Detection of Subsurface Damage Morphology of Lapped Optical Components by Analysis of the Fluorescence Lifetimes of Quantum Dots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
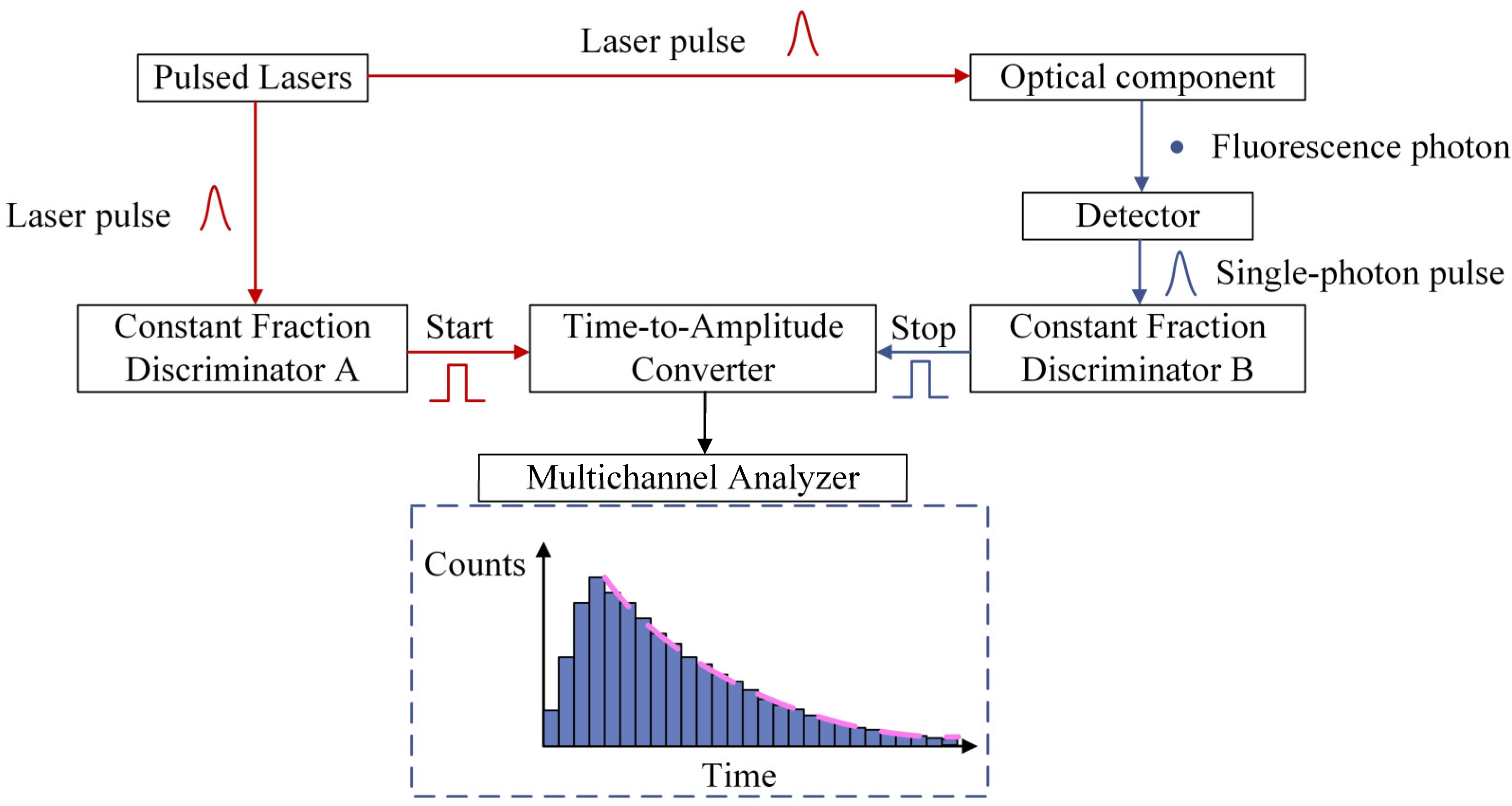
2. Principle
3. Experiments
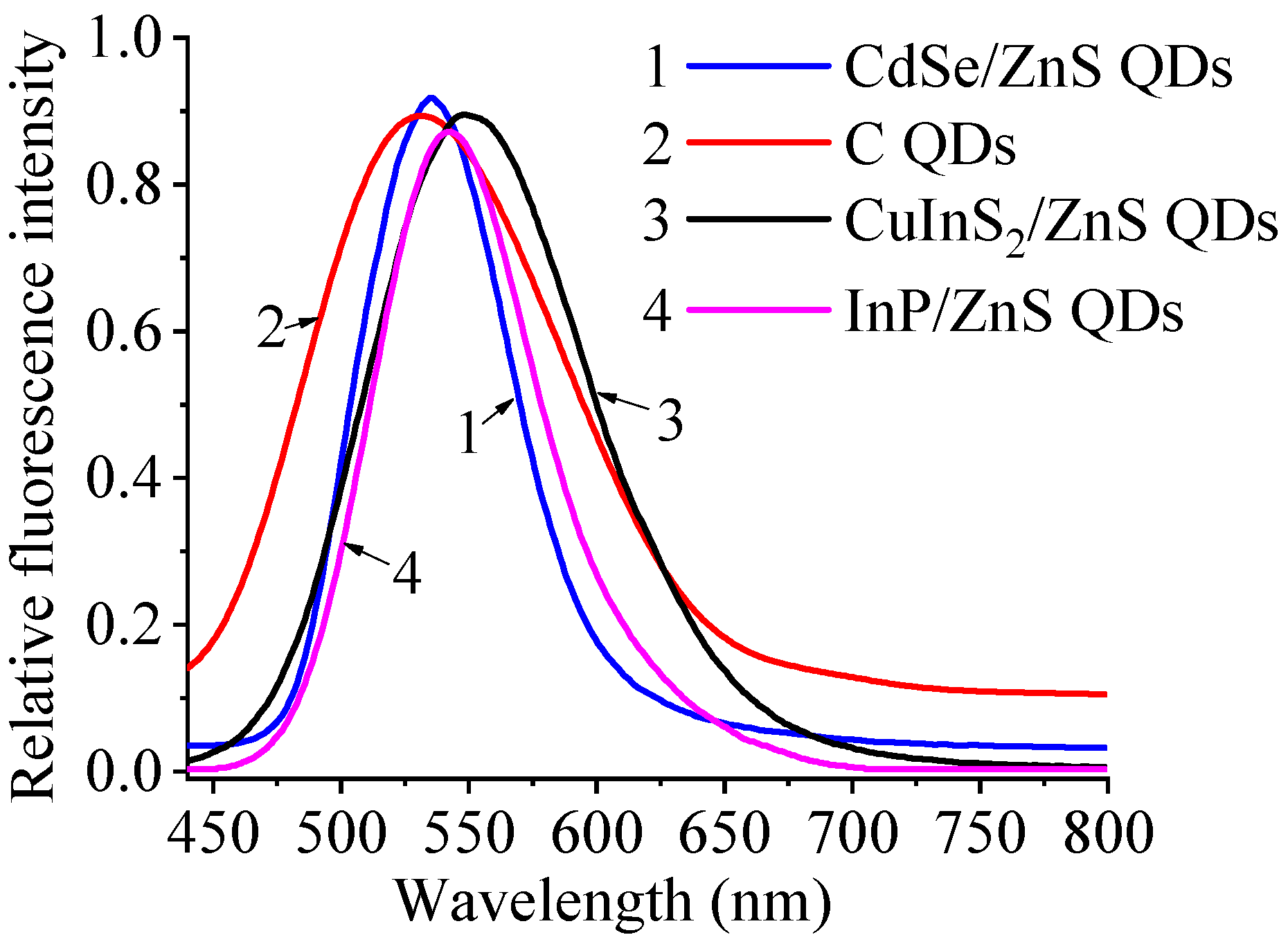
3.1. QD Characterization
3.2. QD Tagging of SSD in Optical Components
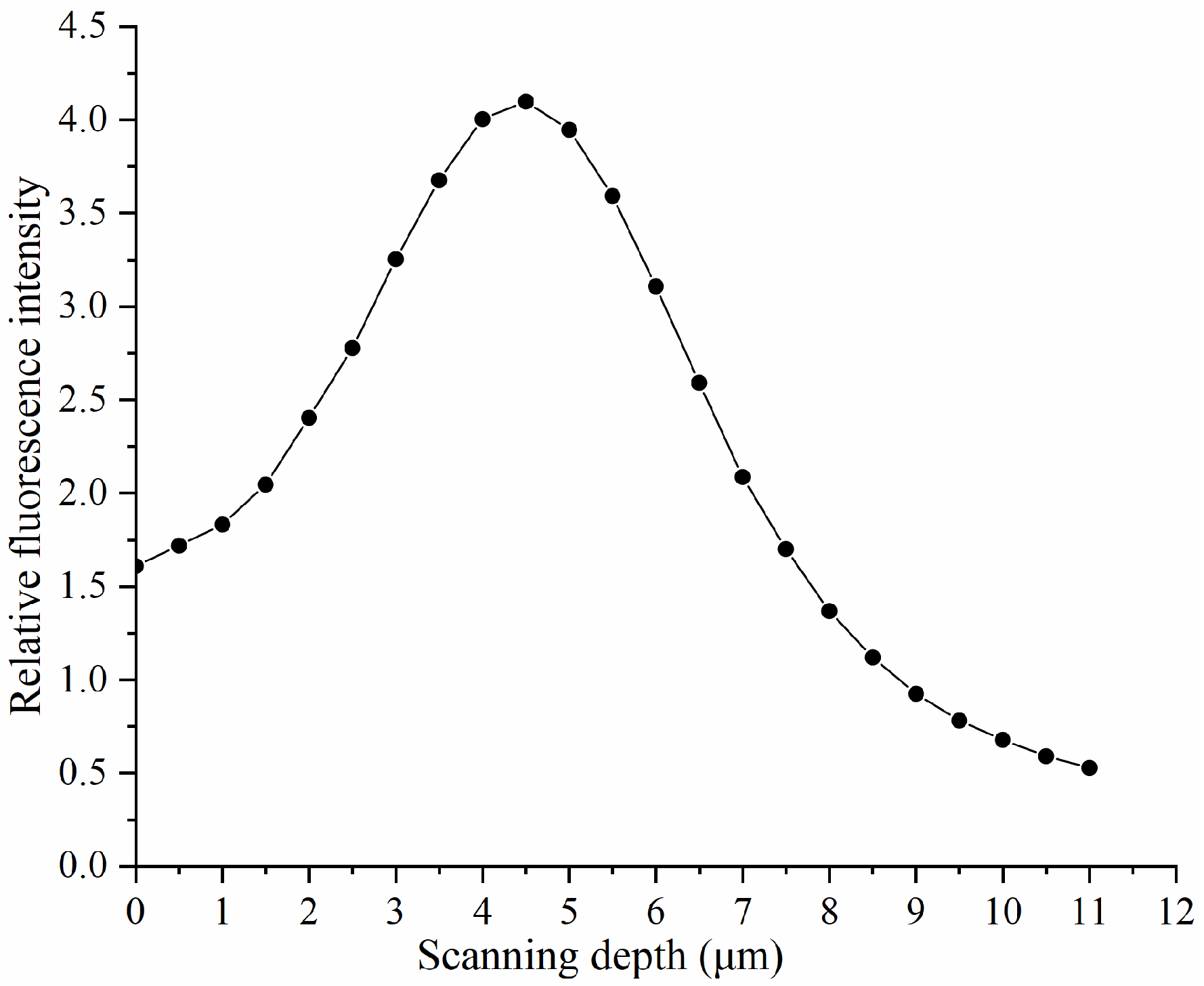
3.3. Acquisition and Characterization of Fluorescence Intensity and Fluorescence Lifetime Images of SSD in Lapped Optical Components
4. Results and Discussion
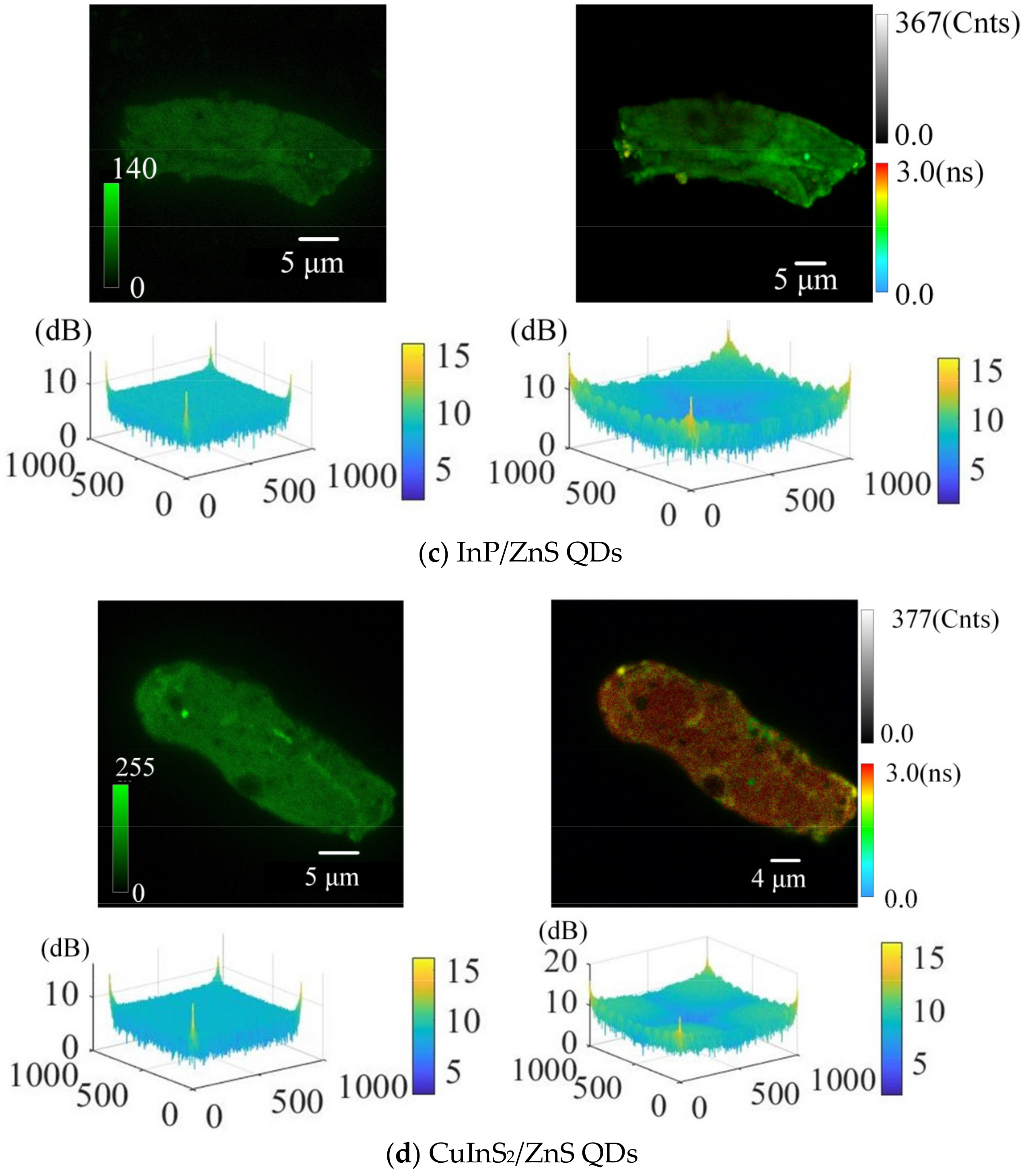
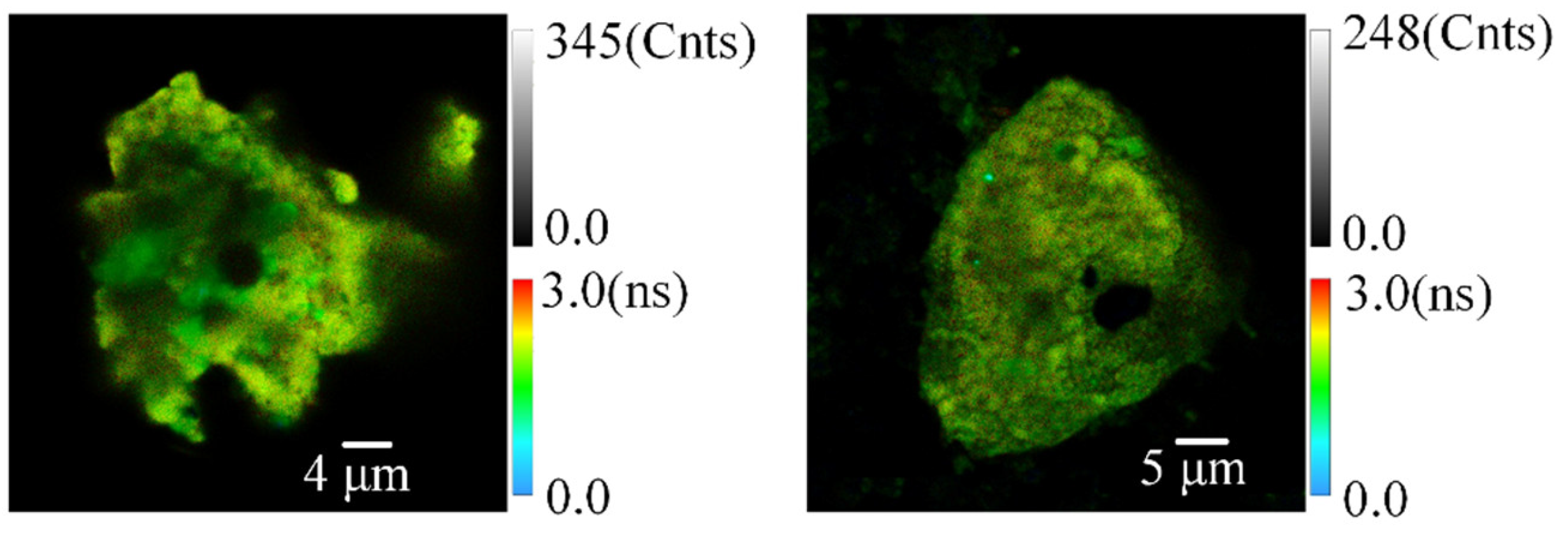
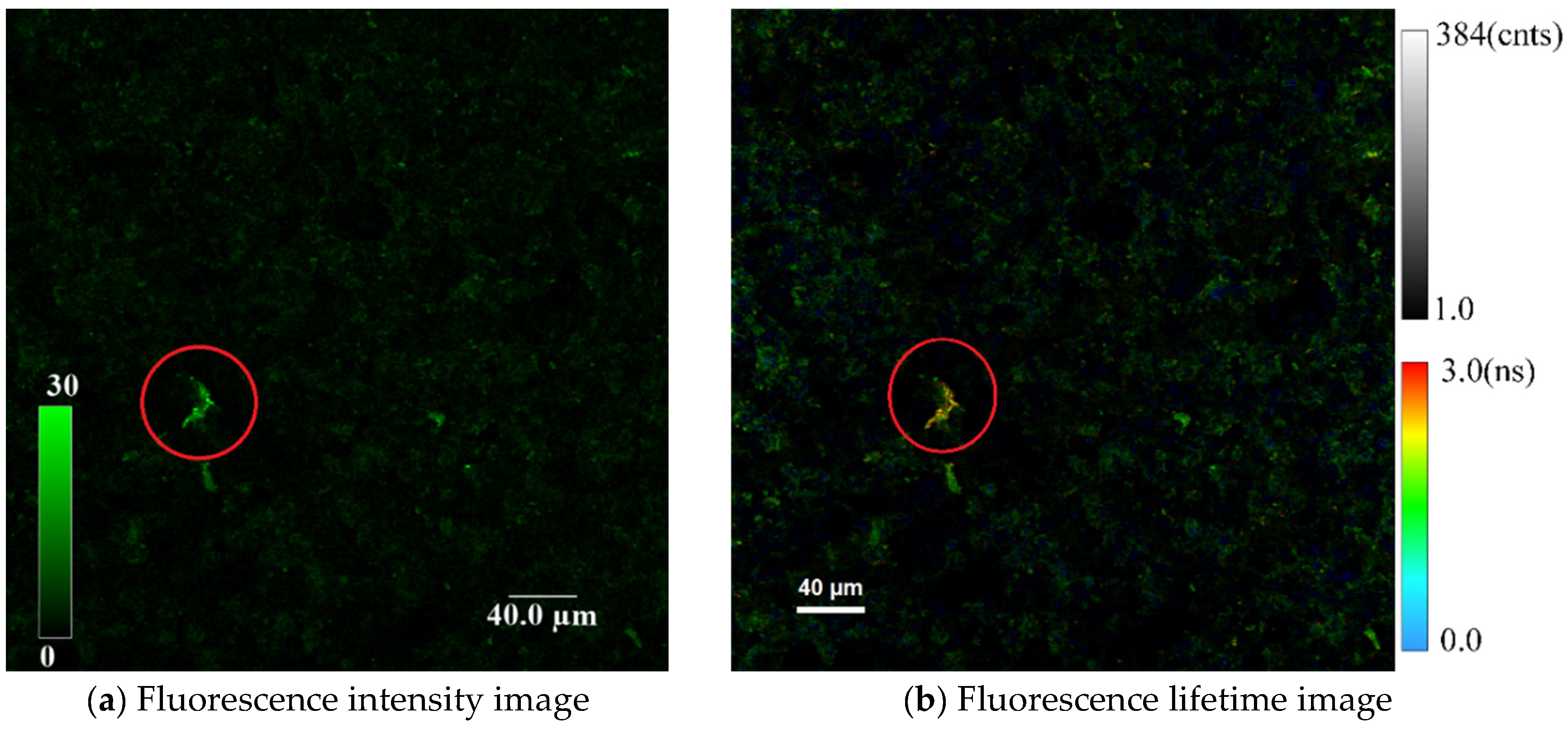
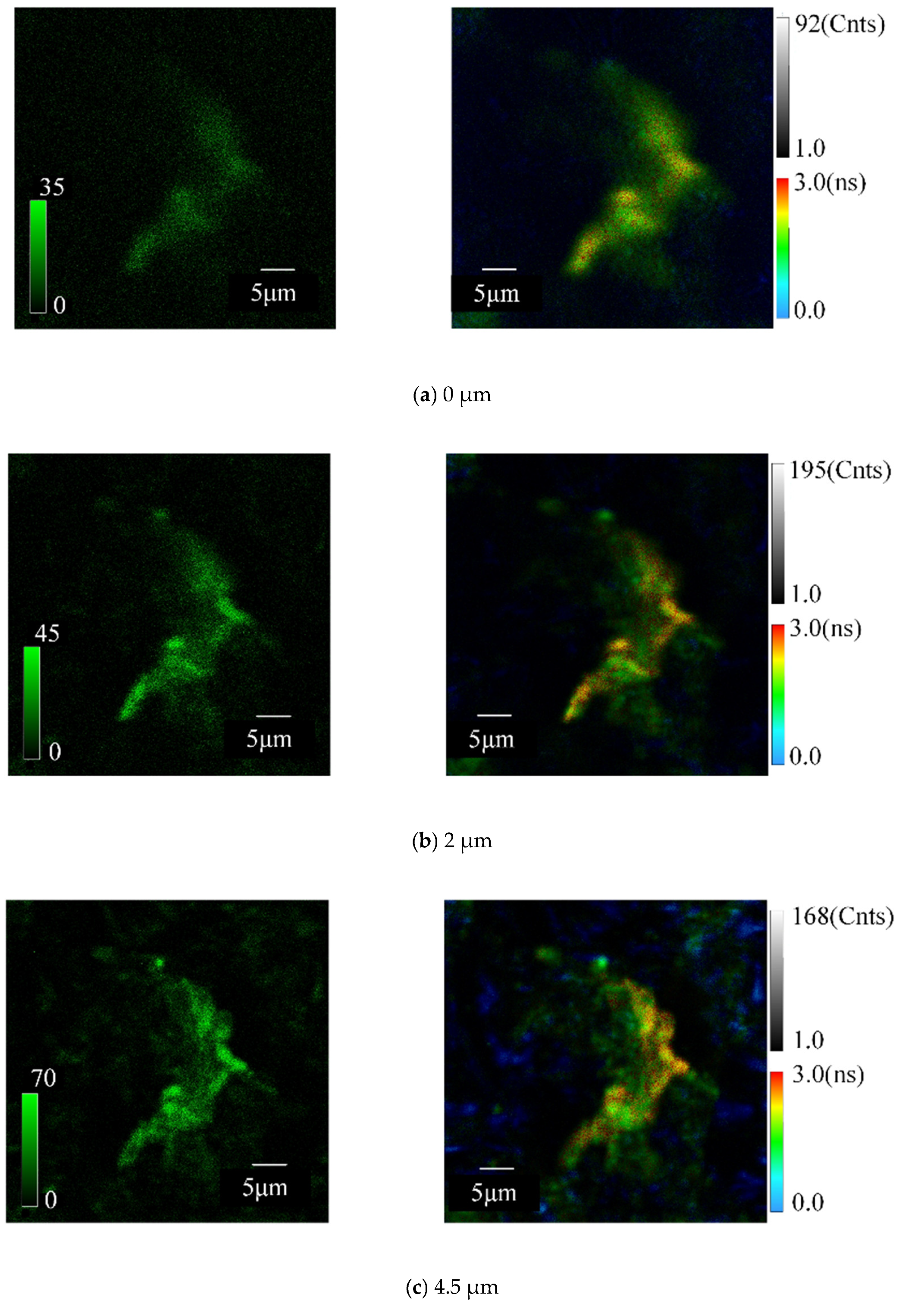
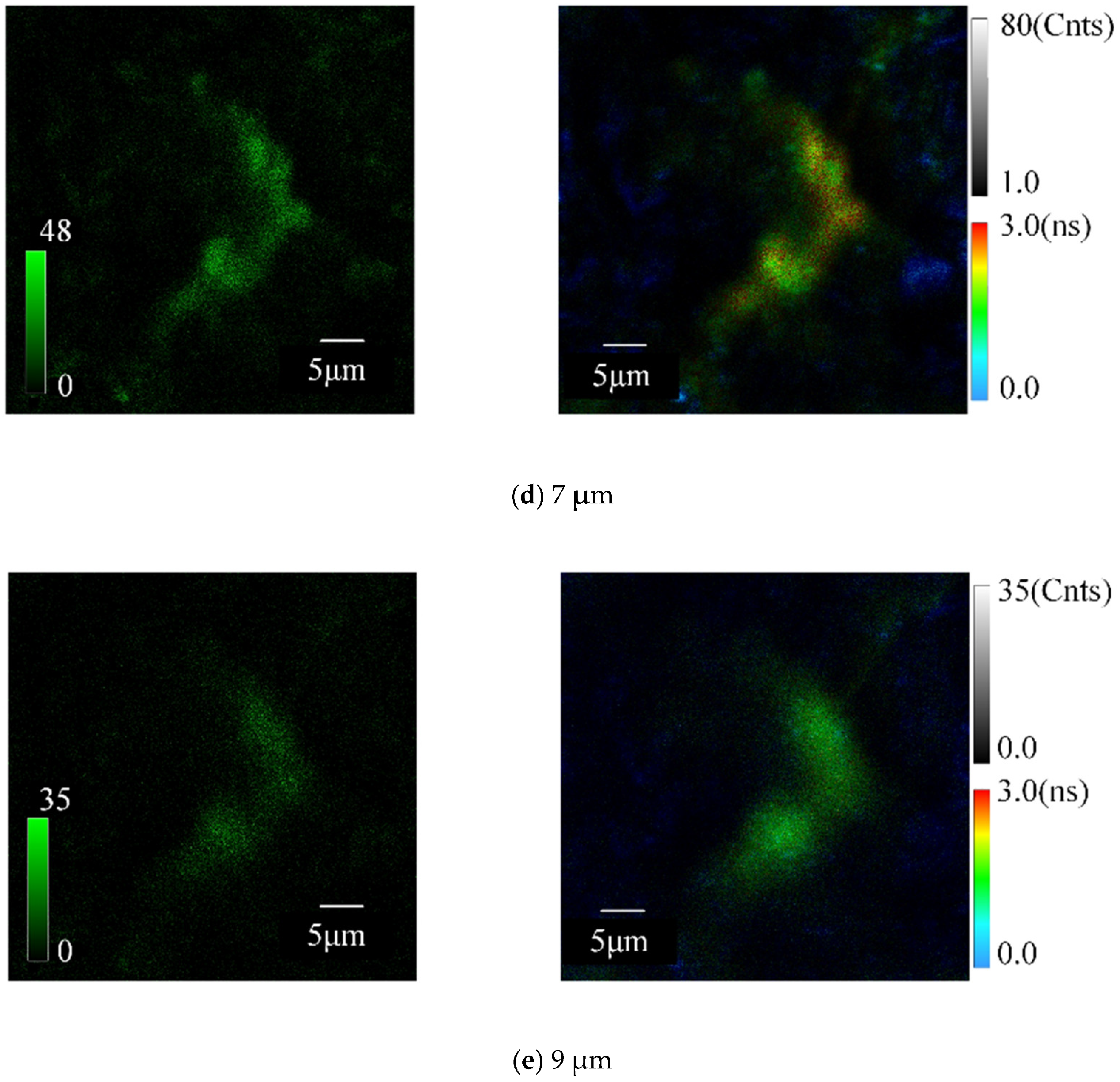
4.1. Comparison of SSD Detection Achieved by Analysis of QD Fluorescence Intensities with That Achieved by Analysis of QD Fluorescence Lifetimes
4.2. The Effect of the Size/Fluorescence Lifetime of QDs on the Detection of SSD Details
4.3. Comparison of Morphological Details at Different SSD Depths
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neauport, J.; Ambard, C.; Cormont, P.; Darbois, N.; Rondeau, O. Subsurface damage measurement of ground fused silica parts by HF etching techniques. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 20448–20456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Howes, T.D. Material-Removal Mechanisms in Grinding Ceramics. CIRP Ann.—Manuf. Technol. 1994, 43, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.L.W.Z.Y. Relationship between subsurface damage and surface roughness of optical materials in grinding and lapping processes. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 205, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temple, P.A. Total Internal Reflection Microscopy: A Surface Inspection Technique. Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 2656–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertussi, B.; Cormont, P.; Palmier, S.; Legros, P.; Rullier, J.L. Initiation of laser-induced damage sites in fused silica optical components. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 11469–11479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, M.D.; Bashkansky, M.; Reintjes, J. Subsurface defect detection in materials using optical coherence tomography. Opt. Express 1998, 2, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bismayer, U.; Brinksmeier, E.; Güttler, B.; Seibt, H.; Menz, C. Measurement of subsurface damage in silicon wafers. Precis. Eng. 1994, 16, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y. Evaluating subsurface damage in optical glasses. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. Rapid Publ. 2011, 6, 11001. [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti, R.; Nakahara, S.; Brus, L.E. Quantum size effects in the redox potentials, resonance Raman spectra, and electronic spectra of CdS crystallites in aqueous solution. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 1086–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klar, T.A.; Jakobs, S.; Dyba, M.; Egner, A.; Hell, S.W. Fluorescence microscopy with diffraction resolution barrier broken by stimulated emission. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8206–8210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, T.; Roesch, A.; Riedel, D.; Jakobs, S. Live-cell STED nanoscopy of mitochondrial cristae. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, W.B.; Mullany, B.A.; Parker, W.C.; Moyer, P.J.; Randles, M.H. Using quantum dots to tag subsurface damage in lapped and polished glass samples. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, 5155–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, W.; Mullany, B.; Parker, W.; Moyer, P.; Randles, M. Using quantum dots to evaluate subsurface damage depths and formation mechanisms in glass. CIRP Ann.