Abstract
The deterioration of numerous eye diseases is highly related to the fundus retinal structures, so the automatic retinal vessel segmentation serves as an essential stage for efficient detection of eye-related lesions in clinical practice. Segmentation methods based on encode-decode structures exhibit great potential in retinal vessel segmentation tasks, but have limited feature representation ability. In addition, they don’t effectively consider the information at multiple scales when performing feature fusion, resulting in low fusion efficiency. In this paper, a newly model, named DEF-Net, is designed to segment retinal vessels automatically, which consists of a dual-encoder unit and a decoder unit. Fused with recurrent network and convolution network, a dual-encoder unit is proposed, which builds a convolutional network branch to extract detailed features and a recurrent network branch to accumulate contextual features, and it could obtain richer features compared to the single convolution network structure. Furthermore, to exploit the useful information at multiple scales, a multi-scale fusion block used for facilitating feature fusion efficiency is designed. Extensive experiments have been undertaken to demonstrate the segmentation performance of our proposed DEF-Net.
1. Introduction
Eyes are the main organ for human to receive information from the outside world, according to the findings in [1], millions of people lose their eyesight every year due to eye diseases [2], which undoubtedly hit the lives of patients hard. Fundus images contain an abundance of retinal structures [3], and abnormal lesions can be found by detecting retinal vessels in the fundus images. Early screening for eye disease has been completed by experienced specialist through manual annotation, but it is an expensive and inefficient task in clinical practice [4,5]. In addition, there are subjective differences in annotation between experts, which aggravates the difficulty of segmentation. Therefore, methods for automatic segmentation of retinal vessels have been explored.
In recent years, deep learning (DL) has been rapidly developed in the fields of image processing, like object detection [6,7,8], image segmentation [9]. Due to its powerful feature extraction capability, which further makes automatic image segmentation possible. The emergence of fully convolutional networks(FCN) [10] introduces the concept to semantic segmentation, and it can obtain a segmentation results of the identical scale as input images. U-shaped network (U-Net) [11] improves the FCN and designs an encoder-decoder structure, which has achieved great success in the field of medical image segmentation, where the encoder is used for feature extraction and the decoder is used for feature reconstruction, and the skip connection preserves both semantic features and detail information.
Encouraged by U-Net, a number of models based on encoder-decoder structure have emerged [12,13]. Inspired by residual connection [14], Ref. [15] was proposed for the segmentation of fundus vessels, where residual connection not only avoided the gradient problem but also preserved additional features. Motivated by densely connected convolutional network (DenseNet) [16], Ref. [17] was designed to remove artifacts from images. Schlemper et al. [18] proposed a gated attention mechanism and embedded it in U-Net, which could adaptively correct the features in the encoder and enhance the propagation of relevant information. Alom et al. [19] designed a recurrent structure for feature extraction, which was able to obtain more contextual information. Mou [20] embedded an integrated attention block in the bottleneck layer, which could handle both spatial and channel information. In [21], Keetha et al. embedded a bi-directional feature network(Bi-FPN) between the encoder and decoder, which was a resource efficient method for lung cancer diagnosis. All these methods have improved on the basis of U-Net, but still have problems as follows: (1) These methods use a single path with convolution structure and capture only limited information during feature extraction. (2) The features from the encoder are not fully exploited at all scales during fusion, and the feature fusion approach is rather simple and fails to fully integrate the features extracted.
Therefore, a dual-encoder fusion network for fundus vascular segmentation, called DEF-Net, is proposed. Here, we build a dual-encoder structure to obtain richer features than a single path with convolution structure. For this purpose, we design an encoder branch for extracting detail information and an encoder branch for capturing contextual information, respectively. To facilitate the fusion efficiency of features, we present a multi-scale fusion block to fuse features from multiple scales. Extensive experiments are conducted and prove the proposed approach with enhanced performance. Core contributions of our work could be summed up as:
- A residual convolution (RC) block based on convolutional structure is designed to capture detail information and a recurrent residual convolution (RRC) block based on recurrent structure is built to obtain rich contextual features. On the basis, a novel dual-encoder structure by RC blocks and RRC blocks is proposed for stronger feature extraction ability.
- A multiscale fusion (MF) block is adopted to integrate features from different scales into a global vector by taking information from multiple scales into account and guide the original scales to facilitate the flow of features at different scales and enhance the fusion efficiency.
- Experiments conducted on fundus image datasets have displayed the overall performance of our method and the results obtain a superior performance compared to other advanced methods.
2. Materials and Methods
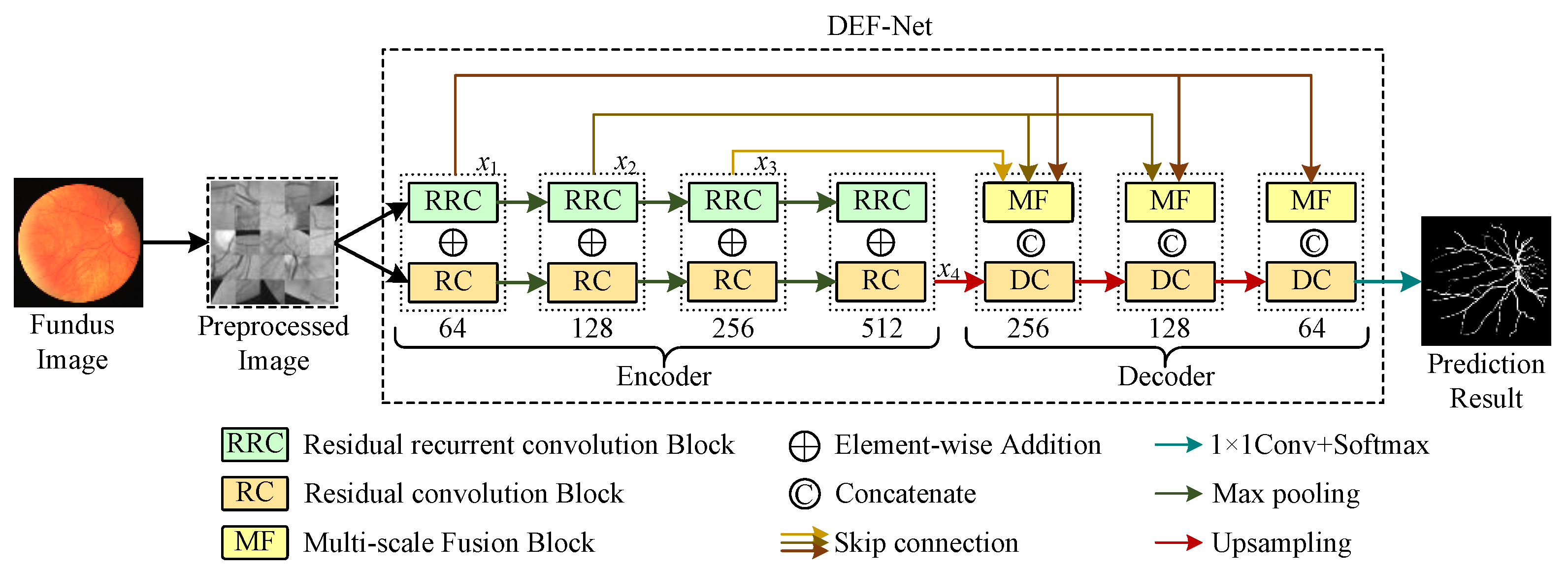
The proposed method is given in Figure 1. The entire segmentation model can be viewed as two parts: a dual-encoder consisting of RC blocks and RRC blocks for extracting rich features, MF blocks that can facilitate multi-scale feature fusion and a decoder composed of RC blocks. The dual-encoder part is used to extract the rich features and the decoder part is used to reconstruct the feature representation and locate the vessels precisely. Detailed descriptions of the dual-encoder and the decoder will be given in the subsections.

