All-SiC Traction Converter for Light Rail Transportation Systems: Design Methodology and Development of 165 kVA Prototype
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. System Description
2.1. General
2.2. Operating Characteristics of the Traction Motor Drive
2.3. Mathematical Modelling
3. Converter Design
3.1. Design Objectives
- The optimum heatsink size for the SiC power MOSFET-based converter is Rth,ha = 0.018 K/W with forced-air cooling for a switching frequency range from 5 to 10 kHz.
- When the same heatsink size is used for Si-IGBTs, Tvj exceeds the pre-specified maximum operating temperature of 120 °C at a switching frequency of 5 kHz. In order to make fC = 5 kHz, a larger size heatsink of Rth,ha = 0.013 K/W should be used only for some of the advanced Si-IGBTs.
- The hybrid IGBT can be operated at fC = 5 kHz even for Rth,ha = 0.018 K/W. Furthermore, the larger heatsink of Rth,ha = 0.013 K/W allows for its operation at fC = 10 kHz.
| Switching Frequency, fC (Hz) | Stator Frequency, fs (Hz) | S = 165 Kva, pf = 0.81 lag, Iout = 200 Arms, Vl-l = 480 Vrms, Mi = 0.905, TA = 40 °C, Rth,h-a = 0.018 K/W ‡ Loss and Tvj Values Calculated for Rth, ha = 0.013 K/W | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si-IGBT Module (FF300R17KE4) Infineon | Si-IGBT Module (CM300DY-34T) Mitsubishi | Hybrid IGBT Module (2MSI400VAE-170-53) Fuji Electric | SiC MOSFET Module (CAS300M17BM2) Wolfspeed/Cree | |||||||||||||||
| IGBT | Diode | IGBT | Diode | IGBT | Diode | MOSFET | Diode | |||||||||||
| Sw. | Cond. | Sw. | Cond. | Sw. | Cond. | Sw. | Cond. | Sw. | Cond. | Sw. | Cond. | Sw. | Cond. | Sw. | Cond. | |||
| 1260 | 60 | Loss (W) | 51 | 163 | 17 | 33 | 50 | 170 | 12 | 50 | 48 | 142 | 6 | 30 | - | - | - | - |
| Tvj (°C) | 94.3 | 75.5 | 84.7 | 76.5 | 77.9 | 73.1 | - | - | ||||||||||
| 3255 | 60 | Loss (W) | 143 | 168 | 47 | 33 | 135 | 177 | 37 | 49 | 127 | 145 | 14 | 31 | - | - | - | |
| Tvj (°C) | 117.1 | 92.4 | 108.2 | 95.8 | 91.2 | 83.8 | - | |||||||||||
