Design and Analysis of Pattern Reconfigurable Antenna Based on RF MEMS Switches
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Antenna Structure Design
2.1. Current Distribution Analysis
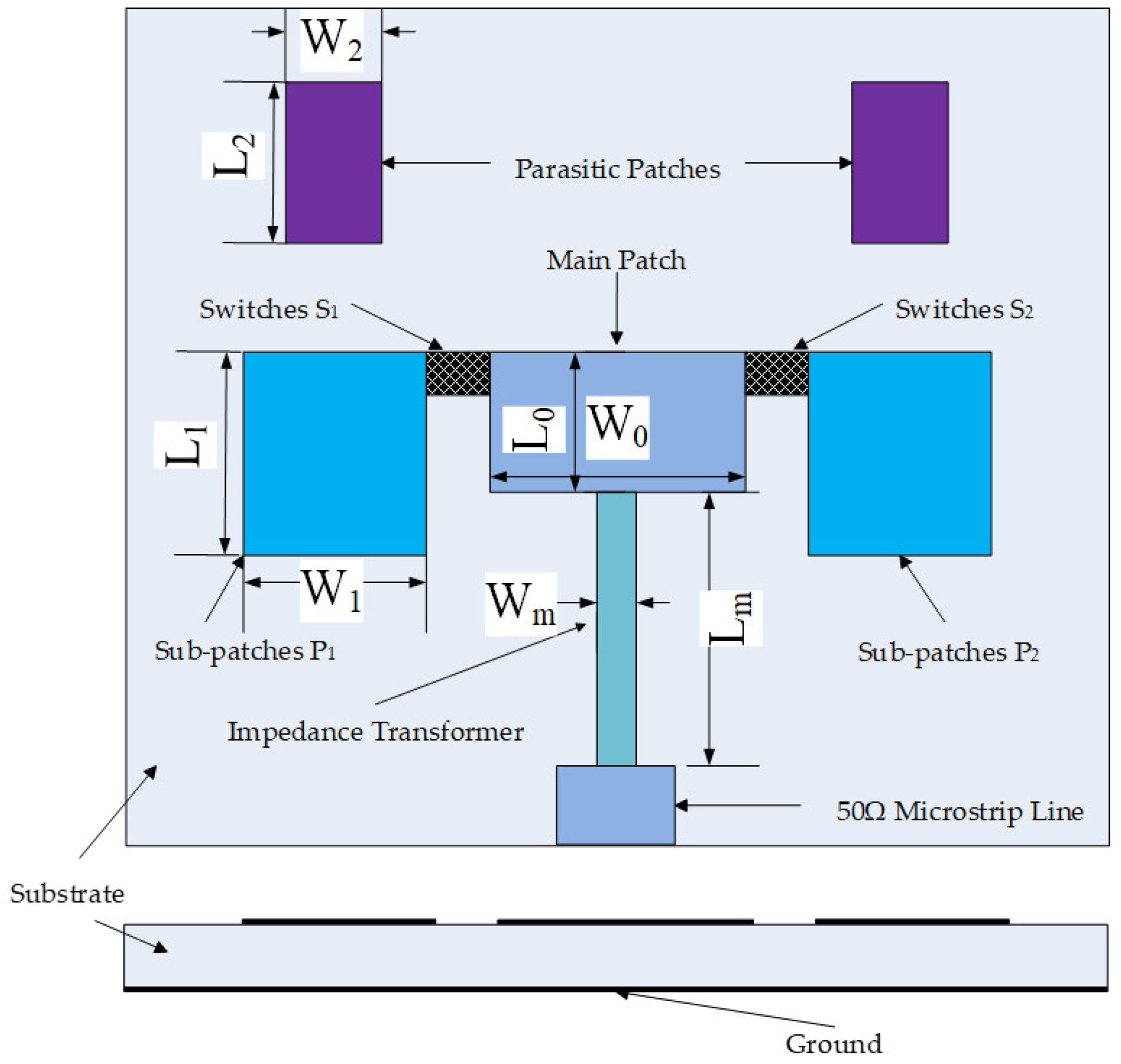
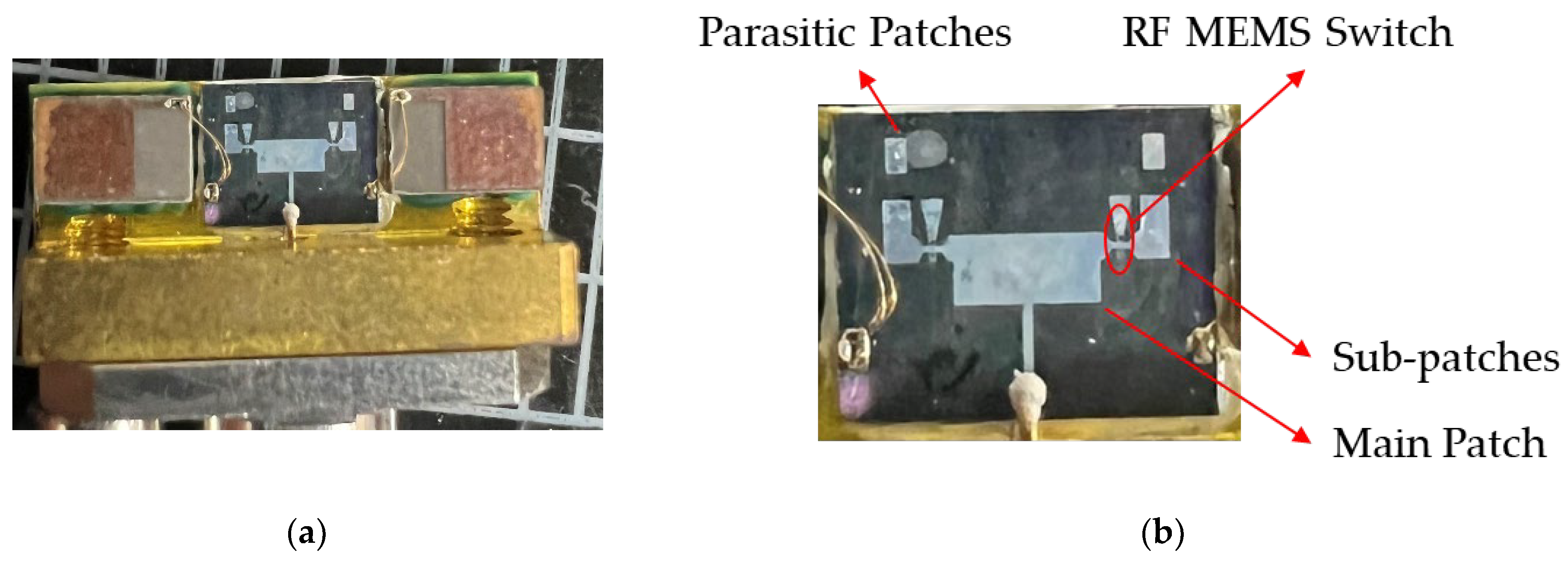
2.2. Main Patch, Sub-Patches and Parasitic Patches Design
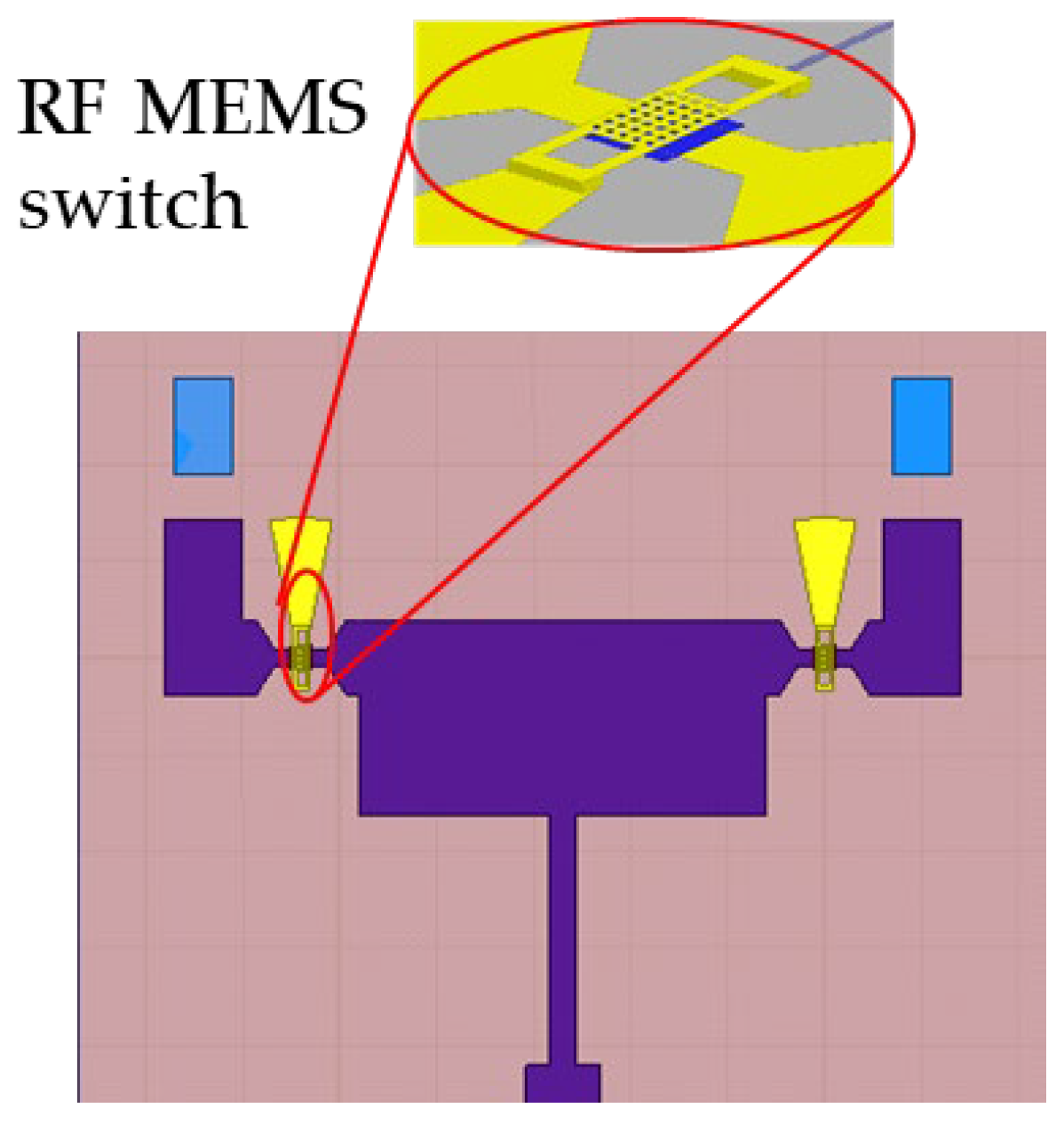
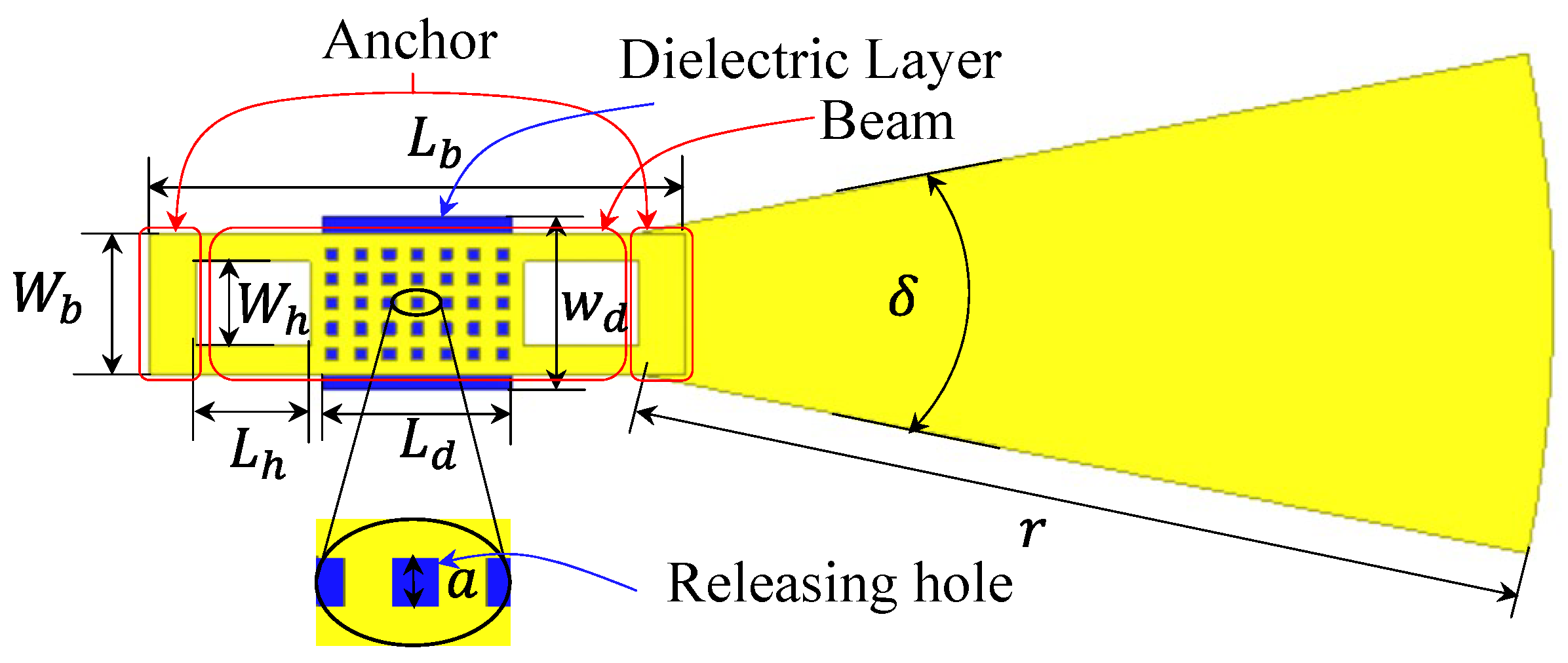
2.3. RF MEMS Switch Design
3. Theory Analysis
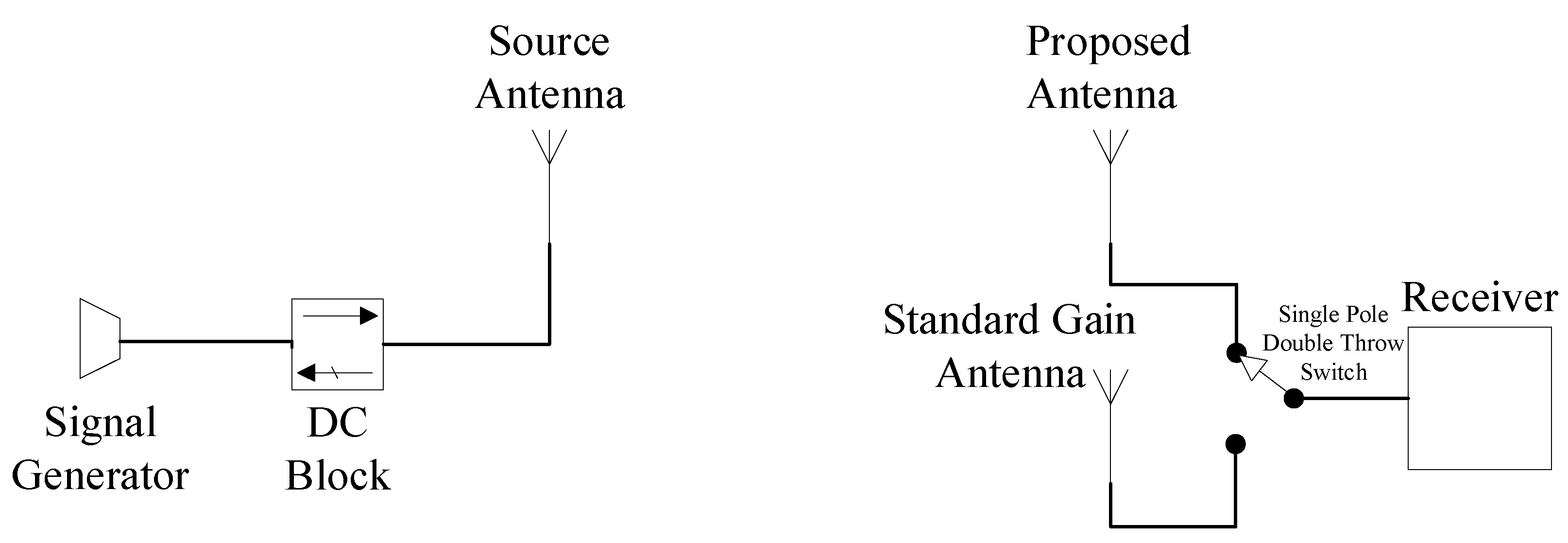
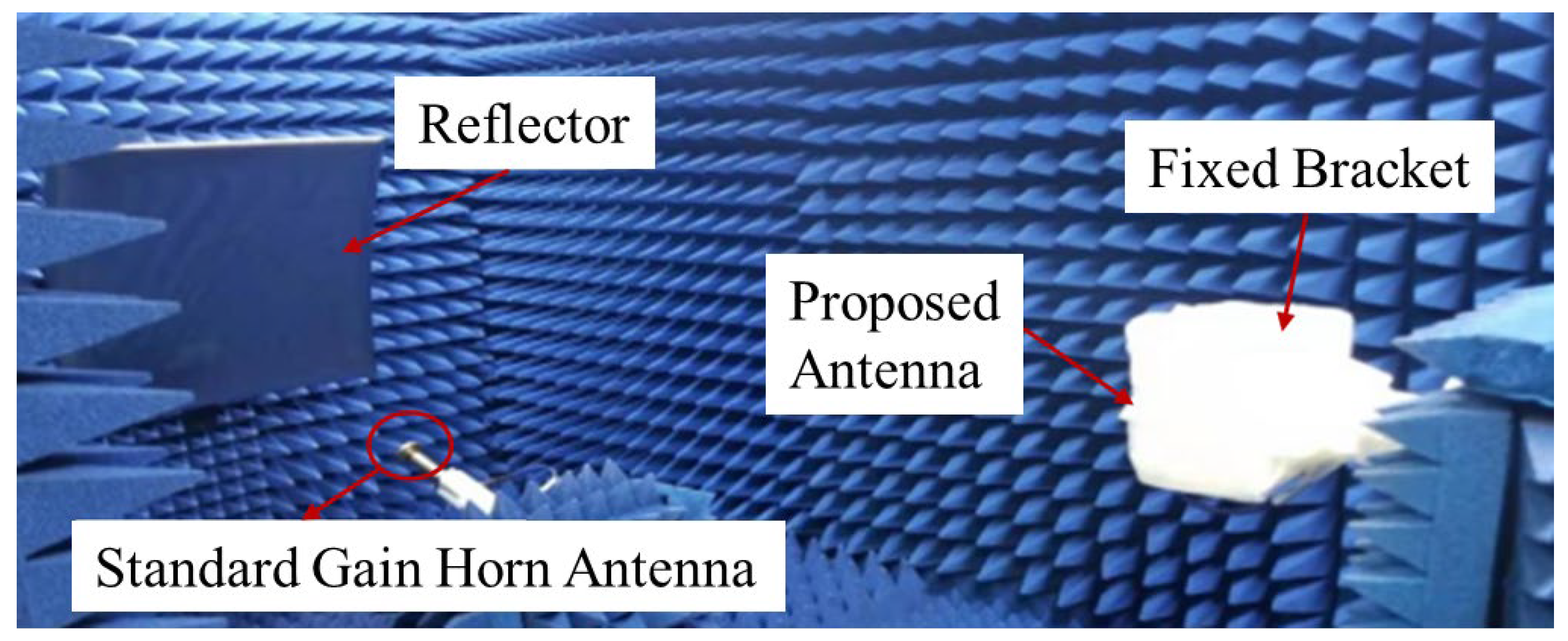
4. Measurement and Results
- (1)
- Connect the test system according to Figure 13 and power on the instrument equipment for preheating;
- (2)
- Calibrate the instrument and set the instrument parameters correctly, set the signal source and make the radiation direction of the transmitting antenna point to the gain reference antenna and the direction of the pattern reconfigurable antenna to be tested, turn on the DC bias power supply and make the pattern reconfigurable antenna enter one of the reconfigurable working modes;
- (3)