—Manuf. Technol. 2010, 59, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, W.B.; Mullany, B.A.; Moyer, P.J.; Parker, W.C.; Randles, M.H. Characterizing quantum dots for use in detecting subsurface damage. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Meeting of the American Society for Precision Engineering, Portland, OR, USA, 19–24 October 2008; pp. 440–443. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, W.B.; Mullany, B.A.; Moyer, P.J.; Parker, W.C.; Randles, M.H. Testing quantum dots as a means of assessing subsurface damage in polished glass. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual Meeting of the American Society For Precision Engineering, Monterey, CA, USA, 4–9 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, W.; Mullany, B.; Parker, W.; Moyer, P. Evaluating Subsurface Damage with Quantum Dots. In Proceedings of the Optical Fabrication and Testing 2010, Jackson Hole, WY, USA, 13–17 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, W.B. A Novel Fluorescence Based Method of Assessing Subsurface Damage in Optical Materials; The University of North Carolina: Charlotte, NC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hong-Xiang, W.; Jing, H.; Jing-He, W.; Ben-Wen, Z.; Yan-Hu, Z. Experimental investigation of subsurface damage depth of lapped optics by fluorescent method. J. Cent. South Univ. 2018, 25, 1678–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Gao, R.; Li, T. Subsurface damage detection of optical elements by analyzing the photobleaching properties of quantum dots. Precis. Eng. 2022, 77, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Hinde, E.; Owen, D.M.; Lowe, S.B.; Reece, P.J.; Gaus, K.; Gooding, J.J. Enhancing Quantum Dots for Bioimaging using Advanced Surface Chemistry and Advanced Optical Microscopy: Application to Silicon Quantum Dots (SiQDs). Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6144–6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goreham, R.V.; Schroeder, K.L.; Holmes, A.; Bradley, S.J.; Nann, T. Demonstration of the lack of cytotoxicity of unmodified and folic acid modified graphene oxide quantum dots, and their application to fluorescence lifetime imaging of HaCaT cells. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Nienhaus, G.U. In Situ monitoring of the intracellular stability of nanoparticles by using fluorescence lifetime imaging. Small 2016, 12, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steponkiene, S.; Valanciunaite, J.; Skripka, A.; Rotomskis, R. Cellular Uptake and Photosensitizing Properties of Quantum Dot-Chlorin e(6) Complex: In Vitro Study. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Gao, R.; Li, T. Technology for subsurface damages detection of optical components based on various fluorescent material. In Proceedings of the AOPC 2022: Novel Optical Design; and Optics Ultra Precision Manufacturing and Testing, Beijing, China, 20 January 2023; pp. 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, F.; Sun, L.; Cai, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Quantum dots from microfluidics for nanomedical application. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. -Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 11, e1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhling, K.; Hirvonen, L.M.; Levitt, J.A.; Chung, P.-H.; Tregidgo, C.; Le Marois, A.; Rusakov, D.A.; Zheng, K.; Ameer-Beg, S.; Poland, S.J.M.P. Fluorescence lifetime imaging (FLIM): Basic concepts and some recent developments. Med. Photonics 2015, 27, 3–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemdana, I.; Mahdouani, M.; Bourguiga, R. Investigation of the radiative lifetime in core-shell CdSe/ZnS and CdSe/ZnSe quantum dots. Phys. B-Condens. Matter 2012, 407, 3313–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Tripathi, S.K. Probing photoluminescence dynamics of colloidal CdSe/ZnS core/shell nanoparticles. J. Lumin. 2014, 155, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
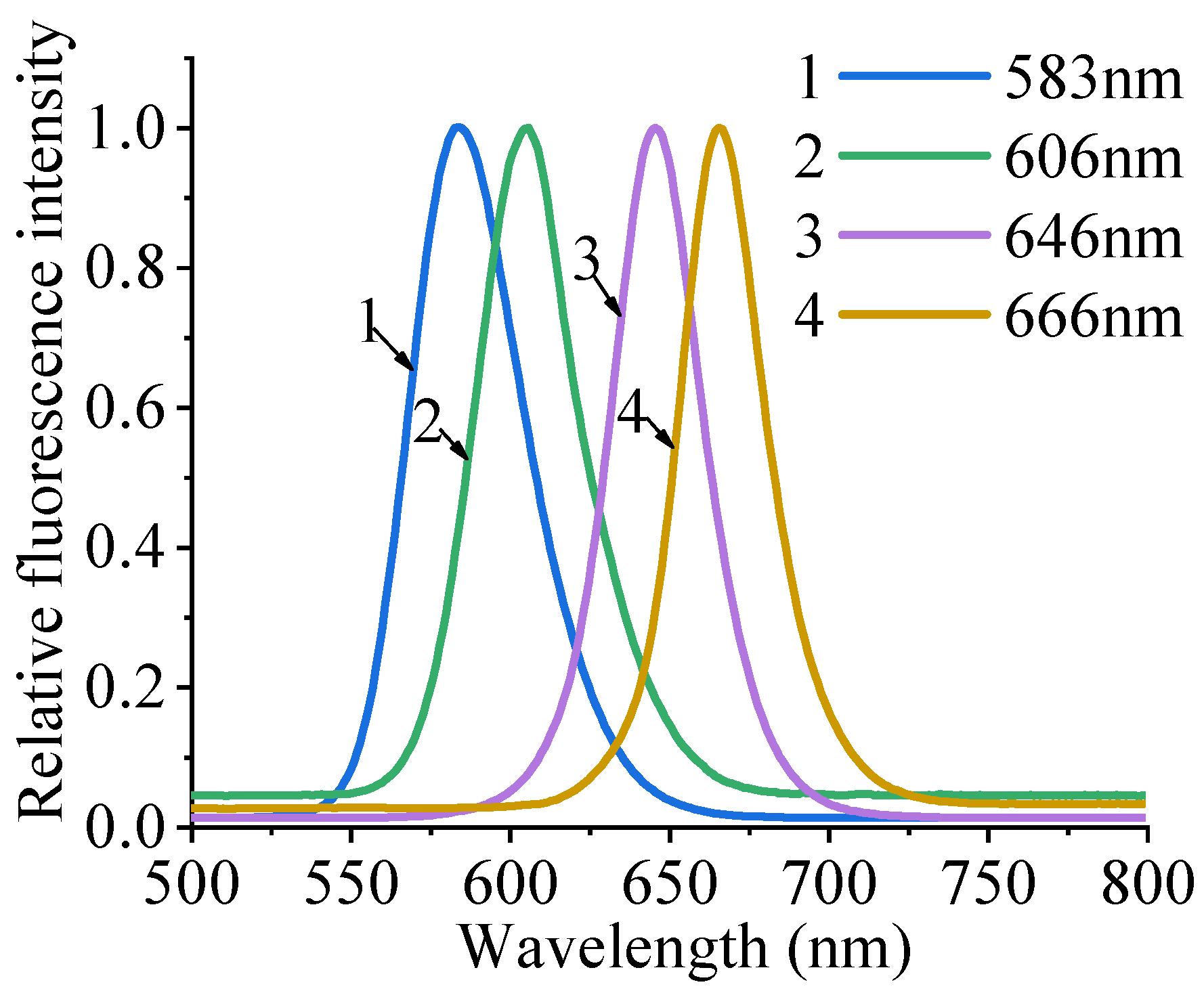


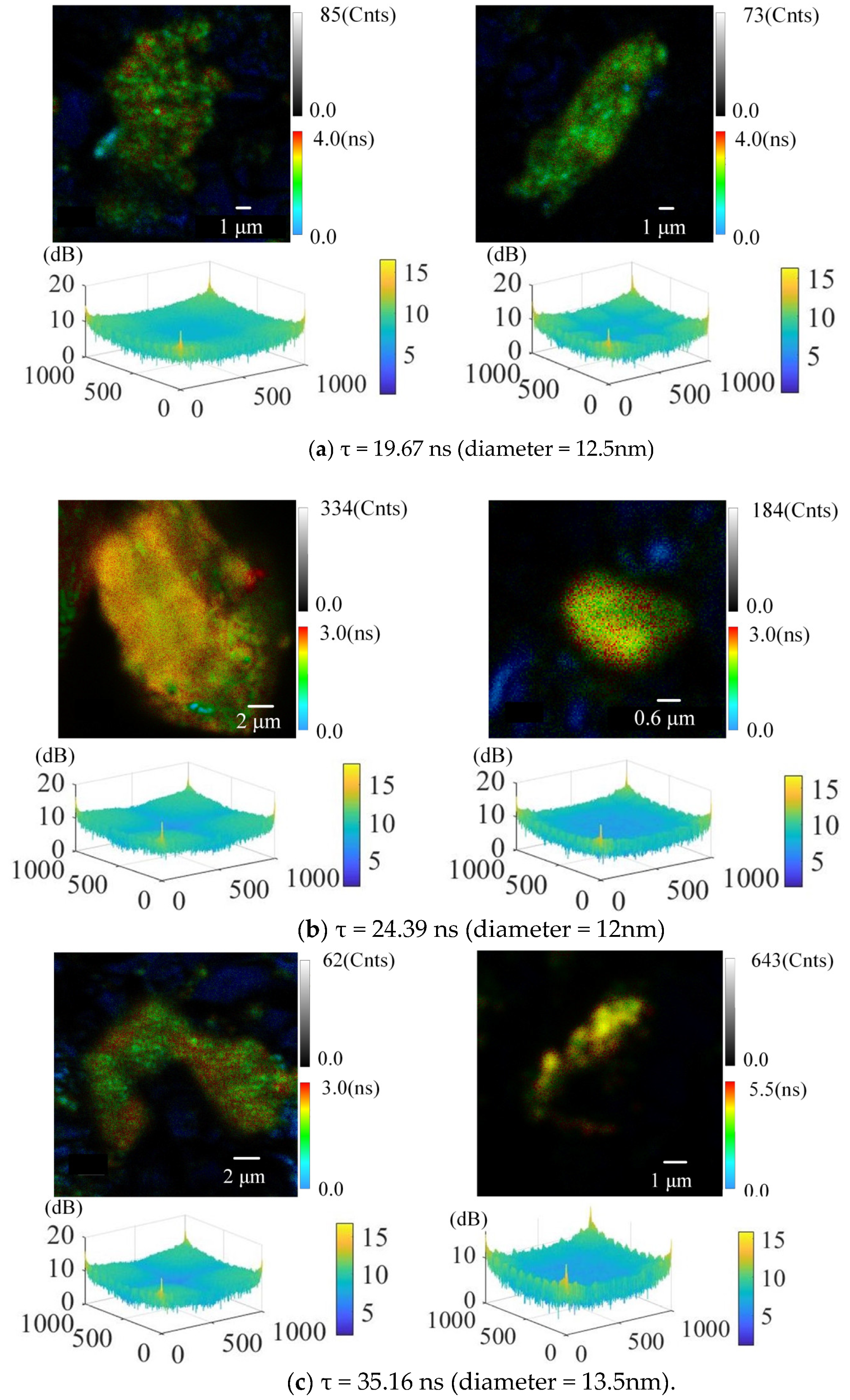
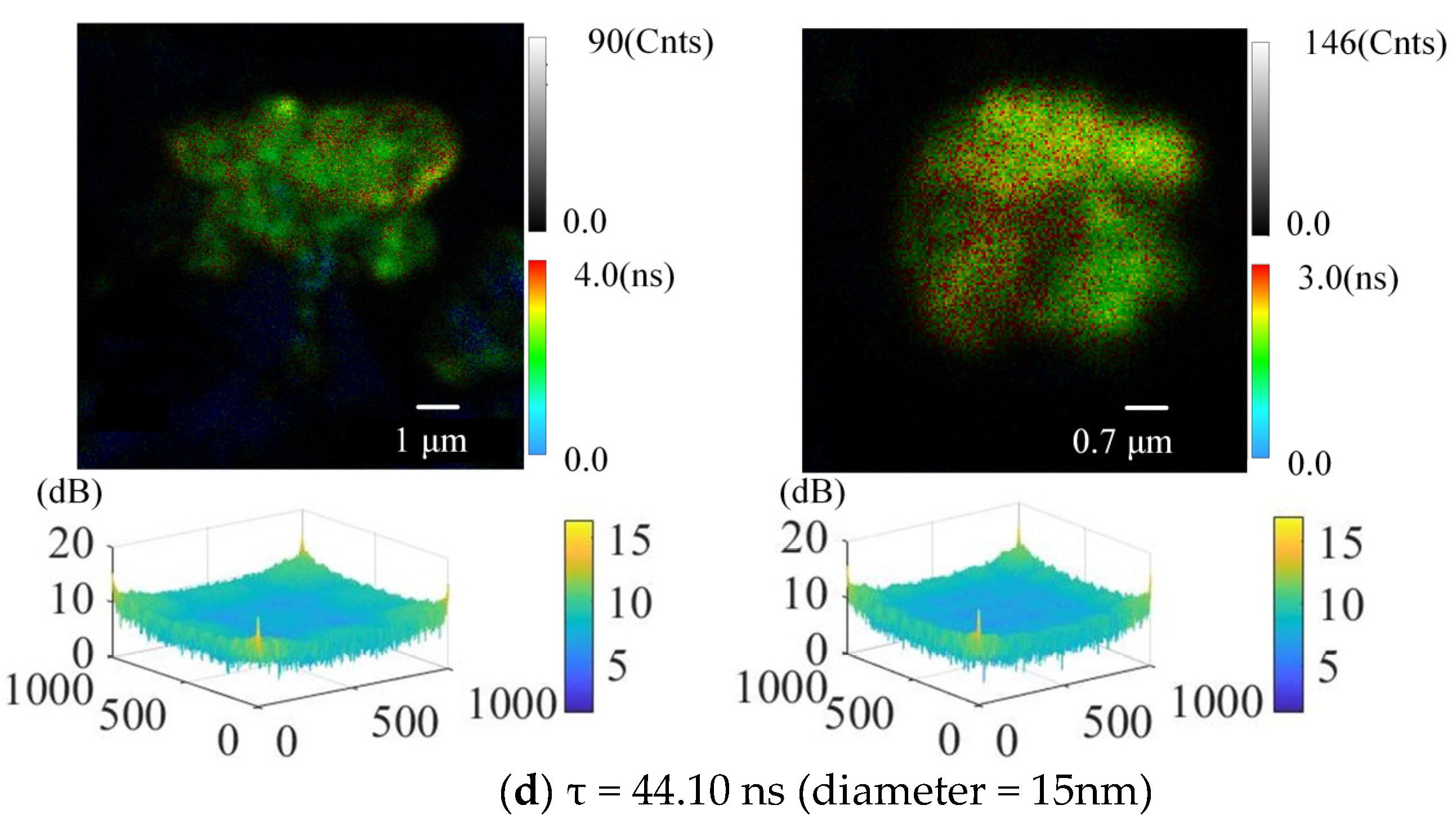

| Fluorescence Peaks | Fluorescence Lifetime τ (ns) | Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| 583 | 24.39 | 12 |
| 606 | 19.67 | 12.5 |
| 646 | 35.16 | 13.5 |
| 666 | 44.10 | 15 |
| Serial Number | Elemental Composition of QDs | Fluorescence Peaks (nm) | Processing Parameters and Steps |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CdSe/ZnS QDs | 544 | (1) D30 diamond lapping slurry, 5 min, lapping speed = 54 rad/min; (2) D6 diamond lapping slurry, 3 min, lapping speed = 54 rad/min. |
| 2 | C QDs | 544 | |
| 3 | InP/ZnS QDs | 544 | |
| 4 | CuInS2/ZnS QDs | 544 | |
| 5 | CdSe/ZnS QDs | 583 | |
| 6 | CdSe/ZnS QDs | 606 | |
| 7 | CdSe/ZnS QDs | 646 | |
| 8 | CdSe/ZnS QDs | 666 |
| Characterization of SSD | Fluorescence Intensity-Based Method | Fluorescence Lifetime-Based Method |
|---|---|---|
| Distribution | Can be detected | |
| Depth | Can be detected | |
| Morphology | Low detection accuracy | High detection accuracy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, R.; He, W. Detection of Subsurface Damage Morphology of Lapped Optical Components by Analysis of the Fluorescence Lifetimes of Quantum Dots. Electronics 2023, 12, 3868. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12183868
Cui Y, Wang C, Liu X, Wu Y, Li Z, Li R, He W. Detection of Subsurface Damage Morphology of Lapped Optical Components by Analysis of the Fluorescence Lifetimes of Quantum Dots. Electronics. 2023; 12(18):3868. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12183868
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Yana, Chunyang Wang, Xuelian Liu, Yajie Wu, Zhengze Li, Rong Li, and Wen He. 2023. "Detection of Subsurface Damage Morphology of Lapped Optical Components by Analysis of the Fluorescence Lifetimes of Quantum Dots" Electronics 12, no. 18: 3868. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12183868
APA StyleCui, Y., Wang, C., Liu, X., Wu, Y., Li, Z., Li, R., & He, W. (2023). Detection of Subsurface Damage Morphology of Lapped Optical Components by Analysis of the Fluorescence Lifetimes of Quantum Dots. Electronics, 12(18), 3868. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12183868







