Mapping Discrete Emotions in the Dimensional Space: An Acoustic Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Discrete (Categorical) versus Dimensional (Continuous) Characterization of Emotions
2.1. Issues in Predicting Emotional Dimensions from the Sound of an Utterance
2.2. Hypothesis
3. The Data Used in the Experiments
3.1. Training Databases
3.2. Testing Databases
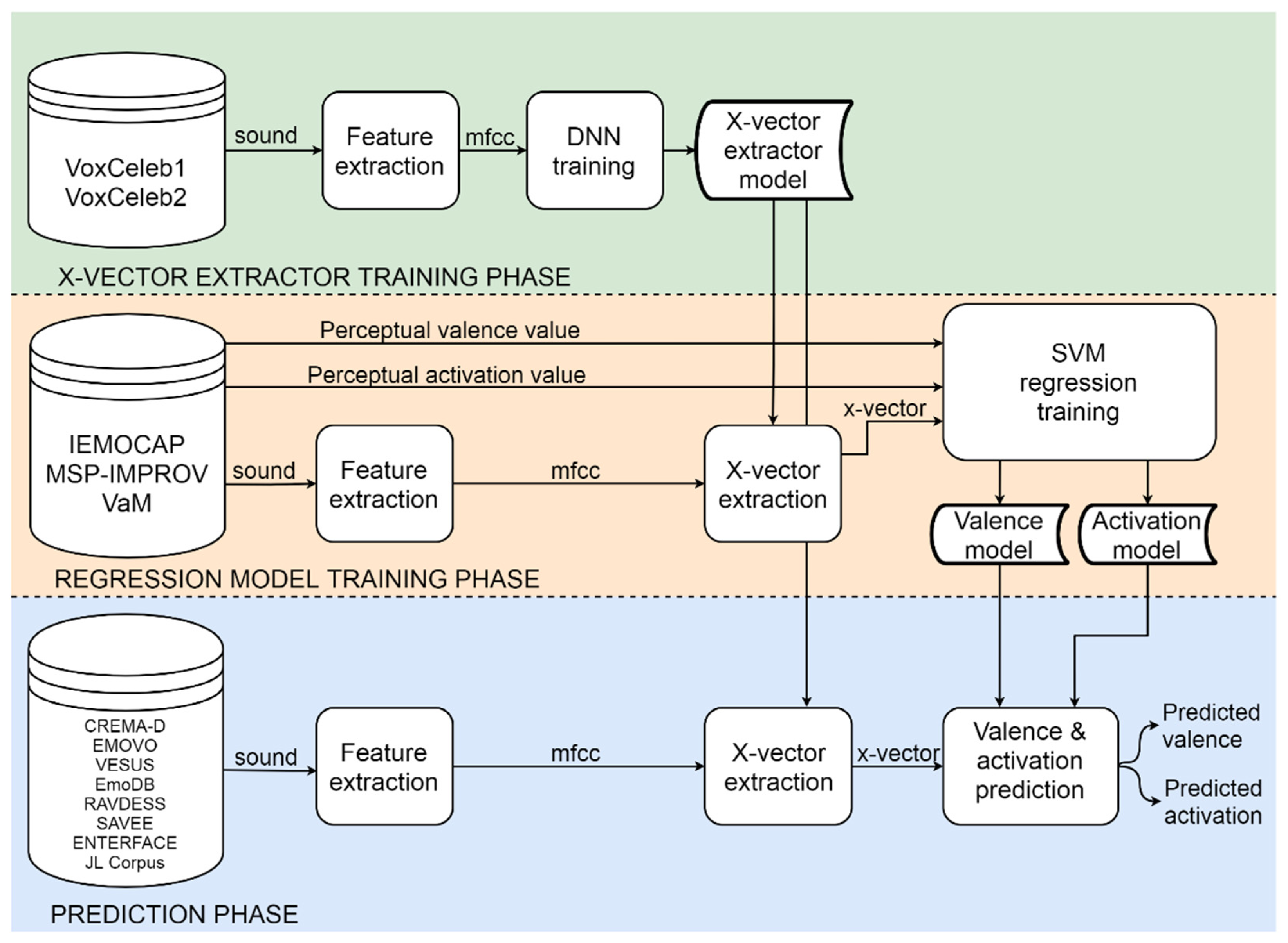
4. System Architecture
4.1. X-Vector Approach to Signal Representation
4.1.1. X-Vector Extractor Training Phase
4.1.2. Regression Model Training Phase
4.1.3. Prediction Phase
4.2. Overall Architecture
5. Results
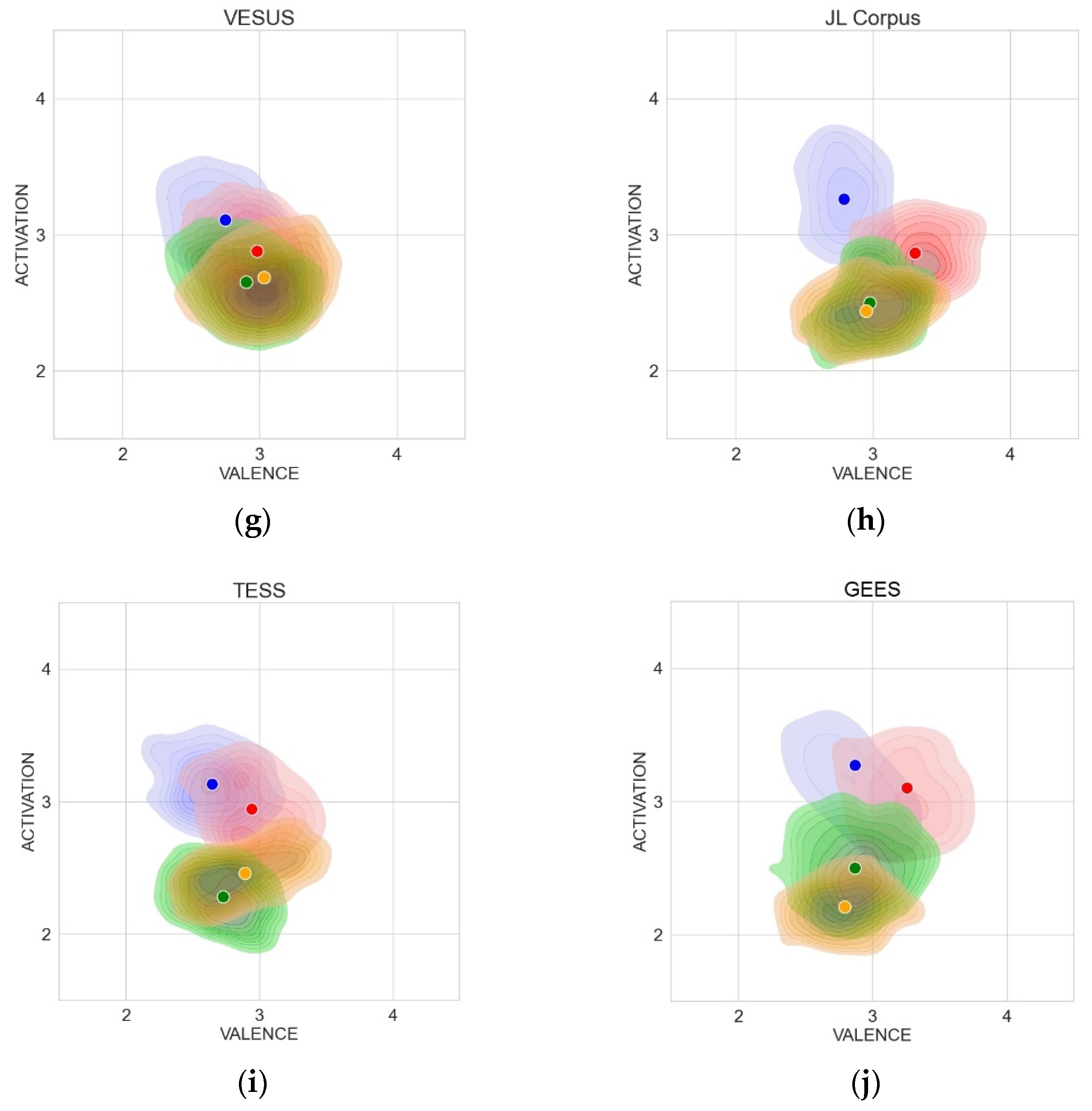
5.1. Visualization of Results
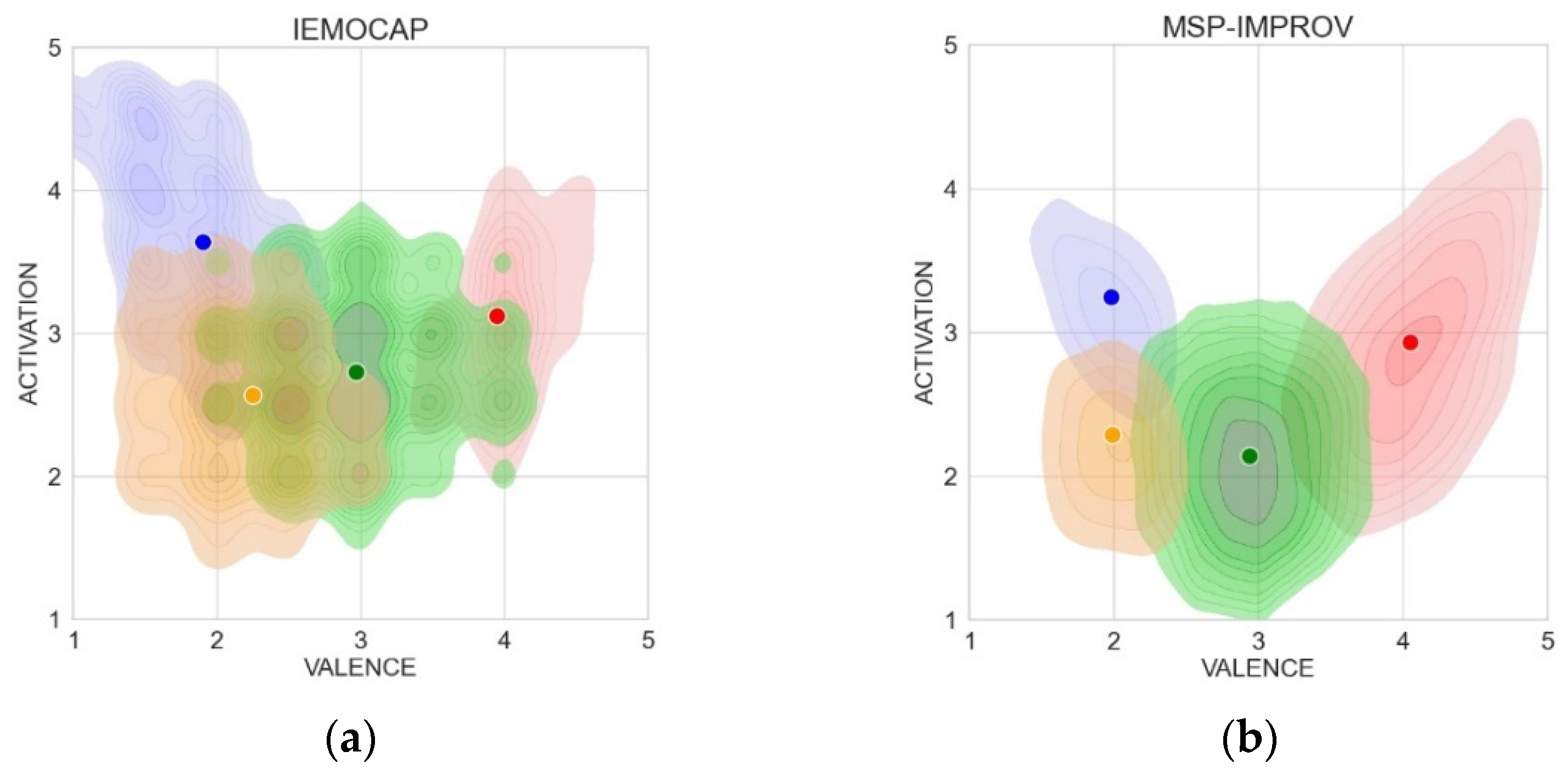
5.2. Ground Truth—Original AV Values Indicated by Annotators
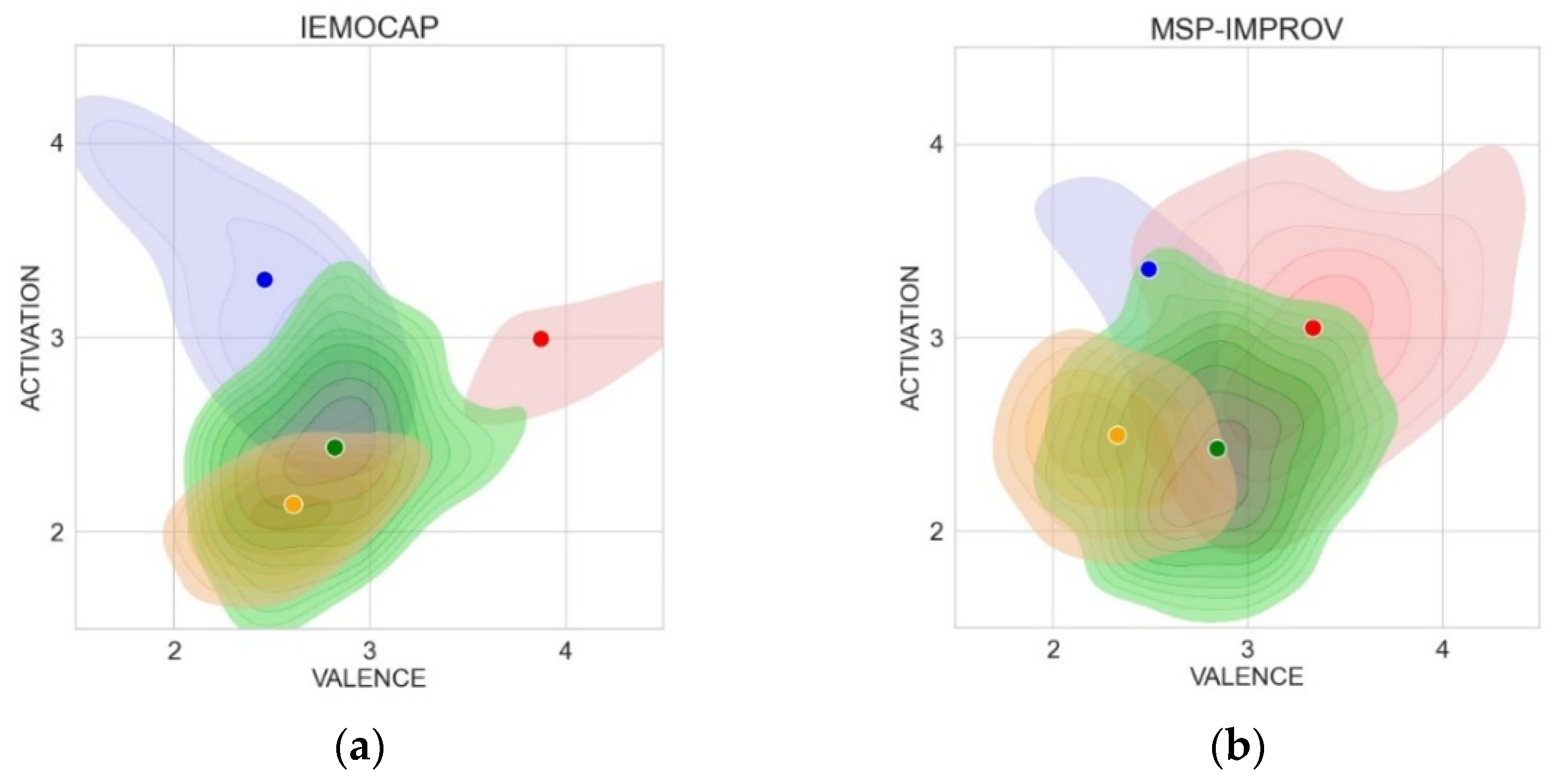
5.3. Regression Evaluation—AV Values Estimated on Combinations of the Test Sets
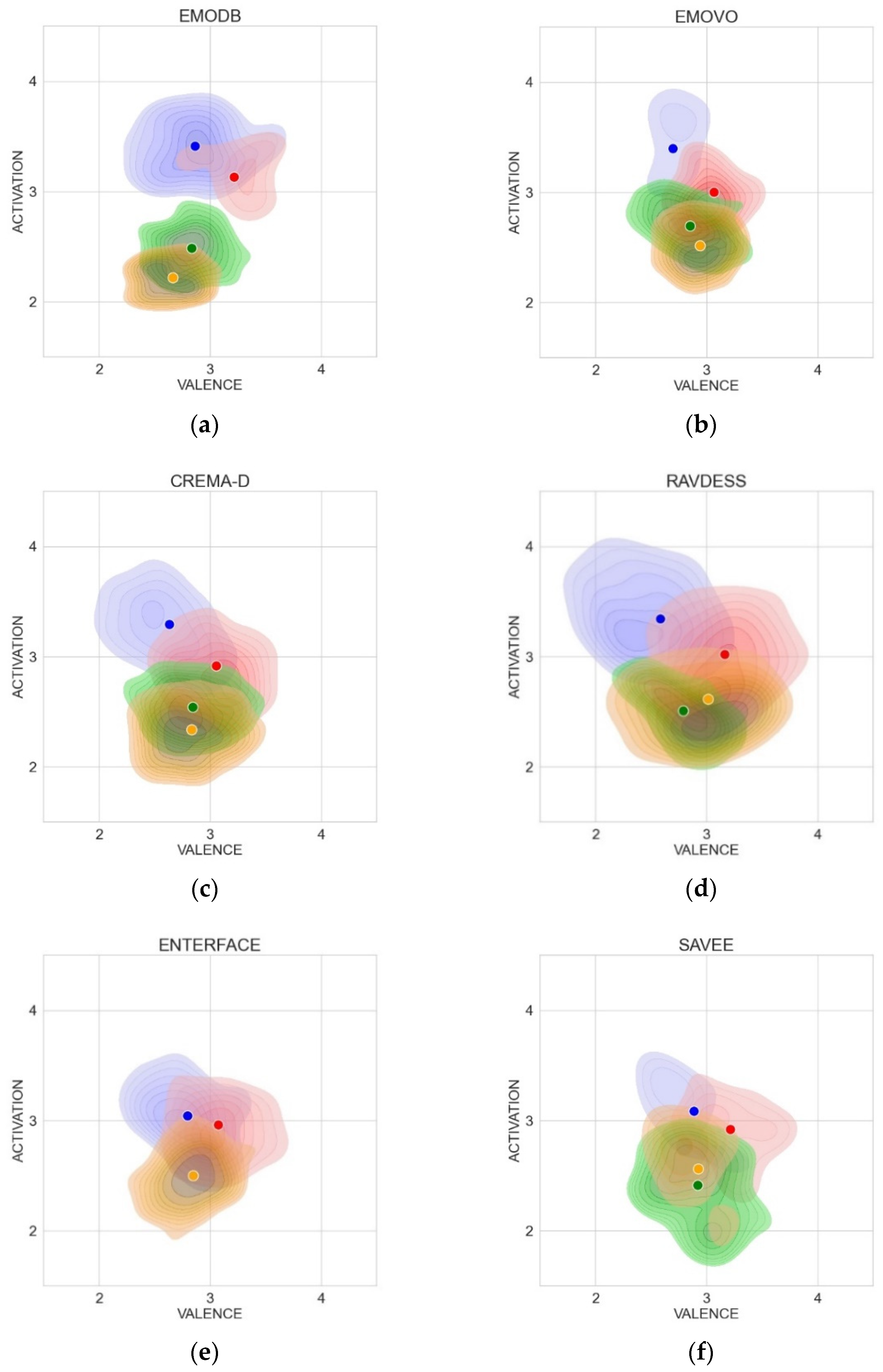
5.4. Cross-Corpus Experiments, AV Values Estimated by Regression on “Unseen” Corpora
5.5. Centroid Distance as a Measure of Regression Quality
5.6. Overall Picture of Emotion Positions in the AV Space
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scherer, K.R. What are emotions? And how can they be measured? Soc. Sci. Inf. 2005, 44, 695–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, H.; Scheck, A.; Schuster, T.; Walter, S.; Limbrecht, K.; Traue, H.C.; Kessler, H. Mapping discrete emotions into the dimensional space: An empirical approach. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Seoul, Korea, 14–17 October 2012; pp. 3316–3320. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, J.A. A circumplex model of affect. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1980, 39, 1161–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, M.A.; Abrams, D.; Martin, G.N. Social cognition and attitudes. In Psychology; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2010; pp. 646–677. [Google Scholar]
- Gunes, H.; Schuller, B. Categorical and dimensional affect analysis in continuous input: Current trends and future directions. Image Vis. Comput. 2013, 31, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D.; Wiese, D.; Vaidya, J.; Tellegen, A. The two general activation systems of affect: Structural findings, evolutionary considerations, and psychobiological evidence. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1999, 76, 820–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.A. Core affect and the psychological construction of emotion. Psychol. Rev. 2003, 110, 145–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oflazoglu, C.; Yildirim, S. Recognizing emotion from Turkish speech using acoustic features. EURASIP J. Audio Speech Music Process. 2013, 2013, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teilegen, A. Structures of Mood and Personality and Their Relevance to Assessing Anxiety, with an Emphasis on Self-Report. In Anxiety and the Anxiety Disorders; Routledge: London, UK, 2019; pp. 681–706. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, M.M.; Lang, P.J. Affective reactions to acoustic stimuli. Psychophysiology 2000, 37, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekman, P. Universals and cultural differences in facial expressions of emotion. In Nebraska Symposium on Motivation; Cole, J., Ed.; University of Nebraska Press: Lincoln, NE, USA, 1972; Volume 19, pp. 207–282. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, N. Cultural differences in emotion: Differences in emotional arousal level between the East and the West. Integr. Med. Res. 2016, 5, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Busso, C.; Bulut, M.; Lee, C.-C.; Kazemzadeh, A.; Mower, E.; Kim, S.; Chang, J.N.; Lee, S.; Narayanan, S.S. IEMOCAP: Interactive emotional dyadic motion capture database. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2008, 42, 335–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busso, C.; Parthasarathy, S.; Burmania, A.; Abdel-Wahab, M.; Sadoughi, N.; Provost, E. MSP-IMPROV: An Acted Corpus of Dyadic Interactions to Study Emotion Perception. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2017, 8, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, M.; Kroschel, K.; Narayanan, S. The Vera am Mittag German audio-visual emotional speech database. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Hannover, Germany, 23 June–26 April 2008; pp. 865–868. [Google Scholar]
- Turabzadeh, S.; Meng, H.; Swash, R.M.; Pleva, M.; Juhar, J. Facial Expression Emotion Detection for Real-Time Embedded Systems. Technologies 2018, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albanie, S.; Nagrani, A.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Emotion Recognition in Speech using Cross-Modal Transfer in the Wild. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 292–301. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, M.M.; Lang, P.J. Measuring emotion: The self-assessment manikin and the semantic differential. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry 1994, 25, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, F.; Paeschke, A.; Rolfes, M.; Sendlmeier, W.F.; Weiss, B. A database of German emotional speech. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2005, Lisbon, Portugal, 4–8 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Costantini, G.; Iaderola, J.; Paoloni, A.; Todisco, M. EMOVO Corpus: An Italian Emotional Speech Database. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC), Reykjavik, Iceland, 26–31 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone, S.R.; Russo, F.A. The Ryerson Audio-Visual Database of Emotional Speech and Song (RAVDESS): A dynamic, multimodal set of facial and vocal expressions in North American English. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, H.; Cooper, D.G.; Keutmann, M.K.; Gur, R.C.; Nenkova, A.; Verma, R. CREMA-D: Crowd-sourced Emotional Multimodal Actors Dataset. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2014, 5, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- University of Surrey. Surrey Audio-Visual Expressed Emotion (SAVEE) Database. Available online: http://kahlan.eps.surrey.ac.uk/savee/ (accessed on 12 October 2021).
- Sager, J.; Shankar, R.; Reinhold, J.; Venkataraman, A. VESUS: A Crowd-Annotated Database to Study Emotion Production and Perception in Spoken English. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2019, Graz, Austria, 15–19 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, O.; Kotsia, I.; Macq, B.; Pitas, I. The eNTERFACE’05 Audio-Visual Emotion Database. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops (ICDEW’06), Atlanta, GA, USA, 3–7 April 2006; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- James, J.; Tian, L.; Watson, C.I. An Open Source Emotional Speech Corpus for Human Robot Interaction Applications. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2018, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pichora-Fuller, M.K.; Dupuis, K. Toronto Emotional Speech Set (TESS); University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jovičić, T.S.; Kašić, Z.; Đorđević, M.; Rajković, M. Serbian emotional speech database: Design, processing and evaluation. In Proceedings of the SPECOM 2004: 9th Conference Speech and Computer, Saint-Peterburg, Russia, 20–22 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, D.; Garcia-Romero, D.; Sell, G.; Povey, D.; Khudanpur, S. X-vectors: Robust DNN embeddings for speaker recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustic, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5329–5333. [Google Scholar]
- Mackova, L.; Cizmar, A.; Juhar, J. Emotion recognition in i-vector space. In Proceedings of the 2016 26th International Conference Radioelektronika (RADIOELEKTRONIKA), Košice, Slovakia, 19–20 April 2016; pp. 372–375. [Google Scholar]
- Abbaschian, B.; Sierra-Sosa, D.; Elmaghraby, A. Deep Learning Techniques for Speech Emotion Recognition, from Databases to Models. Sensors 2021, 21, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieskovská, E.; Jakubec, M.; Jarina, R.; Chmulík, M. A Review on Speech Emotion Recognition Using Deep Learning and Attention Mechanism. Electronics 2021, 10, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, D.; Snyder, D.; Povey, D.; Khudanpur, S. Probing the Information Encoded in X-Vectors. 2019. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.06351 (accessed on 12 October 2021).
