Memristive Circuit Design of Nonassociative Learning under Different Emotional Stimuli
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Memristor Model with Threshold
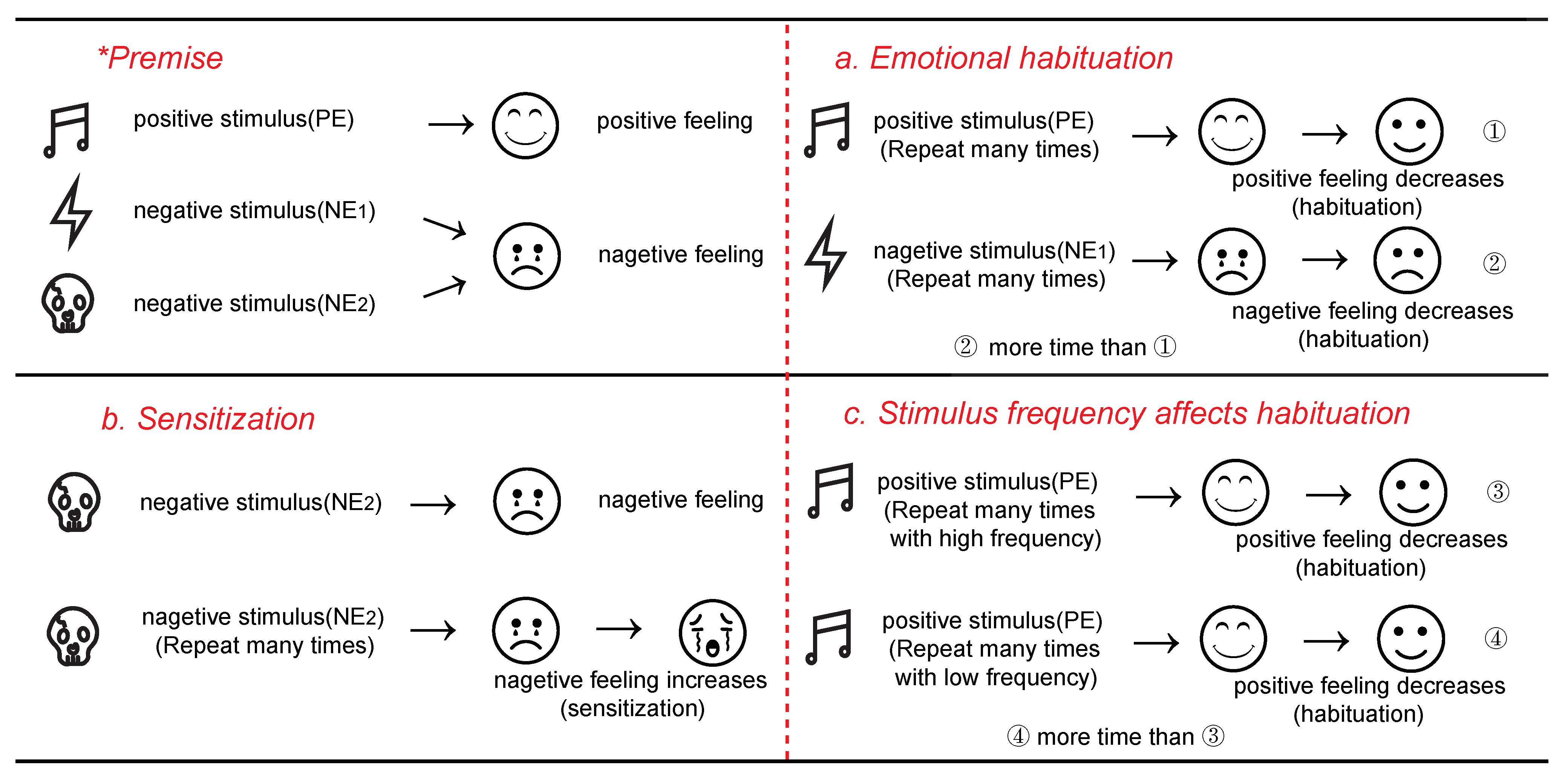
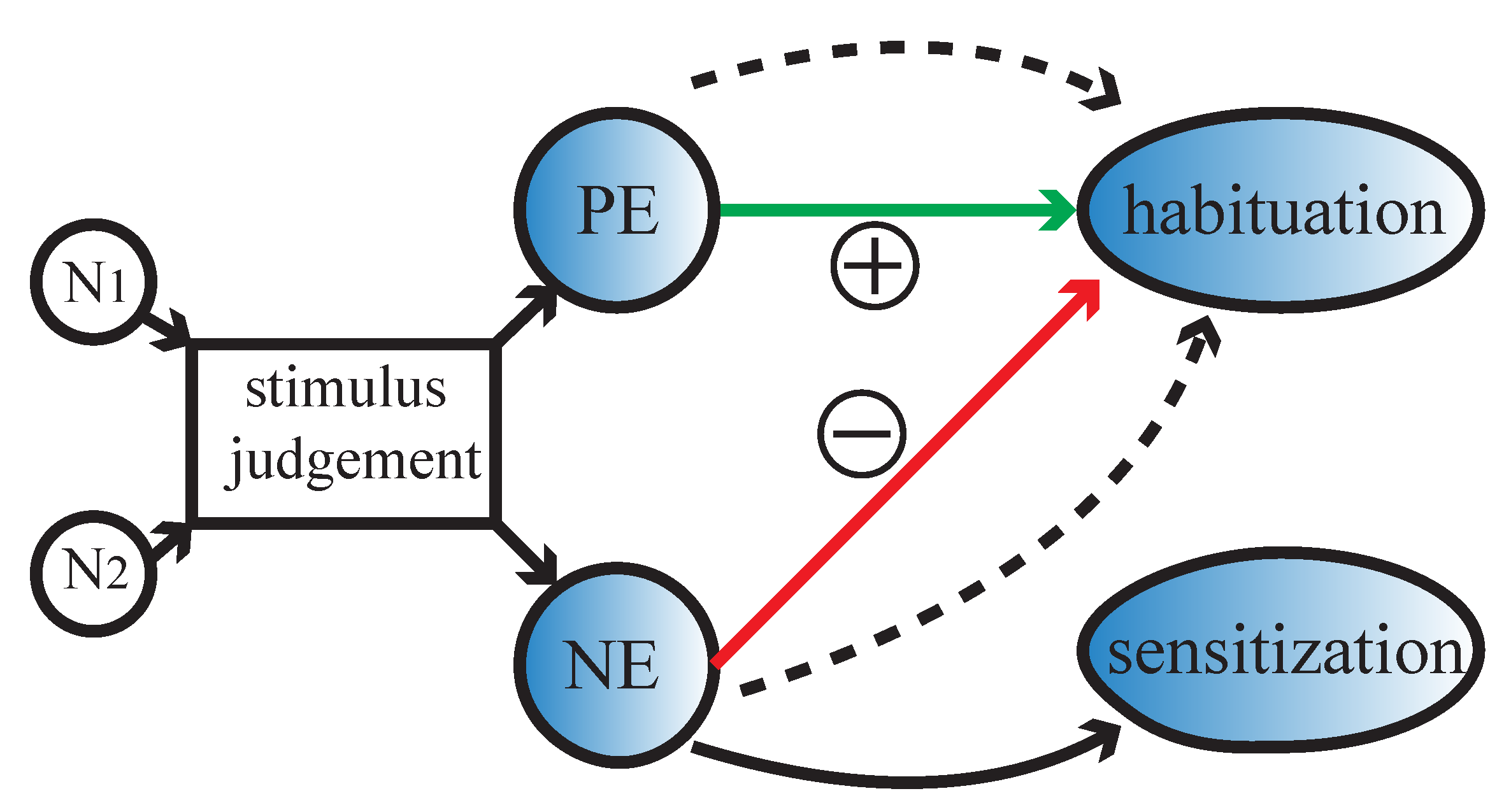
3. Nonassociative Learning under Different Emotional Stimuli
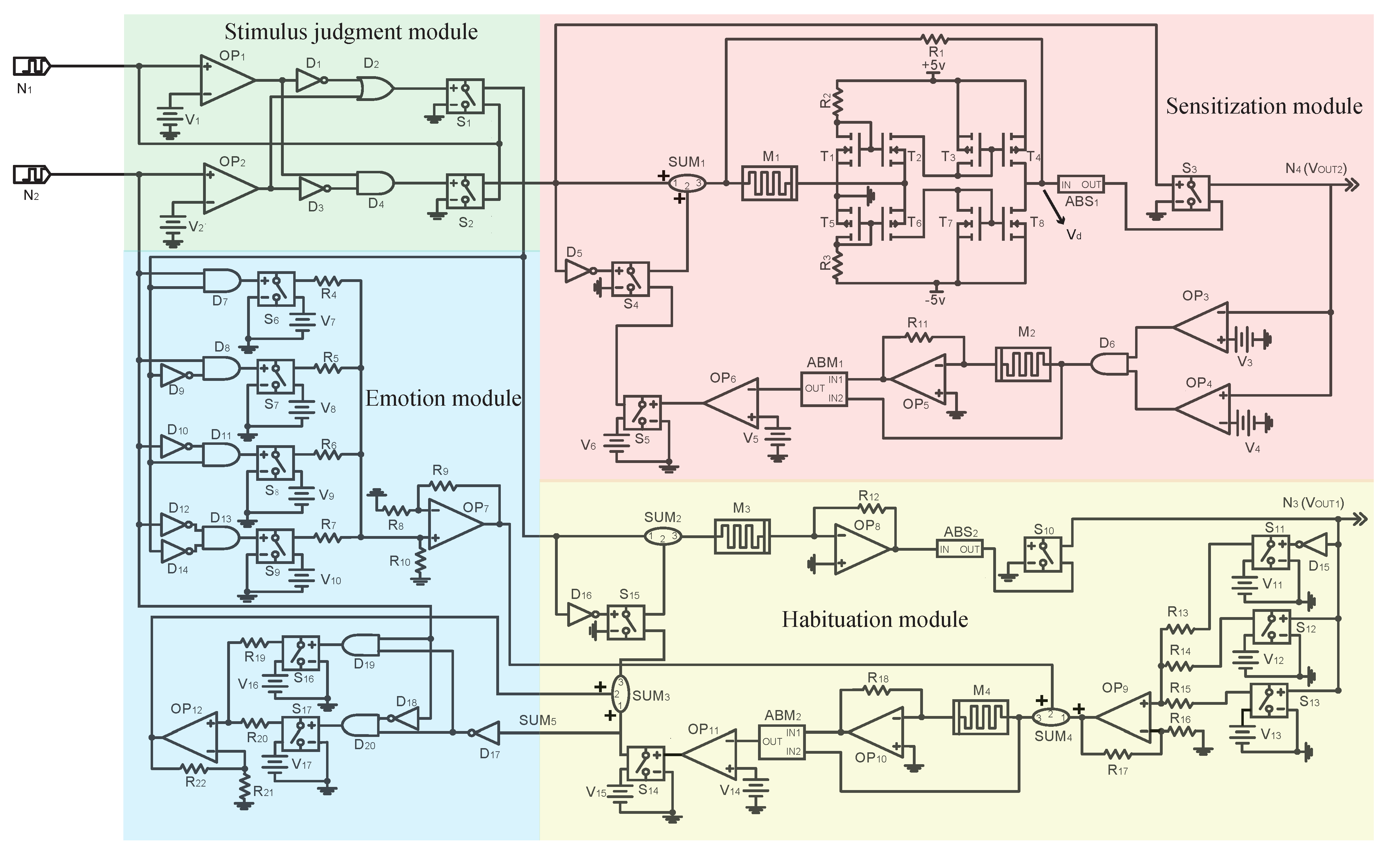
4. Circuit Structure and Module Design
4.1. Stimulus Judgment Module
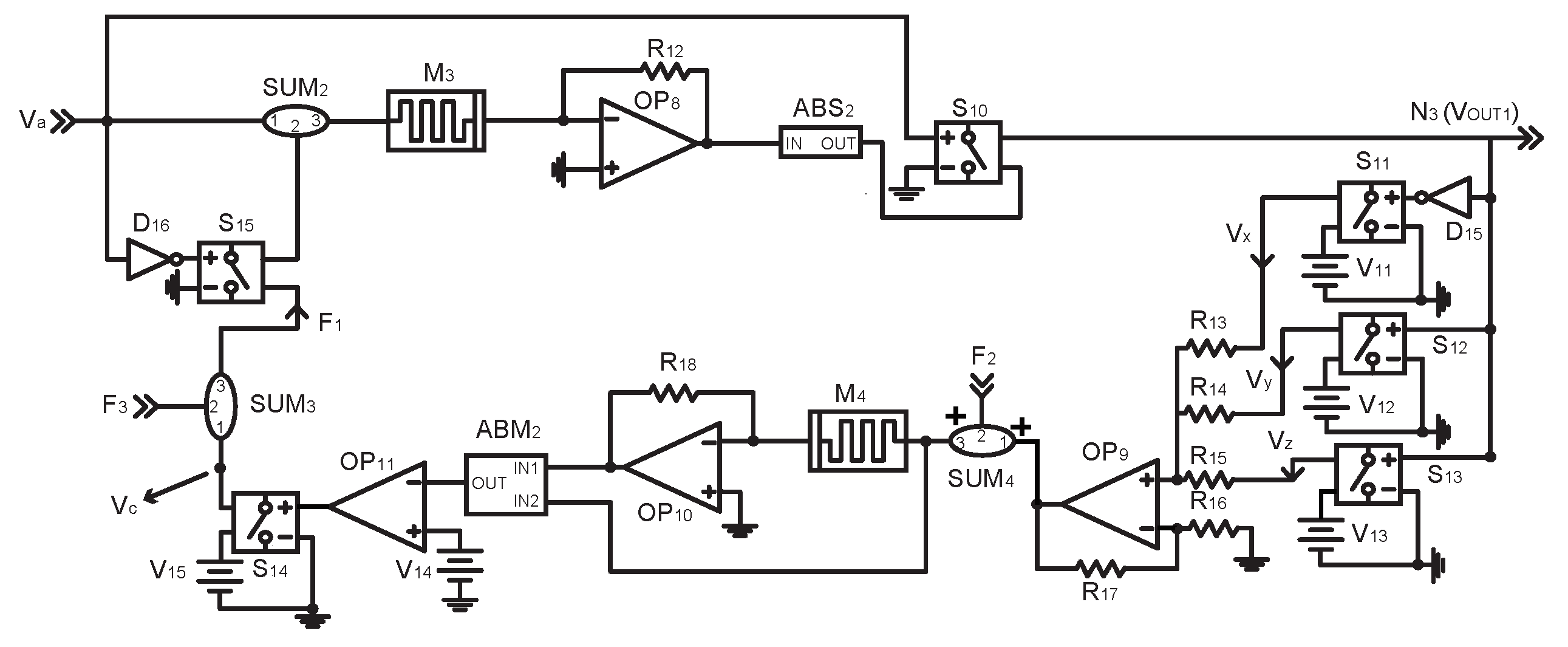
4.2. Habituation Module
4.3. Emotion Module
4.4. Sensitization Module
4.5. Complete Circuit
5. Implementation and Simulation of Circuit
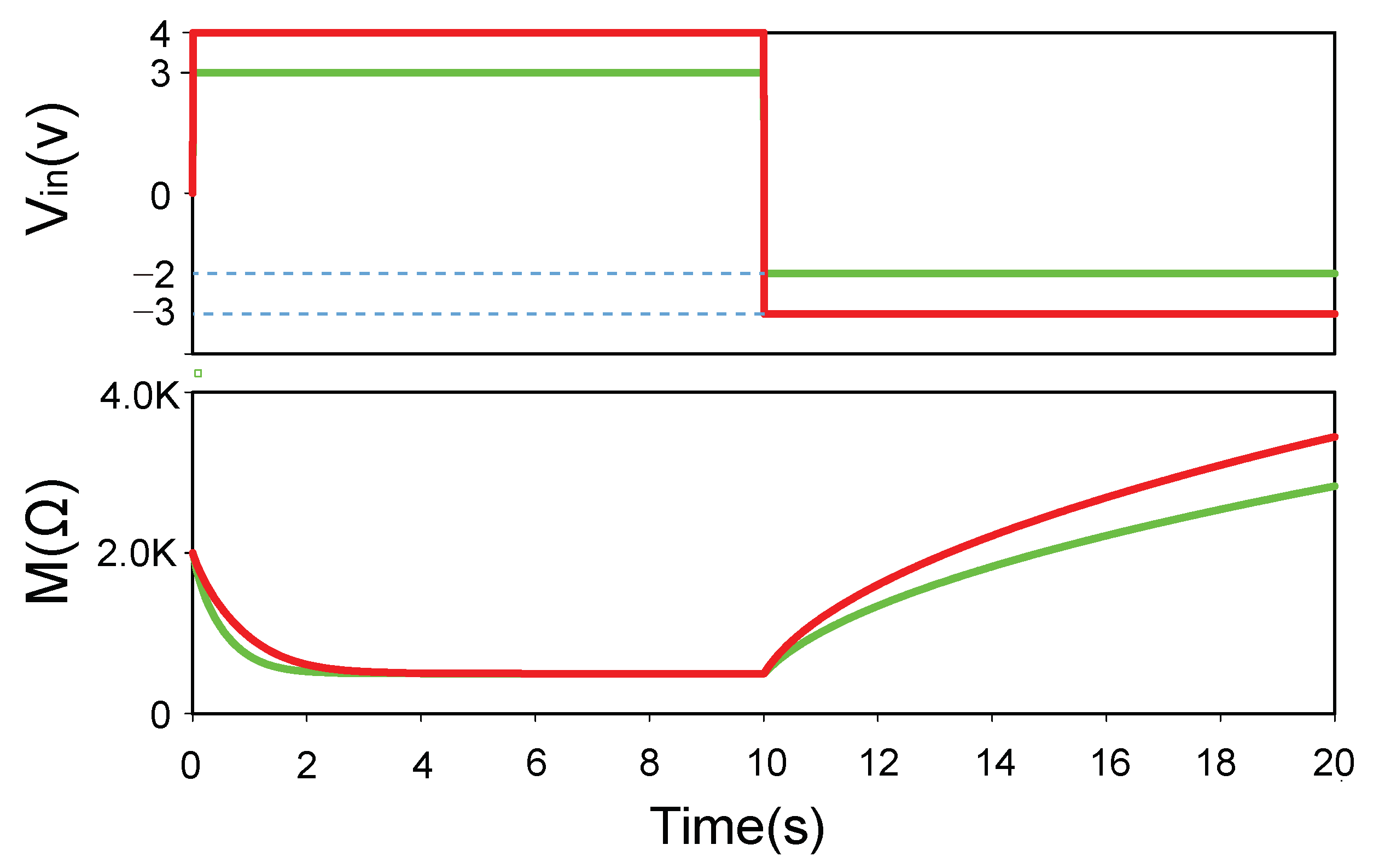
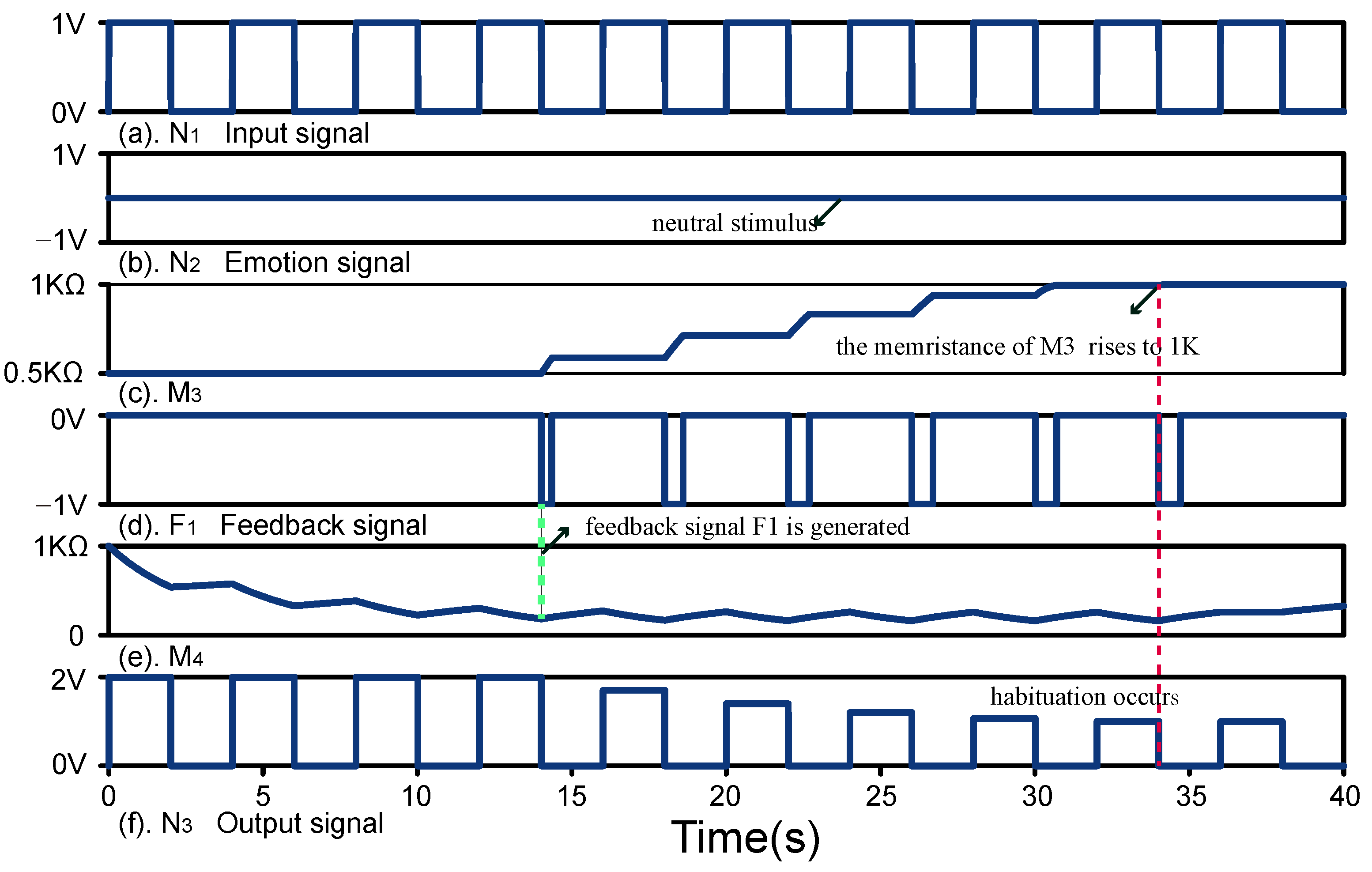
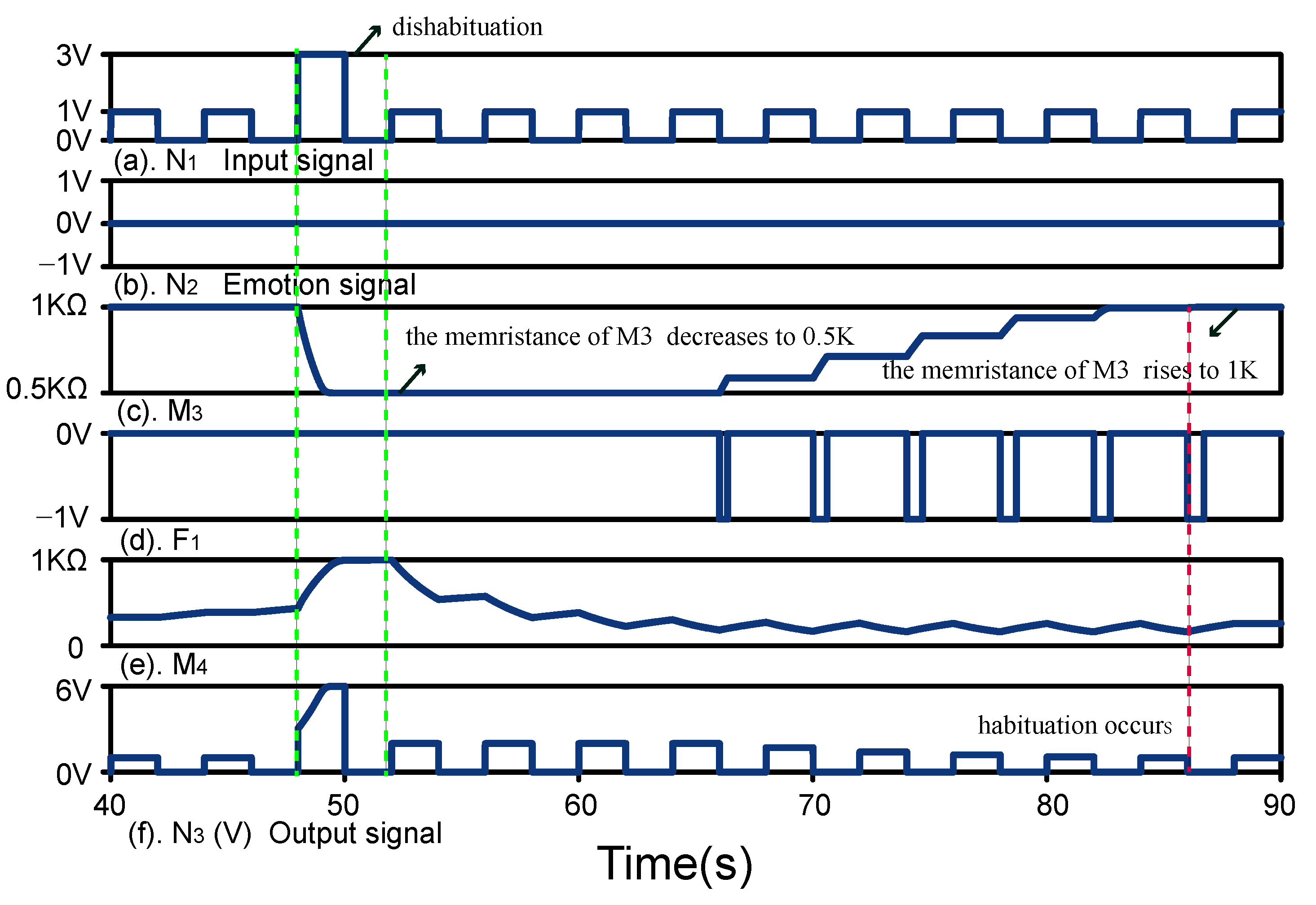
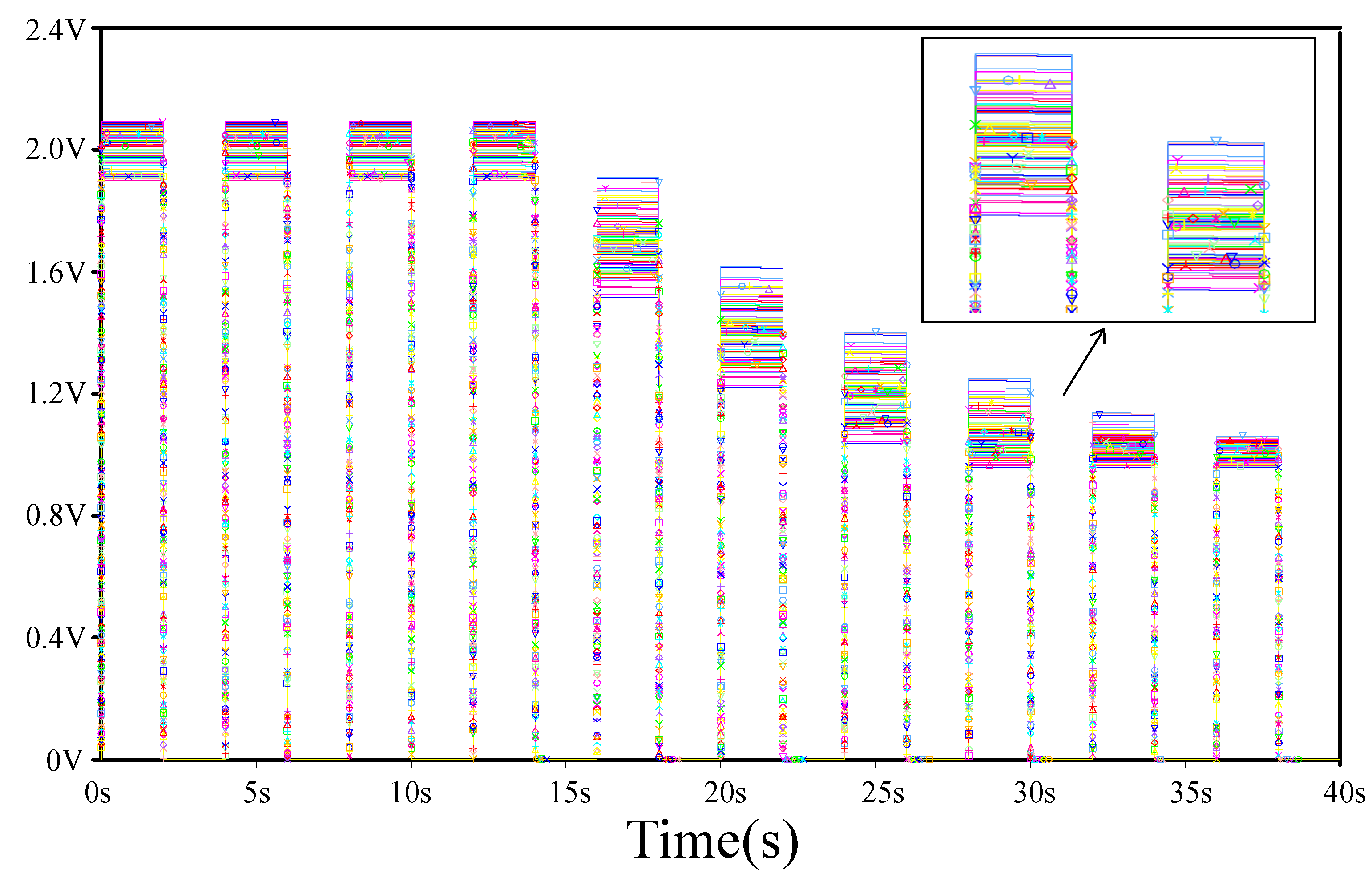
5.1. Habituation and Dishabituation
5.1.1. Habituation
5.1.2. Dishabituation
5.2. Emotional Habituation
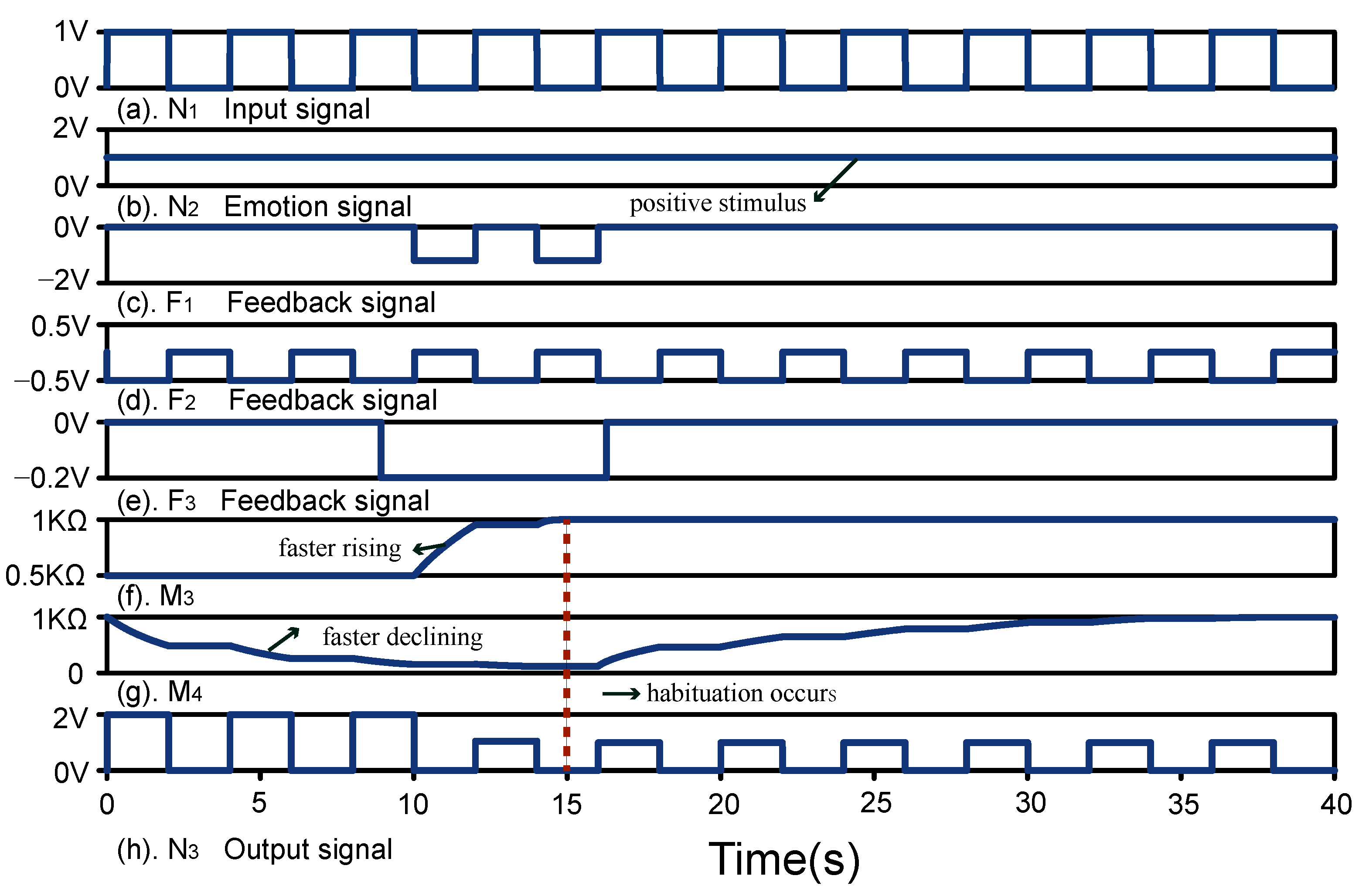
5.2.1. Habituation under Positive Stimulus
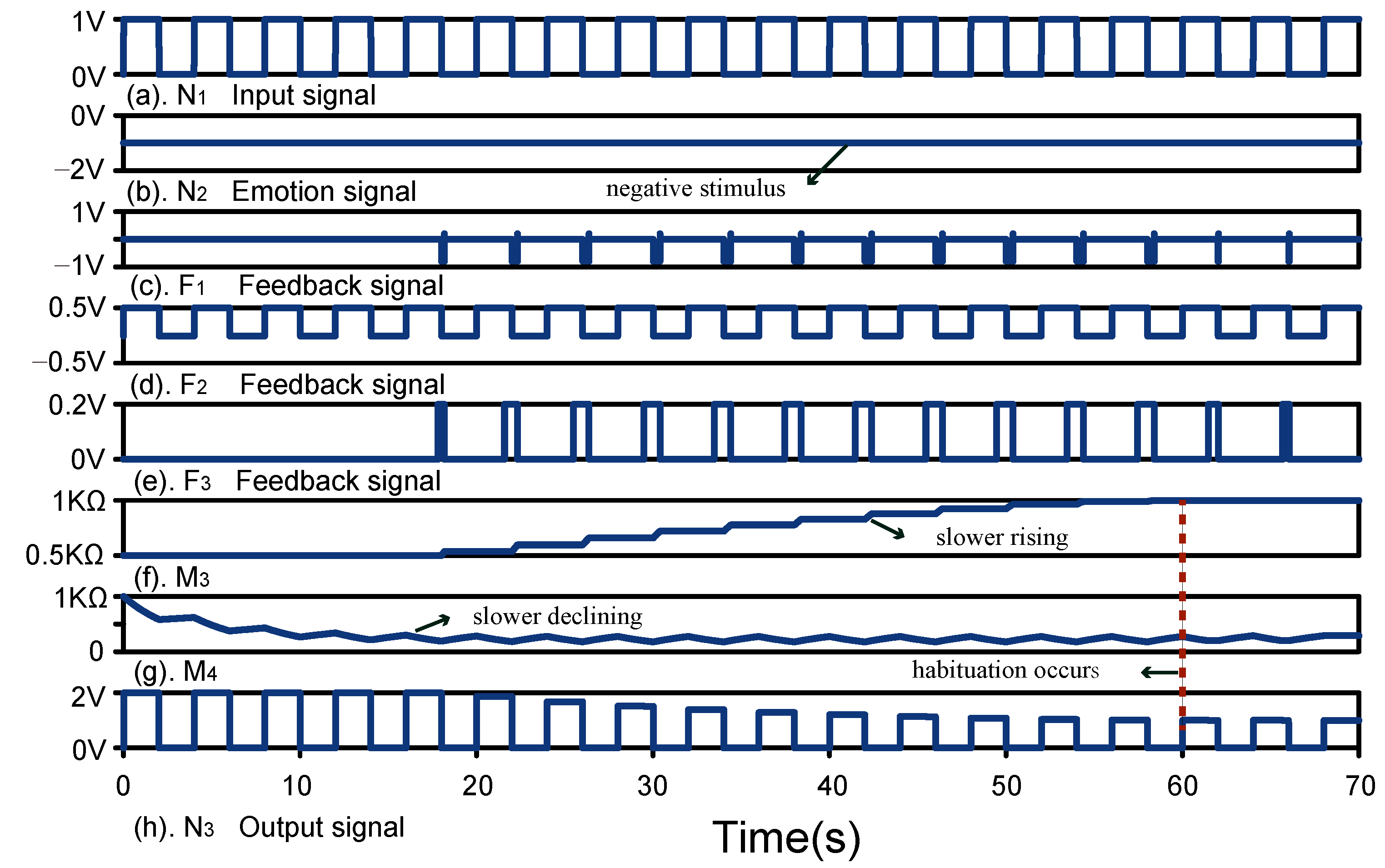
5.2.2. Habituation under Negative Stimulus
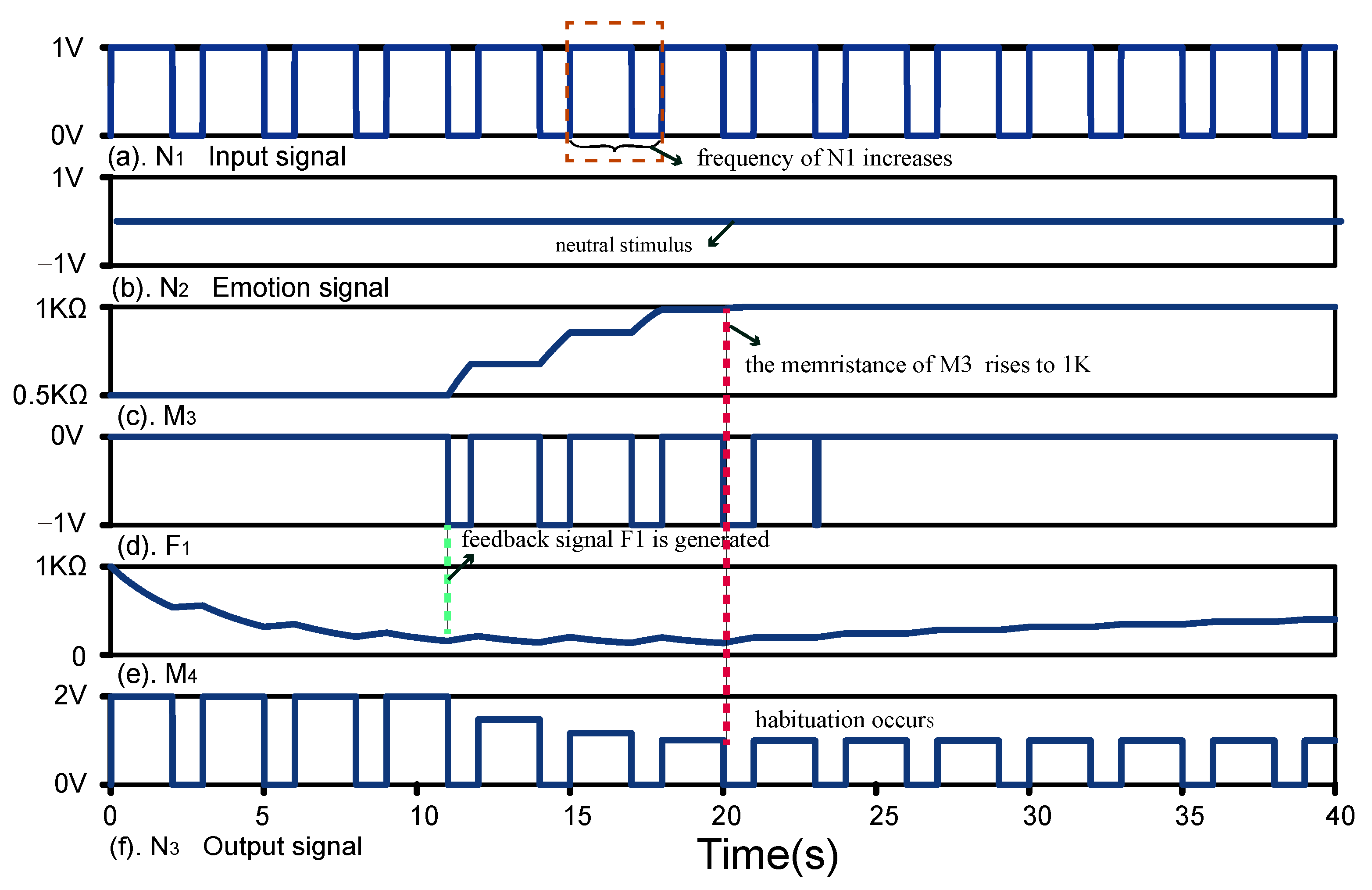
5.3. Frequency-Dependent Habituation
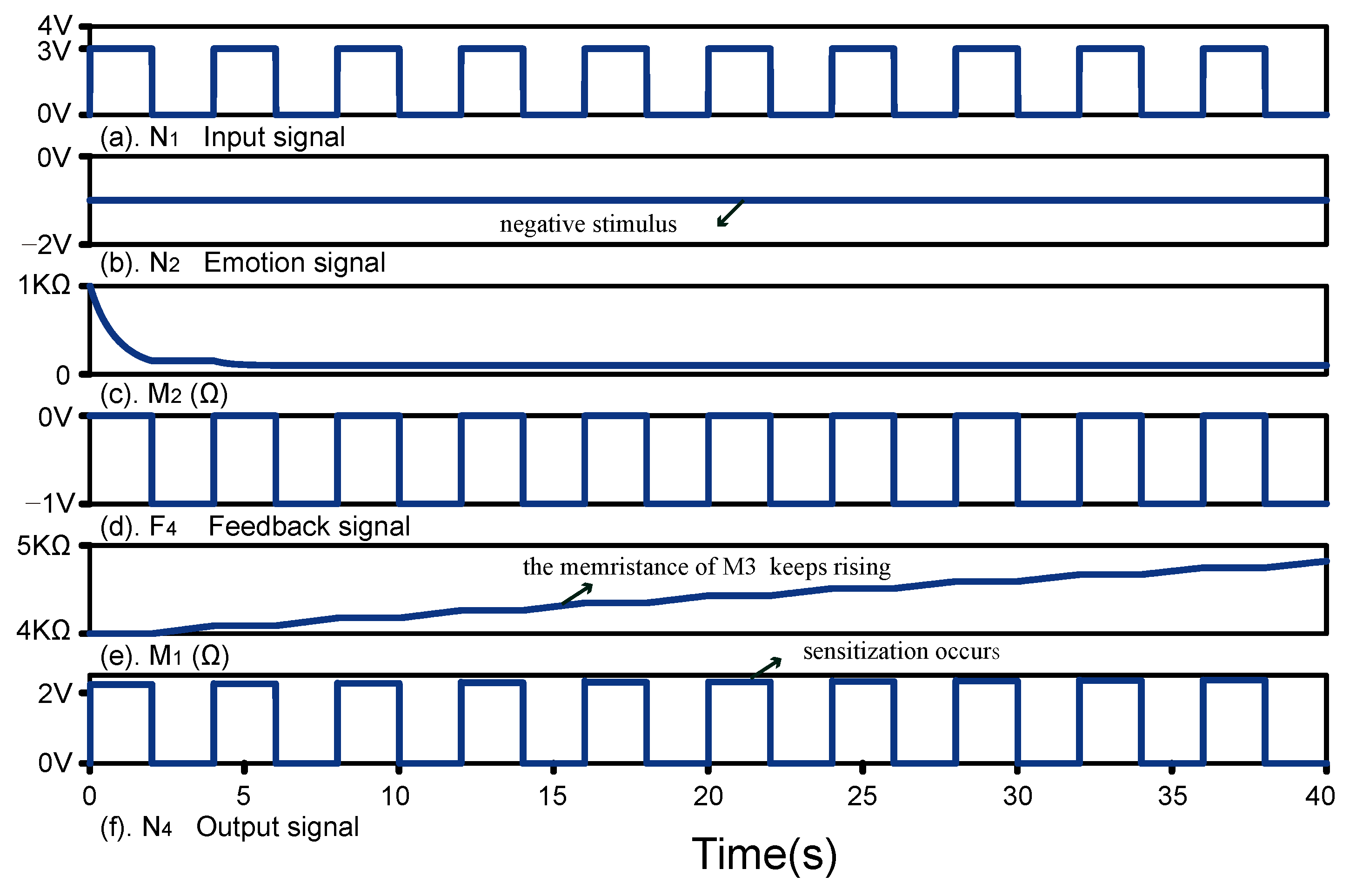
5.4. Sensitisation
5.5. Result Analysis and Comparison Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valencia, D.; Thies, J.; Alimohammad, A. Frameworks for efficient brain–computer interfacing. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2019, 6, 1714–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Huang, Z.; Wunsch, C. Memristor-based HTM spatial pooler with on-device learning for pattern recognition. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2022, 3, 1901–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Wu, W.; Zeng, Z. The design of memristive circuit for affective multi-associative learning. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2020, 14, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, S.; Liu, W.; Guo, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, T. Multi-label image classification via feature/label co-projection. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2021, 51, 7250–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Dong, M.; Yan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Chen, Y.; Huang, T. End-to-end detection-segmentation network for face labeling. IEEE Trans. Emerging Top. Comput. Intell. 2021, 5, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Xiao, S.; Zeng, Z.; Yan, Y.; Huang, T. Adjusting learning rate of memristor-based multilayer neural networks via fuzzy method. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2019, 38, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Wang, Z.; Rong, Z. Intermittent control for quasisyn chronization of delayed discrete-time neural networks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 51, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Kwon, D.; Woo, S.Y.; Lee, S.; Yoo, H.; Kim, J.; Park, B.; Lee, J. Hardware-based spiking neural network using a TFT-Type AND Flash memory array architecturenased on direct feedback alignment. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 73121–73132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Liu, M.; Ning, X.; Chakrabarty, K.; Wang, Y. Fault-tolerant training enabled by on-line fault detection for RRAM-based neural computing systems. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2018, 38, 1611–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L. Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 1971, 18, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strukov, D.B.; Snider, G.S.; Stewart, D.R.; Williams, R.S. The missing memristor found. Nature 2008, 453, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theis, T.N.; Wong, H.S.P. The end of moore’s law: A new beginning for information technology. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2017, 19, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Wu, H.; Gao, B.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J.J.; Qian, H. Fully hardware-implemented memristor convolutional neural network. Nature 2020, 577, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Han, G.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Y. Memristor-based neural network circuit of full-function Pavlov associative memory with time delay and variable learning rate. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 50, 2935–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Han, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P. Memristor-based neural network circuit of operant conditioning accorded with biological feature. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2022, 69, 4475–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Wen, S.; Wang, Y. Memristor-based neural network circuit with multimode generalization and differentiation on pavlov associative memory. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, C. Emotion model of associative memory possessing variable learning rates with time delay. Neurocomputing 2021, 460, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Han, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P. Memristor-based neural network circuit of emotion congruent memory with mental fatigue and emotion inhibition. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2021, 15, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, S.; Han, J.; Wei, H.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, T.; Chen, Y. Memristive LSTM networks for sentiment analysis. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2021, 51, 1794–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Shen, S.; Jin, P.; Wang, G.; Liang, Y. Design of memristor-based combinational logic circuits. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 40, 5825–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Wei, H.; Yan, Z.; Guo, Z.; Yang, Y.; Huang, T.; Chen, Y. Memristor-based design of sparse compact convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2020, 7, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, R.; Yang, L.; Huang, X.D.; Ren, S.G.; Wan, T.Q.; Li, Y.; Miao, X.S. Controlled majority-inverter graph logic with highly nonlinear, self-rectifying memristor. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2021, 68, 4897–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xiao, X.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y. Multiple target recognition and position identification circuit based on memristor. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2022, 151, 154223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, X.; Fang, J.; Wang, Y. Autonomous memristor chaotic systems of infifinite chaotic attractors and circuitry realization. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 94, 2879–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokyildirim, A.; Yesil, A.; Babacan, Y. Implementation of a memristor-based 4D chaotic oscillator and its nonlinear control. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2022, 110, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zeng, Z. Memristor crossbar architectures for implementing deep neural networks. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 110, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.S.; Young, D.L. Nonassociative learning as gated neural integrator and differentiator in stimulus-response pathways. Behav. Brain Funct. 2006, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.I.; Fischer, H.; Whalen, P.J.; McInerney, S.C.; Shin, L.M.; Rauch, S.L. Differential prefrontal cortex and amygdala habituation to repeatedly presented emotional stimuli. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretie, L.; Hinojosa, J.A.; Mercado, F. Cerebral patterns of attentional habituation to emotional visual stimuli. Psychophysiology 2003, 40, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, L.; Duan, S. Habituation characteristic implementation by synapse-like device based on memristor. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 3rd Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (ITNEC), Chengdu, China, 15–17 March 2019; pp. 1465–1469. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Xiao, M.; Shen, D.; Zhou, Y.N. Heterogeneous stimuli induced nonassociative learning behavior in ZnO nanowire memristor. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 125201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Yan, R.; Wang, C.; Sun, J. Memristive circuit implementation of biological nonassociative learning mechanism and its applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2020, 14, 1036–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z. Memristive Circuit Design of Brain-Like Emotional Learning and Generation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Han, J.; Wang, Y. Memristor-Based Neural Network Circuit of Memory With Emotional Homeostasis. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2022, 21, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.; Yang, J.; Lou, Y.; Cai, A.; Yuan, J. Humans’ emotional habituation to pleasant stimuli: Behavioral and electrophysiological evidence. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2015, 36, 3594–3605. [Google Scholar]
- Kvatinsky, S.; Ramadan, M.; Friedman, E.G.; Kolodny, A. VTEAM: A general model for voltage-controlled memristors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2015, 62, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Zhang, K.; Qin, X.; Yang, F.; Sun, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. VETAM-M: A General Model for Voltage-Controlled Memcapacitive-Coupled Memristors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2015, 69, 1717–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Friedman, E.G. Memristive model for synaptic circuits. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2016, 64, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
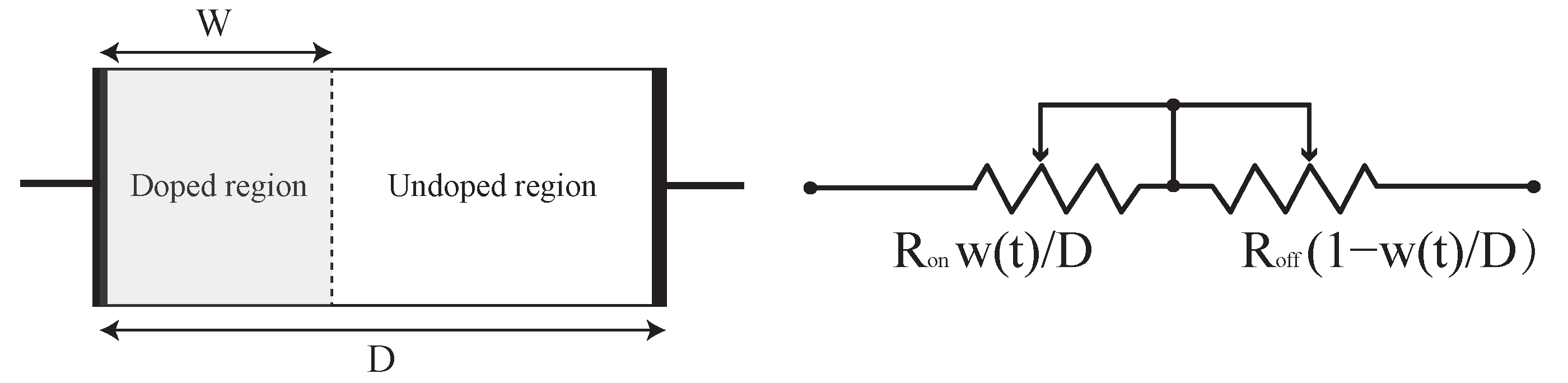



| Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D (nm) | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 500 | 100 | 500 | 100 | |
| 500 | ||||
| 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 3 | 5 | 1 | |
| (A) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| (A) | 1 | 1 | ||
| (A) | ||||
| p | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| low level | low level | 0 | |
| low level | high level | 0 | |
| high level | low level | 0 | |
| high level | high level | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Zhao, L.; Wen, S.; Wang, Y. Memristive Circuit Design of Nonassociative Learning under Different Emotional Stimuli. Electronics 2022, 11, 3851. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11233851
Sun J, Zhao L, Wen S, Wang Y. Memristive Circuit Design of Nonassociative Learning under Different Emotional Stimuli. Electronics. 2022; 11(23):3851. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11233851
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Junwei, Linhao Zhao, Shiping Wen, and Yanfeng Wang. 2022. "Memristive Circuit Design of Nonassociative Learning under Different Emotional Stimuli" Electronics 11, no. 23: 3851. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11233851
APA StyleSun, J., Zhao, L., Wen, S., & Wang, Y. (2022). Memristive Circuit Design of Nonassociative Learning under Different Emotional Stimuli. Electronics, 11(23), 3851. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11233851









