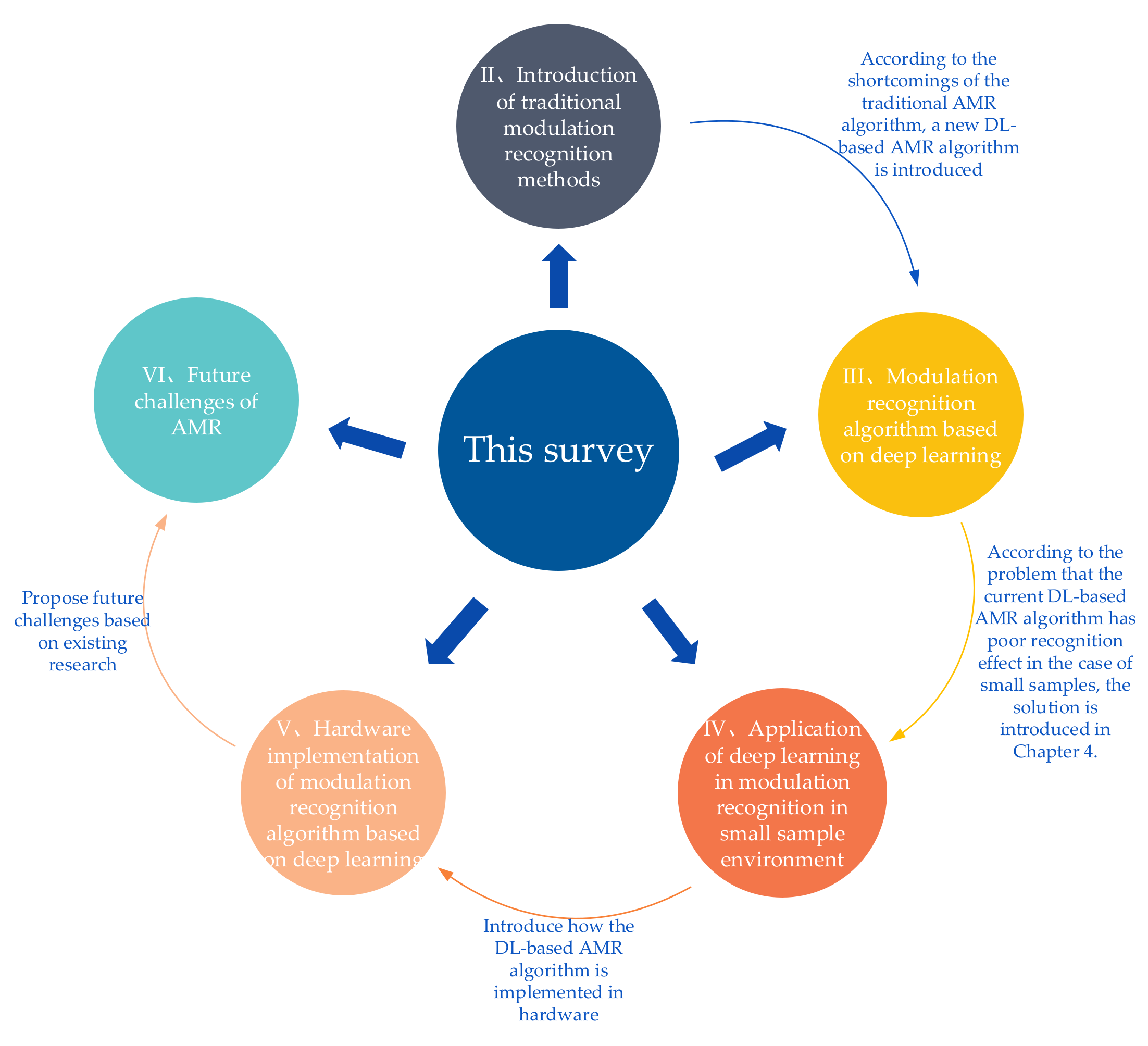
A Review of Research on Signal Modulation Recognition Based on Deep Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- The traditional modulation identification algorithm is investigated, and the characteristics of the signal and the advantages and disadvantages of the traditional modulation identification algorithm are summarized in detail;
- (2)
- This paper introduces the application of CNN, RNN, combined neural network, and other types of neural networks in modulation recognition, and makes a comprehensive summary of new algorithms for modulation recognition based on deep learning from 2020 to 2022;
- (3)
- This paper describes the challenges faced by deep learning in identifying modulated signals in a small sample environment and summarizes the solutions to these challenges.
2. Traditional Methods of Modulation Recognition
2.1. Identification Method Based on Likelihood Ratio
2.2. Feature-Based Recognition Algorithms
3. The Modulation Recognition Method Based on Deep Learning
3.1. Application of Convolutional Neural Network in Modulation Recognition
3.1.1. Convolutional Neural Networks
3.1.2. The Modulation Recognition Method Based on Convolutional Neural Network
- 1.
- A two-dimensional image recognition method based on CNN.
- 2.
- The signal sequence recognition method based on CNN.
