determined by feeling the pulse with the finger.
2.2. Sensing Module Design
The size of the sensing module is 16 mm × 14 mm, and the width of the module is considered as the distance between the radial protrusion and the musculus flexor, because it is convenient to find the appropriate circumferential position of the module with the help of the radial protrusion and musculus flexor. However, the distance between the radial protrusion and the flexor muscle is an individualized parameter. In order to cover the different ages and weights of all possible users, so that they can easily align the sensing module to the artery, the module should still be positionally robust. The wrist circumference in adults is typically between 140 and 180 mm, and the distance difference between the radial protrusion and the musculus flexor is less than 8 mm. Therefore, the module needs to be robust with a minimum of 8 mm tolerance in the width direction, i.e., the signal measured within this range should be distortion-free and genuinely reflect the pulse state if motion artifacts are ignored.
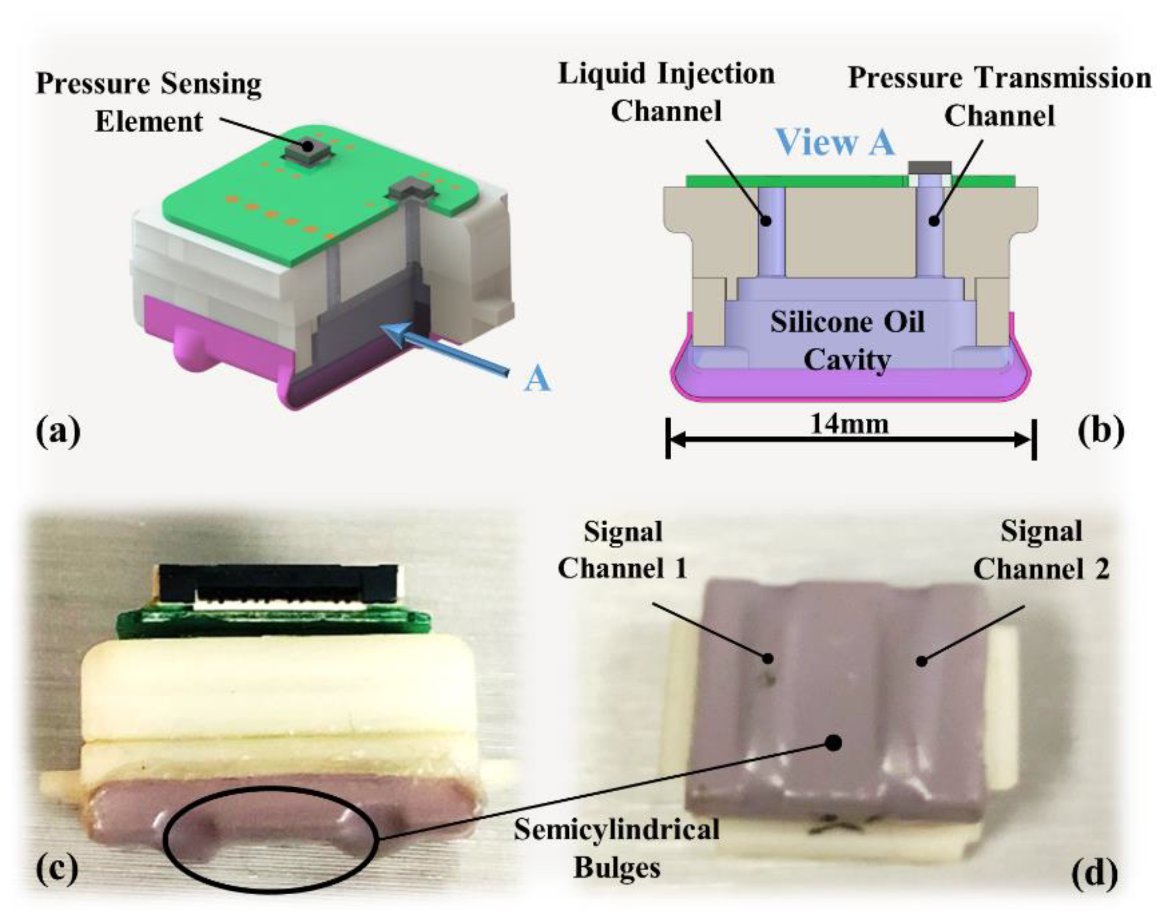
Inspired by the principle of finger-feeling pulse in traditional Chinese medicine [20], we designed a solid–liquid composite sensor structure, and details are shown in Figure 3. Inside the sensing module is a cavity as shown in Figure 3b, which is filled with silicone oil and connected to the outside through two channels above, one for liquid injection and the other for pressure transfer. The sensitive areas are the two semicylindrical bulges on the bottom of the module as shown in Figure 3c. When a stimulus is received, the bulges deform and generate compressive stress, which can be efficiently transmitted to the pressure sensing element according to Pascal’s law. Theoretically, regardless of where the bulges are pressed, the pressure transmitted to the sensing element should be the same.
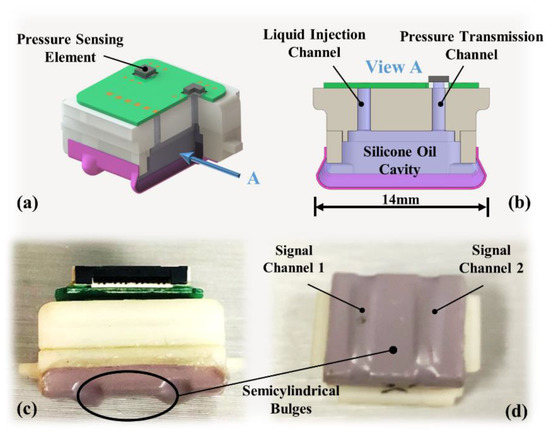
Figure 3.
Sensing module details: (a) module structure schematic; (b) cross-section of the cavity; (c) side view of the sensing module; (d) semicylindrical bulge of the two channels.
The designed sensing module is a dual-channel signals sensor, as shown in Figure 3d, which can measure the pulse at two adjacent locations. The first purpose is to facilitate the alignment of the module in the axial direction of the wrist because at least one of the two channels can be supported by the radius. The second is that the PWTT can be derived by the time difference between the pulse signal in two different locations. PWTT is a BP-related variable and can be used to derive BP [21]. The result calculated by PWTT can be cross-validated with arterial tonometry.
2.3. Fabrication
The sensitive area of the sensing module, i.e., the area in contact with the skin of the wrist, is made of a thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) film with good plasticity and biocompatibility. The cavity is filled with non-volatile and biocompatible dimethyl silicone oil (Dow Corning Inc., Michigan, USA, pmx-200). The pressure sensing element of the module is a silicon piezoresistive die (Uni Sense Technology Co. Ltd., Shenzhen, China, US9173) based on micromachining technology.
