Machine and Deep Learning Algorithms for COVID-19 Mortality Prediction Using Clinical and Radiomic Features
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
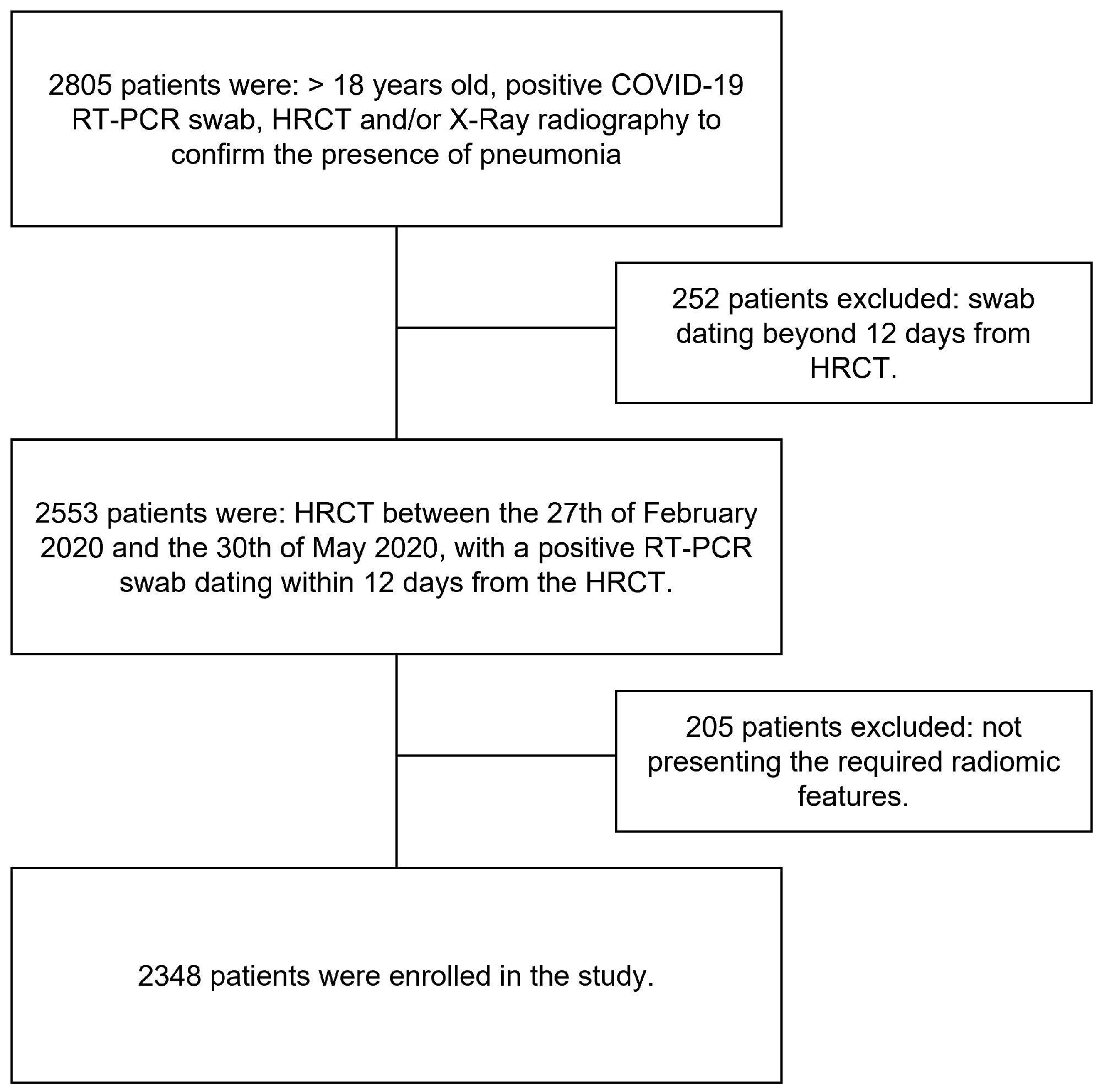
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Clinical Features Collection
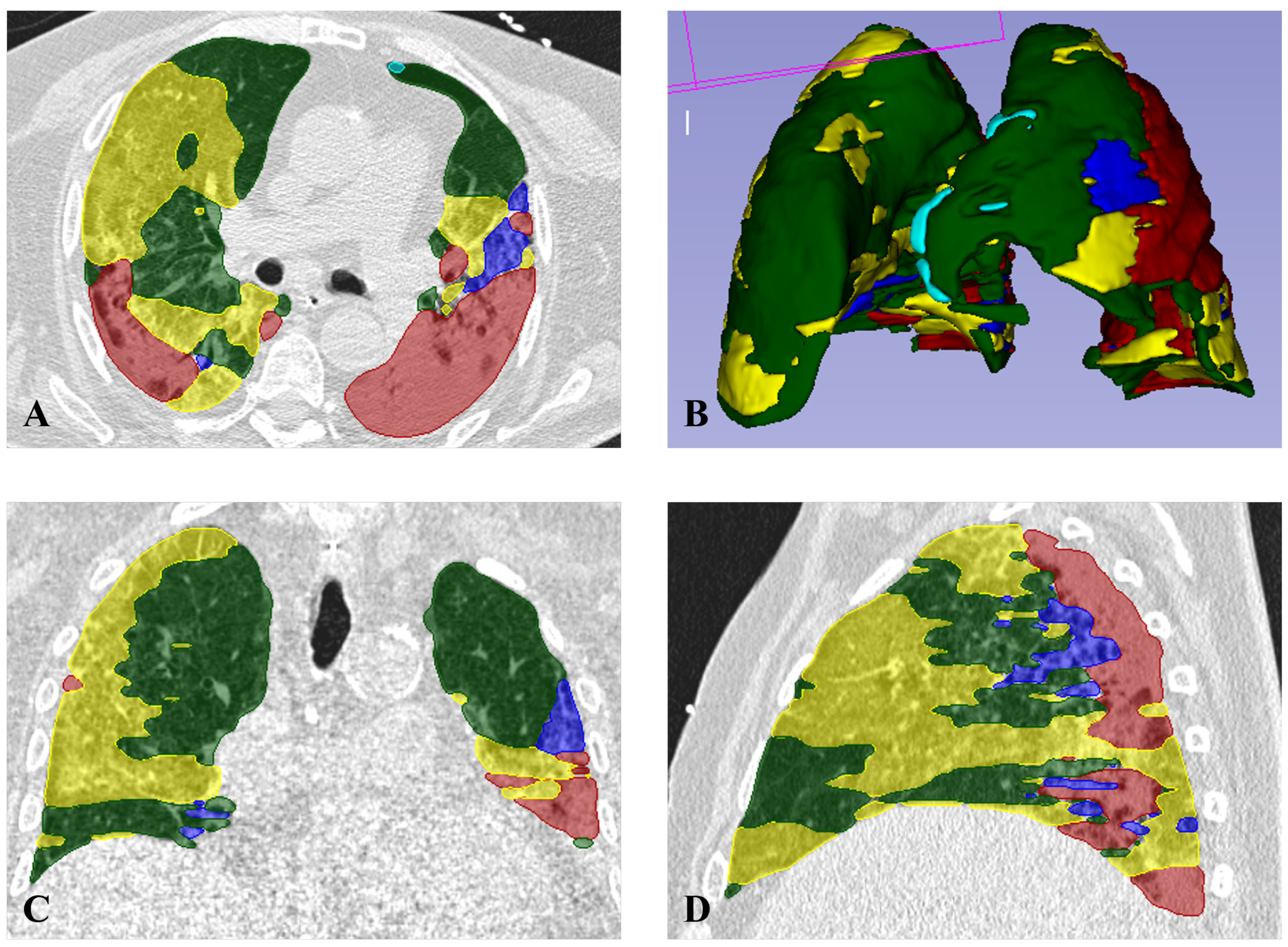
2.3. Radiomic Features Collection
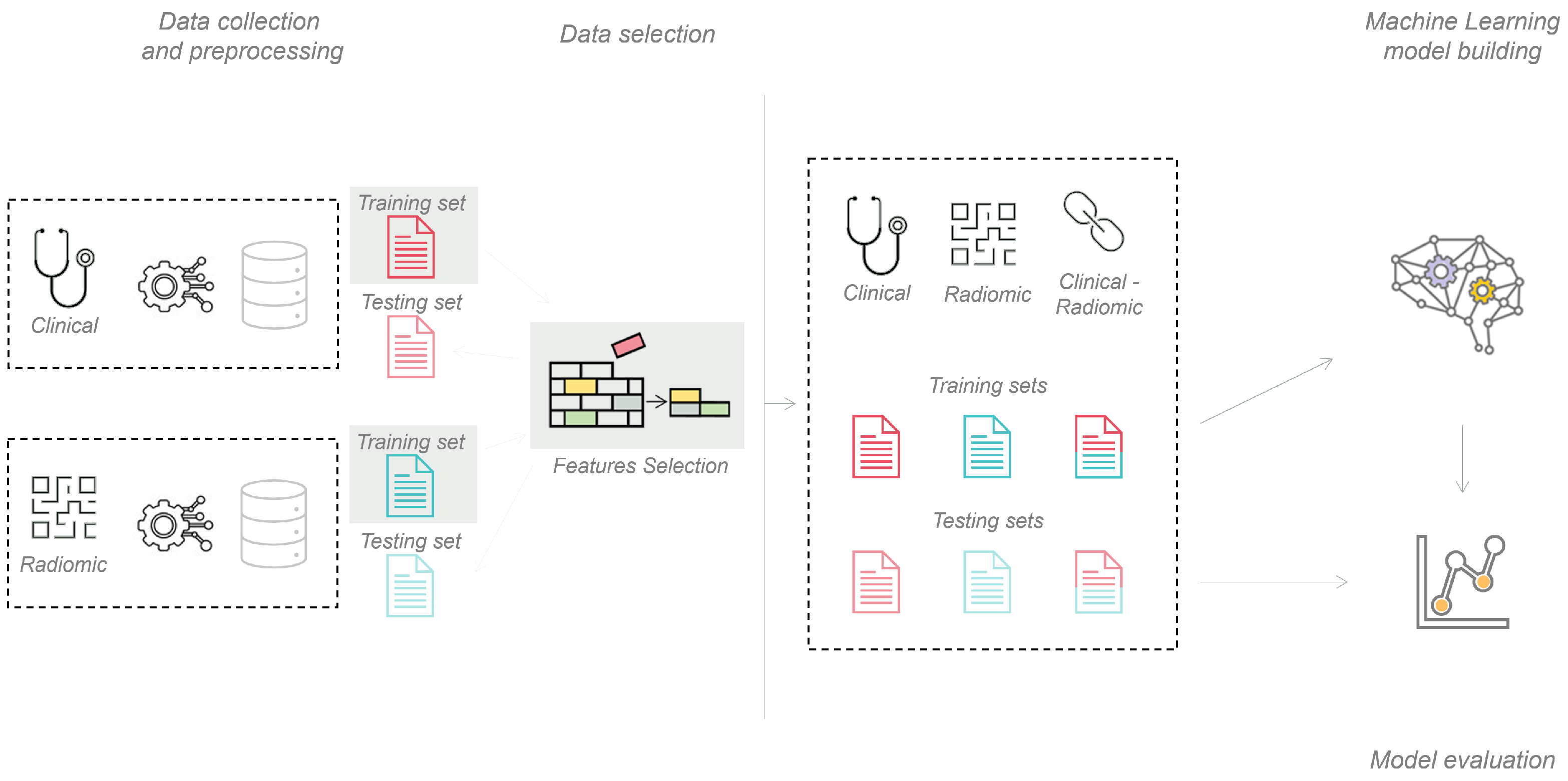
2.4. Machine Learning Pipeline
2.5. Deep Learning Pipeline
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Lau, J.Y.N.; Zhang, K.; Li, W. COVID-19 in early 2021: Current status and looking forward. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2021, 6, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Mao, L.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, L.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Cai, Q.; Qiu, J.; Chen, F. Machine learning-based CT radiomics model distinguishes COVID-19 from non-COVID-19 pneumonia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmeren, J.V.; Cester, D.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Alkadhi, H.; Baessler, B. Radiomics in medical imaging—“how-to” guide and critical reflection. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Qian, Z.; Sun, Z.; Xu, K.; Wang, K.; Liu, S.; Fan, X.; Li, X.; Fan, X.; et al. A radiomic signature as a non-invasive predictor of progression-free survival in patients with lower-grade gliomas. Neuroimage Clin. 2018, 20, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forghani, R.; Savadjiev, P.; Chatterjee, A.; Muthukrishnan, N.; Reinhold, C.; Forghani, B. Radiomics and Artificial Intelligence for Biomarker and Prediction Model Development in Oncology. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 995–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bera, K.; Braman, N.; Gupta, A.; Velcheti, V.; Madabhushi, A. Predicting cancer outcomes with radiomics and artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 19, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Yap, M.H.; Tan, M.; Hasan, M.K. ReCoNet: Multi-level Preprocessing of Chest X-rays for COVID-19 Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks. medrxiv, 2020; Preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, M.; Trojani, V.; Botti, A.; Cucurachi, N.; Galaverni, M.; Cozzi, S.; Borghetti, P.; La Mattina, S.; Pastorello, E.; Avanzo, M.; et al. Novel Harmonization Method for Multi-Centric Radiomic Studies in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 5179–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottino, F.; Tagliente, E.; Pasquini, L.; Napoli, A.D.; Lucignani, M.; Figà-Talamanca, L.; Napolitano, A. COVID Mortality Prediction with Machine Learning Methods: A Systematic Review and Critical Appraisal. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Hu, B.; Kang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, S. Automatic Assessment of Depression and Anxiety through Encoding Pupil-Wave from HCI in VR Scenes. ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput. Commun. Appl. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, T.; Chen, T.; Deng, W. Hyperspectral Image Classification Based on Fusing S3-PCA, 2D-SSA and Random Patch Network. Remote. Sens. 2023, 15, 3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Tang, K.; Liu, Y. A Fine-Tuning Based Approach for Daily Activity Recognition between Smart Homes. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccaro, V.; Celsa, C.; Sambo, M.; Battaglia, S.; Sacchi, P.; Biscarini, S.; Valsecchi, P.; Pieri, T.C.; Gallazzi, I.; Colaneri, M.; et al. Competing-risk analysis of coronavirus disease 2019 in-hospital mortality in a Northern Italian centre from SMAtteo COvid19 REgistry (SMACORE). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Gutiérrez, S.; Esteban-Aizpiri, C.; Lafuente, I.; Barrio, I.; Quiros, R.; Quintana, J.M.; Uranga, A. Machine learning-based model for prediction of clinical deterioration in hospitalized patients by COVID 19. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, P.; Natascha, C.D.; Tessadori, J.; Giovanni, V.; Valerio, G.; Chandra, B.; Muhammad, U.A.; Rosa, S.; Ermanno, C.; Deborah, F.; et al. AIforCOVID: Predicting the clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 applying AI to chest-X-rays. An Italian multicentre study. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 74, 102216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Kapse, S.; Singh, G.; Gattu, R.; Ali, S.; Shah, N.; Marshal, C.; Pierce, J.; Phatak, T.; Gupta, A.; et al. Predicting Mechanical Ventilation and Mortality in COVID-19 Using Radiomics and Deep Learning on Chest Radiographs: A Multi-Institutional Study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Choi, J.W.; Halsey, K.; Tran, T.M.L.; Hsieh, B.; Wang, D.; Eweje, F.; Wang, R.; Chang, K.; Wu, J.; et al. Prognostication of patients with COVID-19 using artificial intelligence based on chest x-rays and clinical data: A retrospective study. Lancet Digit. Health 2021, 3, e286–e294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, B.; Shin, H.; Desai, B.; Gholamrezanezhad, A.; Lei, X.; Perkins, M.; Oberai, A.; Nanda, N.; Cen, S.; Duddalwar, V. Predicting clinical outcomes in COVID-19 using radiomics on chest radiographs. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20210221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Lim, H.; Kim, D.; Chang, J.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, S.W. Machine learning prediction for mortality of patients diagnosed with COVID-19: A nationwide Korean cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, F.S.H.; Hojo-Souza, N.S.; Dos Santos, E.B.; Da Silva, C.M.; Guidoni, D.L. Predicting the Disease Outcome in COVID-19 Positive Patients Through Machine Learning: A Retrospective Cohort Study With Brazilian Data. Front. Artif. Intell. 2021, 4, 2624–8212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiri, I.; Salimi, Y.; Pakbin, M.; Hajianfar, G.; Avval, A.H.; Sanaat, A.; Mo-stafaei, S.; Akhavanallaf, A.; Saberi, A.; Mansouri, Z.; et al. COVID-19 Prognostic Modeling Using CT Radiomic Features and Machine Learning Algorithms: Analysis of a MultiInstitutional Dataset of 14,339 Patients. Phys. A 2021, 145, 105467. [Google Scholar]
