A Novel Power-Saving Reversing Camera System with Artificial Intelligence Object Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A powerful image processing chip;
- An appropriate artificial intelligence edge computing chip;
- A lightweight artificial intelligence network.
2. Methods
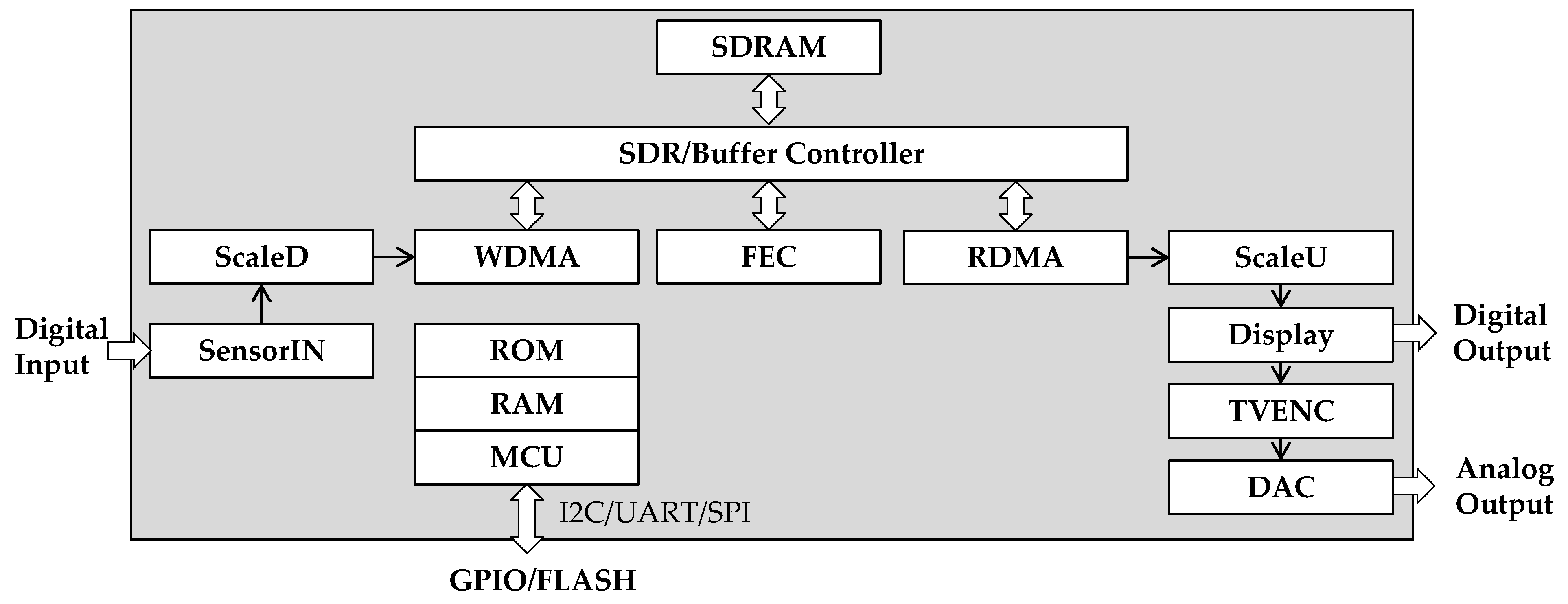
2.1. The Hardware Architecture of the Reversing Camera System
2.2. PIXELPLUS-PR2000
2.3. Image Processing Chip
2.3.1. The I/O Data Format of the IPC
2.3.2. Wide-Angle Image Distortion Correction
