A Survey on CubeSat Missions and Their Antenna Designs
Abstract
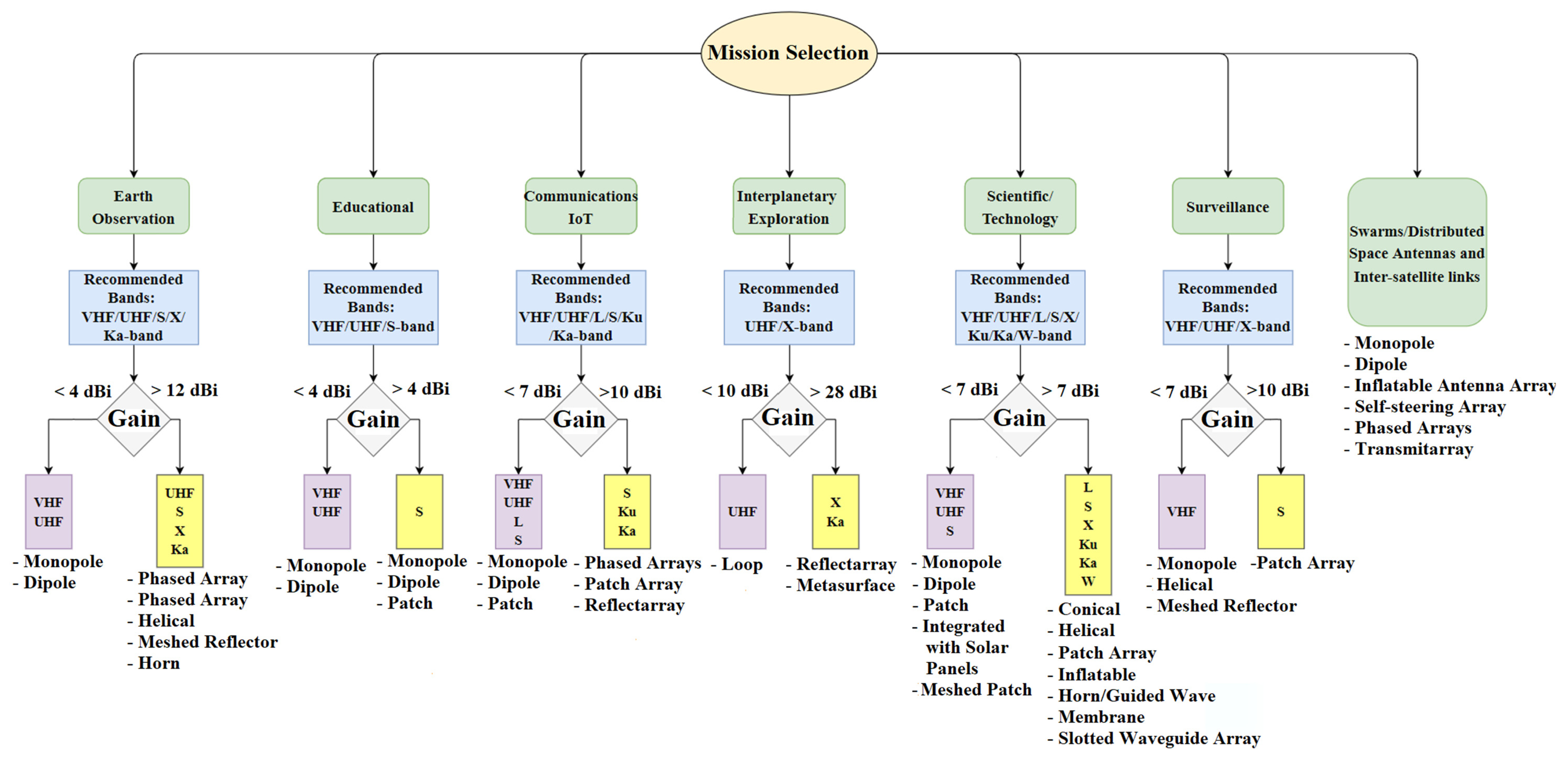
:1. Introduction
2. Background on CubeSats and Their Subsystems
2.1. Mass and Volume
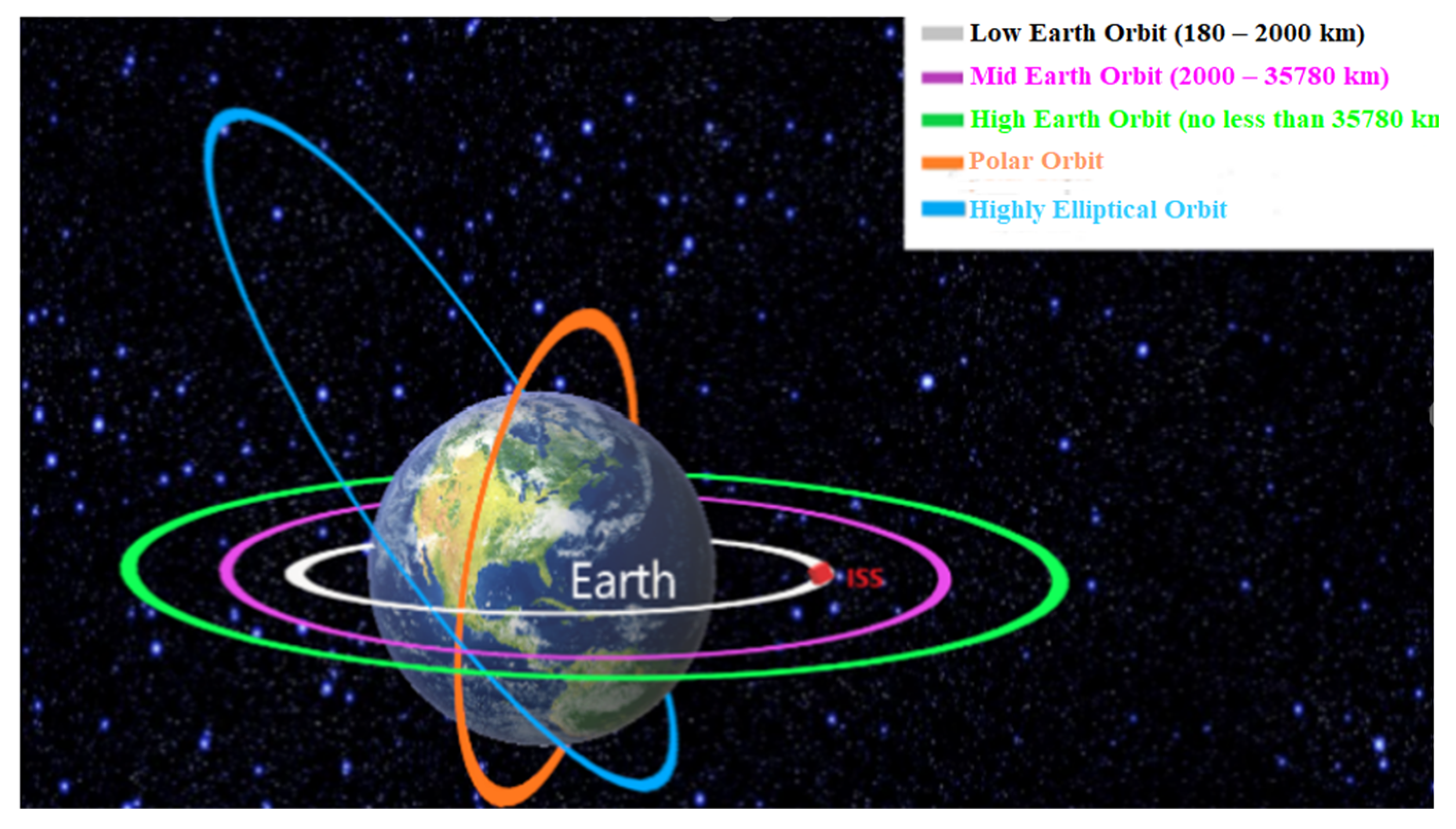
2.2. Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
2.3. Electrical Power Subsystem (EPS)
2.4. Command and Data Handling Subsystem (C&DH)
2.5. Propulsion Subsystem
2.6. Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem (ADCS)
3. Background on Antennas and CubeSat Missions
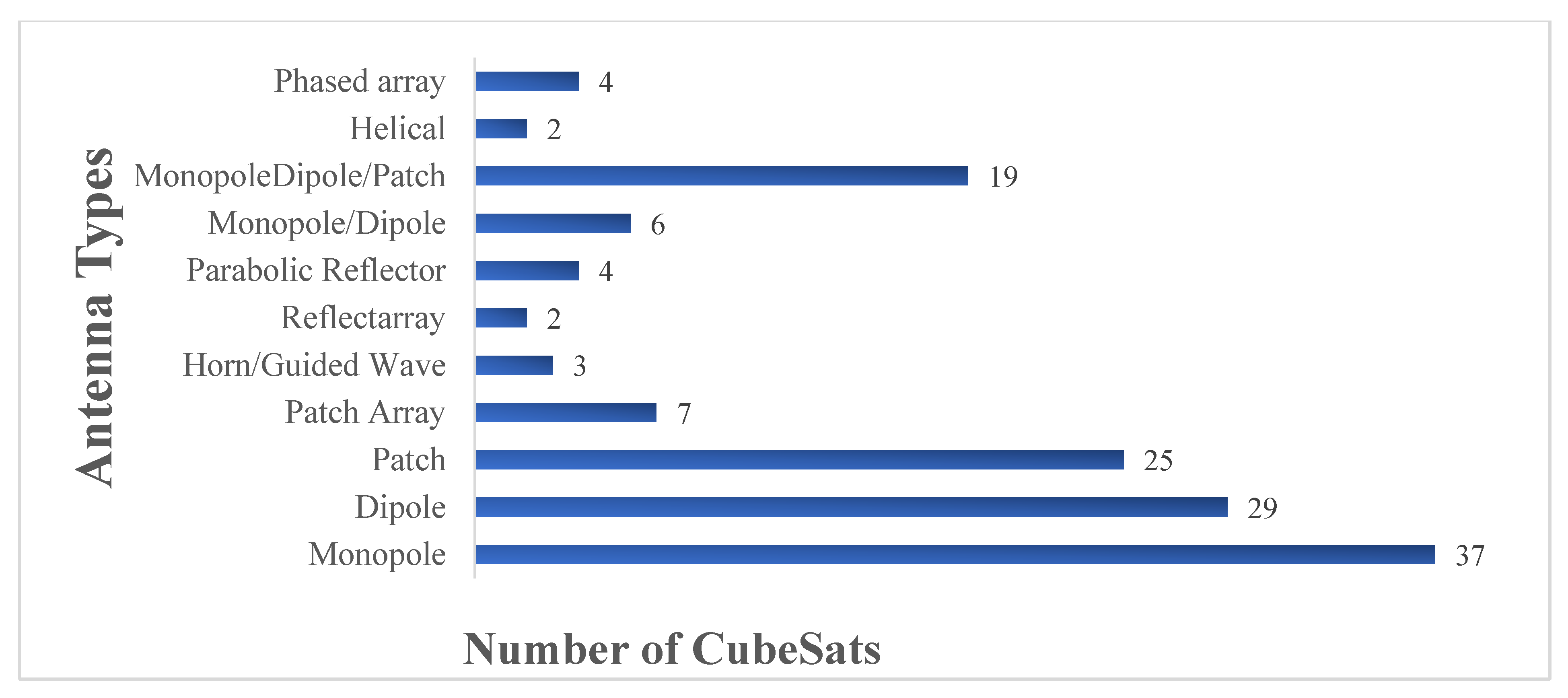
3.1. CubeSat Antenna Specifications
3.2. CubeSat Missions and Their Antenna Designs
4. Single-Element CubeSat Antenna Designs
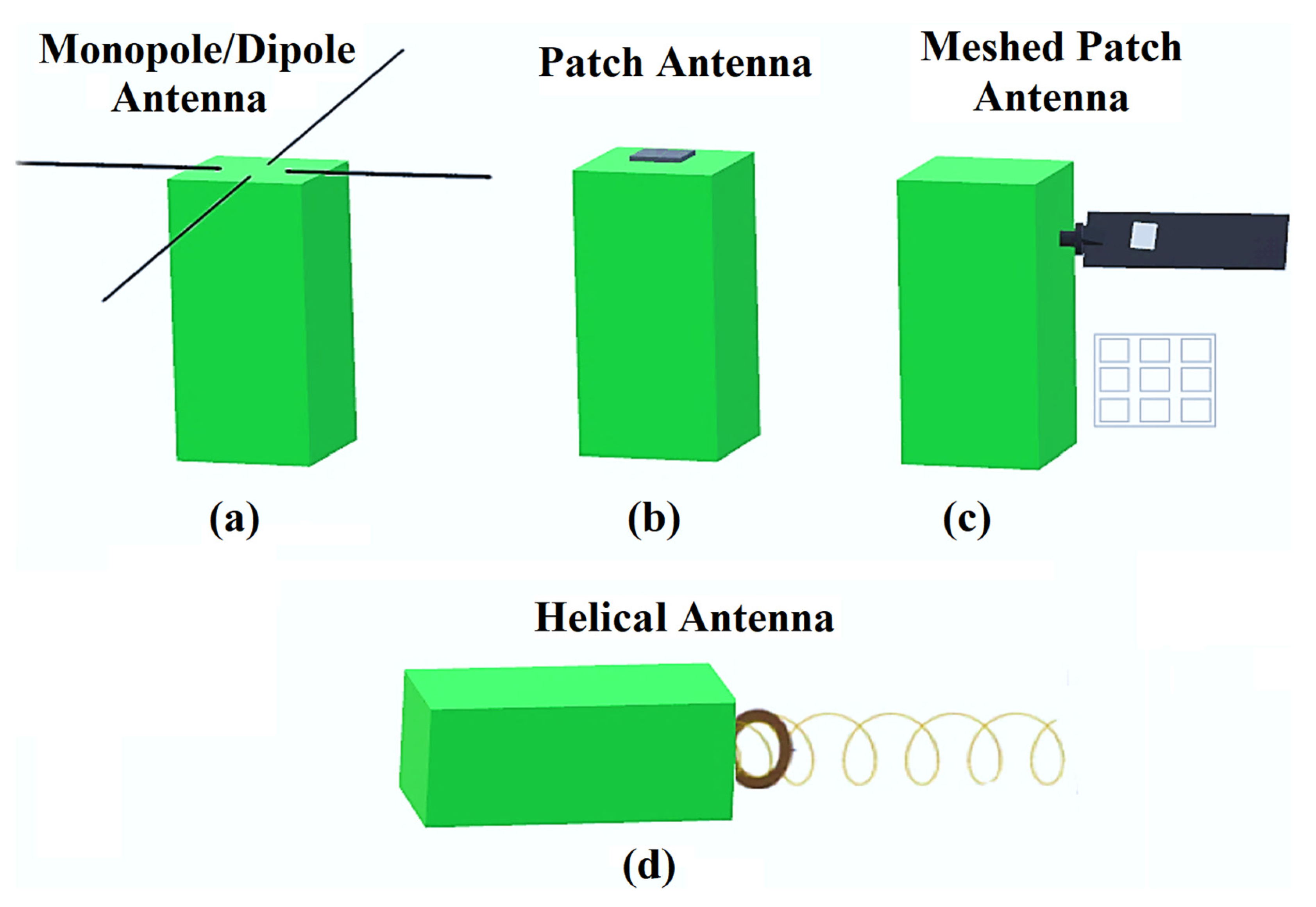
4.1. Monopole and Dipole Antennas
4.2. Planar Antennas
4.3. Antenna Integrated with Solar Panels
4.4. Conical Spiral Helix Antenna
4.5. Other Antenna Designs
4.6. Recommendation for Single-Element Antennas and CubeSat Missions
5. Antenna Arrays for CubeSat
5.1. Linear Arrays for CubeSats
5.2. Planar Arrays for CubeSats
5.3. Reflectarrays, Reflectors, and Transmitarrays for CubeSats
| Type of Antenna | Frequency (GHz) | Gain (dBi) | −10 dB BW (MHz) | Deployable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reflectarray [194] | 26G 8.425 | 33.5 >28 | >100 >100 | Yes Yes |
| Mesh Reflector [195,200] | 35.75 | 42.6 | N/A | Yes |
| Integrated Solar Array and Reflectarray [101] | 36 | 33.5 | >100 | Yes |
| MarCO [196] | 8.425 | 29.2 | 50 | Yes |
| Cassegrain Reflectarray [196] | 35.75 | 48 | N/A | Yes |
| LADeR Reflectarray [198] | 8.4 | 39.6 | N/A | Yes |
| Transmitarray [199] | 24.6 | 31.6 | N/A | Yes |
5.4. Log-Periodic Crossed-Dipole Arrays
5.5. Slotted Waveguide Antenna Arrays
5.6. Inflatable Antenna Arrays
5.7. Retrodirective or Self-Steering Antenna Arrays
5.8. Interferometer (Large Antenna Arrays)
5.9. Arraying Techniques and Correlation Algorithms
5.10. Recommendations for Antenna Arrays
6. Comparison of Single-Element Antennas with Antenna Arrays
6.1. Operating Frequency Bands
6.2. Gain
7. Conclusions
7.1. Lessons Learned
7.2. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shimmin, R.; Agasid, E.; Burton, R.; Carlino, R.; Defouw, G.; Perez, A.; Karacaliglu, A.; Klamm, B.; Rademacher, A.; Schalkwyck, J. Small Spacecraft Technology State of the Art; NASA Mission Design Division Ames Research Center, Moffett Field: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2015; Volume NASA/TP–2015–216648/REV. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Li, Y.; Guang, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, J. Small satellite remote sensing and applications—History, current and future. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4339–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig-Suari, J.; Turner, C.; Ahlgren, W. Development of the standard CubeSat deployer and a CubeSat class PicoSatellite. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings (Cat. No.01TH8542), Big Sky, MT, USA, 10–17 March 2001; Volume 1, pp. 347–353. [Google Scholar]
- Wuerl, A.; Wuerl, M. Lessons learned for deploying a microsatellite from the International Space Station. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 7–14 March 2015; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Twiggs, B.; Puig-Suari, J. CUBESAT Design Specifications Document; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA; California Polytechnical Institute: San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- ESA. First P-Pod Integration. Available online: http://www.esa.int/spaceinimages/Images/2012/02/First_P-POD_integration2 (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Swartwout, M. The first one hundred CubeSats: A statistical look. J. Small Satell. 2013, 2, 213–233. [Google Scholar]
- Klofas, B.; Anderson, J.; Leveque, K. A Survey of Cubesat Communication Systems. In Proceedings of the 5th Annual CubeSat Developers Workshop, San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 9–11 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chahat, N.; Decrossas, E.; Gonzalez-Ovejero, D.; Yurduseven, O.; Radway, M.J.; Hodges, R.E.; Estabrook, P.; Baker, J.D.; Bell, D.J.; Cwik, T.A.; et al. Advanced cubesat antennas for deep space and earth science missions: A review. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2019, 61, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malphrus, B.K.; Freeman, A.; Staehle, R.; Klesh, A.T.; Walker, R. 4—Interplanetary CubeSat missions. In Cubesat Handbook; Cappelletti, C., Battistini, S., Malphrus, B.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 85–121. [Google Scholar]
- Tummala, A.R.; Dutta, A. An overview of cube-satellite propulsion technologies and trends. Aerospace 2017, 4, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santoni, F.; Piergentili, F.; Donati, S.; Perelli, M.; Negri, A.; Marino, M. An innovative deployable solar panel system for Cubesats. Acta Astronaut. 2014, 95, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunce, D.T.; Bassett, K.P.; Ghosh, A.R.; Barnett, P.R.; Haken, D.M.; Coverstone, V.L.; Yost, B.D.; Feller, J.R.; Agasid, E.F. Microvascular Composite Radiators for Small Spacecraft Thermal Management Systems. In Proceedings of the 30th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 6–11 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Brenchley, M.; Unwin, M.; Underwood, C.I.; Clark, K.; Maynard, K.; Boland, L.; Sweeting, M.N. Antennas for small satellites. In Proceedings of the 2008 Loughborough Antennas and Propagation Conference, Loughborough, UK, 17–18 March 2008; pp. 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Selva, D. A survey and assessment of the capabilities of Cubesats for Earth observation. Acta Astronaut. 