Multi-Level Switching of Al-Doped HfO2 RRAM with a Single Voltage Amplitude Set Pulse
Abstract
:1. Introduction
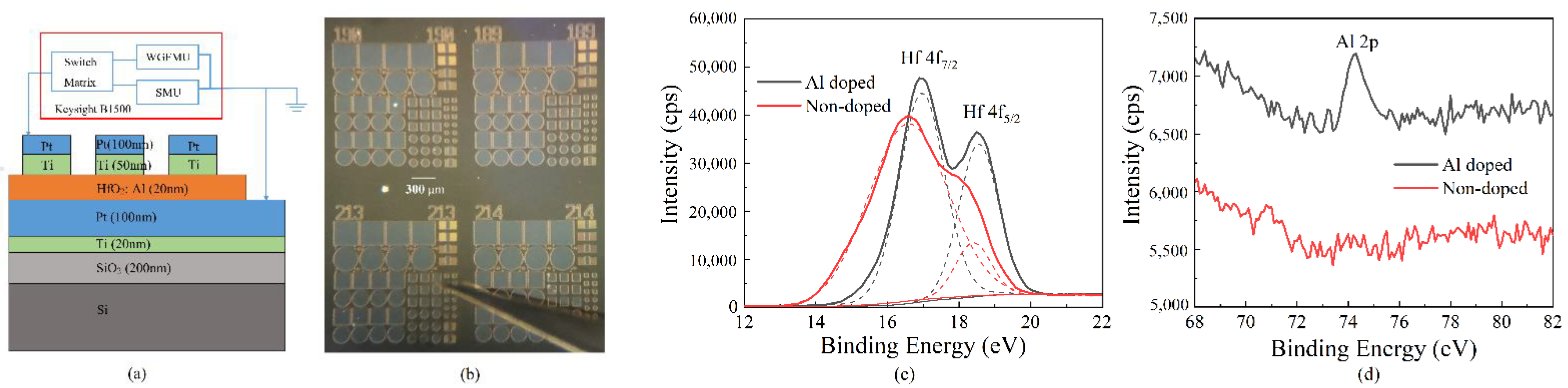
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
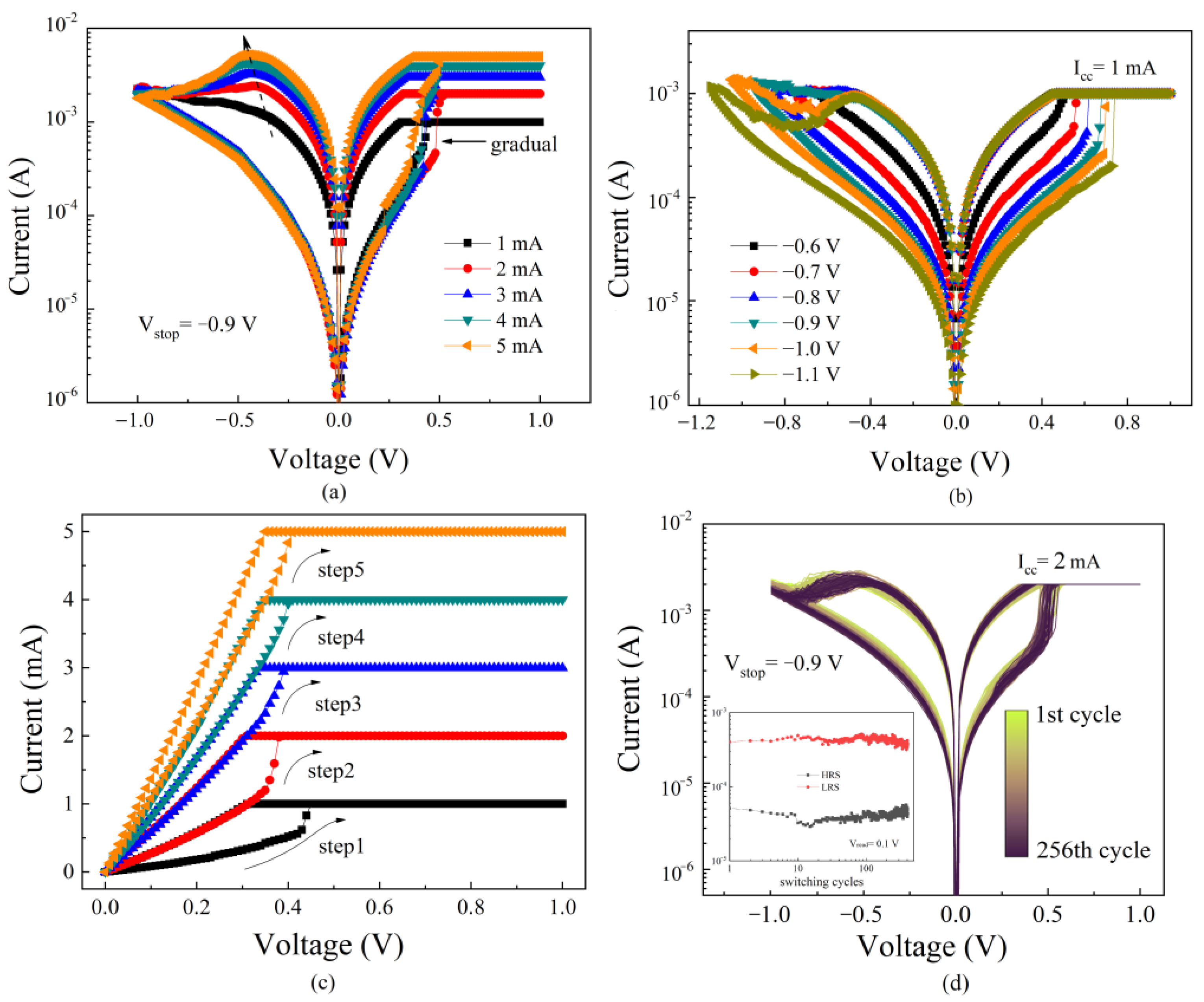
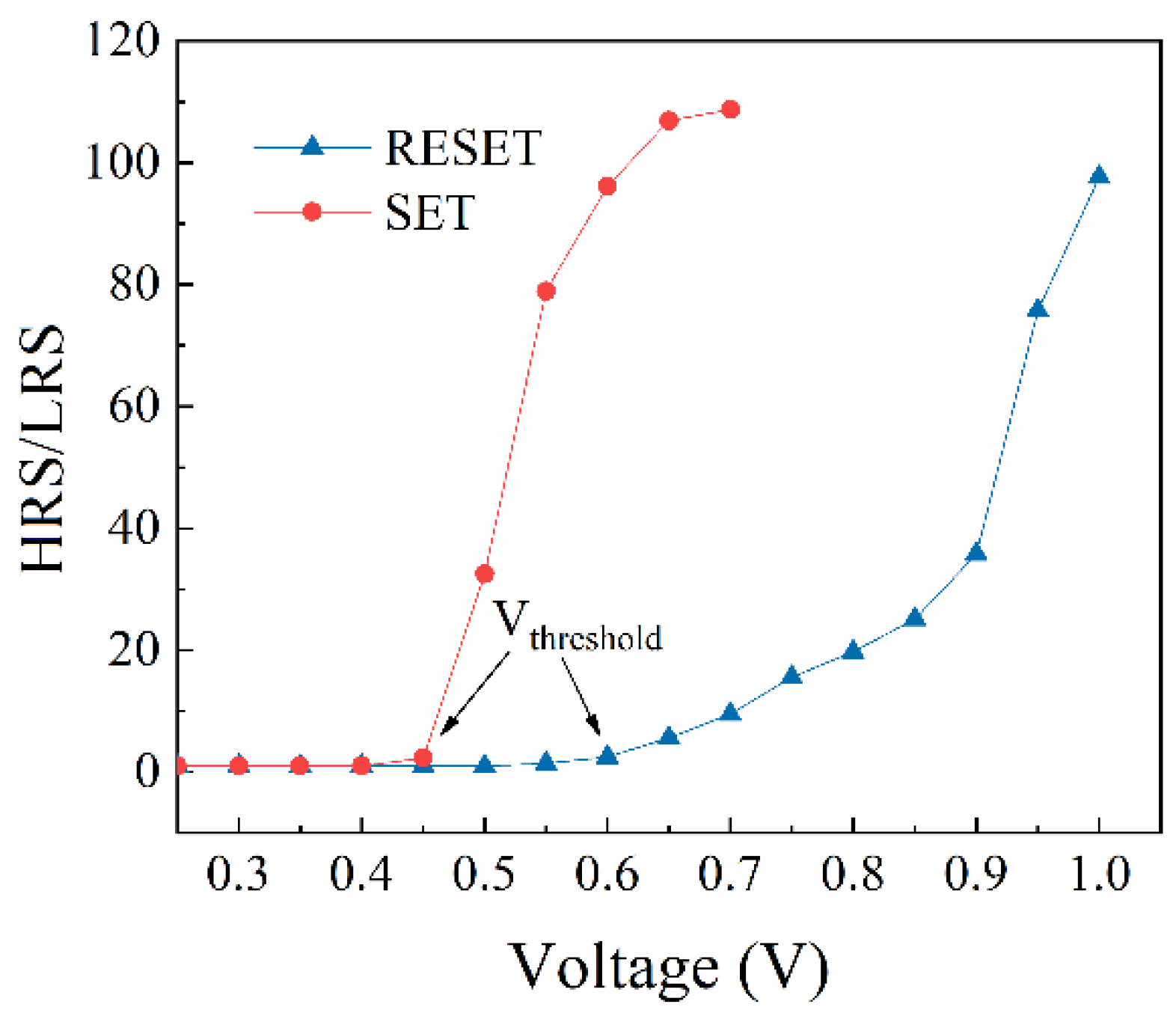
3.1. Direct-Current Characteristics
3.2. Pulse Characteristic
3.3. Multi-Level Switching
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beck, A.; Bednorz, J.G.; Gerber, C.; Rossel, C.; Widmer, D. Reproducible switching effect in thin oxide films for memory applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 77, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatiev, A.; Wu, N.J.; Liu, S.Q.; Chen, X.; Nian, Y.B.; Papaginanni, C.; Strozier, J.; Xing, Z.W. Resistance Switching Memory Effect in Transition Metal Oxide Thin Films. In Proceedings of the 7th Annual Non-Volatile Memory Technology Symposium, San Mateo, CA, USA, 5–8 November 2006; pp. 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, I.G.; Lee, M.S.; Seo, S.; Lee, M.J.; Seo, D.H.; Suh, D.S. Highly Scalable Nonvolatile Resistive Memory Using Simple Binary Oxide Driven by Asymmetric Unipolar Voltage Pulses. In Proceedings of the IEDM Technical Digest. IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–15 December 2004; pp. 587–590. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Long, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Zuo, Q.; Yang, J. Investigation of resistive switching in Cu-doped HfO2 thin film for multilevel non-volatile memory applications. Nanotechnology 2009, 21, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Chen, P.S.; Wu, T.Y.; Chen, Y.S.; Wang, C.C.; Tzeng, P.J. Low Power and High-Speed Bipolar Switching with a Thin Reactive Ti Buffer Layer in Robust HfO2 Based RRAM. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–17 December 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.J.; Wang, J.B.; Zhong, X.L. Electrically-controlled nonlinear switching and multi-level storage characteristics in WOx film-based memory cells. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 116, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.X.; Li, Y.; Su, Y.T.; Wang, Z.R.; Shih, L.Y.; Chang, T.-C.; Chang, K.-C.; Long, S.-B.; Sze, S.M.; Miao, X.-S. Nonvolatile reconfigurable sequential logic in a HfO2 resistive random-access memory array. