A Brief Analysis of Multimodal Medical Image Fusion Techniques
Abstract
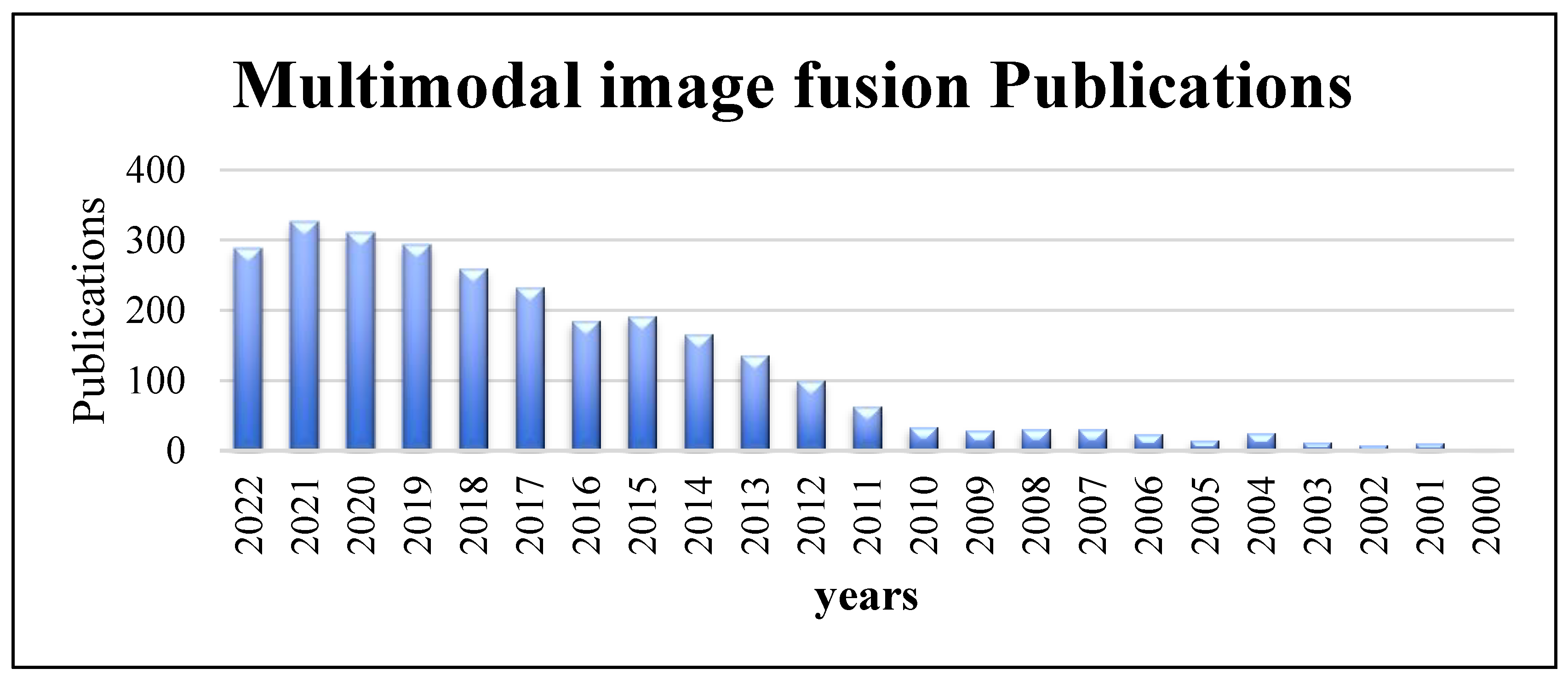
:1. Introduction
2. Medical Imaging Modalities
2.1. Structural Systems
2.1.1. Magnetic Resonance Image (MRI)
2.1.2. Computed Tomography (CT)
2.1.3. X-rays
2.1.4. Ultrasound (US)
2.2. Functional Systems
2.2.1. Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
2.2.2. Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT)
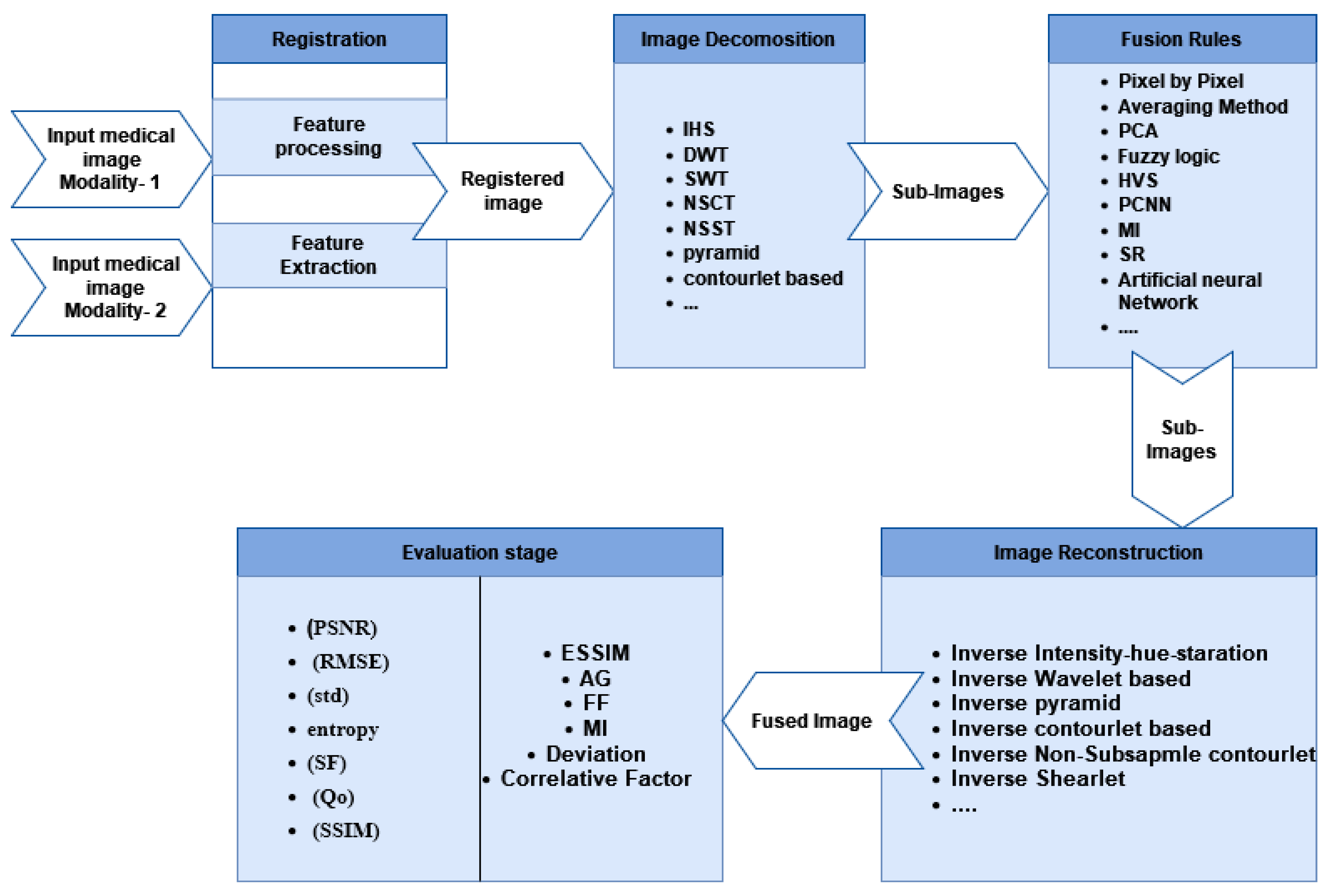
3. Fusion Steps
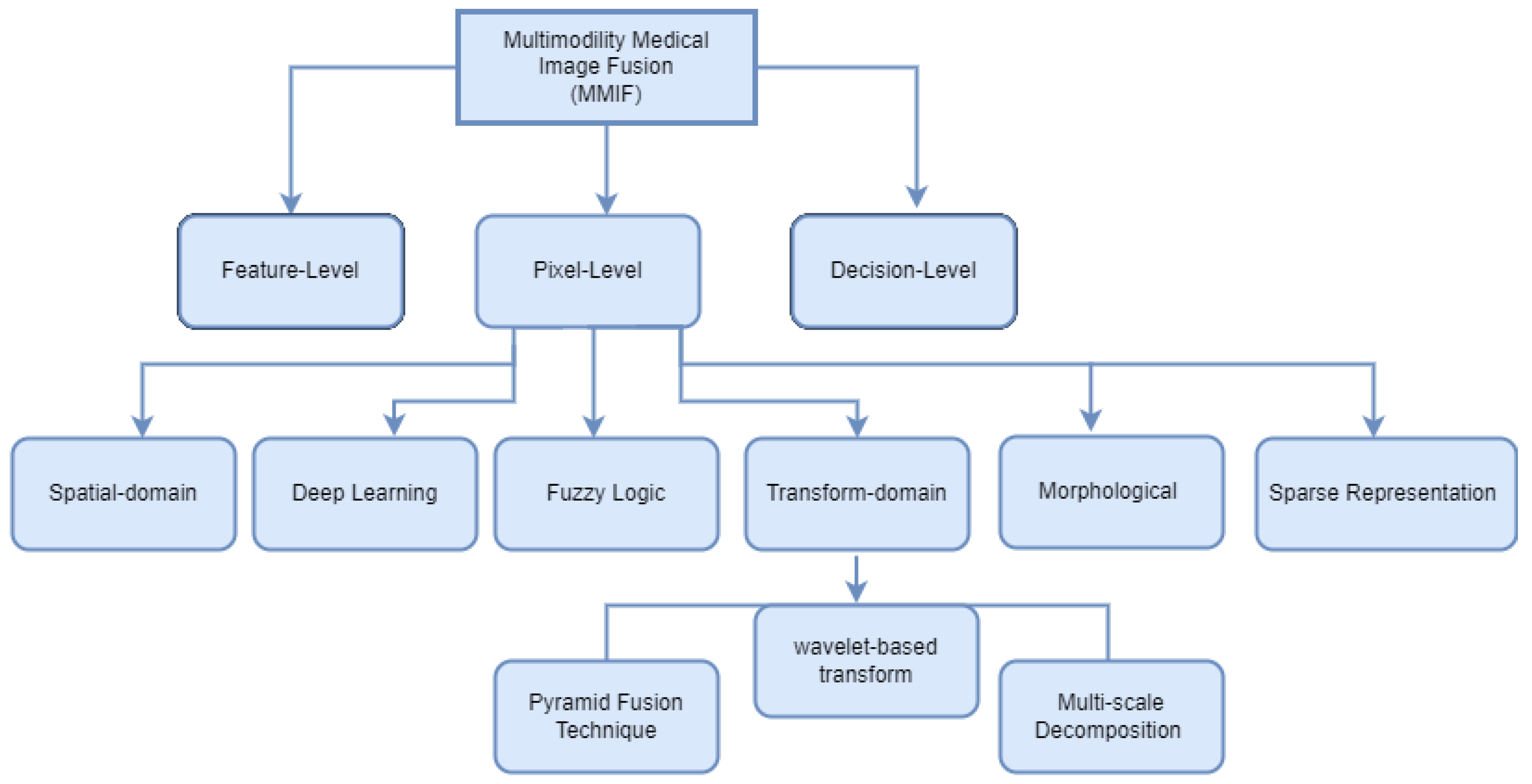
4. MMIF Levels
4.1. Pixel-Level Fusion
4.2. Feature-Level Fusion
4.3. Decision-Level Fusion (Dictionary)
5. Image Fusion Techniques
5.1. Spatial Domain Fusion Techniques
5.2. Transform Fusion Techniques (Multi-Scale Decomposition Methods)
5.2.1. Non-Subsampled Contourlet Transform (NSCT)
5.2.2. Pulse-Coupled Neural Network (PCNN)
5.2.3. Non-Subsampled Shearlet Transform (NSST)
5.3. Fuzzy-Logic-Based Methods
5.4. Morphological Methods
5.5. Sparse Representation Methods
5.6. Deep Learning Fusion Methods
6. Evaluation Metrics
6.1. Metrics Requiring a Reference Image
6.1.1. Root Mean Square Error Ratio (RMSE)
6.1.2. Mutual Information (MI)
6.1.3. Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM)
6.1.4. Correlation Coefficient (CC)
6.1.5. Universal Quality Index (UQI)
6.1.6. Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR)
6.2. Metrics Requiring a Reference Image
6.2.1. Standard Deviation (SD)
6.2.2. Entropy (EN)
6.2.3. Spatial Frequency (SF)
6.2.4. Gradient-Based Index (QAB/F)
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blum, R.S.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, Z. An Overview of lmage Fusion. In Multi-Sensor Image Fusion and Its Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Vajgl, M.; Perfilieva, I.; Hod’áková, P. Advanced f-transform-based image fusion. Adv. Fuzzy Syst. 2012, 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tawfik, N.; Elnemr, H.A.; Fakhr, M.; Dessouky, M.I.; El-Samie, A.; Fathi, E. Survey study of multimodality medical image fusion methods. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 6369–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganasala, P.; Kumar, V. Feature-motivated simplified adaptive PCNN-based medical image fusion algorithm in NSST domain. J. Digit. Imaging 2016, 29, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- PubMed. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Venkatrao, P.H.; Damodar, S.S. HWFusion: Holoentropy and SP-Whale optimisation-based fusion model for magnetic resonance imaging multimodal image fusion. IET Image Process. 2018, 12, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, D. Multi-modality medical image fusion technique using multi-objective differential evolution based deep neural networks. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 2483–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.P.; Dasarathy, B.V. Medical image fusion: A survey of the state of the art. Inf. Fusion 2014, 19, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhat, S.; Koundal, D. Multi-focus image fusion techniques: A survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 5735–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yu, L.; Zhi, C.; Huang, C.; Wang, S.; Zhu, M.; Ke, Z.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, S. A Survey of Multi-Focus Image Fusion Methods. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xian, Y.; Zhang, D.; Su, J.; Hu, X.; Guo, W. Multi-sensor image fusion: A survey of the state of the art. J. Comput. Commun. 2021, 9, 73–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Xu, C.; Wang, C. A review of fusion methods of multi-spectral image. Optik 2015, 126, 4804–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkour, M.; Benhaddou, D.; Tao, C. Temporal data representation, normalization, extraction, and reasoning: A review from clinical domain. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 128, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghassemian, H. A review of remote sensing image fusion methods. Inf. Fusion 2016, 32, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, P.