| 3255 | 155 | Loss (W) | 142 | 169 | 46 | 31.7 | 135 | 177 | 36 | 49 | 126 | 145 | 14 | 31 | - | - | - | - |
| Tvj (°C) | 115.2 | 91.1 | 108.2 | 95.8 | 90.2 | 83.4 | - | - | ||||||||||
| 5000 | 60 | Loss (W) | 240 (205) | 174 (143) | 82 (74) | 34 (28) | 218 (218) | 150 (150) | 48 (48) | 41 (41) | 199 | 148 | 22 | 31 | 20 | 263 | - | 14 |
| Tvj (°C) | 141.9 (127.6) ‡ | 110.7 (101.2) ‡ | 131.2 (117.5) ‡ | 115.8 (102.1) ‡ | 103.4 | 93.5 | 109.2 | 90.2 | ||||||||||
| 5000 | 155 | Loss (W) | 237 (204) | 174 (144) | 79 (69) | 32 (27) | 218 (218) | 150 (150) | 48 (48) | 41 (41) | 199 | 148 | 22 | 31 | 19 | 262 | - | 14 |
| Tvj (°C) | 138.2 (124.9) ‡ | 107.7 (99.1) ‡ | 131.2 (117.5) ‡ | 115.8 (102.1) ‡ | 102.1 | 93.1 | 108 | 89 | ||||||||||
| 10,000 | 60 | Loss (W) | 591 | 190 | 260 | 35 | 416 | 177 | 113 | 49 | 450 (363) | 157 (128) | 42 (41) | 32 (27) | 44 | 271 | - | 14 |
| Tvj (°C) | >200 | 191.6 | 186 | 163.4 | 145 (116.3) ‡ | 126.2 (101.6) ‡ | 115.7 | 95 | ||||||||||
| 10,000 | 155 | Loss (W) | 591 | 191 | 258 | 34 | 416 | 177 | 113 | 49 | 446 (362) | 156 (127) | 42 (41) | 32 (26) | 42 | 270 | - | 13 |
