Prediction of Fruit Maturity, Quality, and Its Life Using Deep Learning Algorithms
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Augmentation methods have been applied to enhance the size of the dataset.
- Developed a deep CNN to identify and classify bananas’ maturity range.
2. Related Work
3. Data Collection
4. Proposed Methodology
4.1. AlexNet
4.2. Proposed CNN Model
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fruit Maturity—An Overview|ScienceDirect Topics. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/fruit-maturity (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- Prabha, D.S.; Kumar, J.S. Assessment of banana fruit maturity by image processing technique. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 1316–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Shamrat, F.M.J.M.; Billah, M.M.; Jubair, M.A.; Alauddin, M.; Ranjan, R. Implementation of Deep Learning Methods to Identify Rotten Fruits. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI), Tirunelveli, India, 3–5 June 2021; pp. 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Haque, A.F.; Hakim, M.A.; Hafiz, R. CNN Based Automatic Computer Vision System for Strain Detection and Quality Identification of Banana. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Automation, Control and Mechatronics for Industry 4.0 (ACMI), Rajshahi, Bangladesh, 8–9 July 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Liu, Y.; Han, X. Apple quality identification and classification by image processing based on convolutional neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayalakshmi, M.; Peter, V.J. CNN based approach for identifying banana species from fruits. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2021, 13, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, H.M.R.; Hakim, A. Classification and Grading of Harvested Mangoes Using Convolutional Neural Network. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2022, 22, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtiani, S.-H.M.; Javanmardi, S.; Jahanbanifard, M.; Martynenko, A.; Verbeek, F.J. Detection of Mulberry Ripeness Stages Using Deep Learning Models. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 100380–100394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Gao, J.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Hao, Z.; Han, Z. E-AlexNet: Quality evaluation of strawberry based on machine learning. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 4530–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Yadav, J.K.P.S.; Yadav, A.K. An Automated Tomato Maturity Grading System Using Transfer Learning Based AlexNet. Ingénierie Des Systèmes D Inf. 2021, 26, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Masawabe, M.M.; Samhan, L.F.; AlFarra, A.H.; Aslem, Y.E.; Abu-Naser, S.S. Papaya Maturity Classifications using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Int. J. Eng. Inf. Syst. (IJEAIS) 2021, 5, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Miragaia, R.; Chávez, F.; Díaz, J.; Vivas, A.; Prieto, M.H.; Moñino, M.J. Plum Ripeness Analysis in Real Environment Using Deep Learning with Convolutional Neural Networks. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermana, A.N.; Rosmala, D.; Husada, M.G. Transfer Learning for Classification of Fruit Ripeness Using VGG16. In Proceedings of the ICCMB 2021: 2021 The 4th International Conference on Computers in Management and Business, Singapore, 30 January–1 February 2021; pp. 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero Mesa, A.; Chiang, J. Non-invasive Grading System for Banana Tiers using RGB Imaging and Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the ICCAI 2021: 2021 7th International Conference on Computing and Artificial Intelligence, Tianjin, China, 23–26 April 2021; pp. 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Gao, J.; Deng, L.; Han, Z. Monitoring the Change Process of Banana Freshness by GoogLeNet. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 228369–228376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saragih, R.E.; Emanuel, A.W.R. Banana Ripeness Classification Based on Deep Learning using Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2021 3rd East Indonesia Conference on Computer and Information Technology (EIConCIT), Surabaya, Indonesia, 9–11 April 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pérez, B.; Vázquez, J.G.; Salomón-Torres, R. Evaluation of Convolutional Neural Networks Hyperparameters with Transfer Learning to Determine Sorting of Ripe Medjool Dates. Agriculture 2021, 11, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.; Rana, Y.; Thakkar, V. Mango Classification Using Shape, Texture and Convolutional Neural Network Features. In ICT Systems and Sustainability: Proceedings of ICT4SD 2021; Springer: Singapore, 2022; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arampongsanuwat, S.; Chaowalit, O. Application of deep convolutional neural networks for mangosteen ripeness classification. ICIC Express Lett. 2021, 15, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septiarini, A.; Hamdani, H.; Hatta, H.R.; Kasim, A.A. Image-based processing for ripeness classification of oil palm fruit. In Proceedings of the 2019 5th International Conference on Science in Information Technology (ICSITech), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 23–24 October 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taofik, A.; Ismail, N.; Gerhana, Y.A.; Komarujaman, K.; Ramdhani, M.A. Design of smart system to detect ripeness of tomato and chili with new approach in data acquisition. In Proceedings of the 2nd Annual Applied Science and Engineering Conference (AASEC 2017), Bandung, Indonesia, 24 August 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapan, N.; Hinal, S. Classification of Mango (Mangifera indica L.) fruit varieties using Convolutional Neural Network. Retrieved 6 December 2022. Available online: https://180slearning.in/pdf_uploads/CRC_17_Sapan.pdf (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- Fruits 360|Kaggle. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/moltean/fruits (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- Introduction to TensorFlow. Available online: https://www.tensorflow.org/learn (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlexNet: The Architecture That Challenged CNNs|by Jerry Wei|Towards Data Science. Available online: https://towardsdatascience.com/alexnet-the-architecture-that-challenged-cnns-e406d5297951 (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- Unnikrishnan, A.; Sowmya, V.; Soman, K.P. Deep AlexNet with Reduced Number of Trainable Parameters for Satellite Image Classification. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 143, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (AlexNet)—Dive into Deep Learning 1.0.0-alpha1.post0 Documentation. Available online: https://d2l.ai/chapter_convolutional-modern/alexnet.html (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- Yamashita, R.; Nishio, M.; Do, R.K.G.; Togashi, K. Convolutional neural networks: An overview and application in radiology. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- What is a Convolutional Neural Network?—MATLAB & Simulink. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/discovery/convolutional-neural-network-matlab.html (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- A Comprehensive Guide to Convolutional Neural Networks—the ELI5 Way|by Sumit Saha|Towards Data Science. Available online: https://towardsdatascience.com/a-comprehensive-guide-to-convolutional-neural-networks-the-eli5-way-3bd2b1164a53 (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- Nagnath, A.; Usha, M. Fruit quality identification using image processing, machine learning, and deep learning: A review. Adv. Appl. Math. Sci. 2022, 21, 2645–2660. [Google Scholar]
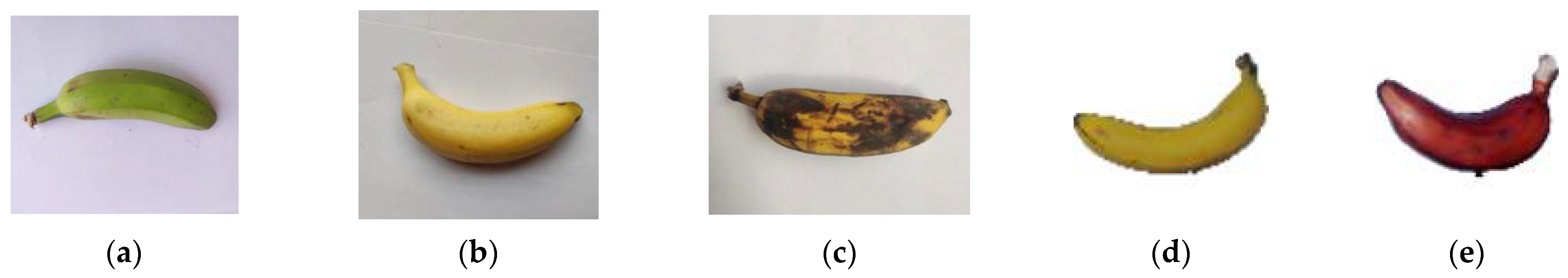




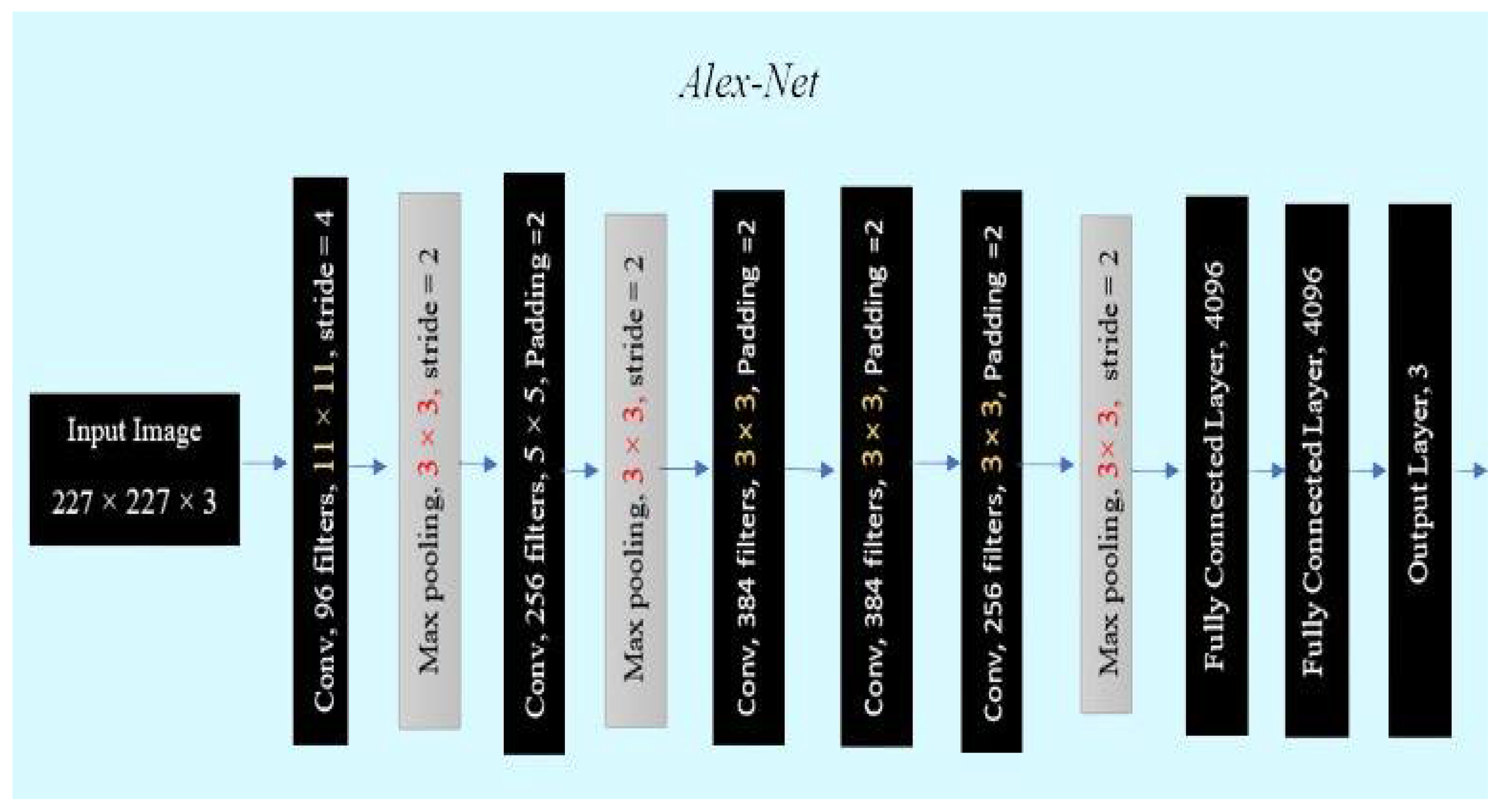

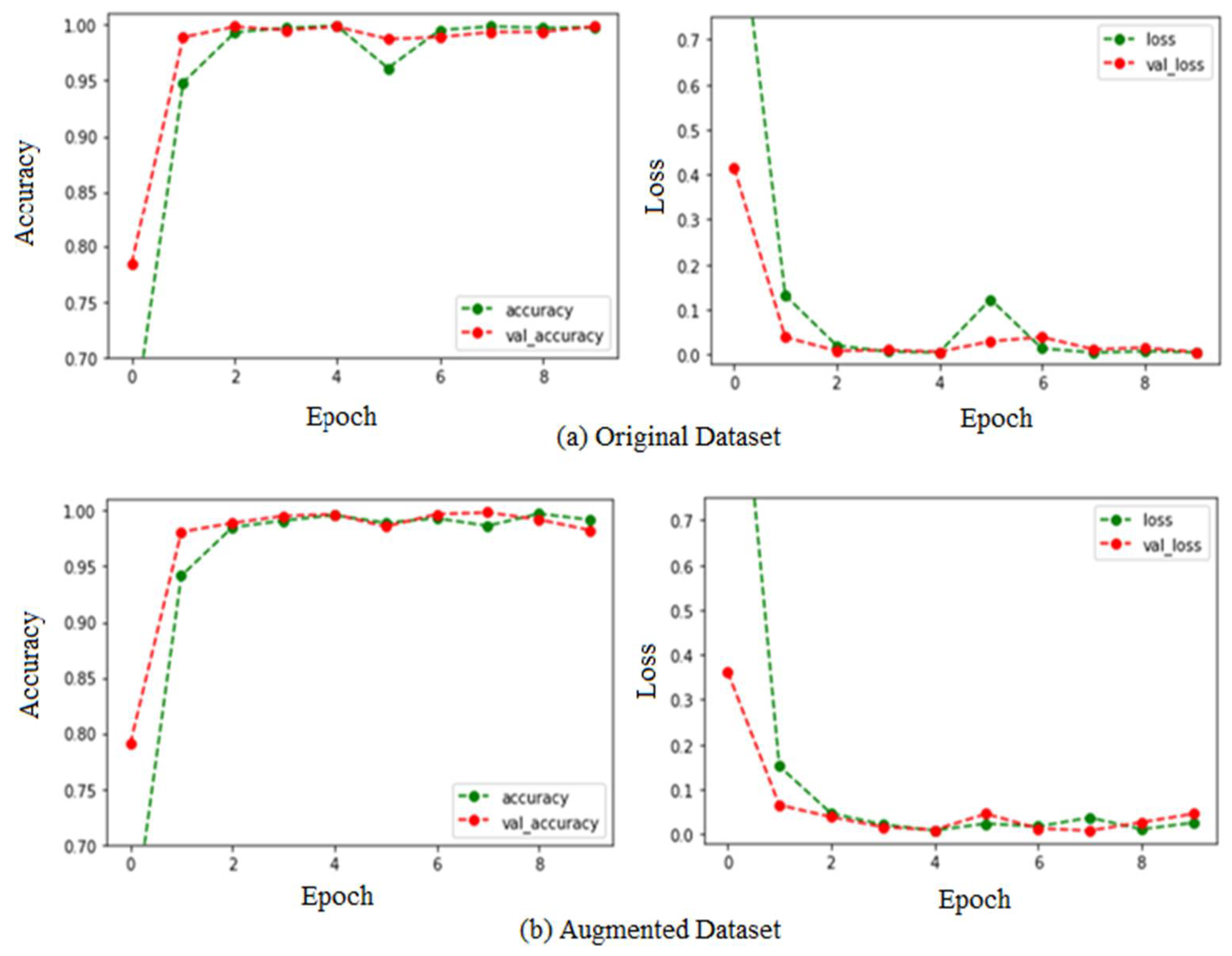
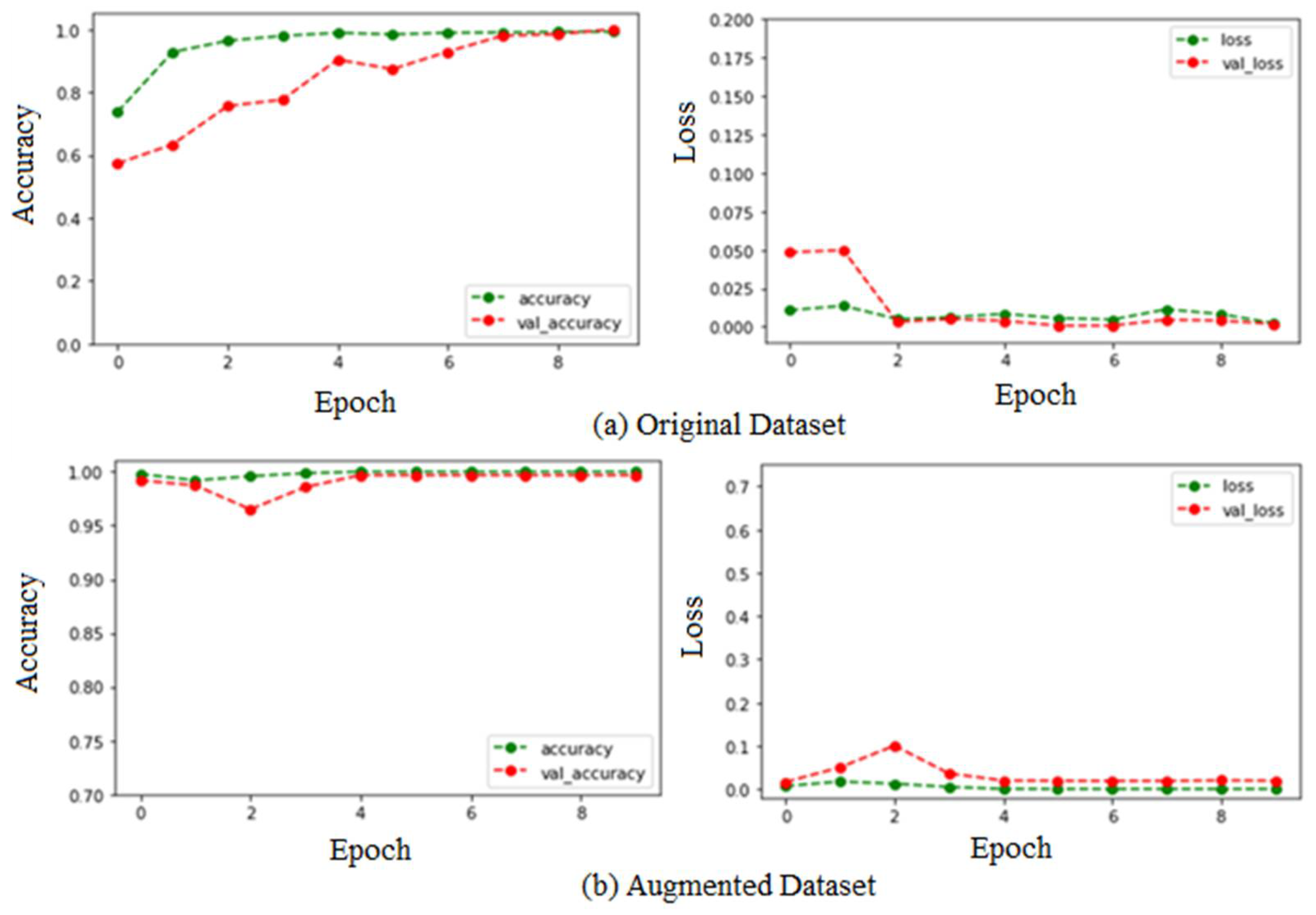
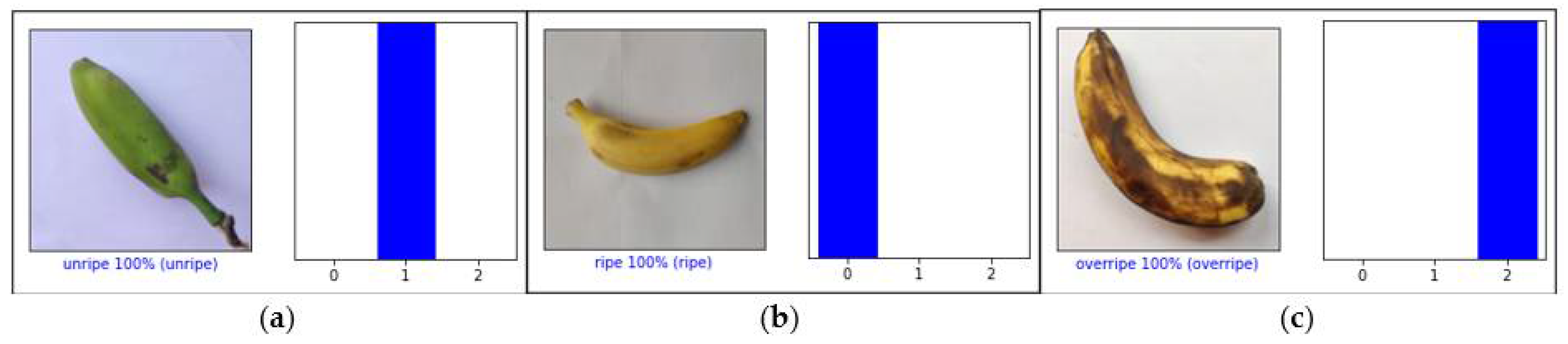
| Year and Ref. | Fruits | Applications | Techniques | Remarks and Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 [7] | Mango | Fruit Grading and Automatic Classification | CNN, VGG16, InceptionV3 | To stop the spoilage of this seasonal fruit and to remove the manual process. Classification accuracy was 99.2%, and grading accuracy was 96.7% |