- Turn on the transmitting antenna and make it emit a constant power signal, adjust the position of the antenna to be tested so that its direction faces the direction of the signal transmitted by the transmitting antenna, and record the signal power intensity received by the spectrum analyzer connected to the reconfigurable antenna to be tested. Place the reconfigurable antenna to be tested near the gain reference antenna, place the gain reference antenna on a slide that can move at a constant speed, and slide the gain reference antenna up and down to measure the power of the electromagnetic wave received in space due to reflection with the gain reference antenna;
- (4)
- The gain value of the pattern reconfigurable antenna at this point and angle can be calculated by formula (8), where is the gain of the gain reference antenna, and the values here are expressed in logarithms:
- (5)
- By measuring the gain values at multiple angles and frequency points using the above method, we can obtain the pattern and gain of the pattern reconfigurable antenna to be tested.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alam, M.; Abbosh, A. Wideband Pattern Reconfigurable Antenna Using Pair of Radial Radiators on Truncated Ground with Switchable Director and Reflector. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 16, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Xiong, J.; Hou, Z.; Zeng, Y. A compact antenna with frequency and pattern reconfigurable characteristics. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2015, 57, 2467–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussopt, L.; Rebeiz, G.M. Intermodulation distortion and power handling in RF MEMS switches, varactors, and tunable filters. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2003, 51, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Sharma, S.K.; Kassegne, S.K. Reconfigurable microstrip rectangular loop antennas using RF MEMS switches. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2008, 50, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, H.; Kovitz, J.M.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. MEMS reconfigurable optimized e-shaped patch antenna design for cognitive radio. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-alaa, M.A.; Elsadek, H.A.; Abdallah, E.A.; Hashish, E.A. Pattern and frequency reconfigurable monopole disc antenna using PIN diodes and MEMS switches. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2014, 56, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovitz, J.M.; Rajagopalan, H.