Figure 1.
The framework of the proposed DEF-Net.
2.1. Dual-Encoder Structure
To extract enough features in the feature encoding stage, we design a two-branch encoder structure, as shown in Figure 1, where the path consisting of RRC blocks captures contextual information at multiple scales, while the path consisting of RC blocks captures detailed information at various scales. The features are down-sampled following the maxpooling operation in U-Net to retain the most distinct features extracted while speeding up the model training. We perform the element-wise addition of features extracted by RRC blocks and RC blocks for the same scale to retain the features extracted by both branches simultaneously. A detailed description of the RC block and RRC block can be seen in the next subsections.
2.1.1. RC Block
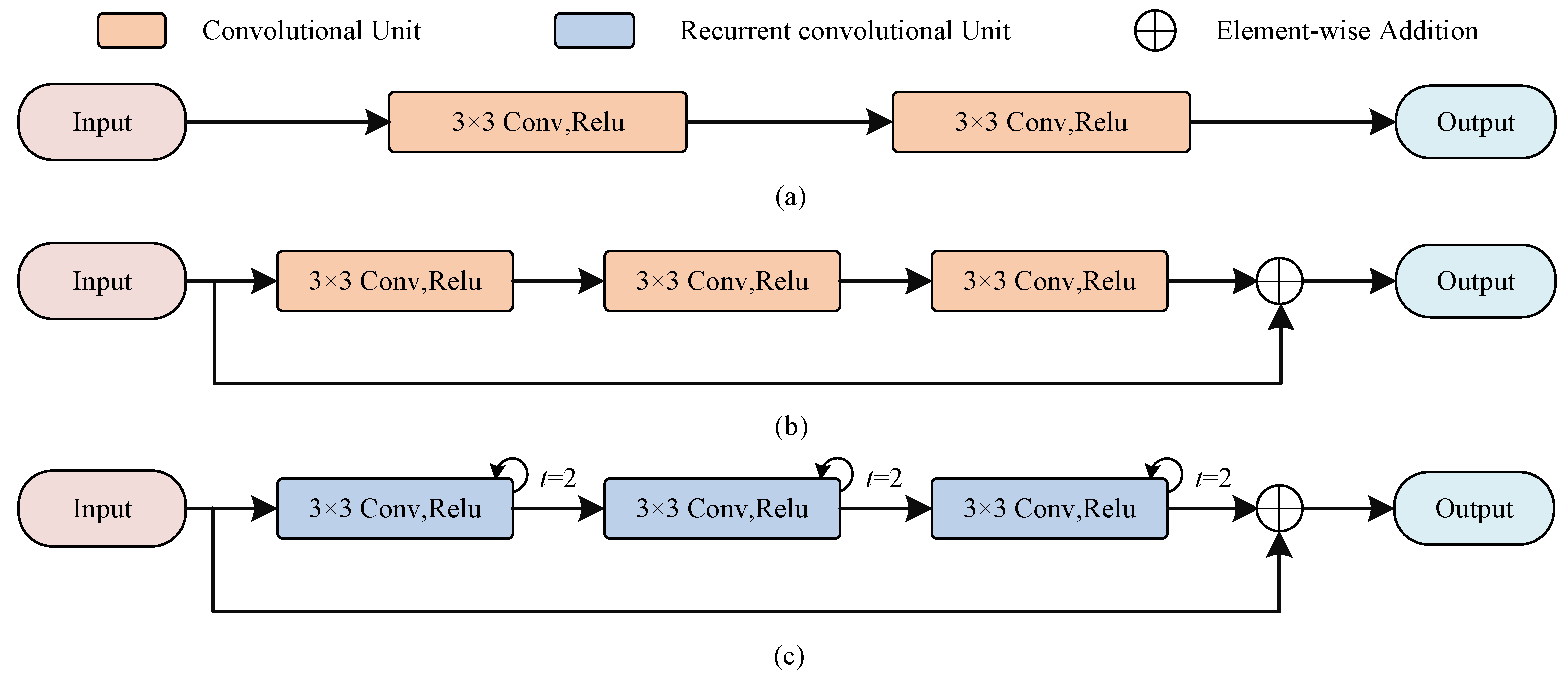
As shown in Figure 2a, the encoder in U-Net uses a stack of two consecutive convolutional units, each containing a convolutional layer of kernel size 3, a batch normalization (BN) layer that accelerates model convergence, and a linear rectification function (ReLU). Let be the feature maps of th layer, be the learnable convolution kernel, and be the bias of layer l. Each convolution unit can be expressed as
where the activation function can be expressed as

Figure 2.
The illustration of RC block and RRC block in our method. (a) The encoder in U-Net; (b) The residual convolution block; (c) The recurrent residual convolution block.
