Reliability Analysis and Fault-Tolerant Operation in a Multilevel Inverter for Industrial Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Analysis of the Topology
3. Fault-Tolerance Approach
3.1. Fault Conditions
3.2. Fault Correction
4. Simulation Results
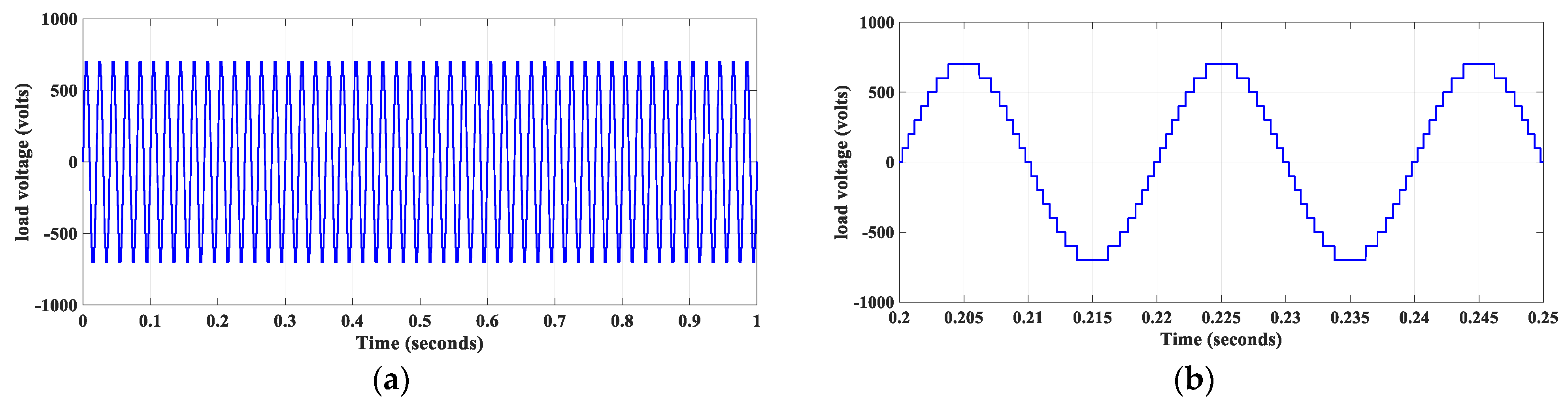
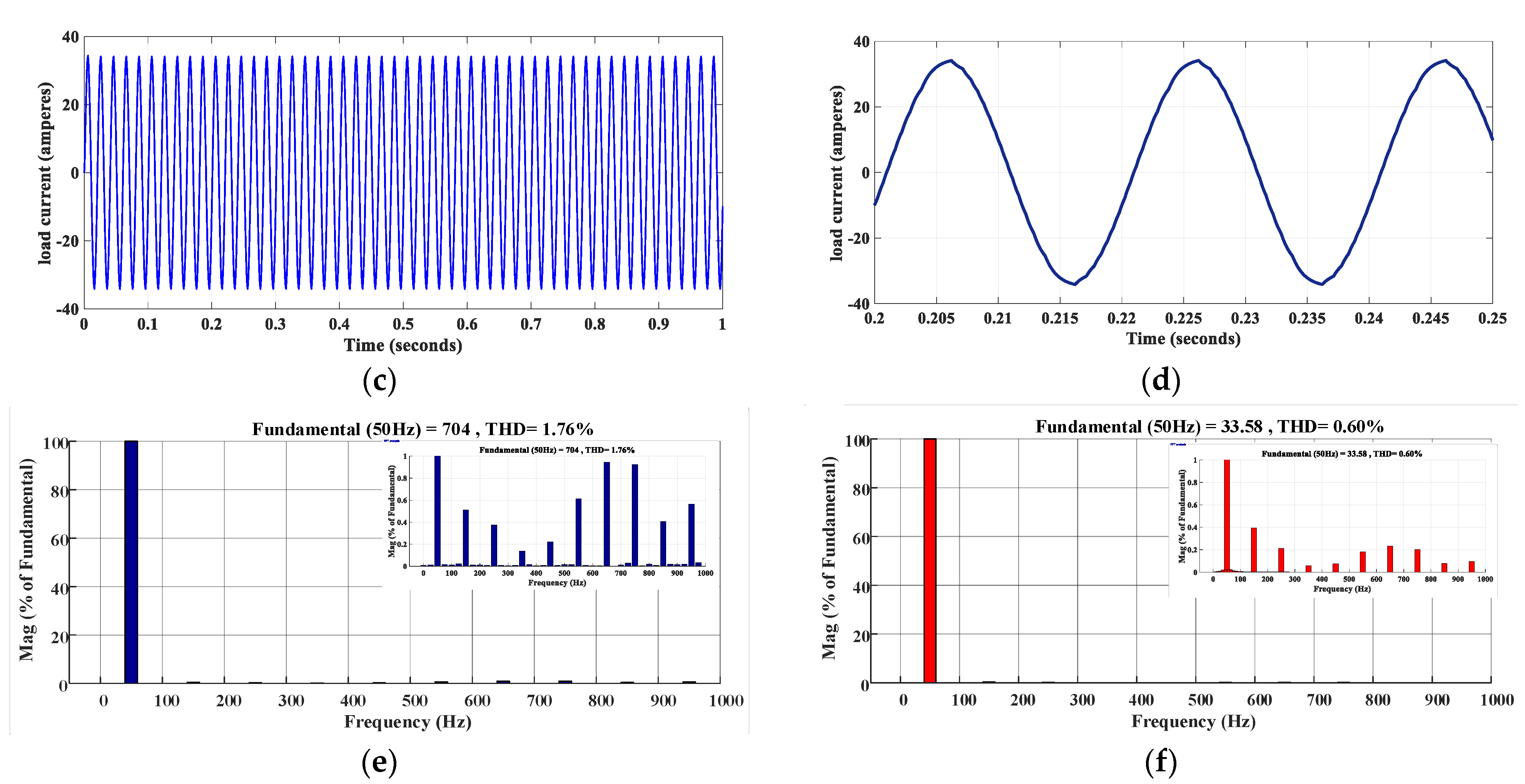
4.1. Healthy Operation
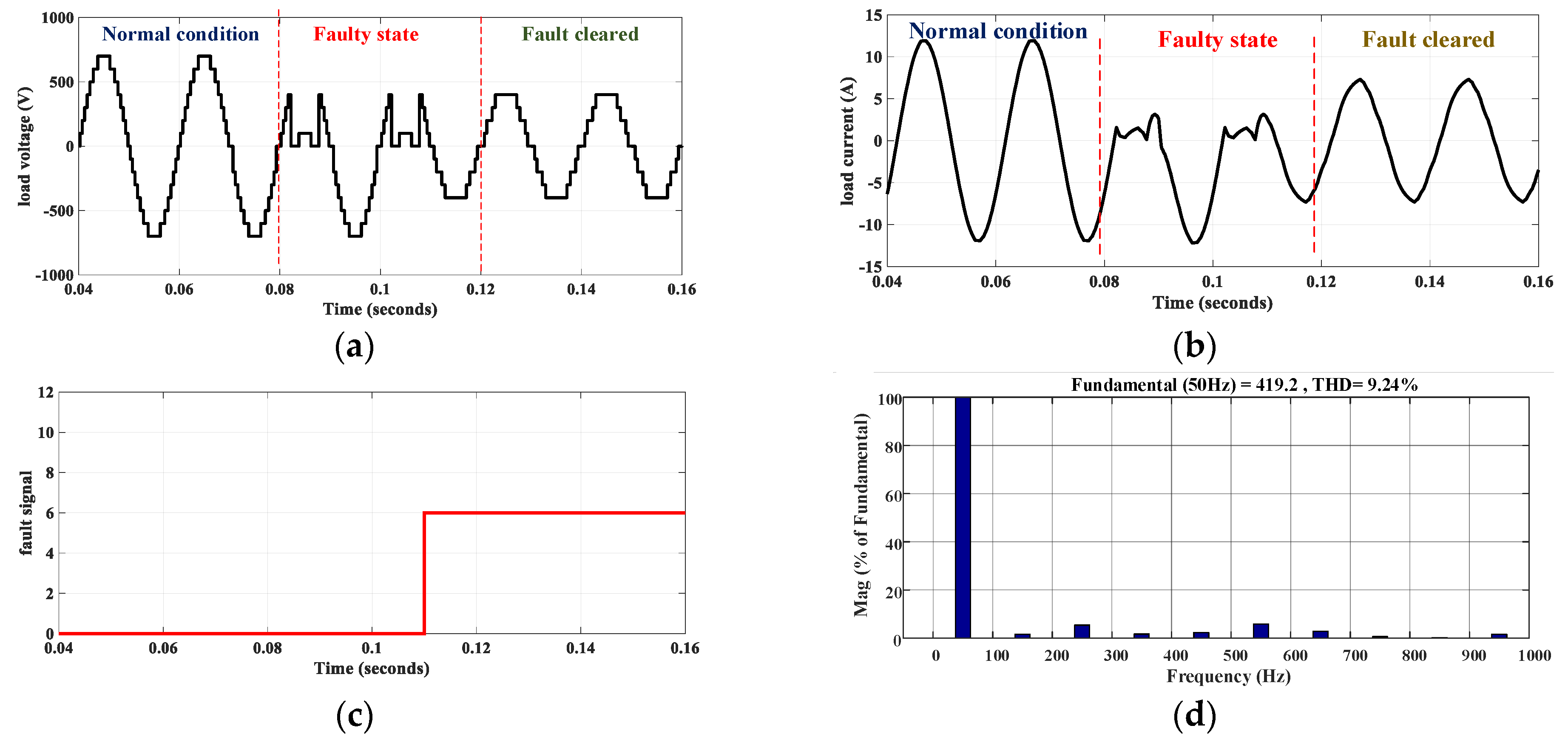
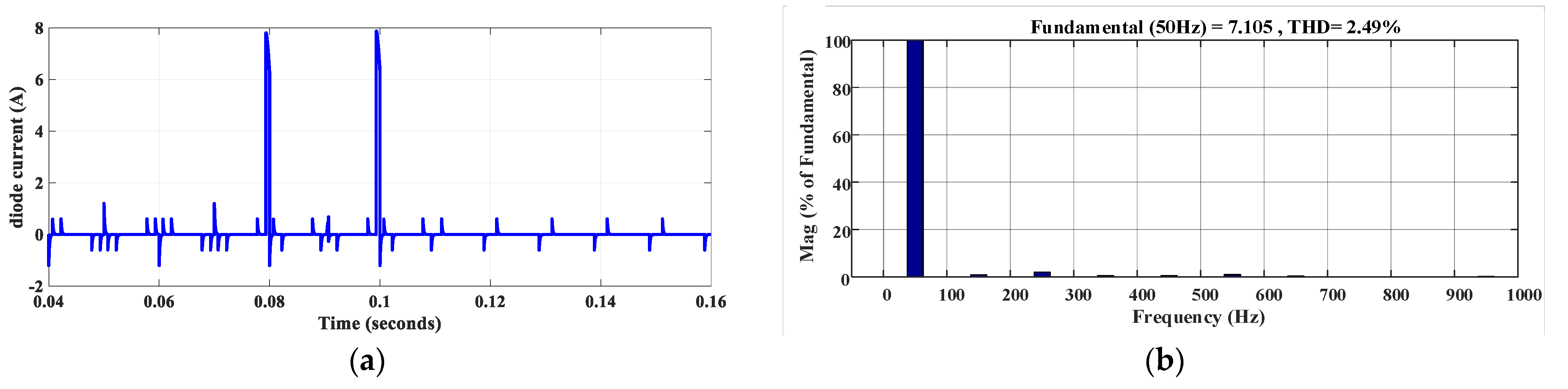
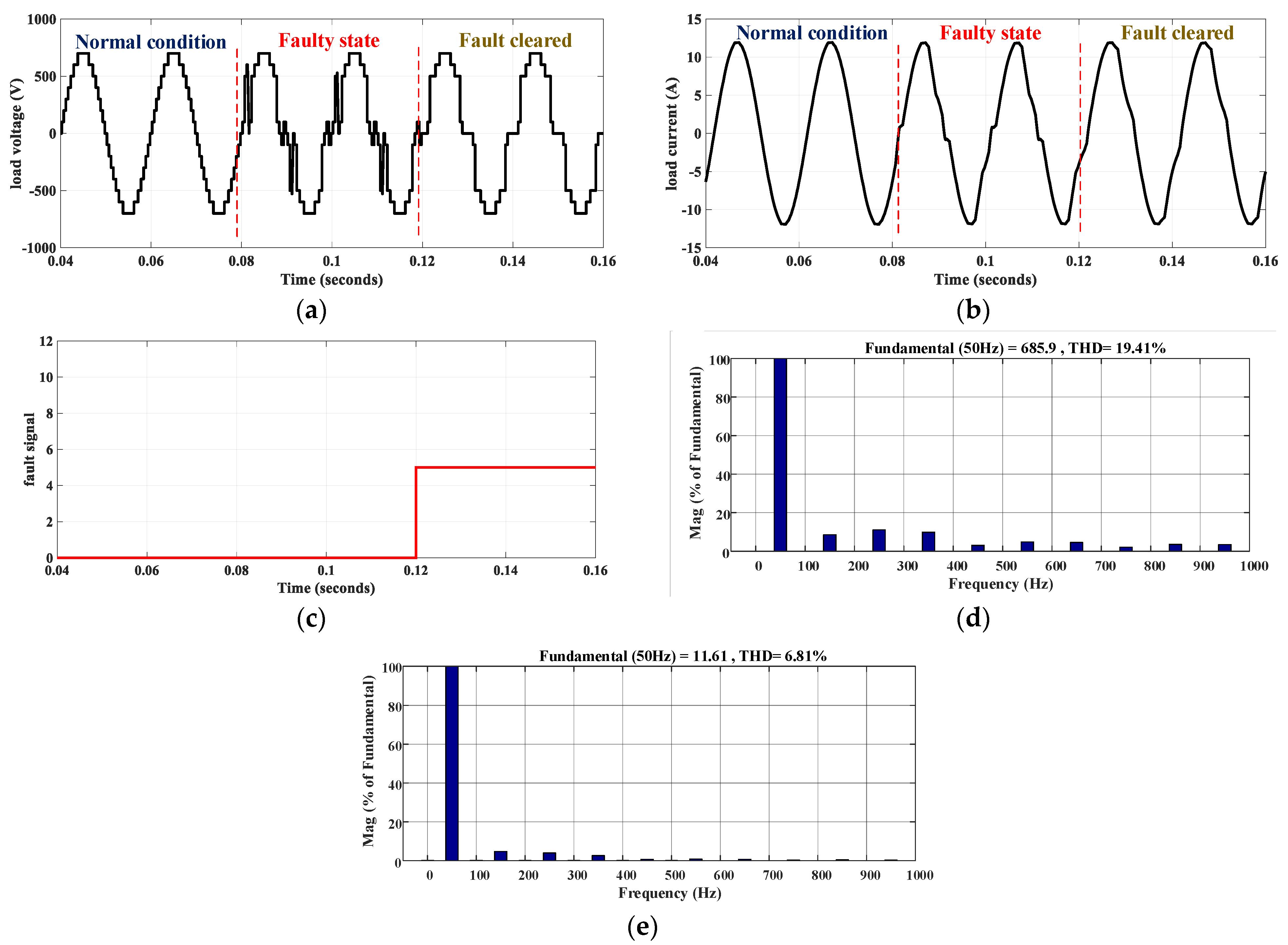
4.2. Fault-Tolerance
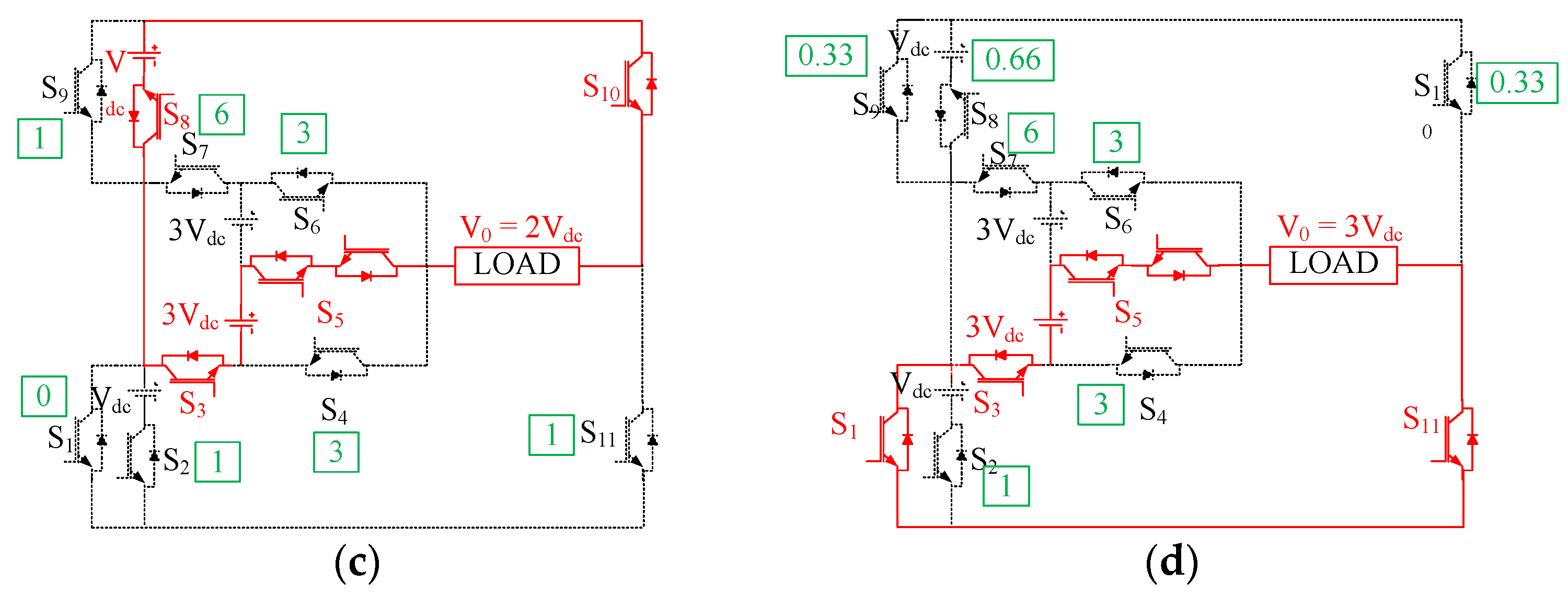
4.3. S9 or S1 Fault
4.4. S2, S8, S10, and S11 Fault
4.5. S3 or S7 Fault
4.6. S4 or S6 Fault
4.7. S5 Fault
5. Reliability Analysis
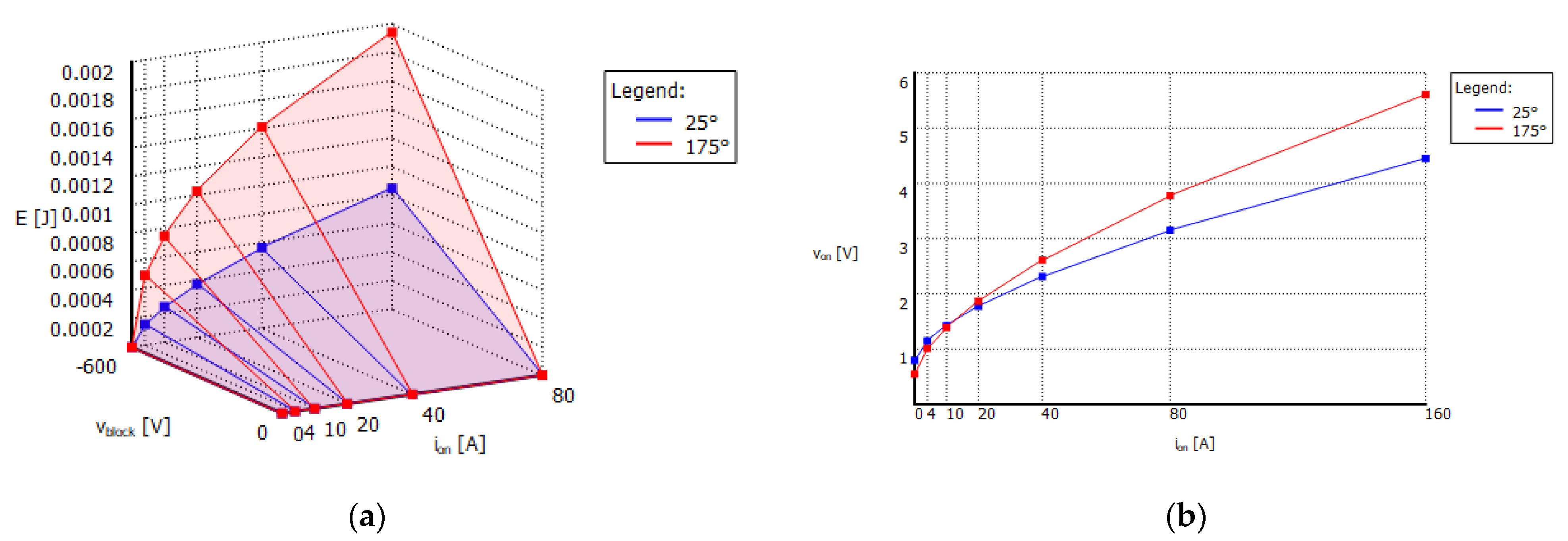
5.1. Component Failure Rate Evaluation
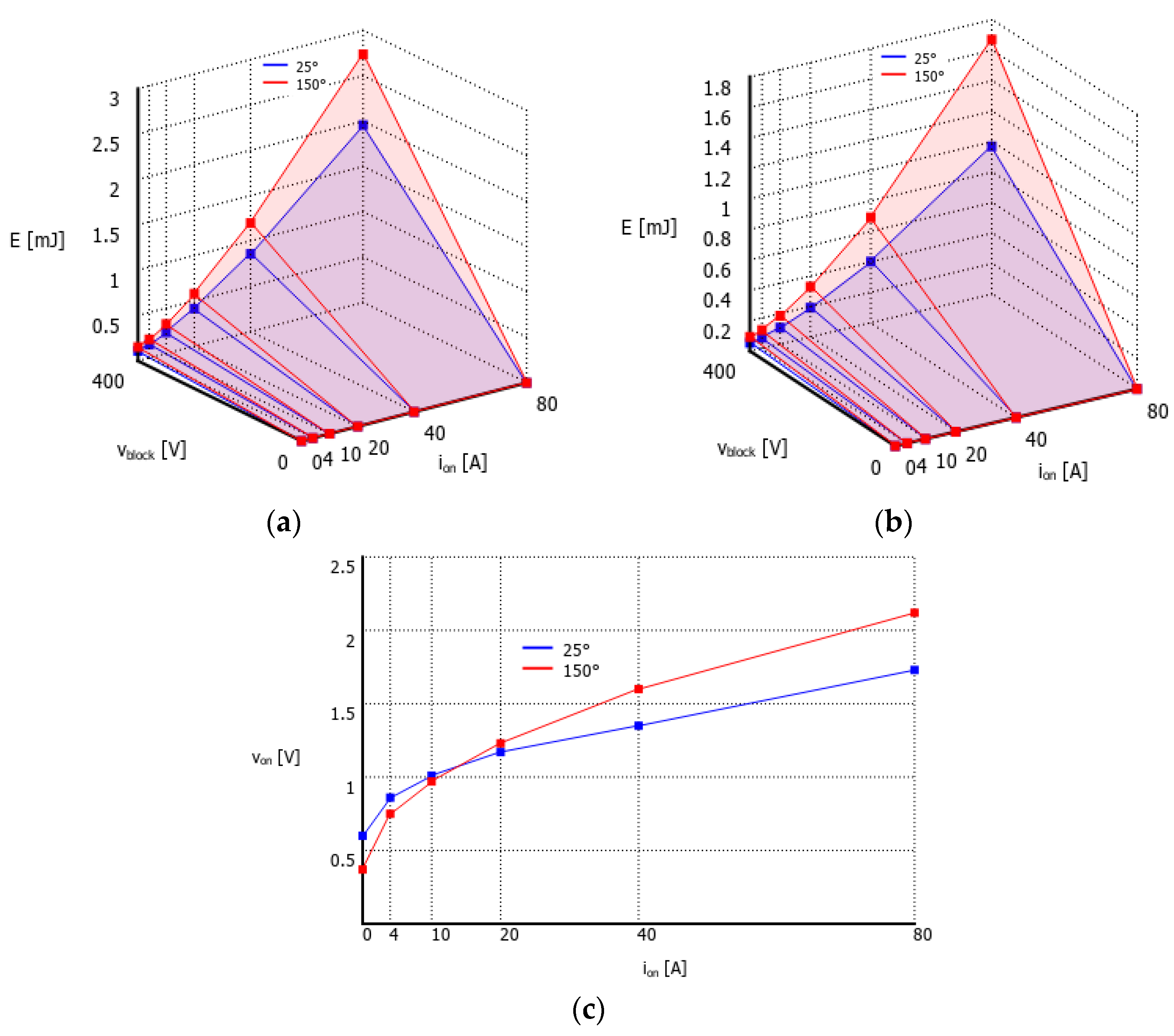
5.2. Power Loss Analysis
5.3. Derivation of the Reliability Function
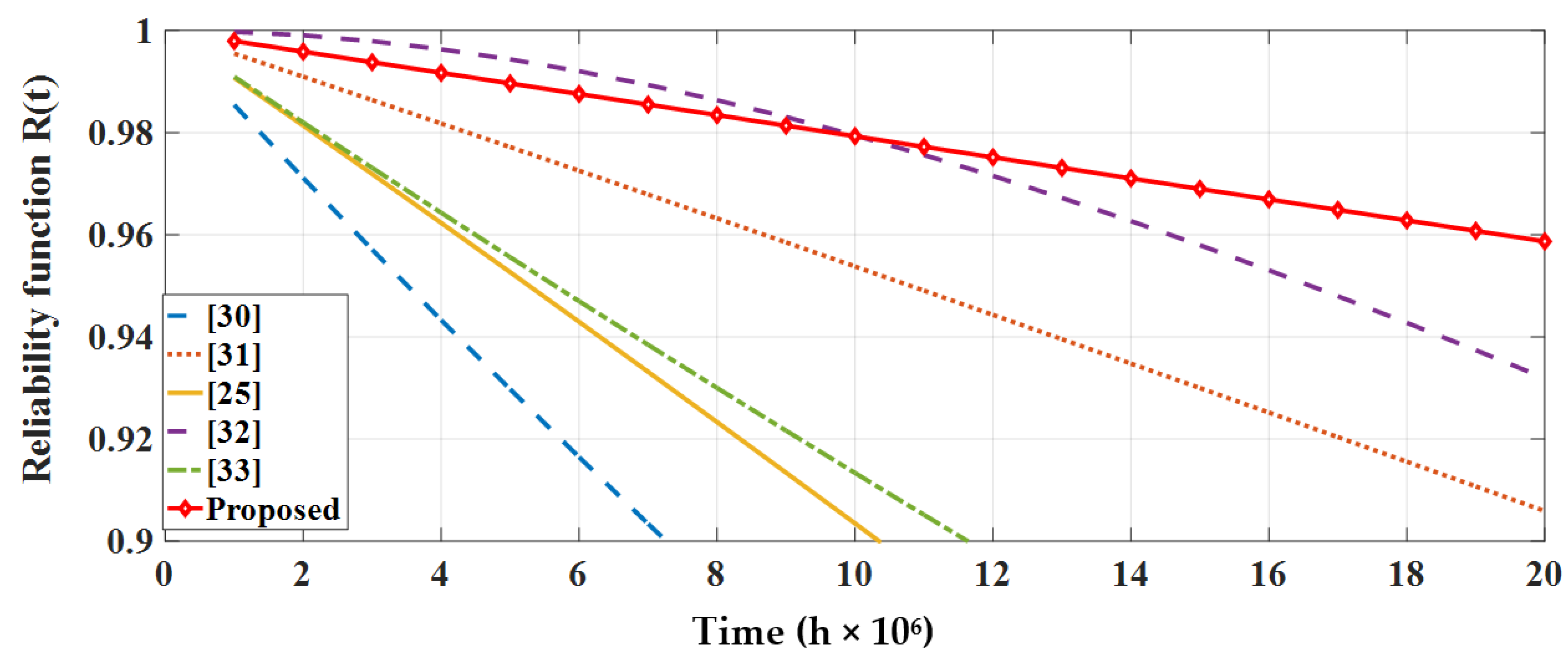
5.4. Reliability Comparison with Recent Literature
6. Comparative Analysis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yilmaz, S.; Dincer, F. Impact of Inverter Capacity on the Performance in Large-Scale Photovoltaic Power Plants—A Case Study for Gainesville, Florida. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stippich, A. Key Components of Modular Propulsion Systems for Next Generation Electric Vehicles. CPSS Trans. Power Electron. Appl. 2017, 2, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Li, H. Master-Slave Cascade Multilevel Inverter for Motor Drive Control of Electric Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 