Employing the TAM Model to Investigate the Readiness of M-Learning System Usage Using SEM Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. The Proposed Model
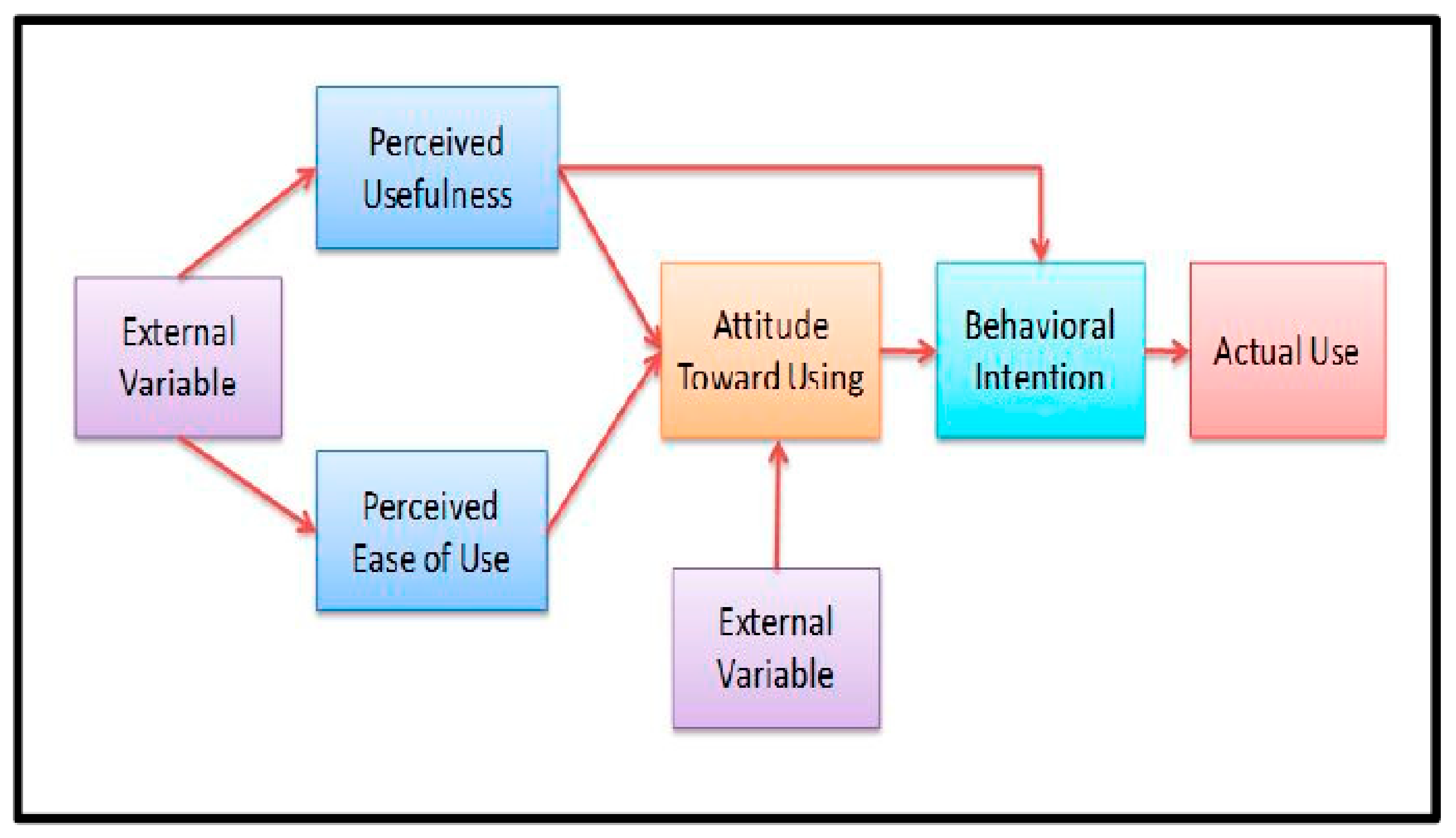
3.1. TAM Model
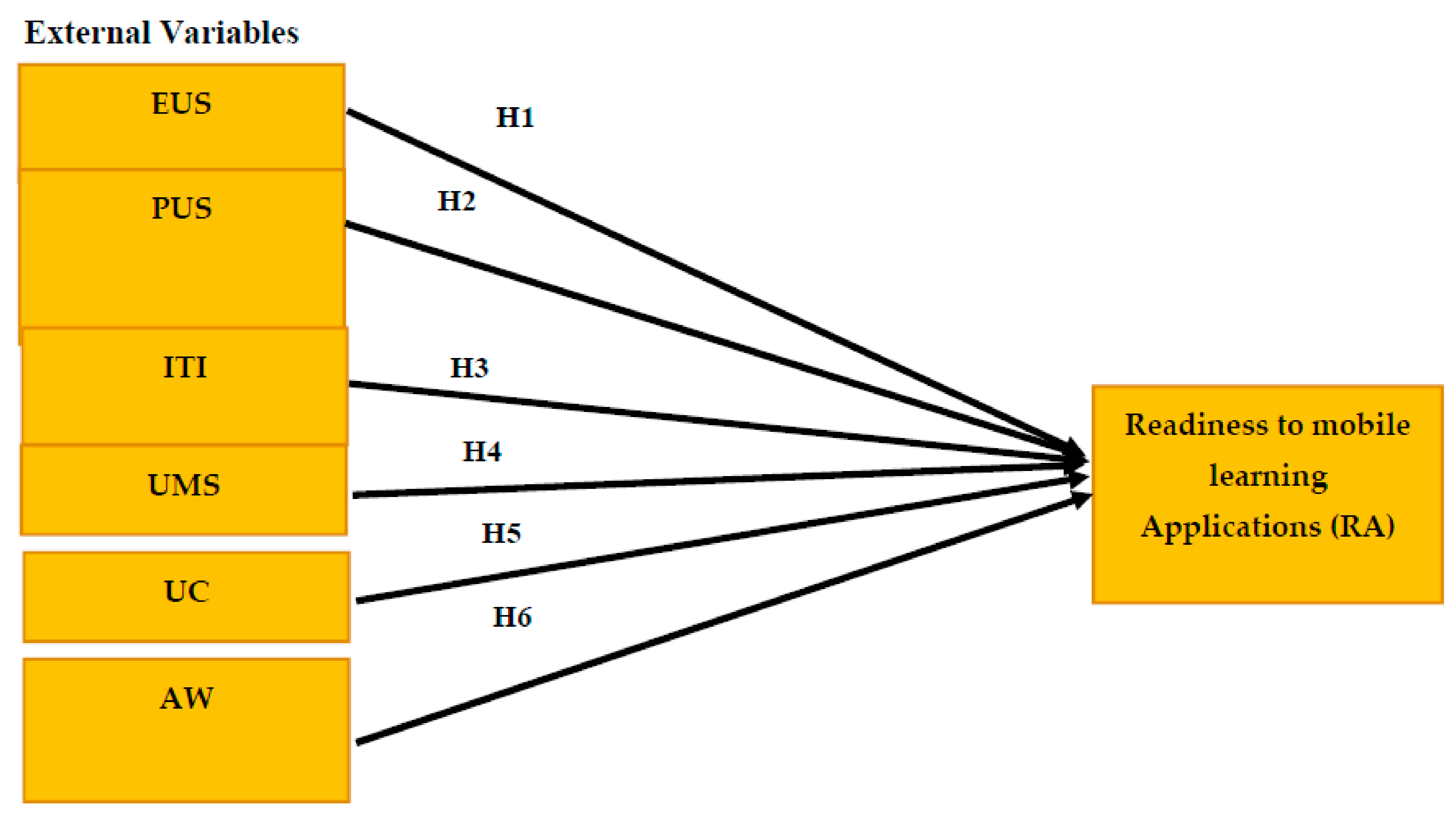
3.2. External Factors
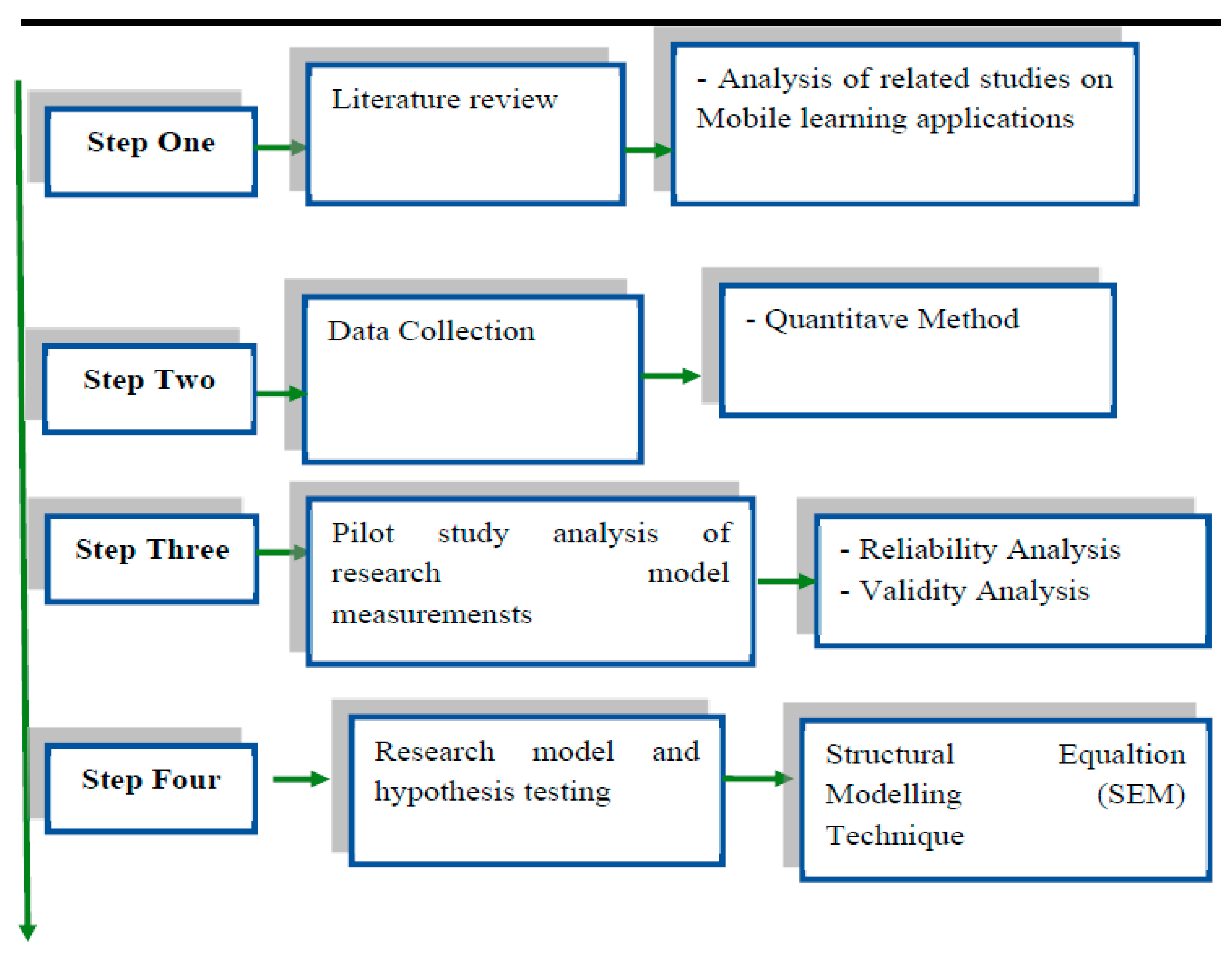
4. Methodology
4.1. Data Collection and Participants
4.2. Population of the Study
4.3. Research Measurements
4.4. Measurement Items Pre-Test
4.5. Pilot Study
5. Data Analysis and Results
5.1. Reliability Analysis
5.2. Convergent and Discriminant Validity Analysis
5.3. Structural Model Analysis Using SEM
6. Discussion
6.1. Research Implications
6.2. Limitations of the Study
7. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almaiah, M.A. Acceptance and usage of a mobile information system services in University of Jordan. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2018, 23, 1873–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaiah, M.A.; Alamri, M.M.; Al-Rahmi, W. Applying the UTAUT model to explain the students’ acceptance of mobile learning system in higher education. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 174673–174686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaiah, M.A.; Jalil, M.M.A.; Man, M. Empirical investigation to explore factors that achieve high quality of mobile learning system based on students’ perspectives. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2016, 19, 1314–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aburub, F.; Alnawas, I. A new integrated model to explore factors that influence adoption of mobile learning in higher education:An empirical investigation. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2019, 24, 2145–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Adwan, A.S.; Albelbisi, N.A.; Hujran, O.; Al-Rahmi, W.M.; Alkhalifah, A. Developing a Holistic Success Model for Sustainable E-Learning: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimmer, C.; Mateescu, M.; Gröhbiel, U. Mobile and ubiquitous learning in higher education settings. A systematic review of empirical studies. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 63, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawai, Y.G.; Almaiah, M.A. Malay language mobile learning system (MLMLS) using NFC technology. Int. J. Educ. Manag. Eng. 2018, 8, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Almaiah, M.A.; Al-Khasawneh, A.; Althunibat, A.; Almomani, O. Exploring the main determinants of mobile learning application usage during Covid-19 pandemic in Jordanian universities. In Emerging Technologies during the Era of COVID-19 Pandemic; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 275–290. [Google Scholar]