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. Design and implementation of broadband MEMS RHCP/LHCP reconfigurable arrays using rotated E-shaped patch elements. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 2497–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadh, B.P.; Madhav, B.T.P.; Kumar, M.S.; Kumar, T.A.; Rao, M.V.; Reddy, S.S.M. MEMS-based reconfigurable and flexible antenna for body-centric wearable applications. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2022, 36, 1389–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, H.; Zakaria, Z.; Jamlos, M.F.; Soh, P.J. A wideband reconfigurable folded planar dipole using MEMS and hybrid polymeric substrates. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2019, 99, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdil, E.; Topalli, K.; Unlu, M.; Civi, O.A.; Akin, T. Frequency tunable microstrip patch antenna using RF MEMS technology. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2007, 55, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkawi, W.M.; Sheta, A.F.A.; Malik, W.A.; Rehman, S.U.; Alkanhal, M.S. RF MEMS switches enabled H-shaped beam reconfigurable antenna. Appl. Comput. Electromagn. Soc. J. (ACES) 2019, 34, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, I.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. RF MEMS Switchable Slot Patch Antenna Integrated With Bias Network. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 4811–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairnar, V.V.; Kadam, B.V.; Ramesha, C.K.; Gudino, L.J. A reconfigurable parasitic antenna with continuous beam scanning capability in H-plane. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2018, 88, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, F.; Tawk, Y.; Woehrle, C.; Costantine, J.; Christodoulou, C. Reconfigurable Cyclical Patch Antenna. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 19–24 July 2015; pp. 2249–2250. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.-T.; Siragusa, R.; Tedjini, S. Beam steering patch antenna using reactive loading and Yagi-antenna concept. Microw Opt. Technol. Lett. 2015, 57, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Wu, B. Radiation pattern reconfigurable antenna using double layer tunable graphene superstrate. In Proceedings of the 2015 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC), Nanjing, China, 6–9 December 2015; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Cai, Y.M.; Yin, Y.; Hu, W. A wideband E-plane pattern reconfigurable antenna with enhanced gain. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2019, 29, 21530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, G.; Ray, K. Broadband Microstrip Antennas; Artech House: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Di Palma, L.; Clemente, A.; Dussopt, L.; Sauleau, R.; Potier, P.; Pouliguen, P. 1-Bit Reconfigurable Unit-Cell for Ka-Band Transmitarrays. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 560–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkawi, W.M.; Malik, W.A.; Sheta, A.F.A.; Alkanhal, M.A. A compact dual circular patch pattern reconfigurable antenna. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2018, 60, 2762–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
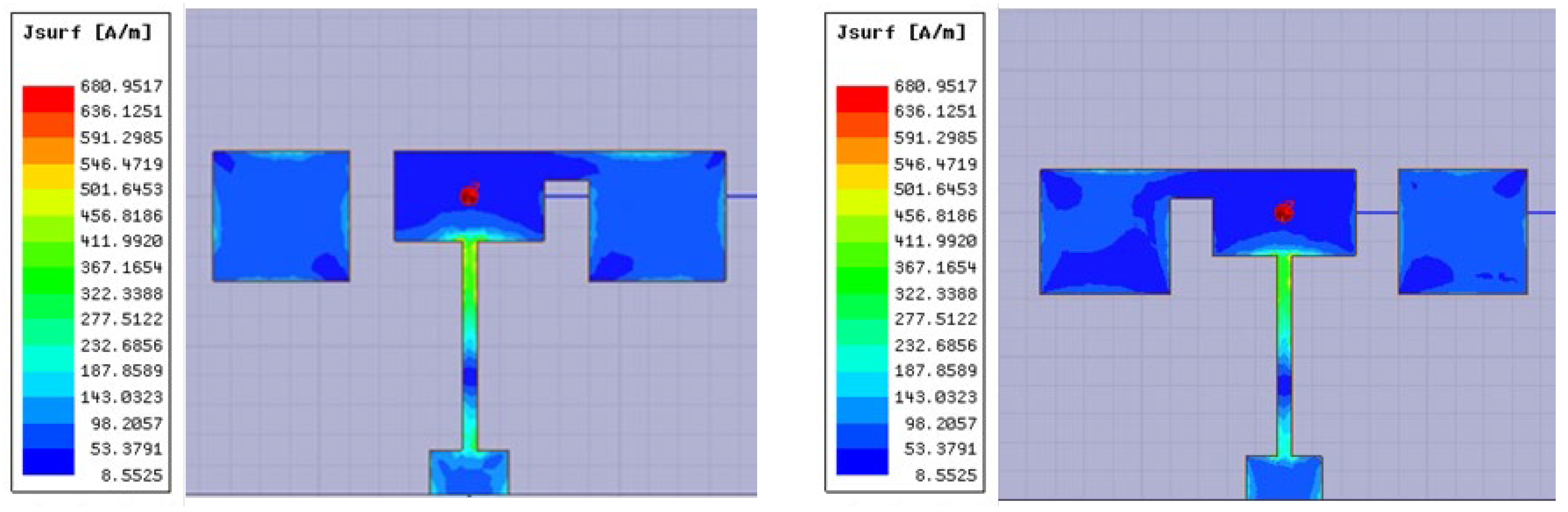






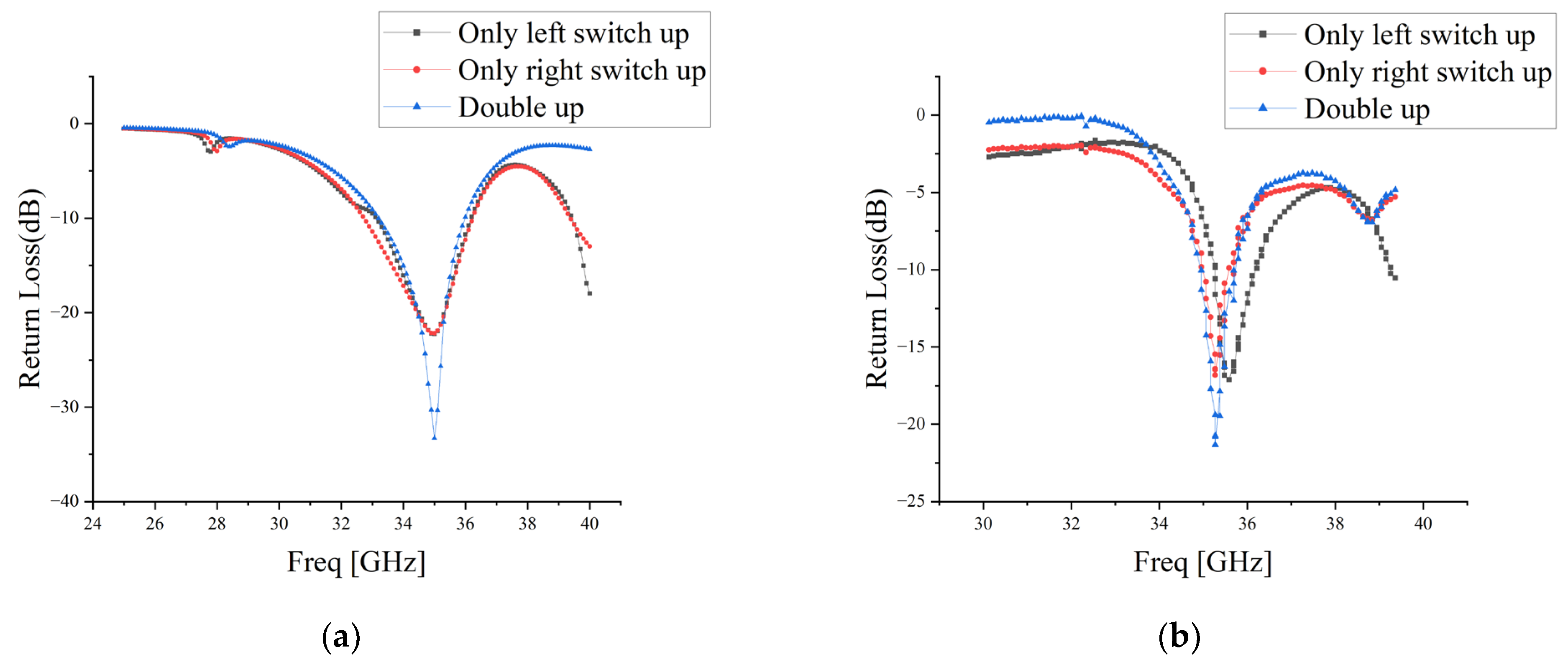

| Antenna Working State | Switch State |
|---|---|
| 1 | Switch S1 is on, switch S2 is off. |
| 2 | Switch S1 is off, switch S2 is on. |
| 3 | Switch S1 is on, switch S2 is on. |
| Symbol | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| W0 | width of the main patch | 900 μm |
| L0 | length of the main patch | 1500 μm |
| W1 | width of the sub-patch | 400 μm |
| L1 | length of the sub-patch | 890 μm |