| Tvj (°C) | >200 | 185.2 | 186 | 163.4 | 142.4 (114.6) ‡ | 125.2 (101.1) ‡ | 114.8 | 93.8 | ||||||||||
3.2. Preliminary Considerations for Optimum Carrier Frequency
3.3. Application of Space Vector PWM
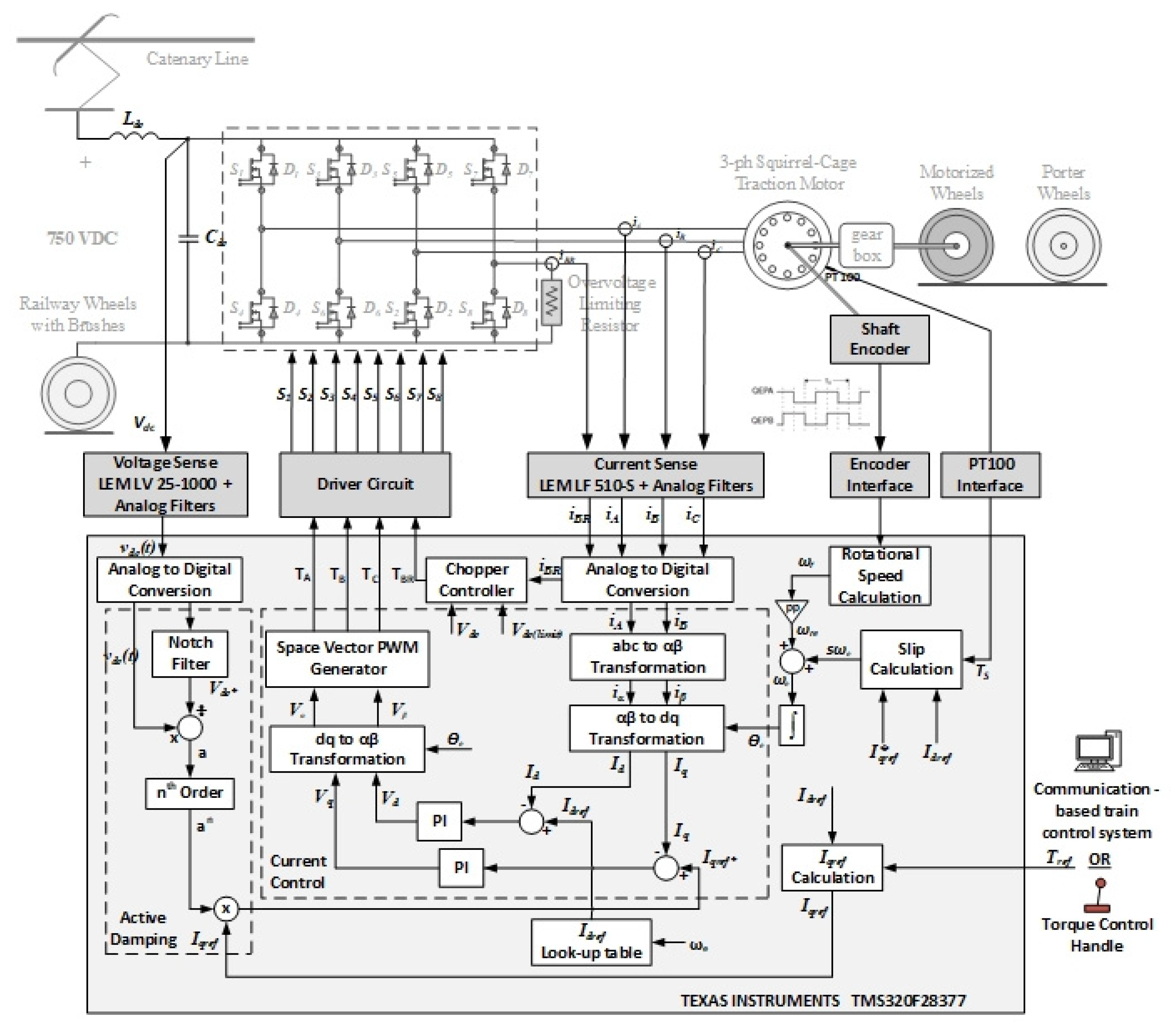
3.4. Controller
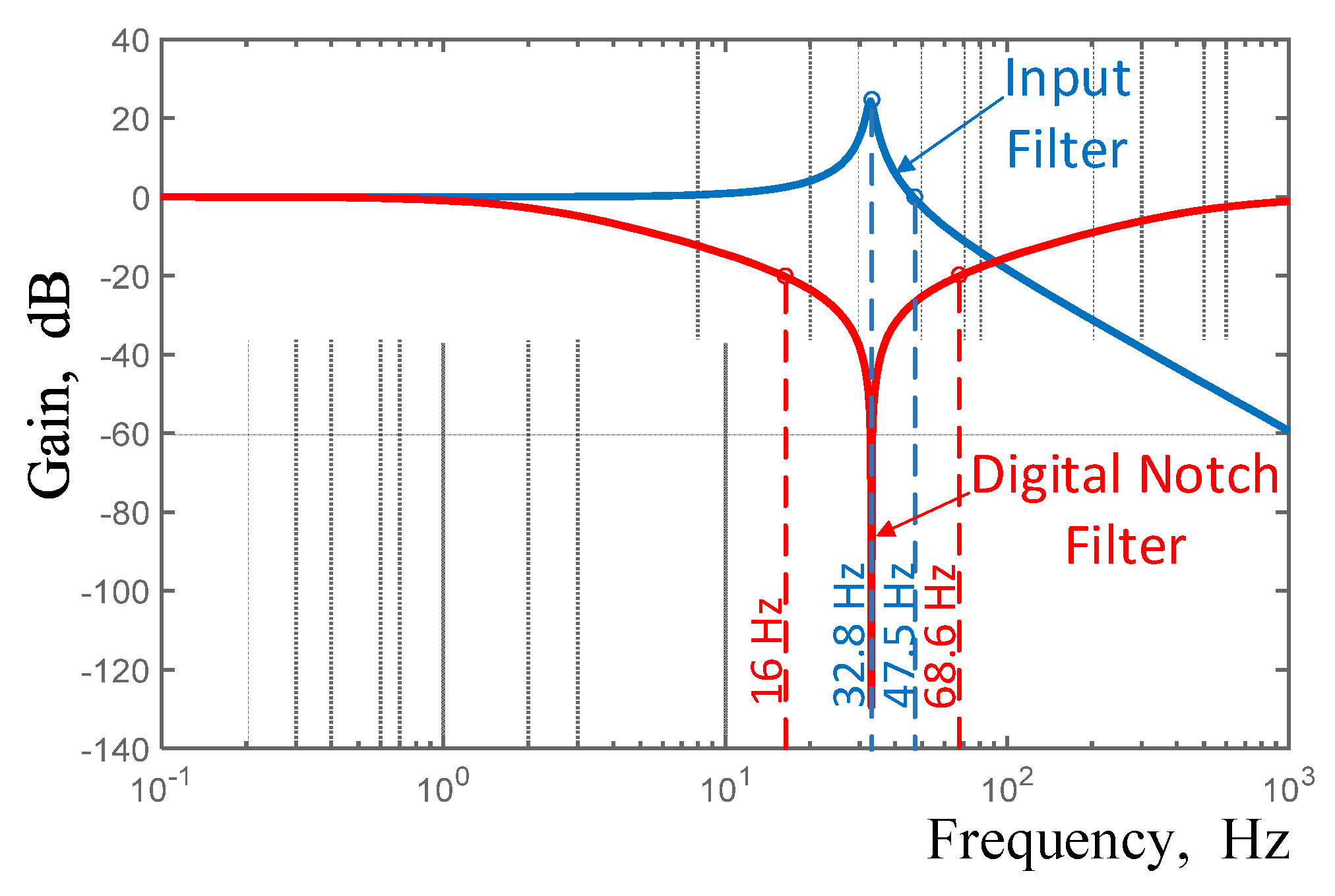
3.5. Input Filter Design
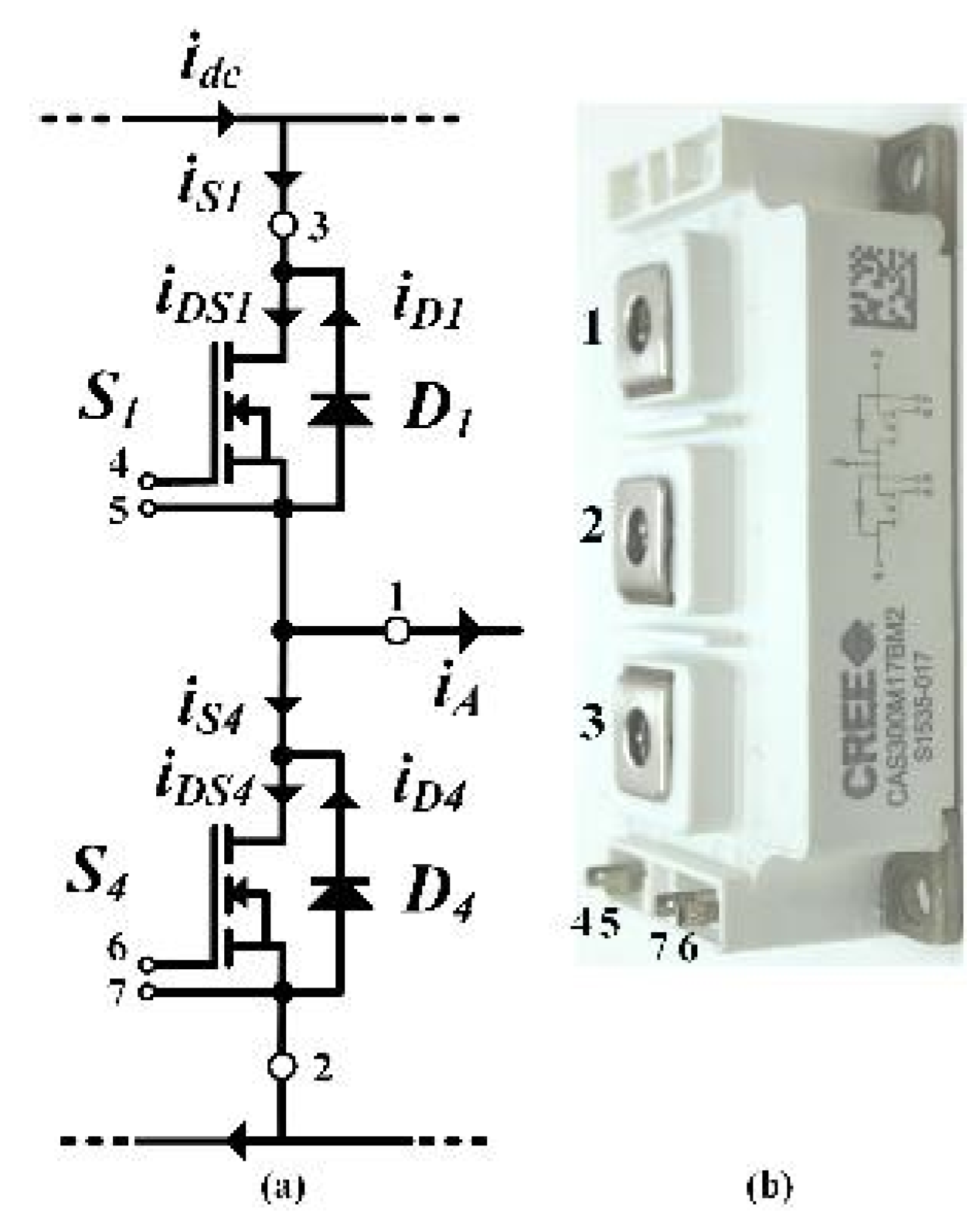
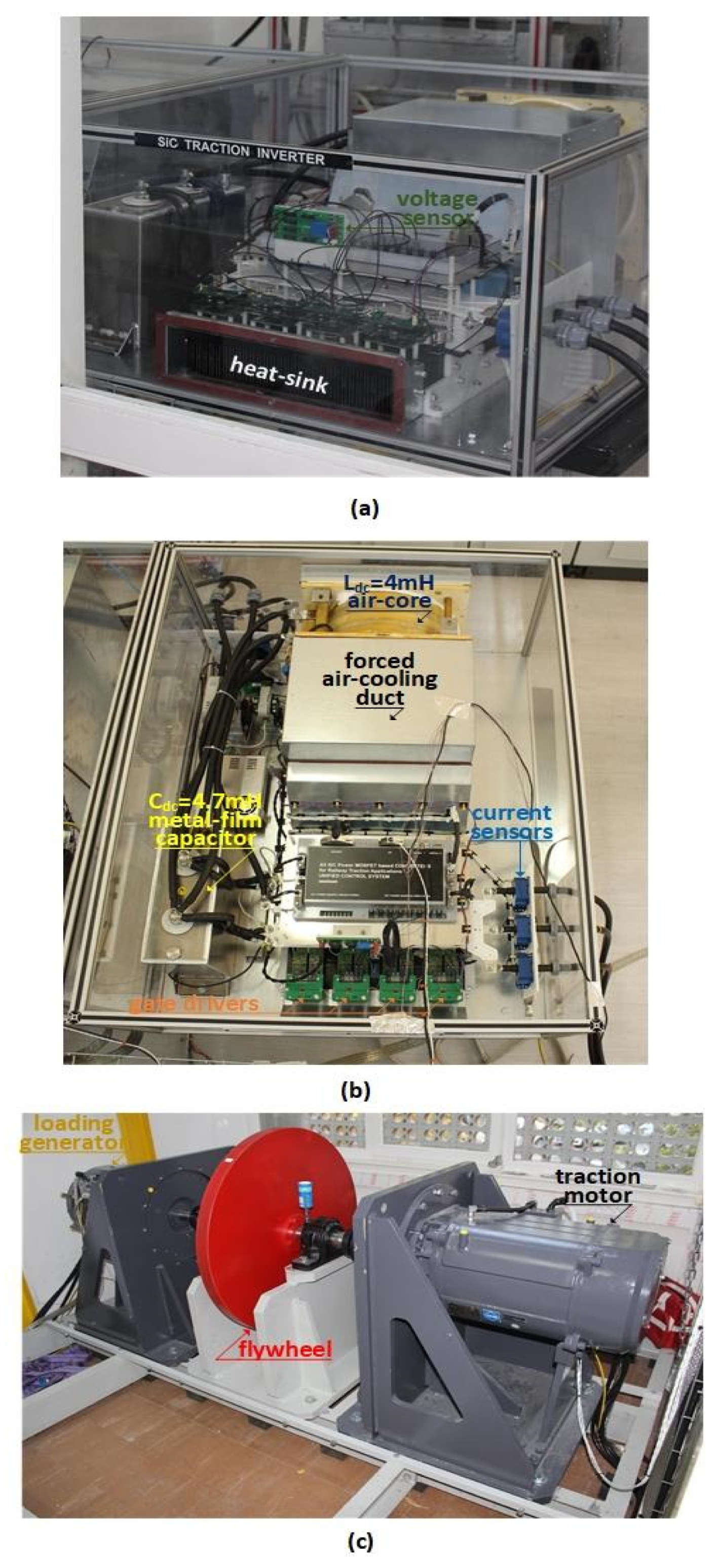
4. Implementation
5. Experimental Results
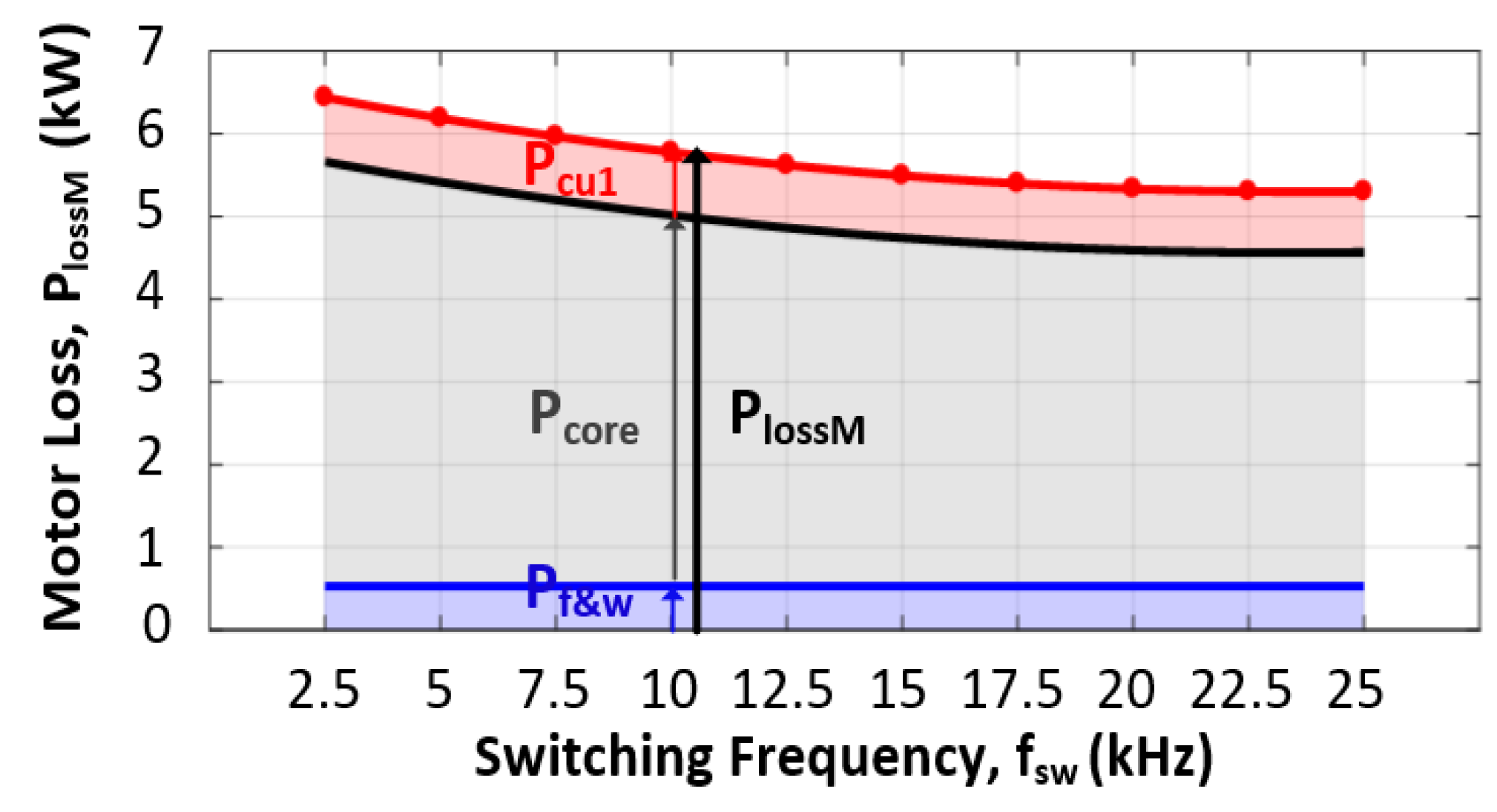
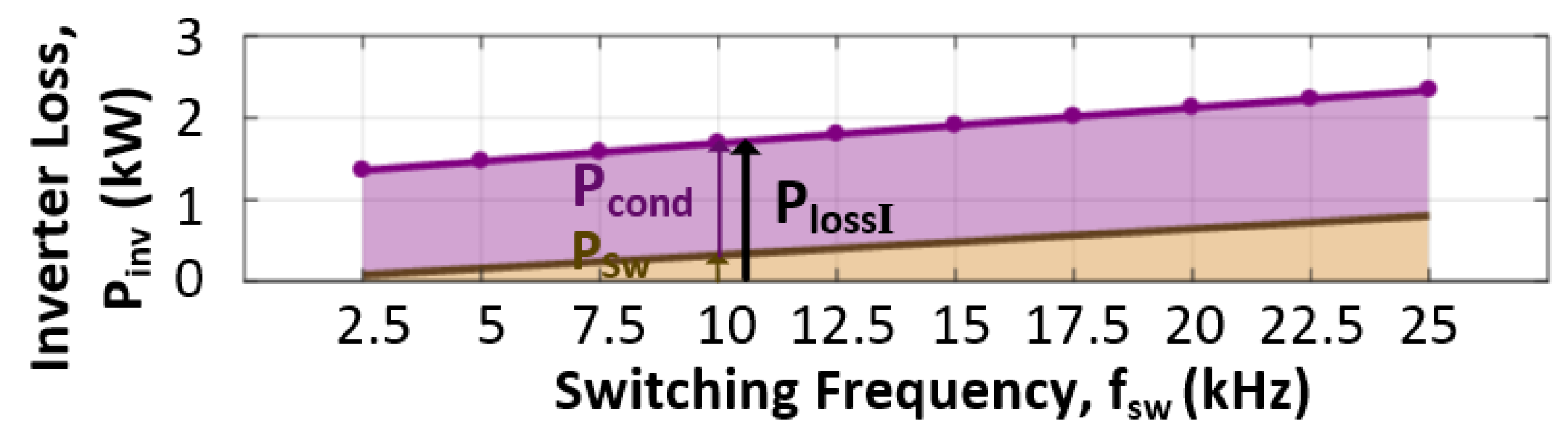
5.1. Determining Optimum Switching Frequency
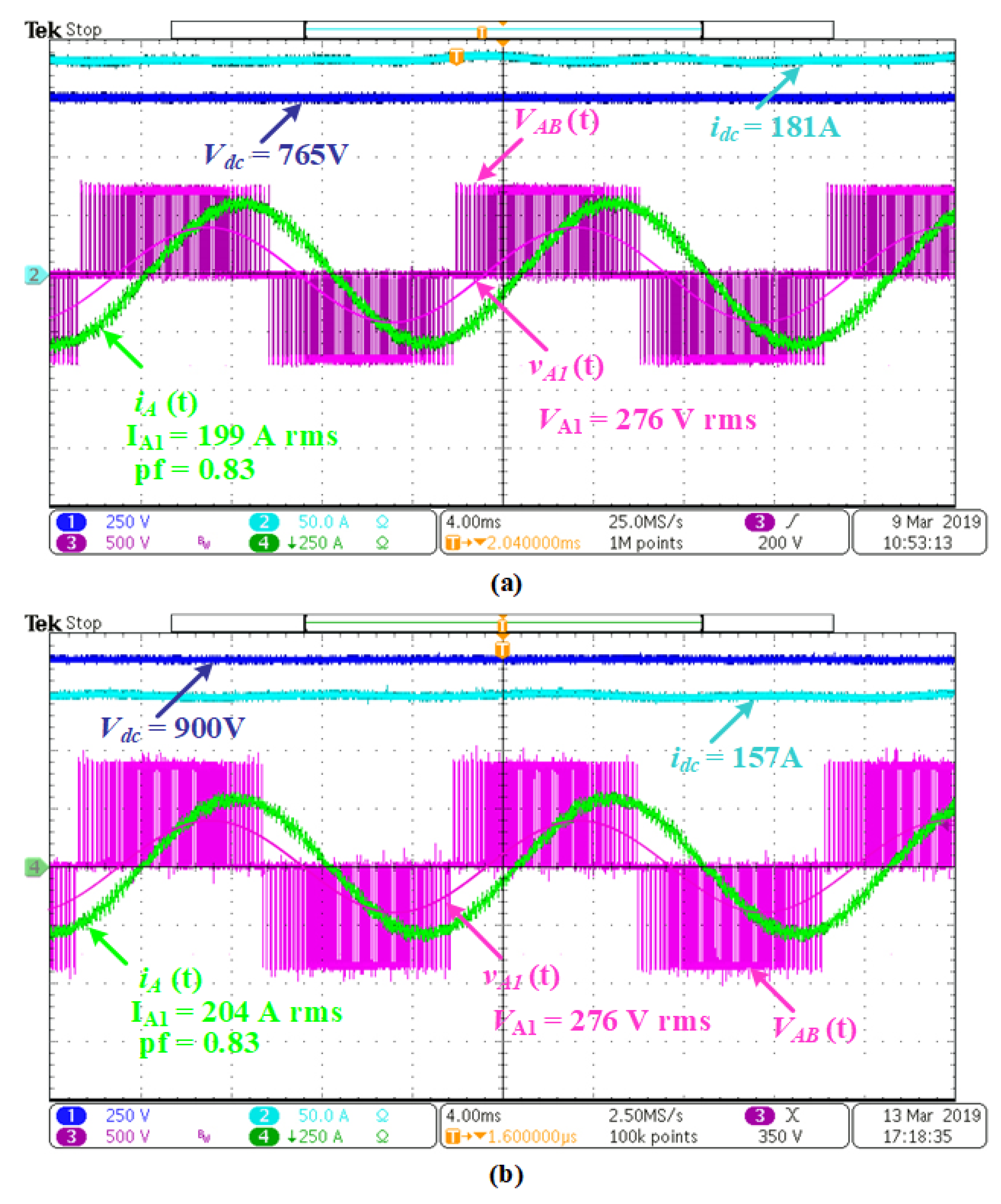
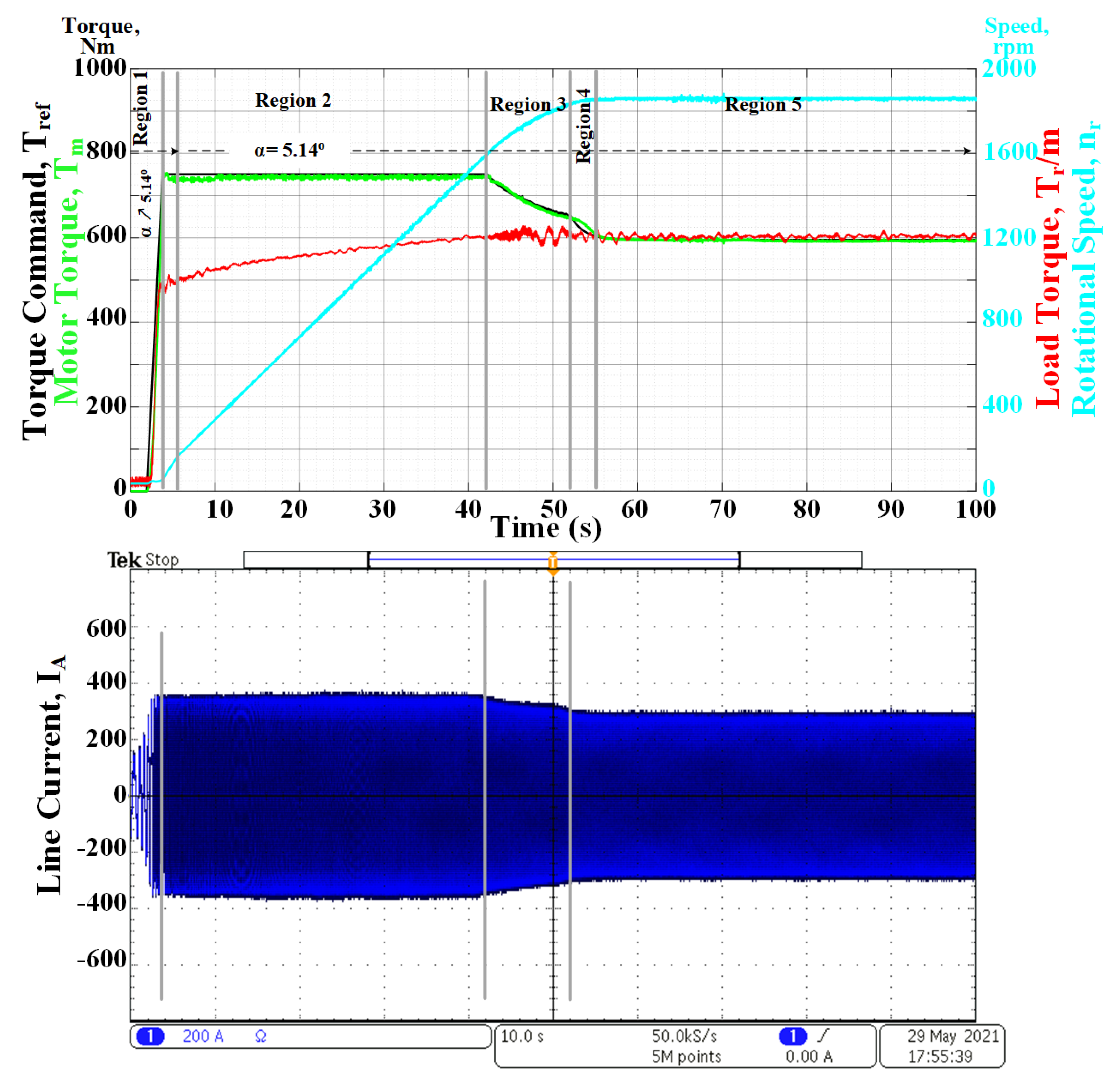
5.2. Steady-State Performance of the Traction Converter
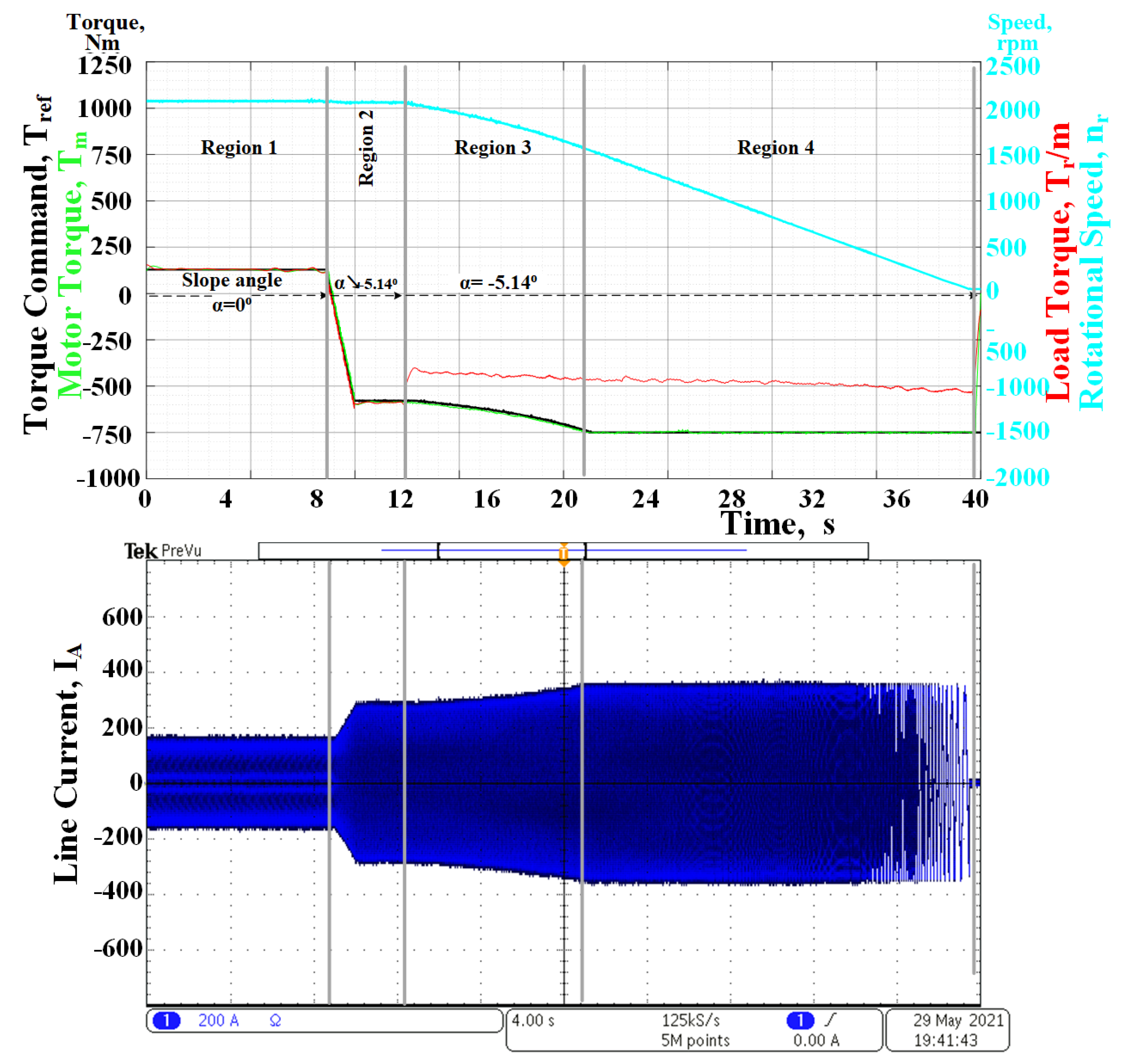
5.3. Regenerative Braking Mode of Operation
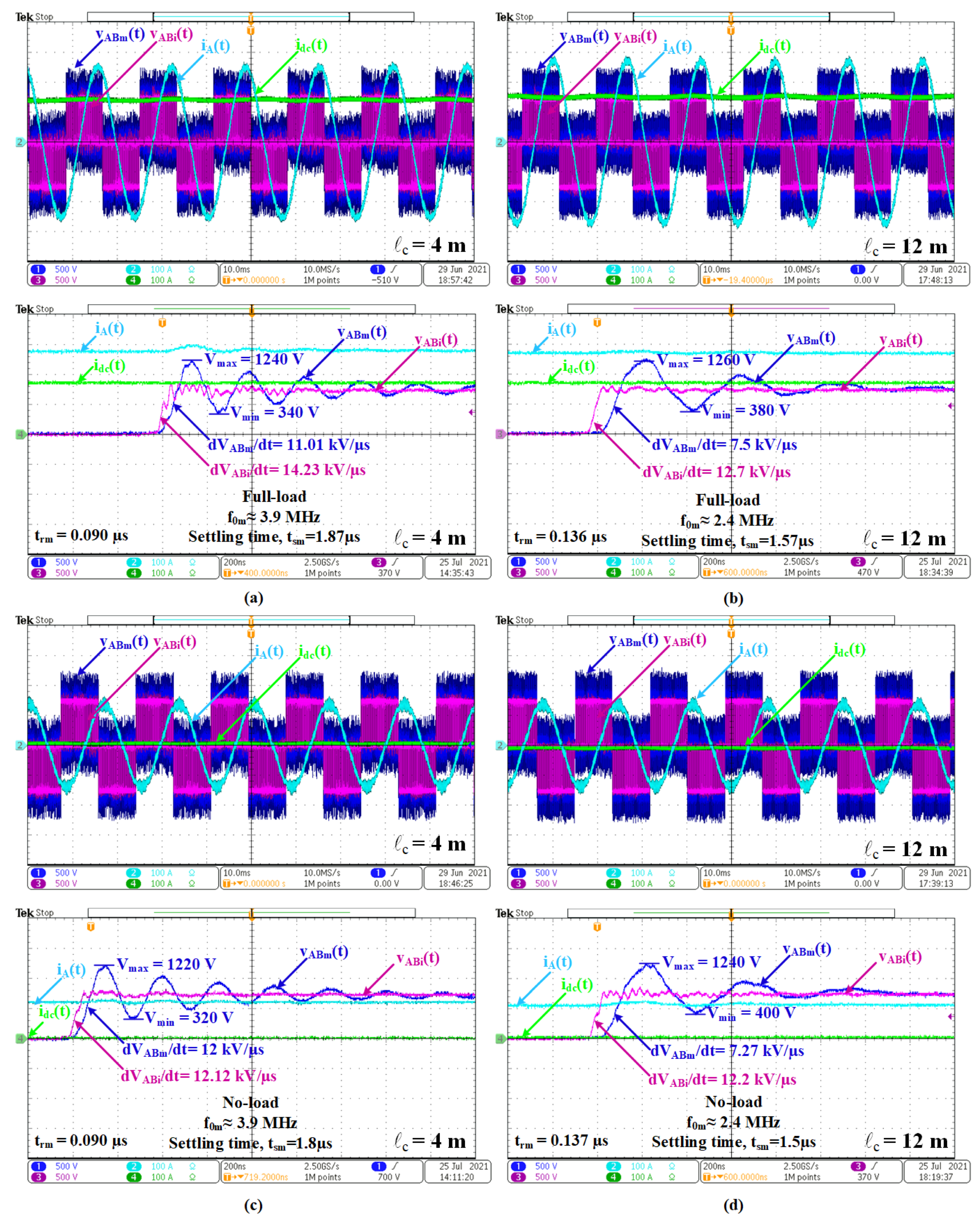
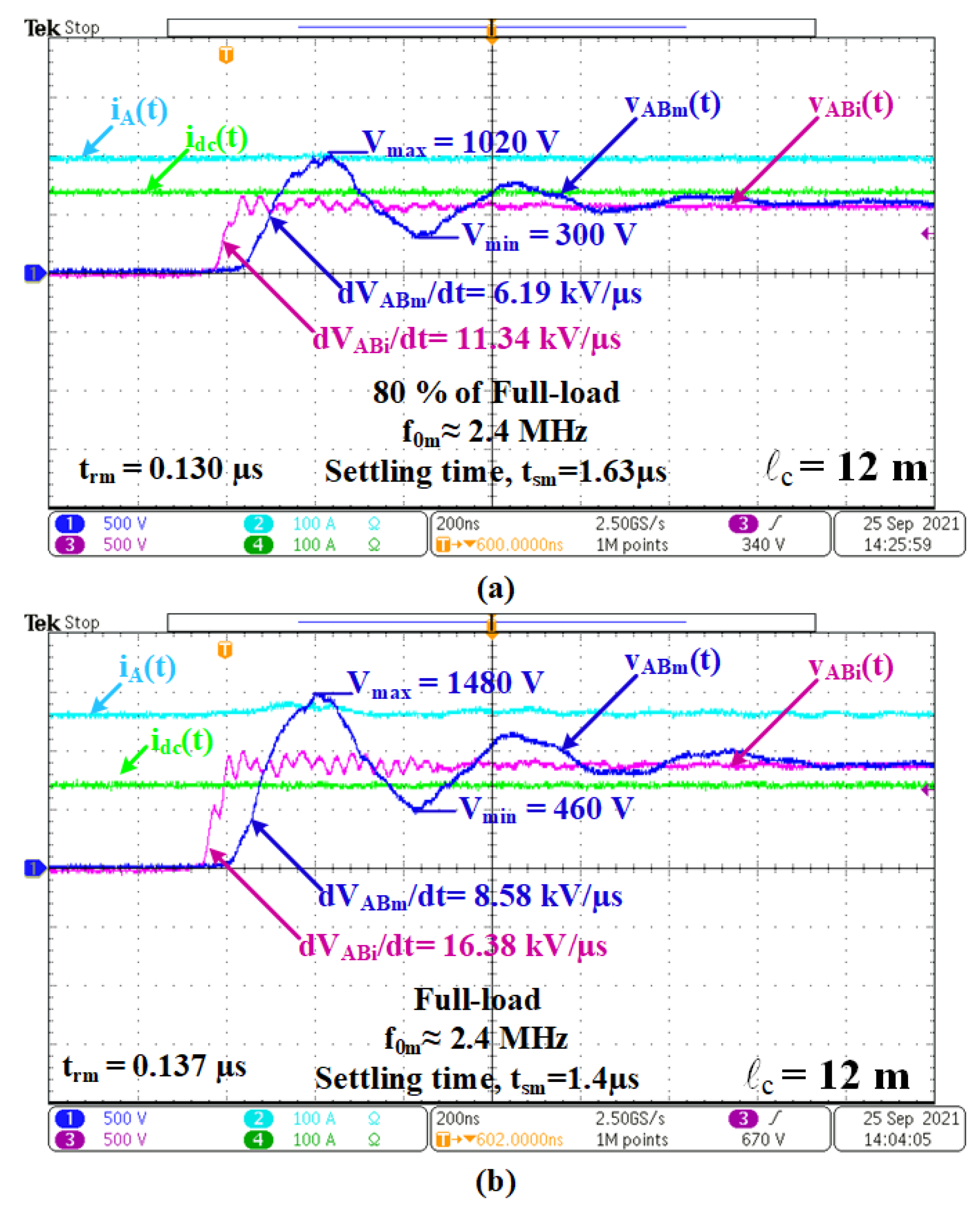
5.4. Switching Waveforms
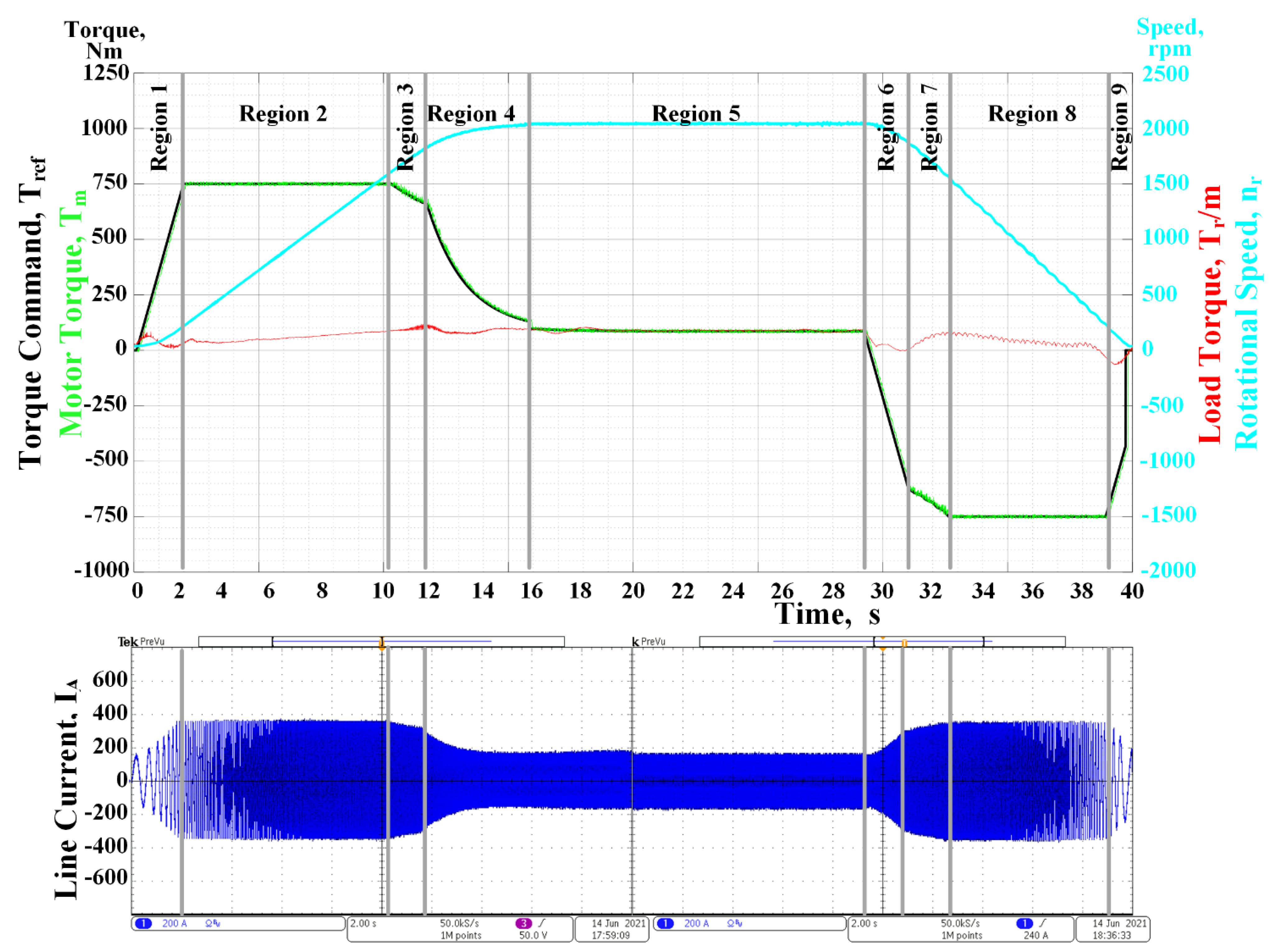
5.5. Dynamic Operation in Real Rail Track Conditions