2012, 74, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffner, J. The Electronic System Design, Analysis, Integration, and Construction of the Cal Poly State University CP1 CubeSat. In Proceedings of the 16th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 12–15 August 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Theoharis, P.I.; Raad, R.; Tubbal, F.; Khan, M.U.A.; Liu, S. Software-Defined Radios for CubeSat Applications: A Brief Review and Methodology. IEEE J. Miniat. Air Space Syst. 2020, 2, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, S.J.; Aarestad, J.; Pollard, L.H.; Wyglinski, A.M.; Kief, C.; Erwin, R.S. Modular FPGA-based software defined radio for CubeSats. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 10–15 June 2012; pp. 3229–3233. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwmeester, J.; Guo, J. Survey of worldwide pico-and nanosatellite missions, distributions and subsystem technology. Acta Astronaut. 2010, 67, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abulgasem, S.; Tubbal, F.; Raad, R.; Theoharis, P.I.; Lu, S.; Iranmanesh, S. Antenna Designs for CubeSats: A Review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 45289–45324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubbal, F.E.; Raad, R.; Chin, K.W. A Survey and Study of Planar Antennas for Pico-Satellites. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 2590–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowland, D.E.; Hill, J.; Uribe, P.; Klenzing, J.; Hunsaker, F.; Fowle, M.; Simms, K.; Hancock, H.; Saulino, M.; Guzman, D.; et al. The NSF Firefly CubeSat mission: Rideshare mission to study energetic electrons produced by lightning. In Proceedings of the 2011 Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2011; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, L.; Rizos, C.; Dempster, A.G. Analysis and comparison of CubeSat lifetime. In Proceedings of the 12th Australian Space Development Conference, Adelaide, Australia, 8–10 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeting, M.N.; Underwood, C.I. Small Satellite Engineering and Applications. In Spacecraft Systems Engineering; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 575–605. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.; Cucinotta, F.; Golightly, M.; Nealy, J.; Qualls, G.; Badavi, F.; De Angelis, G.; Anderson, B.; Clowdsley, M.; Luetke, N.; et al. International space station: A testbed for experimental and computational dosimetry. Adv. Space Res. 2005, 37, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarathinam, N.; Lee, R.; Chesser, H. Characterization of Lithium-Polymer batteries for CubeSat applications. Acta Astronaut. 2011, 68, 1752–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waydo, S. CubeSat design for LEO-based Earth science missions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 9–16 March 2002; pp. 435–445. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, J.; Stras, L.; Jeans, T. Canada’s Smallest Satellite: The Canadian Advanced Nanospace Experiment (CanX-1). In Proceedings of the 16th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellite, Logan, UT, USA, 12–15 August 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M.; Zeiger, F.; Schilling, K. Design and implementation of in-orbit experiments on the pico-satellite UWE-1. In Proceedings of the 57th International Astronautical Congress, IAC-06-E2, Valencia, Spain, 2–6 October 2006; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Long, M.; Lorenz, A.; Rodgers, G.; Tapio, E.; Tran, G.; Jackson, K.; Twiggs, R.; Bleier, T.; Solutions, S. A cubesat derived design for a unique academic research mission in earthquake signature detection. In Proceedings of the 16th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellite, Logan, UT, USA, 12–15 August 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, S. DIY Satellite Platforms: Building a Space-Ready General Base Picosatellite for Any Mission; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lemmer, K. Propulsion for CubeSats. Acta Astronaut. 2017, 134, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.; Hofer, R.; Ziemer, J. Survey of Propulsion Technologies Applicable to Cubesats; Jet Propulsion Laboratory, National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Falbel, G.; Puig-Suari, J.; Peczalski, A. Sun oriented and powered, 3 axis and spin stabilized CubeSats. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 9–16 March 2002; Volume 1, pp. 447–455. [Google Scholar]
- Cockrell, J.; Alena, R.; Mayer, D.; Sanchez, H.; Luzod, T.; Yost, B.; Klumpar, D. EDSN: A Large Swarm of Advanced Yet Very Affordable, COTS-Based Nanosats that Enable Multipoint Physics and Open Source Apps. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellite, Logan, UT, USA, 13–16 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Budianu, A.; Castro, T.J.W.; Meijerink, A.; Bentum, M.J. Inter-satellite links for cubesats. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 2–9 March 2013; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Radhakrishnan, R.; Edmonson, W.W.; Afghah, F.; Rodriguez-Osorio, R.M.; Pinto, F.; Burleigh, S.C. Survey of Inter-Satellite Communication for Small Satellite Systems: Physical Layer to Network Layer View. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 2442–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, R.-O.R.; Fueyo, R.E. A Hands-On Education Project: Antenna Design for Inter-CubeSat Communications [Education Column]. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2012, 54, 211–224. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J. Deep Space Communications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; The Deep Space Network; pp. 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palo, S.E. High rate communications systems for CubeSats. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 17–22 May 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, O. Power Budgets for CubeSat Radios to Support Ground Communications and Inter-Satellite Links. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 12618–12625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-K.; Kim, G.-N.; Park, S.