A Patch Antenna with Enhanced Gain and Bandwidth for Sub-6 GHz and Sub-7 GHz 5G Wireless Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
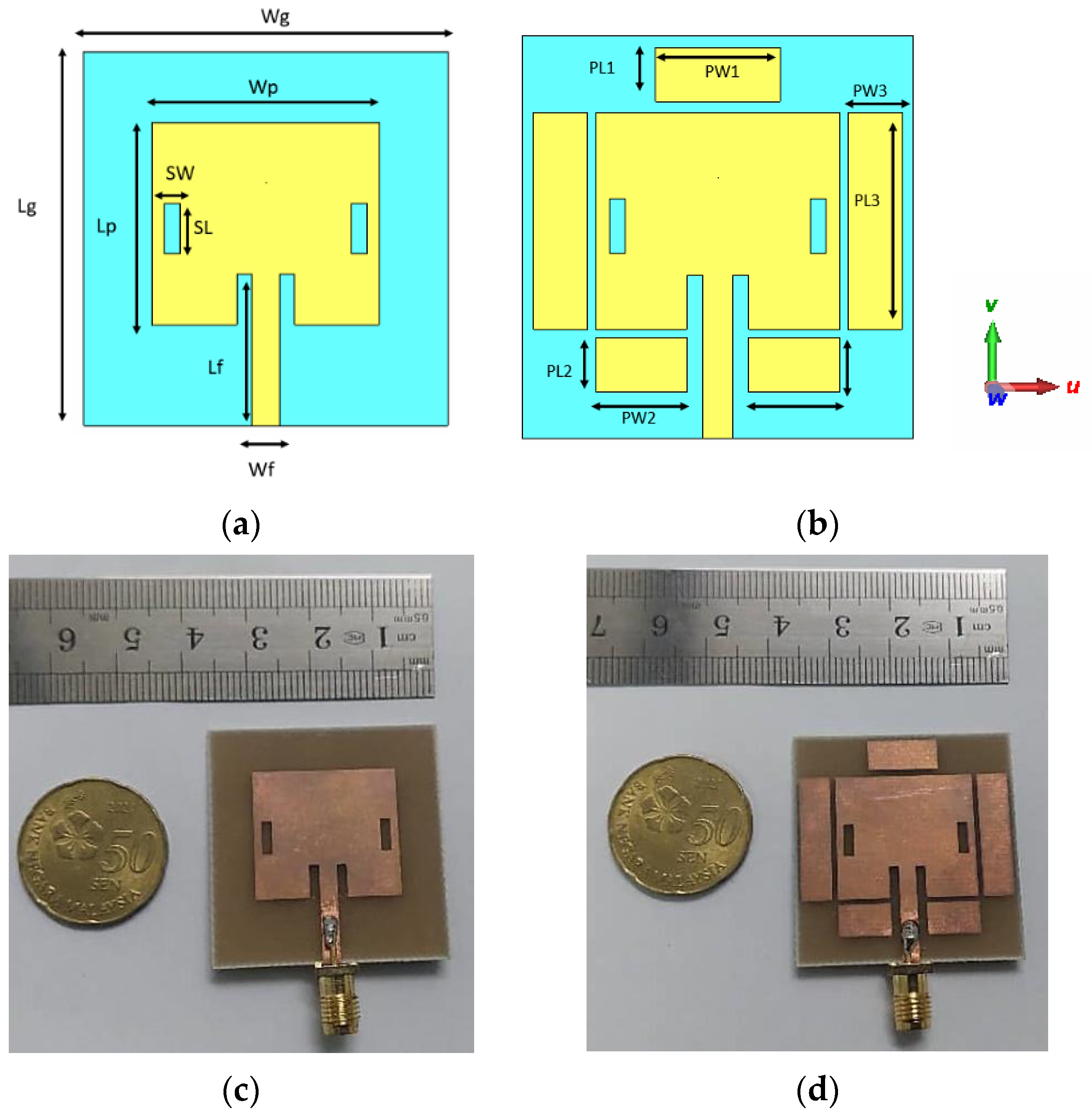
2. Antenna Design Configuration
3. Results and Discussion
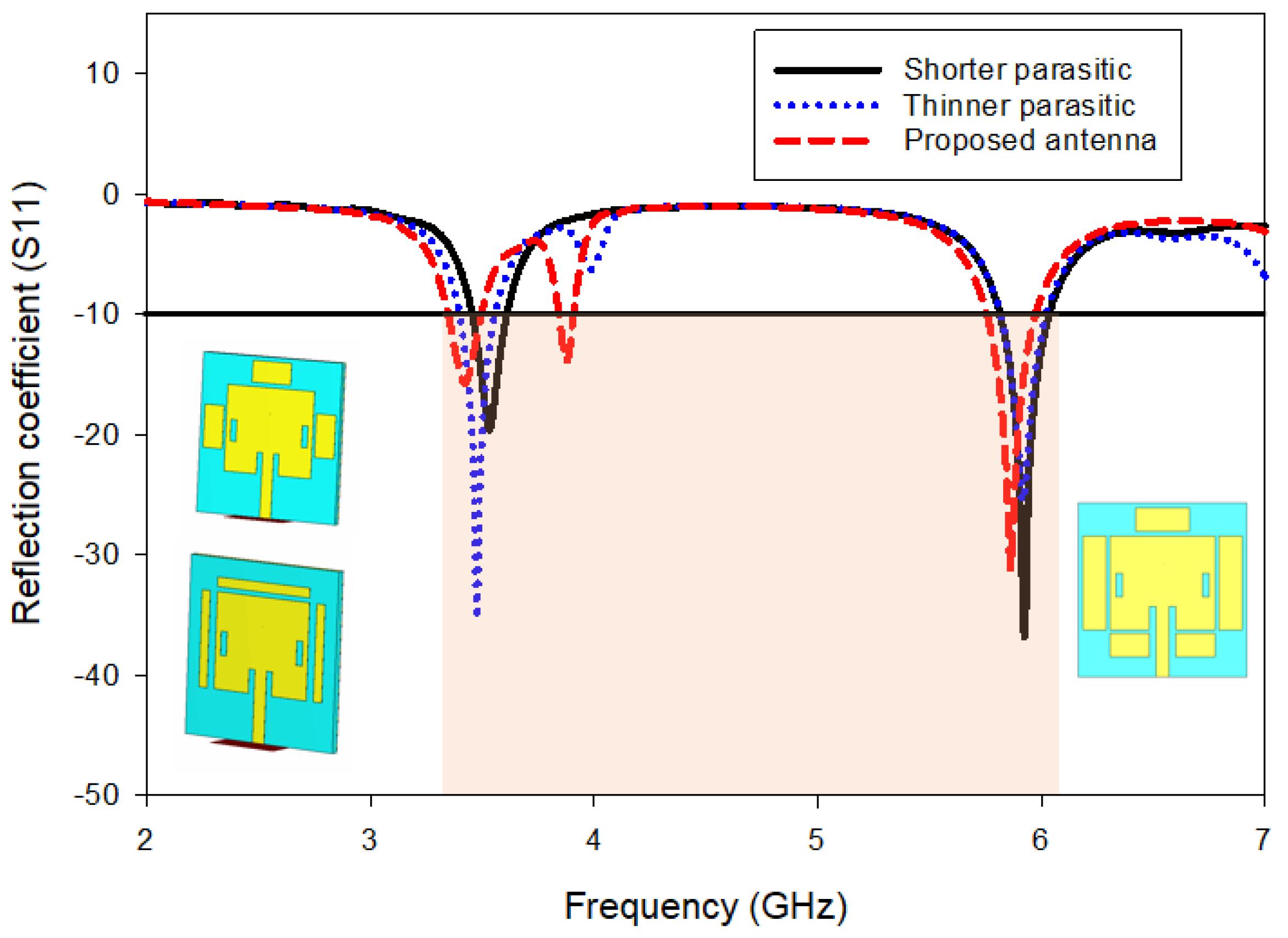
3.1. Reflection Coefficient (|S11|) and Bandwidth
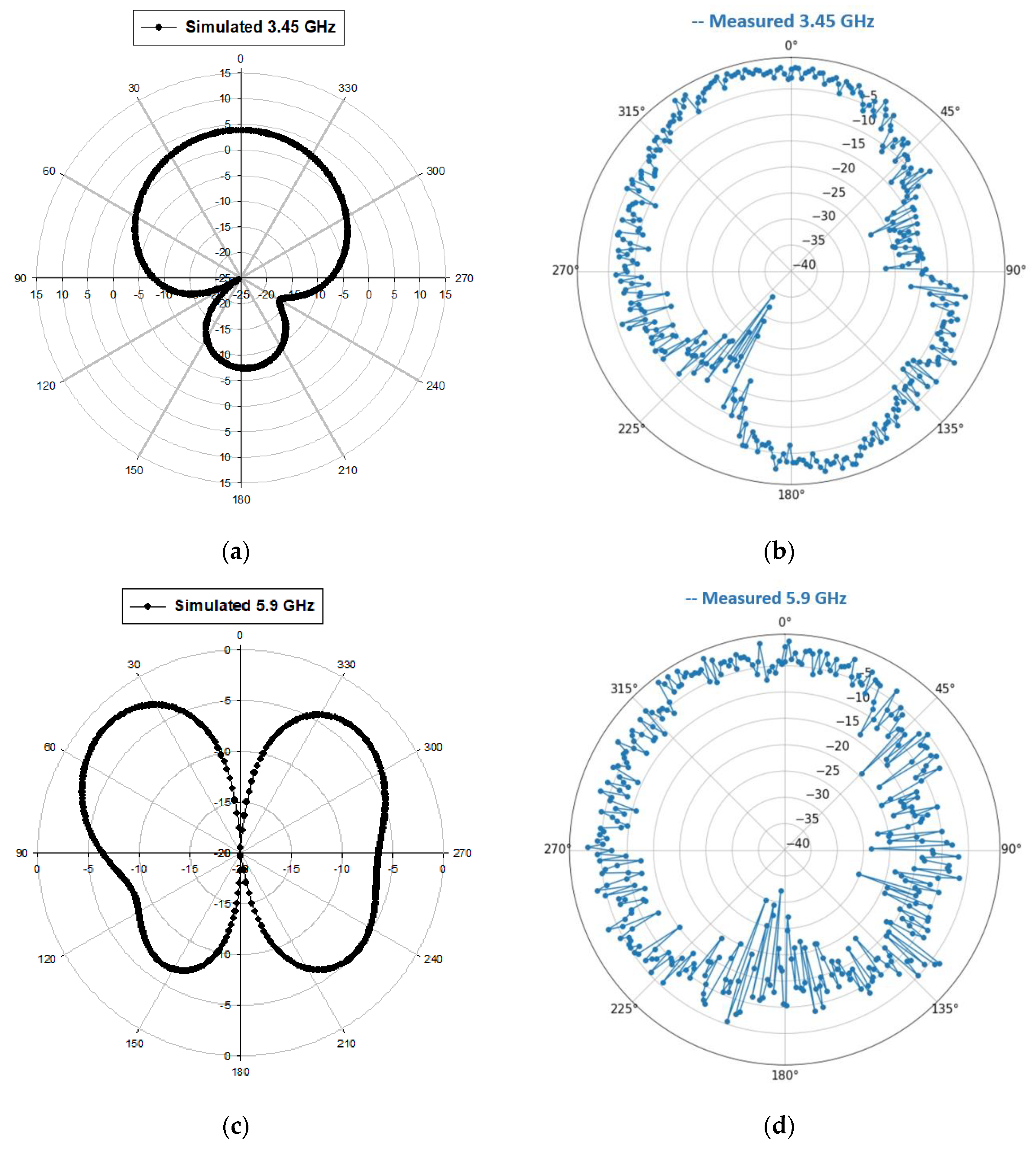
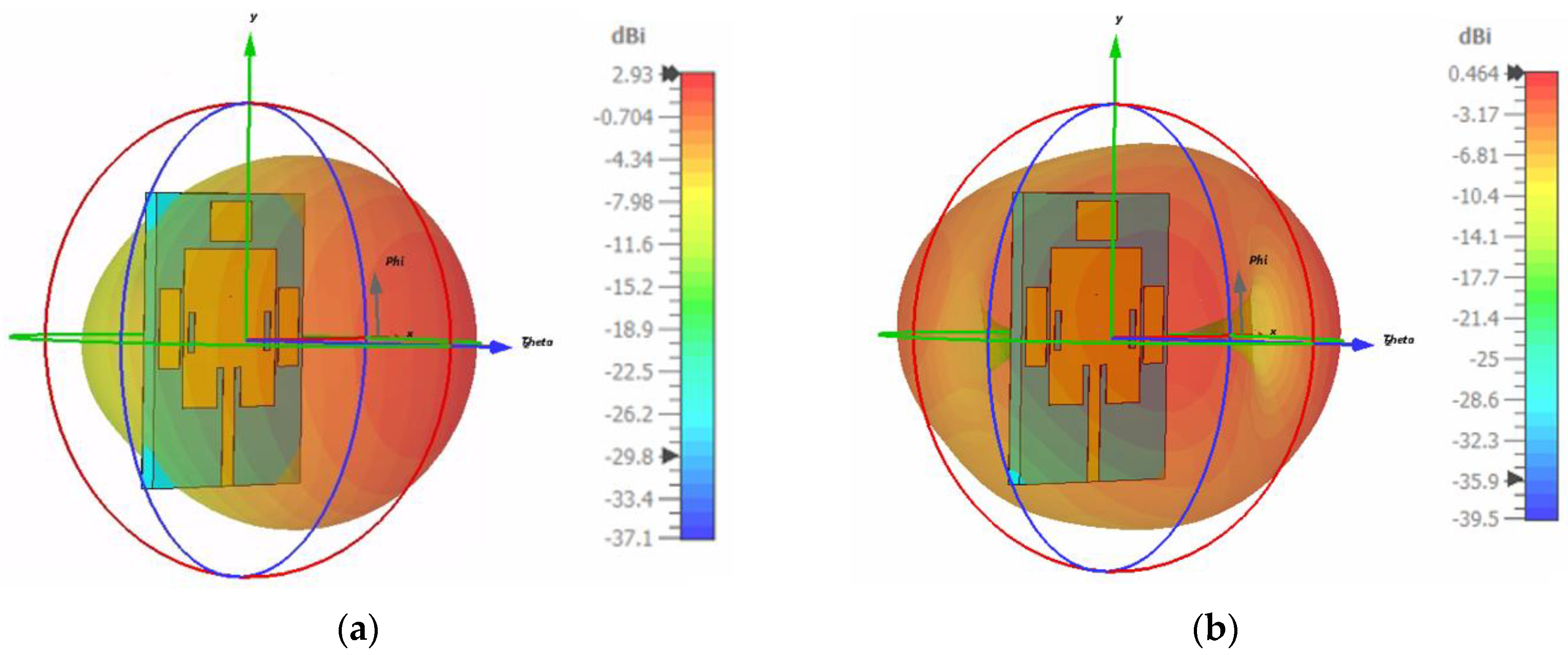
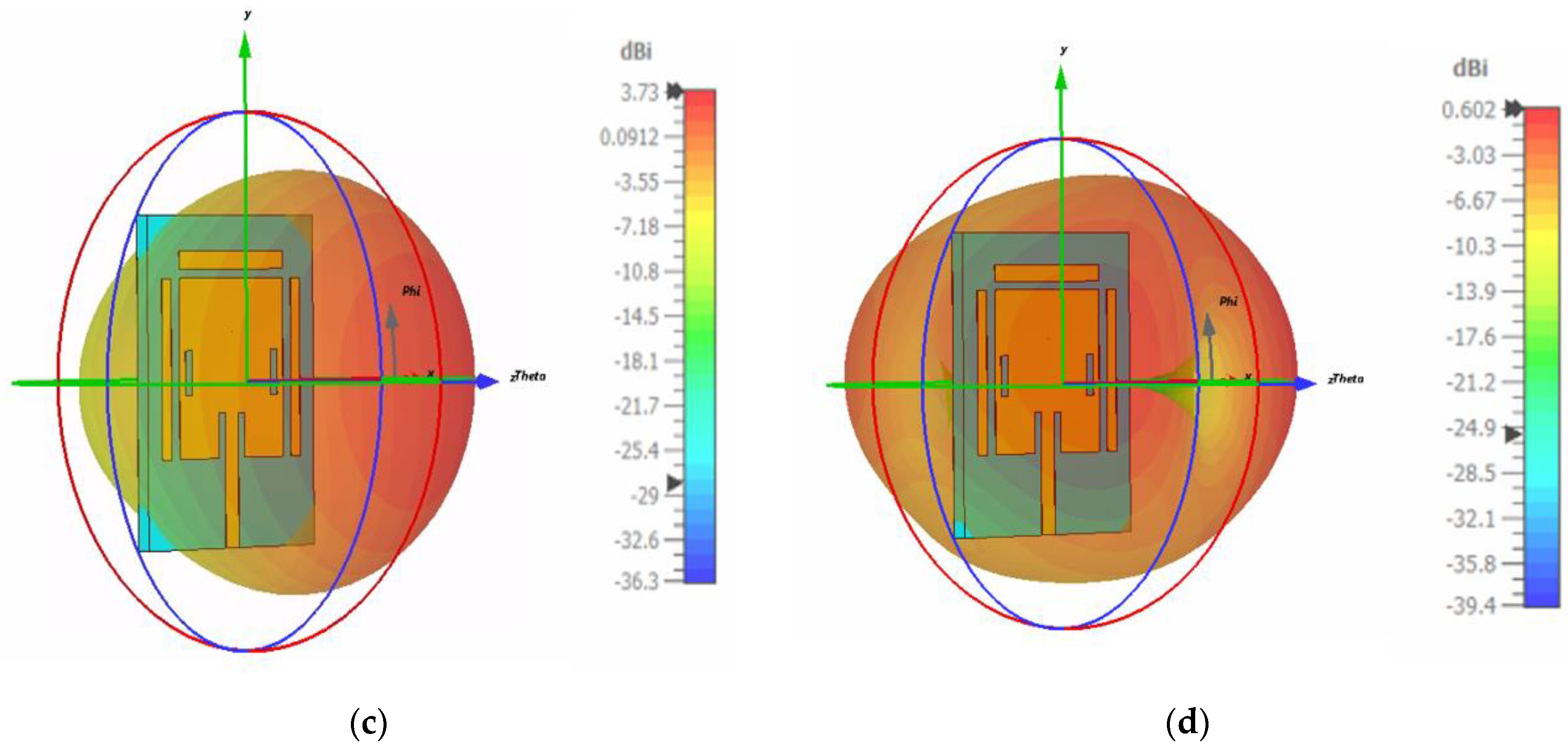
3.2. Radiation Pattern
3.3. Surface Current Density
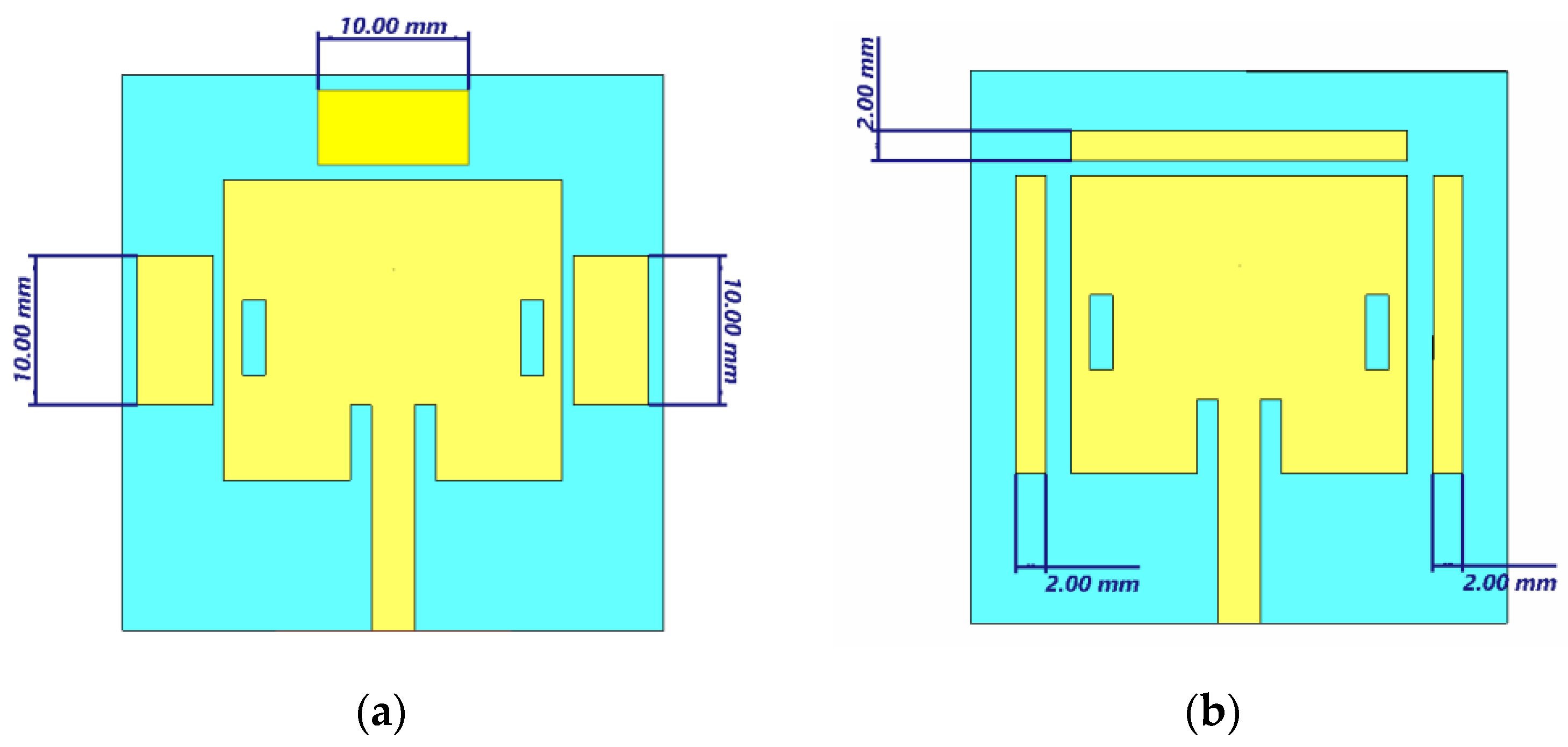
3.4. Parametric Study on Width and Length Parasitic Patch Effect
3.4.1. |S11| and Bandwidth
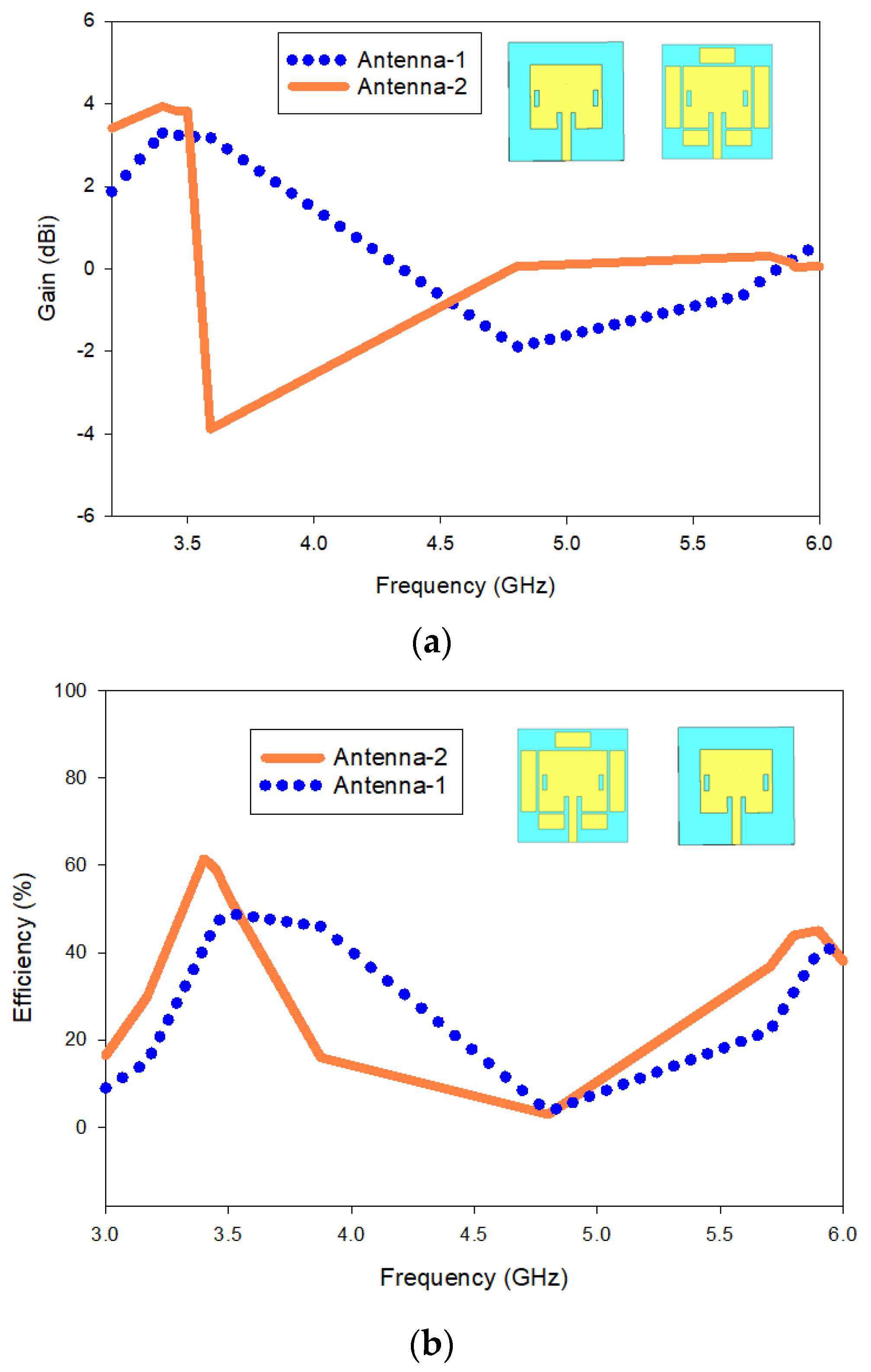
3.4.2. Antenna Gain
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azim, R.; Alam, T.; Paul, L.C.; Aktar, R.; Meaze, A.K.M.M.H.; Islam, M.T. Low Profile Multi-slotted Patch Antenna for Lower 5G Application. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Region 10 Symposium (TENSYMP), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 5–7 June 2020; pp. 