Compared with the encoder in U-Net, the RC blocks changes the number of convolutional units because deeper network models could acquire more features, besides we also add residual connections, which not only can alleviate the gradient problem during model training but also preserve more features additionally. The number of channels of the encoder is set to , respectively, and we also use convolutional kernels of size as U-Net, because small convolutional kernels help to capture detailed information.
2.1.2. RRC Block
Similar to the RC block, inspired by [19], we stack three recurrent convolutions with a residual structure to construct the RRC block, as shown in Figure 2. It allows to receive abundant contextual information through feature accumulation, which forms complementary information with the detailed information obtained from the RC block. Here we use a recurrent convolution with step size 2, the output feature maps can be expressed in relation to the step size t as
where and are the input images, and are the learnable weight, and b denotes the bias. The final result is also output after a ReLU activation
2.2. Decoder
The semantic features as well as detailed features are preserved in U-Net through skip connection, as shown in Figure 3.

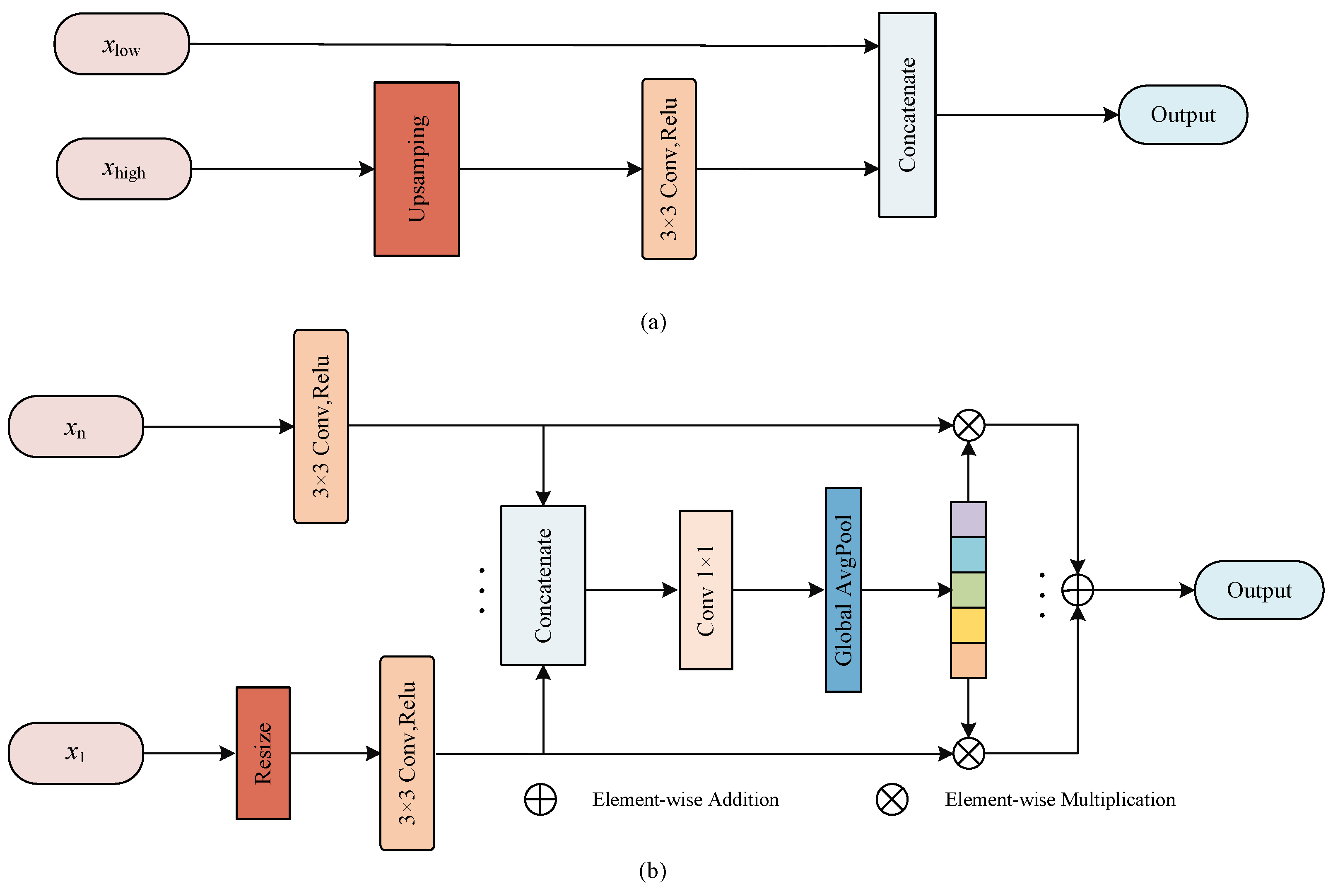
Figure 3.
The illustration of proposed MF block. (a) The fusion scheme in U-Net; (b) The multi-scale fusion block.
Here, the high-level features from the encoder are upsampled to recover the size of the feature map to match the feature map from the previous stage of the decoder so that they can concatenate together, and this process can be described as
where is the low-level feature maps from encoder, is the high-level feature maps from decoder, ⊙ denotes the feature concatenation, denotes the upsampling operation and is the output feature maps after concatenation. In addition, the features extracted from different scales of the encoder are not completely independent, and the utilization of features from multiple scales is helpful to improve the fusion efficiency [22], so we propose a MF block that can better fuse multi-scale information.
2.2.1. Feature Reconstruction
In Figure 3b, the feeds to MF block are the feature maps of multiple scales from encoder unit. First, the feature map size is resized to the same scale by resizing operation, then the convolution is employed to reduce the number of channel numbers and the adjusted feature maps are concatenated together. The whole process can be presented as
where is applied to change the size of feature maps. represents the feature maps from n stage of the encoder, ⊙ denotes the feature concatenation, and is the feature maps after concatenation.
To efficiently utilize the feature maps containing information from various scales, the global pooling in used to abstract into a feature vector
where denotes convolution to reduce dimension, and serves to construct global descriptors.