-Y. Novel Structure and Thermal Design and Analysis for CubeSats in Formation Flying. Aerospace 2021, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences and Medicine. Handbook of Frequency Allocations and Spectrum Protection for Scientific Uses; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Funase, R.; Takei, E.; Nakamura, Y.; Nagai, M.; Enokuchi, A.; Yuliang, C.; Nakada, K.; Nojiri, Y.; Sasaki, F.; Funane, T.; et al. Technology demonstration on University of Tokyo’s pico-satellite “XI-V” and its effective operation result using ground station network. Acta Astronaut. 2007, 61, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doering, T.J. Development of a Reusable Cubesat Satellite Bus Architecture for the KYSAT-1 Spacecraft. Master’s Thesis, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kayal, H.; Baumann, F.; Briess, K.; Montenegro, S. BEESAT: A pico satellite for the on orbit verification of micro wheels. In Proceedings of the Recent Advances in Space Technologies, Istanbul, Turkey, 14–16 June 2007; pp. 497–502. [Google Scholar]
- Konda, Y.; Usuda, T.; Sagami, T.; Omagari, K.; Kashiwa, M.; Matunaga, S. Development of attitude determination and control system for pico-satellite cute-1.7+ APD. In Proceedings of the 16th Workshop on JAXA Astrodynamics and Flight Mechanics, Sagamihara, Japan, 1–2 August 2006; pp. 242–247. [Google Scholar]
- Eide, E.; Ilstad, J. NCUBE-1, the first Norwegian CUBESAT student satellite. In Proceedings of the 16th ESA Symposium on European Rocket and Balloon Programmes and Related Research, St. Gallen, Switzerland, 2–5 June 2003; pp. 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Maeno, M.; Omagari, K.; Iljic, T.; Masumoto, S.; Fujiwara, K.; Konda, Y.; Yamanaka, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Ueno, T.; Ashida, H.; et al. Development of Tokyo Tech Nano-Satellite Cute-1.7+ APD II. In Proceedings of the 17th Workshop on JAXA Astrodynamics and Flight Mechanics, Sagamihara, Japan, 23–24 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- PSSCT (Pico Satellite Solar Cell Testbed). eoPortal Directory. Available online: https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/p/pssct (accessed on 11 January 2022).
- Kitts, C.; Hines, J.; Agasid, E.; Ricco, A.; Yost, B.; Ronzano, K.; Puig-Suari, J. The GeneSat-1 Microsatellite MissionA Challenge in Small Satellite Design. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 14–17 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa, D. CubeSat-to-Ground Communication and Mobile Modular Ground-Station Development. HSGC Rep. Number 2006, 7–15, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Hunyadi, G.; Klumpar, D.M.; Jepsen, S.; Larsen, B.; Obland, M. A commercial off the shelf (COTS) packet communications subsystem for the Montana EaRth-Orbiting Pico-Explorer (MEROPE) CubeSat. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 9–16 March 2002; Volume 1, pp. 473–478. [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen, T.; Prescott, G.; Villa, M.; Brown, D.; Hicks, J.; Edwards, A.; Lyke, J.; George, T.; Mobasser, S.; Yee, K.; et al. KUTESAT-2, a Student Nanosatellite Mission for Testing Rapid-Response Small Satellite Technologies in Low Earth Orbit. In Proceedings of the AIAA 3rd Responsive Space Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 25–28 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tag Archives: First-MOVE. AMSAT-UK. Available online: https://amsat-uk.org/tag/first-move/ (accessed on 11 January 2022).
- Noe, C. Design and Implementation of the Communications Subsystem for the Cal Poly CP2 Cubesat Project; California Polytechnic State University: San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- LaBerteaux, J.; Moesta, J.; Bernard, B. Cajun advanced picosatellite experiment. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE/AIAA 26th Digital Avionics Systems Conference, Dallas, TX, USA, 21–25 October 2007; p. 5-E. [Google Scholar]
- Taraba, M.; Rayburn, C.; Tsuda, A.; MacGillivray, C. Boeing’s CubeSat TestBed 1 Attitude Determination Design and on-Orbit Experience. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellite, Logan, UT, USA, 10–13 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz, A.; Ley, W.; Dachwald, B.; Miau, J.; Juang, J. Flight results of the COMPASS-1 picosatellite mission. Acta Astronaut. 2010, 67, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stras, L.N.; Kekez, D.D.; Wells, G.J.; Jeans, T.; Zee, R.E.; Pranajaya, F.M.; Foisy, D.G. The design and operation of the Canadian advanced nanospace eXperiment (CanX-1). In Proceedings of the AMSAT-NA 21st Space Symposium, Toronto, ON, Canada, 17–19 October 2003; pp. 150–160. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwmeester, J.; Aalbers, G.; Ubbels, W. Preliminary mission results and project evaluation of the delfi-c3 nano-satellite. In 4S Symposium Small Satellites Systems and Services; European Space Agency: Rhodes, Greece, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rankin, D.; Kekez, D.D.; Zee, R.E.; Pranajaya, F.M.; Foisy, D.G.; Beattie, A.M. The CanX-2 nanosatellite: Expanding the science abilities of nanosatellites. Acta Astronaut. 2005, 57, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alminde, L.; Bisgaard, M.; Vinther, D.; Viscor, T.; Østergard, K.Z. The AAU-Cubesat Student Satellite Project: Architectural Overview and Lessons Learned. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2004, 37, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- OUFTI-1 (Orbital Utility for Telecommunicaion Innovation). eoPortal Directory. Available online: https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/o/oufti-1 (accessed on 12 January 2022).
- Janson, S.; Hinkley, D. Spin Dynamics of the Pico Satellite Solar Cell Testbed Spacecraft. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellite, Logan, UT, USA, 10–13 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- RadSat (Radiation-tolerant SmallSat Computer System). Available online: https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/r/radsat (accessed on 13 January 2022).