2.3.3. Image Buffer Controller
2.3.4. TV Encoder
2.4. The Artificial Intelligence Model
2.4.1. The Selection of the Artificial Intelligence Network
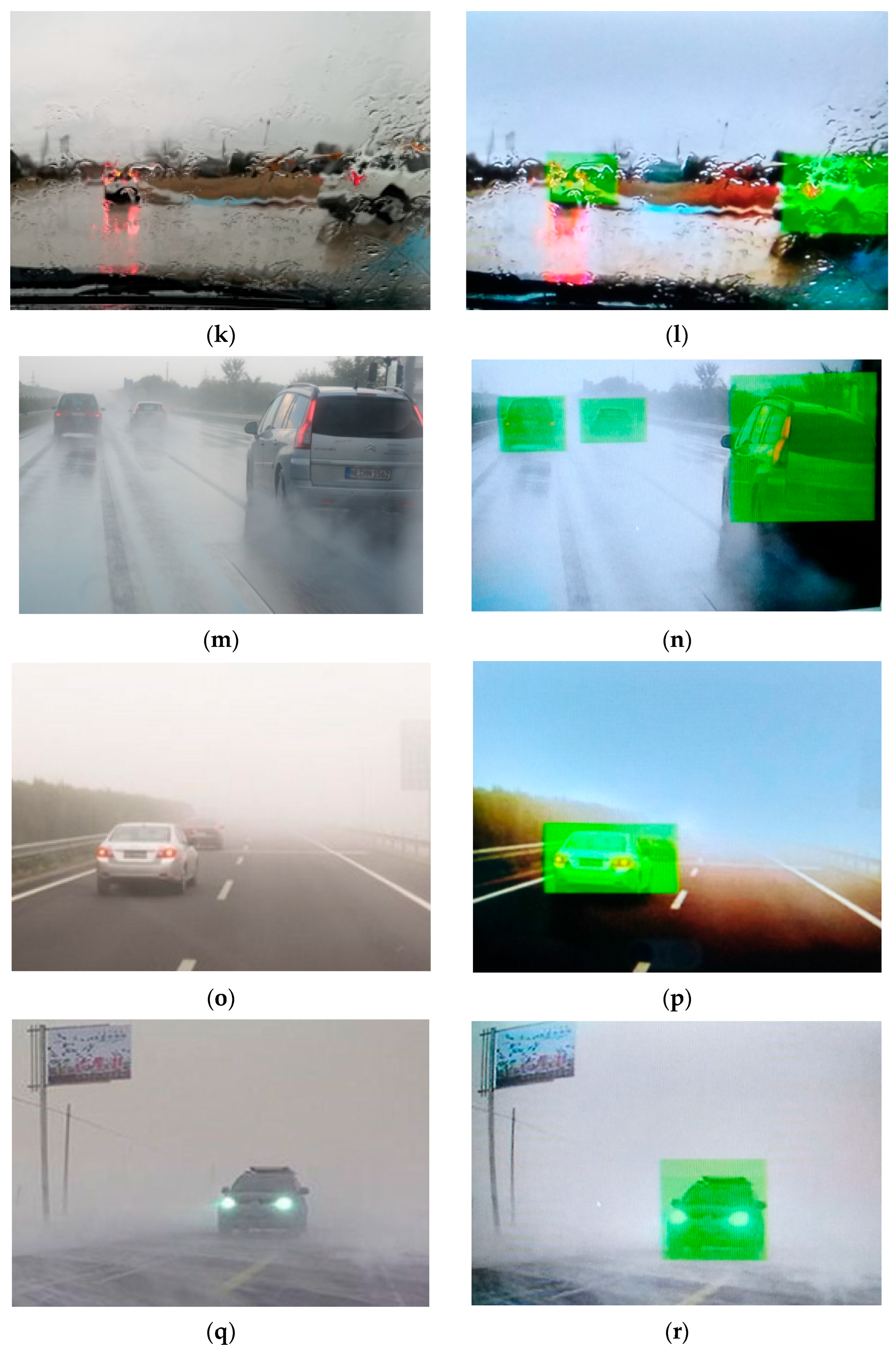
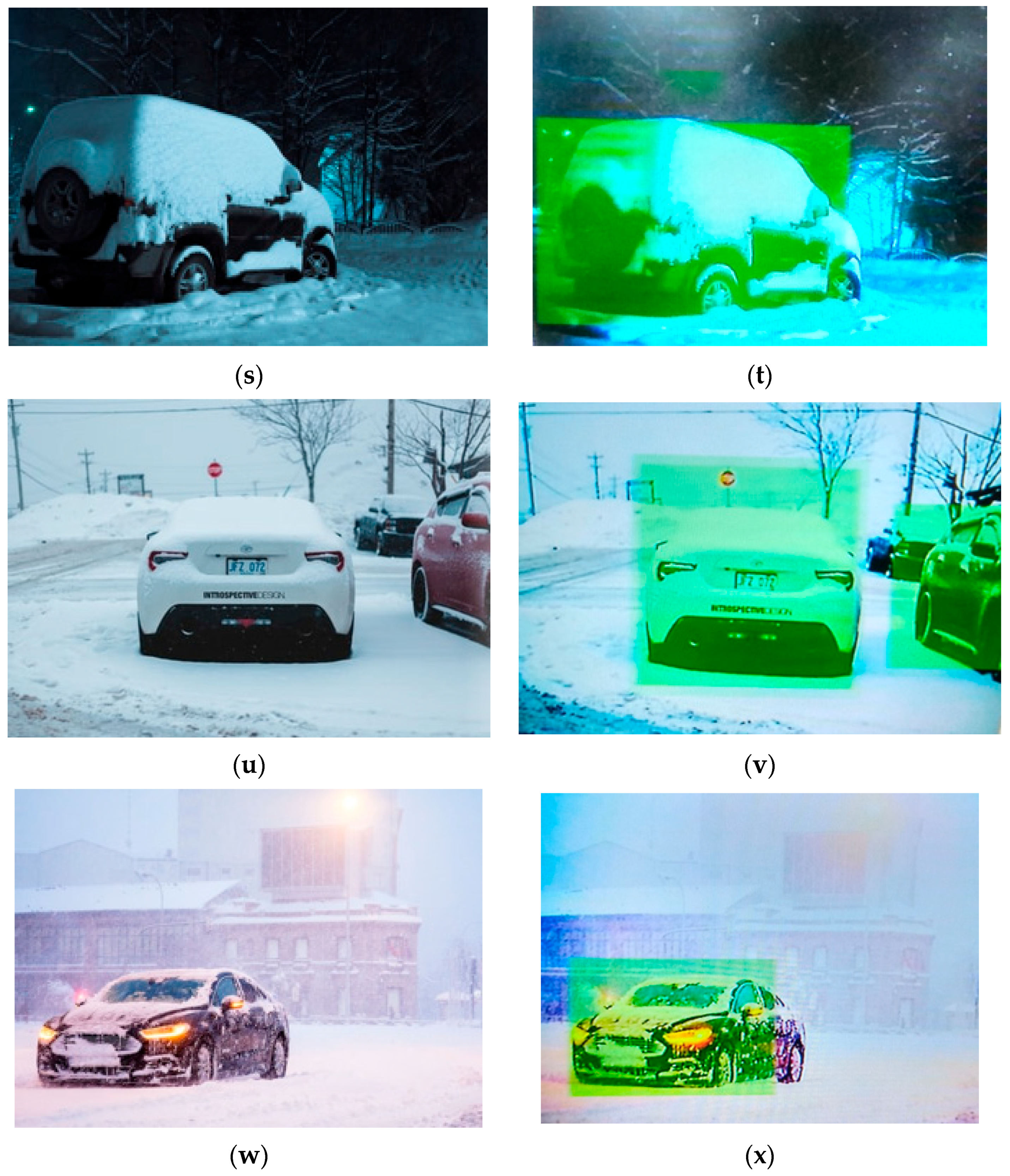