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, S.K.; Ismail, A.M.; Yasin, M.N.M.; Osman, M.N.; Ramli, N. Orbital Angular Momentum Vortex Waves Generation Using Textile Antenna Array for 5G Wearable Applications. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Symposium on Wireless Technology & Applications (ISWTA), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 17–18 August 2022; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualcomm. Global Update on Spectrum for 4G & 5G; White Pap.; Qualcomm Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2020; pp. 1–21. Available online: https://www.qualcomm.com/media/documents/files/spectrum-for-4g-and-5g.pdf (accessed on 7 May 2023).
- Ramli, N.; Ali, M.T.; Yusof, A.L.; Muhamud-Kayat, S.; Aziz, A.A.A. Frequency-reconfigurable stacked patch microstrip antenna using aperture-coupled technique. Int. J. Microw. Opt. Technol. 2014, 9, 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Pragati; Tripathi, S.L.; Patre, S.R.; Singh, S.; Singh, S.P. Triple-band microstrip patch antenna with improved gain. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Emerging Trends in Electrical Electronics & Sustainable Energy Systems (ICETEESES), Sultanpur, India, 11–12 March 2016; pp. 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Jiao, Y.; Li, H.; Zong, W.; Yao, Z.; Shan, F.; Li, Y.; Yue, W.; Gao, S. Ultra-Wideband Patch Antenna for Sub-6 GHz 5G Communications. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Workshop on Electromagnetics: Applications and Student Innovation Competition (iWEM), Qingdao, China, 18–20 September 2019; pp. 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, L.C.; Das, S.C.; Rani, T.; Muyeen, S.M.; Shezan, S.A.; Ishraque, M.F. A slotted plus-shaped antenna with a DGS for 5G Sub-6 GHz/WiMAX applications. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sree, M.F.A.; Elazeem, M.H.A.; Swelam, W. Dual Band Patch Antenna Based on Letter Slotted DGS for 5G Sub-6GHz Application. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2128, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tütüncü, B.; Kösem, M. Substrate Analysis on the Design of Wide-Band Antenna for Sub-6 GHz 5G Communication. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2022, 125, 1523–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Kharusi, K.W.S.; Ramli, N.; Khan, S.; Ali, M.T.; Halim, M.H.A. Gain enhancement of rectangular microstrip patch antenna using air gap at 2.4 GHz. Int. J. Nanoelectron. Mater. 2020, 13, 211–224. [Google Scholar]
- Mekki, A.S.; Hamidon, M.N.; Ismail, A.; Alhawari, A.R.H. Gain Enhancement of a Microstrip Patch Antenna Using a Reflecting Layer. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2015, 2015, 975263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.; Mishra, R.; Kapoor, A.; Kumar, P. Compact wideband-printed antenna for sub-6 GHz fifth-generation applications. Int. J. Smart Sens. Intell. Syst. 2020, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, J.; Sim, C. Wideband CPW-Fed Oval-Shaped Monopole Antenna for Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6 Applications. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 2021, 107, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, J. Quad-Band Circular Polarized Antenna for GNSS, 5G and WIFI-6E Applications. Electronics 2022, 11, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Jiang, S.; Song, R.; He, D. A Dual-Band Conformal Antenna Based on Highly Conductive. Materials 2021, 14, 5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Analysis, C.M. Design of a 5G Sub-6 GHz Vehicular Cellular Antenna Characteristic Mode Analysis. Sensors 2022, 22, 8862. [Google Scholar]
- Lawoye, T.O.; Kumar, P. A High Gain Antenna with DGS for Sub-6 GHz 5G Communications. Adv. Electromagn. 2022, 11, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Patch, A.S.D.; Array, A.; Application, W. A Simple Dual-Polarized Patch Antenna Array for Wi-Fi 6/6E Application. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 11143–11148. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Althuwayb, A.A.; Al-hasan, M.J. Wideband Triple Resonance Patch Antenna for 5G Wi-Fi Spectrum. Prog. Electromagn. Res. Lett. 2020, 93, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, C.; Chen, C.