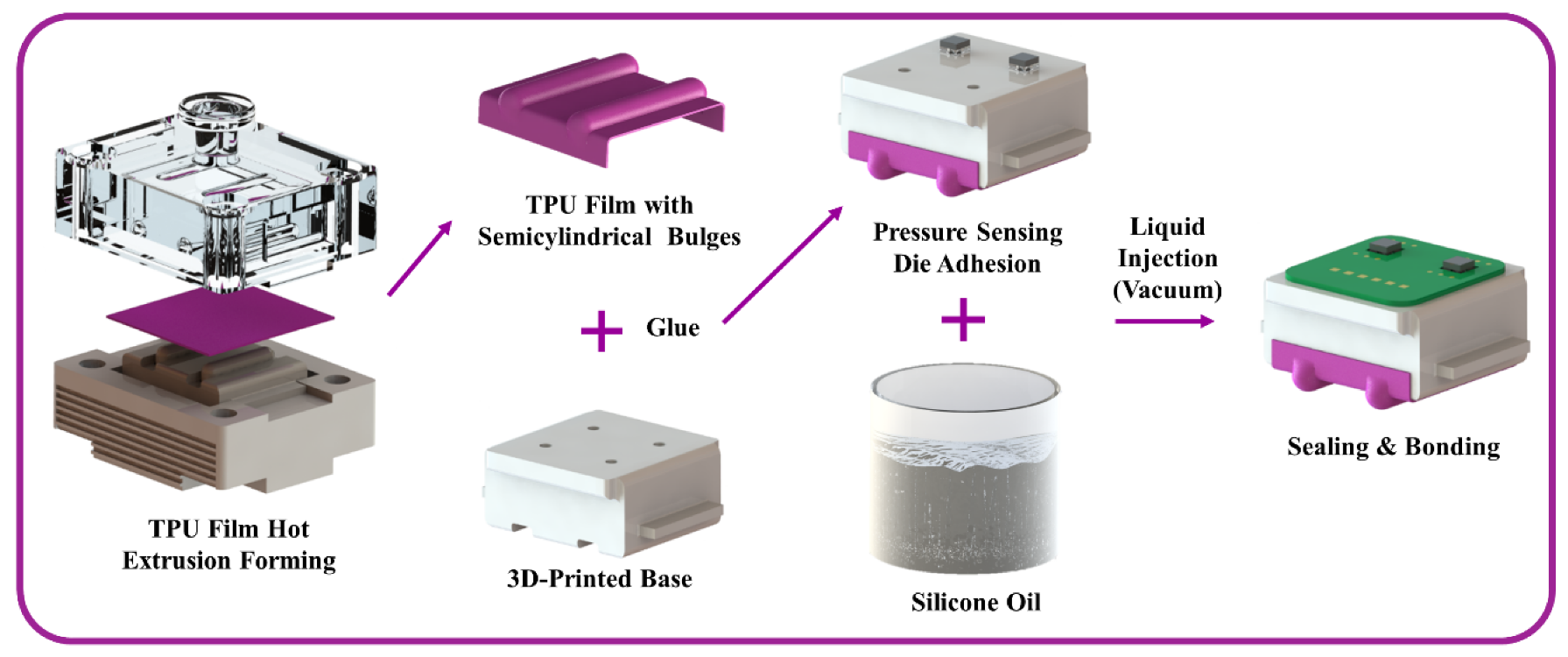
The preparation process of the sensing module is shown in Figure 4. First, the TPU film with two semicylindrical bulges was produced by hot extrusion forming through a mold. Then the formed film was glued together with the 3D-printed base. Second, the pressure sensing element was glued to the base in alignment with the pressure transmission channel. Third, the cavity was filled with degassed silicone oil through the liquid injection channel in a vacuum environment, and then the liquid injection channel was sealed. Finally, after cleaning the pressure sensing element, it was connected to the peripheral circuit using ultrasonic gold wire bonding technology. The sensing module prepared by this process overcomes the disadvantages of stress transfer attenuation and non-uniform stress distribution in the traditional elastic layer.
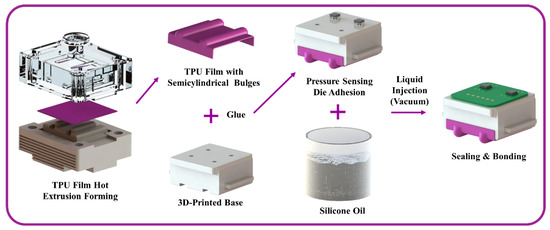
Figure 4.
Preparation process of the sensing module.
2.4. Signal Process
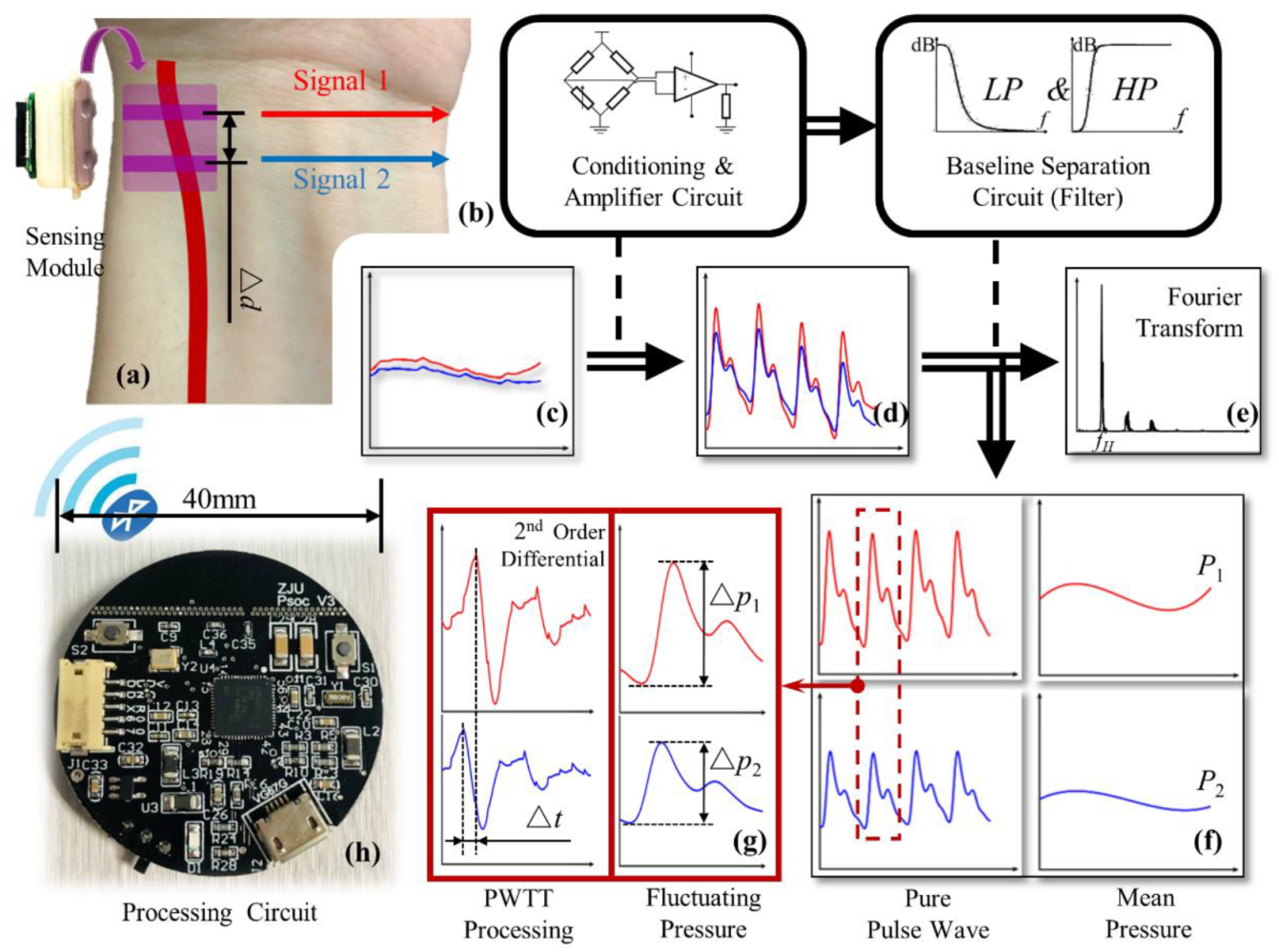
The processing flow of the signal collected by the sensing module is shown in Figure 5. The lower left of the figure is a photo of the processing circuit, which integrates power management, signal acquisition, signal processing, and BLE communication functions. It is mounted in the controller with the battery underneath as shown in Figure 2b.
