Enhanced Real-Time Maintenance Management Model—A Step toward Industry 4.0 through Lean: Conveyor Belt Operation Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Contextualization and Formulation of the Problem
1.2. Background
1.3. Goals, Objectives, and Manuscript Organization
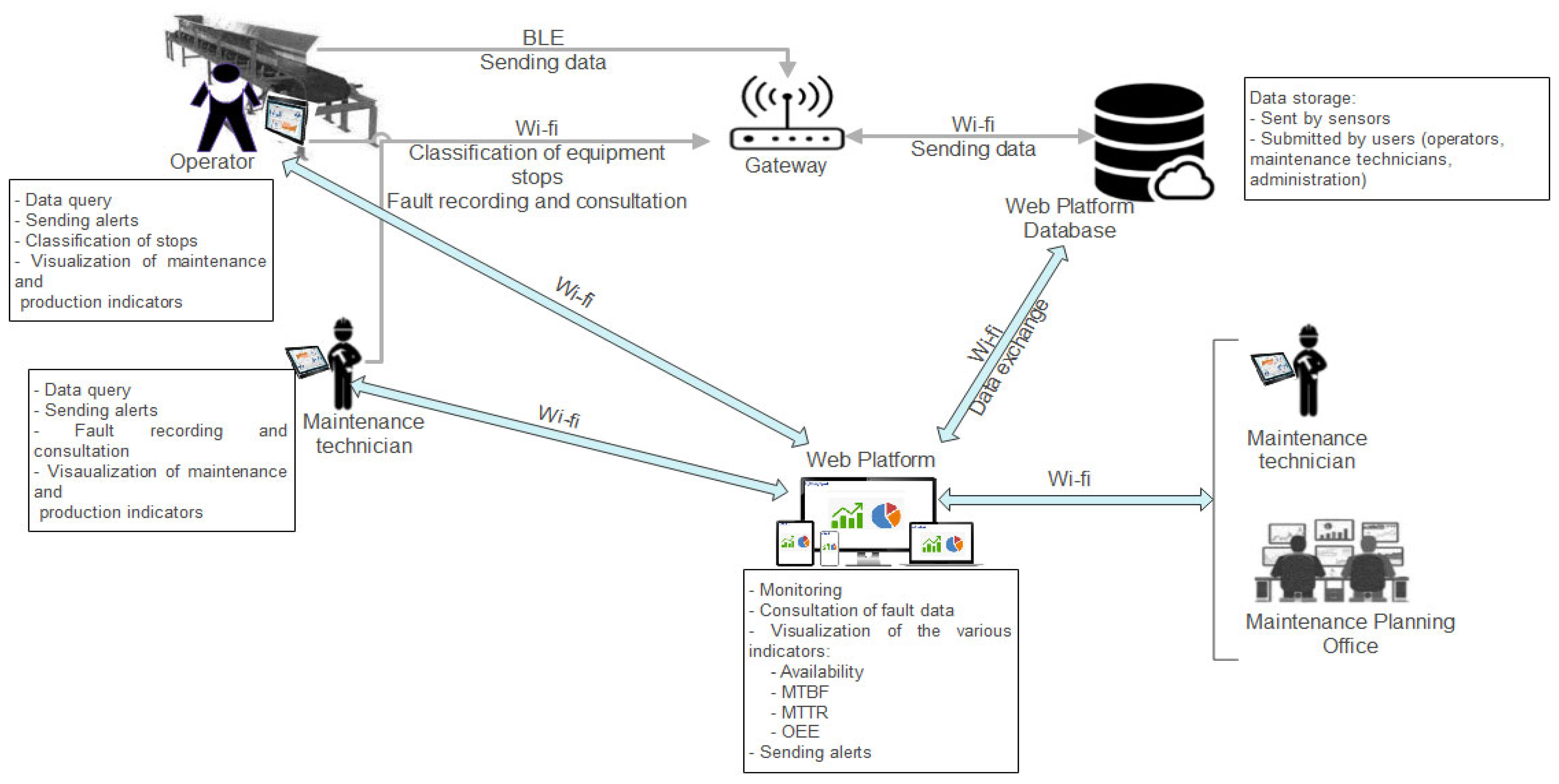
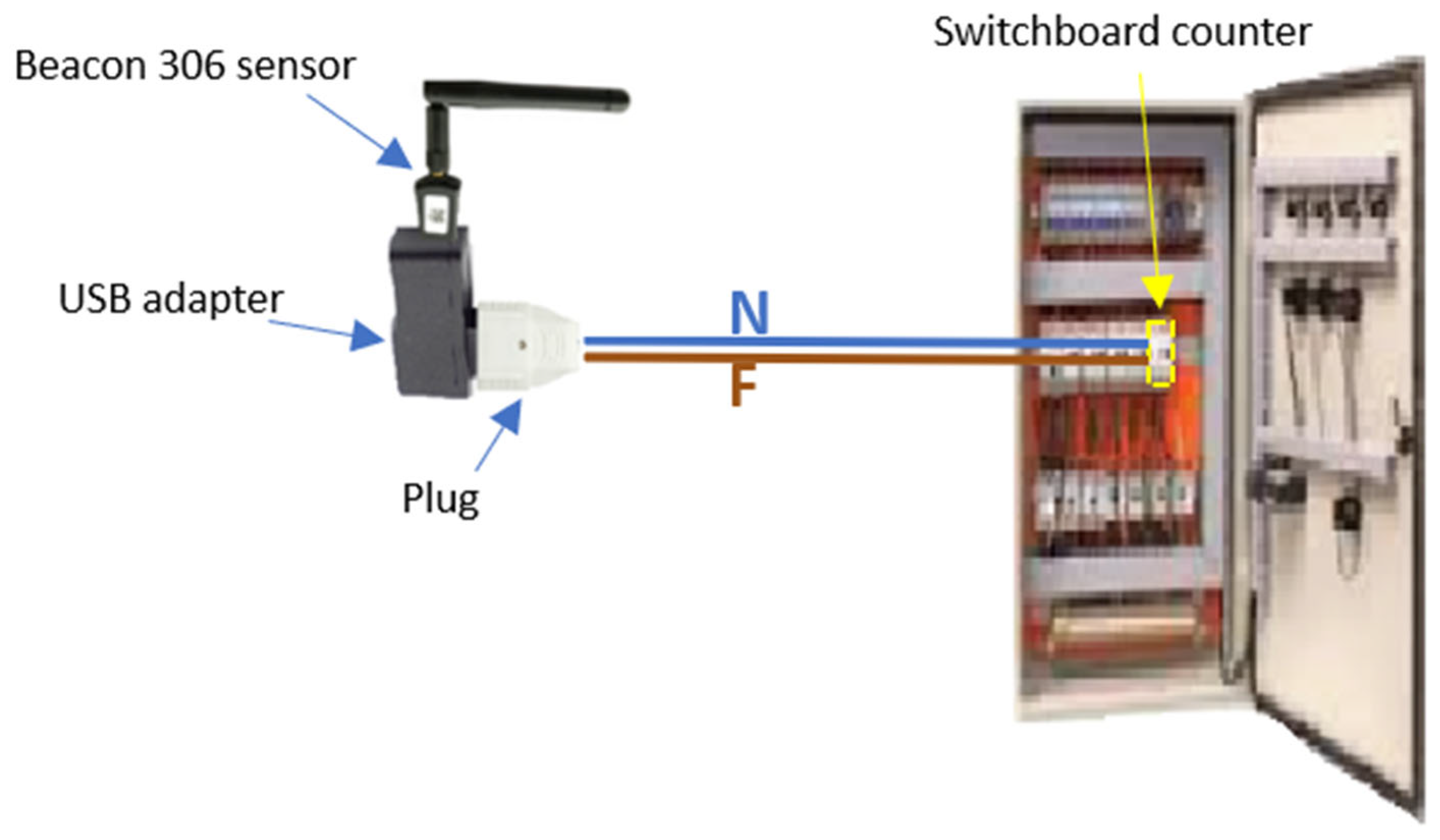
2. Materials and Methods
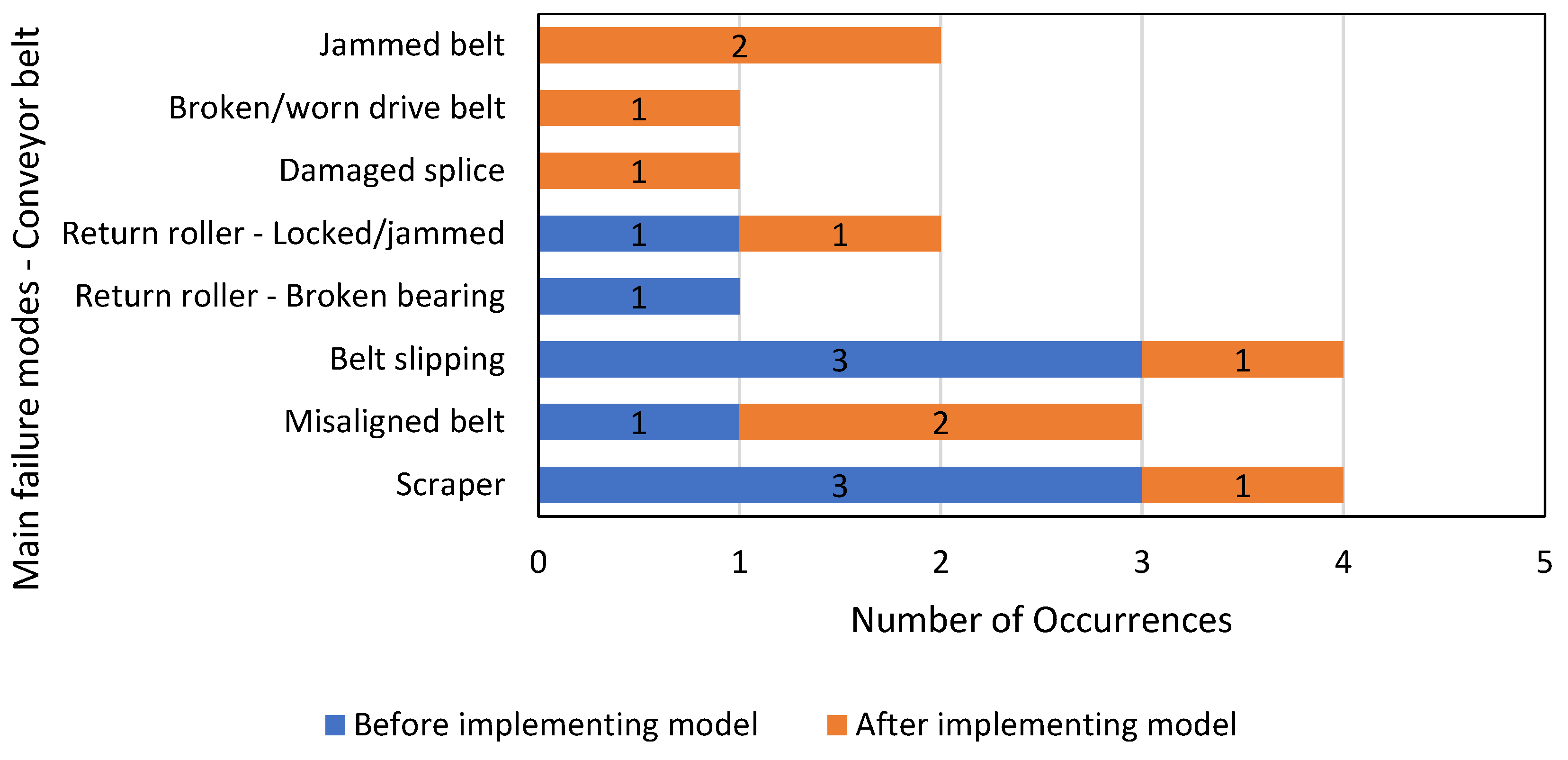
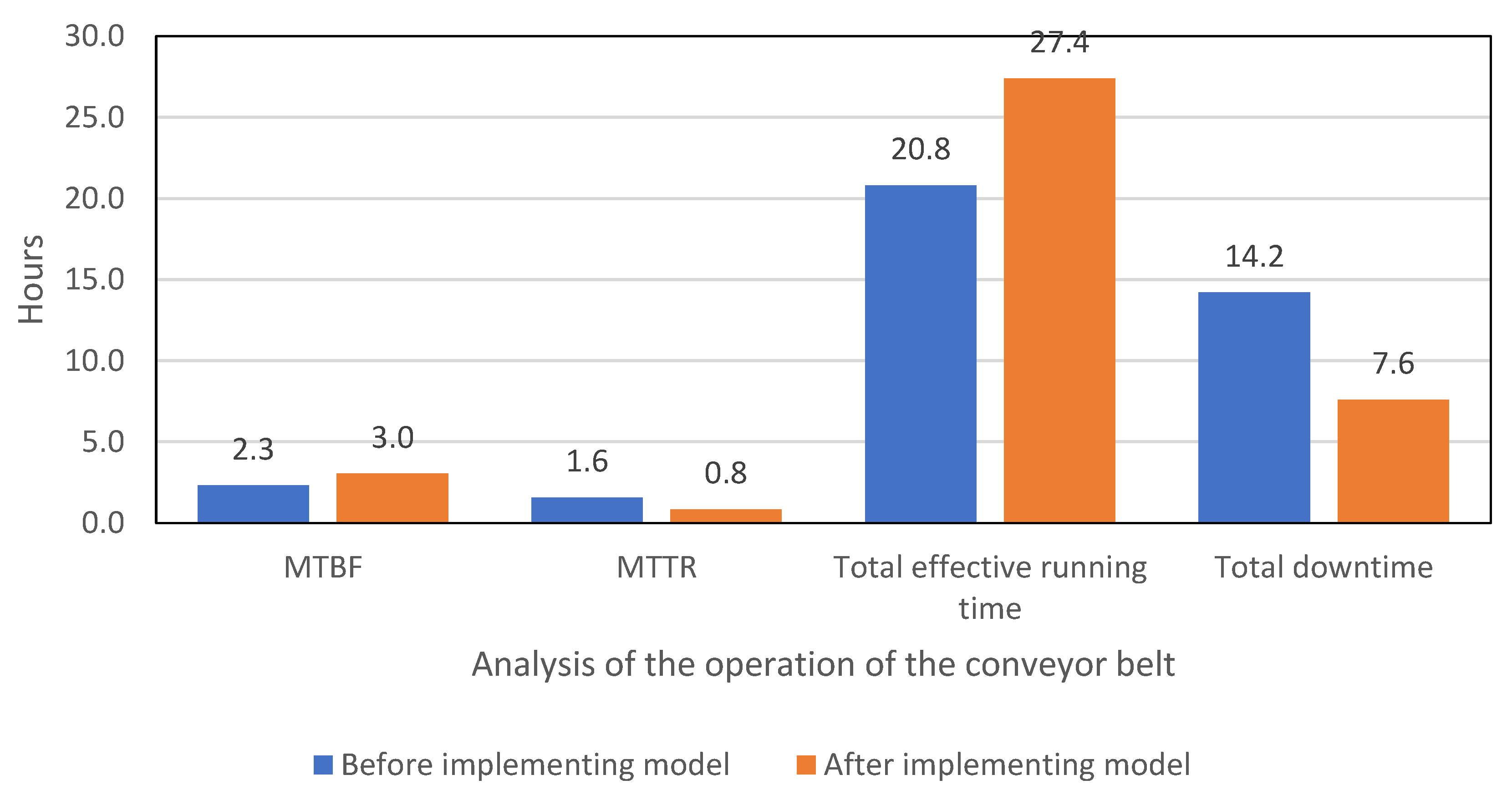
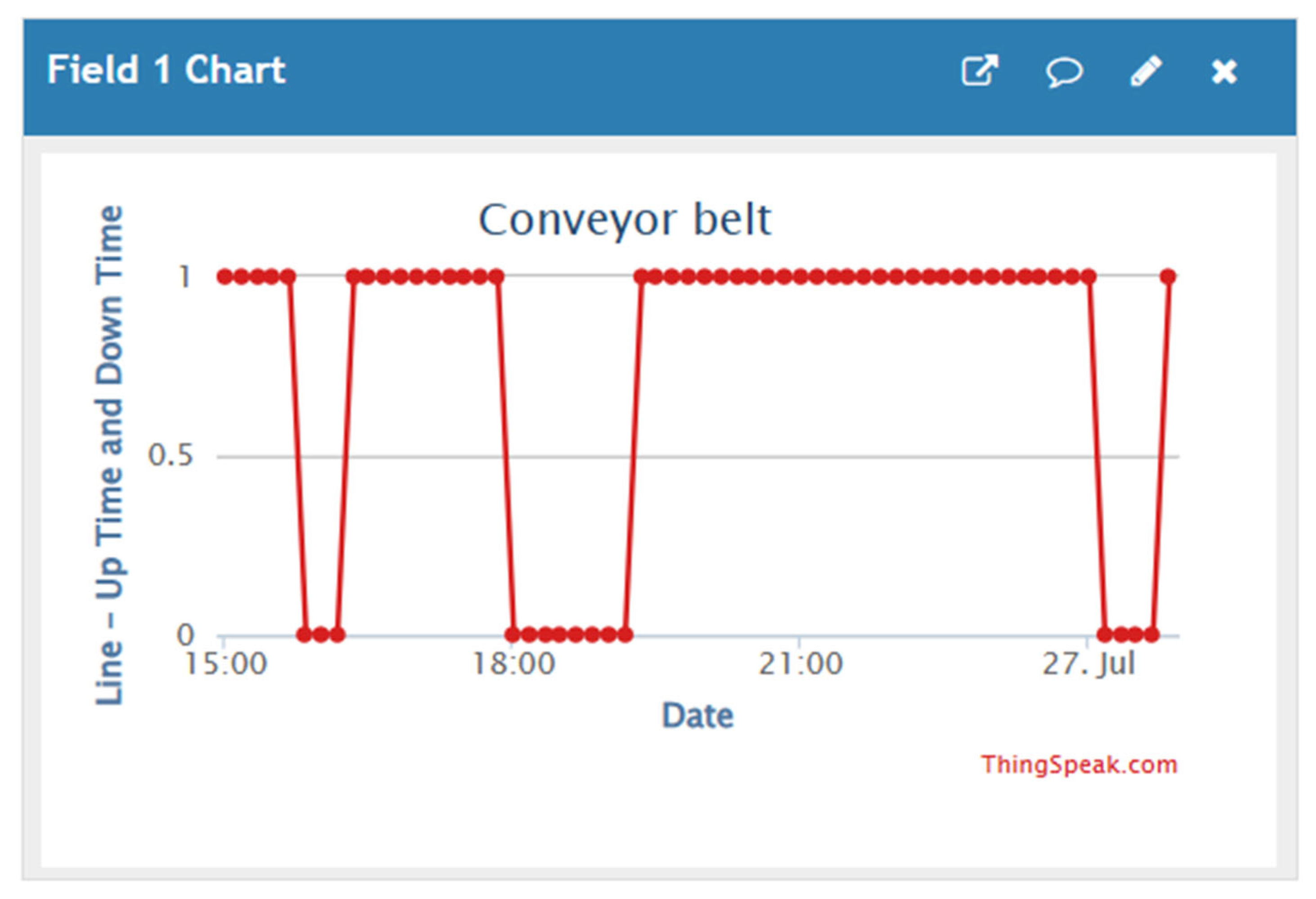
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trybała, P.; Blachowski, J.; Błażej, R.; Zimroz, R. Damage Detection Based on 3D Point Cloud Data Processing from Laser Scanning of Conveyor Belt Surface. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihnastyi, O.; Khodusov, V. Development of the controlling speed algorithm of the conveyor belt based on TOU-tariffs. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Information-Communication Technologies & Embedded Systems, Mykolaiv, Ukraine, 12 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kirjanów-Błażej, A.; Rzeszowska, A. Conveyor Belt Damage Detection with the Use of a Two-Layer Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, L.; Abdullahi, A.O.; Moshrefzadeh, A.; Ball, A.; Conaghan, G.; Kluis, W. Innovative Conveyor Belt Monitoring via Current Signals. Electronics 2023, 12, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błażej, R.; Jurdziak, L.; Kirjanów-Błażej, A.; Bajda, M.; Olchówka, D.; Rzeszowska, A. Profitability of Conveyor Belt Refurbishment and Diagnostics in the Light of the Circular Economy and the Full and Effective Use of Resources. Energies 2022, 15, 7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, G.; Palaniswamy, E.; Sambathkumar, M.; Vijayakumar, R.; Sakthimuruga, T.M. Conveyor belt troubles (bulk material handling). Int. J. Emerg. Eng. Res. Technol. 