- Noca, M.; Jordan, F.; Steiner, N.; Choueiri, T.; George, F.; Roethlisberger, G.; Scheidegger, N.; Peter-Contesse, H.; Borgeaud, M.; Krpoun, R.; et al. Lessons Learned from the First Swiss Pico-Satellite: SwissCube. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellite, Logan, UT, USA, 10–13 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Young-Keun, C.; Byoung-Young, M.; Ki-Lyong, H.; Soo-Jung, K.; Suk-Jin, K. Development of the HAUSAT-2 nanosatellite for low-cost technology demonstration. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Recent Advances in Space Technologies, Istanbul, Turkey, 9–11 June 2005; pp. 173–179. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtulus, C.; Baltaci, T.; Ulusoy, M.; Aydin, B.T.; Tutkun, B.; Inalhan, G.; Cetiner-Yildirim, N.O.; Karyot, T.B.; Yarim, C.; Edis, F.O.; et al. iTU-pSAT I: Istanbul Technical University Student Pico-Satellite Program. In Proceedings of the 2007 3rd International Conference on Recent Advances in Space Technologies, Istanbul, Turkey, 14–16 June 2007; pp. 725–732. [Google Scholar]
- Ricco, A.; Parra, M.; Niesel, D.; McGinnis, M.; Ly, D.; Kudlicki, A.; Hines, J.; Piccini, M.; Timucin, L.; Beasley, C.; et al. PharmaSat: Drug dose dependence results from an autonomous microsystem-based small satellite in low Earth orbit. In 2010 Solid-State Sensors, Actuators, and Microsystems Workshop; Transducer Research Foundation: Hilton Head Island, SC, USA, 2010; pp. 110–113. [Google Scholar]
- Starr, G.J.; Wersinger, J.M.; Chapman, R.; Riggs, L.; Nelson, V.P.; Klingelhoeffer, J.; Stroud, C.E. Application of Embedded Systems in Low Earth Orbit for Measurement of Ionospheric Anomalies. Presented at the International Conference on Embedded Systems and Applications, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 13–16 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kuester, D.G.; Radhakrishna, P.N.P. A 2.4 GHz High Speed Communications System for Cubesat Applications; Colorado Space Grant Consortium; University of Colorado at Boulder: Boulder, CO, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dontchev, K.A.; Ghorakavi, K.; Haag, C.E.; Liu, T.M.; Ramos, R. M-cubed: University of michigan multipurpose minisatellite with optical imager payload. In Proceedings of the AIAA Space 2010 Conference & Exhibition, Anaheim, CA, USA, 30 August –2 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gregorio, A.; Bernardi, T.; Carrato, S.; Kostadinov, I.; Messerotti, M.; Stalio, R. AtmoCube: Observation of the Earth atmosphere from the space to study” space weather” effects. In Proceedings of the Recent Advances in Space Technologies, Istanbul, Turkey, 20–22 November 2003; pp. 188–193. [Google Scholar]
- Aherne, M.; Barrett, T.; Hoag, L.; Teegarden, E.; Ramadas, R. Aeneas--Colony I Meets Three-Axis Pointing. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellite, Logan, UT, USA, 8–11 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Balan, M.; Piso, M.-I.; Stoica, A.M.; Dragasanu, C.; Trusculescu, M.; Dumitru, C. Goliat space mission: Earth observation and near Earth environment monitoring using nanosatellites. In Proceedings of the 59th International Astronautical Congress, Glasgow, UK, 29 September–3 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- CHOMPTT (CubeSat Handling of Multisystem Precision Time Transfer). Available online: https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/c-missions/chomptt (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Stolarski, M.; Dobrowolski, M.; Graczyk, R.; Kurek, K. Space platform for student cubesat pico-satellite. In Photonics Applications in Astronomy, Communications, Industry, and High-Energy Physics Experiments; SPIE: Wilga, Poland, 2009; Volume 7502. [Google Scholar]
- EncinasPlaza, J.M.; VilanVilan, J.A.; AquadoAgelet, F.; BrandiaranMancheno, J.; LopezEstevez, M.; MartinezFernandez, C.; SarmientoAres, F. Xatcobeo: Small Mechanisms for CubeSat Satellites–Antenna and Solar Array Deployment. In Proceedings of the 40th Aerospace Mechanisms Symposium, NASA Kennedy Space Centre, Cocoa Beach, FL, USA, 12–14 May 2010; pp. 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- E1P-2. eoPortal Directory. Available online: https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/e/e1p-2 (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- Francis, C.L. ISM S-Band CubeSat Radio designed for the PolySat System Board; California Polytechnic State University: San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- De Jong, S.; Maddox, E.; Vollmuller, G.J.; Schuurbiers, C.A.; Van Swaaij, R.A.; Ubbels, W.J.; Hamann, R.J. The Delfi-n3Xt nanosatellite: Space weather research and qualification of microtechnology. In Proceedings of the 59th International Astronautical Congress, Scotland, UK, 29 September–3 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Clark, K.; Unwin, M.; Zackrisson, J.; Shiroma, W.A.; Akagi, J.M.; Maynard, K.; Garner, P.; Boccia, L.; Amendola, G.; et al. Antennas for modern small satellites. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2009, 51, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmensiek, R.; Zyl, R.R.V.; Visser, D.F. The design of an HF antenna on a 1U CubeSat. In Proceedings of the 2013 Africon, Pointe aux Piments, Mauritius, 9–12 September 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Move. Available online: https://www.move2space.de/missions/first-move/ (accessed on 29 January 2022).
- Busch, S.; Bangert, P.; Dombrovski, S.; Schilling, K. UWE-3, in-orbit performance and lessons learned of a modular and flexible satellite bus for future pico-satellite formations. Acta Astronaut. 2015, 117, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederstrasser, C.; Hassan, A.; Hermle, J.; Kemp, A.; McGlothlin, A.; Samant, D.; Stein, J. TJ3Sat–The First Satellite Developed and Operated by High School Students. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellite, Logan, UT, USA, 10–13 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sandau, R. Status and trends of small satellite missions for Earth observation. Acta Astronaut. 2010, 66, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, N.; Eyer, J.; Larouche, B.; Zee, R. Precision Formation Flight: The CanX-4 and CanX-5 Dual Nanosatellite Mission. In Proceedings of the 21st Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellite, Logan, UT, USA, 13–16 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell, W.; Allen, G.; Galbraith, C.; Hancock, T.; Leslie, R.; Osaretin, I.; Retherford, L.; Scarito, M.; Semisch, C.; Shields, M.; et al. Nanosatellites for earth environmental monitoring: The MicroMAS project. In Proceedings of the Microwave Radiometry and Remote Sensing of the Environment (MicroRad), Rome, Italy, 5–9 March 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Veljovic, M.J.; Skrivervik, A.K. Aperture-Coupled Low-Profile Wideband Patch Antennas for CubeSat. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 3439–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janson, S.; Welle, R. The NASA Optical Communication and Sensor Demonstration Program. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellite, Logan, UT, USA, 10–15 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmat-Samii, Y.; Manohar, V.; Kovitz, J.M. For Satellites, Think Small, Dream Big: A review of recent antenna developments for CubeSats. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2017, 59, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatomirescu, A.; Pedersen, G.F.; Christiansen, J.; Gerhardt, D. Antenna system for nano-satelite mission GOMX-3. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE-APS Topical Conference on Antennas and Propagation in Wireless Communications (APWC), Cairns, QLD, Australia, 19–23 September 2016; pp. 282–285. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, J.; Perez, J.; Reed, H.; McLelland, A.; Kanipe, D.; Provence, R.; Runkle, T. AggieSat2 Student Satellite Mission. In Proceedings of the 50th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, AIAA, Nashville, TN, USA, 9–12 January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kestilä, A.; Tikka, T.; Peitso, P.; Rantanen, J.; Näsilä, A.; Nordling, K.; Saari, H.; Vainio, R.; Janhunen, P.; Praks, J.; et al. Aalto-1 nanosatellite technical description and mission objectives. Geosci. Instrum. Method. Data Syst. 2013, 2, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Praks, J.; Kestilä, A.; Hallikainen, M.; Saari, H.; Antila, J.; Janhunen, P.; Vainio, R. Aalto-1—An experimental nanosatellite for hyperspectral remote sensing. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011; pp. 4367–4370. [Google Scholar]
- The UNSW-EC0 Cubesat. Australian Centre for Space Engineering Research (ACSER). Available online: https://www.acser.unsw.edu.au/system-basics (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Landsman, H.; Ruckman, L.; Varner, G.S. AURA—A radio frequency extension to IceCube. In Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 604, pp. S70–S75. [Google Scholar]
- Fraile, J.J.F.; Laverón-Simavilla, A.; Calvo, D.; Benavides, E.M. The QBito CubeSat: Applications in Space Engineering Education at Technical University of Madrid. In Proceedings of the 40th COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Moscow, Russia, 2–10 August 2014; Volume 40, p. PE-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hodges, R.E.; Radway, M.J.; Toorian, A.; Hoppe, D.J.; Shah, B.; Kalman, A.E. ISARA—Integrated Solar Array and Reflectarray CubeSat deployable Ka-band antenna. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 19–24 July 2015; pp. 2141–2142. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.P.; Park, S.Y.; Song, Y.B.; Kim, G.N.; Lee, K.; Oh, H.J.; Yim, J.C.; Lee, E.; Hwang, S.H.; Kim, S.; et al. Cubesat development for CANYVAL-X mission. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Space Operations, Deajeon, South Korea, 16–20 May 2016; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Inc., AIAA: Reston, VA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bangert, P.; Kramer, A.; Schilling, K. UWE-4: Integration State of the First Electrically Propelled 1U CubeSat. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellite, Logan, UT, USA, 5–10 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- CUTE-1. eoPortal Directory. Available online: https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/c-missions/cute-i (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Chalermwisutkul, S.; Jirawattanaphol, A.; Jantarachote, V.; Arpanutud, K. Communication system development of the pioneer Thai CubeSat project: KNACKSAT. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), Phuket, Thailand, 30 October–2 November 2017; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Peral, E.; Tanelli, S.; Haddad, Z.; Sy, O.; Stephens, G.; Im, E. Raincube: A proposed constellation of precipitation profiling radars in CubeSat. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 1261–1264. [Google Scholar]
- ION CubeSat Information Sheet. Available online: http://cubesat.ece.illinois.edu/Files/ION_Info_Sheet.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- Fragnier, R.; Contreres, R.; Palacin, B.; Elis, K.; Bellion, A.; Romier, M.; Fur, G.L.; Maleszka, T. Collocated Compact UHF and L-Band Antenna for Nanosatellite Applications. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellite, Logan, UT, USA, 4–9 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bellion, A.; Elis, K.; de Gaetano, S. New compact S-band antenna for Nanosatellite TeleMetry and TeleCommand applications-EyeSat program. In Proceedings of the 2016 10th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Davos, Switzerland, 10–15 April 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Talavera, M.R.; Sodnik, Z.; Lopez, P.; Alonso, A.; Viera, T.; Oppenhauser, G. Preliminary results of the in-orbit test of ARTEMIS with the Optical Ground Station. In High-Power Lasers and Applications; SPIE: Wilga, Poland, 2002; Volume 4635, p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- SPATIUM (Space Precision Atomic-clock TIming Utility Mission). Available online: https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/s/spatium (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Corvus-BC. Available online: https://spaceflight101.com/soyuz-kanopus-v-ik/corvus-bc/ (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Lemur-2. Nanosats Database. Available online: https://www.nanosats.eu/sat/lemur-2 (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Flock 1 Imaging Constellation. EoPortal Dicrectory. Available online: https://earth.esa.int/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/f/flock-1 (accessed on 29 March 2022).
- Kepler Awarded Contributions for Small Satellite Phased Array Technology Development. Available online: https://kepler.space/2020/08/05/kepler-awarded-contributions-for-small-satellite-phased-array-technology-development/ (accessed on 29 March 2022).
- TTU. The International Amateur Radio Union. Available online: http://www.amsatuk.me.uk/iaru/formal_detail.php?serialnum=565 (accessed on 30 March 2022).
- NetSat. Nanosats Database. Available online: https://www.nanosats.eu/sat/netsat (accessed on 31 March 2022).
- TRISAT (NANOsky, Misija Trisat). Nanosats Database. Available online: https://www.nanosats.eu/sat/trisat (accessed on 31 March 2022).
- CICERO 1, …, 12/OSM 1 CICERO. Gunter’s Space Page. Available online: https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/cicero.htm (accessed on 31 March 2022).