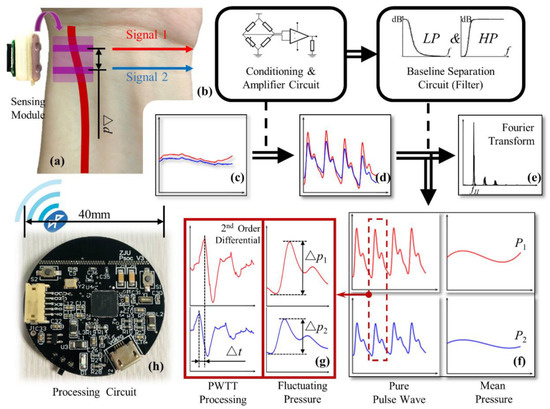
Figure 5.
Signal processing flow chart: (a) sensing module; (b) schematics of conditioning, amplifier, and baseline separation circuit; (c) raw pulse signal; (d) amplified pulse signal; (e) heart rate processing; (f) pure pulse wave signal and the mean pressure signal; (g) PWTT processing; (h) photo of the processing circuit.
The raw signal measured by the sensing module is insignificant, as shown in Figure 5c. First, a distinct pulse signal is obtained through a conditioning and amplifier circuit. Then the heart rate fH can be obtained by Fourier transform of the pulse signal and taking the dominant frequency, as shown in Figure 5e. The baseline separation circuit consists of a high-pass filter and a low-pass filter circuit. After passing through the two filters separately, two pure pulse wave signals and two mean pressure signals are available; the typical signals are shown in Figure 5f. The mean pressure of the two channels is defined as P1 and P2, respectively. The mean pressure here is influenced by the mean BP (MBP) and external pressure, so it can be used to extract the MBP when the external pressure is controllable. The oscillating pressure of the two channels, i.e., the peak-to-peak values of the pure pulse wave signals, are defined as ∆P1 and ∆P2, respectively. The oscillating pressure can be used to extract the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure. Then, the 2nd order differential sequence of the pulse wave is derived, and the moment when it reaches its peak is considered as the initial ejection point of the heart [22]. The pulse wave transmit time (PWTT) in the artery can be obtained as the time difference ∆t between the initial ejection time of two channels, as shown in Figure 5g. Moreover, the pulse wave velocity (PWV) in the artery can be calculated according to the distance ∆d and PWTT between the two signal channels of the sensing module.
Through wireless BLE communication, the measured information can be synchronized to the smartphone for saving and further processing, enabling real-time monitoring of arterial blood pressure.
3. Experiment and Discussion
3.1. Simulation Results on Static Load
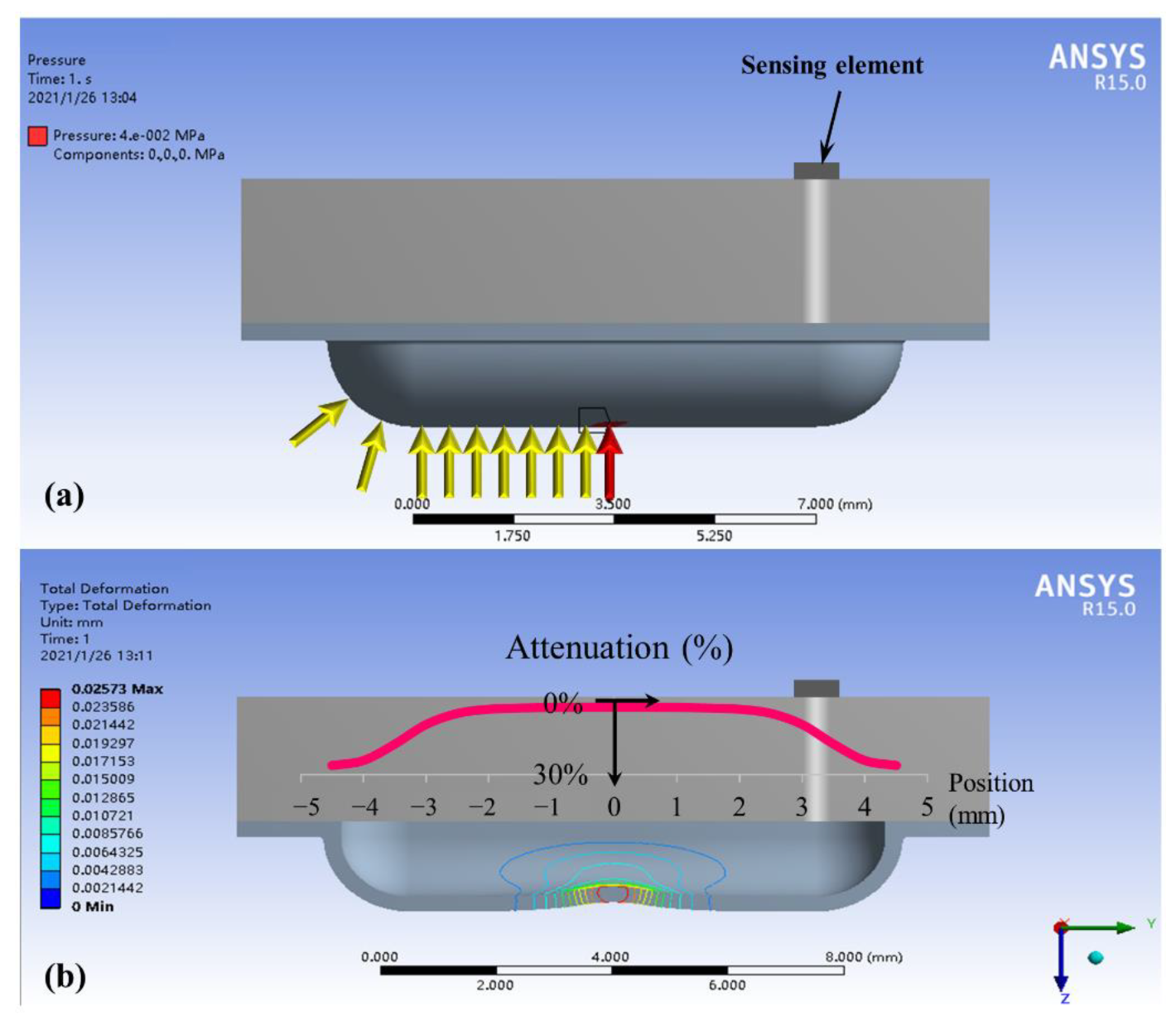
In this section we use finite element analysis (FEA) to demonstrate that the structure of liquid sealed in a film allows the pressure to be uniformly transmitted to the pressure sensing element, realizing the insensitivity to the stimulus location. The static simulation analysis was performed based on ANSYS. A simulation model for the basic structure of the sensing module was built first, and the same load was applied to different positions on the bulge structure, as shown by the arrows in Figure 6a. The red arrow is the center loading position, and the yellow arrows are the loading positions when the load is offset to the left by 0.5 mm each time (symmetric on the right). The pressure value at the sensing element was calculated separately for each loading position and defined as the output pressure.
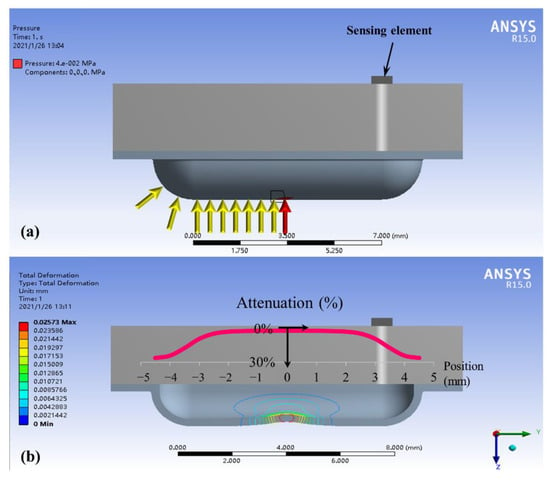
Figure 6.