To embed the global vector into the feature maps of each scale, we use element-wise multiplication to reconstruct the feature maps of various scales, and finally the reconstructed feature maps are fused by element-wise addition. This approach considers the differences between scales of encoder, abstracts the features at different scales by constructing a global descriptor, and reconstructs the feature response at each stage to enrich the feature representation, which is beneficial to increasing the fusion efficiency of encoder and decoder.
2.2.2. Feature Fusion
Similar to U-Net, DEF-Net upsamples the decoder features and fuses them with the corresponding encoder features during feature fusion. Specifically, the feature maps reconstructed by MF are concatenated with previous low-level features and sent to the next stage of decoder for feature processing as
where are the feature maps reconstructed by MF blocks and represents the fusion of MF blocks and decoder feature maps. After the last decoder stage, convolution and softmax activation functions are applied with the segmented prediction results output.
3. Experimental Preparation
To ensure the reliability of the experiments, in this section the relevant preparation of the experiments will be introduced. The data sets and evaluation metrics used, the necessary preprocessing procedures, and the experimental details will be covered in the subsections.
3.1. Experimental Materials and Evaluation Metrics
Experiments for testing DEF-Net performance have been conducted on retinal image datasets, including DRIVE [23], CHASE_DB1 [24], and STARE [25].
The DRIVE dataset contains 40 fundus retinal images, of which 7 are pathological images and the others are clean images. The resolution of each image is , of which the first 20 images are trained with the first annotation as the ground truth.
The CHASE_DB1 dataset contains 14 pairs of fundus images collected from 14 school children, with a resolution of , of which 20 were used for training while rest were used for testing. We use the annotation result of the first expert as the ground truth.
The STARE dataset contains 20 fundus images, and each of them has a resolution of and half of them is used for training. There are 10 pathological images in this dataset. We also use the first expert’s annotation as the label to train the network.
To assess model performance, the following evaluation metrics are used:
where represents the correctly classified vessel pixels, stands for correctly classified background pixels, represents the incorrectly classified vessel pixels, and represents the incorrectly classified background pixels. In addition, area under Receiver Operating Characteristic curves (AUC) is also used to evaluate the overall performance of segmentation.
3.2. Experimental Preprocessing
Appropriate preprocessing operations can effectively enhance model performance. To improve the issue of low contrast caused by light in fundus images, we use the approach based on traditional image processing to enhance the contrast of fundus images.
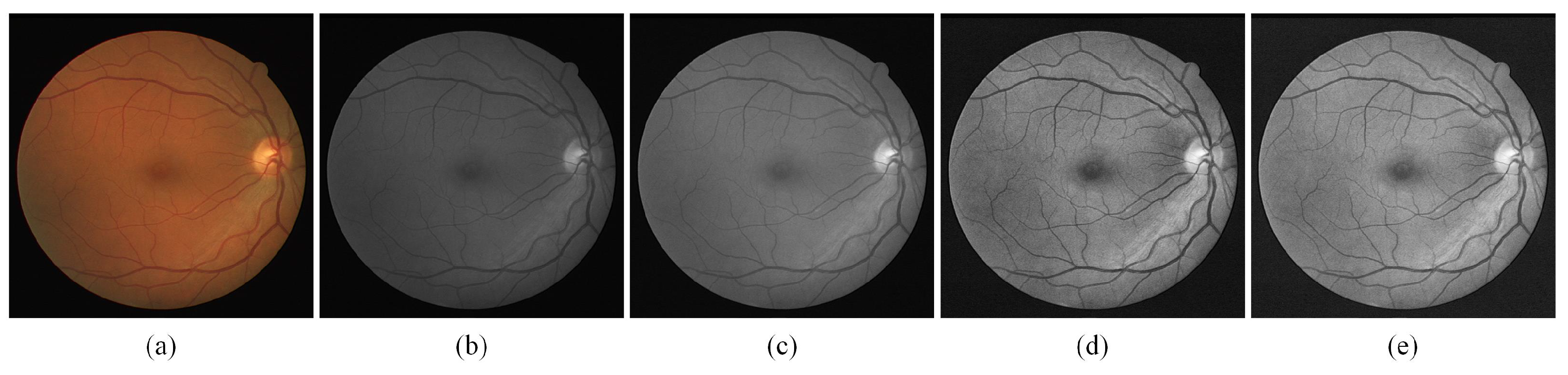
As shown in Figure 4, an original fundus image is shown in (a), and the fundus image is first grayed by converting colorful images to grayscale images as (b). To variation the intensity range of the pixels, normalization is applied as in (c). (d) is the image after the finite adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) process, which shows a significant improvement in the contrast of the image, and (e) is the result obtained after gamma adjustment which compensates the imbalance caused by the fundus light. After the image enhancement referred to above, the contrast of fundus images has dramatically improved, and the enhancement of thin blood vessels in particular will bring notable benefit to experimental accuracy.

Figure 4.
The sample of preprocessing stage. (a)Fundus image; (b) Grayed output result; (c) normalized output result; (d) Output results after CLAHE; (e) Output result after Gamma adjust.
3.3. Experimental Details
The retinal vessel segmentation task is a binary classification task, and to better distinguish vascular pixels from non-vascular pixels, the binary cross-entropy is employed. Supposing there are N pixels in total, the distance of the predicted result P from the ground truth G is assessed as
The network is built with PyTorch and trained on an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 Ti GPU. The models are trained with 50 epochs and 0.001 initial learning rate, the batch size is set to 64.
The dataset used in this paper has a rather small scale. To better train the model and avoid overfitting at the same time, we uses the operation of cropping patches, in which the images are randomly cropped into blocks with a stride of 16 during the training phase. In the test phase, the corresponding segmentation patches are generated by sequentially cropping patches, and we combine these segmentation patches into a complete segmentation result in order, as shown in Figure 1.
4. Results and Analysis
To fully validate the performance of the proposed DEF-Net, extensive experimental results are described in this section. Detailed results and analysis of the ablation experiments as well as the comparison experiments will be provided in the subsections.
4.1. Ablation Experiment
The ablation experiments have been conducted on three datasets, and the results are shown in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3 and Figure 5. To facilitate the subsequent analysis, we first introduce the configuration of the ablation models. RC-Net represents a U-shaped structure composed of RC blocks and using the MF block, while RRC-Net represents a U-shaped structure composed of RRC blocks and using the MF block. DE-Net represents the structure where the RC blocks and RRC blocks are used to form a dual-encoder at the same time and the decoder are RC blocks, and DEF-Net represents the introduction of MF blocks on the basis of DE-Net. The ablation results of the dual-encoder and MF block are described in the subsections.