- Shiri, I.; Sorouri, M.; Geramifar, P.; Nazari, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Salimi, Y.; Khosravi, B.; Askari, D.; Aghaghazvini, L.; Hajianfar, G.; et al. Machine learning-based prognostic modeling using clinical data and quantitative radiomic features from chest CT images in COVID-19 patients. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 132, 104304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tamal, M.; Alshammari, M.; Alabdullah, M.; Hourani, R.; Alola, H.; Hegazi, T. An integrated framework with machine learning and radiomics for accurate and rapid early diagnosis of COVID-19 from Chest X-ray. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 180, 115152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iori, M.; Castelnuovo, C.D.; Verzellesi, L.; Meglioli, G.; Lippolis, D.; Nitrosi, A.; Monelli, F.; Besutti, G.; Trojani, V.; Bertolini, M.; et al. Mortality Prediction of COVID-19 Patients Using Radiomic and Neural Network Features Extracted from a Wide Chest X-ray Sample Size: A Robust Approach for Different Medical Imbalanced Scenarios. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmisano, A.; Vignale, D.; Boccia, E.; Nonis, A.; Gnasso, C.; Leone, R.; Montagna, M.; Nicoletti, V.; Bianchi, A.G.; Brusamolino, S.; et al. AI-SCoRE (artificial intelligence-SARS CoV2 risk evaluation): A fast, objective and fully automated platform to predict the outcome in COVID-19 patients. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 960–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Jiao, Z.; Yang, L.; Choi, J.W.; Xiong, Z.; Halsey, K.; Tran, T.M.L.; Pan, I.; Collins, S.A.; Feng, X.; et al. Artificial intelligence for prediction of COVID-19 progression using CT imaging and clinical data. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Liang, H.; Ou, L.; Chen, B.; Chen, A.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Guan, W.; Sang, L.; Lu, J.; et al. Development and Validation of a Clinical Risk Score to Predict the Occurrence of Critical Illness in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banoei, M.; Dinparastisaleh, R.; Zadeh, A.; Mirsaeidi, M. Machine-learning-based COVID-19 mortality prediction model and identification of patients at low and high risk of dying. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alballa, N.; Al-Turaiki, I. Machine learning approaches in COVID-19 diagnosis, mortality, and severity risk prediction: A review. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2021, 24, 100564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, A.; Garg, A.; Vinod, P.K.; Priyakumar, U.D. Machine Learning Based Clinical Decision Support System for Early COVID-19 Mortality Prediction. Digit. Public Heal. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 626697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuno, T.; Sahashi, Y.; Kawahito, S.; Takahashi, M.; Iwagami, M.; Egorova, N.N. Prediction of in-hospital mortality with machine learning for COVID-19 patients treated with steroid and remdesivir. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subudhi, S.; Verma, A.; Patel, A.; Hardin, C.C.; Khandekar, M.J.; Lee, H.; McEvoy, D.; Stylianop-oulos, T.; Munn, L.L.; Dutta, S.; et al. Comparing machine learning algorithms for predicting ICU admission and mortality in COVID-19. NPJ Digit. Med 2021, 4, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadaga, K.; Prabhu, S.; Umakanth, S.; Vivekananda, B.K.; Niranjana, S.; Rajagopala, C.P.; Krishna, P.K. COVID-19 Mortality Prediction among Patients Using Epidemiological Parameters: An Ensemble Machine Learning Approach. Eng. Sci. 2021, 16, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkayastha, S.; Xiao, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Thepumnoeysuk, R.; Halsey, K.; Wu, J.; Tran, T.; Hsieh, B.; Choi, J.; Wang, D.; et al. Machine Learning-Based Prediction of COVID-19 Severity and Progression to Critical Illness Using CT Imaging and Clinical Data. Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Grassi, R.; Granata, V.; Setola, S.V.; Grassi, F.; Cozzi, D.; Pecori, B.; Izzo, F.; Petrillo, A. Artificial Intelligence and COVID-19 Using Chest CT Scan and Chest X-ray Images: Machine Learning and Deep Learning Approaches for Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qin, L.; Xu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, X.; Kong, B.; Bai, J.; Lu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Song, Q.; et al. Using Artificial Intelligence to Detect COVID-19 and Community-acquired Pneumonia Based on Pulmonary CT: Evaluation of the Diagnostic Accuracy. Radiology 2020, 296, E65–E71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Sun, R.; Sun, W.; Xu, D.; Lan, L.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Xu, H. Radiomics analysis of chest CT to predict the overall survival for the severe patients of COVID-19 pneumonia. Phys. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 105008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Sun, H.; Wang, J.; Xu, H.; Li, S.; Zhao, C.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, T.; Duan, S.; et al. A novel CT-based radiomics in the distinction of severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayounieh, F.; Ebrahimian, S.; Babaei, R.; Mobin, H.K.; Zhang, E.; Bizzo, B.C.; Mohseni, I.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Kalra, M.K. CT Radiomics, Radiologists, and Clinical Information in Predicting Outcome of Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2020, 2, e200322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, K.; Maneerat, N.; Sreng, S.; Hamamoto, K. Ensemble Deep Learning for the Detection of COVID-19 in Unbalanced Chest X-ray Dataset. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10528. [Google Scholar]
- Shiri, I.; Arabi, H.; Salimi, Y.; Sanaat, A.H.; Akhavanalaf, A.; Hajianfar, G.; Askari, D.; Moradi, S.; Mansouri, Z.; Pakbin, M.; et al. COLI-NET: Fully Automated COVID-19 Lung and Infection Pneumonia Lesion Detection and Segmentation from Chest CT Images. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, T.; Talo, M.; Yildirim, E.A.; Baloglu, U.B.; Yildirim, O.; Rajendra Acharya, U. Automated detection of COVID-19 cases using deep neural networks with Xray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, R.; Belfiore, M.P.; Montanelli, A.; Patelli, G.; Urraro, F.; Giacobbe, G.; Fusco, R.; Granata, V.; Petrillo, A.; Sacco, P.; et al. COVID-19 pneumonia: Computer-aided quantification of healthy lung parenchyma, emphysema, ground glass and consolidation on chest computed tomography (CT). Radiol. Medica 2020, 126, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laino, M.E.; Ammirabile, A.; Posa, A.; Cancian, P.; Shalaby, S.; Savevski, V.; Neri, E. The Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Chest Imaging of COVID-19 Patients: A Literature Review. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kang, B.; Ma, J.; Zeng, X.; Xiao, M.; Guo, J.; Cai, m.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Meng, X.; et al. A deep learning algorithm using CT images to screen for Corona virus disease (COVID-19). Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 6096–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, R.; Heinicke, D. Using Small Datasets to Build Models. Available online: https://www.datarobot.com/blog/using-small-datasets-to-build-models (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Avanzo, M.; Trianni, A.; Botta, F.; Talamonti, C.; Stasi, M.; Iori, M. Artificial Intelligence and the Medical Physicist: Welcome to the Machine. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schork, N.J. Artificial Intelligence and Personalized Medicine. In Precision Medicine in Cancer Therapy; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbo, S.; La Mantia, M.; Malta, G.; Albano, G.; Rifiorito, A.; Manco, V.; Falco, V.; Argo, A. Mortality of Hospitalized Patients with SARS-COV-2 Infection in University Tertiary Care of Italy. Euromediterr. Biomed. J. 2023, 18, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wong, A.K.C.; Kamel, M.S. Classification of Imabalanced Data: A Review. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2009, 23, 687–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glas, C. Missing Data. In International Encyclopedia of Education, 3rd ed.; Peterson, P., Baker, E., McGaw, B., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donini, B.; Rivetti, S.; Lanconelli, N.; Bertolini, M. Free software for performing physical analysis of systems for digital radiography and mammography. Med. Phys. 2014, 41, 051903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitrosi, A.; Bertolini, M.; Borasi, G.; Botti, A.; Barani, A.; Rivetti, S.; Pierotti, L. Application of QC_DR Software for Acceptance Testing and Routine Quality Control of Direct Digital Radiography Systems: Initial Experiences using the Italian Association of Physicist in Medicine Quality Control Protocol. Digit. Imaging 2009, 22, 656Y666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coreline. Available online: https://www.aview-lung.com/ (accessed on 4 August 2022).
- Ho, T.; Park, J.; Kim, T.; Park, B.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Choi, S.; Kim, Y.; Lim, J.; et al. Deep Learning Models for Predicting Severe Progression in COVID-19-Infected Patients: Retrospective Study. JMIR Med. Inform. 2021, 9, e24973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Song, B. Chest CT manifestations of new coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A pictorial review. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4381–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Kang, E.; Yong, H.; Kim, C.; Lee, K.; Hwang, S.; Oh, Y. A Stepwise Diagnostic Approach to Cystic Lung Diseases for Radiologists. Korean J. Radiol. 2019, 20, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansell, D.; Bankier, A.; MacMahon, H.; McLoud, T.; Müller, N.; Remy, J. Fleischner Society: Glossary of terms for thoracic imaging. Radiology 2008, 246, 697–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkhede, S. Understanding AUC-ROC Curve. Available online: https://towardsdatascience.com/understanding-auc-roc-curve-68b2303cc9c5 (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Vaid, A.; Somani, S.; Russak, A.J.; De Freitas, J.K.; Chaudhry, F.F.; Paranjpe, I.; Johnson, K.W.; Lee, S.J.; Miotto, R.; Richter, F.; et al. Machine Learning to Predict Mortality and Critical Events in a Cohort of Patients With COVID-19 in New York City: Model Development and Validation. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2020, 22, e24018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulaal, A.; Patel, A.; Charani, E.; Denny, S.; Mughal, N.; Moore, L. Prognostic Modeling of COVID-19 Using Artificial Intelligence in the United Kingdom: Model Development and Validation. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2020, 22, e20259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulaal, A.; Patel, A.; Charani, E.; Denny, S.; Alqahtani, S.A.; Davies, G.W.; Mughal, N.; Moore, L.S.P. Comparison of deep learning with regression analysis in creating predictive models for SARS-CoV-2 outcomes. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2020, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.; Chung, H.; Kang, W.S.; Park, C.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, S.E.; Chung, C.R.; Ko, R.E.; Lee, H.; Seo, J.H.; et al. An Artificial Intelligence Model to Predict the Mortality of COVID-19 Patients at Hospital Admission Time Using Routine Blood Samples: Development and Validation of an Ensemble Model. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2020, 22, e25442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Castelnuovo, A.; Bonaccio, M.; Costanzo, S.; Gialluisi, A.; Antinori, A.; Berselli, N.; Blandi, L.; Bruno, R.; Cauda, R.; Guaraldi, G.; et al. Common cardiovascular risk factors and in-hospital mortality in 3,894 patients with COVID-19: Survival analysis and machine learning-based findings from the multicentre Italian CORIST Study. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 30, 1899–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.L.; Abels, E.; McCaffrey, P. Development of a prognostic model for mortality in COVID-19 infection using machine learning. Mod. Pathol. 2021, 34, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, T.; Fan, M.; Xu, S.; Qiu, W.; Chen, C.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Yan, J.; et al. Development and external evaluation of predictions models for mortality of COVID-19 patients using machine learning method. Neural. Comput. Appl. 2021, 35, 13037–13046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, W.; Lei, S.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, P.