Finite element simulation: (a) loading positions; (b) results of output pressure and film deformation.
The calculated results of the FEA are shown by the red curve in Figure 6b. The Y-axis of the curve is the output pressure attenuation relative to the central loading position (red arrow) when loading at other positions (yellow arrows). Results indicate that the output pressure varies with the position of the load, and the attenuation becomes more pronounced away from the center. The output pressure is attenuated by 5.6% at 2.5 mm away from the center and 25% at 4 mm. This means that the output pressure is nearly the same when the stimulus position is within 5 mm of the middle of the sensing module, and the output pressure error is less than 25% within 8 mm. Even at the furthest edge, the sensing module can obtain a valid signal within 30% attenuation. By consideration of adult vessel size, 2.5 mm away from the center is the location that the whole vessel maintains above the sensing bulge; more misplacement leads to the vessel being only partly above the sensing bulge, which results in a larger measuring error. Fortunately, the approximate pulse finger feeling method can easily guarantee that the module is fixed within the mm misplacement tolerance range.
3.2. Location Robustness on Dynamic Stimulation
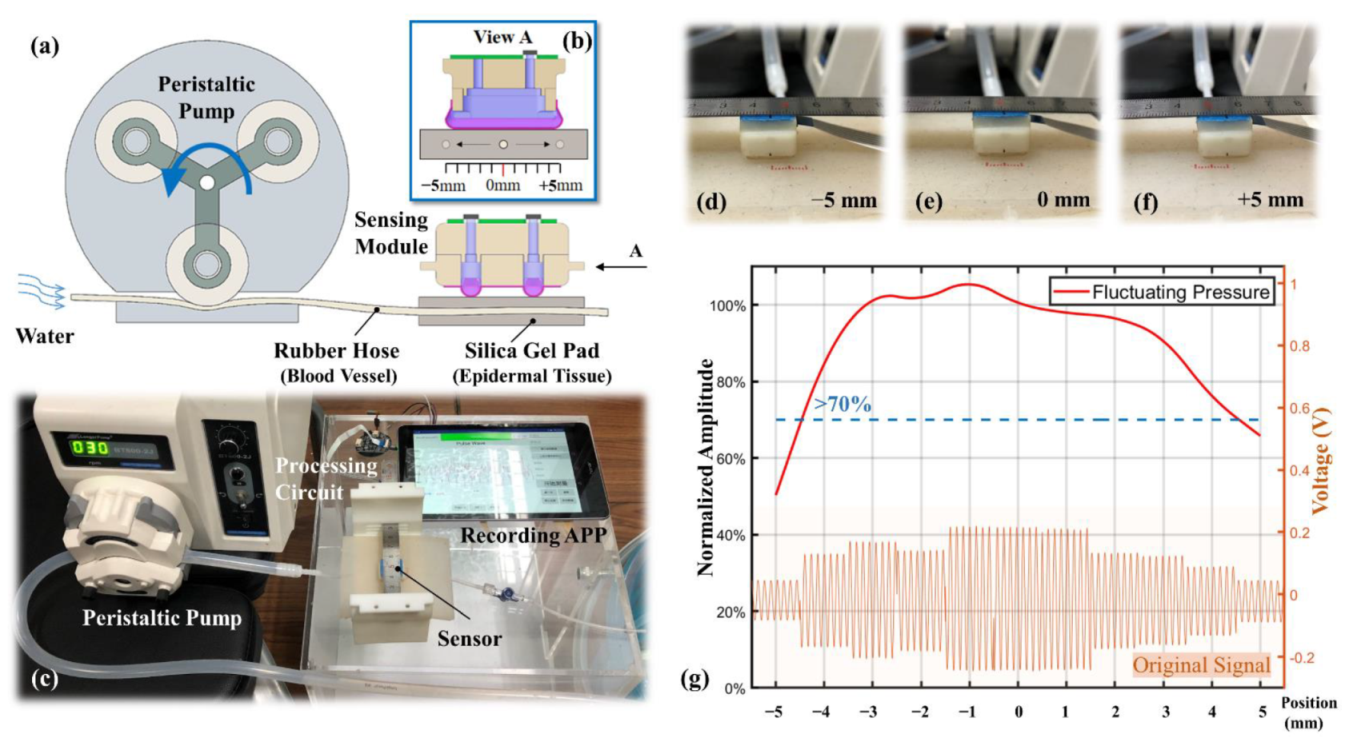
The location robustness in a static load was verified in the simulation analysis. However, the effects of pulse oscillation and epidermal tissue elasticity on pressure signal were not considered in the simulation. Therefore, in this section, the response to the stimulus location of the sensing module under near-real and controlled dynamic conditions is experimentally investigated. The schematic diagram of the experimental platform is shown in Figure 7a. A peristaltic pump was used to simulate the heartbeat, a rubber hose to simulate the blood vessel, and a silica gel pad to simulate the epidermal tissue. The peristaltic pump rollers squeeze the rubber hose from left to right in sequence, intermittently pumping the water through the region where the sensing module is located. The diameter of the rubber hose was 3 mm, which is similar to that of the radial artery vessel. The thickness of the silica gel pad was 5 mm and the hardness was 5 HA, similar to those of the epidermal tissue. The rigid substrate beneath the silica gel pad was used to simulate the radius supporting the radial artery. Figure 7b shows the right elevation of the sensing module and the rubber hose, which illustrates the change in the rubber hose location relative to the sensing module from −5 to 5 mm during the experiment. The photo of the experimental platform is shown in Figure 7c, including a peristaltic pump, a segment of rubber hose, a silica gel pad, a sensing module, a processing circuit, and a smartphone-based recording APP. Figure 7d–f show the close-up photos of the rubber hose positions at the leftmost (−5 mm), middle (0 mm), and rightmost (5 mm), respectively.
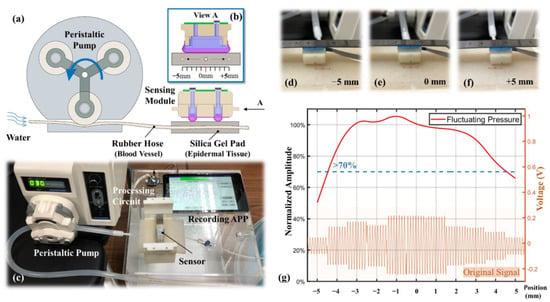
Figure 7.
Experimental setup for location robustness: (a) schematic diagram of the experimental platform; (b) right elevation of the sensing module; (c) photo of the experimental setup; (d–f) different test locations; (g) results of the location robustness experiment.
The rotational speed of the peristaltic pump is set to 30 rpm and with the three rollers in one circle, i.e., the fluctuation frequency is 90 Hz, which is close to the human heart rate. As each roller passes through the rubber hose, the peak pressure is generated. The signals collected at each location of the sensing module are shown at the bottom of Figure 7g. The top of the figure shows the extracted average oscillating pressure versus its location, and the Y-axis is the oscillating pressure attenuation relative to the central location. As can be seen from the figure, the dynamic experimental results are almost the same as the static simulation results. At a distance of ±4 mm from the center, the oscillating pressure decays by 23.7%. The ideal measuring location is from −2.5 to 2.5 mm and the oscillating pressure variation is within 5.4%. Another important result is that the waveforms maintained a close agreement at all the misalignment locations, which is one of the key performances desired in real BP monitoring. In this manner, the designed sensing module demonstrated its capability of alignment-free tonometry BP measurement.
Based on the developed alignment-free sensing module, it was necessary to examine its appropriate capability in BP measuring, which is presented in the following sections.
