E-Ensemble: A Novel Ensemble Classifier for Encrypted Video Identification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A novel E-Ensemble classifier for video identification in network traffic that can detect videos with 82% accuracy in auto-quality mode.
- Evidence that the soft-level classifier combination technique is more stable for video identification in comparison with the hard-level classifier combination technique.
2. Related Work
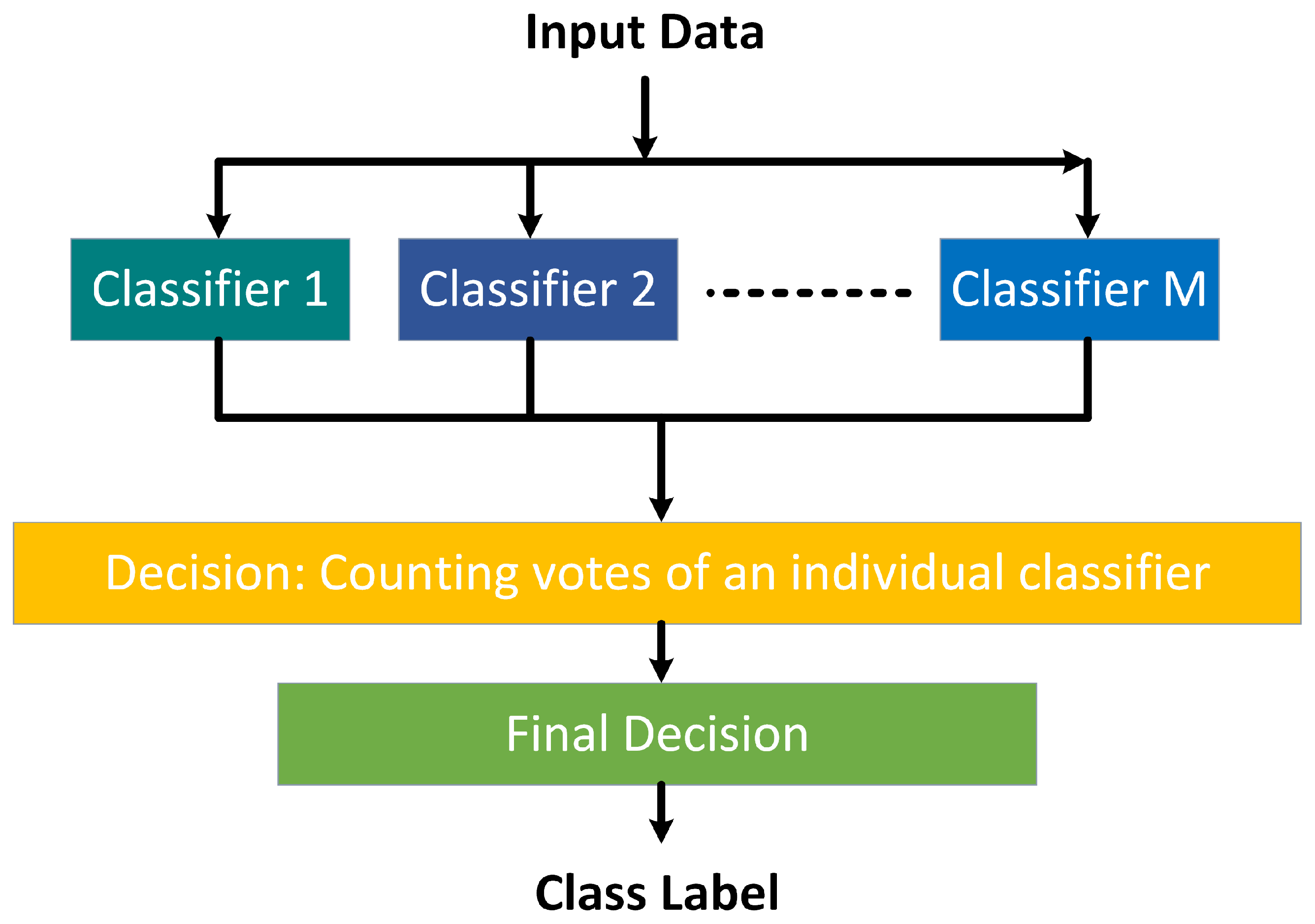
3. Ensemble Classifier
3.1. Hard-Level Combination
Example of Majority Voting
3.2. Soft-Level Combination
Example of the Average Rule
4. Experimental Setup
4.1. Traffic Capture Details
4.2. Dataset Details
5. E-Ensemble for Video Identification
5.1. Bytes per Second (BPS)
5.2. Fingerprint of the Packet Size per Arrival Time (F-PAT)
5.3. Fingerprint of the BPS (F-BPS)
6. Results and Discussion
6.1. Accuracy of Individual Classifiers on the 20-Day Dataset
6.2. Comparison of Different Classifier Combination Techniques
6.3. Comparison of the Individual Classifiers with the Average Voting Technique
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ledwich, M.; Zaitsev, A. Algorithmic extremism: Examining YouTube’s rabbit hole of radicalization. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.11211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buntain, C.; Bonneau, R.; Nagler, J.; Tucker, J.A. YouTube recommendations and effects on sharing across online social platforms. Proc. Acm-Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2021, 5, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuer, H.; Hoch, H.; Breiter, A.; Theocharis, Y. Auditing the biases enacted by YouTube for political topics in Germany. In Proceedings of the Mensch und Computer 2021, Ingolstadt, Germany, 5–8 September 2021; pp. 456–468. [Google Scholar]
- Bromell, D. After Christchurch: Hate, Harm and the Limits of Censorship; Victoria University of Wellington: Wellington, New Zealand, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Solsman, J.E. YouTube’s AI Is the Puppet Master over Most of What You Watch. 2018. Available online: https://www.cnet.com/news/youtube-ces-2018-neal-mohan (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Creators, Y. How YouTube’s Home Screen Works. 2017. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=69tpVNunQEU (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Bremler-Barr, A.; Harchol, Y.; Hay, D.; Koral, Y. Deep packet inspection as a service. In Proceedings of the 10th ACM International on Conference on Emerging Networking Experiments and Technologies, Sydney, Australia, 2–5 December 2014; pp. 271–282. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.U.S.; Abbas, A.; Ali, M.; Jawad, M.; Khan, S.U. Convolutional Neural Networks as Means to Identify Apposite Sensor Combination for Human Activity Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Connected Health: Applications, Systems and Engineering Technologies (CHASE), Washington, DC, USA, 26–28 September 2018; pp. 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, S.U.; Saleem, A.; Soroya, S.H.; Safder, I.; Iqbal, S.; Jamil, S.; Bukhari, F.; Aljohani, N.R.; Nawaz, R. Sentiment analysis of tweets through Altmetrics: A machine learning approach. J. Inf. Sci. 2021, 47, 712–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.U.; Shabbir, M.; Iqbal, S.; Said, A.; Kamiran, F.; Nawaz, R.; Saif, U. Leveraging deep learning and SNA approaches for smart city policing in the developing world. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 56, 102045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, A.; Hassan, S.U.; Tuarob, S.; Nawaz, R.; Shabbir, M. DGSD: Distributed graph representation via graph statistical properties. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 119, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, H.; Anas, M.; Hassan, S.U.; Aljohani, N.R.; Alelyani, S.; Edifor, E.E.; Nawaz, R. Balancing sequential data to predict students at-risk using adversarial networks. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 93, 107274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, H.; Hassan, S.U.; Aljohani, N.R.; Hardman, J.; Alelyani, S.; Nawaz, R. Predicting academic performance of students from VLE big data using deep learning models. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2020, 104, 106189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Rak, R.; Restificar, A.; Nobata, C.; Rupp, C.; Batista-Navarro, R.T.B.; Nawaz, R.; Ananiadou, S. Detecting experimental techniques and selecting relevant documents for protein-protein interactions from biomedical literature. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nawaz, R.; Thompson, P.; Ananiadou, S. Negated bio-events: Analysis and identification. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.U.S.; Abbas, A.; Rehman, A.; Nawaz, R. HateClassify: A Service Framework for Hate Speech Identification on Social Media. IEEE Internet Comput. 2021, 25, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, R.; Sun, Q.; Shardlow, M.; Kontonatsios, G.; Aljohani, N.R.; Visvizi, A.; Hassan, S.U. Leveraging AI and Machine Learning for National Student Survey: Actionable Insights from Textual Feedback to Enhance Quality of Teaching and Learning in UK’s Higher Education. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.; Nawaz, R.; Korkontzelos, I.; Black, W.; McNaught, J.; Ananiadou, S. News search using discourse analytics. In Proceedings of the 2013 Digital Heritage International Congress (Digital Heritage), Marseille, France, 28 October–1 November 2013; Volume 1, pp. 597–604. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, R.; Thompson, P.; McNaught, J.; Ananiadou, S. Meta-knowledge annotation of bio-events. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’10), Valletta, Malta, 17–23 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.U.; Bukhari, S.M.; Maqsood, T.; Fayyaz, M.A.; Dancey, D.; Nawaz, R. SCNN-Attack: A Side-Channel Attack to Identify YouTube Videos in a VPN and Non-VPN Network Traffic. Electronics 2022, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.U.; Bukhari, S.M.; Khan, S.A.; Maqsood, T. ISP can identify YouTube videos that you just watched. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology (FIT), Islamabad, Pakistan, 13–14 December 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, R.; Shmatikov, V.; Tromer, E. Beauty and the burst: Remote identification of encrypted video streams. In Proceedings of the 26th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 17), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 16–18 August 2017; pp. 1357–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Dietterich, T.G. Ensemble methods in machine learning. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Multiple Classifier Systems, Cagliari, Italy, 21–23 June 2000; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, A.; Kolhe, S.; Kamal, R. A hybrid ensemble for classification in multiclass datasets: An application to oilseed disease dataset. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 124, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Z. Hierarchical ensemble of extreme learning machine. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2018, 116, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drotár, P.; Gazda, M.; Vokorokos, L. Ensemble feature selection using election methods and ranker clustering. Inf. Sci. 2019, 480, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Geng, N.; Wang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Jin, Y. Stacking-based ensemble learning of decision trees for interpretable prostate cancer detection. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 77, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuassba, A.O.; Zhang, D.; Luo, X.; Shaheryar, A.; Ali, H. Improving classification performance through an advanced ensemble based heterogeneous extreme learning machines. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moustafa, S.; ElNainay, M.Y.; El Makky, N.; Abougabal, M.S. Software bug prediction using weighted majority voting techniques. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 2763–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valstar, M.F.; Jiang, B.; Mehu, M.; Pantic, M.; Scherer, K. The first facial expression recognition and analysis challenge. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG), Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 21–25 March 2011; pp. 921–926. [Google Scholar]