- Alamri, M.M.; Almaiah, M.A.; Al-Rahmi, W.M. The role of compatibility and task-technology fit (TTF): On social networking applications (SNAs) usage as sustainability in higher education. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 161668–161681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaiah, M.A.; Alyoussef, I.Y. Analysis of the effect of course design, course content support, course assessment and in-structor characteristics on the actual use of E-learning system. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 171907–171922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicha, K.; Rizun, M.; Rutecka, P.; Strzelecki, A. COVID-19 and higher education: First-year students’ expectations toward distance learning. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaiah, M.A.; Al-Khasawneh, A. Investigating the main determinants of mobile cloud computing adoption in university campus. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2020, 25, 3087–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Amri, M.M.; Almaiah, M.A. The Use of Mobile Gamification Technology for Sustainability Learning in Saudi Higher Education. Int. J. 2020, 9, 8236–8244. [Google Scholar]
- Almaiah, M.A.; Alamri, M.M.; Al-Rahmi, W.M. Analysis the effect of different factors on the development of Mobile learning applications at different stages of usage. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 16139–16154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaiah, M.A.; Almulhem, A. A conceptual framework for determining the success factors of e-learning system implemen-tation using Delphi technique. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2018, 96, 5962–5976. [Google Scholar]
- Almaiah, M.A.; Nasereddin, Y. Factors influencing the adoption of e-government services among Jordanian citizens. Electron. Gov. Int. J. 2020, 16, 236–259. [Google Scholar]
- Alghazi, S.S.; Kamsin, A.; Almaiah, M.A.; Wong, S.Y.; Shuib, L. For Sustainable Application of Mobile Learning: An Extend-ed UTAUT Model to Examine the Effect of Technical Factors on the Usage of Mobile Devices as a Learning Tool. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaiah, M.; Al-Khasawneh, A.; Althunibat, A.; Khawatreh, S. Mobile government adoption model based on combining GAM and UTAUT to explain factors according to adoption of mobile government services. Int. Assoc. Online Eng. 2020, 14, 199–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almaiah, M.A.; Al-Zahrani, A.; Almomani, O.; Alhwaitat, A.K. Classification of cyber security threats on mobile devices and applications. In Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain for Future Cybersecurity Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 107–123. [Google Scholar]
- Althunibat, A.; Binsawad, M.; Almaiah, M.A.; Almomani, O.; Alsaaidah, A.; Al-Rahmi, W.; Seliaman, M.E. Sustainable Ap-plications of Smart-Government Services: A Model to Understand Smart-Government Adoption. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubukayr, M.A.; Almaiah, M.A. Cybersecurity concerns in smart-phones and applications: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Information Technology (ICIT), Amman, Jordan, 14–15 July 2021; pp. 725–731. [Google Scholar]