2.4.2. Image Labeling, Training and Testing
3. Results
3.1. Wide-Angle Image Distortion Correction
3.2. Image Buffer Controller
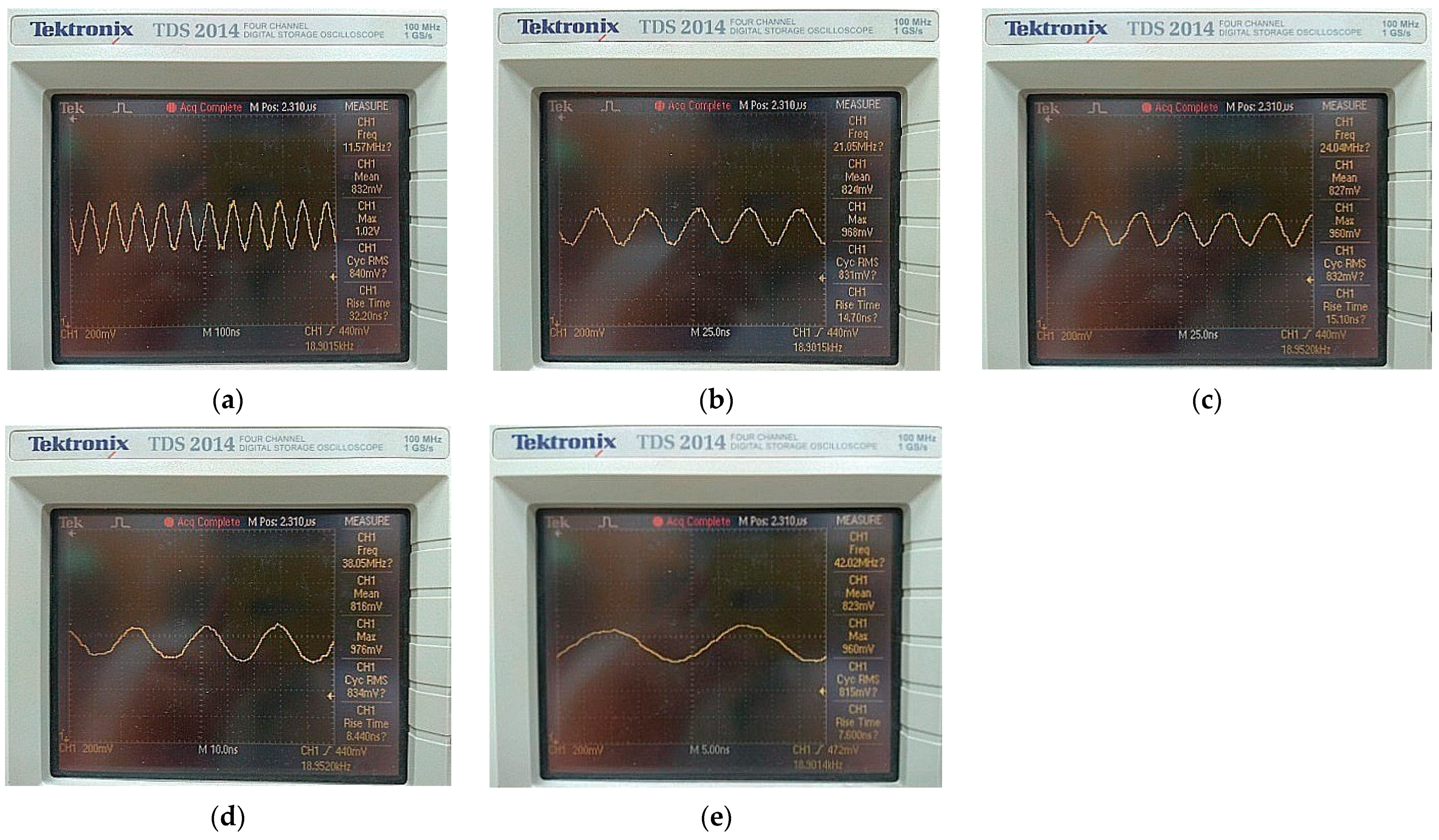
3.3. TV Encoder
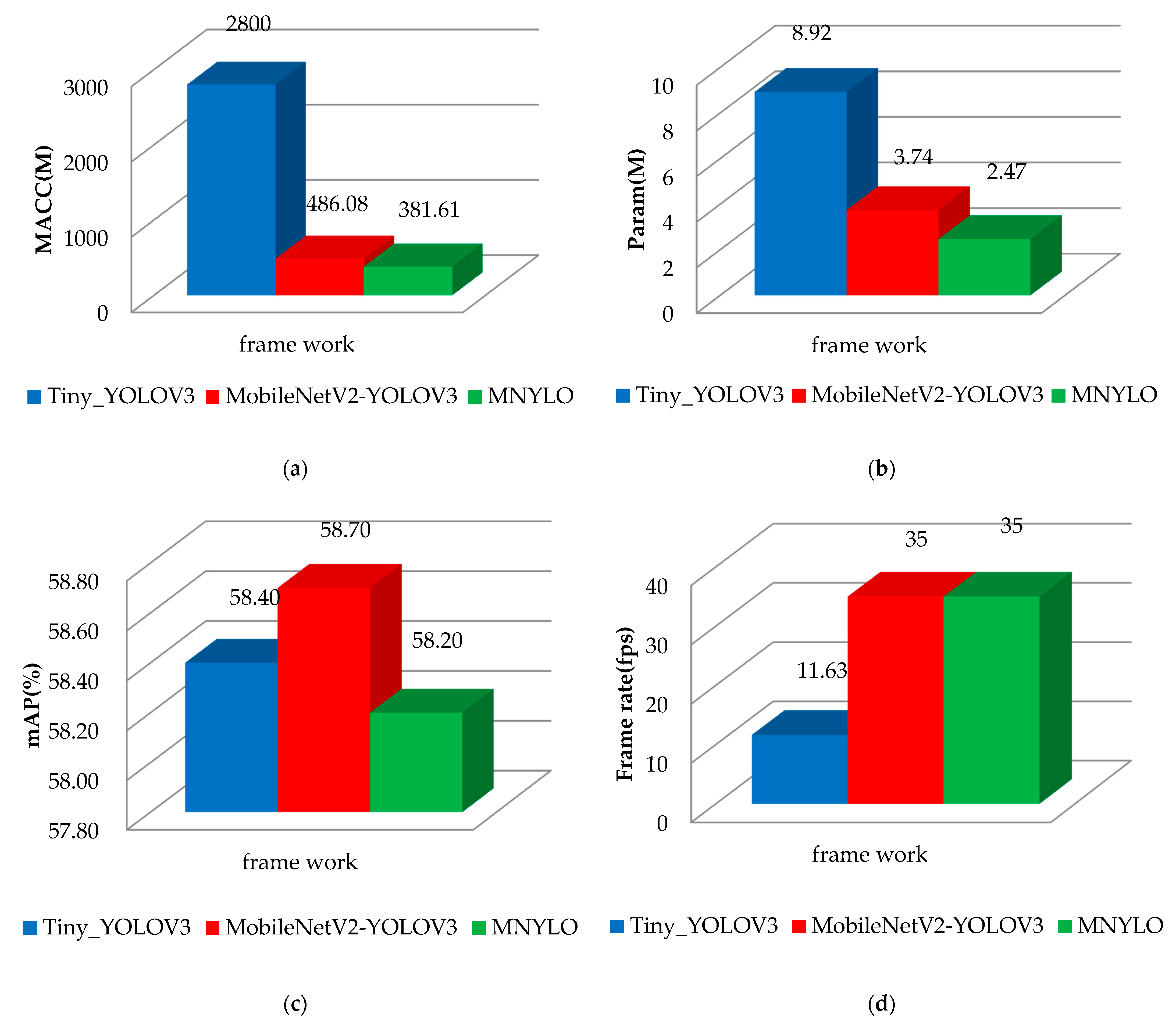
3.4. The Performance of the Artificial Intelligence Model
3.5. The Power Consumption of the Reversing Camera System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Status Report on Road Safety. 2015. Available online: https://www.afro.who.int/publications (accessed on 6 October 2021).