2014, 2, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, C.; Qiao, T.; Qiao, M.; Xiong, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H. Research on audio-visual detection method for conveyor belt longitudinal tear. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 120202–120213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jonge, B.; Scarf, P.A. A review on maintenance optimization. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 285, 805–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi, A.; Khakzad, N.; Khan, F.; MacKinnon, S.; Abbassi, R. The role of human error in risk analysis: Application to pre-and post-maintenance procedures of process facilities. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2013, 119, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorko, G.; Molnár, V.; Michalik, P.; Dovica, M.; Kelemenová, T.; Toth, T. Failure analysis of conveyor belt samples under tensile load. J. Ind. Text. 2019, 48, 1364–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, D.; Gaspar, P.D.; Charrua-Santos, F.; Navas, H. Integrating TPM and Industry 4.0 to Increase the Availability of Industrial Assets: A Case Study on a Conveyor Belt. Processes 2023, 11, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norddin, K.H.N.M.; Saman, M.Z.M. Implementation of total productive maintenance concept in a fertilizer process plant. J. Mek. 2012, 34, 66–82. [Google Scholar]
- Galar, D.; Gustafson, A.; Tormos Martínez, B.V.; Berges, L. Maintenance decision making based on different types of data fusion. Eksploat. Niezawodn. Maint. Reliab. 2012, 14, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Koussaimi, M.A.; Bouami, D.; Elfezazi, S. Improvement maintenance implementation based on downtime analysis approach. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2016, 22, 378–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgic, Y.; Lazakis, I.; Dinwoodie, I.; McMillan, D.; Revie, M. Advanced logistics planning for offshore wind farm operation and maintenance activities. Ocean Eng. 2015, 101, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundage, M.P.; Sexton, T.; Hodkiewicz, M.; Morris, K.C.; Arinez, J.; Ameri, F.; Ni, J.; Xiao, G. Where do we start? Guidance for technology implementation in maintenance management for manufacturing. In Proceedings of the International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, Erie, PA, USA, 10–14 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kao, H.A.; Yang, S. Service innovation and smart analytics for industry 4.0 and big data environment. Procedia CIRP 2014, 16, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, G.W.; Weiss, B.A.; Helu, M. A review of diagnostic and prognostic capabilities and best practices for manufacturing. J. Intell. Manuf. 2019, 30, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, W.; Wang, J.; Wu, P.; Wang, X. Lean management framework for improving maintenance operation: Development and application in the oil and gas industry. Prod. Plan. Control 2021, 32, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, O.; Capaldo, A.; Duran Acevedo, P.A. Lean Maintenance Applied to Improve Maintenance Efficiency in Thermoelectric Power Plants. Energies 2017, 10, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharana, U.C.; Sarmah, S.P.; Rathore, P.K. Application of data mining for spare parts information in maintenance schedule: A case study. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2019, 30, 1055–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurkiewicz, D. Computer-aided maintenance and reliability management systems for conveyor belts. Eksploat. Niezawodn. 2014, 16, 377–382. [Google Scholar]
- Burawat, P. Productivity improvement of highway engineering industry by implementation of lean Six Sigma, TPM, ECRS, AND 5S: A Case study of AAA Co., Ltd. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Rev. 2019, 7, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gupta, V.; Mitra, R.; Koenig, F.; Kumar, M.; Tiwari, M.K. Predictive maintenance of baggage handling conveyors using IoT. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 177, 109033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiangala, K.S.; Wang, Z. An effective predictive maintenance framework for conveyor motors using dual time-series imaging and convolutional neural network in an industry 4.0 environment. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 121033–121049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortorella, G.; Saurin, T.A.; Fogliatto, F.S.; Tlapa, D.; Moyano-Fuentes, J.; Gaiardelli, P.; Seyedghorban, Z.; Vassolo, R.; Mac Cawley, A.F.; Sunder, M.V.; et al. The impact of Industry 4.0 on the relationship between TPM and maintenance performance. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2022, 33, 489–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousopoulou, V.; Nizamis, A.; Vafeiadis, T.; Ioannidis, D.; Tzovaras, D. Predictive maintenance for injection molding machines enabled by cognitive analytics for industry 4.0. Front. Artif. Intell. 