Chaos-Based Secure Communications in Biomedical Information Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methods
2.1. Chaotic System
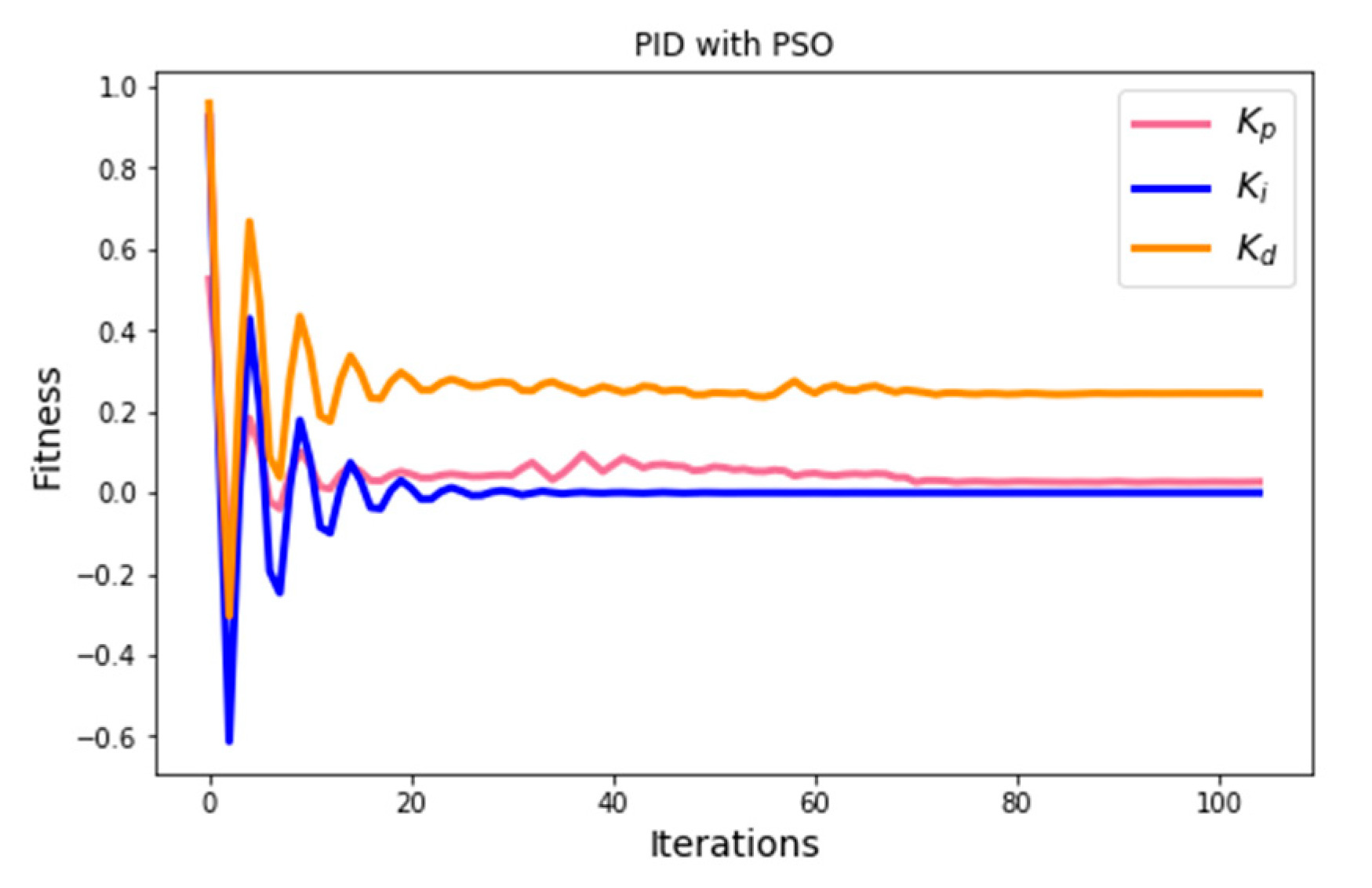
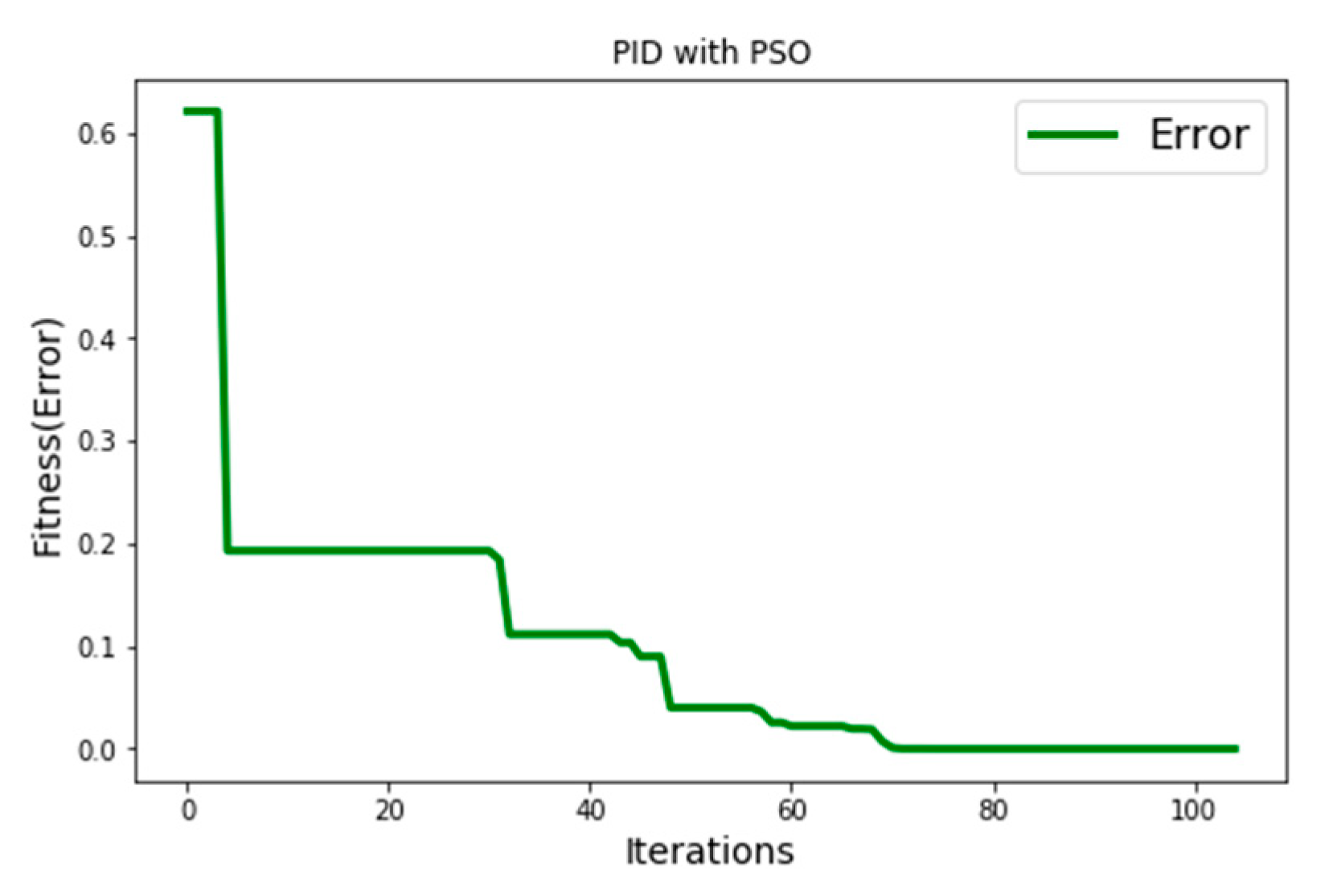
2.2. PD Controller Synchronizing Chaotic Systems
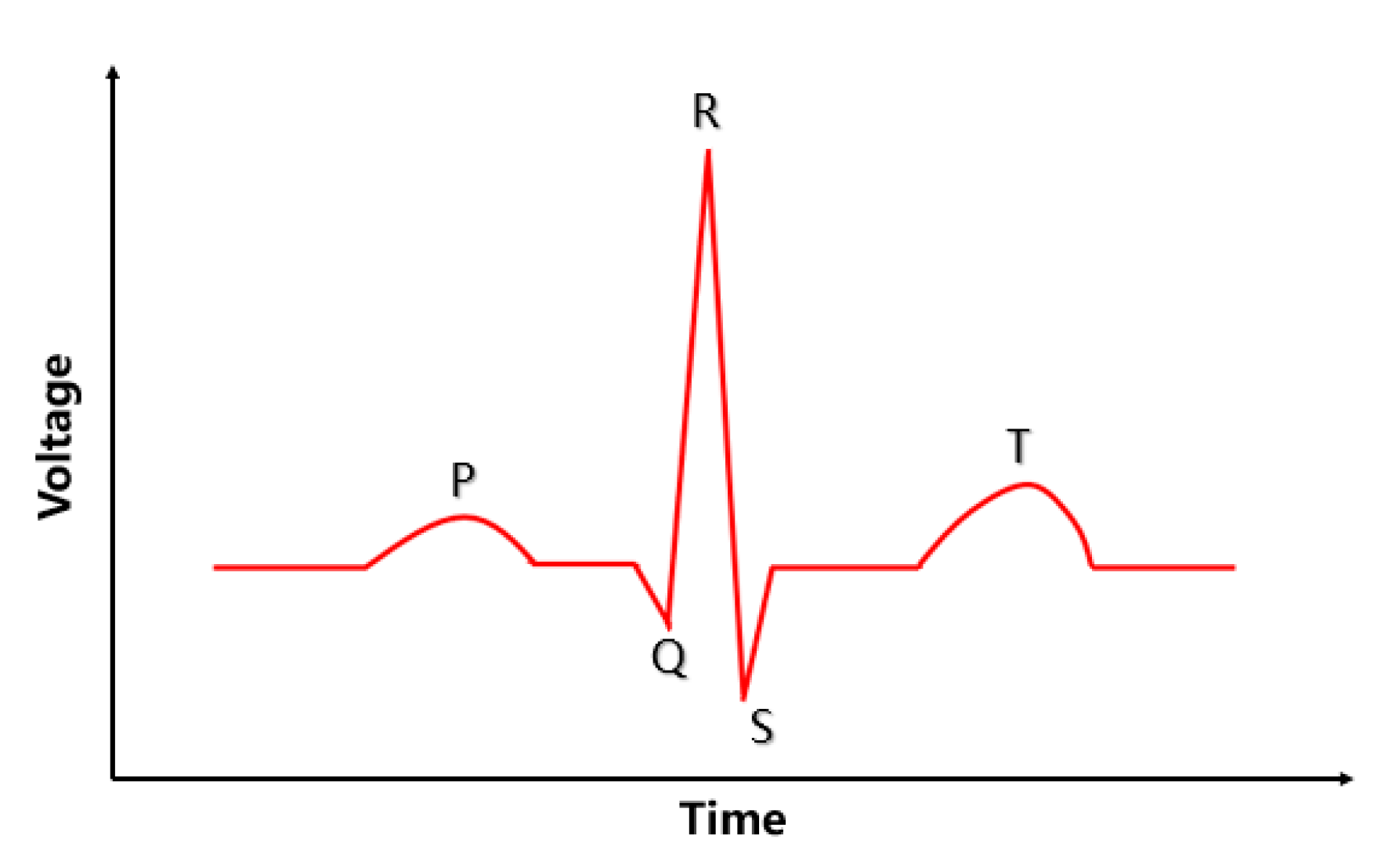
2.3. Biomedical Information
3. Information Security
3.1. Stability of the Chaotic System
3.2. Security of the Chaotic System
3.3. Information Security
4. Architecture of the System and Simulation
4.1. Information Security
4.2. Collection of Biomedical Information
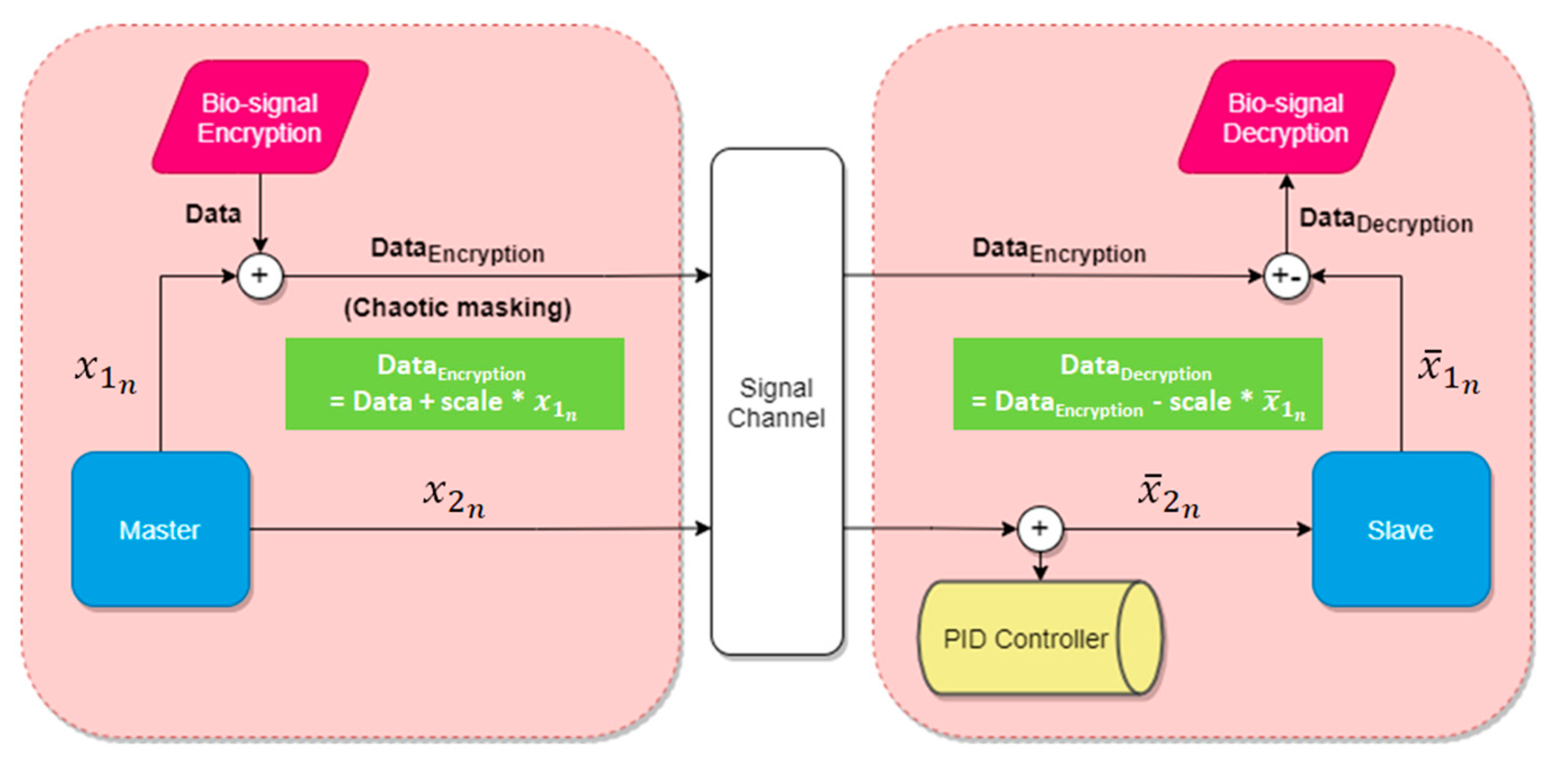
4.3. Encryption and Decryption of the Data
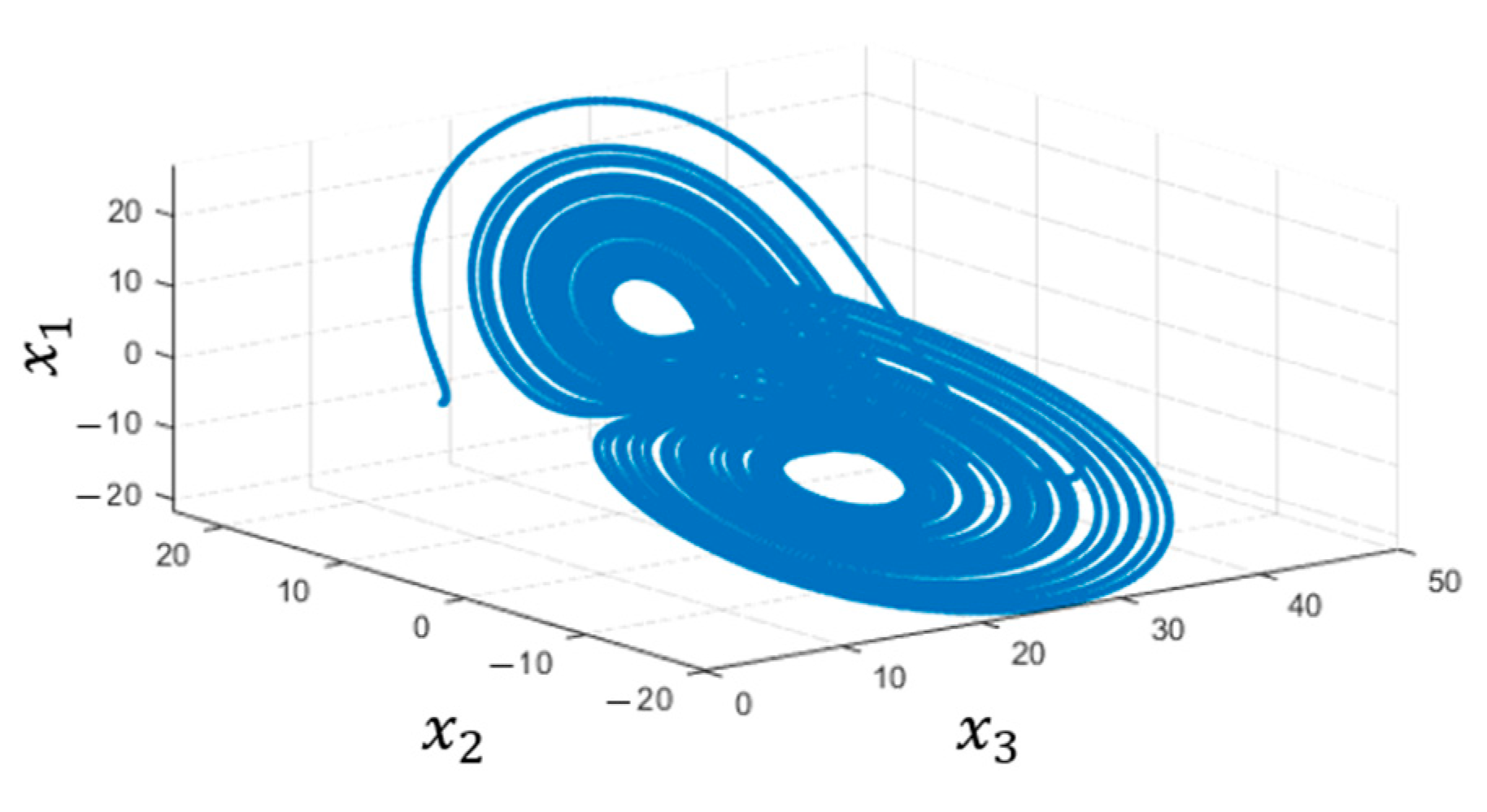
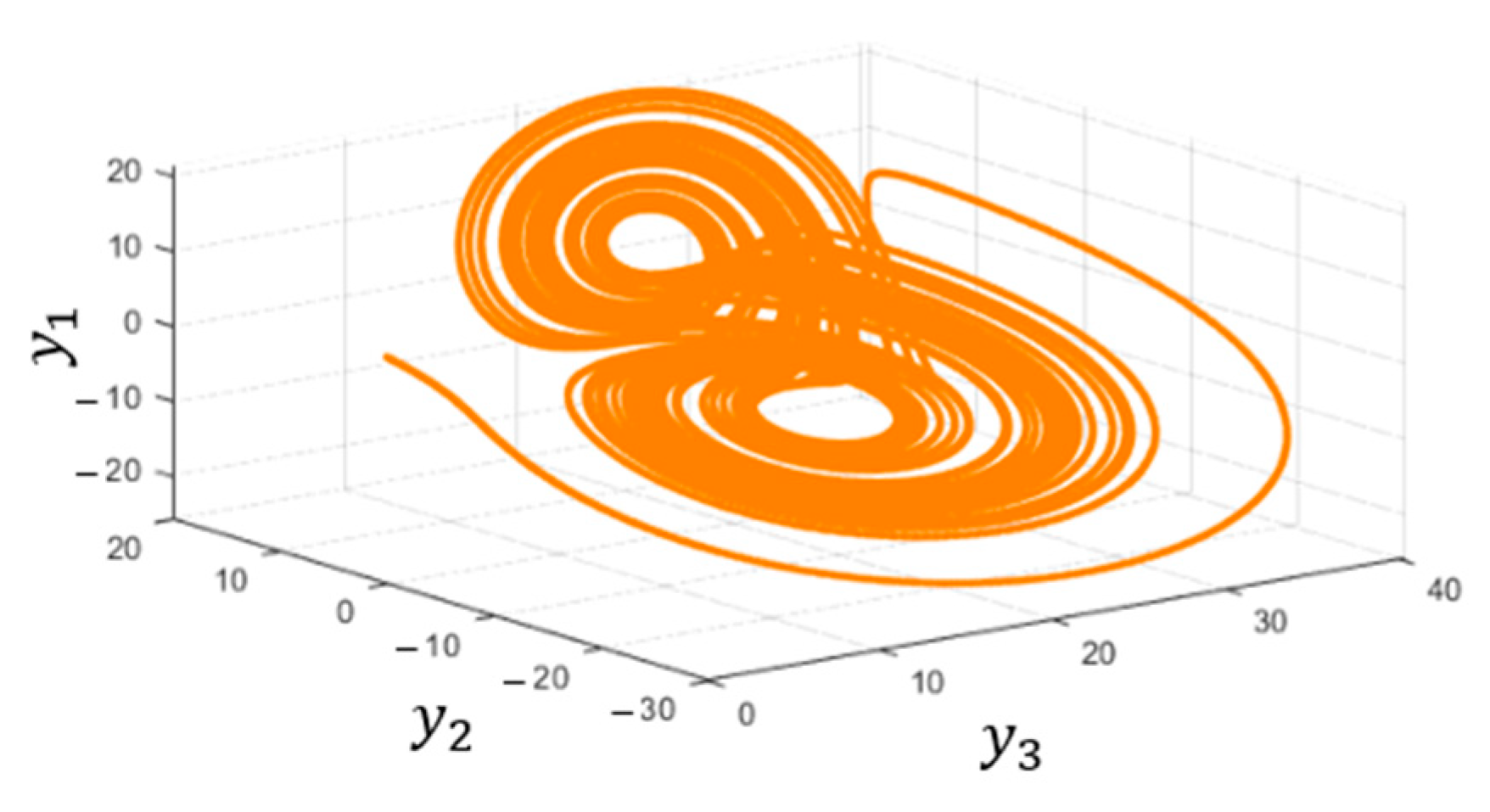
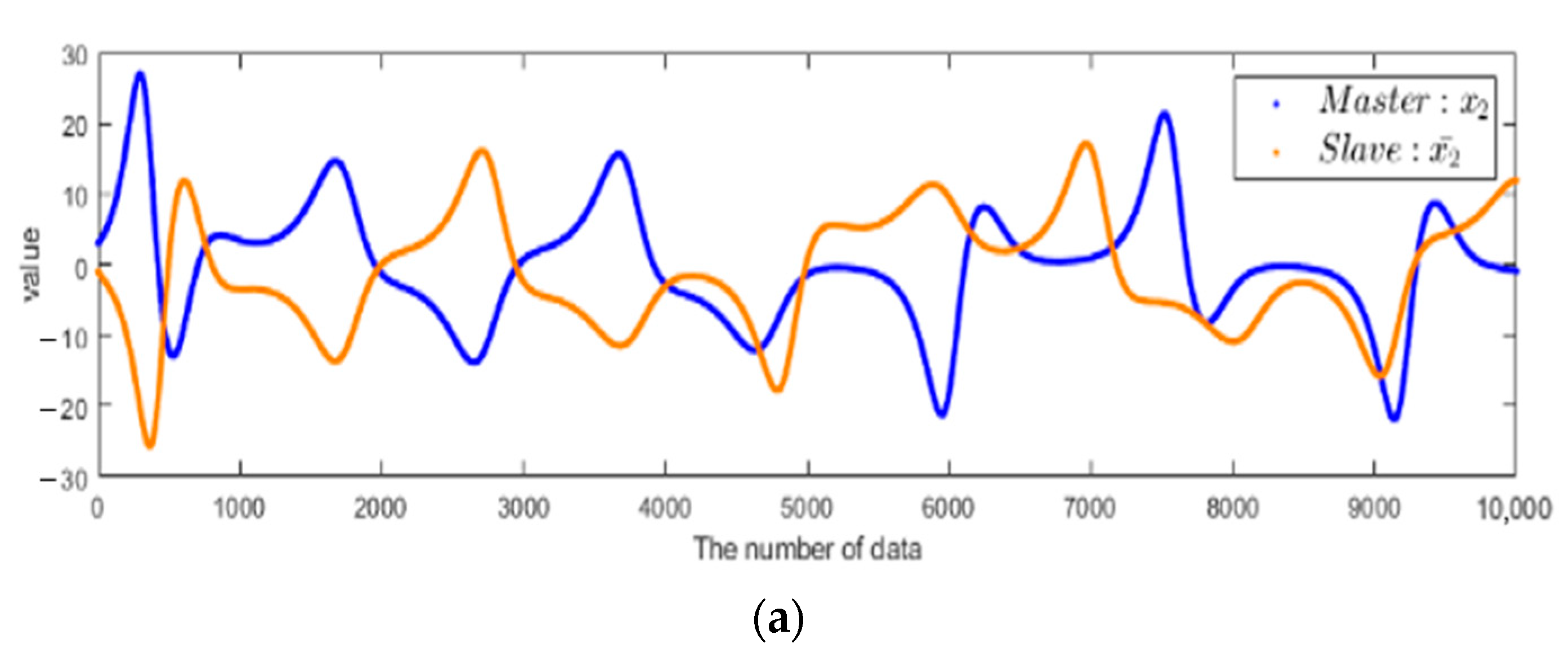
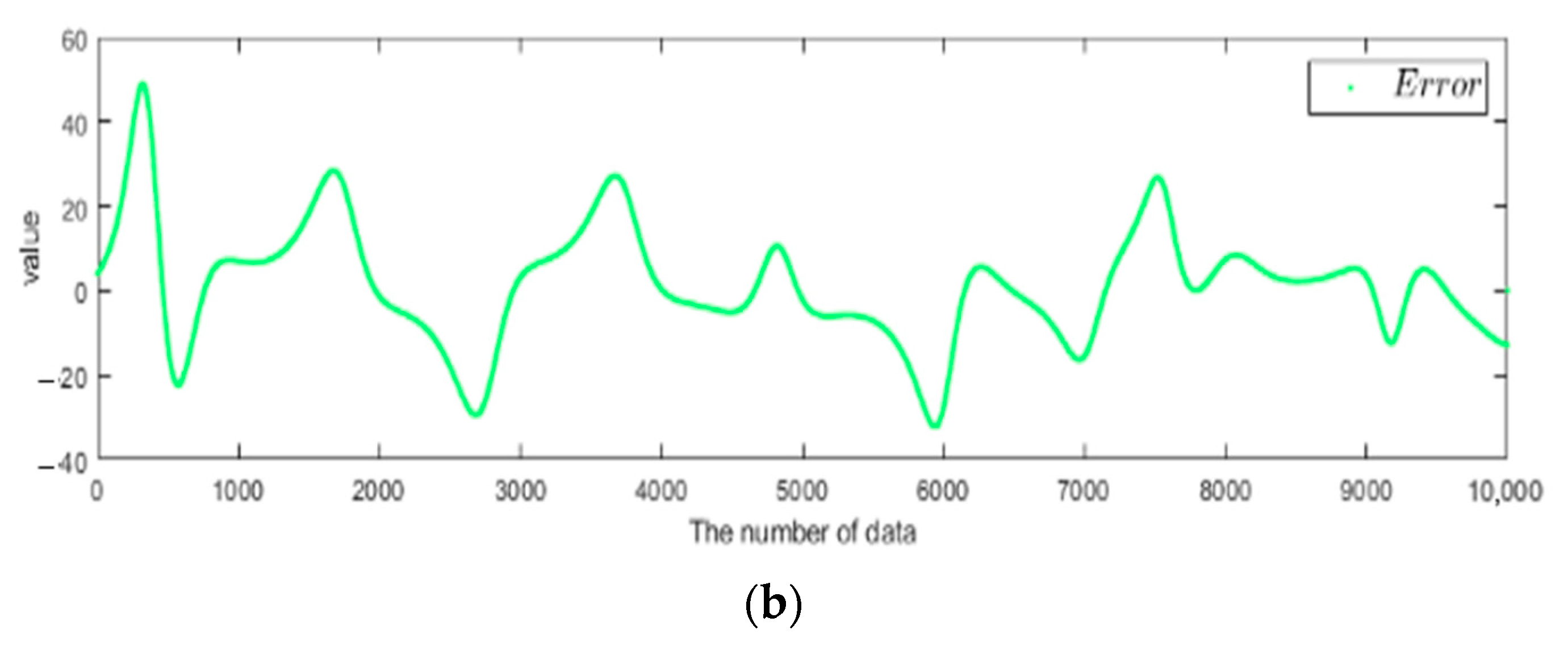
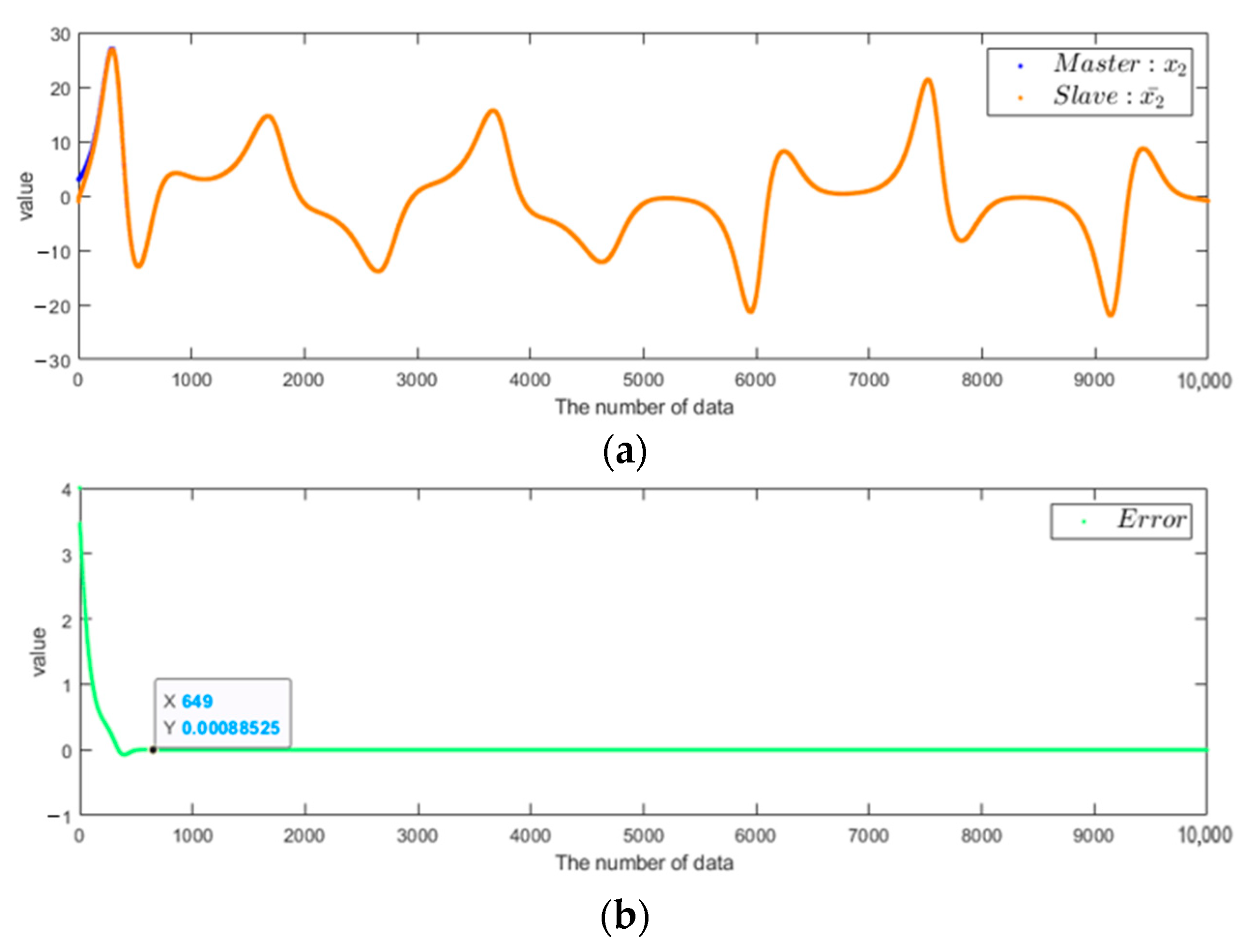
4.4. Simulation and Verification of the Chaotic System
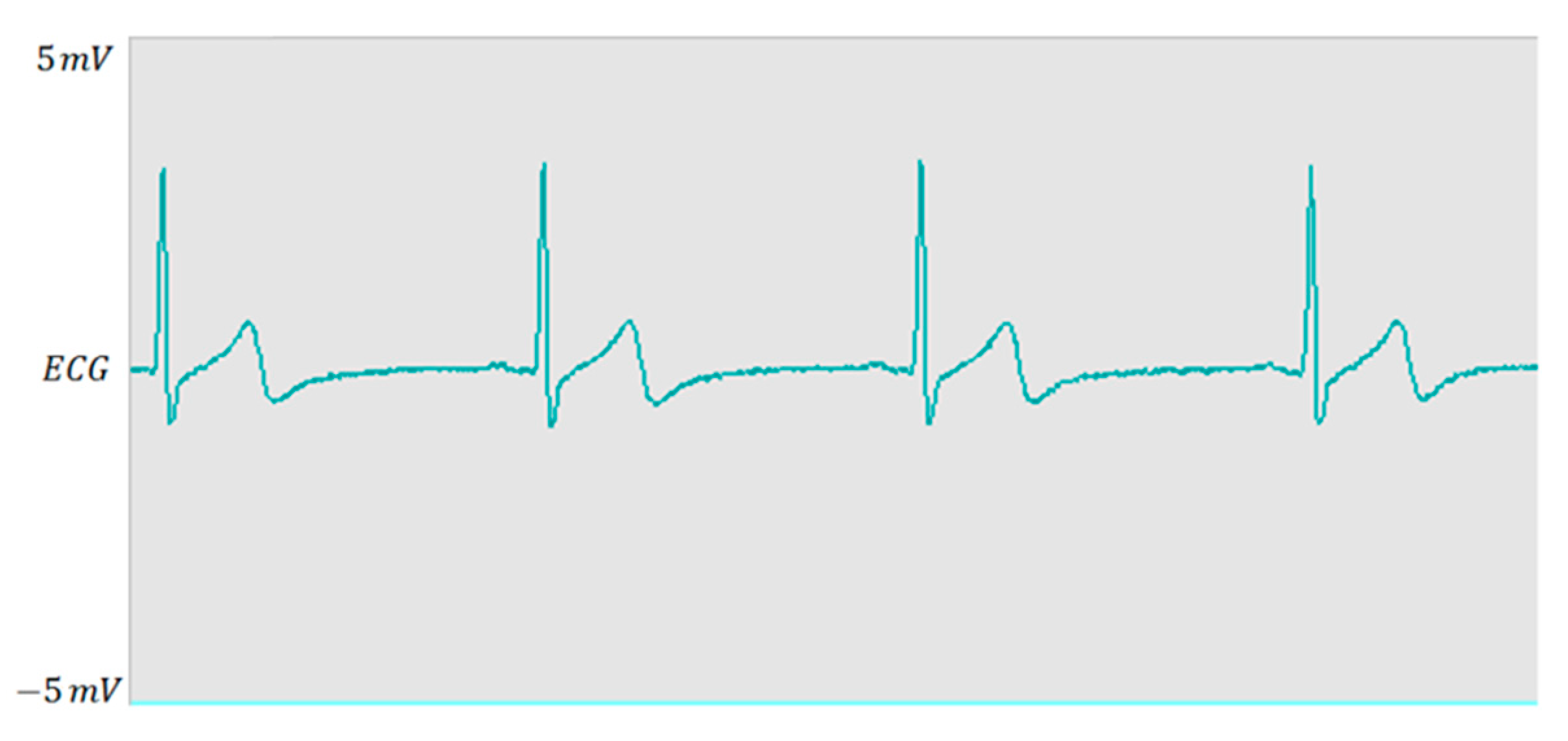
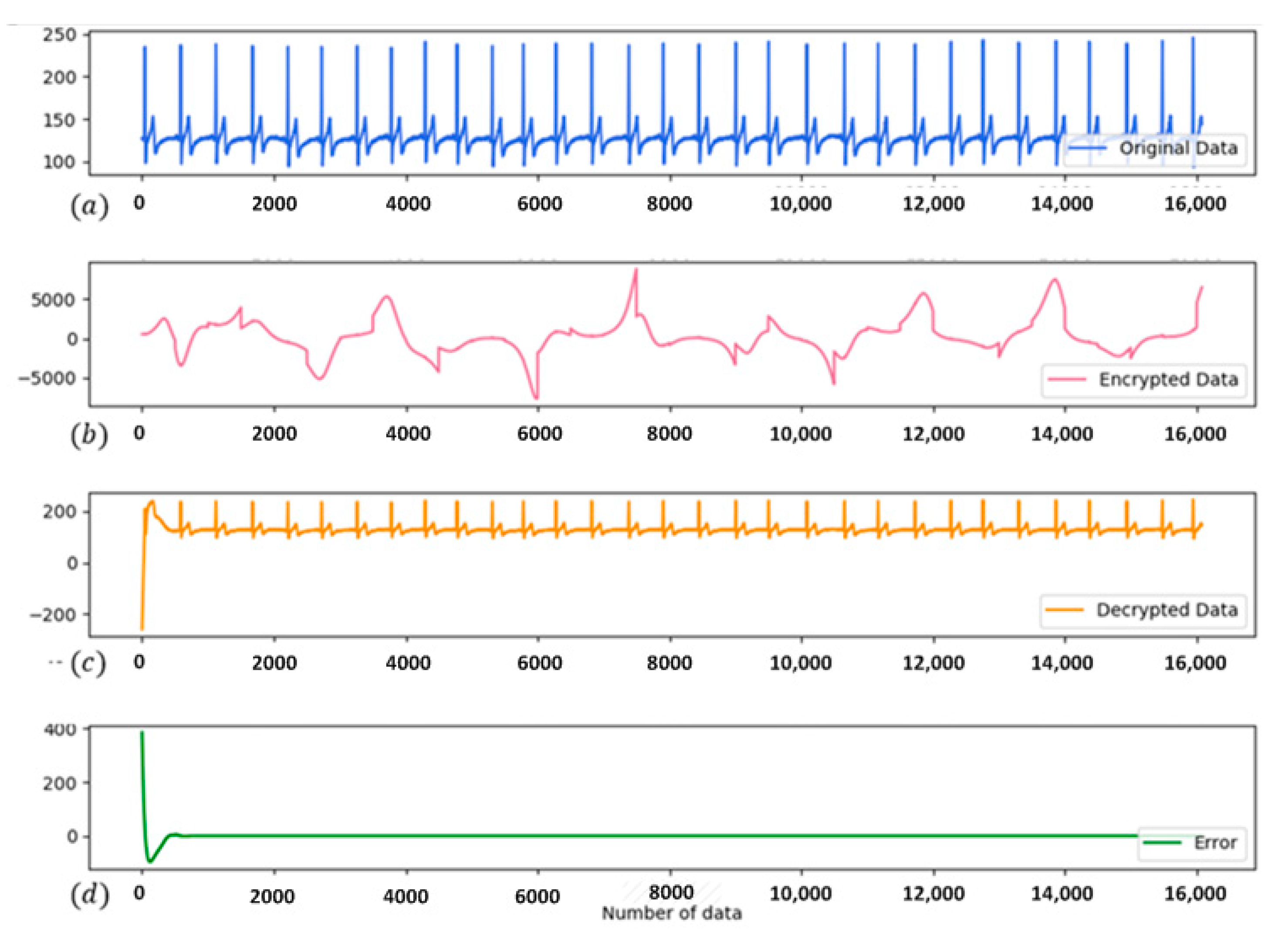