- Preventing Driveway Tragedies: Rear Cameras Help Drivers See What’s Going on behind Them. Available online: https://www.iihs.org/api/datastoredocument/status-report/pdf/49/2 (accessed on 6 October 2021).
- Park, J.; Byun, S.-C.; Lee, B.-U. Lens distortion correction using ideal image coordinates. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2009, 55, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, C.-F.; Hu, C.-M.; Martin, R.R.; Tai, C.-L. Fisheye Video Correction. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2012, 18, 1771–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Lee, B.-U. Lens Distortion Correction of images with Gradient Components. J. Inst. Electron. Inf. Eng. 2013, 50, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Su, J.; Zeng, X. A solution method for image distortion correction model based on bilinear interpolation. Comput. Opt. 2019, 43, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xiong, W.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Dai, Q.; Tu, P.; Hu, G. Fish-Eye Image Distortion Correction Based on Adaptive Partition Fitting. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2021, 126, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Zhou, W.; Ma, S.; Qi, P.; Zhong, J. Model-Free Lens Distortion Correction Based on Phase Analysis of Fringe-Patterns. Sensors 2020, 21, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, S.; Tan, R.; Rei, K.; Makaigawa, Y.; Ikeuchi, K. Raindrop Detection and Removal from Long Range Trajectories. In Proceedings of the ACCV 2014: Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Singapore, 1–5 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, R.; Tan, R.T.; Yang, W.; Su, J.; Liu, J. Attentive Generative Adversarial Network for Raindrop Removal from a Single Image. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 2482–2491. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Patel, V.M. Density-aware single image de-raining using a multi-stream dense network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 695–704. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, D.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q.; Zhu, P.; Meng, D. Progressive image deraining networks: A better and simpler baseline. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 3937–3946. [Google Scholar]
- Al Machot, F.; Ali, M.; Haj Mosa, A.; Schwarzlmüller, C.; Gutmann, M.; Kyamakya, K. Real-time raindrop detection based on cellular neural networks for ADAS. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2016, 16, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, H.; Wu, Q.; Ngan, K.N.; Luo, H.; Wei, H.; Li, H.; Meng, F.; Xu, L. Multi-Scale Shape Adaptive Network for Raindrop Detection and Removal from a Single Image. Sensors 2020, 20, 6733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Liao, J.; Sander, P. Let’s See Clearly: Contaminant Artifact Removal for Moving Cameras. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.08852. [Google Scholar]
- Deshmukh, A.; Singh, S.; Singh, B. Design and development of image defogging system. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Signal and Information Processing (IConSIP), Nanded, India, 6–8 October 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Engin, D.; Genç, A.; Kemal Ekenel, H. Cycle-dehaze: Enhanced cyclegan for single image dehazing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 825–833. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, J.; Xie, Y. Enhanced pix2pix dehazing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 8160–8168. [Google Scholar]
- Tufail, Z.; Khurshid, K.; Salman, A.; Khurshid, K. Optimisation of transmission map for improved image defogging. IET Image Process. 2019, 13, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Guo, X.; Lu, X.; Liu, X.; Sun, B. Image Defogging Algorithm Based on Sparse Representation. Complexity 2020, 2020, 6835367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Li, K.; Chen, T.; Liu, M.; Mei, S.; Xing, K.; Li, Y.H. A Novel UAV Sensing Image Defogging Method. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 2610–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anan, S.; Khan, M.I.; Kowsar, M.M.S.; Deb, K.; Dhar, P.K.; Koshiba, T. Image Defogging Framework Using Segmentation and the Dark Channel Prior. Entropy 2021, 23, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graffieti, G.; Maltoni, D. Artifact-Free Single Image Defogging. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Fu, Y.; Sun, X. Single Image Defogging Algorithm Based on Sky Region Segmentation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1971, 012068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Flexible Architecture for Fisheye Correction in Automotive Rear-View Cameras; AFA: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1998; Available online: http://www.manipal.net/mdn/technology/fisheye_correction.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Tadjine, H.; Hess, M.; Karsten, S. Object Detection and Classification Using a Rear In-Vehicle Fisheye Camera. In Proceedings of the FISITA 2012 World Automotive Congress; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 197, pp. 519–528. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Yuan, Y.; Qin, A.; Miao, Q.-G.; Gong, M.-G. Commonality Autoencoder: Learning Common Features for Change Detection from Heterogeneous Images. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn Syst. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Ma, W.; Gong, M.; Su, L.; Jiao, L.J.I.G.; Letters, R.S. A novel point-matching algorithm based on fast sample consensus for image registration. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 12, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Banff, AB, Canada, 14–16 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A.A. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Canziani, A.; Paszke, A.; Culurciello, E. An analysis of deep neural network models for practical applications. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1605.07678. [Google Scholar]
- Analysis of Deep Neural Networks. Available online: https://culurciello.medium.com/analysis-of-deep-neural-networks-dcf398e71aae (accessed on 8 October 2021).
