Smish: A Novel Activation Function for Deep Learning Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
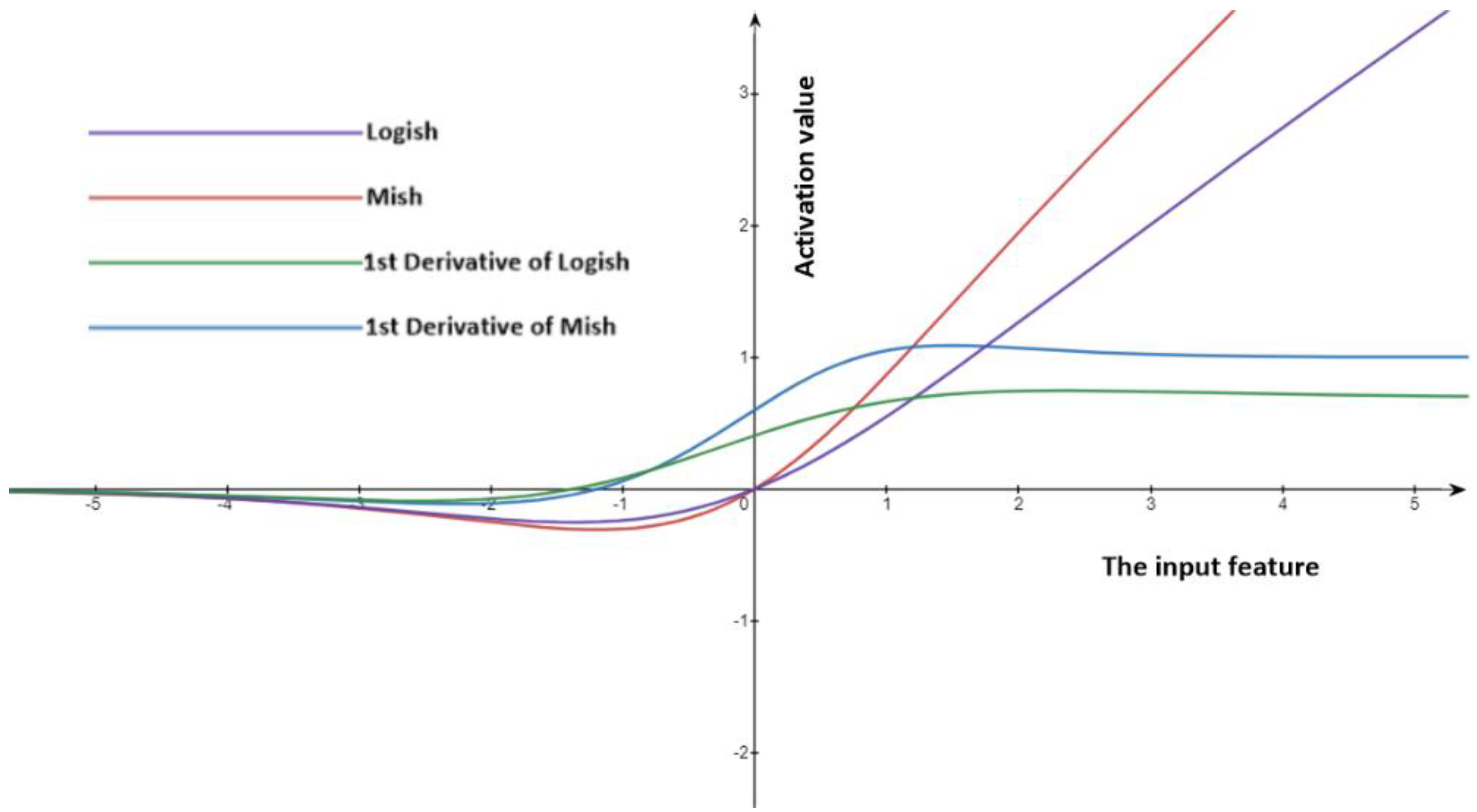
2.1. Mish
2.2. Logish
3. Proposed Smish
3.1. Construction of Smish
3.2. Approximate Linear Transformation
3.3. Nonmonotonicity
4. Analysis of Hyperparameter Tuning for Smish
4.1. Analysis of the Number of Layers
4.2. Analysis of Batch Sizes
4.3. Analysis of learning rates
4.4. Analysis of Different Dropout Rates
4.5. Analysis of Different Optimizers
4.6. Analysis of Different Parameters
5. Experimental Results of Open Datasets
5.1. Datasets and Experimental Settings
5.2. Classification Result on CIFAR10
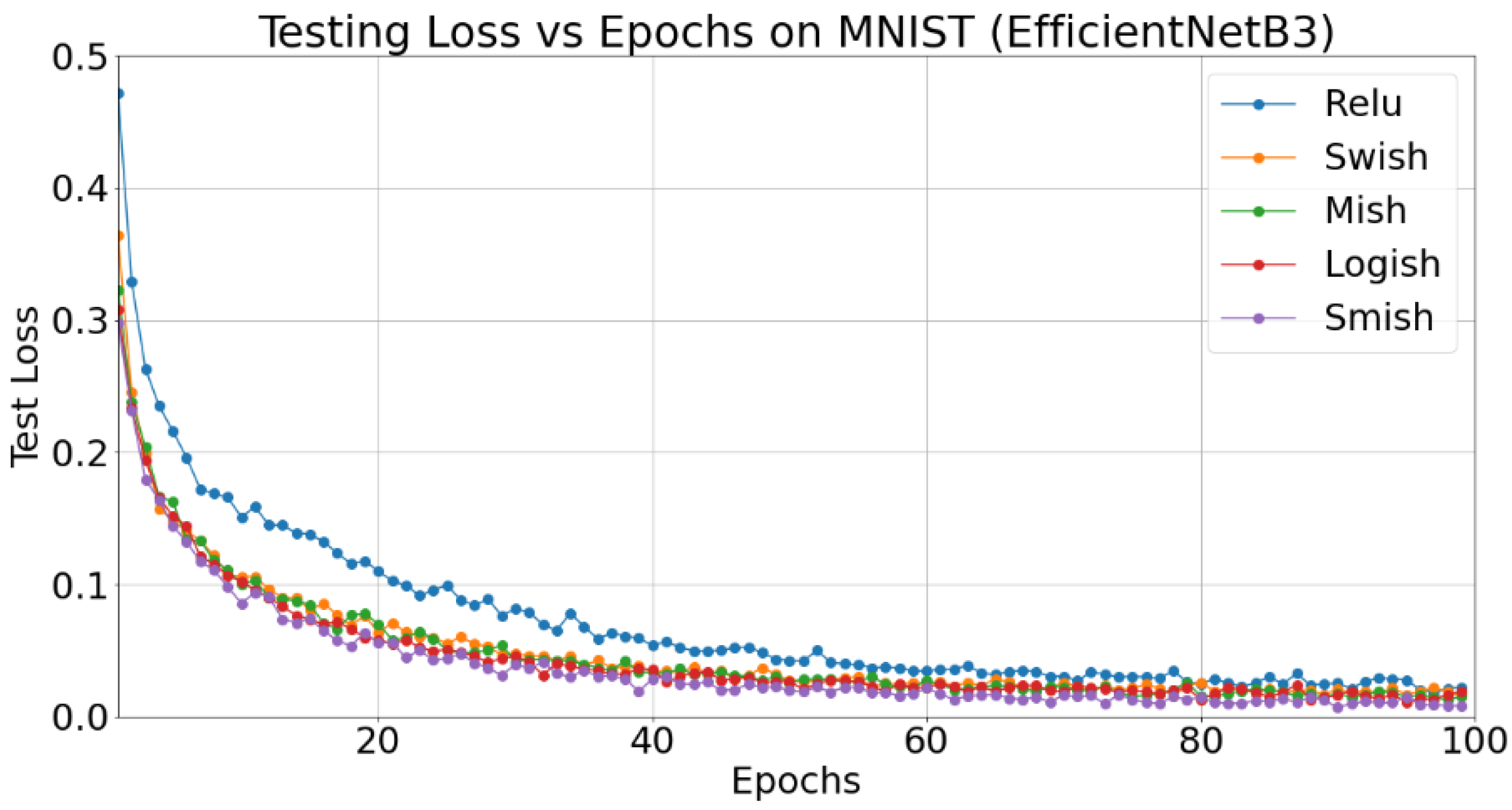
5.3. Classification Results on MNIST
5.4. Classification Results on SVHN
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 6, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zeng, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X. Logish: A new nonlinear nonmonotonic activation function for convolutional neural network. Neurocomputing 2021, 458, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayou, S.; Doucet, A.; Rousseau, J. On the impact of the activation function on deep neural networks training. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Dureja, A.; Pahwa, P. Analysis of non-linear activation functions for classification tasks using convolutional neural networks. Recent Pat. Comput. Sci. 2019, 12, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liu, W.; Bian, J.; Pei, J. Measuring model complexity of neural networks with curve activation functions. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Virtual Event, CA, USA, 6–10 July 2020; pp. 1521–1531. [Google Scholar]
- Obla, S.; Gong, X.; Aloufi, A.; Hu, P.; Takabi, D. Effective activation functions for homomorphic evaluation of deep neural networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 153098–153112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguolo, G.; Nanni, L.; Ghidoni, S. Ensemble of convolutional neural networks trained with different activation functions. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 166, 114048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Min, W.; Wang, Q.; Zou, S.; Chen, X. PFLU and FPFLU: Two novel non-monotonic activation functions in convolutional neural networks. Neurocomputing 2021, 429, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasin, B.A.; Swamy, S.R.; Nirmala, J. Some special families of holomorphic and Al-Oboudi type bi-univalent functions related to k-Fibonacci numbers involving modified Sigmoid activation function. Afr. Mat. 2021, 32, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Goyal, R.; Lall, B. Learning Activation Functions: A new paradigm for understanding Neural Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.09529. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, D. Mish: A self-regularized non-monotonic neural activation function. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.08681. [Google Scholar]