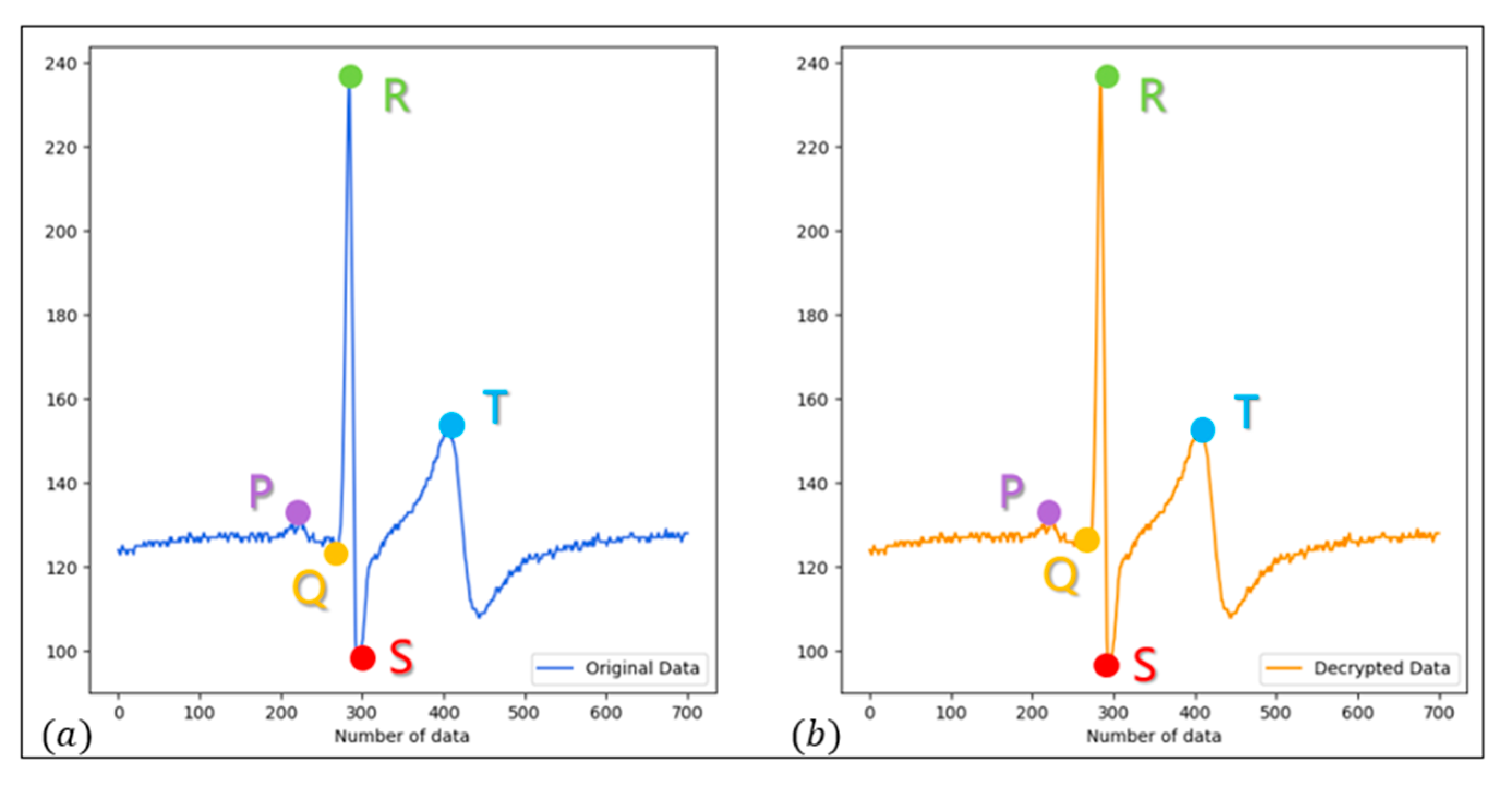
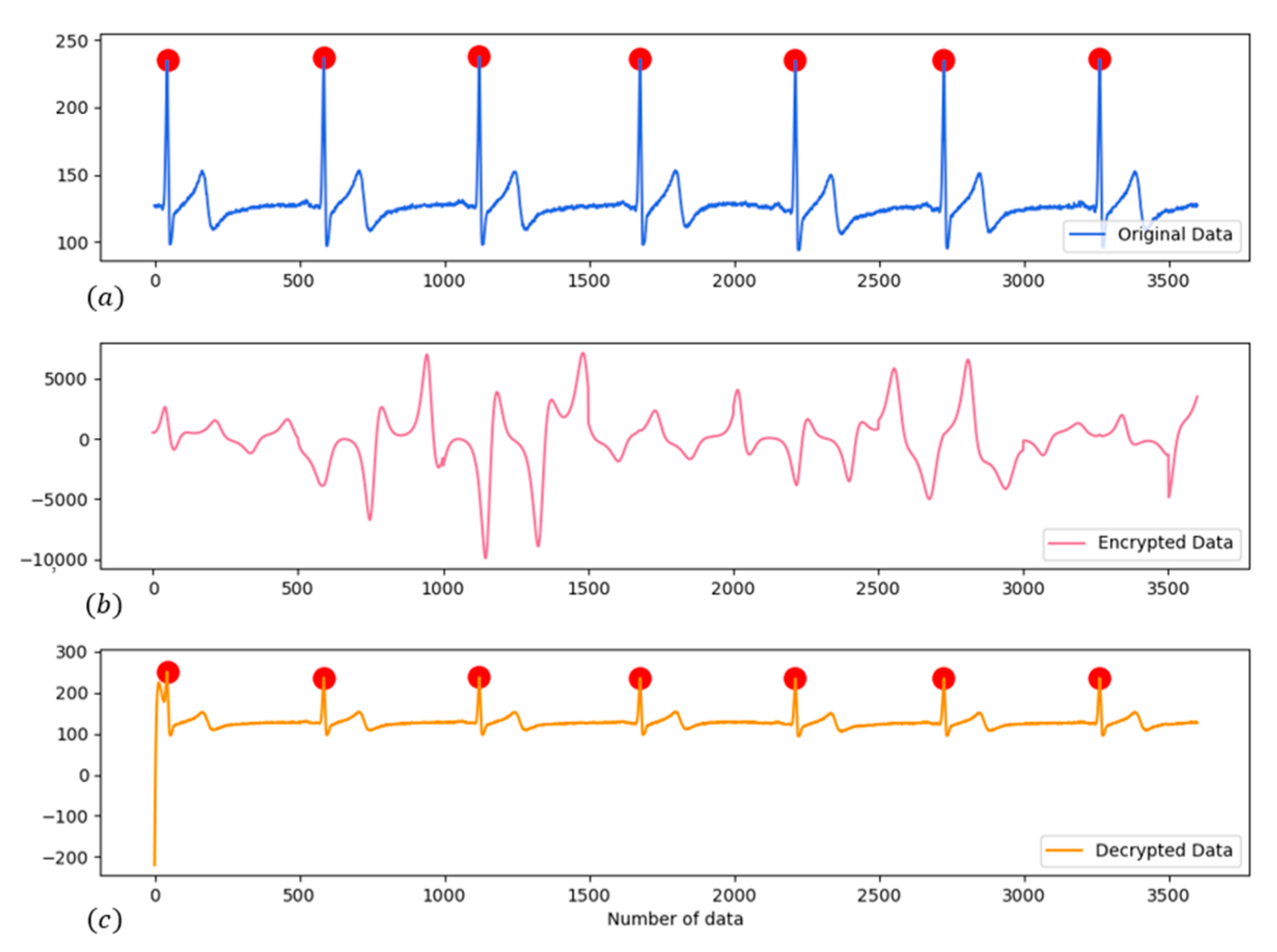
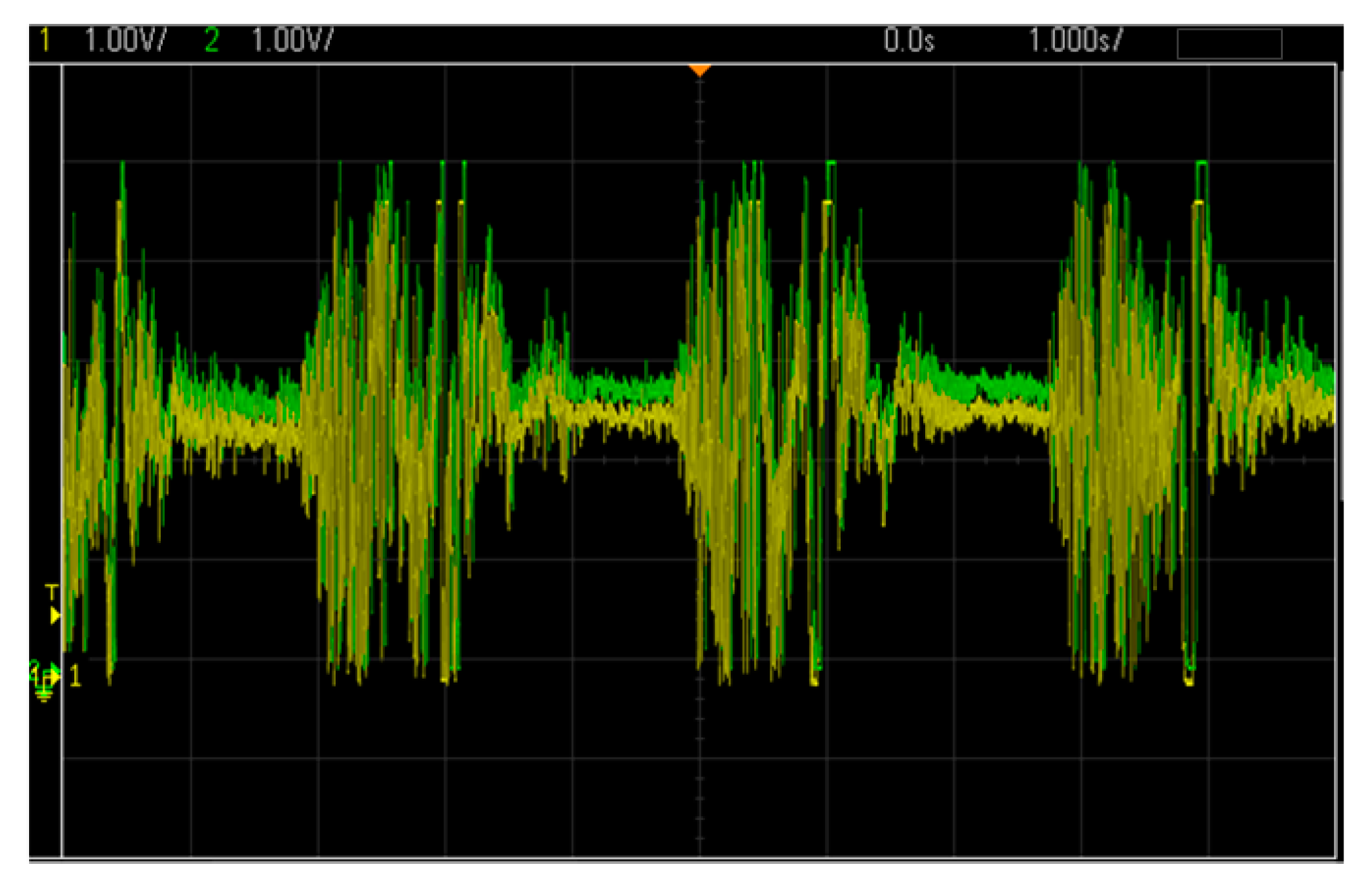
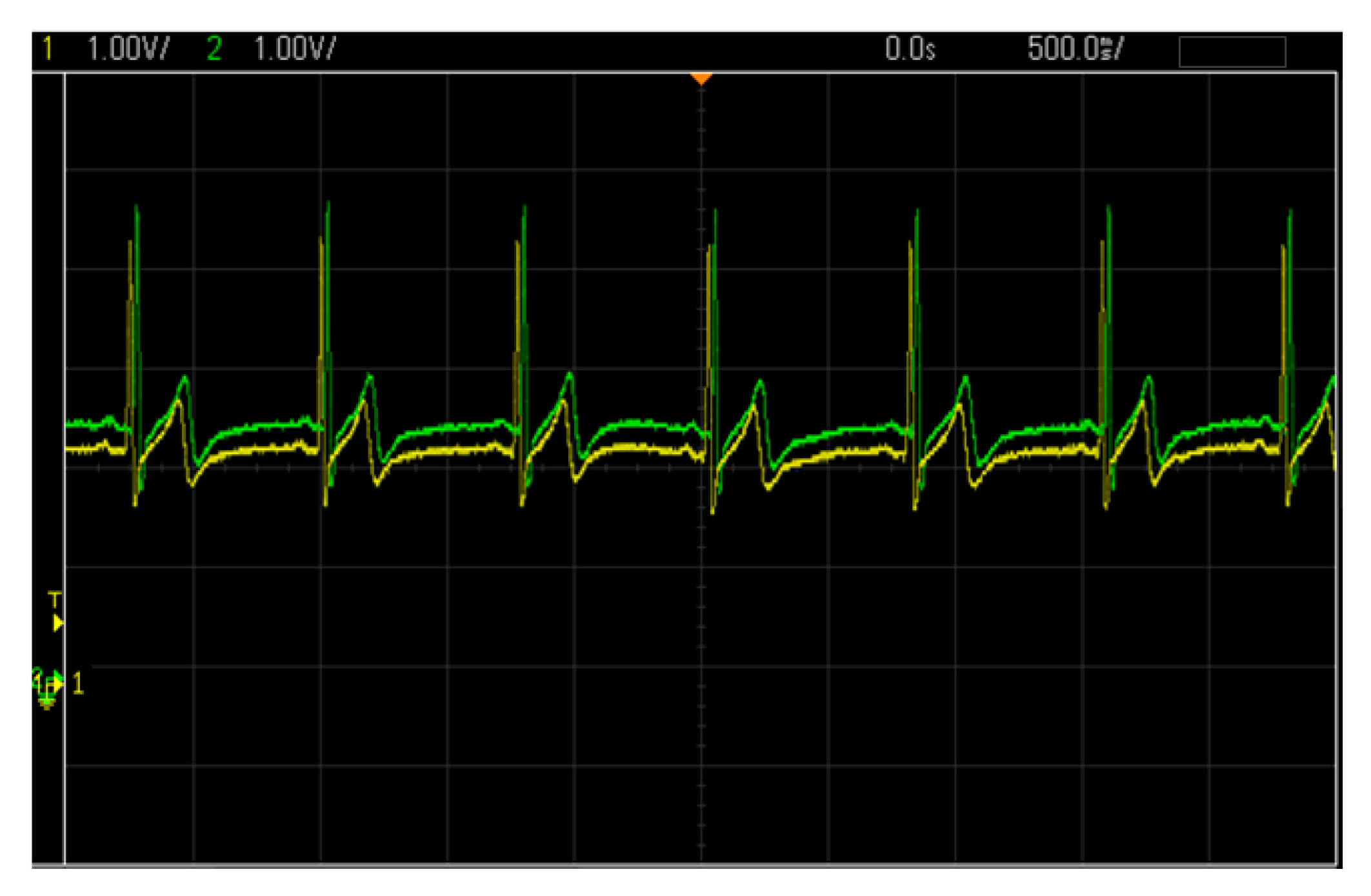
4.5. Simulation and Verification of EMG and ECG
5. Hardware Implementation
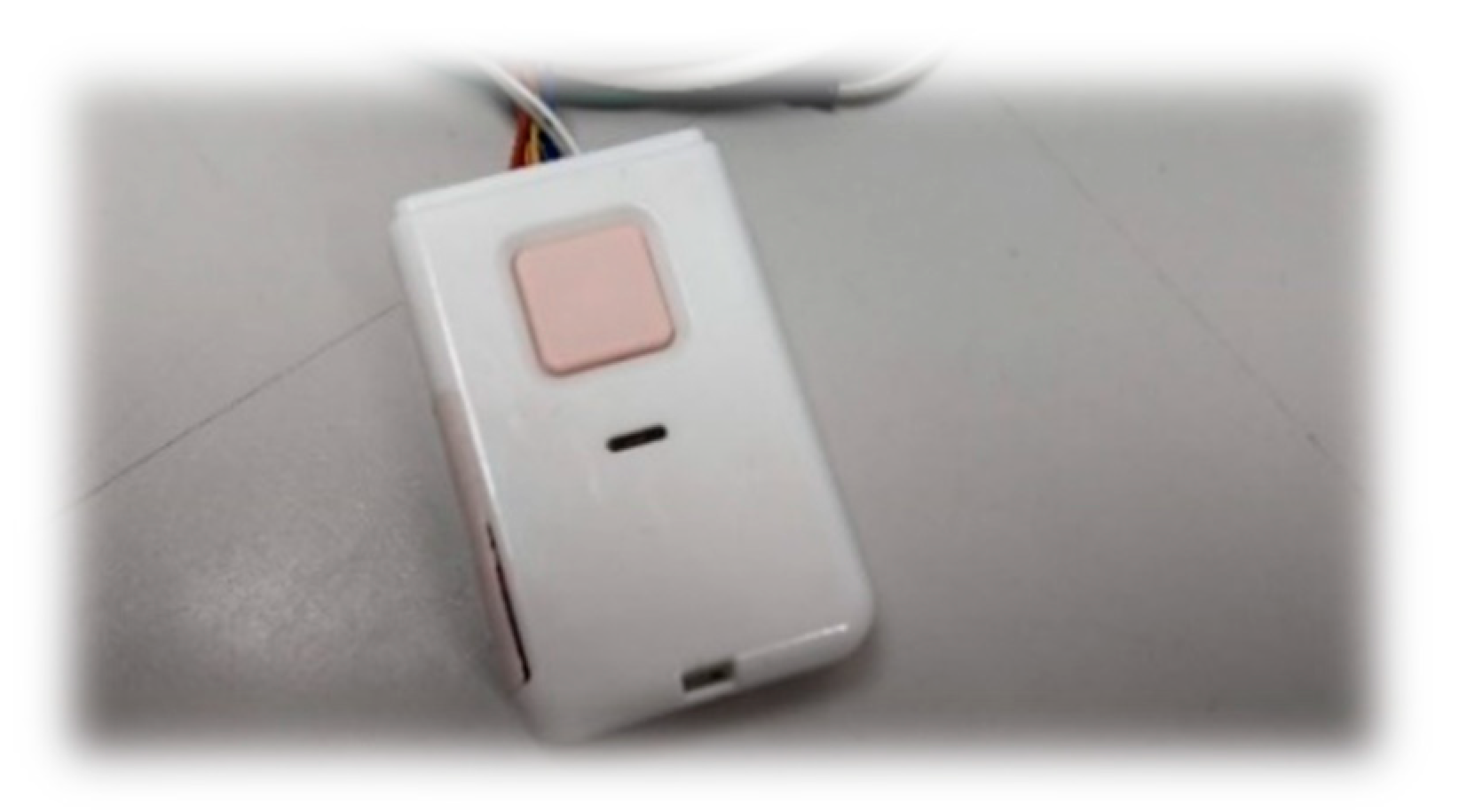
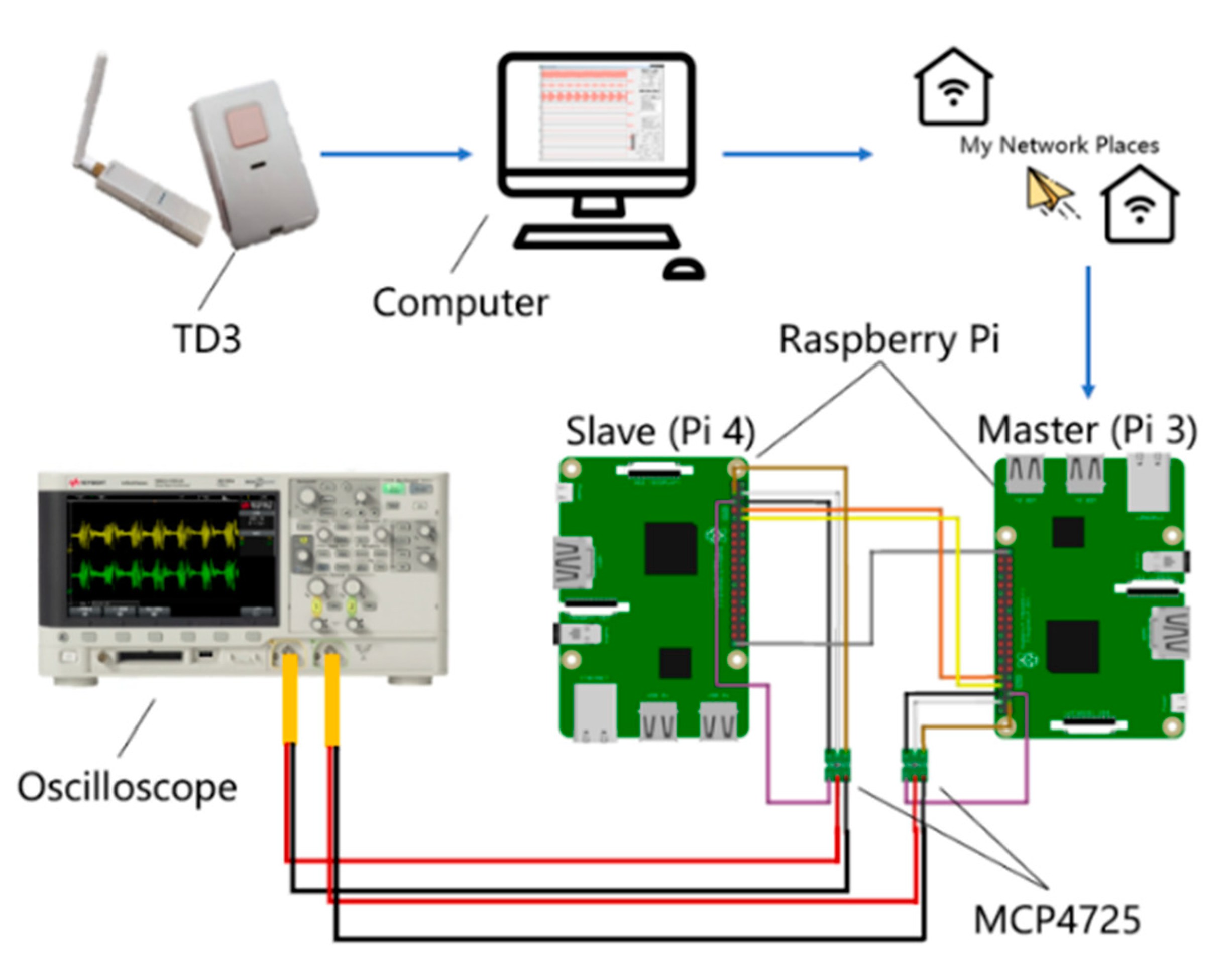
5.1. Implementation with Raspberry Pi
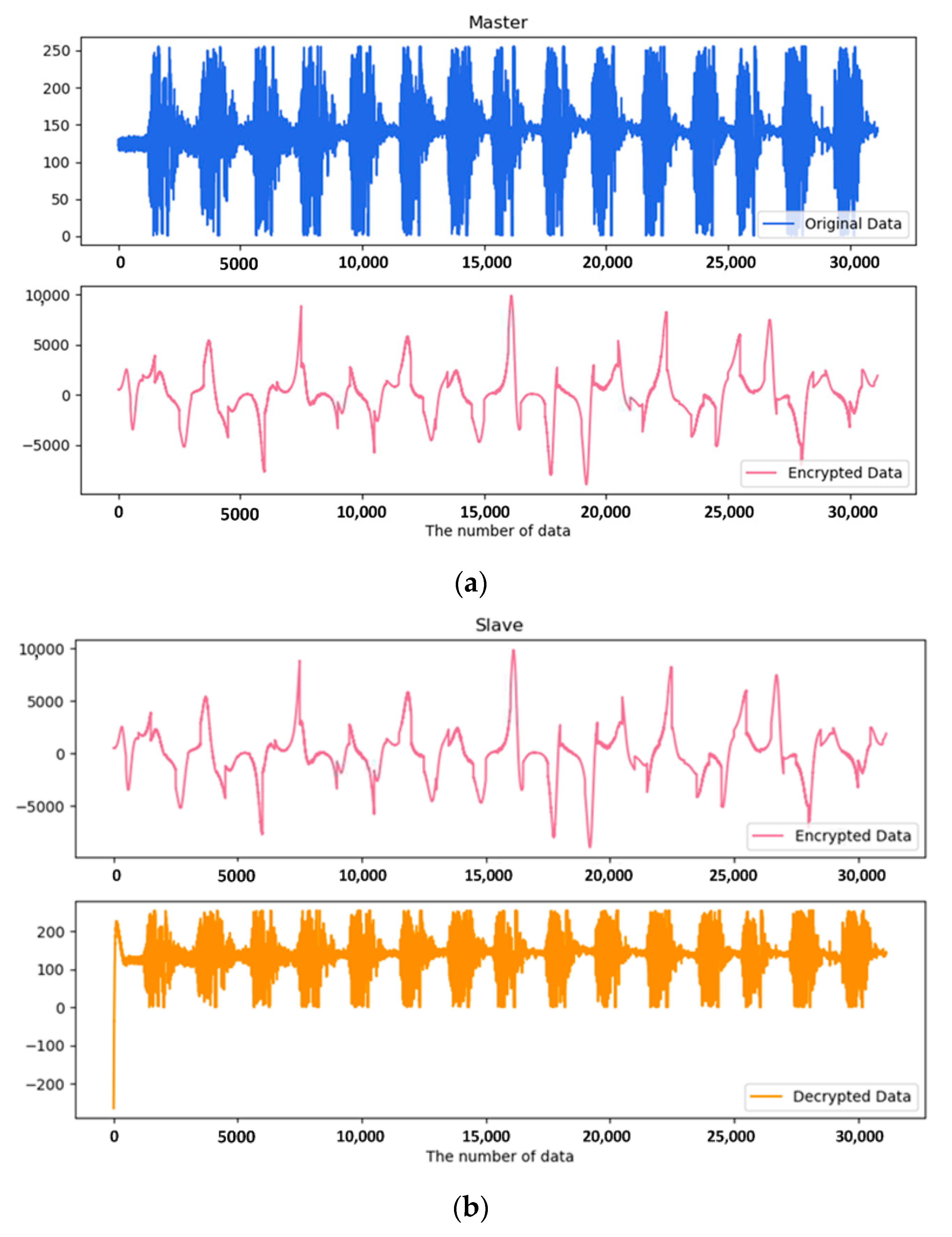
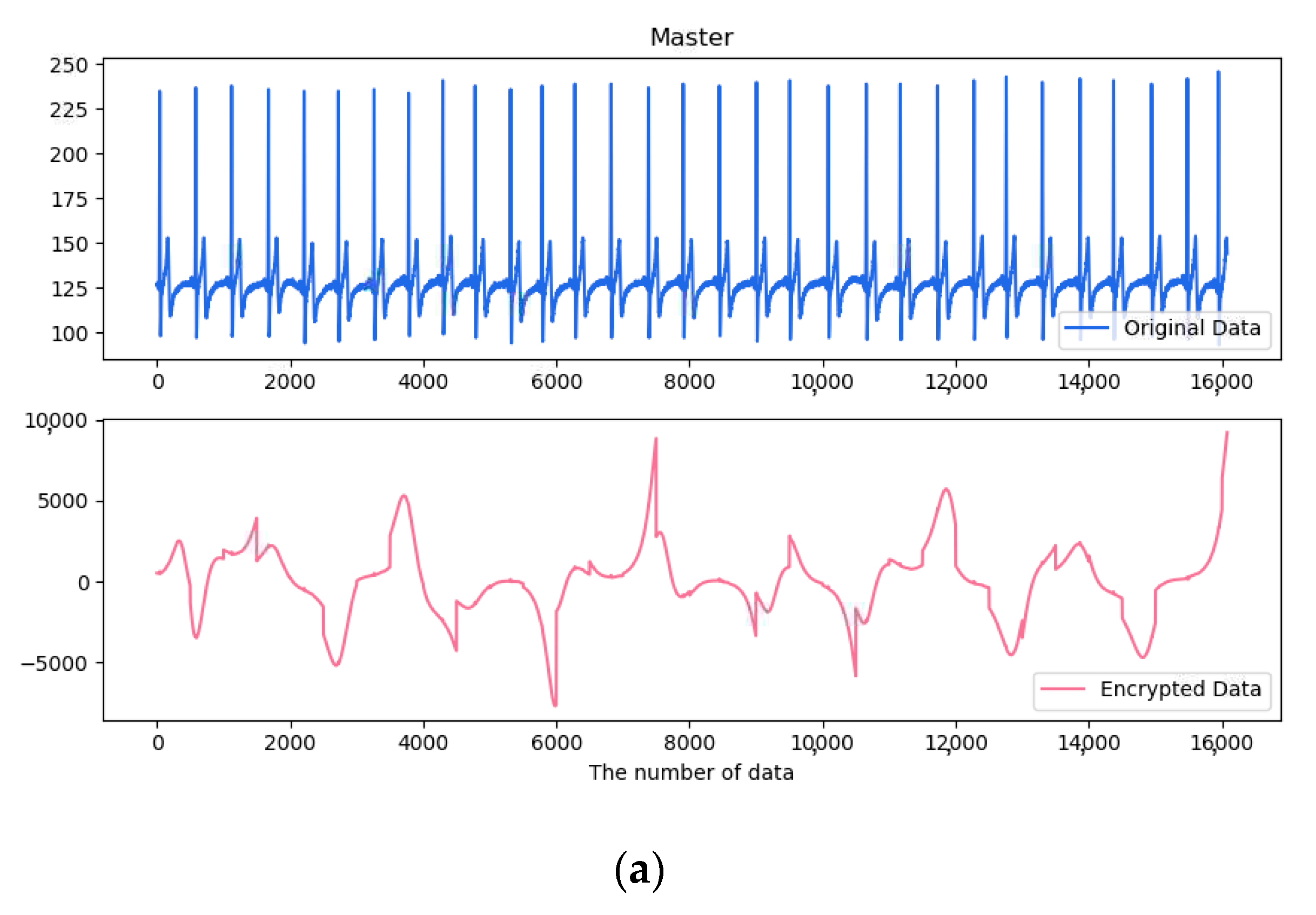
5.2. Result of Implementation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Somani, U.; Lakhani, K.; Mundra, M. Implementing Digital Signature with RSA Encryption Algorithm to Enhance the Data Security of Cloud in Cloud Computing. In Proceedings of the 2010 First International Conference On Parallel, Distributed and Grid Computing (PDGC 2010), Solan, India, 28–30 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, D.S.; Alwan, N.A.; Al-Saidi, N.M.G. Image encryption based on highly sensitive chaotic system. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2183. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.-C.; Chang, G.-F.; Yan, J.-J.; Liao, T.F. EP-based PID control design for chaotic synchronization with application in secure communication. Expert Syst. Appl. 2008, 34, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyghami, S.; Blaabjerg, F. Availab. Modeling in Power Converters Considering Components Aging. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 1981–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Roca, L.; Peterson, J.; Pereira, M.; Cunha, A., Jr. Control of Chaos via OGY Method on a Bistable Energy Harvester. In Proceedings of the 25th ABCM International Congress on Mechanical Engineering (COBEM 2019), Uberlândia, Brazil, 20–25 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pecora, L.M.; Carroll, T.L. Synchronization in chaotic systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1990, 64, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ATaher Azar, A. Sundarapandian Vaidyanathan Advances in Chaos Theory and Intelligent Control; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Liao, X.; Yang, B. Image encryption using 2D Hénon-Sine map and DNA approach. Signal Process. 2018, 153, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, H.; Haas, H. Harnessing Nonlinearity: Predicting Chaotic Systems and Saving Energy in Wireless Communication. Science 2004, 304, 5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.A.; Ahmad, J.; Masood, F.; Shah, S.Y.; Pervaiz, H.; Taylor, W.; Ali Imran, M.; Abbasi, Q.H. Privacy-Preserving Wandering BehaviorSensing in Dementia Patients Using ModifiedLogistic and Dynamic Newton Leipnik Maps. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Qayyum, A.; Ahmad, J.; Boulila, W.; Rubaiee, S.; Arshad; Masood, F.; Khan, F.; Buchanan, W.J. Chaos-Based Confusion and Diffusion of Image Pixels Using Dynamic Substitution. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 140876–140895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdelAty, A.M.; Azar, A.T.; Vaidyanathan, S.; Ouannas, A.; Radwan, A.G. Chapter 