| 2021 [3] | Banana, Apple, and Orange | Ripeness Identification and Maturity Classification | CNN | To reduce harvest losses. Provides good-quality fruits to farmers and people who used this system. Training accuracy was 99.46%, and testing accuracy was 99.6% |
| 2021 [5] | Apple | Quality Identification and Maturity Classification | CNN | For speed and precise apple fruit grading. Achieved high accuracy for grading on maturity level. Grading accuracy was 98.98% |
| 2021 [6] | Banana | Fruit Recognition and Classification | CNN, Alex-Net | To help industrial applications and automate the process of recognition and classification. Classification accuracy was 96.98% |
| 2021 [16] | Banana | Ripeness Classification | CNN | To increase farmers’ income by reducing harvesting loss. To obtain a good-quality banana. Using a pre-trained model for ripeness classification. Classification accuracy was 96.18% |
| 2021 [15] | Banana | Freshness Detection | CNN, GoogLeNet | Providing fresh fruit to customers and automating this task. Bananas are good for bone health, weight loss, heart, and to prevent cancer. Detection accuracy was 98.02% |
| 2021 | Strawberry | Quality Evaluation | Alex-Net | To obtain worldwide cultivated quality strawberry fruit. AlexNet was the best-suited algorithm for this work. Accuracy was 95.75% |
| 2021 | Tomato | Maturity Grading | Alex-Net | To reduce pre- and post-harvesting loss. Accurately and efficiently recognized the maturity of tomato. Detection Accuracy was 100% |
| Title 1 | Original Dataset | Augmented Dataset | Fruit 360 Dataset | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | Testing | Training | Testing | Training | Testing | |
| Ripe (0) | 490 | 210 | 4410 | 1890 | 460 | 196 |
| Unripe (1) | 490 | 210 | 4410 | 1890 | - | - |
| Overripe (2) | 490 | 210 | 4410 | 1890 | 460 | 196 |
| Total Images | 1470 | 630 | 13,230 | 5670 | 920 | 392 |
| 2100 | 18,900 | 1312 | ||||
| Layers (Type) | Image Size | Filters | Filter Size | Pooling Size | Output Shape | Params# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conv2d | 227 × 227 | 32 | 3 × 3 | - | (None, 225, 225, 32) | 896 |