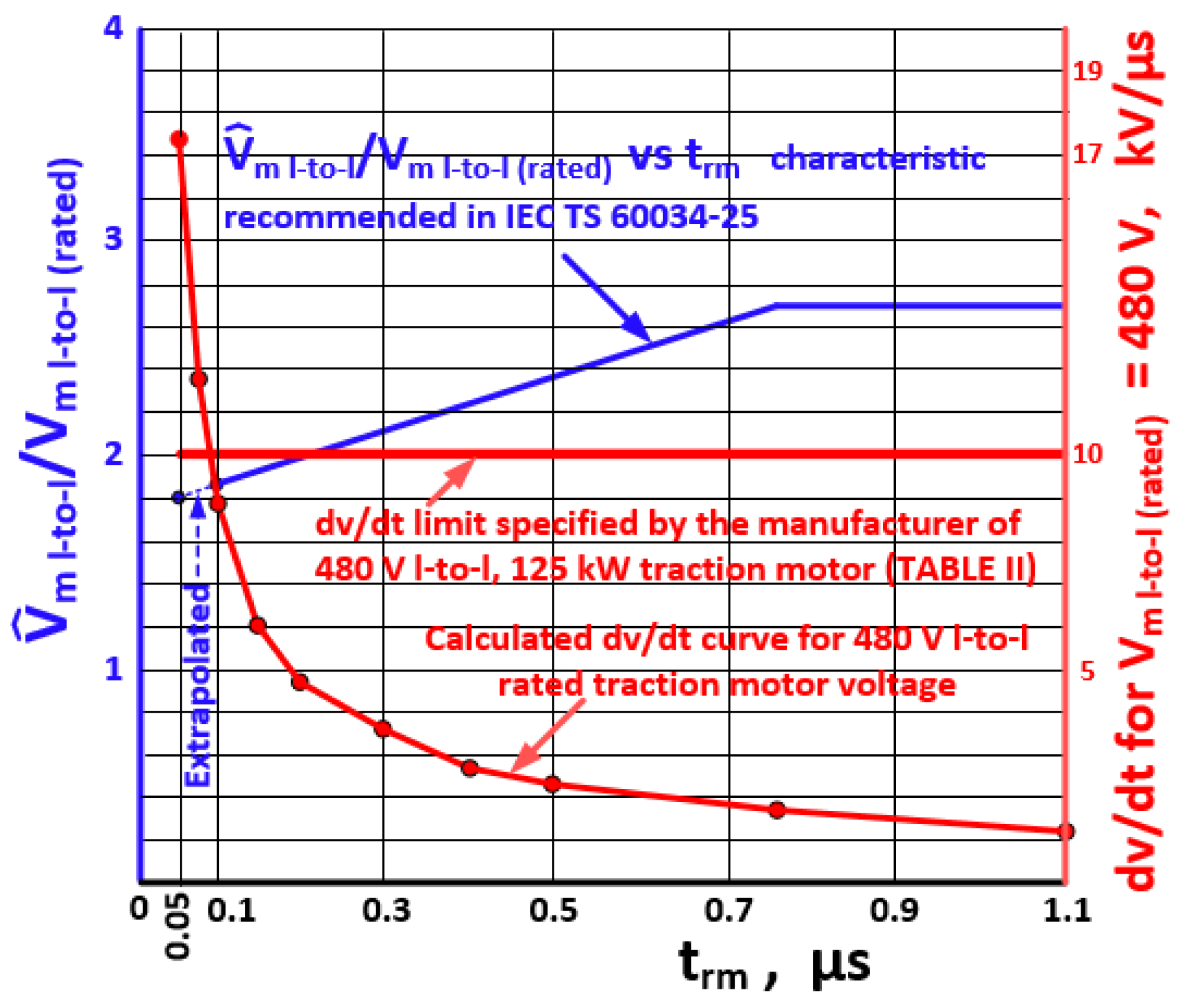
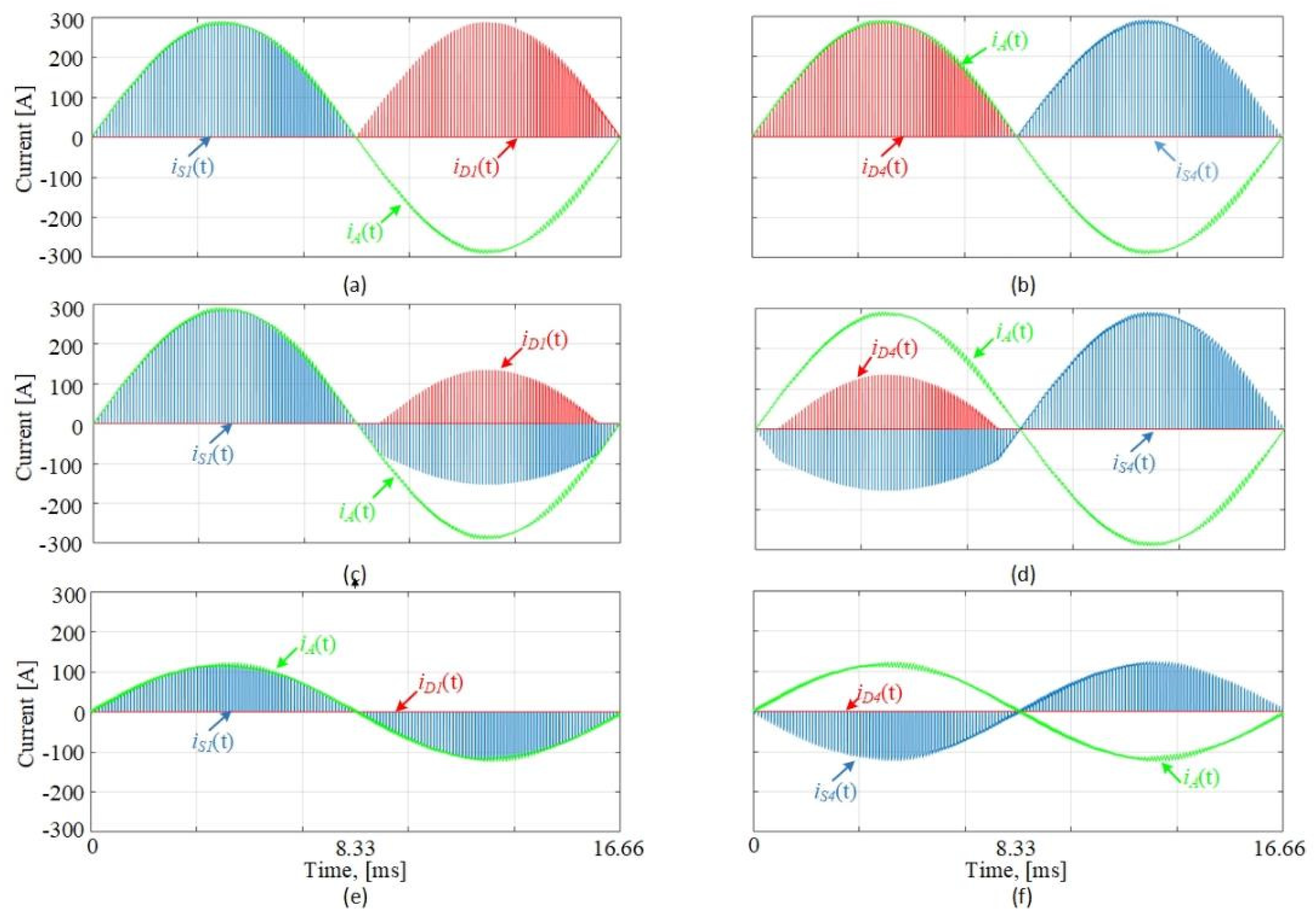
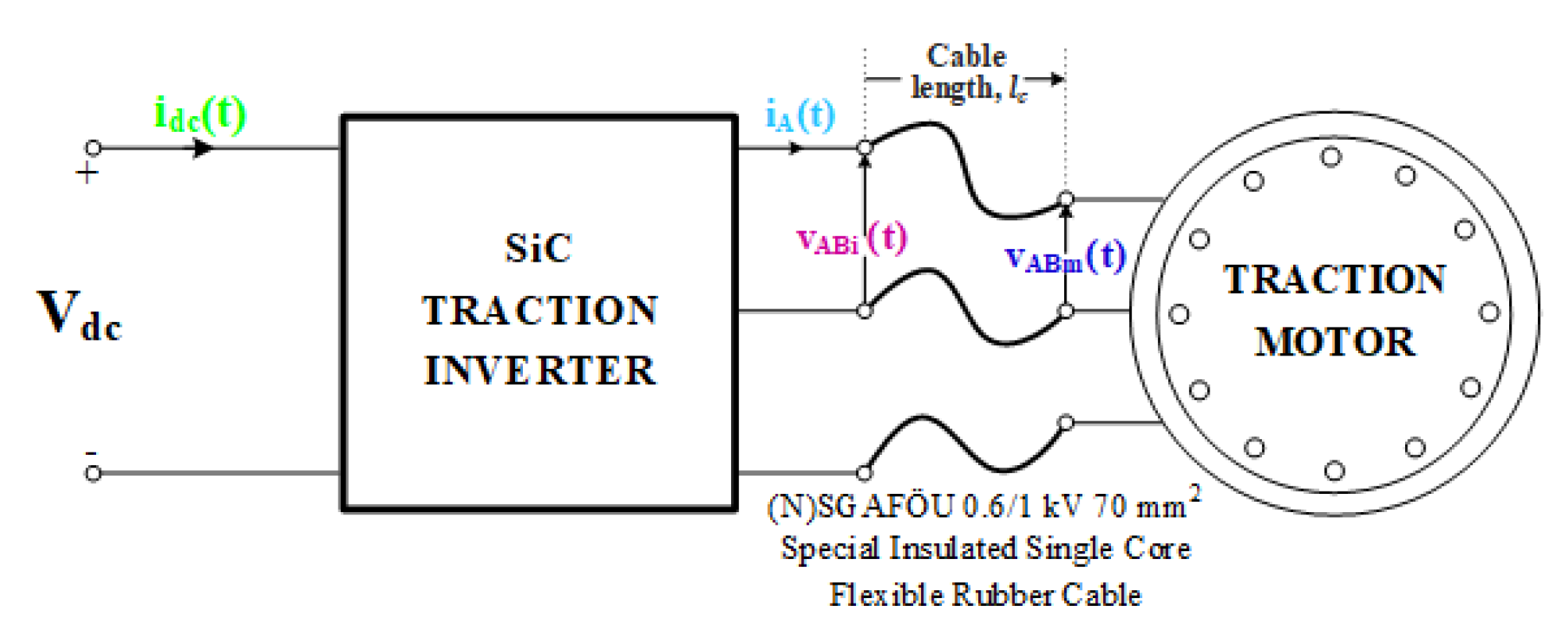
6. Effects of SiC Power MOSFET Operation on Traction Motor
- (i)
- The motor line currents are nearly sinusoidal, e.g., iA(t);
- (ii)
- Although the fundamental components VAbi = VABm 480 V l-to-l rms, the first peak of VABi(t) 780–810 is enhanced to VABm = 1240 V for lc = 4 and 1260 V for lc = 12 m;
- (iii)
- The frequency of oscillation in the line-to-line voltage waveform is lower for longer cables with a shorter settling time;
- (iv)
- The dv/dt of each pulse in the line-to-line PWM voltage waveform at the output of the inverter is usually higher than 10 kV/µs. The cables connecting the inverter to the motor lower these high dv/dts usually to below 10 kV/µs;
- (v)
- Similar conclusions can also be drawn for no-load operations;
- (vi)
- For the application described in this paper, a cable length of around 12 m is more useful than shorter cables, such as 4 m in length.