-H. Multi-modal medical image fusion based on equilibrium optimizer algorithm and local energy functions. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 8416–8431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Tian, X.; Jiang, J.; Ma, J. Image fusion meets deep learning: A survey and perspective. Inf. Fusion 2021, 76, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, J.; Gautam, N.; Tiwari, M.; Tiwari, T.; Suresh, A.; Sundararaj, V.; Rejeesh, M. An image quality enhancement scheme employing adolescent identity search algorithm in the NSST domain for multimodal medical image fusion. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 66, 102480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, B.; Agrawal, S.; Panda, R.; Abraham, A. A survey on region based image fusion methods. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MITA. Available online: https://www.medicalimaging.org/about-mita/modalities (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Bashir, R.; Junejo, R.; Qadri, N.N.; Fleury, M.; Qadri, M.Y. SWT and PCA image fusion methods for multi-modal imagery. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 1235–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermessi, H.; Mourali, O.; Zagrouba, E. Multimodal medical image fusion review: Theoretical background and recent advances. Signal Process. 2021, 183, 108036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, P.-H. A novel approach based on three-scale image decomposition and marine predators algorithm for multi-modal medical image fusion. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 67, 102536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Ma, W.; Jin, Y.; Xu, L. An image decomposition fusion method for medical images. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 4513183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, E. Optimum wavelet-based homomorphic medical image fusion using hybrid genetic–grey wolf optimization algorithm. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 6804–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Fang, L.; Hu, J.; Yin, H. Pixel-level image fusion: A survey of the state of the art. Inf. Fusion 2017, 33, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Wei, G.; Zongxi, S. Medical image fusion based on feature extraction and sparse representation. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2017, 2017, 3020461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, H. Multimodal medical image fusion based on IHS and PCA. Procedia Eng. 2010, 7, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Depoian, A.C.; Jaques, L.E.; Xie, D.; Bailey, C.P.; Guturu, P. Neural network image fusion with PCA preprocessing. In Proceedings of the Big Data III: Learning, Analytics, and Applications, Online Event, 12–16 April 2021; pp. 132–147. [Google Scholar]
- Rehal, M.; Goyal, A. Multimodal Image Fusion based on Hybrid of Hilbert Transform and Intensity Hue Saturation using Fuzzy System. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2021, 975, 8887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.A.; Khan, K.B.; Ahmad, M.; Mazzara, M. Multimodal medical image registration and fusion for quality Enhancement. CMC-Comput. Mater. Contin 2021, 68, 821–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chen, L.; Lu, L.; Ahmad, A.; Jeon, G.; Yang, X. Medical image fusion method by using Laplacian pyramid and convolutional sparse representation. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2020, 32, e5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zheng, M.; Qi, G.; Wang, D.; Xiang, Y. A phase congruency and local Laplacian energy based multi-modality medical image fusion method in NSCT domain. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 20811–20824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, C.; Chellamuthu, C.; Rajesh, R. Medical image fusion using combined discrete wavelet and ripplet transforms. Procedia Eng. 2012, 38, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osadchiy, A.; Kamenev, A.; Saharov, V.; Chernyi, S. Signal processing algorithm based on discrete wavelet transform. Designs 2021, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavana, V.; Krishnappa, H. Multi-modality medical image fusion using discrete wavelet transform. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 70, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaffery, Z.A.; Zaheeruddin; Singh, L. Computerised segmentation of suspicious lesions in the digital mammograms. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. Imaging Vis. 2017, 5, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; He, J.; Lv, Z. Medical image of PET/CT weighted fusion based on wavelet transform. In Proceedings of the 2008 2nd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai, China, 16–18 May 2008; pp. 2523–2525. [Google Scholar]
- Georgieva, V.; Petrov, P.; Zlatareva, D. Medical image processing based on multidimensional wavelet transforms-Advantages and trends. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Sofia, Bulgaria, 7–3 June 2022; p. 020001. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Fang, N.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, W.; Wang, H. Multi-modal Medical Image Fusion Based on Geometric Algebra Discrete Cosine Transform. Adv. Appl. Clifford Algebr. 2022, 32, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, M.N.; Vetterli, M. The contourlet transform: An efficient directional multiresolution image representation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2005, 14, 2091–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Peng, H.; Wang, J. A novel fusion method based on dynamic threshold neural P systems and nonsubsampled contourlet transform for multi-modality medical images. Signal Process. 2021, 178, 107793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lin, Q.; Wang, K.; Cai, K. Improving medical image fusion method using fuzzy entropy and nonsubsampling contourlet transform. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2021, 31, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alseelawi, N.; Hazim, H.T.; Salim ALRikabi, H.T. A Novel Method of Multimodal Medical Image Fusion Based on Hybrid Approach of NSCT and DTCWT. Int. J. Online Biomed. Eng. 2022, 18, 28011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, A.; Chen, Y. Medical image fusion based on sparse representation and PCNN in NSCT domain. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2018, 2018, 2806047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. A medical image fusion method based on SIST and adaptive PCNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 29th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Chongqing, China, 28–30 May 2017; pp. 5189–5194. [Google Scholar]
- Ouerghi, H.; Mourali, O.; Zagrouba, E. Non-subsampled shearlet transform based MRI and PET brain image fusion using simplified pulse coupled neural network and weight local features in YIQ colour space. IET Image Process. 2018, 12, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; He, K.; Xu, D. Medical Image Fusion Technology Based on Low-Rank Representation of Image Blocks and Pulse Coupled Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 7th International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), Xi’an, China, 26–28 June 2022; pp. 473–479. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xia, S. Image fusion of CT and MR with sparse representation in NSST domain. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2017, 2017, 9308745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X. Medical image fusion with parameter-adaptive pulse coupled neural network in nonsubsampled shearlet transform domain. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 68, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biswas, B.; Sen, B.K. Medical image fusion technique based on type-2 near fuzzy set. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Research in Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks (ICRCICN), Kolkata, India, 20–22 November 2015; pp. 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Bhattacharya, M. Evolutionary algorithm based automated medical image fusion technique: Comparative study with fuzzy fusion approach. In Proceedings of the 2009 World Congress on Nature & Biologically Inspired Computing (NaBIC), Coimbatore, India, 9–11 December 2009; pp. 