45th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON 2019), Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 October 2019; pp. 3210–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Yang, T.; Diab, A.M.; Yeoh, S.S.; Bozhko, S.; Wheeler, P. An Enhanced Virtual Space Vector Modulation Scheme of Three-Level NPC Converters for More-Electric-Aircraft Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 5239–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, H. Multilevel Converters: Fundamental Circuits and Systems. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 2048–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorfakhraei, A.; Narimani, M.; Emadi, A. A Review of Multilevel Inverter Topologies in Electric Vehicles: Current Status and Future Trends. IEEE Open J. Power Electron. 2021, 2, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, P.; Kumar, J.; Surjan, B.S. A Review on Reduced Switch Count Multilevel Inverter Topologies. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 22281–22302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Nema, R.K.; Gupta, S. Investigation of Fault-Tolerant Capabilities of Some Recent Multilevel Inverter Topologies. Int. J. Electron. 2021, 108, 1957–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirafzal, B. Survey of Fault-Tolerance Techniques for Three-Phase Voltage Source inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 5192–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, H.; Sun, Z.; Dong, W.; Dong, Y. Fault Diagnosis of Wind Turbine Power Converter Considering Wavelet Transform, Feature Analysis, Judgment and BP Neural Network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 179799–179809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formica, T.J.; Khan, H.A.; Pecht, M.G. The Effect of Inverter Failures on the Return on Investment of Solar Photovoltaic Systems. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 21336–21343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, M.; Maswood, A.I.; Moreddy, A.C.; Gajanayake, C.J.; Lee, M.Y.; Gupta, A.K. Reliability, Dead-Time, and Feasibility Analysis of a Novel Modular Tankless ZCS Inverter for More Electric Aircraft. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2017, 3, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wen, H.; Gan, C. Asynchronized Synchronous Motor-Based More Electric Ship-Less Power Electronics for More System Reliability. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 2353–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaabjerg, F.; Wang, H.; Vernica, I.; Liu, B.; Davari, P. Reliability of Power Electronic Systems for EV/HEV Applications. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 1060–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.P.; Kumar, L.; Gupta, S.; Agrawal, N. A Single-Phase Five-Level Inverter Topology with Switch Fault-Tolerance Capabilities. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 2004–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Hu, L.; Chen, L.; Deng, Y.; He, X. A Multilevel Converter Topology with Fault-Tolerant Ability. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2005, 20, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezana, P.; Aguilera, R.; Rodríguez, J. Fault Detection on Multicell Converter Based on Output Voltage Frequency Analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 2275–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, W.; Huang, A.Q. Fault-Tolerant Design and Control Strategy for Cascaded H-bridge Multilevel Converter-Based STATCOM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 2700–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, A.; Sepahvand, H.; Crow, M.L.; Ferdowsi, M. Fault Detection and Mitigation in Multilevel Converter STATCOMs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalhotra, M.; Kumar, L.; Gautam, S.P.; Gupta, S. Development of Fault-Tolerant MLI Topology. IET Power Electron. 2018, 11, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos, S.; Pou, J.; Zaragoza, J.; Robles, E.; Villate, J.L.; Martín, J.L. Fault-Tolerant Neutral-Point-Clamped Converter Solutions Based on Including a Fourth Resonant Leg. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 2293–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos, S.; Pou, J.; Robles, E.; Gabiola, I.; Zaragoza, J.; Villate, J.L.; Boroyevich, D. Three-Level Converter Topologies with Switch Breakdown Fault-Tolerance Capability. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 982–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos, S.; Pou, J.; Robles, E.; Zaragoza, J.; Martin, J.L. Performance Evaluation of Fault-Tolerant Neutral-Point-Clamped Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 2709–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji-Esmaeili, M.M.; Naseri, M.; Khoun-Jahan, H.; Abapour, M. Fault-Tolerant Structure for Cascaded H-Bridge Multilevel Inverter and Reliability Evaluation. IET Power Electron. 2017, 10, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, H.K.; Panahandeh, F.; Abapour, M.; Tohidi, S. Reconfigurable Multilevel Inverter with Fault Tolerant Ability. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 33, 7880–7893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahad, M.; Siddique, M.D.; Iqbal, A.; Sarwar, A.; Mekhilef, S. Implementation and Analysis of a 15-Level Inverter Topology with Reduced Switch Count. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 40623–40634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Standards Association. 519-2014-IEEE Recommended Practices and Requirements for Harmonic Control in Electric Power Systems; IEEE: Piscataway, HJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Equipment, E. Reliability Prediction of Electronic Equipment; Department of Defense: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Dewangan, N.K.; Gupta, K.K.; Bhatnagar, P. Modified Reduced Device Multilevel Inverter Structures with Open Circuit Fault-Tolerance Capabilities. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2020, 30, e12142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappa, A.; Gupta, S.; Sahu, L.K.; Gupta, K.K. Resilient Multilevel Inverter Topology with Improved Reliability. IET Power Electron. 2020, 13, 3384–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, K. A Fault-Tolerant Single-Phase Five-Level Inverter for Grid-Independent PV Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 7569–7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambusaidi, K.; Pickert, V.; Zahawi, B. New Circuit Topology for Fault Tolerant H-bridge Dc-Dc Converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.P.; Sahu, L.K.; Gupta, S. Reduction in Number of Devices for Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Multilevel Inverters. IET Power Electron. 2016, 9, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
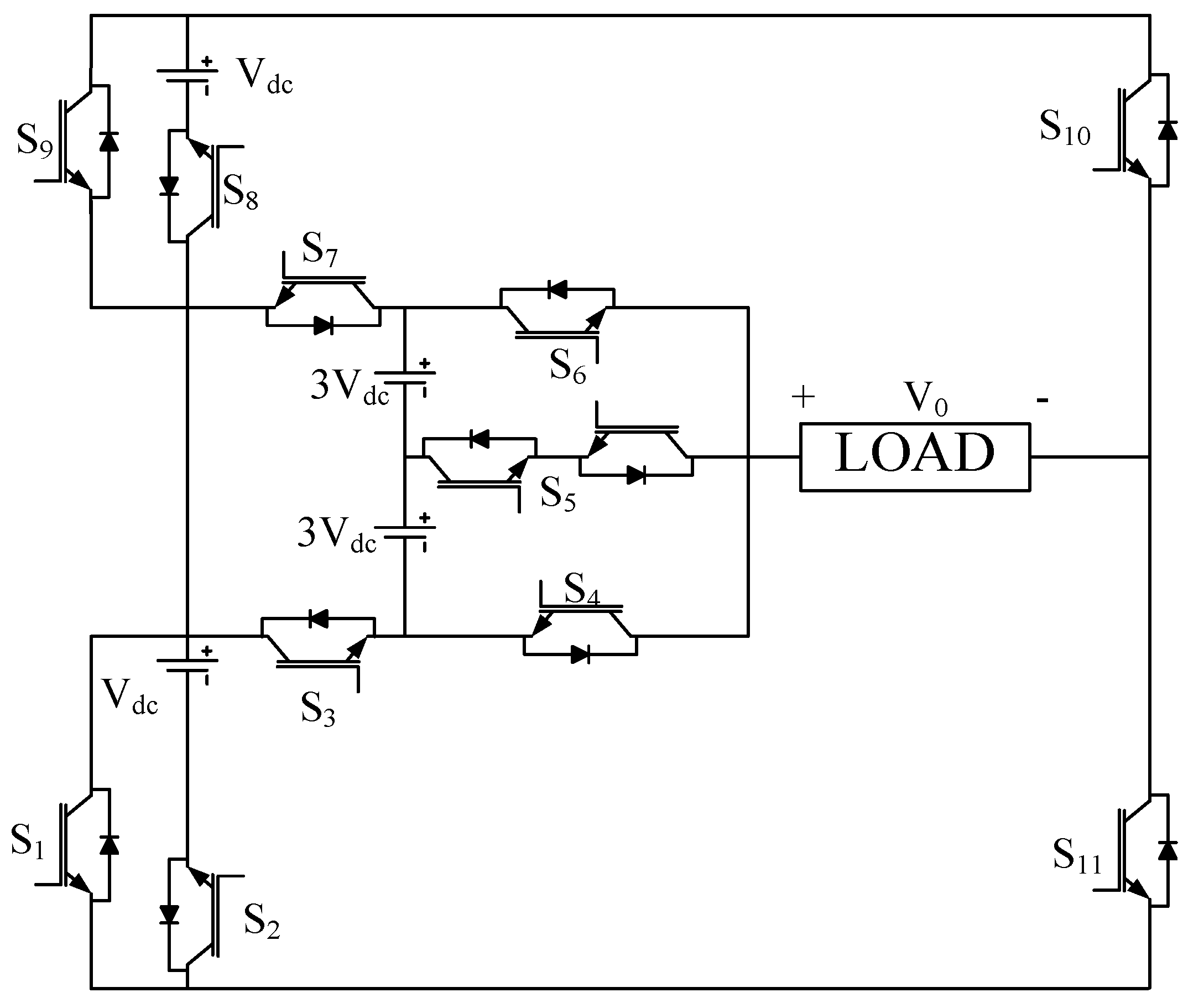






| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | Vout |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Zero |
| 0 0 | 1 1 | 1 0 | 1 0 | 0 0 | 0 1 | 0 1 | 0 0 | 0 0 | 0 0 | 1 1 | Vdc |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 Vdc |
| 1 0 | 0 0 | 1 1 | 0 0 | 1 1 | 0 0 | 0 0 | 0 0 | 0 1 | 0 1 | 1 0 | 3 Vdc |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 Vdc |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 5 Vdc |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 6 Vdc |
| 1 0 | 0 1 | 1 1 | 0 0 | 0 0 | 1 1 | 0 0 | 0 0 | 0 0 | 0 0 | 1 1 | 7 Vdc |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | Zero |
| 0 0 | 0 0 | 0 1 | 0 1 | 0 0 | 1 0 | 1 0 | 1 1 | 0 0 | 1 1 | 0 0 | −Vdc |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | −2 Vdc |