| W2 | width of the parasitic patch | 300 μm |
| L2 | length of the parasitic patch | 450 μm |
| Wm | width of the impedance transformer | 110 μm |
| Lm | length of the impedance transformer | 1300 μm |
| Wn | width of the 50 Ω microstrip line | 190 μm |
| Ln | length of the 50 Ω microstrip line | 380 μm |
| Wb | width of the switch beam | 90 μm |
| Lb | length of the switch beam | 340 μm |
| Wh | width of the hole | 54 μm |
| Lh | length of the hole | 72 μm |
| a | length of releasing hole | 8 μm |
| r | length of the sector stub | 575 μm |
| δ | angle of the sector stub | 25° |
| Literature | Means | Frequency | Reconfigurable Angles | Block Volume (mm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [20] | PIN diodes | 27.5 GHz | 45° | 5.1 × 5.1 × 1.274 |
| [13] | Varactor diode | 2.43 GHz | 80° | 80 × 140 × 1.6 |
| [14] | PIN diodes | 27 GHz | 60° | 9.5 × 9.5 × 1 |
| [15] | Varactor diode | 0.865 GHz | 48° | 150 × 500 × 3.18 |
| [16] | Tunable Graphene Superstrate | 30 GHz | 30° | 16 × 16 × 10.3 |
| [17] | PIN diodes | 2.5 GHz | 60° | - |
| [8] | MEMS switches | 2.5 GHz and 5.4 GHz | 0° | 40 × 28 × 0.1 |
| [9] | MEMS switches | 9.41 GHz | 60° | 50.8 × 27.5 × 3.68 |
| [10] | MEMS switches | 16.05~15.75 GHz | - | 12.6 × 8.6 × 0.5 |