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Kaur, A.; Amita. Improved image fusion of colored and grayscale medical images based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Inf. Eng. 2018, 10, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tirupal, T.; Mohan, B.C.; Kumar, S.S. Multimodal medical image fusion based on Sugeno’s intuitionistic fuzzy sets. ETRI J. 2017, 39, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirupal, T.; Chandra Mohan, B.; Srinivas Kumar, S. Multimodal medical image fusion based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets. In Machines, Mechanism and Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 965–971. [Google Scholar]
- Soille, P. Morphological Image Analysis: Principles and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X. Morphological image fusion using the extracted image regions and details based on multi-scale top-hat transform and toggle contrast operator. Digit. Signal Process. 2013, 23, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Jing, Z. Medical image fusion with a shift-invariant morphological wavelet. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Cybernetics and Intelligent Systems, Chengdu, China, 21–24 September 2008; pp. 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Chai, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z. A novel dictionary learning approach for multi-modality medical image fusion. Neurocomputing 2016, 214, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Feng, X.; He, G.; Wu, J.; Yan, K. Image fusion with nonsubsampled contourlet transform and sparse representation. J. Electron. Imaging 2013, 22, 043019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Huang, X.; Qi, G.; Zheng, M.; Zhu, Z. An image fusion method based on sparse representation and sum modified-Laplacian in NSCT domain. Entropy 2018, 20, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maqsood, S.; Javed, U. Multi-modal medical image fusion based on two-scale image decomposition and sparse representation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 57, 101810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Luo, L.; Mei, X.; Ma, J. Infrared and visible image fusion based on target-enhanced multiscale transform decomposition. Inf. Sci. 2020, 508, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanzade, F.; Ghassemian, H. Multimodal image fusion via sparse representation and clustering-based dictionary learning algorithm in nonsubsampled contourlet domain. In Proceedings of the 2016 8th International Symposium on Telecommunications (IST), Tehran, Iran, 27–28 September 2016; pp. 472–477. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Han, D.K.; Ko, H. Joint patch clustering-based dictionary learning for multimodal image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2016, 27, 198–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polinati, S.; Bavirisetti, D.P.; Rajesh, K.N.; Naik, G.R.; Dhuli, R. The Fusion of MRI and CT Medical Images Using Variational Mode Decomposition. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, G.; Zhao, A.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Guttag, J.; Dalca, A.V. VoxelMorph: A learning framework for deformable medical image registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 1788–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Modat, M.; Gibson, E.; Li, W.; Ghavami, N.; Bonmati, E.; Wang, G.; Bandula, S.; Moore, C.M.; Emberton, M. Weakly-supervised convolutional neural networks for multimodal image registration. Med. Image Anal. 2018, 49, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Kwitt, R.; Styner, M.; Niethammer, M. Quicksilver: Fast predictive image registration–a deep learning approach. NeuroImage 2017, 158, 378–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çiçek, Ö.; Abdulkadir, A.; Lienkamp, S.S.; Brox, T.; Ronneberger, O. 3D U-Net: Learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Athens, Greece, 17–21 October 2016; pp. 424–432. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O. Invited talk: U-net convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2017; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S.