- Duro, D.C.; Franklin, S.E.; Dubé, M.G. A comparison of pixel-based and object-based image analysis with selected machine learning algorithms for the classification of agricultural landscapes using SPOT-5 HRG imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.; Prasad, P.; Sagar, Y. A comparative study of machine learning algorithms as expert systems in medical diagnosis (Asthma). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology, Chengdu, China, 10–12 June 2011; pp. 570–576. [Google Scholar]
- Zhenxiang, L.; Mingbo, H.; Song, L.; Xin, W. Research of P2P traffic comprehensive identification method. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Network Computing and Information Security, Guilin, China, 14–15 May 2011; Volume 1, pp. 307–310. [Google Scholar]
- Afandi, W.; Bukhari, S.M.; Khan, M.U.; Maqsood, T.; Khan, S.U. A Bucket-Based Data Pre-Processing Method for Encrypted Video Detection. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Computer Applications in Industry and Engineering (CAINE), Online, 17–19 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Akdemir, B.; Kara, S.; Polat, K.; Güven, A.; Güneş, S. Ensemble adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system with weighted arithmetical mean and application to diagnosis of optic nerve disease from visual-evoked potential signals. Artif. Intell. Med. 2008, 43, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Jiao, L.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Shang, F. Sparse coding and classifier ensemble based multi-instance learning for image categorization. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glodek, M.; Reuter, S.; Schels, M.; Dietmayer, K.; Schwenker, F. Kalman filter based classifier fusion for affective state recognition. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Multiple Classifier Systems, Nanjing, China, 15–17 May 2013; pp. 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Klement, W.; Wilk, S.; Michalowski, W.; Farion, K.J.; Osmond, M.H.; Verter, V. Predicting the need for CT imaging in children with minor head injury using an ensemble of Naive Bayes classifiers. Artif. Intell. Med. 2012, 54, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, S.E.; Martínez, B.C.; Sánchez-Esguevillas, A.J.; Callejo, L.H. Ensemble network traffic classification: Algorithm comparison and novel ensemble scheme proposal. Comput. Netw. 2017, 127, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Luo, X.; Ma, F.; Che, C.; Wang, J. Network traffic classification based on ensemble learning and co-training. Sci. China Ser. F Inf. Sci. 2009, 52, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Guan, X.; Qin, T. A traffic classification approach based on characteristics of subflows and ensemble learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IFIP/IEEE Symposium on Integrated Network and Service Management (IM), Lisbon, Portugal, 8–12 May 2017; pp. 588–591. [Google Scholar]
- Dvir, A.; Marnerides, A.K.; Dubin, R.; Golan, N. Clustering the unknown-the youtube case. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 February 2019; pp. 402–407. [Google Scholar]