3.3. Individualized Calibration
In this section, the arterial blood pressure (ABP) measured by the sensing module is investigated. The subject’s ABP was artificially and quantitatively altered through an in vivo BP control platform to establish a link with the output of the sensing module. This calibration method combines ABP with hydrostatic pressure and is able to assess the effect of individualization factors, such as vessel thickness and epidermal tissue stiffness. The calibration results can be applied to BP tracking for long-term wear. In this study, artificial alteration of ABP was achieved by adjusting the height of the subject’s wrist relative to the heart. According to Bernoulli’s principle, for every 1.3 cm increase in the height of the wrist relative to the heart, the ABP at the measuring point decreases by 1 mmHg. However, due to the difference in physiological characteristics of the individual body, the signal collected by the sensing module varies from person to person even if the ABP variation is the same. Therefore, it is necessary to recalibrate the sensitivity by the controlled ABP and the corresponding sensor output.
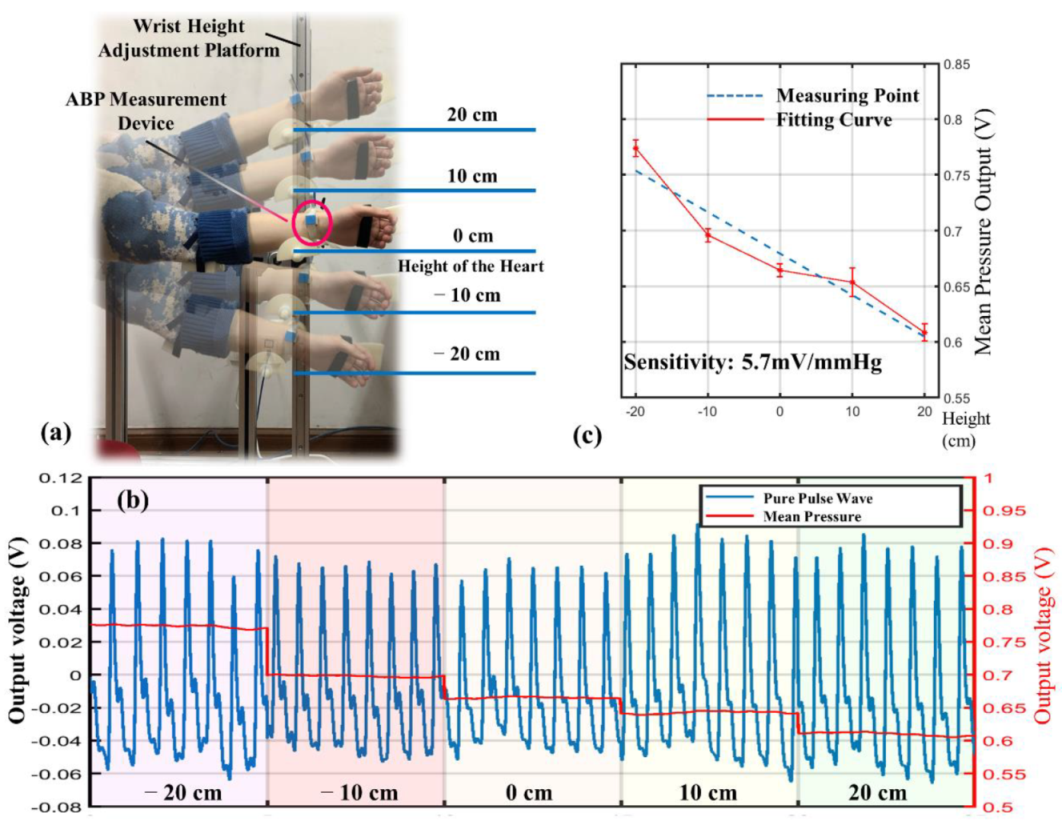
The experimental setup includes a wrist height adjustment platform, as shown in Figure 8a, which is designed with a sliding track allowing the subjects to maintain the posture while changing the height of the wrist. The subject selected for the experiment was healthy, did not smoke, drink, or exercise before the experiment, and was in a resting state without any stimulus during the experiment. Therefore, the BP of the subject was considered to be stable and did not fluctuate significantly during the experiment. The experimental procedure started with finding the height of the heart and defining it as 0 cm. The wrist height was adjusted within ±20 cm, starting from −20 cm and rising 10 cm each time. Each position measurement lasted 30 s, and the measured pulse wave is shown in Figure 8b.
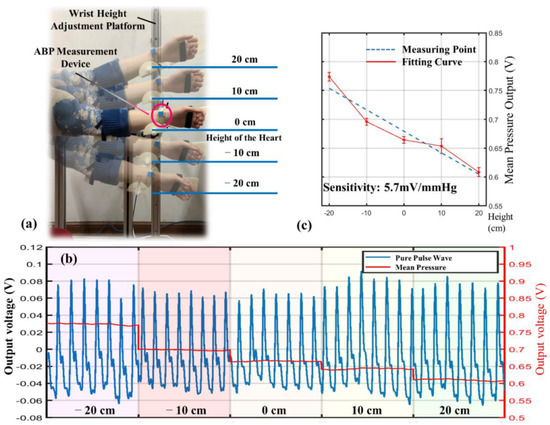
Figure 8.
Individualized calibration results. (a) Experimental setup for ABP control. (b) Pulse signals at different heights. (c) Recalibrated sensitivity.
By the analysis of the experimental data, it can be found that the primary change in the signal as the wrist height rises is the decrease in mean pressure. The change rate is −4.25 mV/cm; that is, the sensitivity of the sensing module is 5.7 mV/mmHg. However, the sensitivity of the sensor was previously calibrated as 8.7 mV/mmHg in a precise pressure chamber. The error between the measured and calibrated sensitivity is a reflection of the individualization factor. This can be explained in two ways. One is that the epidermal tissue induces an attenuation effect on pressure transmission [23,24]. The other is that only part of the sensitive area is in contact with the arterial blood vessels during the measurement, as shown in Figure 5a. The first factor is related to the elasticity and thickness of the epidermis, and the second factor is influenced by the thickness of the artery. Both factors can be attributed to the individualized discrepancies and can be eliminated by recalibration.
3.4. BP Calibration
The individualized factor calibration characterizes the relationship between the variation in the sensing module output and BP during ambulatory BP measurements. However, because the wearing state is different each time, the initial BP also needs to be calibrated. The characteristics of the transmural pressure can be used to calibrate the initial BP. The transmural pressure represents the combined pressure of intravascular pressure, applied pressure, and hydrostatic pressure. It is generally accepted that the compliance of the vessel increases to a maximum value as the transmural pressure goes to zero [25]. In addition, the transmural pressure equal to zero means that the intravascular pressure, i.e., the MBP, is equal to the extravascular pressure when the hydrostatic pressure is equal to zero. This also means that the pulse oscillating pressure measured by the sensing module is the largest [26]. Furthermore, maximum vascular compliance also means that the same pressure change in the vessel causes the most significant change in vessel volume and, therefore, the most extended PWTT [27]. Thus, there can be two ways to determine the initial BP—when the pulse oscillation amplitude reaches its maximum and when the PWTT is the longest. In this study, the transmural pressure was varied by changing the applied pressure of the sensing module, and was decreased to zero and then increased in reverse as the applied pressure increases.