| 0 1 | 0 0 | 0 0 | 0 0 | 1 1 | 0 0 | 1 1 | 0 0 | 1 0 | 1 0 | 0 1 | −3 Vdc |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | −4 Vdc |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | −5 Vdc |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | −6 Vdc |
| 1 0 | 0 0 | 0 0 | 1 1 | 0 0 | 0 0 | 1 1 | 0 1 | 0 0 | 0 1 | 1 0 | −7 Vdc |
| Faulty Switch | Voltage Levels Lost | Levels Regained Post Reconfiguration |
|---|---|---|
| S1 or S9 | ±3 Vdc, ±6 Vdc | All |
| S2 or S8 | ±Vdc, ±2 Vdc, ±4 Vdc, ±5 Vdc, ±7 Vdc | ±3 Vdc, ± 6Vdc |
| S3 or S7 | ±2 Vdc to ±7 Vdc | ±Vdc |
| S4 or S6 | ±5 Vdc, ±6 Vdc, ±7 Vdc | ±Vdc, ±2 Vdc, ±3 Vdc, ±4 Vdc |
| S5 | ±2 Vdc, ± 3 Vdc, ±4 Vdc | ±Vdc, ±5 Vdc, ±6 Vdc, ±7 Vdc |
| S10 or S11 | ±Vdc, ±2 Vdc, ±4 Vdc, ±5 Vdc, 7 Vdc | ±3 Vdc, ±6 Vdc |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Voltage sources | 100 V |
| 300 V | |
| Load impedance | 50 Ω, 100 mH |
| Modulating frequency | 50 Hz |
| Features | NPC | FC | CHB | [15] | [16] | [20] | [24] | [25] | [29] | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of DC voltage sources | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| Required number of capacitors | 0 | 28 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Number of Diodes required | 56 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| Number of IGBTs required | 16 | 16 | 16 | 8 | 22 | 12 | 16 | 20 | 12 | 12 |
| Number of gate drivers required | 16 | 16 | 16 | 7 | 22 | 9 | 16 | 20 | 9 | 11 |