-A. V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Ruan, S.; Canu, S. A review: Deep learning for medical image segmentation using multi-modality fusion. Array 2019, 3, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.P.; Fatt, C.C.; Treacher, A.; Mellema, C.; Trivedi, M.H.; Montillo, A. Anatomically informed data augmentation for functional MRI with applications to deep learning. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2020: Image Processing, Houston, TX, USA, 15–20 February 2020; pp. 172–177. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J.; Peng, H. A medical image fusion method based on convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th International Conference on Information Fusion (Fusion), Xi’an, China, 10–13 July 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Rajalingam, B.; Priya, R. Multimodal medical image fusion based on deep learning neural network for clinical treatment analysis. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2018, 11, 160–176. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, K.-j.; Yin, H.-s.; Wang, J.-q. A novel improved deep convolutional neural network model for medical image fusion. Clust. Comput. 2019, 22, 1515–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zheng, M.; Wei, H.; Qi, G.; Li, Y. Multi-modality medical image fusion using convolutional neural network and contrast pyramid. Sensors 2020, 20, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Duan, H.; Su, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guan, X. Medical image fusion based on convolutional neural networks and non-subsampled contourlet transform. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 171, 114574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Lv, Z.; Li, J. Medical image fusion method by deep learning. Int. J. Cogn. Comput. Eng. 2021, 2, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskicioglu, A.M.; Fisher, P.S. Image quality measures and their performance. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1995, 43, 2959–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Medical Modalities | Invasive/Non-Invasive | Characteristics | Application | Resolution | Cost | Radiation Source and Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Magnetic Resonance Image (MRI) | Non-Invasive |
| Lung/Liver diagnosis and breast cancer assessment. | Higher resolution | Intermediate cost | electric and Magnetic Fields (Non-ionizing) |
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |||||
|
| |||||
Computed Tomography (CT) | Non-Invasive |
| Diagnosis of brain, head and neck cancer diagnosis and Tumor detection | High spatial resolution | Intermediate cost | X-rays (ionizing) |
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |||||
|
| |||||
X-rays | Non-Invasive |
| Widely used for breast cancer assessment | estimated spatial resolution | Low cost | X-rays (ionizing) |
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |||||
|
| |||||
Ultrasound (US) | Non-Invasive |
| The US is applicable on both anatomical and functional body organs such as (Prostate cancer, breast cancer, Liver tumor and Esophageal cancer) | High spatial resolution | low cost | Sound waves (Non-ionizing) |
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |||||
|
| |||||
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) | Invasive |
| Cancer treatments, Gynecological cancer diagnosis, size detection of unrefined tumor, Esophageal cancer diagnosis | high spatial resolution | High cost | Positron (ionizing) |
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |||||
|
| |||||
Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) | Non-Invasive |
| Head and neck cancer diagnosis, Cancer treatment of Bone, Vulgar, Breast, and Lungs, Diagnosis of Liver, Detection of tumors | Inadequate spatial resolution | High cost | Photons (ionizing) |
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |||||
|
| |||||
| Ref. | Year | Image Modalities | Body Organs | Disease | Based Method | Multimodal Fusion Techniques | Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| He et al. [27] | 2010 | MRI/PET | Brain | Alzheimer’s | Spatial Domain | IHS and PCA fusion | AANLIB |