- PICASSO (Pico-Satellite for Atmospheric and Space Science Observations). EoPortal Dicrectory. Available online: https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/p/picasso (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- AMICal-Sat. Gunter’s Space Page. Available online: https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/amical-sat.htm (accessed on 2 April 2022).
- Astrocast Commercial IoT Network Service. EoPortal Dicrectory. Available online: https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/a/astrocast (accessed on 2 April 2022).
- BeeSat 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13. Gunter’s Space Page. Available online: https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/beesat-5.htm (accessed on 4 April 2022).
- RADCUBE. Nanosats Database. Available online: https://www.nanosats.eu/sat/radcube (accessed on 4 April 2022).
- ExoCube 1, 2 (CP 10, 12). Gunter’s Space Page. Available online: https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/exocube.htm (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- CM1 (Cesium Mission 1). eoPortal Dicrectory. Available online: https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/c-missions/cesium-mission-1 (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- CAS-9. The International Amateur Radio Union. Available online: http://www.amsatuk.me.uk/iaru/formal_detail.php?serialnum=804 (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- PIXL-1 CubeSat Mission. eoPortal Dicrectory. Available online: https://eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/content/-/article/pixl-1 (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- W-Cube Transmits the First 75 GHz Signal from Space. KUVA SPACE. Available online: https://kuvaspace.com/2021/09/01/w-cube-transmits-the-first-75-ghz-signal-from-space/ (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Fleet Space’s Centauri 5 Satellite Successfully Launched from the SpaceX Transporter-5 Rideshare Mission. Stanews. Available online: https://news.satnews.com/2022/05/25/fleet-spaces-centauri-5-satellite-successfully-launched-from-the-spacex-transporter-5-rideshare-mission/ (accessed on 6 April 2022).
- ELO Alpha. Gunter’s Space Page. Available online: https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/elo-alpha.htm (accessed on 6 April 2022).
- Loren, C.; Chi-Kuang, C.; Cheng-Ling, K.; Jann-Yenq, L.; Duann, Y.; Chandran, A.; Tzu-Wei, F.; Priyadarshan, H.; Kandi, K.A.; Evonosky, W.; et al. IDEASSat: The Ionosphere Dynamics Explorer and Attitude Subsystem Satellite. In Proceedings of the 31nd Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellite, Logan, UT, USA, 5–10 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kleos Space to Launch Development Technology into Orbi—3rd July 2020. sUAS News. Available online: https://www.suasnews.com/2020/06/kleos-space-to-launch-development-technology-into-orbit-3rd-july-2020/ (accessed on 7 April 2022).
- Two NanoAvionics-Built Smallsats Were Passengers on the SpaceX Transporter-2 Mission Launch to Successful Orbit. Satnews. Available online: https://news.satnews.com/2021/07/06/two-nanoavionics-built-smallsats-were-passengers-on-the-spacex-transporter-2-mission-launch-to-successful-orbit/ (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Palmroth, M.; Praks, J.; Vainio, R.; Janhunen, P.; Kilpua, E.K.J.; Afanasiev, A.; Ala-Lahti, M.; Alho, A.; Asikainen, T.; Asvestari, E.; et al. FORESAIL-1 CubeSat Mission to Measure Radiation Belt Losses and Demonstrate Deorbiting. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 124, 5783–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Into the Future Trend Beyond 5G: NCKU-Developed Satellite IRIS-A Successfully Launched into Space. Available online: https://web.ncku.edu.tw/p/406-1000-235668,r3344.php?Lang=en (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- HYPSO (HYPerspectral Smallsat for Ocean Observation. EoPortal Dicrectory. Available online: https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/h/hypso (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Thales Alenia Space to Build Two Prototype Satellites for Constellation Venture. Spacenews. Available online: https://spacenews.com/thales-alenia-space-to-build-two-prototype-satellites-for-constellation-venture/ (accessed on 9 April 2022).
- SatNOGS DB. Available online: https://db.satnogs.org/satellite/BZWR-6172-2785-3507-5423 (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Planetum-1. Spacemanic. Available online: https://www.spacemanic.com/missions/planetum-1/ (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- SpaceBEE 1, 2, 3, 4. Gunter’s Space Page. Available online: https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/spacebee.htm (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Tsuda, Y.; Sako, N.; Eishima, T.; Ito, T.; Arikawa, Y.; Miyamura, N.; Tanaka, A.; Nakasuka, S. University of Tokyo’s CubeSat Project-Its Educational and Technological Significance. In Proceedings of the 15th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 13–16 August 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Costantine, J.; Tawk, Y.; Christodoulou, C.G.; Banik, J.; Lane, S. CubeSat Deployable Antenna Using Bistable Composite Tape-Springs. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2012, 11, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphey, T.; Jeon, S.; Biskner, A.; Sanford, G. Deployable Booms and Antennas Using Bi-Stable Tape-Springs. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellite, Logan, UT, USA, 9–12 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Murphey, T.W.; Sanford, G.E.; Jeon, S. Deployable Space Boom Using Bi-Stable Tape Spring Mechanism. U.S. Patent No. 8,770,522 B1, 8 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Leao, T.F.C.; Mooney-Chopin, V.; Trueman, C.W.; Gleason, S. Design and Implementation of a Diplexer and a Dual-Band VHF/UHF Antenna for Nanosatellites. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2013, 12, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, H.J.; Haider, M.M.; Siddique, M.K.; Amin, M. Analysis of G-shape antennas mounted on a CUBESAT. In Proceedings of the 2008 2nd International Conference on Advances in Space Technologies, Islamabad, Pakistan, 29–30 November 2008; pp. 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Schraml, K.; Narbudowicz, A.; Chalermwisutkul, S.; Heberling, D.; Ammann, M.J. Easy-to-deploy LC-loaded dipole and monopole antennas for cubesat. In Proceedings of the 2017 11th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EUCAP), Paris, France, 19–24 March 2017; pp. 2303–2306. [Google Scholar]
- Wilke, R.; Reiffenrath, M.; Parow-Souchon, K.; Heberling, D. S-Band, UHF and VHF Communication System for Cubesats including Ground Station Software. In Proceedings of the 8th Pico- and Nanosatellite Workshop, Würzburg, Germany, 15–16 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Raad, R.; Theoharis, P.I.; Tubbal, F. Dual-Band Folded-End Dipole Antenna for Plastic CubeSats. IEEE J. Miniat. Air Space Syst. 2020, 1, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Babuscia, A.; Corbin, B.; Knapp, M.; Jensen-Clem, R.; van de Loo, M.; Seager, S. Inflatable antenna for cubesats: Motivation for development and antenna design. Acta Astronaut. 2013, 91, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubbal, F.E.; Raad, R.; Chin, K.W. A wideband F-shaped patch antenna for S-band CubeSats communications. In Proceedings of the 2016 10th International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Systems (ICSPCS), Surfers Paradise, QLD, Australia, 19–21 December 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Liao, S.; Wang, J.; Xue, K.; Balfour, E.A.; Luo, Y. A New Patch Antenna Designed for CubeSat: Dual feed, L/S dual-band stacked, and circularly polarized. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2016, 58, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, O.F.G.; Vargas, R.E.D.; Perez, J.A.H.; Erazo, S.B.C. S-band koch snowflake fractal antenna for cubesats. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE ANDESCON, Arequipa, Peru, 19–21 October 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tubbal, F.; Raad, R.; Chin, K.W.; Butters, B. S-band Planar Antennas for a CubeSat. Int. J. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2015, 7, 559–568. [Google Scholar]
- Abulgasem, S.; Tubbal, F.; Raad, R.; Theoharis, P.I.; Liu, S.; Khan, M.U.A. A wideband metal-only patch antenna for CubeSat. Electronics 2020, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaseelan, S.; Murugan, M. High gain patch antenna for CubeSat. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking (WiSPNET), Chennai, India, 23–25 March 2016; pp. 52–54. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.T.; Cho, M.; Samsuzzaman, M.; Kibria, S. Compact Antenna for Small Satellite Applications [Antenna Applications Corner]. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2015, 57, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakoyiannis, C.G.; Constantinou, P. A compact microstrip antenna with tapered peripheral slits for CubeSat RF Payloads at 436MHz: Miniaturization techniques, design & numerical results. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Workshop on Satellite and Space Communications, Toulouse, France, 1–3 October 2008; pp. 255–259. [Google Scholar]
- Yekan, T.; Baktur, R. Conformal Integrated Solar Panel Antennas: Two effective integration methods of antennas with solar cells. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2017, 59, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.N. Integrated Solar Panel Antennas for Cube Satellites; Utah State University: Logan, UT, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, E.H.; Leung, K.W. Transparent Dielectric Resonator Antennas for Optical Applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, B.K.; Podilchak, S.K.; Antar, Y.M.M. Circularly polarized meshed patch antenna for cubesats and other small sattelites. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), Fajardo, PR, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 1547–1548. [Google Scholar]