- Nagrani, A.; Chung, J.S.; Zisserman, A.V. VoxCeleb: A large-scale speaker identification dataset. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Stockholm, Sweden, 20–24 August 2017; pp. 2616–2620. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.S.; Nagrani, A.; Zisserman, A. VoxCeleb2: Deep Speaker Recognition. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2018, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, T.; Peddinti, V.; Povey, D.; Khudanpur, S. Audio augmentation for speech recognition. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2015, Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Scikit. Epsilon-Support Vector Regression. Available online: https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.svm.SVR.html (accessed on 12 October 2021).
- Waskom, M.L. Seaborn: Statistical data visualization. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, P.; Churamani, N.; Lakomkin, E.; Siqueira, H.; Sutherland, A.; Wermter, S. The OMG-Emotion Behavior Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Schuller, B.; Vlasenko, B.; Eyben, F.; Wollmer, M.; Stuhlsatz, A.; Wendemuth, A.; Rigoll, G. Cross-Corpus Acoustic Emotion Recognition: Variances and Strategies. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2010, 1, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuller, B.; Zhang, Z.; Weninger, F.; Rigoll, G. Selecting training data for cross-corpus speech emotion recognition: Prototypicality vs. generalization. In Proceedings of the Afeka-AVIOS Speech Processing Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, 22 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Parry, J.; Palaz, D.; Clarke, G.; Lecomte, P.; Mead, R.; Berger, M.; Hofer, G. Analysis of Deep Learning Architectures for Cross-Corpus Speech Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2019, Graz, Austria, 15–19 September 2019. [Google Scholar]


| Database | Modality | Language | Speakers/Total No. of Audio Files | Emotions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EmoDB | Au | German | 10/535 | ang, bor, anx, hap, sad, disg, neu. |
| EMOVO | Au | Italian | 6/588 | disg, fear, ang, joy, surp, sad, neu. |
| RAVDESS | AuVi | English | 24/1440 | calm, hap, sad, ang, fear, surp, disg. |
| CREMA-D | AuVi | English | 91/442 | hap, sad, ang, fear, disg, neu. |
| SAVEE | AuVi | English | 4/480 | ang, disg, fear, hap, sad, surp, neu. |
| VESUS | AuVi | English | 10/ | hap, sad, ang, fear, neu. |
| eNTERFACE | AuVi | English | 44/1293 | hap, sad, surp, ang, disg, fear, neutral is not included. |
| JL Corpus | Au | New Zealand English | 4/4840 | neu, hap, sad, ang, exc. |
| TESS | Au | Canadian English | 2/2800 | ang, disg, fear, hap, pleasant surp, sad, neu. |
| GEES | Au | Serbian | 6/2790 | neu, hap, ang, sad, fear. |
| Training Set | Dim | IEMOCAP Test Set | MSP-IMPROV Test Set | VaM Test Set | MIX3 Test Set | MIX2 Test Set | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCC | MAE | CCC | MAE | CCC | MAE | CCC | MAE | CCC | MAE | ||
| IEMOCAP train | Val | 0.631 | 0.573 | 0.356 | 0.649 | 0.054 | 0.458 | 0.513 | 0.592 | 0.517 | 0.604 |
| Act | 0.750 | 0.407 | 0.404 | 0.671 | 0.059 | 0.598 | 0.532 | 0.557 | 0.547 | 0.557 | |