| Bashir et al. [20] | 2019 | CT/MRI | Brain | - | PCA | - | |
| X-ray and MRI | Leg | ||||||
| Rehal et al. [29] | 2021 | MRI/PET | Brain | - | 2-DHT and HIS | - | |
| Zhu et al. [32] | 2019 | CT/MRI | - | - | Laplacian Pyramid | local Laplacian energy and NSCT domain | - |
| MRI/PET | - | - | - | ||||
| SPECT/MRI | - | - | - | ||||
| Liu et al. [31] | 2020 | CT/MRI | Brain | lesions | Laplacian pyramid and SR | ALINDA | |
| Wang et al. [39] | 2022 | SPECT-T1/SPECT-TC | Brain | - | DCT | Discrete cosine transform in geometric algebra (GA DCT). | - |
| Bhavana et al. [35] | 2015 | MRI/PET | Brain | normal Axial | DWT | DWT | - |
| MRI/PET | Normal Coronal | - | |||||
| MRI/PET | Alzheimer’s | - | |||||
| Bashir et al. [20] | 2019 | CT/MRI | - | - | SWT | - | |
| X-ray and MRI | - | - | - | ||||
| Xia et al. [44] | 2018 | CT/MRI | - | - | NSCT | NSCT-SR-PCNN | - |
| MR1_T1/MR2_T2 | - | - | - | ||||
| MR-T1/PET | - | - | - | ||||
| MR-T2/PET | - | - | - | ||||
| Li et al. [41] | 2021 | MRI/SPEC | - | - | NSCT | - | |
| MRI/PET | - | - | - | ||||
| MR1_T1/MR2_T2 | - | - | - | ||||
| Ouerghi et al. [46] | 2018 | MRI/PET | Brain | Alzheimer’s brain | PCNN | PCNN | AANLIB |
| Tumor | - | ||||||
| Qiu et al. [48] | 2017 | CT/MRI | - | - | NSST | SR in NSST Domain | - |
| Yin et al. [49] | 2018 | CT/MR | - | - | PA-PCNN in NSST Domain | - | |
| MR-T1/MR-T2 | - | - | - | ||||
| MR/PET | - | - | - | ||||
| MR/SPECT | - | - | - | ||||
| Tirupa2l et al. [54] | 2017 | CT/MRI | - | - | Fuzzy method | Fuzzy method | - |
| - | - | Sugeno’s intuitionistic fuzzy set | - | ||||
| MRI/PET | Brain | Alzheimer’s | Fuzzy method | - | |||
| Sugeno’s intuitionistic fuzzy set | - | ||||||
| MRI/SPEC | Brain | Tumor | Fuzzy method | - | |||
| Sugeno’s intuitionistic fuzzy set | - | ||||||
| CT/PET | - | - | Fuzzy method | - | |||
| - | - | Sugeno’s intuitionistic fuzzy set | - | ||||
| Kumar et al. [53] | 2018 | CT/MRI | - | - | intuitionistic fuzzy sets | - | |
| MRI/SPEC | - | - | - | ||||
| MRI/PET | - | - | - | ||||
| Tirupal et al. [55] | 2022 | CT/MRI | Brain | - | Fuzzy method | interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy set (IVIFS) | - |
| MR/MRA | - | - | |||||
| MRI/SPECT | - | - | |||||
| Yang et al. [58] | 2008 | CT/MRI | - | - | Morphological Method | Shift-Invariant Morphological Wavelet | - |
| Li et al. [61] | 2018 | CT/MRI | - | - | Sparse Representation | NSCT and SR | AANLIB |
| Shabanzade et al. [64] | 2016 | MRI/PET | - | - | SR and Clustering-Based Dictionary Learning in NSCT Domain | - | |
| Kim et al. [65] | 2016 | MR/CT | - | - | clustering-based dictionary learning | - | |
| MR/PET | - | - | - | ||||
| Maqsood et al. [60] | 2020 | CT/MRI | - | - | Two-scale Image Decomposition and Sparse Representation | - | |
| Polinati et al. [66] | 2021 | CT/MRI | Brain | cerebrovascular, neoplastic, degenerative, and infectious diseases | adaptive sparse representation | - | |
| Rajalingam et al. [76] | 2018 | CT/MRI | - | - | Deep Learning | CNN | - |
| MRI/PET | - | - | - | ||||
| Xia et al. [77] | 2019 | CT/MR | Abdomen | - | CNN | AANLIB | |
| CT/PET | - | - | |||||
| CT/MRI | Brain | - | |||||
| Wang et al. [78] | 2020 | CT/MRI | - | - | Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Contrast Pyramid | - | |
| MR-T1/MR-T2 | - | - | - | ||||
| MRI/PET | - | - | - | ||||
| MRI/SPECT | - | - | - | ||||
| Li et al. [80] | 2021 | CT/MRI | Brain | - | Deep learning model | - |
| Based Method | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Spatial Domain |
|
|
| Pyramidal |
|
|
| DWT |
|
|
| Multi-scale Decomposition techniques |
|
|
| Sparse Representation |
|
|
| Deep Learning |
|
|
| Ref. and Year | Image Modality | IF Technique | MI | CC | EN | SF | QAB/F | AG | Time(s) | SD | SSIM | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| He et al. [27] 2010 | MRI/PET | IHS and PCA fusion | 2.9586 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Bashir et al. [20] 2019 | CT/MRI | PCA | - | - | 5.9796 | - | - | - | - | 0.2073 | - | 0.2886 | |
| X-ray/MRI | - | - | 6.3419 | - | - | - | - | 0.2259 | - | 0.2062 | |||