- Tariq, S.; Baktur, R. Circularly polarized UHF up- and downlink antennas integrated with CubeSat solar panels. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 19–24 July 2015; pp. 1424–1425. [Google Scholar]
- Yekan, T.; Baktur, R. Polarization reconfigurable antenna for small satellite application. In Proceedings of the 2016 United States National Committee of URSI National Radio Science Meeting (USNC-URSI NRSM), Boulder, CO, USA, 6–9 January 2016; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Neveu, N.; Garcia, M.; Casana, J.; Dettloff, R.; Jackson, D.R.; Chen, J. Transparent microstrip antennas for CubeSat applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Wireless for Space and Extreme Environments, Baltimore, MD, USA, 7–9 November 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Jackson, D.R.; Chen, J.; Fink, P.W.; Lin, G.Y. Broadband transparent circularly-polarized microstrip antennas for CubeSats. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), Fajardo, PR, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 1545–1546. [Google Scholar]
- Montano, R.; Neveu, N.; Palacio, S.; Martinez, E.; Jackson, D.R.; Chen, J. Development of Low-profile Antennas for CubeSats. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 2–7 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa, D.; Hummer, K.; Ciffone, M. Deployable Helical Antenna for nano-Satellites. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 2–7 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Muri, P.; Challa, O.; McNair, J. Enhancing small satellite communication through effective antenna system design. In Proceedings of the Milcom 2010 Militar Communications Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 31 October–3 November 2010; pp. 347–352. [Google Scholar]
- Ernest, A.J.; Tawk, Y.; Costantine, J.; Christodoulou, C.G. A Bottom Fed Deployable Conical Log Spiral Antenna Design for CubeSat. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantine, J.; Tawk, Y.; Christodoulou, C.G.; Maqueda, I.; Sakovsky, M.; Pellegrino, S. A new UHF deployable antenna for cubeSats. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 19–24 July 2015; pp. 1426–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Costantine, J.; Tran, D.; Shiva, M.; Tawk, Y.; Christodoulou, C.G.; Barbin, S.E. A deployable quadrifilar helix antenna for CubeSat. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation, Chicago, IL, USA, 8–14 July 2012; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Vourch, C.J.; Drysdale, T.D. V-Band Bull’s Eye Antenna for CubeSat Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2014, 13, 1092–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borthakur, M.; Khan, T.; Dash, S.K.K. Circularly polarized dual-band cylindrical dielectric resonator antenna for Cubesat applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 XXXIInd General Assembly and Scientific Symposium of the International Union of Radio Science (URSI GASS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 19–26 August 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Dicandia, F.A.; Genovesi, S. A compact CubeSat antenna with beamsteering capability and polarization agility: Characteristic modes theory for breakthrough antenna design. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2020, 62, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ovejero, D.; Chahat, N.; Sauleau, R.; Chattopadhyay, G.; Maci, S.; Ettorre, M. Additive Manufactured Metal-Only Modulated Metasurface Antennas. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 6106–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, P.A.; Steinbeck, J.W.; Minelli, R.J.; Muller, C. Large, deployable S-band antenna for 6U CubeSat. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 8–13 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design; Wiley-Interscience: Hopoken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Romanofsky, R. Array Phase Shifters: Theory and Technology. In Antenna Engineering Handbook; NASA, McGraw Hil: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mailloux, R.J. Phased Array Antenna Array, 2nd ed.; Artech House Boston: Norwood, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Budianu, A.; Meijerink, A.; Bentum, M.J. Swarm-to-Earth communication in OLFAR. Acta Astronaut. 2015, 107, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomar, W.; Degnan, J.; Mancewicz, S.; Sidley, M.; Cutler, J.; Gilchrist, B. An extendable solar array integrated Yagi-Uda UHF antenna for CubeSat platforms. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), Spokane, WA, USA, 3–8 July 2011; pp. 3022–3024. [Google Scholar]
- Maciulis, L.; Buzas, V. LituanicaSAT-2: Design of the 3U in-Orbit Technology Demonstration CubeSat. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2017, 32, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.; Sharma, S.K.; Chieh, J.C.S.; Rowland, J. W-band circular polarized series fed single plane beamsteering array antenna with 4-bit phase shifter for cubesat applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–14 July 2017; pp. 2555–2556. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Raad, R.; Theoharis, P.I.; Tubbal, F.E. A Printed Yagi Antenna for CubeSat with Multi-Frequency Tilt Operation. Electronics 2020, 9, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.; Hawkins, J.; Thorsen, D. Improving cubesat downlink capacity with active phased array antennas. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 1–8 March 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Pittella, E.; Pisa, S.; Pontani, M.; Nascetti, A.; D’Atanasio, P.; Zambotti, A.; Hadi, H. Feature article: Reconfigurable S-band patch antenna system for cubesat satellites. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2016, 31, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascetti, A.; Pittella, E.; Teofilatto, P.; Pisa, S. High-Gain S-band Patch Antenna System for Earth-Observation CubeSat Satellites. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmensiek, R. Design of a wideband circularly polarized 2 x 2 array with shorted annular patches at X-band on a CubeSat. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), Phuket, Thailand, 30 October–2 November 2017; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, R.; Anagnostou, D.E.; Horst, S.J.; Hoffman, J.P. Two antenna arrays for remote sensing applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 4–11 March 2017; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Theoharis, P.I.; Raad, R.; Tubbal, F.; Abulgasem, S. High-Gain Circular Polarized Microstrip Patch Array for X-band CubeSat Applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 15th International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Systems (ICSPCS), Sydney, Australia, 13–15 December 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hodges, R.E.; Hoppe, D.J.; Radway, M.J.; Chahat, N.E. Novel deployable reflectarray antennas for CubeSat communications. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 17–22 May 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chahat, N.; Hodges, R.E.; Sauder, J.; Thomson, M.; Peral, E.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. CubeSat Deployable Ka-Band Mesh Reflector Antenna Development for Earth Science Missions. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 2083–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, R.E.; Chahat, N.; Hoppe, D.J.; Vacchione, J.D. A Deployable High-Gain Antenna Bound for Mars: Developing a new folded-panel reflectarray for the first CubeSat mission to Mars. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2017, 59, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozar, D.M. Wideband reflectarrays using artificial impedance surfaces. Electron. Lett. 2007, 43, 148–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, M.; Sauder, J.F.; Hodges, R.; Pellegrino, S. Large-Area Deployable Reflectarray Antenna for CubeSats. In Proceedings of the AIAA Scitech 2019 Forum AIAA SciTech Forum: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–11 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Veljovic, M.J.; Skrivervik, A.K. Circularly Polarized Transmitarray Antenna for CubeSat Intersatellite Links in K-Band. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2020, 19, 1749–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahat, N.; Sauder, J.; Hodges, R.; Thomson, M.; Samii, Y.R.; Peral, E. Ka-band high-gain mesh deployable reflector antenna enabling the first radar in a CubeSat: RainCube. In Proceedings of the 2016 10th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Davos, Switzerland, 10–15 April 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Costantine, J.; Tawk, Y.; Ernest, A.; Christodoulou, C.G. Deployable antennas for CubeSat and space communications. In Proceedings of the 2012 6th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EUCAP), Prague, Czech Republic, 26–30 March 2012; pp. 837–840. [Google Scholar]
- Akbar, P.R.; Saito, H.; Zhang, M.; Hirokawa, J.; Ando, M. Parallel-Plate Slot Array Antenna for Deployable SAR Antenna Onboard Small Satellite. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuscia, A.; Choi, T.; Lee, C.; Cheung, K.M. Inflatable antennas and arrays for interplanetary communication using CubeSats and smallsats. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 7–14 March 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Iwami, R.T.; Chun, T.F.; Tonaki, W.G.; Shiroma, W.A. A power-detecting, null-scanning, retrodirective array for a CubeSat platform. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS), Honololu, HI, USA, 4–9 June 2017; pp. 662–665. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, B.; Ohta, A.; Tamamoto, M.; Shiroma, G.; Miyamoto, R.; Shiroma, W. Self-Steering Antenna Arrays for Distributed Picosatellite Networks. In Proceedings of the 17th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellite, Logan, UT, USA, 11–14 August 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, B.T.; Roque, J.D.; Sung, S.S.; Shiroma, G.S.; Miyamoto, R.Y.; Shiroma, W.A. A quadruple subharmonic phase-conjugating array for secure picosatellite crosslinks. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest (IEEE Cat. No.04CH37535), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 6–11 June 2004; Volume 3, pp. 1687–1690. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno, T.J.; Roque, J.D.; Murakami, B.T.; Yoneshige, L.K.; Shiroma, G.S.; Miyamoto, R.Y.; Shiroma, W.A. Antennas for distributed nanosatellite networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACES International Conference on Wireless Communications and Applied Computational Electromagnetics, Honolulu, HI, USA, 3–7 April 2005; pp. 606–609. [Google Scholar]