3.2. Application of the Recurrent Neural Network in Modulation Recognition
3.2.1. Recurrent Neural Networks
3.2.2. Modulation Recognition Based on Recurrent Neural Network
3.3. Application of Combination Neural Network in Modulation Recognition
3.4. Applications of Other Neural Networks in Modulation Recognition
4. Modulation Recognition Based on Deep Learning in Small Sample Environment
4.1. The Small Sample AMR Algorithm Based on Signal Data Enhancement
4.1.1. Generate Dummy Data
4.1.2. Data Augmentation Method Based on Semi-Supervised Learning
4.2. Small-Sample AMR Algorithm Combining Deep Learning and Transfer Learning
5. Hardware Implementation of Modulation Recognition Algorithm Based on Deep Learning
6. Research Challenges and Future Directions
6.1. Further Research on DL-Based AMR Algorithms in Visible Light Communication Systems
6.2. Improving Modulation Recognition Accuracy in Small Sample Scenarios
6.3. Strengthening the Research on Adaptive Modulation Identification
6.4. Designing more Lightweight Modulation Recognition Networks
6.5. Design the Modulation Identification Method of OFDM Signal
7. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lv, Z.; Singh, A.K.; Li, J. Deep Learning for Security Problems in 5G Heterogeneous Networks. IEEE Netw. 2021, 7, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucchi, L.; Jayousi, S.; Caputo, S.; Panayirci, E. Physical-Layer Security in 6G Networks. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2021, 8, 1901–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, W.; Yu, H.; Ali, R.; Ullah, R. Advanced Physical-Layer Technologies for Beyond 5G Wireless Communication Networks. Sensors 2021, 21, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, X.; Shan, T.; Shi, D.; Jin, Z. A Recognition Method of Modulation Mode of Non-cooperative Communication Signal. Mod. Def. Technol. 2022, 14, 1603. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Mathews, V.J.; Detienne, D.H. A phase likelihood-based algorithm for blind identification of PSK signals. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Florence, Italy, 4–9 May 2014; pp. 5730–5734. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul, A.O.; Salam, R.E.; Sheriff, S.R.; Al-Araji, K.; Mezher, Q. Nasir. A unified practical approach to modulation classification in cognitive radio using likelihood-based techniques. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 28th Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE), Halifax, NS, Canada, 3–6 May 2015; pp. 1024–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Nuaimi, D.H.; Hashim, I.A.; Zainal, I.S.; Salman, L.B.; MatIsa, N.A. Performance of Feature-Based Techniques for Automatic Digital Modulation Recognition and Classification—A Review. Electronics 2019, 140, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, P.F.; Chen, L.; Wu, X.W. Automatic modulation classification: A deep learning enabled approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 10760–10772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, T.J.; Corgan, J.; Clancy, C.T. Convolutional radio modulation recognition networks. In Engineering Applications of Neural Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 213–226. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, S.; Meert, W.; Giustiniano, D.; Lenders, V.; Pollin, S. Deep learning models for wireless signal classification with distributed low cost spectrum sensors. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2018, 4, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Yang, J.; Gui, G. Data-driven deep learning for automatic modulation recognition in cognitive radios. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 4074–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh, P.; Banerjee, S.; Hempel, M.; Sharif, H. A novel deep learning and polar transformation framework for an adaptive automatic modulation classification. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 13243–13258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, T.J.; Roy, T.; Clancy, T.C. Over-the-air deep learning based radio signal classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2018, 12, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Li, Y. IAFNet: Few-Shot Learning for Modulation Recog-nition in Underwater Impulsive Noise. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 26, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, L.; Feng, Z.; Chen, F.; Hang, L. Meta-SGD: Learning to Learn Quickly for Few-Shot Learn; Cornell University: Ithaca, Greece, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Shao, G.; Shao, S. Automatic modulation classification for short burst underwater acoustic communication signals based on hybrid neural networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 227793–227809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh-The, T.; Pham, Q.-V.; Nguyen, T.-V. Automatic Modulation Classification: A Deep Architecture Survey. IEEE Access 2021, 163, 142950–142971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Gui, G. A Comprehensive Survey of Deep Learning-based Automatic Modulation Recognition Methods. Radio Commun. Technol. 2022, 48, 697–710. [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, F.O.; Dobre, A.; Popescu, D.C. On the likelihood-based approach to modulation classification. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2009, 8, 5884–5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani-Kebrya, A.; Kim, I.; Kim, D.I.; Chan, F.; Inkol, R. Likelihood-Based Modulation Classification for Multiple-Antenna Receiver. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2013, 61, 3816–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cabric, D.; Wang, F.; Zhong, Z.J. Cooperative Modulation Classification for Multipath Fading Channels via Ex-pectation Maximization. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 6698–6711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedtke, F.F.J. Computer simulation of an automatic classification procedure for digitally modulated communication signals with unknown parameters. Signal Process. 1984, 6, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, E.E.; Nandi, A.K.T. Automatic Identification of Digital Modulation Types. Signal Process. 1995, 47, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, H.; Li, J.; Dong, L.T. Study of modulation recognition based on HOCs and SVM. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE 59th Vehicular Technology Conference. VTC 2004-Spring, Milan, Italy, 17–19 May 2004; pp. 898–902. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, L.; Hong, Z.; Xu, W.; Nan, X.; Yuan, X. Modulation recognition of communication signals based on high order cumulants and support vector machine. J. China Univ. Posts Telecommun. 2012, 19, 1005–8885. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Wei, G.; Song, C.; Lai, L. Hierarchical digital modulation recognition based on higher-order cumulants. In Proceedings of the 2012 Second International Conference on Instrumentation, Measurement, Computer, Communication and Control, Harbin, China, 8–10 December 2012; 8, pp. 1645–1648. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, M.; Xiao, X.; Li, L. Cyclic spectral features based modulation recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Communication Technology. ICCT 96, Beijing, China, 5–7 May 1996; 2, pp. 792–795. [Google Scholar]
- Like, E.; Chakravarthy, V.; Husnay, R.; Wu, Z. Modulation Recognition in Multipath Fading Channels Using Cyclic Spectral Analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE GLOBECOM 2008-2008 IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 8 December 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shuli, D.; Zhi, L.; Lin, Z.T. A Modulation Recognition Algorithm based on Cyclic Spectrum and SVM Classification. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 4th Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (ITNEC), Chongqing, China, 12–14 June 2020; pp. 2123–2127. [Google Scholar]
- Spooner, C.M.; Mody, A.N.; Chuang, J.; Petersen, J. Modulation recognition using second- and higher-order cyclostationarity. DyS-PAN 2017, 10, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Aslam, M.W.; Zhu, Z.; Nandi, A.K.T. Automatic Modulation Classification Using Combination of Genetic Programming and KNN. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2012, 11, 2742–2750. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; Lin, Y. A Method for Modulation Recognition Based on Entropy Features and Random Forest. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Software Quality, Reliability and Security Companion (QRS-C), Prague, Czech Republic, 25–29 July 2017; pp. 243–246. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Ren, G.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Gu, X.T. Automatic digital modulation recognition using artificial neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Networks and Signal Processing, Nanjing, China, 14–17 December 2003; pp. 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Patras, P.; Haddadi, H. Deep Learning in Mobile and Wireless Networking: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Sur-Veys Tutor. 2019, 21, 2224–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Jiang, H.; Wang, H.; Alwageed, H.; Zhou, Y.; Sebdani, M.; Yao, Y. Modulation Classification Based on Signal Constella-tion Diagrams and Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 30, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Chen, C. Modulation Pattern Recognition Based on Resnet50 Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Information Communication and Signal Processing (ICICSP), Weihai, China, 28–30 September 2019; pp. 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- An, Z.; Zhang, T.; Shen, M.; De Carvalho, E.; Ma, B.; Yi, C.; Song, T. Series-Constellation Feature Based Blind Modulation Recognition for Beyond 5G MIMO-OFDM Systems with Channel Fading. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2022, 8, 793–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Fu, M.; Cui, Y.; Chen, X. Modulation Format Recognition and OSNR Estimation Using CNN-Based Deep Learning. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2017, 29, 1667–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zha, X. Modulation Recognition Based on IQ-eyes Diagrams and Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 5th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 6–9 December 2019; pp. 1570–1574. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, X.; Peng, H.; Qin, X.; Li, G.; Yang, S. A Deep Learning Framework for Signal Detection and Modulation Classification. Sensors 2019, 19, 4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Ren, W.; Yang, Z. Radar Signal Modulation Recognition Based on Sep-ResNet. Sensors 2021, 21, 7474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, D.; Tang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhai, W.; Qu, C. LPI Radar Signal Recognition Based on Dual-Channel CNN and Feature Fusion. Symmetry 2022, 14, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Sun, X.; Yu, X.; Li, X. Modulation Pattern Recognition of Communication Signals Based on Fractional Low-Order Choi-Williams Distribution and Convolutional Neural Network in Impulsive Noise Environment. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 19th International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT), Xi’an, China, 16–19 October 2019; pp. 188–192. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, G.; Fan, L.; Yang, L. Modulation recognition algorithm using innovative CNN and cyclic-spectrum graph. In Proceedings of the 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments (ICEMI), Changsha, China, 1–3 November 2019; pp. 466–473. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, S. Modulation Recognition Method of Complex Modulation Signal Based on Convolution Neural Net-work. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 9th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC), Chongqing, China, 11–13 December 2020; pp. 1179–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, H.; Zhou, X.; Huo, J.; Yuan, J. Joint OSNR monitoring and modulation format identification on signal amplitude histo-grams using convolutional neural network. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2021, 61, 102455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Zhang, Y.J. Cyclic Cumulant Based on Communication Signal Multilayer Neural Network Modulation Pattern Recognition. CCIOT 2018, 10, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gu, H.; Gui, G.; Sari, H. Deep Learning-Based Signal Modulation Identification in OFDM Systems. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 114631–114638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, L.; Jian, X.; Chang, X.; Peng, F. A modulation recognition method based on enhanced data representation and convolu-tional neural network. IMCEC 2021, 4, 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Gui, J.; Yin, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Gui, G.; Gacanin, H.; Sari, H.; Adachi, F. Automatic Modulation Classification for MIMO Systems via Deep Learning and Zero-Forcing Equalization. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 5688–5692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh-The, T.; Nguyen, T.V.; Pham, Q.V.; da Costa, D.B.; Kim, D.S. MIMO-OFDM Modulation Classification Using Three-Dimensional Convolutional Network. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 6738–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, J. Automatic classification of communication signals using higher order statistics. In Proceedings of the ICASSP, San Francisco, CA, USA, 23–26 March 1992; 5, pp. 221–224. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Ren, Y. Recognition of digital modulation signals based on high order cumulants and support vector machines. In Proceedings of the 2009 ISECS International Colloquium on Computing, Communication, Control, and Management, Sanya, China, 8–9 August 2009; pp. 271–274. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Z. Recognition of digital modulation signals based on high-order cumulants. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Wireless Communications & Signal Processing (WCSP), Nanjing, China, 15–17 October 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhao, X. Study on Modulation ecognition Based on Higher-order Cumulants. J. Southwest Univ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 33, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J.; Gui, G. Deep Learning-Based Cooperative Automatic Modulation Classification Method for MIMO Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 4575–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Wu, Y.; Soh, Y.C. Robust adaptive gradient-descent training algorithm for recurrent neural networks in discrete time domain. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2008, 19, 1841–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zeng, Y.; Han, Z.; Gong, Y.C. Automatic modulation recognition using deep learning architectures. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 19th International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), Kalamata, Greece, 25–28 June 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, T. Toward convolutional neural networks on pulse repetition interval modulation recognition. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2008, 22, 2286–2289. [Google Scholar]
- Norgren, E.J.D. Pulse repetition interval modulation classification using machine learning. Ph.D. Thesis, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 11 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Z. Attention-Based Radar PRI Modulation Recognition with Recurrent Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 57426–57436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, G.; Jiang, C. Research on Modulation Recognition Method in Low SNR Based on LSTM. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2189, 012003. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.; Qu, Q.; Zeng, X.; Liang, J.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X. Self-Attention Bi-LSTM Networks for Radar Signal Modulation Recogni-tion. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2021, 69, 5160–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Q.; Wang, H.; Yang, L. Study on Fast-Changing Mixed-Modulation Recognition Based on Neural Network Algorithms. KSII 2020, 14, 4664–4681. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, W.; Yang, Q.; Jiao, X.; Niu, Y.; Ji, G. A Transformer-based CTDNN Structure for Automatic Modulation Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2021 7th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 10–13 December 2021; pp. 159–163. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, D.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X. Automatic modulation classification using recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 3rd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 13–16 December 2017; pp. 695–700. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Je, J.; Kim, K. A deep learning method for the automatic modulation recognition of received radio signals. J. Korea Inst. Inf. Commun. Eng. 2019, 23, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Cong, C.T.; Gulliver, A. Adoption of hybrid time series neural network in the underwater acoustic signal modulationn identification. J. Frankl. Inst. 2020, 357, 13906–13922. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Zhao, L.; Yue, G.; Ma, B.; Li, W. IRLNet: A Short-Time and Robust Architecture for Automatic Modulation Recognition. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 143661–143676. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Gao, W.; Huang, Q. Automatic Modulation Recognition Based on a DCN-BiLSTM Network. Sensors 2021, 21, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Z.; Vikalo, H. Real-Time Radio Technology and Modulation Classification via an LSTM Auto-Encoder. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil, N.; Ganesan, I.; Vijay, M. Ensemble of Deep Learning Enabled Modulation Signal. Wirel. Commun.-Tions Mob. Comput. 2022, 10, 1307715. [Google Scholar]
- Dampage, U.; Amarasooriya, R.; Samarasinghe, S.; Karunasingha, N. Combined Classifier-Demodulator Scheme Based on LSTM Architecture. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemzadeh, P.; Hempel, M.; Sharif, H. High-Efficiency Automatic Modulation Classifier for Cognitive Radio IoT. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 9467–9477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, N.E.; O’Shea, T. Deep architectures for modulation recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks (DySPAN), Baltimore, MD, USA, 6–9 March 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Z. Deep Learning Based Modulation Recognition with Multi-Cue Fusion. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 1757–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, Z.; Nie, J.; Zhang, W. A Novel Attention Cooperative Framework for Automatic Modulation Recogni-tion. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 15673–15686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoku, J.N.; Morocho-Cayamcela, M.E.; Lim, G.D. Net: Efficient Hybrid Deep Learning Model for Robust Automatic Modu-lation Recognition. IEEE Netw. Lett. 2021, 3, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Qiu, S.; Li, L. Modulation recognition method of satellite communication based on CLDNN model. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 30th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Kyoto, Japan, 20–23 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Tu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Y. Digital Signal Modulation Classification with Data Augmentation Using Generative Adversarial Nets in Cognitive Radio Networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 15713–15722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, R. Automatic modulation recognition based on CNN and GRU. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2022, 27, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Luo, C.; Parr, G.; Luo, Y. A Spatiotemporal Multi-Channel Learning Framework for Automatic Modulation Recognition. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2020, 9, 1629–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Qin, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, A. Modulation Recognition of Communication Signal Based on Convolutional Neural Network. Symmetry 2021, 13, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, D.; Jian, F.; Xiang, W.; Chao, W.; Xiang, J.; Nan, W. Automatic Modulation Recognition Based on Hybrid Neural Network. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2021, 2021, 1530–8669. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Tao, M.; Wang, L.; Su, J.; Yang, X. Automatic Modulation Recognition Based on Adaptive Attention Mechanism and ResNeXt WSL Model. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 2953–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Huang, S.; Zhang, R.; Feng, Z.; Liu, L. Multitask-Learning-Based Deep Neural Network for Automatic Modulation Classification. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 2192–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, X.; Leng, C.; Wang, J.; Mao, S. Modulation Recognition of Underwater Acoustic Signals using Deep Hybrid Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 1, 5977–5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Zeng, X.; Wang, F. Research on Modulation Signal Recognition Based on CLDNN Network. Electronics 2022, 11, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Yao, J.; Qi, J.; Wang, L. Electromagnetic Modulation Signal Classification Using Dual-Modal Feature Fusion CNN. Entropy 2022, 24, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.A.; Ergun, E. Automatic modulation classification using different neural network and PCA combinations. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 178, 114931. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Hu, S.; Yu, C.; Zhu, P.; Peng, X.; Ouyang, J. Deep Learning in Digital Modulation Recognition Using High Order Cumulants. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 63760–63766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Ren, Z.; Li, L.; Zhu, Z. Automatic Modulation Classification Based on Deep Feature Fusion for High Noise Level and Large Dynamic Input. Sensors 2021, 21, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, L.; Tian, W.; Shao, W. Toward intelligent wireless communications: Deep learning-based physical layer technologies. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2021, 7, 589–597. [Google Scholar]