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Geng, Z.; et al. Open resource of clinical data from patients with pneumonia for the prediction of COVID-19 outcomes via deep learning. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsimas, D.; Lukin, G.; Mingardi, L.; Nohadani, O.; Orfanoudaki, A.; Stellato, B.; Wiberg, H.; Gonzalez-Garcia, S.; Parra-Calderón, C.L.; Robinson, K.; et al. COVID-19 mortality risk assessment: An international multi-center study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Zhang, B.; Fu, M.; Li, M.; Yuan, X.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, J.; Guo, H.; Lu, Y. Clinical and inflammatory features based machine learning model for fatal risk prediction of hospitalized COVID-19 patients: Results from a retrospective cohort study. Ann. Med. 2021, 53, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaid, A.; Jaladanki, S.; Xu, J.; Teng, S.; Kumar, A.; Lee, S.; Somani, S.; Paranjpe, I.; De Freitas, J.K.; Wanyan, T.; et al. Federated Learning of Electronic Health Records to Improve Mortality Prediction in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: Machine Learning Approach. JMIR Med. Inform. 2021, 9, e24207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, O.; Zhang, X.; Xu, K.; Suo, C.; Wang, Q.; Song, Y.; Yu, K.; et al. Early prediction of mortality risk among patients with severe COVID-19, using machine learning. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 1918–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikemura, K.; Bellin, E.; Yagi, Y.; Billett, H.; Saada, M.; Simone, K.; Stahl, L.; Szymanski, J.; Goldstein, D.Y.; Reyes Gil, M. Using Automated Machine Learning to Predict the Mortality of Patients With COVID-19: Prediction Model Development Study. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2021, 23, e23458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tezza, F.; Lorenzoni, G.; Azzolina, D.; Barbar, S.; Leone, L.A.C.; Gregori, D. Predicting in-Hospital Mortality of Patients with COVID-19 Using Machine Learning Techniques. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachel, A.; Daniel, K.; Ding, D.; Francois, F.; Phillips, M.; Lighter, J. Development and validation of a machine learning model to predict mortality risk in patients with COVID-19. BMJ Health Care Inform. 2021, 28, e100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Population Features | Number |
|---|---|
| Total patients | 2348 |
| Survived patients | 2061 (88%) |
| Dead patients | 287 (12%) |
| Mean Age ± sd [min–max] | 63 ± 16 [18–100] |
| Mean Survived Age ± sd [min–max] | 61 ± 16 [18–99] |
| Mean Dead Age ± sd [min–max] | 80 ± 10 [45–100] |
| Women | 1085 (46%) |
| Dead women | 98 (9%) |
| Men | 1263 (54%) |
| Dead men | 186 (15%) |
| Clinical Features | |
|---|---|
| Age | Sex |
| CRP value | Obesity |
| Vascular Diseases | Dementia |
| Heart Failure | COPD |
| Dyslipidemia | Cancer |
| Arrhythmias | Cardiac Ischaemia |
| Cerebrovascular diseases | Diabetes |
| Chronic Renal Failure | Hypertension |
| Ground Glass Opacities | Consolidations |
| PI > 60% | |
| Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|
| C | 15 |
| gamma | 0.0001 |
| kernel | rbf |