-C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Lee, Y.-L.; Chiang, C.-Y. Very Small-Size Uniplanar Printed Monopole Antenna for Dual-Band WLAN Laptop Computer Applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 2916–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizi, S.A.R. Bandwidth Enhancement Techniques. Trends Res. Microstrip Antennas 2017, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna theory: A review. Proc. IEEE 1992, 80, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameters | Antenna-1 | Antenna-2 (Proposed) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.45 GHz | 5.9 GHz | 3.45 GHz | 5.9 GHz | |
| Bandwidth | 140 MHz | 150 MHz | 160 MHz | 220 MHz |
| Gain | 2.79 dBi | 0.1 dBi | 3.83 dBi | 0.576 dBi |
| Directivity | 6.08 dBi | 1.79 dBi | 5.93 dBi | 2.75 dBi |
| Efficiency | 47% | 40% | 59% | 45% |
| Antenna dimension | 36 mm × 37 mm | 36 mm × 37 mm | ||
| Ref. | Frequency (GHz) | Antenna Size (mm2) | Bandwidth (MHz) | Gain (dBi) | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [6] | 2.55, 3.5 and 4.75 | 50 × 80 | 2920 | 2.52, 3.05 and 4.31 | Antenna is bigger and does not cover n77/n78 band |
| [7] | 3.12 | 20 × 35 | 2560 | 2.44 | Single band and low gain |
| [8] | 4.53 and 4.97 | 77 × 70.11 | Not reported | 5 and 4.57 | Antenna is bigger and did not cover n77/n78 and n96 band |
| [9] | 5.65 | 52.92 × 55.56 | 135 | 7.15 | Single-band only, the antenna is bigger, and the bandwidth is narrow |
| [10] | 2.4 | 80 × 80 | 72.837 | 7.91 | Single band, the antenna is bigger, and the bandwidth is narrow |
| [11] | 2.392 | 60 × 55 | 44.7 | 5.2 | Single band, the antenna is bigger and has a very narrow bandwidth |
| [12] | 3.65 | 28 × 20 | 700 | 2.5 | Single band and low gain |
| This work | 3.45 and 5.9 | 36 × 37 | 160 and 220 | 3.83 and 0.537 | Smaller in size, dual-band, wider bandwidth, and moderate gain for sub-6 GHz band but has low gain for sub-7 GHz band |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noor, S.K.; Jusoh, M.; Sabapathy, T.; Rambe, A.H.; Vettikalladi, H.; M. Albishi, A.; Himdi, M. A Patch Antenna with Enhanced Gain and Bandwidth for Sub-6 GHz and Sub-7 GHz 5G Wireless Applications. Electronics 2023, 12, 2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122555
Noor SK, Jusoh M, Sabapathy T, Rambe AH, Vettikalladi H, M. Albishi A, Himdi M. A Patch Antenna with Enhanced Gain and Bandwidth for Sub-6 GHz and Sub-7 GHz 5G Wireless Applications. Electronics. 2023; 12(12):2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122555
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoor, Shehab Khan, Muzammil Jusoh, Thennarasan Sabapathy, Ali Hanafiah Rambe, Hamsakutty Vettikalladi, Ali M. Albishi, and Mohamed Himdi. 2023. "A Patch Antenna with Enhanced Gain and Bandwidth for Sub-6 GHz and Sub-7 GHz 5G Wireless Applications" Electronics 12, no. 12: 2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122555
APA StyleNoor, S. K., Jusoh, M., Sabapathy, T., Rambe, A. H., Vettikalladi, H., M. Albishi, A., & Himdi, M. (2023). A Patch Antenna with Enhanced Gain and Bandwidth for Sub-6 GHz and Sub-7 GHz 5G Wireless Applications. Electronics, 12(12), 2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122555