- Ya, W.; Zhi, L.; Chun, L.; Yu, C.; Chao, W.; Yi, C.; Yi, L. Research on Pulse Position Modulation and Demodulation System of Space Laser Communication Based on DBN-SVM. In Proceedings of the 2021 13th International Conference on Advanced Infocomm Technology (ICAIT), Yanji, China, 15–18 October 2021; pp. 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Wang, X.; Tian, Y.; Wang, R. A novel radar signal recognition method based on a deep restricted Boltzmann machine. Eng. Rev. 2017, 37, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, S.; Li, G.; Xu, Y. The Recognition Method of MQAM Signals Based on BP Neural Network and Bird Swarm Algorithm. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 36078–36086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Shen, J.; Zhou, X. Research on Digital Modulation recognition based on BP neural Network. ITOEC 2022, 6, 1813–1817. [Google Scholar]
- Research on Small Sample Recognition Method of Radar Signal Based on Deep Learning. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/304 (accessed on 6 April 2021).
- Zhou, H.; Bai, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, L.; Zheng, S.; Shen, W.; Xu, J.; Yang, X. Few-shot electromagnetic signal classification: A data union augmentation method. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2022, 35, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, J.; Kim, J. Semi-supervised learning with generative adversarial networks on digital signal modulation classification. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2018, 55, 243–254. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Jiao, L.; Zheng, S.; Yang, L.; Shen, W.; Yang, X. Generative adversarial network-based electromagnetic signal classifi-cation: A semi-supervised learning framework. China Commun. 2020, 17, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. SAR Ship Detection Based on Resnet and Transfer Learning. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 1188–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Huang, J.; Cheng, Q.; Meng, H.; Han, Z. Automatic Modulation Recognition: A Few-Shot Learning Method Based on the Capsule Network. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 474–477. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, K.; He, Y.; Jing, X.; Han, J. Adversarial Transfer Learning for Deep Learning Based Automatic Modulation Classification. IEEE Signal Process Lett. 2020, 27, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Li, P.; Wu, B.; Yuan, S.; Chen, Y. An Adaptive Focal Loss Function Based on Transfer Learning for Few-Shot Radar Signal Intra-Pulse Modulation Classification. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.; Wang, B. Modulation Recognition of Underwater Acoustic Communication Signals Based on Data Transfer. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 8th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC), Chongqing, China, 24–26 May 2019; pp. 243–246. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, Z.; Zi, W.; Zhao, W.; Mu, L.; Nadeem, F.H.; Fu, H.Y. Modulation Format Recognition based on Transfer Learning for Visible Light Communication Systems. In Proceedings of the 26th Optoelectronics and Communications Conference, Hong Kong, China, 3–7 July 2021; p. JS2B.12. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Shang, J.; Leong, P.H.W.; Liu, C. Modulation recognition using an FPGA-based convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2019 22nd International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Harbin, China, 11–14 August 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.-L.; Li, S.-M.; Yu, L.-J. Implementation of Deep Learning-Based Au-tomatic Modulation Classifier on FPGA SDR Platform. Electronics 2018, 7, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Yan, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W. A Real-Time Modulation Recognition System Based on Software-Defined Radio and Multi-Skip Residual Neural Network. J. Abbr. 2020, 8, 221235–221245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emad, A.; Mohamed, H.; Farid, A.; Hassan, M.; Sayed, R.; Aboushady, H.; Mostafa, H. Deep Learning Modulation Recognition for RF Spectrum Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Daegu, Korea, 22–28 May 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yaman, U.; Nicholas, J.; Giulio, G.; Michaela, B.; Philip, L.; Magnus, J.; Kees, V. FINN: A Framework for Fast, Scalable Binarized Neural Network Inference. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM/SIGDA International Symposium on Field-Programmable Gate Arrays, New York, NY, USA, 22–24 February 2017; pp. 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Stephen, T.; David, B.; Philip, L.; Ryan, K.; Alireza, K.; Siddharth. Real-time Au-tomatic Modulation Classification using RFSoC. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Parallel and Dis-tributed Processing Symposium Workshops (IPDPSW), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–22 May 2020; pp. 