- Alksasbeh, M.; Abuhelaleh, M.; Almaiah, M. Towards a model of quality features for mobile social networks apps in learning environments: An extended information system success model. Int. Assoc. Online Eng. 2019, 13, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almaiah, M.A.; Al-Khasawneh, A.; Althunibat, A. Exploring the critical challenges and factors influencing the E-learning system usage during COVID-19 pandemic. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2020, 25, 5261–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Emran, M.; Mezhuyev, V.; Kamaludin, A. Technology Acceptance Model in M-learning context: A systematic review. Comput. Educ. 2018, 125, 389–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaiah, M.A.; Jalil, M.A.; Man, M. Extending the TAM to examine the effects of quality features on mobile learning acceptance. J. Comput. Educ. 2016, 3, 453–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salloum, S.A.; Alhamad, A.Q.; Al-Emran, M.; Monem, A.A.; Shaalan, K. Exploring students’ acceptance of e-learning through the development of a comprehensive technology acceptance model. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 128445–128462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulhem, A.A.; Almaiah, M.A. A Conceptual Model to Investigate the Role of Mobile Game Applications in Education during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Electronics 2021, 10, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Amri, M.; Almaiah, M.A. Sustainability Model for Predicting Smart Education Technology Adoption Based on Student Perspectives. Int. J. Adv. Soft Comput. Appl. 2021, 13, 60–77. [Google Scholar]
- Almaiah, M.A.; Almomani, O.; Al-Khasawneh, A.; Althunibat, A. Predicting the Acceptance of Mobile Learning Applications during COVID-19 Using Machine Learning Prediction Algorithms. In Emerging Technologies during the Era of COVID-19 Pandemic; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 348, p. 319. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, F.D. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Q. 1989, 1, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almaiah, M.A.; Alismaiel, O.A. Examination of factors influencing the use of mobile learning system: An empirical study. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2019, 24, 885–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mulhem, A. Exploring the Key Factors in the Use of an E-Learning System Among Students at King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia. Int. Assoc. Online Eng. 2020, 14, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alamri, M.M.; Almaiah, M.A.; Al-Rahmi, W.M. Social media applications affecting Students’ academic performance: A model developed for sustainability in higher education. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldossry, B. Evaluating the madrasati platform for the virtual classroom in Saudi arabian education during the time of Covid-19 Pandemic. Eur. J. Open Educ. E-Learn. Stud. 2021, 6, 3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrasati. Ministry of Education, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. 2021. Available online: https://backtoschool.sa/ (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Khalife, W. The effectiveness of using active learning based on distance learning on improving academic achievement and developing the trend towards distance learning for the learning technologies course for mathematics education students. Sci. J. Phys. Educ. Sports Sci. 2019, 87, 321–334. [Google Scholar]
- Khanfar, A.R. Distance-learning entrepreneurship education in the time of corona virus—COVID-19 challenges & solution. J. Entrep. Educ. 2020, 23, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- MOE. Ministry of Education, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. 2020. Available online: https://www.moe.gov.sa/ar/mediacenter/MOEnews/Pages/MR2-2020-453.aspx (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Almaiah, M.A.; Jalil, M.A.; Man, M. Preliminary study for exploring the major problems and activities of mobile learning syst m: A case study of Jordan. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2016, 93, 580–594. [Google Scholar]
- Almaiah, M.A.; Alamri, M.M. Proposing a new technical quality requirements for mobile learning applications. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2018, 96, 6955–6968. [Google Scholar]
- Almaiah, M.A. Thematic analysis for classifying the main challenges and factors influencing the successful implementation of e-learning system using Nvivo. Int. J. Adv. Trends Comput. Sci. Eng. 2020, 9, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfi, A.; Alsyouf, A.; Almaiah, M.A.; Alrawad, M.; Abdo, A.A.; Al-Khasawneh, A.L.; Ibrahim, N.; Saad, M. Factors Influencing the Adoption of Big Data Analytics in the Digital Transformation Era: Case Study of Jordanian SMEs. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, A.; Palmer, E.; Strelan, P. A taxonomy of factors affecting attitudes towards educational technologies for use with technology acceptance models. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2019, 50, 2394–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Thong, J.Y.; Xu, X. Consumer acceptance and use of information technology: Extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. MIS Q. 2012, 1, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, N.; Feroz, I.; Anjum, A. Usability Analysis of Educational Information Systems from Student’s Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Big Data in Management, Manchester, UK, 15 May 2020; pp. 130–135. [Google Scholar]