| [11] | MEMS switches | 1.8 GHz | - | 37 × 72 × 1.75 |
| [21] | PIN diodes | 1.3~1.8 GHz | 270° | 24 × 40 × 1.57 |
| [12] | MEMS switches | 4.57 GHz and 4.88 GHz | - | 40 × 40 × 0.25 |
| [5] | MEMS switches | 2~3.2 GHz | - | 120 × 100 × 10 |
| This paper | MEMS switches | 35 GHz | 16° | 3.7 × 5.2 × 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lai, C. Design and Analysis of Pattern Reconfigurable Antenna Based on RF MEMS Switches. Electronics 2023, 12, 3109. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12143109
Deng Z, Wang Y, Lai C. Design and Analysis of Pattern Reconfigurable Antenna Based on RF MEMS Switches. Electronics. 2023; 12(14):3109. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12143109
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Zhongliang, Yucheng Wang, and Chengqi Lai. 2023. "Design and Analysis of Pattern Reconfigurable Antenna Based on RF MEMS Switches" Electronics 12, no. 14: 3109. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12143109
APA StyleDeng, Z., Wang, Y., & Lai, C. (2023). Design and Analysis of Pattern Reconfigurable Antenna Based on RF MEMS Switches. Electronics, 12(14), 3109. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12143109