Table 1.
Ablation experiment on DRIVE dataset.

Table 2.
Ablation experiment on CHASE_DB1 dataset.

Table 3.
Ablation experiment on STARE dataset.

Figure 5.
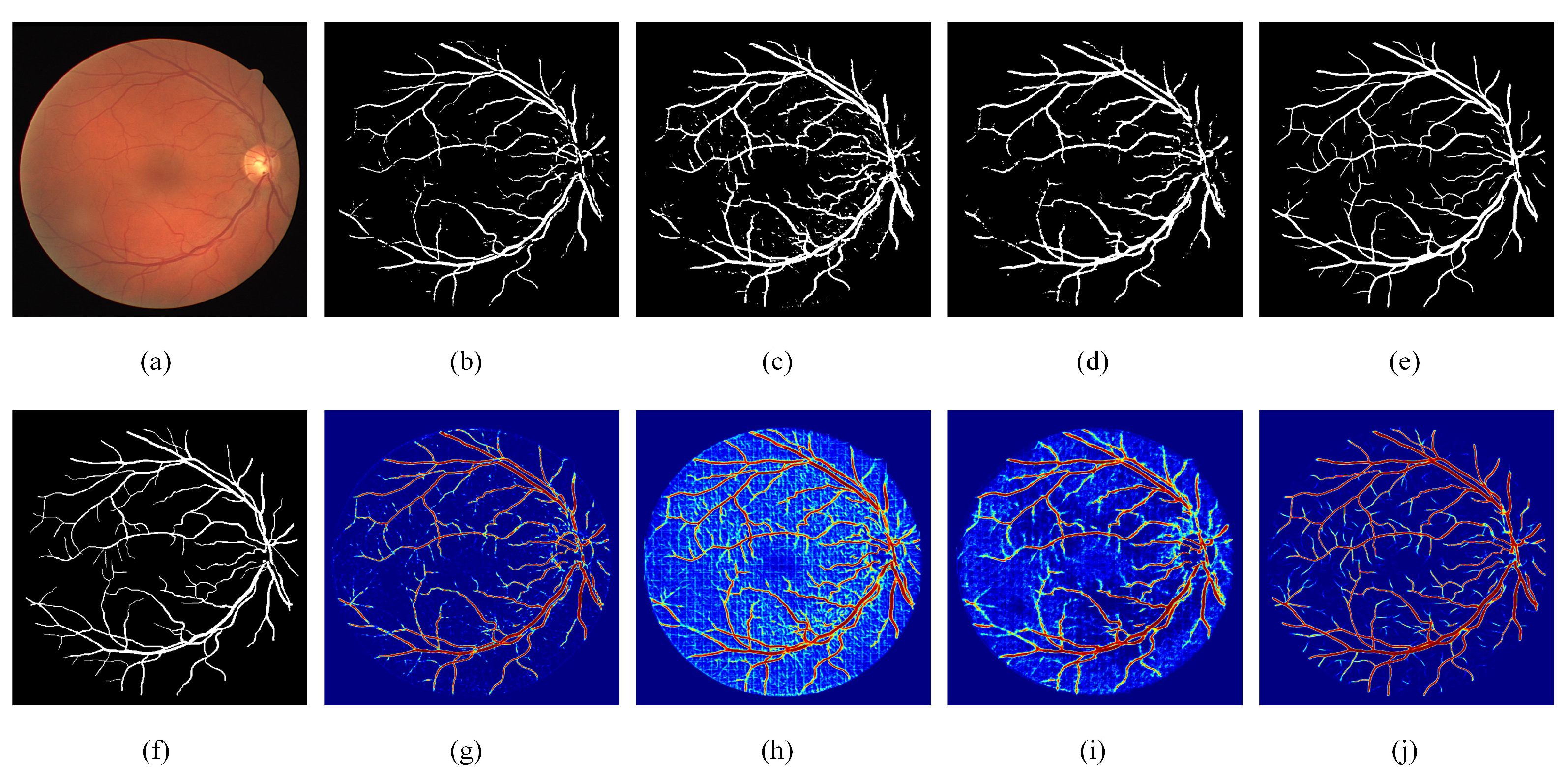
Visual examples of ablation experiments. (a) Fundus image; (b) Segmentation result of RC-Net; (c) Segmentation result of RRC-Net; (d) Segmentation result of DE-Net; (e) Segmentation result of DEF-Net; (f) Ground truth of the fundus image; (g) Heatmap of RC-Net; (h) Heatmap of RRC-Net; (i) Heatmap of DE-Net; (j) Heatmap of DEF-Net.
4.1.1. Effect of the Dual-Encoder
From Table 1, we can see that when only RC blocks are used to construct the encoder, the performance of RC-Net is not desirable, especially is only 0.7205, which indicates that the model has a low segmentation accuracy for vascular pixels. When only RRC blocks are used to construct the encoder, the value of reaches 0.8581 due to the accumulation of features, but the value of is only 0.9196, which indicates that the features accumulated by RRC blocks are beneficial to the segmentation of vascular pixels, but not useful for the segmentation of background pixels. Comparing the results of RC-Net, RRC-Net and DEF-Net, it can be seen that the effectiveness of using both RC blocks and RRC blocks to form a dual-branch encoder shows better robustness than that of a single-path encoder. Specifically, DEF-Net achieves optimal values on both and , which are comprehensive evaluation metrics. The results on the other two datasets also showed that the dual-encoder structure achieves a balance in most metrics, allowing the segmentation performance on vessel pixels.
The visualization results of ablation experiments are given in Figure 5. As can be seen from the heat map, the features extracted by RC-Net through standard convolution are different from those accumulated by RRC-Net, RC-Net contains more detailed information while RRC-Net contains more contextual information. When using the dual encoder, it is enabled not only to use the information extracted from both paths simultaneously, but also to rectify the incorrectly segmented pixels to an extent.