- Chiluveru, S.R.; Chunarkar, S.; Tripathy, M.; Kaushik, B.K. Efficient Hardware Implementation of DNN-based Speech Enhancement Algorithm with Precise Sigmoid Activation Function. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 68, 3461–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.F.; Ma, W.P. A novel quantum neural network based on multi-level activation function. Laser Phys. Lett. 2021, 18, 025201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomogaev, A.S.; Dementev, D.A.; Krasnenko, D.M.; Shtylenko, A.S. Exploring the possibility of applying different neuronal activation functions to a single-circuit. ACS J. Phys. Conf. Series 2021, 1889, 022007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuraola, A.; Patel, N.; Nguang, S.K. Efficient activation functions for embedded inference engines. Neurocomputing 2021, 442, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, L.; Neagu, D.; Ma, R.; Campean, F. Quantum ReLU activation for Convolutional Neural Networks to improve diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease and COVID-19. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 187, 115892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcehre, C.; Moczulski, M.; Denil, M.; Bengio, Y. Noisy activation functions. In Proceedings of the International conference on machine learning, PMLR, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; pp. 3059–3068. [Google Scholar]
- Cheridito, P.; Jentzen, A.; Riekert, A.; Rossmannek, F. A proof of convergence for gradient descent in the training of artificial neural networks for constant target functions. J. Complex. 2022, 101646, (in press). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammo, F.M.; Al-Hamdani, M.N. Detecting the Speaker Language Using CNN Deep Learning Algorithm. Iraqi J. Comput. Sci. Math. 2022, 3, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapatsinski, V. Learning fast while avoiding spurious excitement and overcoming cue competition requires setting unachievable goals: Reasons for using the logistic activation function in learning to predict categorical outcomes. Lang. Cogn. Neurosci. 2021, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjabi, I.; Ouahabi, A.; Benzaoui, A.; Jacques, S. Multi-block color-binarized statistical images for single-sample face recognition. Sensors 2021, 21, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apicella, A.; Donnarumma, F.; Isgrò, F.; Prevete, R. A survey on modern trainable activation functions. Neural Netw. 2021, 138, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Li, J.; Wei, B.; Yang, L.; Fei, C.; Naik, N. Adaptive Activation Function Generation Through Fuzzy Inference for Grooming Text Categorisation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–26 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, Y.H.; Jheng, Y.J.; Tsaih, R.H. The Cramming, Softening and Integrating Learning Algorithm with Parametric ReLu Activation Function for Binary Input/Output Problems. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Budapest, Hungary, 14–19 July 2019; pp. 1–7, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Duan, A.; Li, K.; Yin, Z. Prediction of vehicle casualties in major traffic accidents based on neural network. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Chongqing, China, 2019; Volume 2073, p. 020098. [Google Scholar]