| MSP-IMPROV train | Val | 0.375 | 0.713 | 0.610 | 0.510 | −0.031 | 0.723 | 0.441 | 0.623 | 0.460 | 0.616 |
| Act | 0.484 | 0.651 | 0.696 | 0.393 | 0.005 | 0.756 | 0.600 | 0.494 | 0.631 | 0.477 | |
| VaM train | Val | −0.024 | 0.737 | −0.005 | 0.860 | 0.063 | 0.315 | −0.029 | 0.784 | −0.025 | 0.814 |
| Act | 0.096 | 0.604 | 0.023 | 0.726 | 0.044 | 0.544 | 0.024 | 0.676 | 0.022 | 0.686 | |
| MIX3 train | Val | 0.646 | 0.555 | 0.554 | 0.539 | 0.029 | 0.484 | 0.639 | 0.516 | 0.637 | 0.527 |
| Act | 0.678 | 0.458 | 0.657 | 0.430 | −0.014 | 0.648 | 0.729 | 0.402 | 0.750 | 0.391 | |
| MIX2 train | Val | 0.646 | 0.558 | 0.561 | 0.534 | 0.025 | 0.524 | 0.632 | 0.520 | 0.641 | 0.525 |
| Act | 0.673 | 0.466 | 0.667 | 0.424 | −0.014 | 0.661 | 0.726 | 0.404 | 0.753 | 0.390 | |
| Tested Corpus | Dimension | Emotion Clusters | MIX3 Train Set | MIX2 Train Set |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMO DB | valence | angry-happy | 0.35 | 0.36 |
| activation | angry-sad | 1.19 | 1.20 | |
| CREMA-D | valence | angry-happy | 0.42 | 0.42 |
| activation | angry-sad | 0.96 | 0.98 | |
| RAVDESS | valence | angry-happy | 0.58 | 0.58 |
| activation | angry-sad | 0.73 | 0.75 | |
| eNTERFACE | valence | angry-happy | 0.28 | 0.28 |
| activation | angry-sad | 0.54 | 0.55 | |
| SAVEE | valence | angry-happy | 0.33 | 0.36 |
| activation | angry-sad | 0.52 | 0.51 | |
| VESUS | valence | angry-happy | 0.23 | 0.24 |
| activation | angry-sad | 0.42 | 0.44 | |
| EMOVO | valence | angry-happy | 0.37 | 0.35 |
| activation | angry-sad | 0.88 | 0.90 | |
| JL Corpus | valence | angry-happy | 0.48 | 0.52 |
| activation | angry-sad | 0.77 | 0.82 | |
| TESS | valence | angry-happy | 0.33 | 0.30 |
| activation | angry-sad | 0.62 | 0.67 | |
| GEES | valence | angry-happy | 0.38 | 0.39 |
| activation | angry-sad | 1.02 | 1.06 | |
| Mean distance | valence | angry-happy | 0.375 | 0.380 |
| Mean distance | activation | angry-sad | 0.765 | 0.788 |
| CCC | MAE | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Valence | mean | 0.637 | 0.519 |
| stdev | 0.015 | 0.009 | |
| Activation | mean | 0.763 | 0.385 |
| stdev | 0.010 | 0.009 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trnka, M.; Darjaa, S.; Ritomský, M.; Sabo, R.; Rusko, M.; Schaper, M.; Stelkens-Kobsch, T.H. Mapping Discrete Emotions in the Dimensional Space: An Acoustic Approach. Electronics 2021, 10, 2950. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10232950
Trnka M, Darjaa S, Ritomský M, Sabo R, Rusko M, Schaper M, Stelkens-Kobsch TH. Mapping Discrete Emotions in the Dimensional Space: An Acoustic Approach. Electronics. 2021; 10(23):2950. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10232950
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrnka, Marián, Sakhia Darjaa, Marian Ritomský, Róbert Sabo, Milan Rusko, Meilin Schaper, and Tim H. Stelkens-Kobsch. 2021. "Mapping Discrete Emotions in the Dimensional Space: An Acoustic Approach" Electronics 10, no. 23: 2950. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10232950
APA StyleTrnka, M., Darjaa, S., Ritomský, M., Sabo, R., Rusko, M., Schaper, M., & Stelkens-Kobsch, T. H. (2021). Mapping Discrete Emotions in the Dimensional Space: An Acoustic Approach. Electronics, 10(23), 2950. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10232950