4.1.2. Effect of the MF Block
The ablation results for MF block can be obtained by comparing DENet with DEF-Net. Combining the three datasets, DEF-Net performs obviously better than DENet in both and , which indicates that the addition of MF blocks can significantly enhance the segmentation precision of the model. This is because the MF blocks effectively exploit the potential expression of information from multiple scales. In addition, DEF-Net achieved the best on the DRIVE dataset and the best on other two datasets, it further indicates the setting of dual-encoder and MF block could achieve the best performance. The visualization results in Figure 5 also illustrate that after adding MF blocks, the reconstructed features can better facilitate the fusion of the encoder and decoder features, especially the segmentation effect for thin vessels has been significantly improved.
4.2. Comparisons with Advanced Methods
To comprehensively assess the model’s robustness, we conduct a comparison of DEF-Net against other competing methods, quantitative and qualitative results are described in Section 4.2.1 and Section 4.2.2, respectively.
4.2.1. Quantitative Result
In Table 4, DEF-Net achieves the best values in and , which indicates that our proposed method shows advantages in segmenting vascular pixels. AAUNet [26] achieves the best , and it uses an enhanced convolution to replace the standard convolution, but the detail information is lost during this process, thus resulting in a lower . IterNet [27] uses multiple sub-UNet to build the model, resulting in feature redundancy, and its is only 0.7791.
In Table 5, DEF-Net achieves the best values for most of the metrics in the CHASE_DB1 dataset, with of 0.9857, of 0.8076, and of 0.8053, which fully demonstrates the robustness of the proposed method. Compared with R2UNet [19], which only uses recurrent structure, our proposed DEF-Net has a 3.83% improvement on , which indicates that the dual-encoder has a more powerful feature extraction capability. The method in [28] uses a joint pixel-level as well as a segmentation-level loss to train the model, which is not effective in improving the model segmentation performance like . The best results are achieved by NFN+ [29] on and , which utilizes a cascade structure to model the vessels implicitly, but our proposed approach still achieves superior results to that method.
In Table 6, on the STARE dataset, SD-UNet [30] achieves the best and results, but the method is less sensitive to vascular pixels, achieving only 0.7548 of . Ref. [31] proposed a dual-decoder structure to deal with thick and thin vessels separately. Compared to this method, we enhance the feature extraction at the encoding stage and achieved better segmentation performance, obtaining the best and . Sine-Net [32] uses a cascaded U-Net structure, and the method reduces the size of the U-Net to decrease the computation, which sacrifices the model’s segmentation accuracy for blood vessels leading to a lower . In general, DEF-Net achieves the best results on and for all three datasets, which strongly demonstrates the improvement and effectiveness of the proposed method in segmenting vascular pixels. In addition, our method can balance each metric better and has better robustness.

Table 4.
Comparison results with advanced methods on DRIVE dataset.
Table 4.
Comparison results with advanced methods on DRIVE dataset.
| Method | Year | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2UNet [19] | 2018 | 0.9784 | 0.8171 | 0.9556 | 0.7792 | 0.9813 |
| Joint Loss [28] | 2018 | 0.9752 | - | 0.9542 | 0.7653 | 0.9818 |
| LadderNet [33] | 2019 | 0.9793 | 0.8202 | 0.9561 | 0.7856 | 0.9810 |
| R-sGAN [34] | 2019 | - | 0.7882 | - | 0.7901 | 0.9795 |
| AAUNet [26] | 2020 | 0.9847 | - | 0.9558 | 0.7941 | 0.9798 |
| IterNet [27] | 2020 | 0.9813 | 0.8218 | 0.9574 | 0.7791 | 0.9831 |
| SATNet [35] | 2021 | 0.9822 | 0.8174 | 0.9684 | 0.8117 | 0.9870 |
| Lightweight [36] | 2021 | 0.9806 | - | 0.9568 | 0.7921 | 0.9810 |
| Bridege-Net [37] | 2022 | 0.9834 | 0.8203 | 0.9565 | 0.7853 | 0.9818 |
| DEF-Net | 2022 | 0.9789 | 0.8236 | 0.9556 | 0.8138 | 0.9763 |

Table 5.
Comparison results with advanced methods on CHASE_DB1 dataset.
Table 5.
Comparison results with advanced methods on CHASE_DB1 dataset.
| Method | Year | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2UNet [19] | 2018 | 0.9815 | 0.7928 | 0.9634 | 0.7756 | 0.9820 |
| Joint Loss [28] | 2018 | 0.9781 | - | 0.9610 | 0.7633 | 0.9809 |
| LadderNet [33] | 2019 | 0.9839 | 0.8031 | 0.9656 | 0.7978 | 0.9818 |
| Cascade [38] | 2019 | - | - | 0.9603 | 0.7730 | 0.9792 |
| Three stage [39] | 2019 | 0.9776 | - | 0.9607 | 0.7641 | 0.9806 |
| IterNet [27] | 2020 | 0.9851 | 0.8073 | 0.9655 | 0.7970 | 0.9823 |
| NFN+ [29] | 2020 | 0.9832 | - | 0.9688 | 0.7933 | 0.9855 |
| Sine-Net [32] | 2021 | 0.9828 | - | 0.9676 | 0.7856 | 0.9845 |
| Lightweight [36] | 2021 | 0.9810 | - | 0.9635 | 0.7818 | 0.9819 |
| DEF-Net | 2022 | 0.9857 | 0.8076 | 0.9626 | 0.8053 | 0.9835 |

Table 6.
Comparison results with advanced methods on STARE dataset.
Table 6.