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 6649–6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.S.; Kim, G.H.; Kwak, K.; Jeong, D.S.; Ju, H. Enhanced Reconfigurable Physical Unclonable Function Based on Stochastic Nature of Multilevel Cell RRAM. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2019, 66, 1717–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.L.; Loy, J.J.; Dananjaya, P.A.; Tan, F.; Ng, C.M.; Lew, W.S. Oxide-based RRAM materials for neuromorphic computing. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 8720–8746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Fang, Y.C.; Yu, Z.Z.; Wang, Z.W.; Zhang, T.; Yin, M.H.; Lin, M.; Yang, Y.C.; Cai, Y.M.; Huang, R. Nonassociative learning implementation by a single memristor-based multi-terminal synaptic device. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 18897–18904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Gao, B.; Fang, Z.; Yu, H.Y.; Kang, J.F.; Wong, H.S.P. Stochastic learning in oxide binary synaptic device for neuromorphic computing. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Zhong, Y.P.; Zhang, J.J.; Xu, L.; Wang, Q.; Sun, H.J.; Tong, H.; Cheng, X.M.; Miao, X.S. Activity-Dependent Synaptic Plasticity of a Chalcogenide Electronic Synapse for Neuromorphic Systems. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jo, S.H.; Chang, T.; Ebong, I.; Bhadviya, B.B.; Mazumder, P.; Lu, W. Nanoscale Memristor Device as Synapse in Neuromorphic Systems. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1297–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yu, S.; Wong, H.S.P.; Chen, Y.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Wang, S.M.; Gu, P.Y.; Chen, F.; Tsai, M.J. AlOx-Based Resistive Switching Device with Gradual Resistance Modulation for Neuromorphic Device Application. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE International Memory Workshop, Milan, Italy, 20–23 May 2012; p. 12803543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzum, D.; Yu, S.; Wong, H.S.P. Synaptic electronics: Materials, devices and applications. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Jung, S.H.; Kim, M.H.; Cho, S.; Park, B.G. Gradual bipolar resistive switching in Ni/Si3N4/n+-Si resistive-switching memory device for high-density integration and low-power applications. Solid-State Electron. 2015, 114, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, M.M.; Wilk, G.D.; Starodub, D.; Gustafsson, T.; Garfunkel, E.; Chabal, Y.J.; Grazul, J.; Muller, D.A. HfO2 and Al2O3 gate dielectrics on GaAs grown by atomic layer deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 152904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Tang, C.; Fonseca, L.R.C.; Ramprasad, R. Recent progress in ab initio simulations of hafnia-based gate stacks. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 7399–7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Niu, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.K.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wu, H.P.; Zhai, S.J.; Shi, P.; Song, S.; Song, Z.T.; et al. Toward a Reliable Synaptic Simulation Using Al-Doped HfO2 RRAM. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 10648–10656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covi, E.; Brivio, S.; Fanciulli, M.; Spiga, S. Synaptic potentiation and depression in Al: HfO2-based memristor. Microelectron. Eng. 2015, 147, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Chen, B.; Gao, B.; Lun, Z.Y.; Xin, Z.; Liu, R.; Liu, L.F.; Han, D.D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.Y.; et al. Self-Compliance Multilevel Resistive Switching Characteristics in TiN/HfOx/Al/Pt RRAM Devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference of Electron Devices and Solid-state Circuits, Hong Kong, China, 2–5 June 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yan, X. Overview of resistive random-access memory (rram): Materials, filament mechanisms, performance optimization, and prospects. Rapid Res. Lett. 2019, 13, 1900073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. A Multi-level Memristor Based on Al-Doped HfO2 Thin Film. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Traore, B.; Blaise, P.; Sklenard, B.; Vianello, E.; Magyari-Kope, B.; Nishi, Y. HfO₂/Ti interface mediated conductive filament formation in RRAM: An Ab Initio Study. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2018, 65, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Chen, B.; Zhang, F.F.; Liu, L.F.; Liu, X.Y.; Kang, J.F.; Yu, H.Y.; Yu, B. A Novel Defect-Engineering-Based Implementation for High-Performance Multilevel Data Storage in Resistive Switching Memory. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2013, 60, 1379–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, C.; Shen, W.; Dong, Z.; Chen, Z.; Huang, P.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Kang, J. The Characteristics of Binary Spike-Time Dependent Plasticity in HfO2-Based RRAM and Applications for Pattern Recognition. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woo, J.; Moon, K.; Song, J.; Lee, S.; Kwak, M.; Park, J.; Hwang, H. Improved Synaptic Behavior under Identical Pulses using AlOx/HfO2 Bilayer RRAM Array for Neuromorphic Systems. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2016, 37, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamgir, Z.; Beckmann, K.; Holt, J.; Cady, N.C. Pulse width and height modulation for multi-level resistance in bi-layer TaOx based RRAM. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 063111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, P.K.; Prajapat, M.; Barman, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Roy, A. Multilevel resistance state of Cu/La2O3/Pt forming-free switching devices. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 4411–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, F.; Larentis, S.; Balatti, S.; Gilmer, D.C.; Ielmini, D. Resistive Switching by Voltage-Driven Ion Migration in Bipolar RRAM—Part I: Experimental Study. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2012, 59, 2461–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, H.Y.; Wu, S.C.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, S.; Hou, T.H.; Wong, H.S.P.; Nishi, Y. Multi-level control of conductive nano-filament evolution in HfO2 ReRAM by pulse-train operations. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 5698–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cianci, E.; Molle, A.; Lamperti, A.; Wiemer, C.; Spiga, S.; Fanciulli, M. Phase Stabilization of Al:HfO2 Grown on InxGa1–xAs Substrates (x = 0, 0.15, 0.53) via Trimethylaluminum-Based Atomic Layer Deposition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 3455–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traore, B.; Blaise, P.; Vianello, E.; Grampeix, H.; Jeannot, S.; Perniola, L.; De Salvo, B.; Nishi, Y. On the origin of low-resistance state retention failure in HfO₂-based RRAM and impact of doping/alloying. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2015, 62, 4029–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Kang, J.F.; Chen, Y.S.; Zhang, F.F.; Chen, B.; Huang, P.; Liu, L.F.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Tran, X.A.; et al. Oxide-Based RRAM: Unified Microscopic Principle for Both Unipolar and Bipolar Switching. In Proceedings of the International Electron Devices Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 5–7 December 2011; pp. 17.4.1–17.4.