- El Jaafari, I.; Ellahyani, A.; Charfi, S. Parametric rectified nonlinear unit (PRenu) for convolution neural networks. Signal Image Video Processing 2021, 15, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Gao, D. AIS: A nonlinear activation function for industrial safety engineering. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.13861. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrycks, D.; Gimpel, K. Gaussian Error Linear Units (Gelus). arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.08415. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Q.; Li, X.; Yin, Q.; Feng, L.; Zhao, J.; Teng, Y.; Duan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, M.; Wang, J.; et al. A Study on the Generalized Normalization Transformation Activation Function in Deep Learning Based Image Compression. In Proceedings of the 6th International Congress on Information and Communication Technology; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 351–359. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Abouelnaga, Y.; Ali, O.S.; Rady, H.; Moustafa, M. Cifar-10: Knn-based ensemble of classifiers. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 15–17 December 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1192–1195. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Lille, France, 7–9 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Bottou, L. Large-scale machine learning with stochastic gradient descent. In Proceedings of the COMPSTAT’2010; Physica-Verlag HD: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler, M.D. Adadelta: An adaptive learning rate method. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1212.5701. [Google Scholar]
- Lydia, A.; Francis, S. Adagrad—An optimizer for stochastic gradient descent. Int. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2019, 6, 566–568. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Bingham, G.; Miikkulainen, R. Discovering parametric activation functions. Neural Netw. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, M.J.; Jung, W.; Ahn, J.H. AESPA: Accuracy Preserving Low-degree Polynomial Activation for Fast Private Inference. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.06699. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.; Tan, M.; Gong, B.; Wang, J.; Yuille, A.L.; Le, Q.V. Adversarial examples improve image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 819–828. [Google Scholar]
- You, Z.; Gao, H.; Li, S.; Guo, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Multiple activation functions and data augmentation based light weight network for in-situ tool condition monitoring. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Train Time (ms) | Loss | Val_Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 1 | 1664.87985 | 2.093894768 | 0.317399998 |