- (a)
- Insulation systems may be enhanced in future traction motors for use with SiC power MOSFET-based traction converters at the expense of a higher cost; and/or
- (b)
7. Conclusions and Future Work
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

Appendix B
Appendix C
| Thermal Data All in K/W | Si IGBT Module (FF300R17KE4P) Infineon | Si IGBT Module (CM300DY-34T) Mitsubishi | Si IGBT & SiC SBD Hybrid Module (2MSI400VAE-170-53) Fuji Electric | SiC MOSFET Module (CAS300M17BM2) Wolfspeed/Cree | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGBT | Diode | IGBT | Diode | IGBT | Diode | MOSFET | Diode | |
| Rth(j-c) | - | - | 0.044 | 0.068 | 0.033 | 0.07 | 0.071 | 0.065 |
| Rth(c-h) | - | - | 0.0313 | 0.0313 | 0.0313 | |||
| Rth(j-h) | 0.114 | 0.117 | - | - | - | - | ||
| Rth(h-a) 0 | 0.018 * | 0.018 * | 0.018 * | 0.018 * | ||||
| Rth(h-a) ‡ | 0.013 † | 0.013 † | 0.013 † | 0.018 * | ||||
Appendix D
References
- Makishima, S.; Fujimoto, K.; Kondo, K. The Direct Benefit of SiC Power Semiconductor Devices for Railway Vehicle Traction Inverters. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2018 International Power Electronics Conference (IPEC-Niigata 2018-ECCE Asia), Niigata, Japan, 20–24 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Elasser, A.; Chow, T.P. Silicon Carbide Benefits and Advantages for Power Electronics Circuits and Systems. Proc. IEEE 2002, 90, 969–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Lin, X.; Ravi, L.; Yan, N.; Burgos, R. Advancement of SiC High-frequency Power Conversion Systems for Medium-Voltage High-Power Applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 9th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC2020-ECCE Asia), Nanjing, China, 29 November–2 December 2020; pp. 717–724. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, M.; Ilves, K. On the comparative assessment of 1.7 kV, 300 a full SiC-MOSFET and Si-IGBT power modules. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, 20–24 March 2016; pp. 276–282. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, S.; She, X.; Datta, R.; Todorovic, M.H.; Mandrusiak, G. Comparison of 1.7 kV, 450 A SiC-MOSFET and Si-IGBT based modular three phase power block. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1–5 October 2017; pp. 5119–5125. [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi, M.; Hasegawa, S.; Sumitani, H.; Iwasaki, M.; Hino, S.; Watanabe, T.; Hamada, K.; Miura, N.; Nakata, S.; Yamakawa, S. Remarkable Advances in SiC Power Device Technology for Ultra High Power Systems. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 9–11 December 2013; pp. 6.5.1–6.5.4. [Google Scholar]
- Morya, A.K.; Gardner, M.C.; Anvari, B.; Liu, L.; Yepes, A.G.; Doval-Gandoy, J.; Toliyat, H.A. Wide Bandgap Devices in AC Electric Drives: Opportunities and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2019, 5, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Wang, X.; Deng, Z. Evaluation of Three Improved Space-Vector-Modulation Strategies for the High-Speed Permanent Magnet Motor Fed by a SiC/Si Hybrid Inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 4399–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, J.; Ladoux, P.; Piton, M. Characterization and Implementation of Dual-SiC MOSFET Modules for Future Use in Traction Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 4079–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaertner, M.; Cavallaro, D.; Pulvirenti, M.; Zanetti, E.; Saggio, M.; Ferrara, M. SiC MOSFETs as Enabler for the future ePowertrain and its behaviour under Short Circuit Condition. In Proceedings of the 2019 AEIT International Conference of Electrical and Electronic Technologies for Automotive (AEIT AUTOMOTIVE), Turin, Italy, 2–4 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Srdic, S.; Lukic, S.; Kang, Y.; Choi, E.; Tafti, E. A SiC-Based 100 kW High-Power-Density (34 kW/L) Electric Vehicle Traction Inverter. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Portland, OR, USA, 23–27 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Kim, H.; Chen, H.; Erickson, R.; Maksimovic, D. High Efficiency SiC Traction Inverter for Electric Vehicle Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), San Antonio, TX, USA, 4–8 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Mahmud, M.H.; Allee, E.; Zhao, Y.; Mantooth, A. An Optimized Silicon Carbide based 2 × 250 kW Dual Inverter for Traction Applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), New Orleans, LA, USA, 15–19 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bucher, A.; Schmidt, R.; Werner, R.; Leipenat, M.; Hasenohr, C.; Werner, T.; Schmitz, S.; Heitmann, A. Design of a Full SiC Voltage Source Inverter for Electric Vehicle Applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 18th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’16 ECCE Europe), Karlsruhe, Germany, 5–9 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z. A 100 kW Forced-Air-Cooled SiC MOSFET Converter Achieving a Power Density of 1.657 kW/L and an Efficiency over 98.5%. In Proceedings of the IEEE 9th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC2020-ECCE Asia), Nanjing, China, 29 November–2 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- She, X.; Datta, R.; Todorovic, M.H.; Mandrusiak, G.; Dai, J.; Frangieh, T.; Cioffi, P.; Rowden, B.; Mueller, F. High Performance Silicon Carbide Power Block for Industry Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 3738–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, R.S.K.; Aberg, B.; Olimmah, M.; Yang, L.; Rahman, D.; Lemmon, A.N.; Yu, W.; Husain, I. Estimation, Minimization, and Validation of Commutation Loop Inductance for a 135-kW SiC EV Traction Inverter. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 8, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, W.; Kempitiya, A.; Vodyakho, O. Reduction of Power Losses of SiC MOSFET Based Power Modules in Automotive Traction Inverter Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Luo, Y.; Moorthy, R.S.K.; Rahman, D.; Yu, W.; Husain, I. Design and Test of a Planarized High Power Density 100 kW SiC Traction Inverter with 1kV DC-Link. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Portland, OR, USA, 23–27 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Wang, W. The Potential Impact of Using Traction Inverters with SiC MOSFETs for Electric Buses. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 51561–51572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, T.E.; Wood, R.A. 1000-H Evaluation of a 1200-V, 880-A All-SiC Dual Module. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 2192–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladoux, P.; Mermet, M.; Casarin, J.; Fabre, J. Outlook for SiC devices in Traction Converters. In Proceedings of the 2012 Electrical Systems for Aircraft, Railway and Ship Propulsion, Bologna, Italy, 16–18 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Chang, G.; Gong, W.; Packwood, M.; Pottage, D.; Wang, Y.; Luo, H.; Liu, G. High-Voltage Hybrid IGBT Power Modules for Miniaturization of Rolling Stock Traction Inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 1266–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltau, N.; Wiesner, E.; Stumpf, E.; Idaka, S.; Hatori, K. Electric-Energy Savings using 3.3 kV Full-SiC Power-Modules in Traction Applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 15th International Conference on Ecological Vehicles and Renewable Energies (EVER), Monte-Carlo, Monaco, 10–12 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yıldırım, D.; Akşit, M.H.; Yolaçan, C.; Pul, T.; Ermiş, C.; Aghdam, B.H.; Çadırcı, I.; Ermiş, M. Full-Scale Physical Simulator of All SiC Traction Motor Drive with Onboard Supercapacitor ESS for Light-Rail Public Transportation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 6290–6301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Kato, H.; Fukushima, T. Development of SiC Applied Traction System for Shinkansen High-speed Train. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Power Electronics Conference (IPEC-Niigata 2018-ECCE Asia), Niigata, Japan, 20–24 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Li, X.; Chang, G.; Qi, F.; Packwood, M.; Pottage, D.; Wang, Y.; Luo, H.; Dai, X.; Liu, G. Characterization of a 3.3-kV Si-SiC Hybrid Power Module in Half-Bridge Topology for Traction Inverter Application. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 13429–13440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Liu, Q.; Dinavahi, V.R. Real-Time Hardware-in-the-Loop Emulation of High-Speed Rail Power System with SiC-Based Energy Conversion. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 122348–122359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Wenqing, M.; YuLiang, W.; Yongcan, L.; Xiangyu, F.; Yan, J. Experimental Study of the PWM Control Strategy For SiC Traction Inverter of Metro Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Gijon, Spain, 18 November–16 December 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Merkert, A.; Krone, T.; Mertens, A. Characterization and Scalable Modeling of Power Semiconductors for Optimized Design of Traction Inverters with Si- and SiC-Devices. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 2238–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Li, W.; He, X. Comprehensive Comparison between Two-Level, Three-Level, and Hybrid Three-Level SiC Inverter for High Power High Speed Drive System. In Proceedings of the IEEE 9th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC2020-ECCE Asia), Nanjing, China, 29 November–2 December 2020; pp. 1884–1889. [Google Scholar]
- European Standard BS EN 50163; Railway Applications-Supply Voltages of Traction Systems. European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization: Brussel, Belgium, 2004.
- Mohan, N.; Undeland, T.M.; Robbins, W.P. Power Electronics: Converters, Applications, and Design; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, A.P.; Holmes, D.G. Pulse Width Modulation for Power Converters; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Infineon AN2019-05. Available online: https://www.infineon.com/dgdl/Infineon-AN2019-05_PC_and_TC_Diagrams-ApplicationNotes-v02_01-EN.pdf?fileId=5546d46269e1c019016a594443e4396b (accessed on 26 March 2022).
- Comparison Between Ce Alloys and Competitive Materials. Available online: https://www.materials.sandvik/da-dk/produkter/ce-alloys/comparsion-with-competitive-materials/ (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- BS EN 50388; Railway Applications-Power Supply and Rolling Stock—Technical Criteria for the Coordination between Power Supply (Substation) and Rolling Stock to Achieve Interoperability. ISO: London, UK, 2012.
- Buhrkall, L. Traction System Case Study, Traction Systems and EMC, Denmark. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4760166/authors#authors (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- Youssef, M.; Abu-Qahouq, J.; Orabi, M. The electromagnetic compatibility design considerations of the input filter of a 3-phase inverter in a railway traction system. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Atlanta, GA, USA, 12–16 December 2010; pp. 4210–4216. [Google Scholar]
- Abad, G. Power Electronics and Electric Drives for Traction Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Chichester, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Apparatus, European Standard EN50121-3-2; Railway Applications—Electromagnetic Compatibility Rolling Stock. European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization: Brussel, Belgium, 2015.
- European Standard IEC TS 60034-25; Rotating Electrical Machines—Part 25: Guidance for the Design and Performance of a.c. Motors Specifically Designed for Converter Supply. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- Wei, Y.; Du, X.; Woldegiorgis, D.; Mantooth, A. Application of An Active Gate Driver for Paralleling Operation of Si IGBT and SiC MOSFET. In Proceedings of the IEEE 12th Energy Conversion Congress & Exposition—Asia (ECCE-Asia), Singapore, 24–27 May 2021; pp. 314–319. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, W.J.; Liang, J.; Cui, W.T.; Ng, W.T.; Nishio, H.; Sumida, H.; Nakajima, H. A Smart Gate Driver for SiC Power MOSFETs with Aging Compensation and Ringing Suppression. In Proceedings of the 2021 33rd International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices and ICs (ISPSD), Nagoya, Japan, 30 May–3 June 2021; pp. 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Yao, W. An Active Gate Driver Design to Reduce Voltage and Current Overshoots for SiC MOSFET Modules. In Proceedings of the IEEE 9th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC2020-ECCE Asia), Nanjing, China, 29 November–2 December 2020; pp. 915–920. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Ortiz-Gonzalez, J.; Alatise, O.; Pickert, V. Investigation into the Switching Transient of SiC MOSFET Using Voltage/Current Source Gate Driver. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives (PEMD 2020), Online Conference, 15–17 December 2020; pp. 657–662. [Google Scholar]
- European Standard BS EN 60034-18-41; Rotating Electrical Machines Partial Discharge Free Electrical Insulation Systems (Type I) Used in Electrical Rotating Machines Fed from Voltage Converters. Qualification and Quality Control Tests. European Committee for Standards: Brussel, Belgium, 2019.