| Rehal et al. [29] 2021 | MRI/PET | 2-DHT and HIS | - | - | - | - | - | 6.91 | - | - | - | - | |
| Zhu et al. [32] 2019 | CT/MRI | local Laplacian energy and NSCT domain | 2.2188 | - | - | - | 0.8502 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| MRI/PET | 1.7422 | - | - | - | 0.3475 | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| SPECT/MRI | 2.6134 | - | - | - | 0.5455 | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| Liu et al. [31] 2020 | CT/MRI | Laplacian pyramid and sparse representation | 2.7088 | - | - | 2.6533 | - | 8.9159 | - | 8.1978 | - | - | |
| Wang et al. [39] 2022 | SPECT-T1/SPECT-TC | Set1 | Laplacian pyramid | 2.477 | 0.692 | 3.4538 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.742 | 0.134 |
| Set2 | 2.966 | 0.655 | 3.9194 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.721 | 0.152 | |||
| Set3 | 2.736 | 0.704 | 3.6714 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.729 | 0.143 | |||
| Set4 | 1.926 | 0.651 | 3.6212 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.605 | 0.140 | |||
| Bhavana et al. [35] 2015 | MRI/PET | DWT | - | - | - | - | - | 6.8573 | - | 2.2966 | - | - | |
| MRI/PET | - | - | - | - | - | 7.9881 | - | 2.63 | - | - | |||
| MRI/PET | - | - | - | - | - | 10.586 | - | 0.3808 | - | - | |||
| Polinati et al. [66] 2021 | CT/MRI | DTCWT | 3.656 | - | - | - | 0.500 | 8.933 | - | - | 0.499 | 0.034 | |
| CT/MRI | 4.030 | - | - | - | 0.435 | 7.421 | - | - | 0.413 | 0.029 | |||
| CT/MRI | 3.878 | - | - | - | 0.418 | 6.231 | - | - | 0.674 | 0.028 | |||
| CT/MRI | 3.360 | - | - | - | 0.483 | 6.390 | - | - | 0.350 | 0.029 | |||
| Bashir et al. [20] 2019 | CT/MRI | SWT | - | - | 6.1523 | - | - | - | - | 0.1419 | - | 0.1605 | |
| X-ray/MRI | - | - | 6.2769 | - | - | - | - | 0.206 | - | 0.2528 | |||
| Xia et al. [44] 2018 | CT/MRI | NSCT-SR-PCNN | 2.2426 | - | - | - | 0.5887 | - | - | 55.406 | 0.9567 | - | |
| MR1_T1/MR2_T2 | 2.2047 | - | - | - | 0.5732 | - | - | 58.764 | 1.2812 | - | |||
| MR-T1/PET | 2.7559 | - | - | 6.9474 | 0.5681 | 7.5961 | - | 67.025 | - | - | |||
| MR-T2/PET | 2.0676 | - | 6.9363 | 0.5451 | 7.4678 | 63.117 | - | - | |||||
| Li et al. [41] 2021 | MRI/SPEC | NSCT | 8.9643 | - | - | - | 0.6992 | - | - | 69.198 | - | - | |
| MRI/PET | 9.7471 | - | - | - | 0.6176 | - | - | 72.662 | - | - | |||
| MR1_T1/MR2_T2 | 10.489 | - | - | - | 0.5801 | - | - | 100.26 | - | - | |||
| Ouerghi et al. [46] 2018 | MRI/PET | PCNN | - | - | 0.754 | 30.415 | 0.4932 | - | 180 | 72.971 | - | - | |
| - | - | 3.6176 | 35.606 | 0.5852 | - | 180 | 56.974 | - | - | ||||
| Qiu et al. [48] 2017 | CT/MRI | SR in NSST Domain | 3.1898 | - | - | - | 0.5378 | - | 0.7523 | - | |||
| Yin et al. [49] 2018 | CT/MR | PA-PCNN in NSST Domain | 0.783 | - | 5.113 | - | - | - | 7.68 | 87.165 | - | - | |
| MR-T1/MR-T2 | 0.876 | - | 5.169 | - | - | - | 7.68 | 80.932 | - | - | |||
| MR/PET | 0.868 | - | 4.946 | - | - | - | 7.68 | 62.479 | - | - | |||
| MR/SPECT | 0.826 | - | 4.794 | - | - | - | 7.68 | 58.018 | - | - | |||
| Polinati et al. [64] 2021 | CT/MRI | NSST | 3.703 | - | - | - | 0.373 | 8.368 | - | - | 0.520 | 0.027 | |
| CT/MRI | 4.116 | - | - | - | 0.421 | 7.471 | - | - | 0.600 | 0.024 | |||
| CT/MRI | 4.214 | - | - | - | 0.446 | 6.349 | - | - | 0.590 | 0.022 | |||
| CT/MRI | 3.740 | - | - | - | 0.439 | 6.217 | - | - | 0.634 | 0.022 | |||
| Tirupal et al. [54] 2017 | CT/MRI | Fuzzy method | - | - | - | 9.579 | 0.412 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Sugeno’s intuitionistic fuzzy set | - | - | - | 17.29 | 0.859 | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| MRI/PET | Fuzzy method | - | - | - | 23.22 | 0.247 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Sugeno’s intuitionistic fuzzy set | - | - | - | 42.38 | 0.771 | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| MRI/SPEC | Fuzzy method | - | - | - | 14.42 | 0.324 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Sugeno’s intuitionistic fuzzy set | - | - | - | 30.61 | 0.713 | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| CT/PET | Fuzzy method | - | - | - | 12.96 | 0.274 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Sugeno’s intuitionistic fuzzy set | - | - | - | 14.5 | 0.758 | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| Kumar et al. [53] 2018 | CT / MRI | intuitionistic fuzzy sets | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 36.866 | - | - | |