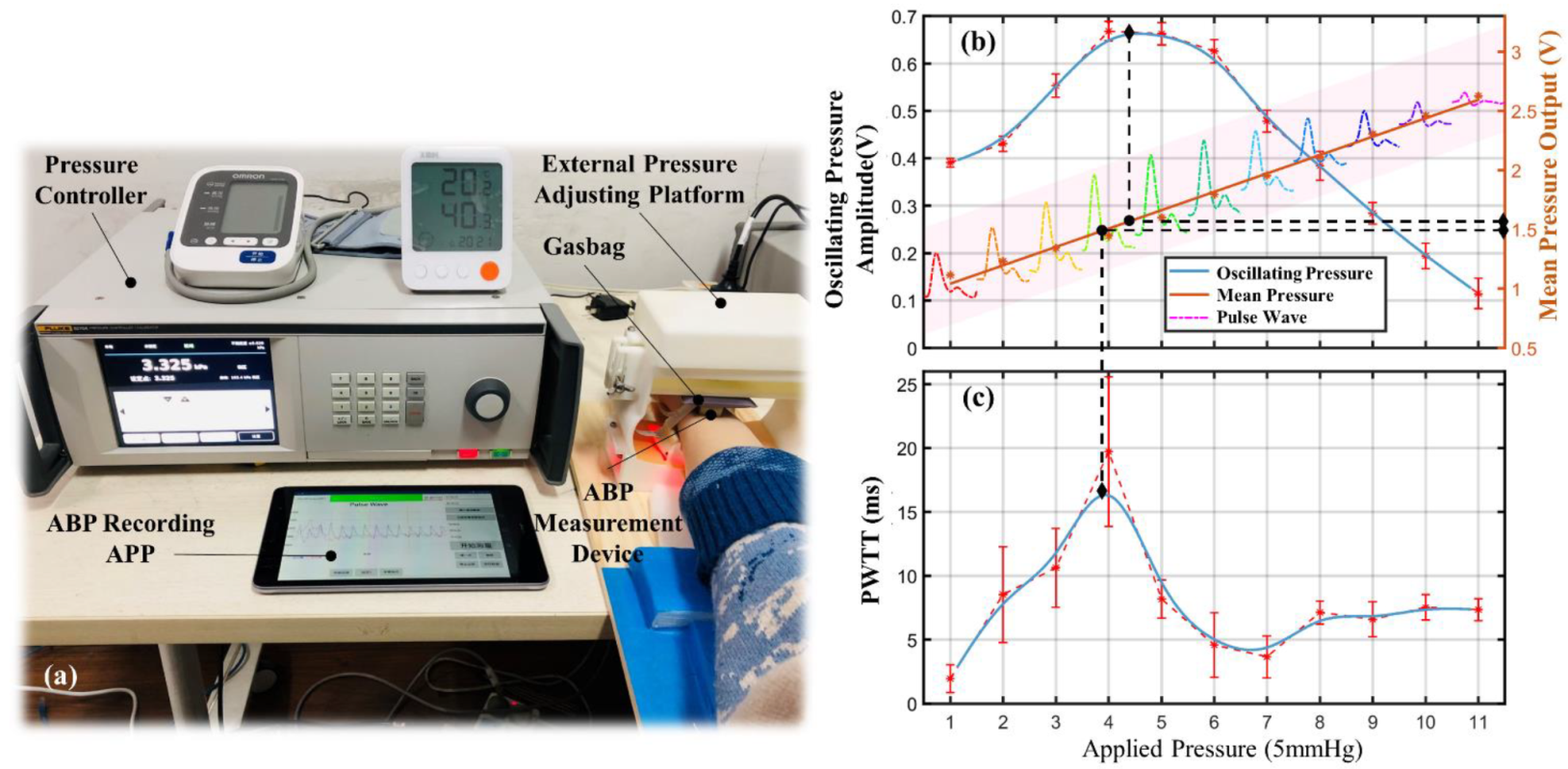
The experimental setup containing a pressure controller, a gasbag, and an ABP measurement device is shown in Figure 9a. The pressure applied to the wrist by the sensing module was controlled by the pressure controller and a gasbag above the module. Before the experiment, the subject was required to align the sensing module with the gasbag after wearing the ABP measurement device, and the subject’s wrist remained stationary throughout the experiment. The pressure on the wrist was then controlled to increase gradually and uniformly until the acquired pulse waveform begins to distort, indicating that the artery is almost closed.
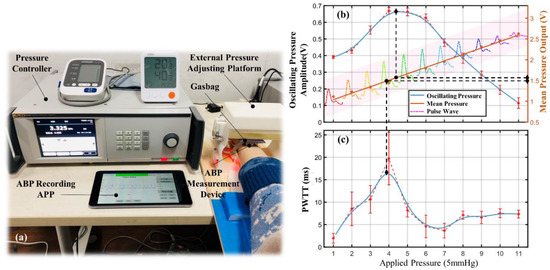
Figure 9.
Pulse characteristics at different applied pressures.(a) Experimental setup for initial BP calibration. (b) Mean pressures and oscillating pressures. (c) PWTT.
The experimental results for one subject are presented in Figure 9b. The mean pressure measured by the sensing module keeps rising uniformly with the increase in the applied pressure. The oscillating pressure and the PWTT also progressively increase at the beginning due to the decreased transmural pressure. As the applied pressure continued to increase, the oscillating pressure and the PWTT started to decrease from a certain point because the transmural pressure decreased to zero and then increased in reverse. The turning point is the MBP state for the subject, as shown by the dashed line in Figure 8c. The mean pressure at this point corresponds to the MBP, and the oscillating pressure corresponds to the difference between systolic and diastolic pressures.
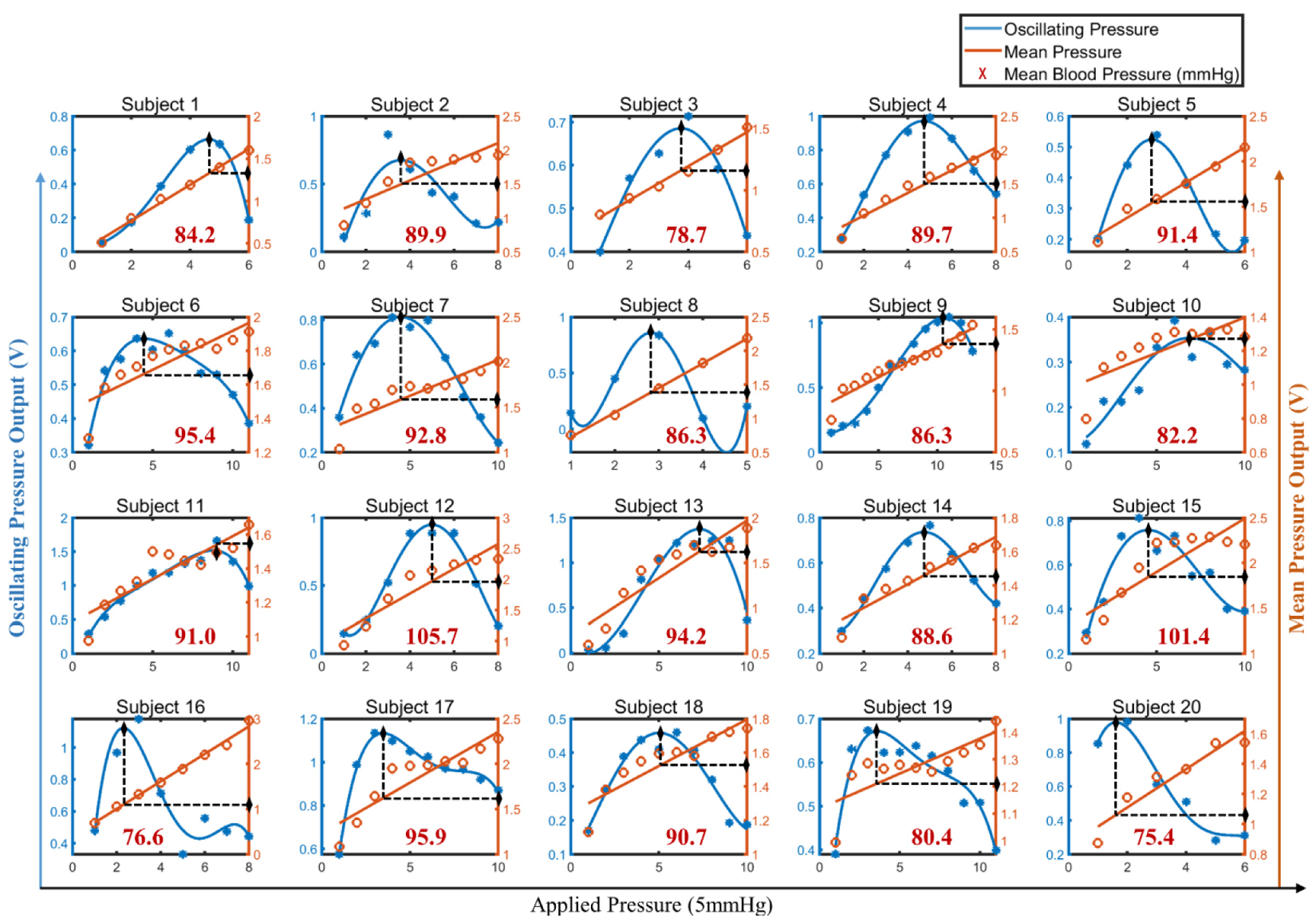
According to the IEEE standard [28], twenty healthy adults were selected for evaluating the effectiveness of the designed BP measurement device. Their personal information and BP measured by a commercial sphygmomanometer (Omorn Inc., Japan, HEM-7124) 5 min before the test are shown in Table 1. The initial BP was calibrated by the same method for the 20 subjects, and the extracted mean and oscillating pressures are presented in Figure 10. The calibration results of the MBP are shown in red.