| class weight | balanced |
| Machine Learning | Deep Learning | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical | Radiomic |
Clinical- Radiomic | Clinical | Radiomic |
Clinical- Radiomic | |
| AUC | 0.794 | 0.771 | 0.803 | 0.825 | 0.844 | 0.864 |
| ACC | 0.770 | 0.800 | 0.813 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.766 |
| SENS | 0.763 | 0.809 | 0.816 | 0.733 | 0.698 | 0.814 |
| SPEC | 0.826 | 0.733 | 0.791 | 0.784 | 0.788 | 0.759 |
| Model | AUC | ACC | SENS | SPEC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our model ML | 0.803 | 0.813 | 0.816 | 0.791 |
| Our model DL | 0.864 | 0.766 | 0.814 | 0.759 |
| Vaid et al., 2020 [61] | 0.890 | 0.976 | 0.442 | 0.991 |
| Abdulaal et al., 2020 [62] | 0.901 | 0.862 | 0.875 | 0.859 |
| Abdulaal et al., 2020 [63] | 0.869 | 0.837 | 0.500 | 0.966 |
| Ko et al., 2020 [64] | - | 0.930 | 0.920 | 0.930 |
| Di et al., 2020 [65] | - | 0.834 | 0.950 | 0.308 |
| Banoei et al., 2021 [29] | 0.910 | 0.750 | 0.900 | 0.870 |
| Booth et al., 2021 [66] | 0.930 | - | 0.760 | 0.910 |
| Li et al., 2021 [67] | 0.918 | 0.799 | 0.774 | 0.903 |
| Ning et al., 2020 [68] | 0.856 | 0.787 | 0.882 | 0.783 |
| Bertsimas et al., 2020 [69] | 0.902 | 0.850 | - | 0.866 |
| An et al., 2020 [20] | 0.962 | - | 0.920 | 0.918 |
| Guan et al., 2021 [70] | - | 0.991 | 0.876 | - |
| Vaid et al., 2021 [71] | 0.836 | 0.780 | 0.805 | 0.702 |
| Hu et al., 2021 [72] | 0.895 | - | 0.892 | 0.687 |
| Ikemura et al., 2021 [73] | 0.903 | - | 0.838 | 0.836 |
| Tezza et al., 2021 [74] | 0.840 | - | 0.788 | 0.774 |
| Stachel et al., 2021 [75] | 0.990 | 0.960 | 0.240 | 0.970 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Verzellesi, L.; Botti, A.; Bertolini, M.; Trojani, V.; Carlini, G.; Nitrosi, A.; Monelli, F.; Besutti, G.; Castellani, G.; Remondini, D.; et al. Machine and Deep Learning Algorithms for COVID-19 Mortality Prediction Using Clinical and Radiomic Features. Electronics 2023, 12, 3878. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12183878
Verzellesi L, Botti A, Bertolini M, Trojani V, Carlini G, Nitrosi A, Monelli F, Besutti G, Castellani G, Remondini D, et al. Machine and Deep Learning Algorithms for COVID-19 Mortality Prediction Using Clinical and Radiomic Features. Electronics. 2023; 12(18):3878. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12183878
Chicago/Turabian StyleVerzellesi, Laura, Andrea Botti, Marco Bertolini, Valeria Trojani, Gianluca Carlini, Andrea Nitrosi, Filippo Monelli, Giulia Besutti, Gastone Castellani, Daniel Remondini, and et al. 2023. "Machine and Deep Learning Algorithms for COVID-19 Mortality Prediction Using Clinical and Radiomic Features" Electronics 12, no. 18: 3878. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12183878
APA StyleVerzellesi, L., Botti, A., Bertolini, M., Trojani, V., Carlini, G., Nitrosi, A., Monelli, F., Besutti, G., Castellani, G., Remondini, D., Milanese, G., Croci, S., Sverzellati, N., Salvarani, C., & Iori, M. (2023). Machine and Deep Learning Algorithms for COVID-19 Mortality Prediction Using Clinical and Radiomic Features. Electronics, 12(18), 3878. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12183878