- Fayyaz, M.A.B.; Johnson, C. Object detection at level crossing using deep learning. Micromachines 2020, 11, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, A.S.; Bukhari, S.M.A.H.; Khan, M.U.S.; Maqsood, T.; Fayyaz, M. Traffic Pattern Plot: Video Identification in Encrypted Network Traffic. 2022. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/362761222_Traffic_Pattern_Plot_Video_Identification_in_Encrypted_Network_Traffic (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Mohandes, M.; Deriche, M.; Aliyu, S.O. Classifiers combination techniques: A comprehensive review. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 19626–19639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuncheva, L.I. Combining Pattern Classifiers: Methods and Algorithms; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kittler, J.; Hatef, M.; Duin, R.P.; Matas, J. On combining classifiers. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1998, 20, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delgado, R. A semi-hard voting combiner scheme to ensemble multi-class probabilistic classifiers. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 3653–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z.; Shen, K. Walls have ears: Traffic-based side-channel attack in video streaming. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2018-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Honolulu, HI, USA, 16–19 April 2018; pp. 1538–1546. [Google Scholar]









| Layer ID | Layer (Type) | Output Shape | Param # |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Conv1D | (None, 120, 1024) | 7168 |
| 2 | MaxPooling1D | (None, 60, 1024) | 0 |
| 3 | Conv1D | (None, 60, 512) | 2097664 |
| 4 | MaxPooling1D | (None, 30, 512) | 0 |
| 5 | Conv1D | (None, 30, 512) | 1311232 |
| 6 | MaxPooling1D | (None, 15, 512) | 0 |
| 7 | Dropout | (None, 15, 512) | 0 |
| 8 | Flatten | (None, 7680) | 0 |
| 9 | Dense | (None, Number of videos) | 337964 |
| Layer ID | Layer (Type) | Output Shape | Param # |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Conv1D | (None, 21, 300) | 1800 |
| 2 | MaxPooling1D | (None, 21, 300) | 0 |
| 3 | Conv1D | (None, 21, 512) | 461312 |
| 4 | MaxPooling1D | (None, 10, 512) | 0 |
| 5 | Conv1D | (None, 10, 512) | 262656 |
| 6 | MaxPooling1D | (None, 10, 512) | 0 |
| 7 | Conv1D | (None, 10, 300) | 153900 |
| 8 | MaxPooling1D | (None, 10, 300) | 0 |
| 9 | Dropout | (None, 10, 300) | 0 |
| 10 | Flatten | (None, 3000) | 0 |
| 11 | Dense | (None, Number of videos) | 129043 |
| Dataset | BPS | F-PAT | F-BPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Month | 73.07 | 75.88 | 63.05 |
| Day1 | 62.79 | 62.33 | 56.74 |
| Day2 | 66.05 | 67.44 | 60.47 |
| Day3 | 70.87 | 76.28 | 67.27 |
| Day4 | 73.38 | 72.08 | 57.47 |
| Day5 | 69.47 | 65.61 | 57.54 |
| Day6 | 70.97 | 72.81 | 63.13 |
| Day7 | 71.83 | 77.46 | 64.79 |
| Day8 | 68.84 | 68.84 | 55.81 |
| Day9 | 64.19 | 68.37 | 59.53 |
| Day10 | 65.12 | 61.86 | 50.7 |
| Day11 | 69.77 | 64.19 | 57.67 |
| Day12 | 70 | 46.33 | 57.8 |
| Day13 | 69.3 | 65.12 | 54.88 |
| Day14 | 69.3 | 68.37 | 61.86 |
| Day15 | 63.72 | 71.16 | 59.53 |
| Day16 | 69.77 | 74.42 | 64.65 |
| Day17 | 67.44 | 71.63 | 63.26 |
| Day18 | 63.26 | 72.09 | 53.95 |
| Day19 | 64.65 | 72.09 | 55.35 |
| Day20 | 59.07 | 68.37 | 54.42 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bukhari, S.M.A.H.; Afandi, W.; Khan, M.U.S.; Maqsood, T.; Qureshi, M.B.; Fayyaz, M.A.B.; Nawaz, R. E-Ensemble: A Novel Ensemble Classifier for Encrypted Video Identification. Electronics 2022, 11, 4076. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11244076
Bukhari SMAH, Afandi W, Khan MUS, Maqsood T, Qureshi MB, Fayyaz MAB, Nawaz R. E-Ensemble: A Novel Ensemble Classifier for Encrypted Video Identification. Electronics. 2022; 11(24):4076. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11244076
Chicago/Turabian StyleBukhari, Syed M. A. H., Waleed Afandi, Muhammad U. S. Khan, Tahir Maqsood, Muhammad B. Qureshi, Muhammad A. B. Fayyaz, and Raheel Nawaz. 2022. "E-Ensemble: A Novel Ensemble Classifier for Encrypted Video Identification" Electronics 11, no. 24: 4076. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11244076
APA StyleBukhari, S. M. A. H., Afandi, W., Khan, M. U. S., Maqsood, T., Qureshi, M. B., Fayyaz, M. A. B., & Nawaz, R. (2022). E-Ensemble: A Novel Ensemble Classifier for Encrypted Video Identification. Electronics, 11(24), 4076. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11244076