Table 1.
BP information for the 20 subjects.
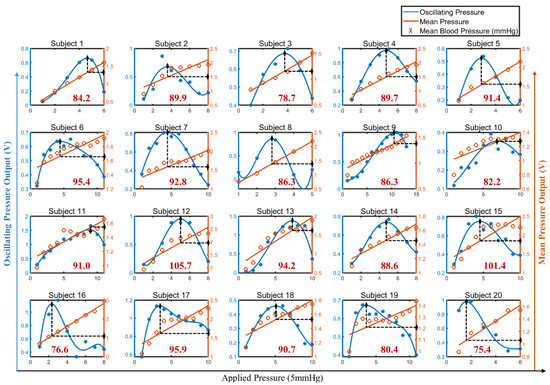
Figure 10.
Initial BP caalibration results for the 20 subjects.
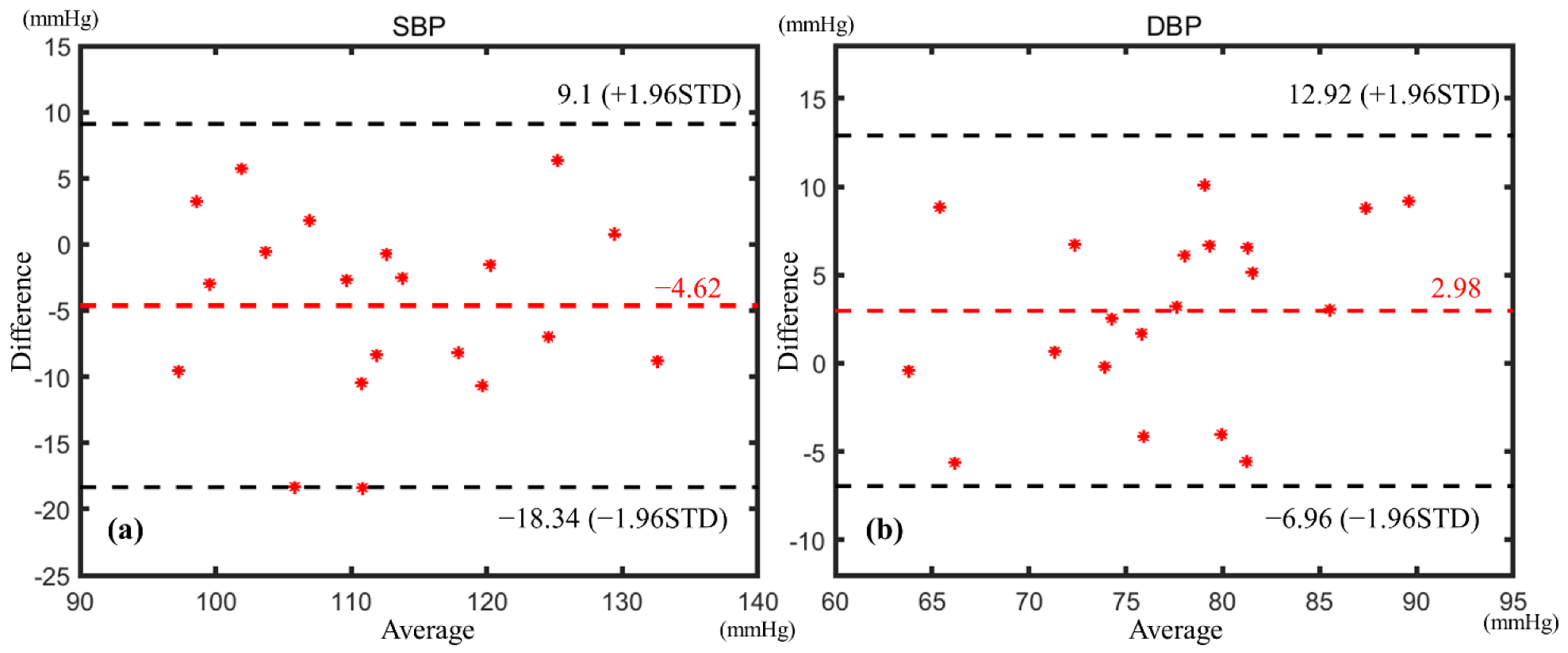
Because the BP procedure in this study is based on arterial tonometry, the MBP was obtained from the corresponding mean pressure, and the differential pressure (DP) between systolic pressure and diastolic pressure was obtained from the corresponding oscillating pressure. The BP measurement results of the subject were determined by the MBP and the DP. In order to enable comparison with the commercial cuff sphygmomanometers, the results were converted to SBP and DBP by the 4/6 principle. Then, the Bland–Altman method was used to analyze the correlation between the derived BP and the BP measured by the commercial sphygmomanometer; the results are shown in Figure 11. All measuring results fall within the confidence interval. The mean error of SBP is −4.62 mmHg with a standard deviation of ±7.0 mmHg, and the mean error of DBP is 2.98 mmHg with a standard deviation of ±5.07 mmHg. The BP measurement results are in accordance with the AAMI standard [29] of 5 ± 8 mmHg. The above experimental results indicate that the BP measurement device proposed in this paper has considerable stability and can adapt to different people.
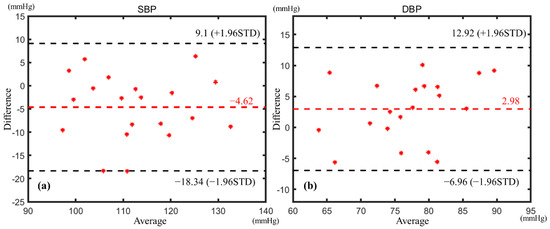
Figure 11.
Bland–Altman analysis of (a) SBP and (b) DBP.