| Number of Relays | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Number of Transformers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Number of voltage levels generated | 9 | 9 | 9 | 5 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 7 | 15 |
| Fault-tolerant operation | NO | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Redundant switches required | - | - | YES | NO | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fahad, M.; Alsultan, M.; Ahmad, S.; Sarwar, A.; Tariq, M.; Khan, I.A. Reliability Analysis and Fault-Tolerant Operation in a Multilevel Inverter for Industrial Application. Electronics 2022, 11, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11010098
Fahad M, Alsultan M, Ahmad S, Sarwar A, Tariq M, Khan IA. Reliability Analysis and Fault-Tolerant Operation in a Multilevel Inverter for Industrial Application. Electronics. 2022; 11(1):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11010098
Chicago/Turabian StyleFahad, Mohammad, Marwan Alsultan, Shafiq Ahmad, Adil Sarwar, Mohd Tariq, and Irfan Ahmad Khan. 2022. "Reliability Analysis and Fault-Tolerant Operation in a Multilevel Inverter for Industrial Application" Electronics 11, no. 1: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11010098
APA StyleFahad, M., Alsultan, M., Ahmad, S., Sarwar, A., Tariq, M., & Khan, I. A. (2022). Reliability Analysis and Fault-Tolerant Operation in a Multilevel Inverter for Industrial Application. Electronics, 11(1), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11010098