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.W.; Tzeng, W.H.; Liu, K.C.; Lin, H.C.; Chang, K.M.; Chan, Y.C.; Kuo, C.-C.; Chen, P.-S.; Lee, H.-Y.; Chen, F.; et al. Effect of ITO electrode with different oxygen contents on the electrical characteristics of HfOx RRAM devices. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 231, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Liu, L.F.; Chen, Y.S.; Kang, J.F. Resistive switching characteristics in HfOx layer by using current sweep mode. Microelectron. Eng. 2012, 94, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Long, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Xu, D.; Lv, H.; Liu, Q.; Liu, M. Improving the Resistive Switching Reliability via Controlling the Resistance States of RRAM. In Proceedings of the IEEE 22nd International Symposium on the Physical and Failure Analysis of Integrated Circuits, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 29 June–2 July 2015; pp. 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diokh, T.; Le-Roux, E.; Jeannot, S.; Gros-Jean, M.; Candelier, P.; Nodin, J.F.; Jousseaume, V.; Perniola, L.; Grampeix, H.; Cabout, T.; et al. Investigation of the Impact of the Oxide Thickness and RESET Conditions on Disturb in HfO2-RRAM Integrated in a 65nm CMOS Technology. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS), Monterey, CA, USA, 14–18 April 2013; pp. 5E.4.1–5E.4.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.K.; Ho, C.H.; Lien, D.H.; Retamal, J.R.D.; Kang, C.F.; Chen, K.M.; Huang, T.H.; Yu, Y.C.; Wu, C.I.; He, J.H. A Fully Transparent Resistive Memory for Harsh Environments. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, H. Multi-Level Switching of Al-Doped HfO2 RRAM with a Single Voltage Amplitude Set Pulse. Electronics 2021, 10, 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10060731
Lin J, Wang S, Liu H. Multi-Level Switching of Al-Doped HfO2 RRAM with a Single Voltage Amplitude Set Pulse. Electronics. 2021; 10(6):731. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10060731
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Jinfu, Shulong Wang, and Hongxia Liu. 2021. "Multi-Level Switching of Al-Doped HfO2 RRAM with a Single Voltage Amplitude Set Pulse" Electronics 10, no. 6: 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10060731
APA StyleLin, J., Wang, S., & Liu, H. (2021). Multi-Level Switching of Al-Doped HfO2 RRAM with a Single Voltage Amplitude Set Pulse. Electronics, 10(6), 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10060731