- Alqahtani, A.Y.; Rajkhan, A.A. E-learning critical success factors during the covid-19 pandemic: A comprehensive analysis of e-learning managerial perspectives. Educ. Sci. 2020, 10, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent, K.; Hyland, P.; Sawang, S. Factors influencing the adoption of information technology in a construction business. Australas. J. Constr. Econ. Build. 2012, 12, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ergüzen, A.; Erdal, E.; Ünver, M.; Özcan, A. Improving Technological Infrastructure of Distance Education through Trustworthy Platform-Independent Virtual Software Application Pools. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shihi, H.; Sharma, S.K.; Sarrab, M. Neural network approach to predict mobile learning acceptance. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2018, 23, 1805–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshurideh, M.; Al Kurdi, B.; Salloum, S.A.; Arpaci, I.; Al-Emran, M. Predicting the actual use of m-learning systems: A comparative approach using PLS-SEM and machine learning algorithms. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2020, 224976525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, A.Y. A two-staged SEM-neural network approach for understanding and predicting the determinants of m-commerce adoption. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobucci, D. Everything you always wanted to know about SEM (structural equations modeling) but were afraid to ask. J. Consum. Psychol. 2009, 19, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hew, T.S.; Leong, L.Y.; Ooi, K.B.; Chong, A.Y. Predicting drivers of mobile entertainment adoption: A two-stage SEM-artificialneural-network analysis. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2016, 56, 352–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, S.; Abdullah, R.; Safaei, M.; Nazir, S. An integrated SEM-eural Network approach for predicting determinants of adoption of wearable healthcare devices. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2019, 2019, 8026042. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.K. Integrating cognitive antecedents into TAM to explain mobile banking behavioral intention: A SEM-neural network modeling. Inf. Syst. Front. 2019, 21, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, W.Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, L. Predicting and explaining patronage behavior toward web and traditional stores using neural networks: A comparative analysis with logistic regression. Decis. Support Syst. 2006, 41, 514–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, H.; Rolph, F.; Anderson, E.; Babin, B.J.; Black, W.C. Multivariate Data Analysis: A Global Perspective; Pearson: London, UK, 2010; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, F.T.; Chong, A.Y. A SEM–neural network approach for understanding determinants of inter organizational system standard adoption and performances. Decis. Support Syst. 2012, 54, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, L.Y.; Hew, T.S.; Tan, G.W.; Ooi, K.B. Predicting the determinants of the NFC-enabled mobile credit card acceptance: A neural networks approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 5604–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabukovšek, S.S.; Kalinic, Z.; Bobek, S.; Tominc, P. SEM–ANN based research of factors’ impact on extended use of ERP systems. Cent. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 27, 703–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, C.R.; Woodfield, W.; Harrison, J.B. A framework for institutional adoption and implementation of blended learning in higher education. Internet High. Educ. 2013, 18, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkarney, W.; Albraithen, M. Are critical success factors always valid for any case? A contextual perspective. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 63496–63512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althunibat, A.; Almaiah, M.A.; Altarawneh, F. Examining the Factors Influencing the Mobile Learning Applications Usage in Higher Education during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Electronics 2021, 10, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aini, Q.; Budiarto, M.; Putra, P.O.H.; Rahardja, U. Exploring e-learning challenges during the global COVID-19 pandemic: A review. Jurnal Sistem Informasi 2020, 16, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althunibat, A.; Abdallah, M.; Almaiah, M.A.; Alabwaini, N.; Alrawashdeh, T.A. An Acceptance Model of Using Mobile-Government Services (AMGS). CMES-COMP. MODEL. ENG. 2022, 131, 865–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althunibat, A.; Altarawneh, F.; Dawood, R.; Almaiah, M.A. Propose a New Quality Model for M-Learning Application in Light of COVID-19. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaiah, M.A.; Al-lozi, E.M.; Al-Khasawneh, A.; Shishakly, R.; Nachouki, M. Factors Affecting Students’ Acceptance of Mobile Learning Application in Higher Education during COVID-19 Using ANN-SEM Modelling Technique. Electronics 2021, 10, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagozzi, R.P.; Davis, F.D.; Warshaw, P.R. Development and test of a theory of technological learning and usage. Hum. Relat. 1992, 45, 660–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagozzi, R.P.; Yi, Y. Specification, evaluation, and interpretation of structural equation models. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2011, 40, 8–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, J.; Shirkey, G.; John, R.; Wu, S.R.; Park, H.; Shao, C. Applications of structural equation modeling (SEM) in ecological studies: An updated review. Ecol. Processes 2016, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Characteristic | Sample (n) | Frequency (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 160 | 30.8% |
| Female | 360 | 69.2% | |
| Age | 18–20 | 30 | 5.7% |
| 21–25 | 410 | 78.8% | |
| Over 25 | 80 | 15.3% | |
| Level | Undergraduate | 395 | 75.9% |