4. Conclusions
Arterial tonometry is a noninvasive BP measurement method with high accuracy. However, sensor–artery alignment is a major problem that obstructs the application of arterial tonometry. In this study, a novel solid–liquid mixture pulse sensing module was proposed to address the existing problems. The flexible film with semicylindrical bulges and unique liquid-filled structure greatly reduces the pulse measuring error caused by position deviation. Having a rational circuit and algorithm design, it is able to extract the mean and oscillating pressures of the subject’s pulse. In addition, the device has the ability to measure PWTT, which can serve as a complement to arterial tonometry and is especially suitable for ambulatory BP monitoring. The location robustness of the sensing module was verified by simulation and experiment. The ideal measuring location ranges from −2.5 to 2.5 mm of the module and the pressure variation is within 5.4%, which can be easily achieved by finger feeling in a real application of a wearable BP monitoring scenario. At a distance of ±4 mm from the module center, although the pressure decays by 23.7%, the dynamic waveform is conserved well, which is important for wearable application. For different potential users, the individualization factor can be calibrated by an ABP control platform, and the initial BP can be calibrated by an applied pressure regulation platform. The alignment deviation errors can be further eliminated by the individual calibration procedure in a practical BP measuring step. BP measurement experiments were performed on 20 subjects, and the experimental procedure followed IEEE standards. The results indicate that the wearable device performs well for BP measurements and the error of the results meet the AAMI standards. The device is expected to provide a new solution for wearable continuous BP monitoring.
In next phase, we plan to (1) combine arterial tonometry and the PWTT method for BP measurement, and use the device for noninvasive continuous BP measurement in clinical trials; (2) study the interference of human motion on the measurement, and improve the accuracy of the measurement in motion in terms of the device structure design and an anti-motion algorithm.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.L.; software, B.Z.; validation, B.Z., C.Y. and F.X.; formal analysis, B.Z.; data curation, C.Y. and F.X.; writing—original draft preparation, B.Z.; writing—review and editing, W.L.; supervision, W.L. and X.F.; funding acquisition, W.L., L.H. and X.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 51875506, the Science Fund for Creative Research Groups of National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 51821093, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 51775485.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of College of Biomedical Engineering & Instrument Science, Zhejiang University ([2021]-39).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Acknowledgments
The authors are also sincerely grateful to the students participating in the experiment.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kannel, W.B.; Mcgee, D.L. Kannel WB and McGee DL. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease: The Framingham study. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1979, 241, 2035–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.Y.; Chen, W.W.; Gao, R.L.; Liu, L.S.; Zhu, M.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Wu, Z.S.; Li, H.J.; Gu, D.F.; Yang, Y.J.; et al. China cardiovascular diseases report 2018: An updated summary. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 25, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Menezes, S.T.; Giatti, L.; Brant, L.C.; Griep, R.H.; Schmidt, M.I.; Duncan, B.B.; Suemoto, C.K.; Ribeiro, A.L.; Barreto, S.M. Hypertension, Prehypertension, and Hypertension Control: Association With De-cline in Cognitive Performance in the ELSA-Brasil Cohort. Hypertension 2020, 77, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.R.; Viera, A.J.; Shimbo, D. Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring in Clinical Practice: A Review. Am. J. Med. 2014, 128, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rastegar, S.; GholamHosseini, H.; Lowe, A. Non-invasive continuous blood pressure monitoring systems: Current and proposed technology issues and challenges. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2019, 43, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Choudhury, M.I.; Roy, S.; Prasad, A. Computational Study to Investigate Effect of Tonometer Geometry and Pa-tient-Specific Variability on Radial Artery Tonometry. J. Biomech. 2017, 58, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachuee, M.; Kiani, M.M.; Mohammadzade, H.; Shabany, M. Cuffless Blood Pressure Estimation Algorithms for Continuous Health-Care Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 64, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.C.Y.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Liu, Y. Modeling of Pulse Transit Time under the Effects of Hydrostatic Pressure for Cuffless Blood Pressure Measurements. In Proceedings of the 2006 3rd IEEE/EMBS International Summer School on Medical Devices and Biosensors, Cambridge, MA, USA, 4–6 September 2006; Volume 36, pp. 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, M.R.; Madhav, K.V.; Krishna, E.H.; Komalla, N.R.; Reddy, K.A. On the performance of AS-LMS based adaptive filter for reduction of mo-tion artifacts from PPG signals. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Hangzhou, China, 10–12 May 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ram, M.R.; Madhav, K.V.; Krishna, E.H.; Komalla, A.R.; Reddy, K.A. A Novel Approach for Motion Artifact Reduction in PPG Signals Based on AS-LMS Adaptive Filter. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2011, 61, 1445–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurylyak, Y.; Lamonaca, F.; Grimaldi, D. A Neural Network-based method for continuous blood pressure estimation from a PPG signal. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 6–9 May 2013; pp. 280–283. [Google Scholar]
- He, R.; Huang, Z.P.; Ji, L.Y.; Wu, J.K.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.Q. Beat-to-beat ambulatory blood pressure estimation based on random forest. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Wearable & Implantable Body Sensor Networks, Chicago, IL, USA, 19–22 May 2019; pp. 194–198. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, F.; Fu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, X.-R.; Hong, X.; He, Q.; Li, Y. A Novel Continuous Blood Pressure Estimation Approach Based on Data Mining Techniques. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2017, 21, 1730–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikenfeld, J.; Jajack, A.; Rogers, J.; Gutruf, P.; Tian, L.; Pan, T.; Li, R.; Khine, M.; Kim, J.; Wang, K. Wearable sensors: Modalities, challenges, and prospects. Lab. Chip. 2018, 18, 217–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, X.; Huang, Y.; Ding, X.; Luo, N.; Li, C.; Zhao, N.; Chen, S.-C. Alignment-Free Liquid-Capsule Pressure Sensor for Cardiovascular Monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, X.; Hu, H.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; Lin, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, Z.; Huang, B.; Gong, H.; et al. Monitoring of the central blood pressure waveform via a conformal ultrasonic device. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, A.; Kim, C.S.; Naji, M.; Natarajan, K.; Hahn, J.O.; Mukkamala, R. Smartphone-based blood pressure monitoring via the oscillometric fin-ger-pressing method. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaap8674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pressman, G.L.; Newgard, P.M. A Transducer for the Continuous External Measurement of Arterial Blood Pressure. IRE Trans. Bio-Med. Electron. 1963, 10, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M. The Yellow Emperor’s Classic of Medicine: A New Translation of the Neijing Suwen With Commentary; Shambhala: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Buxi, D.; Redoute, J.-M.; Yuce, M. A survey on signals and systems in ambulatory blood pressure monitoring using pulse transit time. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, R1–R26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.; Young, D.J. Skin-Coupled Personal Wearable Ambulatory Pulse Wave Velocity Monitoring System Using Micro-electromechanical Sensors. Sens. J. IEEE 2014, 14, 3490–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Gu, C.; Zeng, R.; Yu, P.; Fu, X. A Novel Inverse Solution of Contact Force Based on a Sparse Tactile Sensor Array. Sensors 2018, 18, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, S.H.; Choi, Y.Y.; Kim, D.J.; Bien, F.; Kim, J.J. Tissue-Informative Mechanism for Wearable Non-invasive Continuous Blood Pressure Monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaltis, P.; Reisner, A.; Asada, H. A hydrostatic pressure approach to cuffless blood pressure monitoring. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Berlin, Germany, 1 September 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soh, K.-S.; Lee, M.-H.; Yoon, Y.-Z. Pulse type classification by varying contact pressure. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2000, 19, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Allen, J.; Murray, A. Effect of external cuff pressure on arterial compliance. Comput. Cardiol. 2005, 2005, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IEEE Standard Association. IEEE Standard for Wearable Cuffless Blood Pressure Measuring Devices; IEEE: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Stergiou, G.S.; Palatini, P.; Asmar, R.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Kollias, A.; Lacy, P.; McManus, R.J.; Myers, M.G.; Parati, G.; Shennan, A.; et al. Recommendations and Practical Guidance for performing and reporting validation studies according to the Universal Standard for the validation of blood pressure measuring devices by the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation/European Society of Hypertension/International Organization for Standardization (AAMI/ESH/ISO). J. Hypertens. 2019, 37, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).