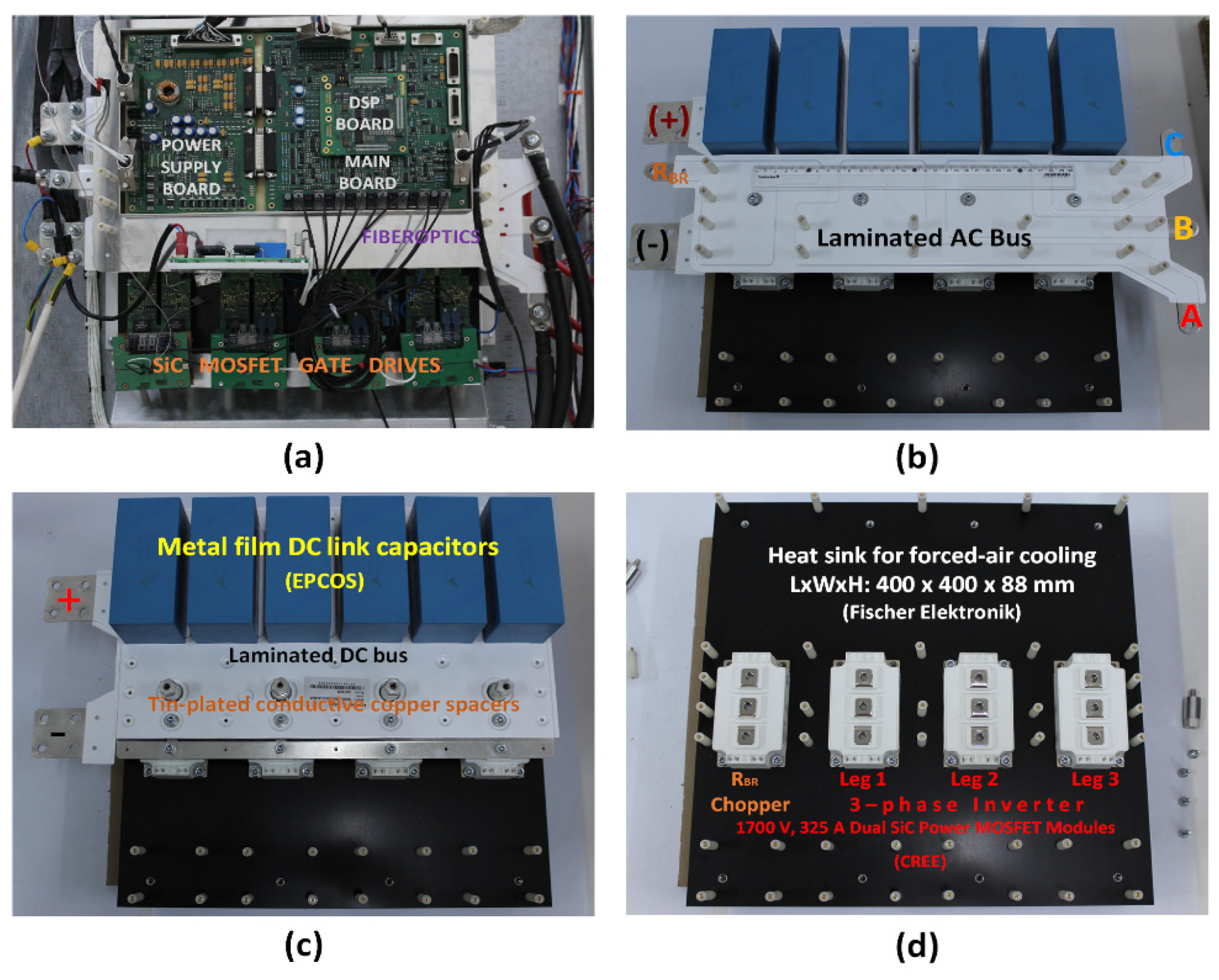

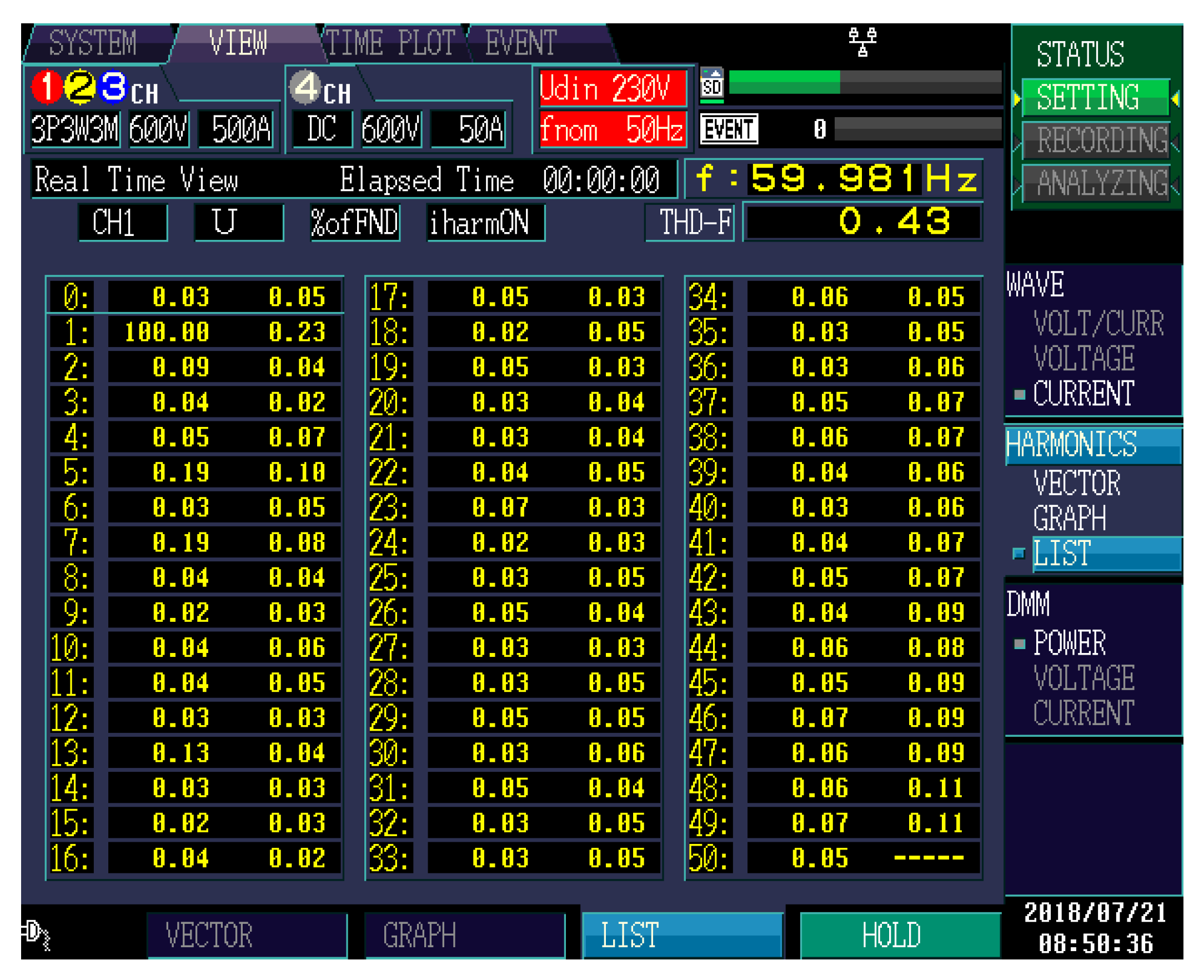


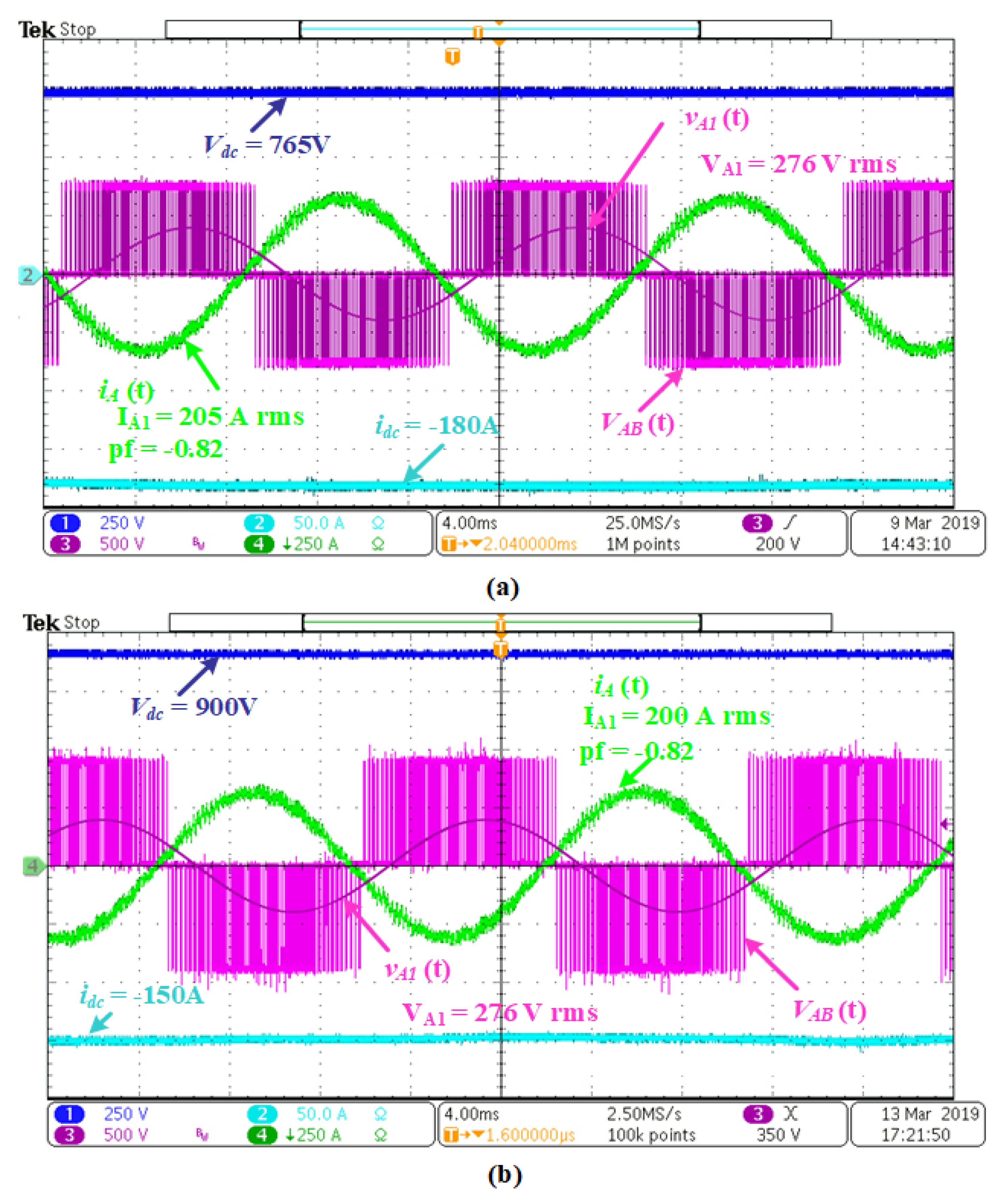
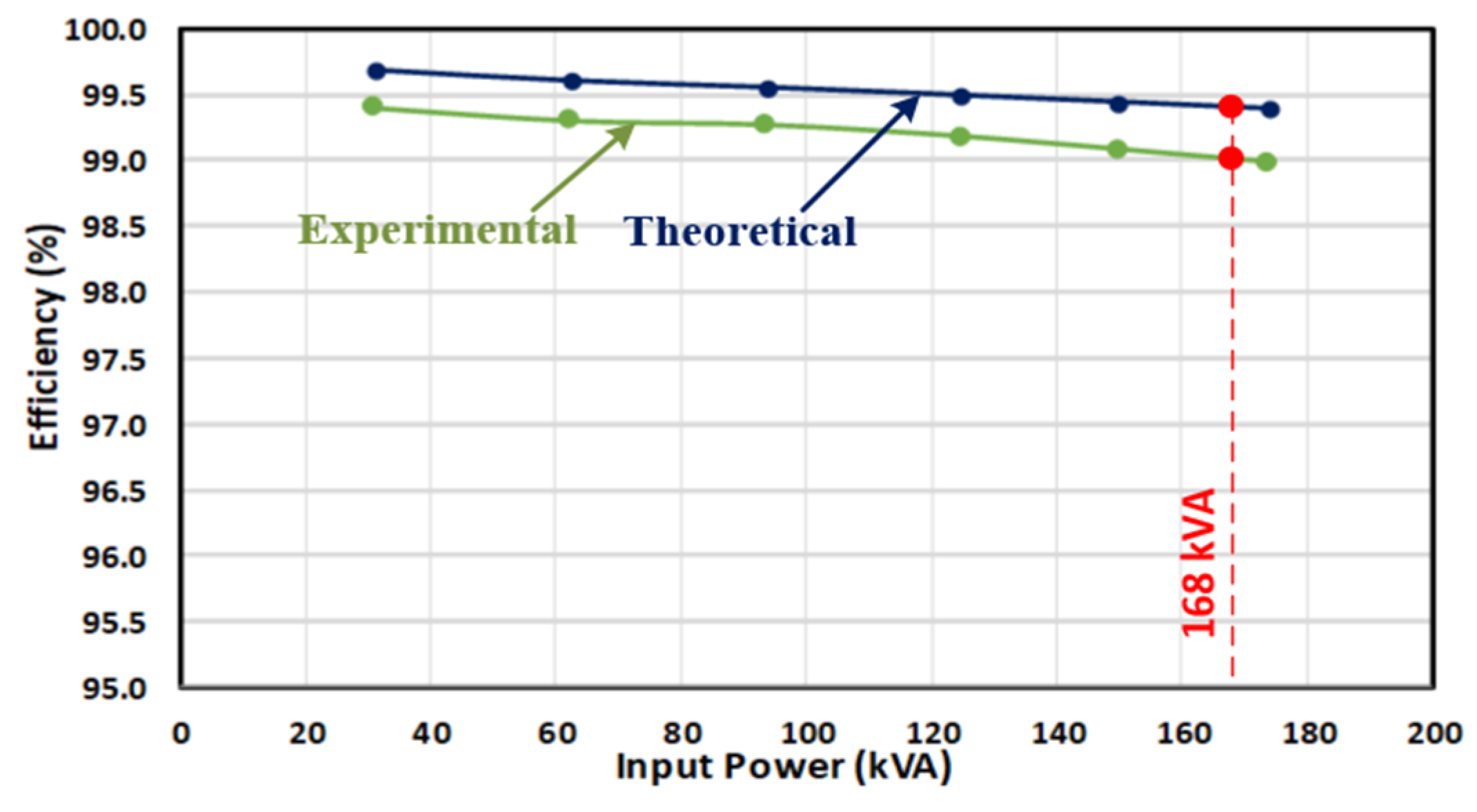
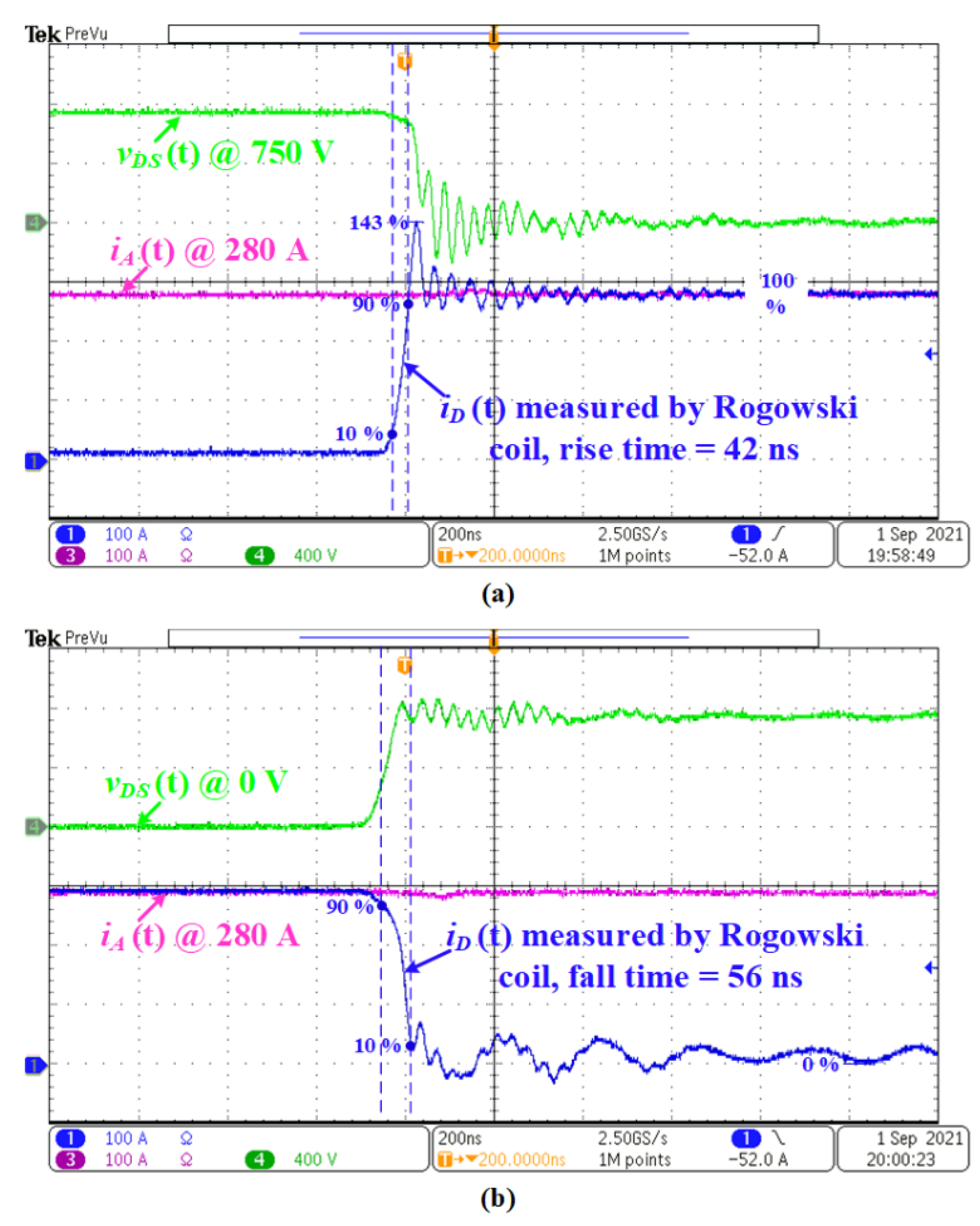
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Vehicle body structure | 5 Cars, M + T + T + T + M |
| Number of traction motors, m | 4 |
| New wheel radius, r | 300 mm |
| Gear ratio, n | 7.5 |
| Maximum slope | 8.5% |
| Maximum speed | 50 km/h |
| Acceleration up to 35 km/h | 1.2 m/s2 max. |
| Deceleration from 50 km/h | 1.3 m/s2 max. |
| Jerk limit | 1.0 m/s3 |
| Vehicle mass, M | 39 tons unloaded (AW0) 56 tons loaded (AW3) 58 tons fully loaded (AW4) |
| Jgb+Jw | 182 kg-m2 |
| A B C D Curve radius, R | 0.0405 m/s2 0.0023 s−1 3.81 kg/m 0.053 m 30 m (Minimum) |
| 4-Pole, 60 Hz, 475 V, 125 kW, 0.81 pf (S1), η = 93.5% | |
| Rated Torque | 671 Nm | |
| Rated Speed | 1779 rpm | |
| Max. Torque | 940 Nm | |
| Max. Speed Jm | 5100 rpm 0.67 kg-m2 | |
| Average Torque | 500 Nm |
| Average Speed | 1500 rpm | |
| Average Power | 80 kW | |
| Max. Torque | 943 Nm | |
| Max. Speed | 2250 rpm | |
| Max. Power | 128 kW | |
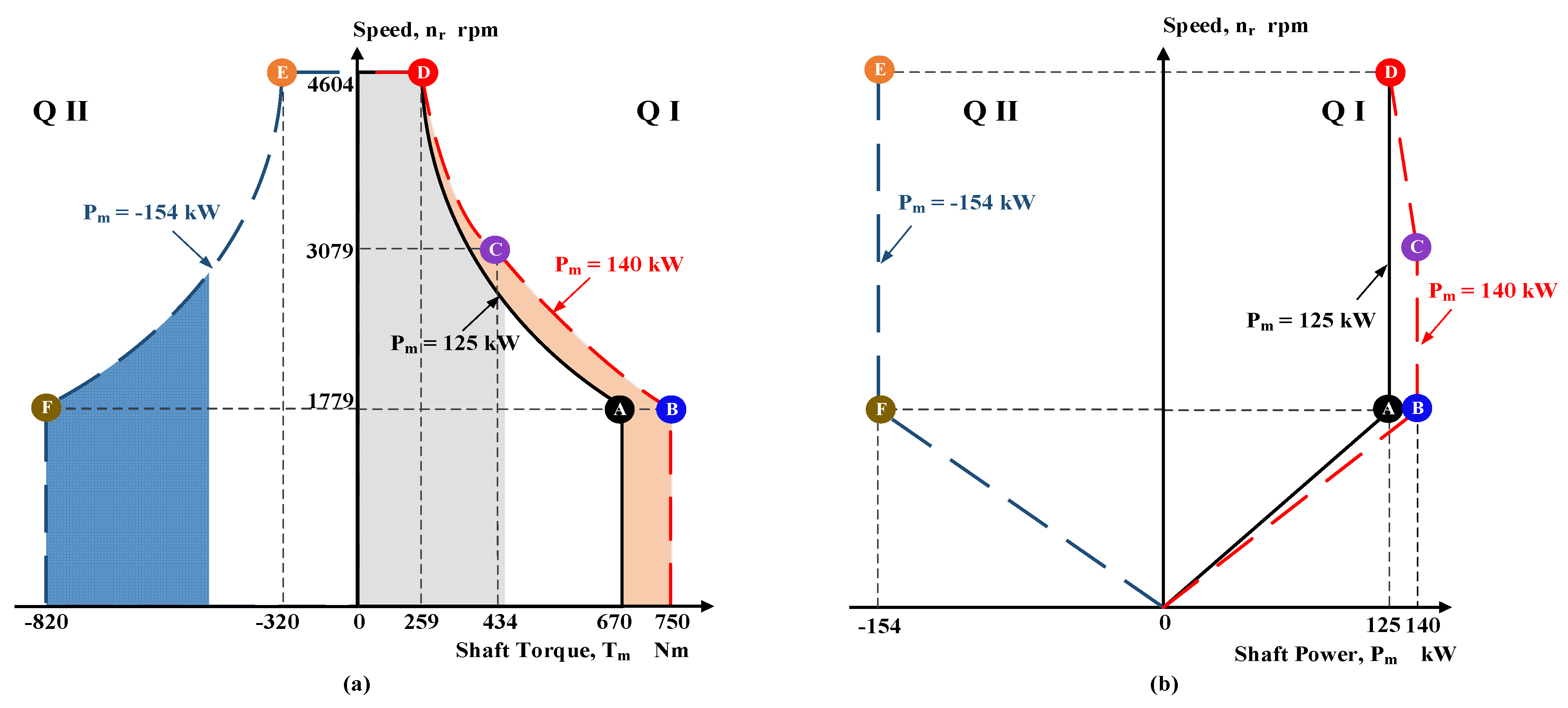
| Operating Points in Figure 2 | Stator Freq. (Hz) | Shaft Speed (rpm) | Converter Output Power (kVA) | Stator Voltage V l-to-l | Motor Output Power (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 60 | 1779 | 165 at 0.81 pf lag | 480 | 125 |
| B | 60 | 1774 | 185 at 0.81 pf lag | 140 | |
| C | 104 | 3079 | 170 at 0.89 pf lag | 140 | |
