Electronics 2023, 12(2), 307; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12020307 - 6 Jan 2023
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 1390
Abstract
As big data and data mining technology advance, research on the collection and analysis of medical data on the internet of medical things (IoMT) has gained increasing attention. Medical institutions often collect users’ signs and symptoms from their devices for analysis. However, the
[...] Read more.
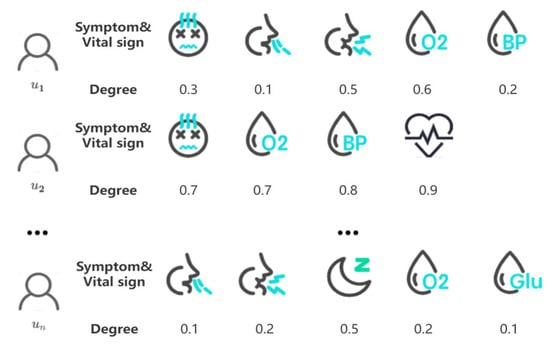
As big data and data mining technology advance, research on the collection and analysis of medical data on the internet of medical things (IoMT) has gained increasing attention. Medical institutions often collect users’ signs and symptoms from their devices for analysis. However, the process of data collection may pose a risk of privacy leakage without a trusted third party. To address this issue, we propose a medical data collection based on local differential privacy and Count Sketch (MDLDP). The algorithm first uses a random sampling technique to select only one symptom for perturbation by a single user. The perturbed data is then uploaded using Count Sketch. The third-party aggregates the user-submitted data to estimate the frequencies of the symptoms and the mean extent of their occurrence. This paper theoretically demonstrates that the designed algorithm satisfies local differential privacy and unbiased estimation. We also evaluated the algorithm experimentally with existing algorithms on a real medical dataset. The results show that the MDLDP algorithm has good utility for key-value type medical data collection statistics in the IoMT.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Security and Privacy Preservation in Big Data Age)
►
Show Figures