2020, 3, 578152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasiulewicz-Kaczmarek, M.; Legutko, S.; Kluk, P. Maintenance 4.0 technologies–new opportunities for sustainability driven maintenance. Manag. Prod. Eng. Rev. 2020, 11, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, D.; Lodewijks, G.; Pang, Y.; Mei, J. Integrated decision making for predictive maintenance of belt conveyor systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2019, 188, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurprihatin, F.; Angely, M.; Tannady, H. Total productive maintenance policy to increase effectiveness and maintenance performance using overall equipment effectiveness. J. Appl. Res. Ind. Eng. 2019, 6, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virk, S.I.; Khan, M.A.; Lakho, T.H.; Indher, A.A. Review of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) & Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) Practices in Manufacturing Sectors. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial & Mechanical Engineering and Operations Management, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 26–27 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sahrupi, S.; Juriantoro, J. Usulan Penerapan Total Productive Maintenance pada Transfer Conveyor 17A. J. Sist. Dan Manaj. Ind. 2018, 2, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, P.D.; Silva, P.D.; Nunes, J.; Andrade, L.P. Characterization of the specific electrical energy consumption of agrifood industries in the central region of Portugal. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 590, 878–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, J.; Silva, P.D.; Andrade, L.P.; Gaspar, P.D. Characterization of the specific energy consumption of electricity in the Portuguese sausage industry. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 186, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.D.; Gaspar, P.D.; Nunes, J.; Andrade, L.P.A. Specific electrical energy consumption and CO2 emissions assessment of agrifood industries in the central region of Portugal. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 675–677, 1880–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, J.; Silva, P.D.; Andrade, L.P.; Domingues, L.; Gaspar, P.D. Energy assessment of the Portuguese meat industry. Energy Effic. 2016, 9, 1163–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, D.; Gaspar, P.D.; Silva, P.D.; Andrade, L.P.; Nunes, J. Energy consumption and efficiency measures in the Portuguese food processing industry. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e14862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varandas, L.; Faria, J.; Gaspar, P.D.; Aguiar, M.L. Low-Cost IoT Remote Sensor Mesh for Large-Scale Orchard Monitorization. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2020, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, P.D.; Fernandez, C.M.; Soares, V.N.G.J.; Caldeira, J.M.L.P.; Silva, H. Development of technological capabilities through the Internet of Things (IoT): Survey of opportunities and barriers for IoT implementation in Portugal’s agro-industry. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, P.D.; Soares, V.N.G.J.; Caldeira, J.M.L.P.; Andrade, L.P.; Soares, C.D. Techno-logical modernization and innovation of traditional agri-food companies based on ICT solutions—The Portuguese case study. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e14271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, P.K.; Sahoo, B.S. Leverage of multiple predictive maintenance technologies in root cause failure analysis of critical machineries. Procedia Eng. 2016, 144, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lodewijks, G. Strategies for automated maintenance of belt conveyor systems. Bulk Solids Handl. 2004, 24, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- De Nardis, L.; Mohammadpour, A.; Caso, G.; Ali, U.; Di Benedetto, M.-G. Internet of Things Platforms for Academic Research and Development: A Critical Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelghany, E.S.; Farghaly, M.B.; Almalki, M.M.; Sarhan, H.H.; Essa, M.E.-S.M. Machine Learning and IoT Trends for Intelligent Prediction of Aircraft Wing AntiIcing System Temperature. Aerospace 2023, 10, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrioaia, D.A. Cyber security analysis of IoT devices transmitting data in the Thingspeak platform cloud. J. Eng. Stud. Res. 2022, 28, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.W.; Shi, J.F.; Zou, K.K.; Li, N.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yan, D.X.; Li, Z.M. Synergistically optimizing interlaminar and electromagnetic interference shielding behavior of carbon fiber composite based on interfacial reinforcement. Carbon 2022, 200, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, A.C.; Sanguesa, J.A.; Martinez, F.J.; Garrido, P.; Calafate, C.T. Mitigating electromagnetic noise when using low-cost devices in industry 4.0. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 63267–63282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Breakdown Time | Repair Time | Stop Classification |