- Bagri, D.S.; Statman, J.I.; Gatti, M.S. Proposed array-based deep space network for NASA. Proc. IEEE 2007, 95, 1916–1922. [Google Scholar]
- Napier, P.J.; Thompson, A.R.; Ekers, R.D. The very large array: Design and performance of a modern synthesis radio telescope. Proc. IEEE 1983, 71, 1295–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogstad, D.H.; Pham, T.T.; Mileant, A. Antenna Arraying Techniques in the Deep Space Network; Deep-Space Communications and Navigation Series; No. xiii; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; 166p. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, K.M. Eigen Theory for Optimal Signal Combining: A Unified Approach. JPL Telecommunicayions Data Acquis. Prog. Rep. 1996, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rogstad, D.H. The SUMPLE Algorithm for Aligning Arrays of Receiving Radio Antennas: Coherence Achieved with Less Hardware and Lower Combining Loss; The Interplanetary Network Progress Report; Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.H.; Kar-Ming, C.; Vilnrotter, V.A. Fast eigen-based signal combining algorithms for large antenna arrays. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference (Cat. No.03TH8652), Helena, MY, USA, 8–15 March 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1123–1129. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.F.; Wang, X.H.; Gao, C.J.; Huang, Q.L.; Shi, X.W. Adaptive correlation algorithm for aligning antenna arrays in deep space communication. Electron. Lett. 2013, 49, 733–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
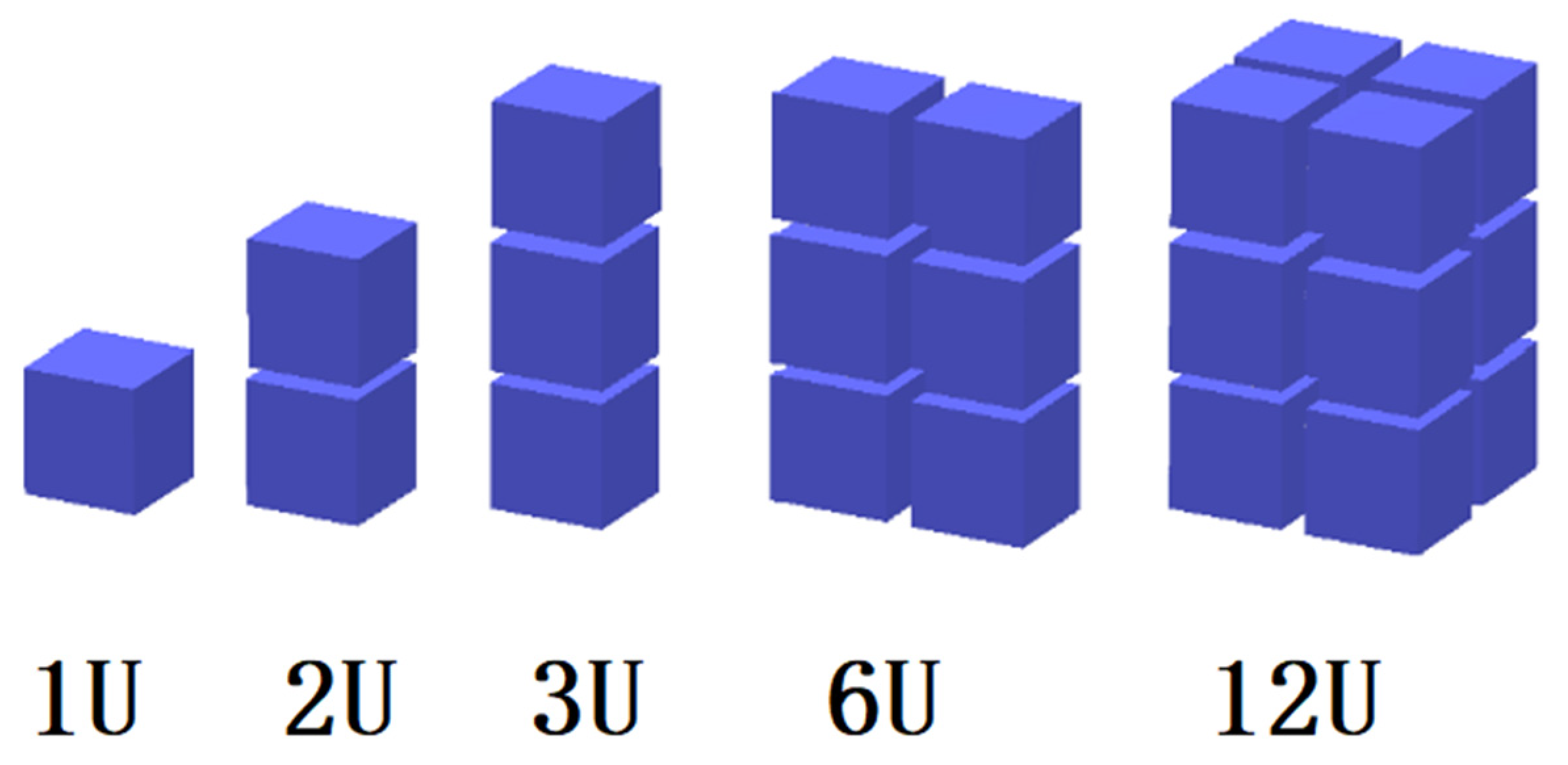





| Size | Dimensions | Wet Mass |
|---|---|---|
| 1U | 10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm | 1.3 kg |
| 2U | 10 cm × 10 cm × 20 cm | 2.6 kg |
| 3U | 10 cm × 10 cm × 30 cm | 3.9 kg |
| 6U | 10 cm × 20 cm × 30 cm | 7.8 kg |
| 12U | 10 cm × 10 cm × 60 cm | 15.6 kg |
| Restrictions | Description |
|---|---|
| Size and Mass | Light weight and compact to fit the 10 cm × 10 cm size of a CubeSat surface in the case of 1U (without considering deployment volume). |
| Deployment | Deployment mechanism must be chosen or designed to minimize risk of deployment failure. |
| Attitude Control | Choice between active or passive control systems will determine the antenna pointing accuracy, as well as the choice of fixed or steering beam antenna. |
| Frequency Band and Bandwidth | Set by the mission specifications and allocated by the ITU or FCC. Dictates the uplink and downlink. |
| Loss | Antenna radiation or aperture efficiency must be higher than 50%. Antenna must match well with a reflection coefficient less than −10 dB. |
| Orbit (Communication Range) | Low Earth orbit: 400–2000 km Inter-satellite: Depends on swarm architecture Deep space: >2 × 106 km |
| Gain | Choice between low gain (LG), medium gain (MG), or high gain (HG), according to the available RF power budget and orbit. |
| Link Budget | High enough gain to provide the required SNR according to the modulation used. |
| Footprint | Dictate the beam width or the shape of the radiation pattern, as well as the size of the aperture. |
| Space Environment and Durability | Withstand thermal variations from −40 to +85 Celsius. Must pass thermal-vacuum cycling test (TVCT) and vibration test. |
| Cost | Off-the-shelf materials to reduce budget. |
| Polarization | Circular polarization to reduce losses due to polarization mismatch. Satisfy the cross-polarization levels set by the mission specifications. |
| Band Designator | Dimensions |
|---|---|
| HF | 3–30 MHz |
| VHF | 30–300 MHz |
| UHF | 300–1000 MHz |
| L | 1–2 GHz |
| S | 2–4 GHz |
| Ku | 12–18 GHz |
| Ka | 26.5–40 GHz |
| V | 40–75 GHz |
| W | 75–110 GHz |
| CubeSat Mission Name | Antenna Type | Mission Type | Size | Frequency Band | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XI-IV (CO-57) [44] | Monopole and Dipole | Educational | 1U | VHF/UHF | 2003 |
| DTUSat-1 [45] | Monopole and Dipole | Educational | 1U | UHF | 2003 |
| QuakeSat [30] | Four Monopoles | Earth Observation Technology Demonstration | 3U | UHF | 2003 |
| CUTE-1 [46] | Three Monopoles | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF | 2003 |
| Cute-1.7 + APD [47] | Dipole | Technology Demonstration | 2U | UHF and L-Band | 2003 |
| XI-V (CO-58) [44] | Dipole | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF | 2005 |
| NCube [48] | Monopole and Patch | Educational | 1U | VHF, UHF, and S-Band | 2005 |
| Cute-1.7 + APD II [49] | Three Monopoles | Educational Technology Demonstration | 2U | UHF and L-Band | 2006 |
| CP1 [16,50] | Dipole | Scientific | 1U | UHF | 2006 |
| GeneSat-1 [51] | Monopole | Scientific | 3U | UHF and S-Band | 2006 |
| Mea Huaka [52] | Monopole | N/A | 1U | UHF | 2006 |
| MEROPE [53] | Dipole | Scientific | 1U | UHF | 2006 |
| KUTESat-2 [54] | Dipoles | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF and VHF | 2006 |
| ION [55] | Dipole | Technology Demonstration | 3U | UHF | 2006 |
| CP2/CP4 [50,56] | Dipole | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF | 2007 |
| CAPE-1 [57] | Monopole | Educational | 1U | UHF | 2007 |
| CSTB1 [58] | Dipole | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF | 2007 |
| COMPASS-1 [59] | Monopole and Dipole | Earth Observation | 1U | UHF and VHF | 2008 |
| CanX-1 [60] | Monopoles | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF | 2008 |
| Delfi-C3 [61] | Monopole and Dipole | Educational | 3U | UHF and VHF | 2008 |
| CanX-2 [62] | Monopole and Patch | Technology Demonstration | 3U | UHF and S-Band | 2008 |
| AAU [63] | Dipoles | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF | 2008 |
| PSSCT [64,65] | Patch | Technology Demonstration | 12.5 cm × 12.5 cm × 25 cm | UHF | 2008 |
| SEED-2 [66] | Monopoles | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF | 2008 |
| SwissCube [67] | Monopoles | Scientific | 1U | UHF | 2009 |
| BeeSat (Known as DRAGON SAT with AggieSat2) [46] | Monopoles | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF | 2009 |
| CP3/CP6 [50] | Dipole | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF | 2009 |
| HAUSAT-2 [68] | Dipoles | Educational | 1U | UHF | 2009 |
| ITUpSat-I [69] | Four Monopoles | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF | 2009 |
| Pharmasat- [70] | Patch | Scientific | 3U | S-Band | 2009 |
| AubieSat-1 [71] | Dipole | Educational Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF | 2011 |
| CP5 [50] | Dipole | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF | 2011 |
| Hermes [72] | Monopole | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF and S-Band | 2011 |
| KySat [45] | Three Monopoles | Educational Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF, VHF, and S-Band | 2011 |
| M-Cubed [73] | Monopole and Dipole | Educational Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF and VHF | 2011 |
| E1P-2 [74] | Monopole | Scientific | 1U | UHF | 2011 |
| AtmoCube [74] | Dipole | Scientific | 1U | UHF | 2012 |
| Aeneas [75] | Parabolic Meshed Reflector | Surveillance | 3U | UHF | 2012 |
| Goliat [76] | Monopole | Earth Observation | 1U | UHF and S-Band | 2012 |
| UNICUBESAT [77] | Monopole | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF | 2012 |
| PWSat [78] | Two Monopoles | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF | 2012 |
| XaTcobeo [79] | Four Monopoles | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF | 2012 |
| e-st@r [80] | Dipole | Educational | 1U | UHF | 2012 |
| CAPE-2 [57] | Monopole | Educational | 1U | UHF and VHF | 2013 |
| CP8(IPEX) [50,81] | Monopole | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF | 2013 |
| Delfin3Xt [82] | Monopole and Patch | Technology Demonstration | 3U | UHF, VHF, and S-Band | 2013 |
| ExoplanetSat [83] | Patch | Technology Demonstration | 3U | S-Band | 2013 |
| FireFly [22] | Monopole | Scientific | 3U | UHF | 2013 |
| ZACUBE-1 [84] | Dipole | Scientific | 1U | HF | 2013 |
| MOVE I [85] | Dipole | Educational | 1U | UHF and VHF | 2013 |
| UWE-3 [86] | Monopoles | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF | 2013 |
| FunCube [78] | Monopoles | Educational | 1U | VHF and UHF | 2013 |
| TJ3Sat [87] | Monopoles | Educational | 1U | UHF | 2013 |
| ALL-STAR [88] | Cavity-Backed Antenna | Educational | 3U | UHF and S-Band | 2014 |
| CanX-4&5 [89] | Monopole, Dipole, and Patch | Technology Demonstration | 1U | VHF, UHF, and S-Band | 2014 |
| DTUSat-2 [73] | Dipole | Technology Demonstration | 1U | S-Band and L-Band | 2014 |
| MicroMAS [90] | Parabolic Reflector and Monopole | Earth Observation | 3U | UHF | 2014 |
| OPUSat [91] | Monopole | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF and VHF | 2014 |
| VELOX-PII [85] | Dipole | Educational | 1U | UHF and VHF | 2014 |
| AeroCube-OCSD [44,92] | Patch | Technology Demonstration | 1.5U | UHF | 2015 |
| Firebird [93] | Dipole | Scientific | 1.5U+1.5U | UHF and VHF | 2015 |
| GOMX-3 [94] | Four Monopoles, Patch, and Helical | Technology Demonstration | 3U | UHF, S-Band, and L-Band | 2015 |
| AggieSat2 (Known as DRAGON SAT with Bevo-1) [95] | Dipole and Patch | Educational Technology Demonstration | 1U | S-Band | 2016 |
| CP10(ExoCube) [50,81] | Parabolic Reflector | Scientific | 3U | UHF | 2016 |
| OUFTI-1 [94] | Monopoles | Educational | 1U | UHF | 2016 |