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Mahapatra, R.; Singh, A. Automatic Modulation Recognition: An FPGA Implementation. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 1-1. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, N.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, Y.; Hu, F. Visible Light Communication in 6G: Advances, Challenges, and Prospects. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2020, 15, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Majhi, S.; Gui, G.; Wu, H.-C.; Yuen, C. A Survey of Blind Modulation Classi-fication Techniques for OFDM Signals. Sensors 2022, 22, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X. Graphic Constellations and DBN Based Automatic Modulation Classification. VTC Spring 2017, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Z.; Hou, C.; Hou, C.; Wang, W. Radar Signal Intra-Pulse Modulation Recognition Based on Convolutional Neural Network and Deep Q-Learning Network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 49125–49136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Yu, X.; Guo, Q. LPI Radar Waveform Recognition Based on CNN and TPOT. Symmetry 2019, 11, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, G.; Wu, H. A Novel Automatic Modulation Classifier Using Graph-Based Constellation Analysis for Mary QAM. J. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2019, 23, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, W.; Zhen, Y.; Liang, S.; Yi, Z.; Hao, Z.; Kun, X. Intelligent optical performance monitor using multi-task learning based artificial neural network. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 11281–11291. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Lin, C.; Xu, W.; Gao, Y.; Feng, Z.; Zhu, F. Robust and Fast Automatic Modulation Classification with CNN under Multipath Fading Channels. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 2051–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Han, F.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, J. Spectrum Analysis and Convolutional Neural Network for Automatic Modulation Recognition. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2019, 8, 929–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perenda, E.; Rajendran, S.; Pollin, S. Automatic Modulation Classification Using Parallel Fusion of Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Third International Balkan Conference on Communications and Networking, Skopje, North Macedonia, 10 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, H.; Wang, C.; Gan, C.; Xiang, Y. Automatic Modulation Classification Using CNN-LSTM Based Dual-Stream Structure. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 13521–13531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Yang, H.; Li, Y. Modulation Identification of Underwater Acoustic Communications Signals Based on Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2019 Marseille, Marseille, France, 17–20 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sabour, S.; Frosst, N.; Hinton, G. Dynamic Routing Between Capsules. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.09829, 3859–3869. [Google Scholar]



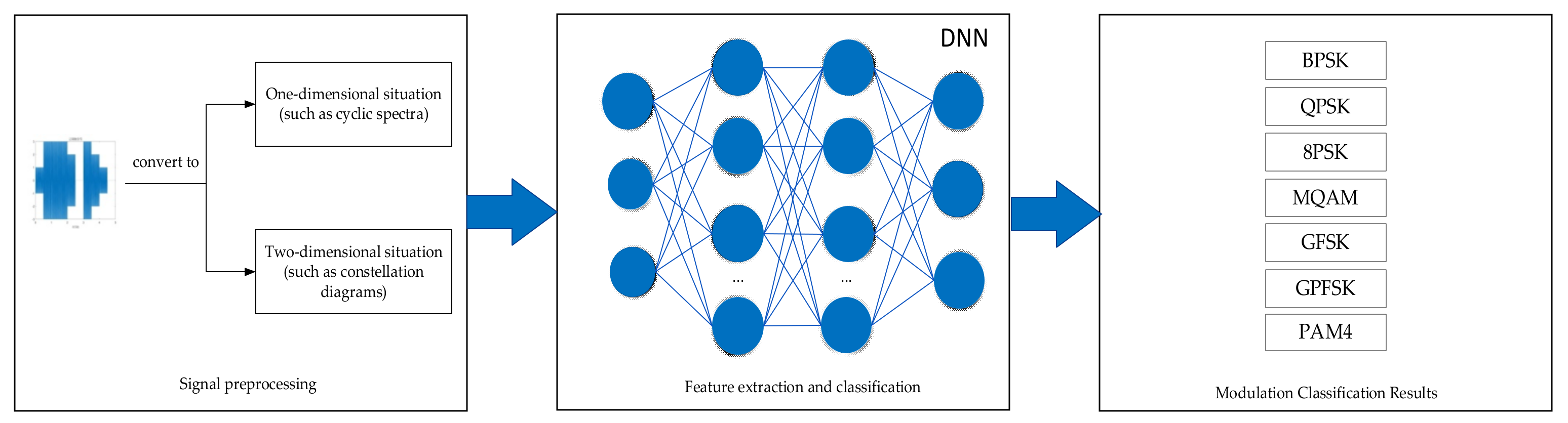









| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Modulation identification method based on the likelihood ratio | Have a complete theoretical foundation | The derivation of the likelihood function is complicated, and the amount of calculation is large |
| The classification effect is very good | Poor applicability | |
| Better performance at low signal-to-noise ratio | Requires a small amount of prior knowledge Requires a lot of prior knowledge | |
| Feature-based modulation identification | Simple theoretical analysis | The identification system is complex |
| Features are easy to extract when the signal-to-noise ratio is high | There is no complete theoretical basis |
| Author | Year | Input Signal | Model | Modulation Signal Type | Recognition Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D. Hong et al. [67] | 2017 | IQ signal | Two-layer GRU | WB-FM, AM-SSB, AM- DSB, BPSK, QPSK, 8PSK, 16QAM, 64QAM, BFSK, CPFSK, PAM4 | 91% (−4 dB) |
| Kim, H et al. [68] | 2019 | Amplitude phase of IQ signal | LSTM | 8PSK, AM-DSB-BPSK, PFSK, GFSK, PAM4, QAM16, QAM64, QPSK, WBFM | 80% (6 dB) |
| Wang, Yan et al. [69] | 2020 | IQ signal | HSNet | 16QAM, 32QAM, BPSK, QPSK, 8PSK, PAM, CPFSK, GFSK, FM, SSB | 86% (0 dB) |
| H. Yang et al. [70] | 2021 | Polar coordinate representation of the signal | IRS + LSTM | BPSK, QPSK, 8PSK, 16QAM, 64QAM, GFSK, CPFSK, 4PAM, WBFM, AM–DSB | 90% (0 dB) |
| Liu et al. [71] | 2021 | IQ signal | DCN-BiLSTM | AM-DSB, AM-SSB, WBFM, BPSK, 8PSK, QPSK, CPFSK, GFSK, PAM4, 16QAM, 64QAM | 90% (4 dB) |
| Zi. et al. [72] | 2022 | IQ signal | LSTM | 8PSK, AM-DSB, AM-SSB, BPSK, CPFSK, GFSK, PAM4, QAM16, QAM64, QPSK, WBFM | 90% (8 dB) |
| V.N.Senthil Kumaran [73] | 2022 | Original signal | EDL-MSC (GRU + Bi LSTM + SSAE) | 8PSK, BPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM, QPSK | 92% (−4 dB) |
| UdayaDampage [74] | 2022 | IQ signal | LSTM + Bi LSTM | BPSK, QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM, 256QAM | 90% (0 dB) |
| P. Ghasemzadeh [75] | 2022 | IQ signal | S-QRNN | OOK, 4ASK, 8ASK, BPSK, QPSK, 8PSK, 16PSK, 32PSK, 16APSK, 32APSK, 64APSK, 128APSK, 16QAM et | 90% (5 dB) |
| Author | Year | Input Signal | Model | Modulation Signal Type | Recognition Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. Tang et al. [81] | 2018 | Outline constellation map | CNN + GAN | 4ASK, BPSK, OQPSK, 8PSK, 16QAM, 32QAM, 64QAM | 100% (−2 dB) |