Comparison results with advanced methods on STARE dataset.
| Method | Year | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Joint Loss [28] | 2018 | 0.9801 | - | 0.9612 | 0.7581 | 0.9846 |
| Hierarchical [40] | 2018 | 0.8810 | - | 0.9570 | 0.7910 | 0.9700 |
| SD-UNet [30] | 2019 | 0.9850 | - | 0.9725 | 0.7548 | 0.9899 |
| DUNet [41] | 2019 | 0.9832 | 0.8143 | 0.9641 | 0.7595 | 0.9878 |
| IterNet [27] | 2020 | 0.9881 | 0.8146 | 0.9701 | 0.7715 | 0.9886 |
| AAUNet [26] | 2020 | 0.9824 | - | 0.9640 | 0.7598 | 0.9878 |
| Hybird [31] | 2021 | - | 0.8155 | 0.9626 | 0.7946 | 0.9821 |
| Sine-Net [32] | 2021 | 0.9807 | - | 0.9711 | 0.6776 | 0.9946 |
| WA-Net [42] | 2022 | 0.9665 | 0.8176 | 0.9865 | 0.7767 | 0.9877 |
| DEF-Net | 2022 | 0.9838 | 0.8186 | 0.9607 | 0.7958 | 0.9815 |
4.2.2. Qualitative Result
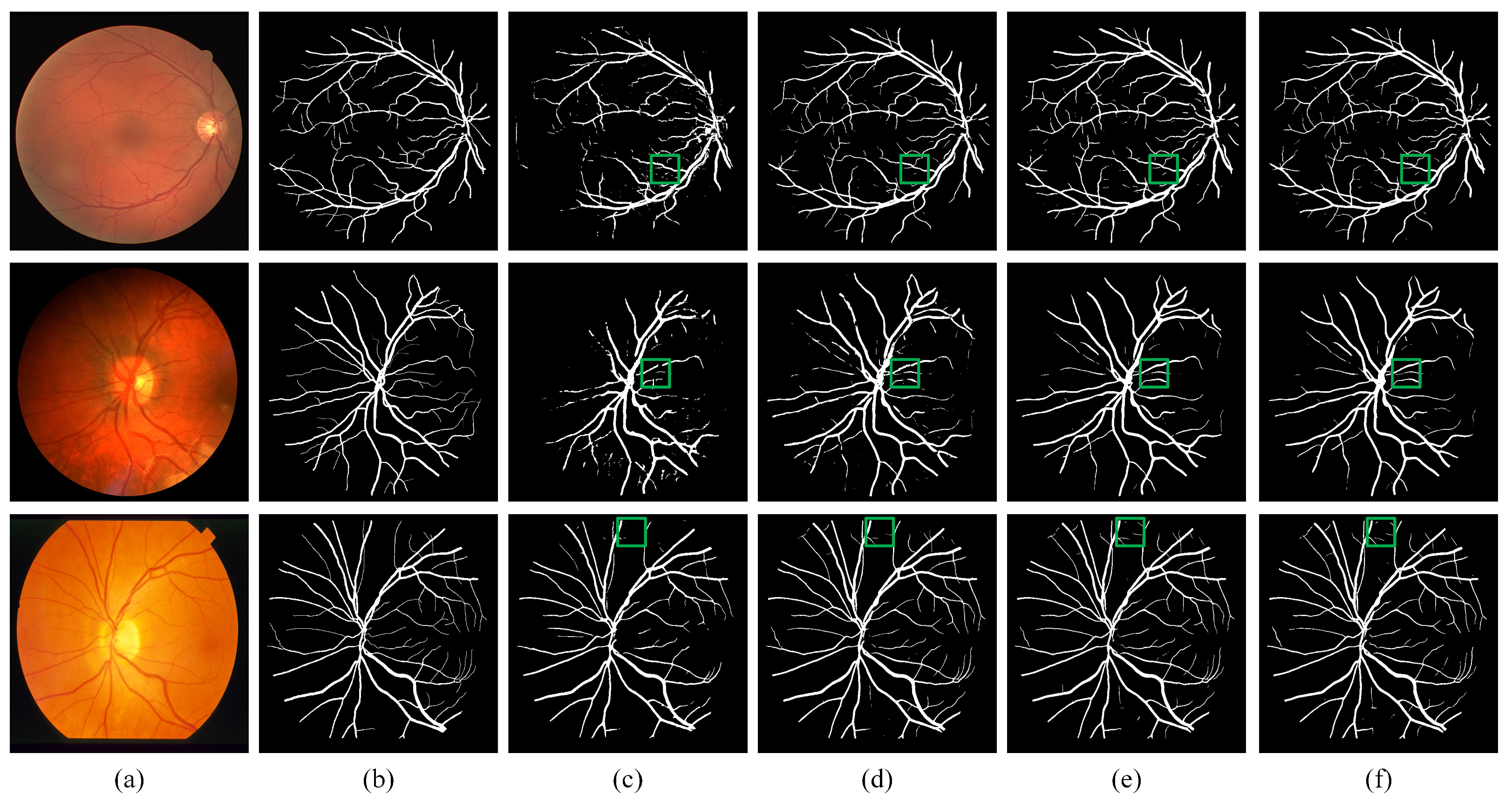
We visualize the results of DEF-Net with other approaches in Figure 6. By comparing the area of the green box in the figure, we can see that although R2UNet [19] can accumulate more contextual information through the recurrent structure, it lacks the ability to capture detailed features, while our DEF-Net not only captures contextual information but also retains more detailed features. Attention U-Net [18] obtains more accurate segmentation results than U-Net [11] due to the gated attention mechanism embedded in U-Net, but neither of them consider information at multiple scales when fusing features, the proposed DEF-Net promotes the propagation of effective information at multiple scales, so it has better continuity for segmentation of vessels and achieved the closest segmentation results to ground truth segmentation results. Overall, the structure of the dual-encoder combined with MF block achieves the best segmentation performance.

Figure 6.