|---|---|---|
| 12:48:27 | 0 h:5 min:40 s | Conveyor belt jam |
| 12:11:08 | 0 h:2 min:04 s | Conveyor belt misalignment |
| 11:42:33 | 0 h:4 min:21 s | Conveyor belt jam |
| 11:02:11 | 0 h:1 min:06 s | Conveyor belt misalignment |
| 10:40:02 | 0 h:0 min:49 s | Conveyor belt jam |
| 10:10:40 | 0 h:1 min:30 s | Conveyor belt jam |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendes, D.; Gaspar, P.D.; Charrua-Santos, F.; Navas, H. Enhanced Real-Time Maintenance Management Model—A Step toward Industry 4.0 through Lean: Conveyor Belt Operation Case Study. Electronics 2023, 12, 3872. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12183872
Mendes D, Gaspar PD, Charrua-Santos F, Navas H. Enhanced Real-Time Maintenance Management Model—A Step toward Industry 4.0 through Lean: Conveyor Belt Operation Case Study. Electronics. 2023; 12(18):3872. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12183872
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendes, David, Pedro D. Gaspar, Fernando Charrua-Santos, and Helena Navas. 2023. "Enhanced Real-Time Maintenance Management Model—A Step toward Industry 4.0 through Lean: Conveyor Belt Operation Case Study" Electronics 12, no. 18: 3872. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12183872
APA StyleMendes, D., Gaspar, P. D., Charrua-Santos, F., & Navas, H. (2023). Enhanced Real-Time Maintenance Management Model—A Step toward Industry 4.0 through Lean: Conveyor Belt Operation Case Study. Electronics, 12(18), 3872. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12183872