| 15 | 1 | 1657.337511 | 2.084924269 | 0.326699999 |
| 10 | 1 | 1688.491895 | 2.054765987 | 0.356000003 |
| 5 | 1 | 1683.588445 | 1.366328526 | 0.626699996 |
| 0.1 | 1 | 1697.313161 | 1.278249788 | 0.790999961 |
| 0.01 | 1 | 1719.354016 | 1.111771631 | 0.818499994 |
| 0.005 | 1 | 1708.812285 | 2.102614927 | 0.299999994 |
| 0.001 | 1 | 1718.249439 | 2.102625656 | 0.299999994 |
| 1 | 20 | 1722.055284 | 1.059448051 | 0.717399988 |
| 1 | 15 | 1723.015788 | 1.032156754 | 0.723999621 |
| 1 | 10 | 1717.969835 | 1.057105231 | 0.755299997 |
| 1 | 5 | 1727.269962 | 1.081895041 | 0.851999986 |
| 1 | 1 | 1724.575549 | 0.870445440 | 0.909814782 |
| 1 | 0.5 | 1717.444711 | 1.033060956 | 0.833099973 |
| 1 | 0.1 | 1725.162607 | 0.92743938 | 0.815499973 |
| 1 | 0.05 | 1730.499959 | 1.000445652 | 0.791300011 |
| 1 | 0.01 | 1731.330632 | 1.108899283 | 0.755499971 |
| Model | EfficientNetB3 | EfficientNetB5 | EfficientNetB6 | EfficientNetB7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ReLU | 0.812400 | 0.818400 | 0.838900 | 0.837200 |
| Swish | 0.820700 | 0.840400 | 0.846900 | 0.856600 |
| Mish | 0.823200 | 0.837800 | 0.842700 | 0.853000 |
| Logish | 0.833500 | 0.843500 | 0.850700 | 0.858000 |
| Smish | 0.841000 | 0.854900 | 0.851000 | 0.859400 |
| Model | EfficientNetB3 | EfficientNetB5 | EfficientNetB6 | EfficientNetB7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ReLu | 0.564600 | 0.128999 | 0.986900 | 0.990800 |
| Swish | 0.912500 | 0.752599 | 0.987700 | 0.991900 |
| Mish | 0.397300 | 0.189899 | 0.987800 | 0.992600 |
| Logish | 0.925700 | 0.784300 | 0.990100 | 0.992800 |
| Smish | 0.977800 | 0.966500 | 0.998900 | 0.993500 |
| Model | EfficientNetB3 | EfficientNetB5 | EfficientNetB6 | EfficientNetB7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ReLu | 0.829095 | 0.854179 | 0.851605 | 0.195874 |
| Swish | 0.860787 | 0.882683 | 0.844729 | 0.195874 |
| Mish | 0.864897 | 0.889405 | 0.830670 | 0.775738 |
| Logish | 0.863745 | 0.890174 | 0.899739 | 0.848494 |
| Smish | 0.874232 | 0.893977 | 0.901467 | 0.911417 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Ren, H.; Wang, A. Smish: A Novel Activation Function for Deep Learning Methods. Electronics 2022, 11, 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11040540
Wang X, Ren H, Wang A. Smish: A Novel Activation Function for Deep Learning Methods. Electronics. 2022; 11(4):540. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11040540
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xueliang, Honge Ren, and Achuan Wang. 2022. "Smish: A Novel Activation Function for Deep Learning Methods" Electronics 11, no. 4: 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11040540
APA StyleWang, X., Ren, H., & Wang, A. (2022). Smish: A Novel Activation Function for Deep Learning Methods. Electronics, 11(4), 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11040540