- NVIDIA. Available online: https://www.nvidia.com/ (accessed on 8 October 2021).
- List of Nvidia Graphics Processing Units. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Nvidia_graphics_processing_units8 (accessed on 8 October 2021).
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 12993–13000. [Google Scholar]












| AI Model | Parameters | Top-5 Error |
|---|---|---|
| AlexNet [29] | 60 MB | 15.3% |
| GoogleNet [30] | 4 MB | 6.67% |
| VGG Net [31] | 138 MB | 7.3% |
| ResNet [32] | 60 MB | 3.57% |
| The Main Scene | The 1th Sub-Scene | The 2nd Sub-Scene | Number of Images |
|---|---|---|---|
| On the road | daytime | Rainy day | 5000 pics |
| Non-rainy day | 5000 pics | ||
| nighttime | Rainy day | 5000 pics | |
| Non-rainy day | 5000 pics | ||
| In the parking lot | outdoor | Nighttime | 5000 pics |
| Nighttime | 5000 pics | ||
| indoor | Bright ambient light | 5000 pics | |
| Dim ambient light | 5000 pics |
| Item | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution | 720P 1 | 720P 1 | 1080P 2 | 1080P 2 | 1080P 2 |
| Frame rate (fps) | 30 fps | 30 fps | 30 fps | 30 fps | 30 fps |
| Defined Subcarrier Frequency | 11.55 MHz | 21.00 MHz | 24.00 MHz | 38.00 MHz | 42.00 MHz |
| Measured Subcarrier Frequency | 11.57 MHz | 21.05 MHz | 24.04 MHz | 38.05 MHz | 42.02 MHz |
| Error rate (%) | 0.17% | 0.24% | 0.17% | 0.13% | 0.05% |
| Model | Resolution | MACC 1 | Param 1 | mAP 2 | Frame Rate 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiny_YOLOV3 | 416 × 416 | 2.8 Giga | 8.92 Mega | 58.4% | 11.63 fps |
| MobileNetV2-YOLOV3 | 224 × 224 | 486.08 Mega | 3.74 Mega | 58.7% | 35 fps |
| MNYLO | 224 × 224 | 381.61 Mega | 2.47 Mega | 58.2% | 35 fps |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hung, K.-C.; Lin, M.-C.; Lin, S.-F. A Novel Power-Saving Reversing Camera System with Artificial Intelligence Object Detection. Electronics 2022, 11, 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11020282
Hung K-C, Lin M-C, Lin S-F. A Novel Power-Saving Reversing Camera System with Artificial Intelligence Object Detection. Electronics. 2022; 11(2):282. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11020282
Chicago/Turabian StyleHung, Kuo-Ching, Meng-Chun Lin, and Sheng-Fuu Lin. 2022. "A Novel Power-Saving Reversing Camera System with Artificial Intelligence Object Detection" Electronics 11, no. 2: 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11020282
APA StyleHung, K.-C., Lin, M.-C., & Lin, S.-F. (2022). A Novel Power-Saving Reversing Camera System with Artificial Intelligence Object Detection. Electronics, 11(2), 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11020282