14—Applications of Continuous-time Fractional Order Chaotic Systems. In Mathematical Techniques of Fractional Order Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 409–449. [Google Scholar]
- Leonov, G.A.; Kuznetsov, N.V. On differences and similarities in the analysis of Lorenz, Chen, and Lu systems. Appl. Math. Comput. 2015, 256, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, J.C. Particle Swarm Optimization. In Evolutionary and Swarm Intelligence Algorithms, Studies in Computational Intelligence; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 779, pp. 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- AL-Ziarjawey, H.A.J.; Çankaya, I. Heart Rate Monitoring and PQRST Detection Based on Graphical User Interface with Matlab. Int. J. Inf. Electron. Eng. 2015, 5, 311–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukhin, A.; Soto, J.; Nechvatal, J.; Smid, M.; Barker, E.; Leigh, S.; Levenson, M.; Vangel, M.; Banks, D.; Heckert, A.; et al. A Statistical Test Suite for Random and Pseudorandom Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications; Report for National Institute of Standards and Technology; U.S. Department of Commerce: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, September 2010.
- Corinto, F.; Krulikovskyi, O.V.; Haliuk, S.D. Memristor-Based Chaotic Circuit for Pseudo-Random Sequence Generators. In Proceedings of the 2016 18th Mediterranean Electrotechnical Conference (MELECON), Lemesos, Cyprus, 18–20 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, M.; Agarwal, N.; Reddy, S. Design and Development of Daughter Board for USB-UART Communication between Raspberry Pi and PC. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing, Communication & Automation, Noida, India, 15–16 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zirkohia, M.M.; khorashadizadeh, S. Paperchaos synchronization using higher-order adaptive PID controllerMajid. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2018, 94, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Chazal, P.; Reilly, R.B. Automatic Classification of ECG Beats Using Waveform Shape and Heart Beat Interval Features. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP ‘03), Hong Kong, China, 6–10 April 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zade, M.C. Control the Chaotic Rikitake System by PID Controller. SSRG Int. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. (SSRG-IJEEE) 2015, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar]










| NIST Test | p-Value |
|---|---|
| Frequency (Monobit) | 0.082918 |
| Frequency within a Block | 0.757670 |
| Runs | 0.370782 |
| Longest Run of Ones in a Block | 0.225761 |
| Binary Matrix Rank | 0.555467 |
| Discrete Fourier Transform (Spectral) | 0.897775 |
| Non-overlapping Template Matching | 0.484386 |
| Overlapping Template Matching | 0.260229 |
| Universal Statistical | 0.881887 |
| Linear Complexity | 0.518763 |
| Serial | 0.725205 |
| Approximate Entropy | 0.626338 |
| Cumulative Sums (Cusum) | 0.104932 |
| Random Excursions | 0.416972 |
| Random Excursions Variant | 0.552373 |
| SUM | 0.497431 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, T.-L.; Chen, H.-C.; Peng, C.-Y.; Hou, Y.-Y. Chaos-Based Secure Communications in Biomedical Information Application. Electronics 2021, 10, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10030359
Liao T-L, Chen H-C, Peng C-Y, Hou Y-Y. Chaos-Based Secure Communications in Biomedical Information Application. Electronics. 2021; 10(3):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10030359
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Teh-Lu, Hsin-Chieh Chen, Chiau-Yuan Peng, and Yi-You Hou. 2021. "Chaos-Based Secure Communications in Biomedical Information Application" Electronics 10, no. 3: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10030359
APA StyleLiao, T.-L., Chen, H.-C., Peng, C.-Y., & Hou, Y.-Y. (2021). Chaos-Based Secure Communications in Biomedical Information Application. Electronics, 10(3), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10030359