| F. Liu et al. [82] | 2020 | IQ sequence, cyclic spectrum | CNN + GRU | 2PSK, 2ASK, 2FSK, 4PSK, 4ASK, 16QAM, 64QAM | 100% (0 dB) |
| J. Xu et al. [83] | 2021 | IQ sequence | MCLDNN(CNN + LSTM + FC) | WBFM, AM-DSB, AM-SSB, BPSK, CPFSK, GFSK, 4-PAM, 16-QAM, 64-QAM, QPSK, and 8PSK | 90% (0 dB) |
| Jiang K et al. [84] | 2021 | IQ sequence | CNN + Bi LSTM + Attention | 2ASK, 4ASK, BPSK, QPSK, 8PSK, 64QAM | 93.14% (10 dB) |
| Duan, Q et al. [85] | 2021 | Original signal | MCBL (CNN + Bi LSTM + Attention) | 8PSK, AM-DSB, BPSK, CPFSK, GFSK, PAM4, QAM16, QAM64, QPSK, WBFM | 93% (0 dB) |
| Z. Liang et al. [86] | 2021 | Time-frequency diagram | ResNeXt WSL(ResNeXt + Attention) | 8PSK, BPSK, AM-DSB, QPSK, QAM16, QAM64, CPFSK, GFSK, PAM4, and WBFM, | 90% (0 dB) |
| S. Chang et al. [87] | 2022 | Sampled signal | MLDNN(CNN + Bi GRU + SAFN) | AM-DSB, AM-SSB, WBFM. 8PSK, BPSK, CPFSK, GFSK, 4PAM, 16QAM, 64QAM, QPSK | 84% (0 dB) |
| W. Zhang et al. [88] | 2022 | Sampled signal | GRU + CNN | BPSK, QPSK, BFSK, QFSK, 16QAM, 64QAM, OFDM | 99.45% (true channel) |
| Zou B et al. [89] | 2022 | IQ sequence | ASCLDNN (Attention + CLDNN) | BPSK, 8PSK, CPFSK, GFSK, PAM4, PAM16, QAM64, QPSK, AM-DSB, AM-SSB, WBFM | 90% (0 dB) |
| Bai J et al. [90] | 2022 | IQ sequences and GAF images | DMFF-CNN (Complex Value Network + ResNet50) | 2FSK, AM, DSB, FM, OFDM, QAM16, QPSK, SSB | 91% (−10 dB) |
| Reference A | Author | Year | Input Signal Type | Model | Recognition Accuracy | Advanced Techniques Mentioned in Reference A | Author | Year | Input Signal Type | Model | Recognition Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [36] | Pengshengliang et al. | 2019 | Constellation Chart | GoogleNet, AlexNet | 90% (3 dB) | [118] | Fen Wang | 2019 | Constellation Chart | GCP-DBN | 95% (0 dB) |
| [40] | Zhuolun LI et al. | 2019 | Eye Chart | Improved ResNet | >95% (5 dB) | [36] | Pengshengliang | 2019 | Constellation Chart | Goog-le-Net, AlexNet | 90% (3 dB) |
| [41] | Xiong Zha et al. | 2021 | Constellation and eye charts | Designed multi-input CNN | 92% (3 dB) | [36] | Pengshengliang | 2019 | Constellation Chart | Goog-le-Net, AlexNet | 90% (3 dB |
| [42] | Yongjiang Mao et.al | 2021 | Time and frequency diagram | Sep-ResNet | 93.44% (−10 dB) | [119] | Zhiyu Qu | 2020 | Time and frequency diagram | CNN | 96.1% (−6 dB) |
| [43] | Daying Quan et al. | 2021 | Time and frequency diagram | Dual-channel CNN | 97% (−6) | [120] | Jian Wan | 2019 | Time and frequency diagram | CNN+TPOT | 94.42% (−4 dB) |
| [45] | Gao Jingpeng et al. | 2019 | Circulation spectrogram | CNN | 90.48% (−2 dB) | [121] | Xiao Yan | 2018 | Constellation and eye charts | Modulation classifier using the minimum angle search | >90% (15 dB) |
| [47] | Hongjing Lv et al. | 2021 | Magnitude histogram | CNN | 100% | [122] | Zhiquan Wan | 2019 | Magnitude histogram | MTL-ANN | 100% |
| [49] | Sheng Hong et al. | 2019 | IQ Signal | CNN | 98% (8 dB) | [92] | Wenwu Xie | 2019 | High-order cumulative volume | DNN | 99% (−5 dB) |
| [73] | V.N.Senthil Kumaran et al. | 2022 | IQ Signal | EDL-MSC (GRU + BI LSTM+SSAE) | 92% (−4 dB) | [69] | Duona Zhang | 2020 | IQ Signal | HsNet | 86% (0 dB) |
| [81] | Pejman Ghasemzadeh et al. | 2022 | IQ Signal | S-QRNN | 90% (5 dB) | [123] | Sai Huang | 2020 | Signal cyclic correntropy vector (CCV) | LSTM+DenseNet(LSMD) | 90% (−6 dB) |
| [80] | Tuo Wang et al. | 2021 | IQ Signal, Constellation Chart | SCMS (CNN + IndRNN) +VCD | 100% (0 dB) | [124] | Yuan Zeng | 2019 | Spectrum diagram | SCNN, SCNN2 | 80% (0 dB) |
| [79] | Judith Nkechinyere Njokuet al. | 2021 | IQ Signal | CGDNet | 90% (18 dB) | [123] | Sai Huang | 2020 | Signal cyclic correntropy vector (CCV) | LSTM + DenseNet(LSMD) | 90% (−6 dB) |
| [82] | Fugang Liu et al. | 2022 | Circulation spectrogram + IQ Signal | CNN + GRU | 100% (0 dB) | [119] | Zhiyu Qu | 2020 | Time frequency diagram | CNN | 96.1% (−6 dB) |
| [83] | Jialang Xu et al. | 2020 | IQ Signal | MCLDNN (CNN+LSTM + FC) | 90% (0 dB) | [125] | Erma Perenda | 2019 | IQ Signal | 1D-CNN | Close to 90% (0 dB) |
| [84] | Kaiyuan Jiang et al. | 2021 | IQ Signal | CNN + Bi LSTM + Attention | 93.14% (10 dB) | [71] | Kai Liu | 2021 | IQ Signal | DCN-Bi-LSTM | 90% (4 dB) |
| [88] | W.Zhang et al. | 2022 | Sampling signal | GRU + CNN | 99.45% (Real channel) | [126] | Zufan Zhang | 2020 | IQ Signal | CNN-LSTM | 83% (−2 dB) |
| [100] | HuajiZHOU et al. | 2022 | IQ Signal | GAN + CNN | 90% (400 signal samples) | [127] | Xiaohui Yao | 2019 | Sampling signal | GAN | 92% (12,000 signal samples) |
| [104] | Lixin Li et al. | 2021 | IQ Signal | AMR-CapsNet | 80% (8103 signal samples) | [128] | Sabour, S. | 2017 | Handwritten digital picture | CapsNet | 95.7% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, W.; Luo, Z.; Hu, Q. A Review of Research on Signal Modulation Recognition Based on Deep Learning. Electronics 2022, 11, 2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11172764
Xiao W, Luo Z, Hu Q. A Review of Research on Signal Modulation Recognition Based on Deep Learning. Electronics. 2022; 11(17):2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11172764
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Wenshi, Zhongqiang Luo, and Qian Hu. 2022. "A Review of Research on Signal Modulation Recognition Based on Deep Learning" Electronics 11, no. 17: 2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11172764
APA StyleXiao, W., Luo, Z., & Hu, Q. (2022). A Review of Research on Signal Modulation Recognition Based on Deep Learning. Electronics, 11(17), 2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11172764