| Max pooling2d | 112 × 112 | - | - | 2 × 2 | (None, 112, 112, 32) | 0 |
| Conv2d_1 | 112 × 112 | 64 | 3 × 3 | - | (None, 110, 110, 64) | 18,496 |
| Max_pooling2d_1 | 56 × 56 | - | - | 2 × 2 | (None, 55, 55, 64) | 0 |
| Conv2d_2 | 56 × 56 | 64 | 3 × 3 | - | (None, 53, 53, 64) | 36,928 |
| Flatten | Fully Connected Layer | (None, 179776) | 0 | |||
| Dropout | 20% | (None, 179776) | 0 | |||
| Dense | “Units = 64, Activation = relu” | (None, 64) | 11,505,728 | |||
| Dense_1 | “Units = 3 (Categorical), Activation = softmax” | (None, 3) | 195 | |||
| Datasets | CNN | AlexNet | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | Validation | Training | Validation | |
| Original Dataset | 99.18% | 98.25% | 99.18% | 81.75% |
| Augmented Dataset | 99.42% | 99.36% | 99.80% | 99.44% |
| Fruit 360 Dataset | 100% | 81.96% | 100% | 81.75% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aherwadi, N.; Mittal, U.; Singla, J.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Yassine, A.; Hossain, M.S. Prediction of Fruit Maturity, Quality, and Its Life Using Deep Learning Algorithms. Electronics 2022, 11, 4100. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11244100
Aherwadi N, Mittal U, Singla J, Jhanjhi NZ, Yassine A, Hossain MS. Prediction of Fruit Maturity, Quality, and Its Life Using Deep Learning Algorithms. Electronics. 2022; 11(24):4100. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11244100
Chicago/Turabian StyleAherwadi, Nagnath, Usha Mittal, Jimmy Singla, N. Z. Jhanjhi, Abdulsalam Yassine, and M. Shamim Hossain. 2022. "Prediction of Fruit Maturity, Quality, and Its Life Using Deep Learning Algorithms" Electronics 11, no. 24: 4100. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11244100
APA StyleAherwadi, N., Mittal, U., Singla, J., Jhanjhi, N. Z., Yassine, A., & Hossain, M. S. (2022). Prediction of Fruit Maturity, Quality, and Its Life Using Deep Learning Algorithms. Electronics, 11(24), 4100. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11244100