| D | 155 | 4604 | 154 at 0.88 pf lag | 125 | |
| E | 155 | 4604 | 176 at 0.81 pf lag | 154 | |
| F | 58 | 1779 | 172 at 0.83 pf lag | 154 |
| Stator Frequency, fS (Hz) | Carrier Frequency, fC (Hz) | |
|---|---|---|
| Adjustable | Constant | |
| 10 | 1260 | 3255 |
| 30 | 1260 | 3255 |
| 60 | 1260 | 3255 |
| 100 | 2100 | 3255 |
| 155 | 3255 | 3255 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yıldırım, D.; Akşit, M.H.; Çadırcı, I.; Ermiş, M. All-SiC Traction Converter for Light Rail Transportation Systems: Design Methodology and Development of 165 kVA Prototype. Electronics 2022, 11, 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11091438
Yıldırım D, Akşit MH, Çadırcı I, Ermiş M. All-SiC Traction Converter for Light Rail Transportation Systems: Design Methodology and Development of 165 kVA Prototype. Electronics. 2022; 11(9):1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11091438
Chicago/Turabian StyleYıldırım, Doğan, Mehmet Hakan Akşit, Işık Çadırcı, and Muammer Ermiş. 2022. "All-SiC Traction Converter for Light Rail Transportation Systems: Design Methodology and Development of 165 kVA Prototype" Electronics 11, no. 9: 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11091438
APA StyleYıldırım, D., Akşit, M. H., Çadırcı, I., & Ermiş, M. (2022). All-SiC Traction Converter for Light Rail Transportation Systems: Design Methodology and Development of 165 kVA Prototype. Electronics, 11(9), 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11091438