| BEVO-1 [95] | Dipole and Patch | Educational Technology Demonstration | 1U | S-Band | 2016 |
| Aalto-I [96,97] | Crossed-Dipole and Patch | Technology Demonstration | 3U | VHF, UHF, and S-band | 2017 |
| CXBN-2 [70] | Quadrature Spring Steel Array | Technology Demonstration | 2U | UHF and S-Band | 2017 |
| EC0 (UNSW-EC0) [98] | Monopole | Education | 2U | UHF | 2017 |
| ICECube [99] | Dipole and Patch | Technology Demonstration | 3U | UHF | 2017 |
| QBITO [100] | Four Monopoles | Education purpose | 2U | UHF | 2017 |
| ISARA [101] | Reflectarray Integrated with Solar Panels | Technology Demonstration Communications | 3U | UHF and Ka-Band | 2017 |
| RadSat [99] | Monopole | Technology Demonstration | 3U | UHF | 2018 |
| SPATIUM [102] | Monopole | Scientific | 2U | UHF | 2018 |
| UWE-4 [103] | Dipole | Technology Demonstration | 1U | UHF | 2018 |
| CANYCAL-X [102] | Patch and Monopole | Technology Demonstration | 1U+2U | UHF and S-Band | 2018 |
| AeroCube-11R3 [104] | Patch | Technology Demonstration | 3U | UHF | 2018 |
| KNACKSA [105] | Two Dipoles | Technology Demonstration Earth observation | 1U | VHF and UHF | 2018 |
| CHOMPTT [62] | Monopole | Technology Demonstration | 3U | UHF | 2018 |
| MarCO [9] | Reflectarray, Patch Array, and Loop | Interplanetary Exploration | 6U | UHF and X-Band | 2018 |
| RainCube [106] | Parabolic Mesh Reflector | Earth Observation Technology Demonstration | 6U | Ka-Band | 2018 |
| AzTechSat-1 [107] | Patch | Educational | 1U | UHF and VHF | 2019 |
| ANGELS [108] | Square Array Inverted F | Technology Demonstration | 12U | UHF and L-Band | 2019 |
| ARMADILLO [51] | Monopole | Technology Demonstration | 3U | UHF | 2019 |
| EyeSat [109] | Patch | Educational | 3U | S-Band and X-Band | 2019 |
| OPS-SAT [92] | Dipole | Technology Demonstration | 3U | UHF and S-Band and X-Band | 2019 |
| SORTIE [103] | Dipole | Technology Demonstration | 6U | UHF | 2019 |
| Artemis [110] | Horn | Technology Demonstration | 1U | L-Band and Ku-Band | 2020 |
| SERB [111] | Patch | Technology Demonstration | 3U | S-Band | 2020 |
| Landmapper-BC5 [112] | Monopole and Horn | Earth observation | 6U | UHF and Ka-Band | 2020 |
| Lemur-2 [113] | Monopoles and Patch Array | Earth observation | 3U | UHF and S-Band | 2020 |
| Flock [114] | N/A | Earth observation | 3U | UHF and X-Band | 2020 and 2022 |
| Kepler [115] | Phased Array | Communications IoT | 6U | S-Band and Ku-Band | 2018 and 2020–2022 |
| TTU100 [116] | Dipole and Patch Array | Technology Demonstration Earth Observation | 1U | UHF and X-Band | 2020 |
| NetSat [117] | Dipoles | Technology Demonstration Educational | 3U | UHF | 2020 |
| TRISAT [118] | Patch and Dipoles | Technology Demonstration | 3U | UHF and S-Band | 2020 |
| Quetzal | Dipoles | Educational | 1U | UHF | 2020 |
| OSM1-CICERO [119] | Phased Array | Earth Observation | 6U | UHF and X-Band | 2020 |
| PICASSO [120] | Patch and Dipoles | Earth Observation | 3U | VHF, UHF, and S-Band | 2020 |
| AMICal Sat [121] | Patch and Dipoles | Demonstration Earth Observation | 2U | VHF, UHF, and S-Band | 2020 |
| Astrocast [122] | Patch and Patch Array | Communications IoT | 3U | L-band | 2021 |
| BEESAT 5–8 [123] | N/A | Technology Demonstration | 0.25 | UHF | 2021 |
| RADCUBE [124] | Dipoles | Scientific | 3U | UHF | 2021 |
| ExoCube-2 [125] | Monopoles | Scientific | 3U | UHF | 2021 |
| Cesium Satellite [126] | Active Phased Array | Technology Demonstration | 6U | Ka-Band | 2021 |
| CAS-9 [127] | Monopole | Communications | 6U | VHF and UHF | 2021 |
| SOMP2b [128] | Monopoles | Communications | 2U | UHF | 2021 |
| W-Cube [129] | Array of Concentric Ring Antennas (Bull’s Eye) | Scientific Technology Demonstration | 3U | W-Band | 2021 |
| Centauri [130] | Active Phased Array | Communications IoT | 6U | S-Band | 2018, 2021, and 2022 |
| ELO Alpha [131] | Helical, Patch Array, and Dipoles | Communications IoT | 3U | ISM | 2021 |
| IDEASSat [132] | Monopole and Patch | Technology Demonstration Earth Observation | 3U | UHF and S-Band | 2021 |
| KSF1 [133] | Monopoles, Patch Array, and Helical | Surveillance | 6U | VHF and S-Band | 2021 |
| D2/AtlaCom-1 [134] | Monopoles and Patch Array | Educational Earth Observation | 6U | UHF and X-Band | 2021 |
| FORESAIL-1 [135] | Monopoles | Scientific Technology Demonstration | 3U | UHF | 2022 |
| IRIS-A [136] | Monopoles | Communications IoT | 2U | UHF | 2022 |
| HYPSO [137] | Patch, Monopole, and Dipoles | Technology Demonstration Earth Observation | 6U | UHF and S-Band | 2022 |
| Spark-2 [138] | Patch and Monopoles | Communications IoT (5G) | 12U | S-Band | 2022 |
| SanoSat-1 [139] | Dipole | Educational | 1U | UHF | 2022 |
| Planetum-1 [140] | Monopole | Educational | 1U | UHF | 2022 |
| SpaceBEE [141] | Dipole | Communications IoT | 0.25U | VHF | 2018–2022 |
| 2003 | 2005–2011 | 2012–2013 | 2014–2015 | 2016–2017 | 2018–2019 | 2020–2022 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monopole and Dipole | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Patch | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Reflector | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Helical | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Reflectarrays | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Arrays | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Phased Arrays | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Horn | ✓ |
| Type of Antenna | Frequency (GHz) | Gain (dBi) | −10 dB BW (MHz) | Deployable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monopole and Dipole [142,148,149] | 0.146 (uplink) 0.438 (downlink) | 2–4 | N/A | Yes |
| G-Shaped Monopole (3 structures) [147] | Structure I: 0.150 Structure II: 0.180 Structure III: 0.330 | 3.757 2.671 2.774 | 58 77 147 | No |
| Dual-Band Folded-End Dipole [150] | 2.5 4.7 | 4.9 7.55 | 500 250 | No |
| Type of Antenna | Frequency (GHz) | Gain (dBi) | −10 dB BW (MHz) | Deployable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflatable parabolic reflector with patch feed [152] | 2.4 | 16 | N/A | Yes |
| F-shaped patch [153] | 2.45 | 8 | 1200 | No |
| Dual-feed, L/S dual-band stack patch [154] | 1.57 2.2 | 5.4 6 | N/A | No |
| Koch curve fractal microstrip [155] | 2.3 | 4.18 | 290 | No |
| Shorted patch [156] | 2.45 | 2.52 | 550 | No |
| Metal only patch [157] | 2.45 | 8.5 | 1100 | No |
| Tapered line feeder patch [158] | 2.46 | 9.6 | Narrow | No |
| V-shaped asymmetrical slits [159] | 2.285 | 6 | 0.4 | No |
| Tapered peripheral slits [160] | 0.436 | 0.7–1.4 | 4 | No |
| L-band patch with frequency tuning slots [94] | 1.54 | 5.5 | 40 | No |
| Type of Antenna | Frequency (GHz) | Gain (dBi) | −10 dB BW (MHz) | Deployable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transparent meshed [167] | 2.4 | 6.16 | 40 | No |
| Dual-feed meshed patch [164] | 2.4 | 6.25 | N/A | No |
| Dual patch meshed (81% transparency) [168] | 2.5 | 5.09 | N/A | No |
| L-shaped slots meshed (89% transparency) [168] | 2.4 | 4.4 | 140 | No |
| Meander shaped slot [165] | 0.485 0.500 | 4 | 15 | No |
| Polarization reconfigurable slot [166] | 2.3 | 7 | N/A | No |
| Transparent mesh patch [169] | 2.4 | N/A | 80 | No |
| Transparent meshed [167] | 2.4 | 6.16 | 40 | No |
| Dual-feed meshed patch [164] | 2.4 | 6.25 | N/A | No |
| Type of Antenna | Frequency (GHz) | Gain (dBi) | −10 dB BW (MHz) | Deployable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Helical [170] | 0.400 | 13 | N/A | Yes |
| Hemispherical Helical [171] | 2.45 | 13.2 | N/A | Yes |
| Bottom-Fed [172] | 2.2–3.1 | 11.2 | 900 | Yes |
| Conical [173] | 0.300–0.600 | 5 | 300 | Yes |
| Quadrifilar Helix [174] | 0.250–0.500 | 5.41 | Various | Yes |
| Type of Antenna | Frequency (GHz) | Gain (dBi) | −10 dB BW (GHz) | Deployable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bull’s Eye [175] | 60.08 | 19.1 | 5.06 | No |
| Cylindrical DRA Antenna [176] | 7.4 11.1 | 5.2 4.8 | 0.6 0.8 | No |
| Balance Inductive Exciters (BIEs) [177] | 2.425 | 6.3 | 0.5 | No |
| Metal-Only Metasurface [178] | 32 | 24.4 | 2 | No |
| Type of Antenna | Frequency (GHz) | Gain (dBi) | −10 dB BW (MHz) | Deployable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yagi-Uda on solar panels [184] | 0.435 | 11.5 | 53 | Yes |
| Quad 4-monopole array [185] | 0.436 | 2d | N/A | Yes |
| W-Band 16 × 32 series fed phased antenna array [186] | 85.4 | 30 | 800 | No |
| Printed Yagi [187] | 1.3 2.4 3.0 | 5.28 6.12 8.17 | 100 190 250 | No |
| Type of Antenna | Frequency (GHz) | Gain (dBi) | −10 dB BW (GHz) | Deployable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 × 2 Planar Active Phased Array [188] | 2.4 | 5 | 0.1 | No |
| 4-Element Patch Array [189,190] | 2.45 | 8.3 | 1500 | No |
| Planar Phased Array [38] | 5.8 | 5.8 | N/A | No |
| 2 × 2 Annular Planar Array [191] | 8.25 | 13 | 0.7 | No |
| 4 × 4 Dual-Frequency, Dual-Polarization Stack Array [192] | 14 35 | 15.82 14.84 | 0.3 1.7 | No |
| 6 × 6 Planar Patch Array [193] | 10.4 | 20.1 | 2 | No |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Theoharis, P.I.; Raad, R.; Tubbal, F.; Theoharis, A.; Iranmanesh, S.; Abulgasem, S.; Khan, M.U.A.; Matekovits, L. A Survey on CubeSat Missions and Their Antenna Designs. Electronics 2022, 11, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11132021
Liu S, Theoharis PI, Raad R, Tubbal F, Theoharis A, Iranmanesh S, Abulgasem S, Khan MUA, Matekovits L. A Survey on CubeSat Missions and Their Antenna Designs. Electronics. 2022; 11(13):2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11132021
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Sining, Panagiotis Ioannis Theoharis, Raad Raad, Faisel Tubbal, Angelos Theoharis, Saeid Iranmanesh, Suhila Abulgasem, Muhammad Usman Ali Khan, and Ladislau Matekovits. 2022. "A Survey on CubeSat Missions and Their Antenna Designs" Electronics 11, no. 13: 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11132021
APA StyleLiu, S., Theoharis, P. I., Raad, R., Tubbal, F., Theoharis, A., Iranmanesh, S., Abulgasem, S., Khan, M. U. A., & Matekovits, L. (2022). A Survey on CubeSat Missions and Their Antenna Designs. Electronics, 11(13), 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11132021