| MRI/SPEC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 10.779 | - | - | |||
| MRI/PET | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5.5054 | - | - | |||
| Tirupal et al. [55] 2022 | CT/MRI | interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy set (IVIFS) | - | - | 6.8026 | 30.78 | 0.8451 | 18.526 | - | - | - | - | |
| MR/MRA | - | - | 7.1052 | 36.22 | 0.7165 | 18.701 | - | - | - | - | |||
| MRI/SPECT | - | - | 5.9753 | 35.32 | 0.7868 | 17.127 | - | - | - | - | |||
| Yang et al. [58] 2008 | CT/MRI | Shift-Invariant Morphological Wavelet | 5.472 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Li et al. [61] 2018 | CT/MRI | NSCT and SR | - | - | - | - | 0.7298 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Maqsood et al. [62] 2020 | CT/MRI | Two-scale Image Decomposition and Sparse Representation | 3.6949 | - | 6.987 | - | 0.7997 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| CT/MRI | 4.4388 | - | 7.597 | - | 0.7842 | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| CT/MRI | 4.7421 | - | 7.9945 | - | 0.7169 | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| CT/MRI | 4.358 | - | 5.4681 | - | 0.9737 | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| Shabanzade et al. [64] 2016 | MRI/PET | SR and Clustering-Based Dictionary Learning in NSCT Domain | 2.4501 | - | - | - | 0.6473 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Polinati et al. [64] 2021 | CT/MRI | ASR | 3.984 | - | - | - | 0.535 | 8.561 | - | - | 0.563 | 0.034 | |
| CT/MRI | 4.279 | - | - | - | 0.47 | 6.662 | - | - | 0.593 | 0.029 | |||
| CT/MRI | 4.186 | - | - | - | 0.465 | 5.065 | - | - | 0.674 | 0.028 | |||
| CT/MRI | 3.666 | - | - | - | 0.541 | 5.772 | - | - | 0.651 | 0.029 | |||
| Kim et al. [65] 2016 | MR/CT | Clustering-based dictionary learning | 2.704 | - | - | - | 0.248 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| MR/PET | 2.616 | - | - | - | 0.309 | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| Rajalingam et al. [76] 2018 | CT/MRI(1) | CNN | 0.873 | - | - | - | 0.8662 | 0.084 | 2.094 | 0.7782 | - | - | |
| CT/MRI(2) | 1.516 | - | - | - | 0.7172 | 0.0886 | 2.051 | 0.954 | - | - | |||
| MRI/PET(1) | 1.435 | - | - | - | 0.7832 | 0.0893 | 2.274 | 0.998 | - | - | |||
| MRI/PET(2) | 1.245 | - | - | - | 0.5872 | 0.0895 | 2.127 | 0.8023 | - | - | |||
| Xia et al. [77] 2019 | CT/MRI | CNN | - | 33.97 | 7.176 | 13.64 | - | 7.112 | 3.115 | 45.907 | - | - | |
| CT/PET | - | 64.43 | 7.622 | 11.354 | - | 6.545 | 8.763 | 75.422 | - | - | |||
| CT/MRI | - | 11.5 | 6.188 | 8.031 | - | 3.395 | 11.046 | 21.386 | - | - | |||
| Wang et al. [78] 2020 | CT/MRI | CNN and Contrast Pyramid | 1.092 | - | 0.7445 | - | 0.4449 | - | 12.867 | - | - | - | |
| MR-T1/MR-T2 | 1.092 | - | 0.7445 | - | 0.4449 | - | 12.867 | - | - | - | |||
| MRI/PET | 1.092 | - | 0.7445 | - | 0.4449 | - | 12.867 | - | - | - | |||
| MRI/SPECT | 1.092 | - | 0.7445 | - | 0.4449 | - | 12.867 | - | - | - | |||
| Li et al. [80] 2021 | CT/MRI | DL model | 1.8145 | - | 0.5429 | 15.394 | - | - | - | - | 0.9020 | 39.92 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saleh, M.A.; Ali, A.A.; Ahmed, K.; Sarhan, A.M. A Brief Analysis of Multimodal Medical Image Fusion Techniques. Electronics 2023, 12, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12010097
Saleh MA, Ali AA, Ahmed K, Sarhan AM. A Brief Analysis of Multimodal Medical Image Fusion Techniques. Electronics. 2023; 12(1):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12010097
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaleh, Mohammed Ali, AbdElmgeid A. Ali, Kareem Ahmed, and Abeer M. Sarhan. 2023. "A Brief Analysis of Multimodal Medical Image Fusion Techniques" Electronics 12, no. 1: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12010097
APA StyleSaleh, M. A., Ali, A. A., Ahmed, K., & Sarhan, A. M. (2023). A Brief Analysis of Multimodal Medical Image Fusion Techniques. Electronics, 12(1), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12010097