Visual examples of qualitative results. (a) Fundus images; (b) Ground truth of fundus images; (c) Results of R2U-Net; (d) Results of U-Net; (e) Results of Attention-UNet; (f) Results of proposed DEF-Net.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we propose a novel retinal vessel segmentation method, called DEF-Net, which can segment the fundus vessels efficiently. First, this paper proposes a dual-encoder structure, which can simultaneously utilize convolution and recurrent convolution to extract detail features and contextual features. Second, the features at different encoder stage are fused by a multi-scale fusion block, which enhance the propagation of effective information from encoder, and promote the fusion efficiency with the decoder features, which improve the overall segmentation performance. We conduct relevant experiments on DRIVE, CHASE_DB1, and STARE, analyze the effectiveness of each component of the model by combining visualization results and evaluation metrics. The superiority of the proposed method is also demonstrated by comparison with other advanced models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L., G.G., L.Y., Y.L. and H.Y.; methodology, G.G.; software, G.G.; validation, G.G. and L.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, G.G. and L.Y.; writing—review and editing, J.L., G.G. and Y.L.; visualization, G.G. and J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Key Scientific Research Project of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province (grant number 20A120011), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 11947058, 61973103, 61473265, 61803344) and the Outstanding Foreign Scientist Support Project in Henan Province of China (grant number GZS2019008).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank Y. Liu for assistance with the experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bourne, R.R.; Stevens, G.A.; White, R.A.; Smith, J.L.; Flaxman, S.R.; Price, H.; Jonas, J.B.; Keeffe, J.; Leasher, J.; Naidoo, K.; et al. Causes of vision loss worldwide, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2013, 1, e339–e349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutam, B.; Hashmi, M.F.; Geem, Z.W.; Bokde, N.D. A Comprehensive review of deep learning strategies in retinal disease diagnosis using fundus images. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 57796–57823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Bo, W.; Hu, C.; Kang, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, K.; Fu, H. Applications of deep learning in fundus images: A review. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 69, 101971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chuah, J.H.; Ali, R.; Wang, Y. Retinal vessel segmentation using deep learning: A review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 111985–112004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, J.; Yang, L.; Bian, G.; Yu, H. ResDO-UNet: A deep residual network for accurate retinal vessel segmentation from fundus images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 79, 104087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhao, C.; Yan, Z.; Liu, P.; Duckett, T.; Stolkin, R. A novel weakly-supervised approach for RGB-D-based nuclear waste object detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 19, 3487–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Kang, H.; Li, C.; Liu, P.; Liu, Z. Lightweight and efficient neural network with SPSA attention for wheat ear detection. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2022, 8, e931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Fan, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, E.; Peng, J.; Liang, Z. Automatic detection and location of weld beads with deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Gu, Y.; Huo, B.; Liu, Y.; Bian, G. A shape-guided deep residual network for automated CT lung segmentation. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 108981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Gu, Y.; Bian, G.; Liu, Y. An attention-guided network for surgical instrument segmentation from endoscopic images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 106216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Gu, Y.; Bian, G.; Liu, Y. DRR-Net: A dense-connected residual recurrent convolutional network for surgical instrument segmentation from endoscopic images. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics 2022, 4, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Lian, S.; Luo, Z.; Li, S. Weighted Res-UNet for high-quality retina vessel segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 9th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME), Hangzhou, China, 19–21 October 2018; pp. 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Ren, Q.; Xu, Y.; Yu, Y. Dense U-net based on patch-based learning for retinal vessel segmentation. Entropy 2019, 21, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlemper, J.; Oktay, O.; Schaap, M.; Heinrich, M.; Kainz, B.; Glocker, B.; Rueckert, D. Attention gated networks: Learning to leverage salient regions in medical images. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 53, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alom, M.Z.; Hasan, M.; Yakopcic, C.; Taha, T.M.; Asari, V.K. Recurrent residual convolutional neural network based on U-Net (R2U-Net) for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.06955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, L.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, H.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, Y.; Su, P.; Yang, J.; Chen, L.; Frangi, A.F.; et al. CS2-Net: Deep learning segmentation of curvilinear structures in medical imaging. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 67, 101874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keetha, N.V.; Annavarapu, C.S.R. U-Det: A modified U-Net architecture with bidirectional feature network for lung nodule segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.09293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavani, M.; Murugan, R.; Goel, T. An efficient dehazing method of single image using multi-scale fusion technique. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staal, J.; Abramoff, M.; Niemeijer, M.; Viergever, M.A.; Ginneken, B.V. Ridge-based vessel segmentation in color images of the retina. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2004, 23, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraz, M.M.; Remagnino, P.; Hoppe, A.; Uyyanonvara, B.; Rudnicka, A.R.; Owen, C.G.; Barman, S.A. An ensemble classification-based approach applied to retinal blood vessel segmentation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 2538–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, E.; Perfetti, R. Retinal blood vessel segmentation using line operators and support vector classification. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2007, 26, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.; Holambe, R.; Waghmare, L. AAUNet: An attention augmented convolution based UNet for change detection in high resolution satellite images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision and Image Processing (ICCVIP), Bangkok, Thailand, 29–30 November 2022; pp. 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Verma, M.; Nakashima, Y.; Nagahara, H.; Kawasaki, R. IterNet: Retinal image segmentation utilizing structural redundancy in vessel networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Snowmass Village, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020; pp. 3656–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Yang, X.; Cheng, K.T. Joint segment-level and pixel-wise losses for deep learning based retinal vessel segmentation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 1912–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, W. NFN+: A novel network followed network for retinal vessel segmentation. Neural Netw. 2020, 126, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Szemenyei, M.; Pei, Y.; Yi, Y.; Zhou, W. SD-UNet: A structured dropout U-Net for retinal vessel segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 19th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE), Islamabad, Pakistan, 16–18 December 2019; pp. 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Bian, G. A hybrid deep segmentation network for fundus vessels via deep-learning framework. Neurocomputing 2021, 448, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atli, I.; Gedik, O.S. Sine-Net: A fully convolutional deep learning architecture for retinal blood vessel segmentation. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2021, 24, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J. LadderNet: Multi-path networks based on U-Net for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.07810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, F.; Iqbal, T.; Awan, S.M.; Mahmood, Z.; Khan, G.Z. A robust segmentation of blood vessels in retinal images. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology (FIT), Islamabad, Pakistan, 16–18 December 2019; pp. 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Fang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Cai, Q.; Gao, Y. SAT-Net: A side attention network for retinal image segmentation. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 5146–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, M.; Yin, S. Lightweight attention convolutional neural network for retinal vessel image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 1958–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, M.; Chen, Z.; Hu, K.; Li, X.; Gao, X. Bridge-Net: Context-involved U-net with patch-based loss weight mapping for retinal blood vessel segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 195, 116526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, X.; Ren, J. Blood vessel segmentation from fundus image by a cascade classification framework. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 88, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Yang, X.; Cheng, K.T. A three-stage deep learning model for accurate retinal vessel segmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 23, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Lu, J.; Wei, C.; Huang, H.; Cai, X.; Chen, X. A hierarchical image matting model for blood vessel segmentation in fundus images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 2367–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Q.; Meng, Z.; Pham, T.D.; Chen, Q.; Wei, L.; Su, R. DUNet: A deformable network for retinal vessel segmentation. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2019, 178, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Carrillo, D.E.; Dalmau-Cedeño, O.S. Width attention based convolutional neural network for retinal vessel segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 209, 118313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).