| Postgraduate | 125 | 24.0% | |
| Mobile Owner | Android | 60 | 11.6% |
| iPhone | 460 | 88.4% | |
| Prior experience with Mobile Learning App | Yes | 480 | 92.3% |
| No | 40 | 7.7% | |
| Universities | KFU | 215 | 41.3% |
| KSU | 105 | 20.1% | |
| KKU | 110 | 21.1% | |
| DU | 90 | 17.3% | |
| Total | Total | 520 | 100% |
| Constructs | Cronbach’s Alpha | AVE |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of use | 0.792 | 0.937 |
| Perceived Usefulness | 0.873 | 0.918 |
| University management support | 0.821 | 0.829 |
| Awareness | 0.890 | 0.811 |
| University culture | 0.905 | 0.850 |
| IT infrastructure | 0.897 | 0.882 |
| Readiness | 0.852 | 0.912 |
| EUS | UMS | UC | AW | ITI | PUS | RA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EUS | 0.821 | ||||||
| UMS | 0.797 | 0.863 | |||||
| UC | 0.630 | 0.758 | 0.990 | ||||
| AW | 0.646 | 0.684 | 0.545 | 0.775 | |||
| ITI | 0.759 | 0.769 | 0.563 | 0.689 | 0.887 | ||
| PUS | 0.769 | 0.792 | 0.643 | 0.707 | 0.790 | 0.743 | |
| RA | 0.530 | 0.623 | 0.506 | 0.643 | 0.527 | 0.614 | 0.765 |
| Hypotheses | Path | Impact | β | p-Values | SE | t-Value | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | EUS→RA | Positive (+) | 0.421 | 0.006 | 0.051 | 4.733 | Supported |
| H2 | PUS→RA | Positive (+) | 0.417 | 0.019 | 0.042 | 4.137 | Supported |
| H3 | ITI→RA | Positive (+) | 0.399 | 0.001 | 0.075 | 1.331 | Supported |
| H4 | UMS→RA | Positive (+) | 0.331 | 0.005 | 0.044 | 3.471 | Supported |
| H5 | UC→RA | Positive (+) | 0.371 | 0.009 | 0.091 | 3.114 | Supported |
| H6 | AW→RA | Positive (+) | 0.405 | 0.022 | 0.06687 | 5.108 | Supported |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almaiah, M.A.; Al-Otaibi, S.; Lutfi, A.; Almomani, O.; Awajan, A.; Alsaaidah, A.; Alrawad, M.; Awad, A.B. Employing the TAM Model to Investigate the Readiness of M-Learning System Usage Using SEM Technique. Electronics 2022, 11, 1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11081259
Almaiah MA, Al-Otaibi S, Lutfi A, Almomani O, Awajan A, Alsaaidah A, Alrawad M, Awad AB. Employing the TAM Model to Investigate the Readiness of M-Learning System Usage Using SEM Technique. Electronics. 2022; 11(8):1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11081259
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmaiah, Mohammed Amin, Shaha Al-Otaibi, Abdalwali Lutfi, Omar Almomani, Arafat Awajan, Adeeb Alsaaidah, Mahmoad Alrawad, and Ali Bani Awad. 2022. "Employing the TAM Model to Investigate the Readiness of M-Learning System Usage Using SEM Technique" Electronics 11, no. 8: 1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11081259
APA StyleAlmaiah, M. A., Al-Otaibi, S., Lutfi, A., Almomani, O., Awajan, A., Alsaaidah, A., Alrawad, M., & Awad, A. B. (2022). Employing the TAM Model to Investigate the Readiness of M-Learning System Usage Using SEM Technique. Electronics, 11(8), 1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11081259










