THANet: Transferring Human Pose Estimation to Animal Pose Estimation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
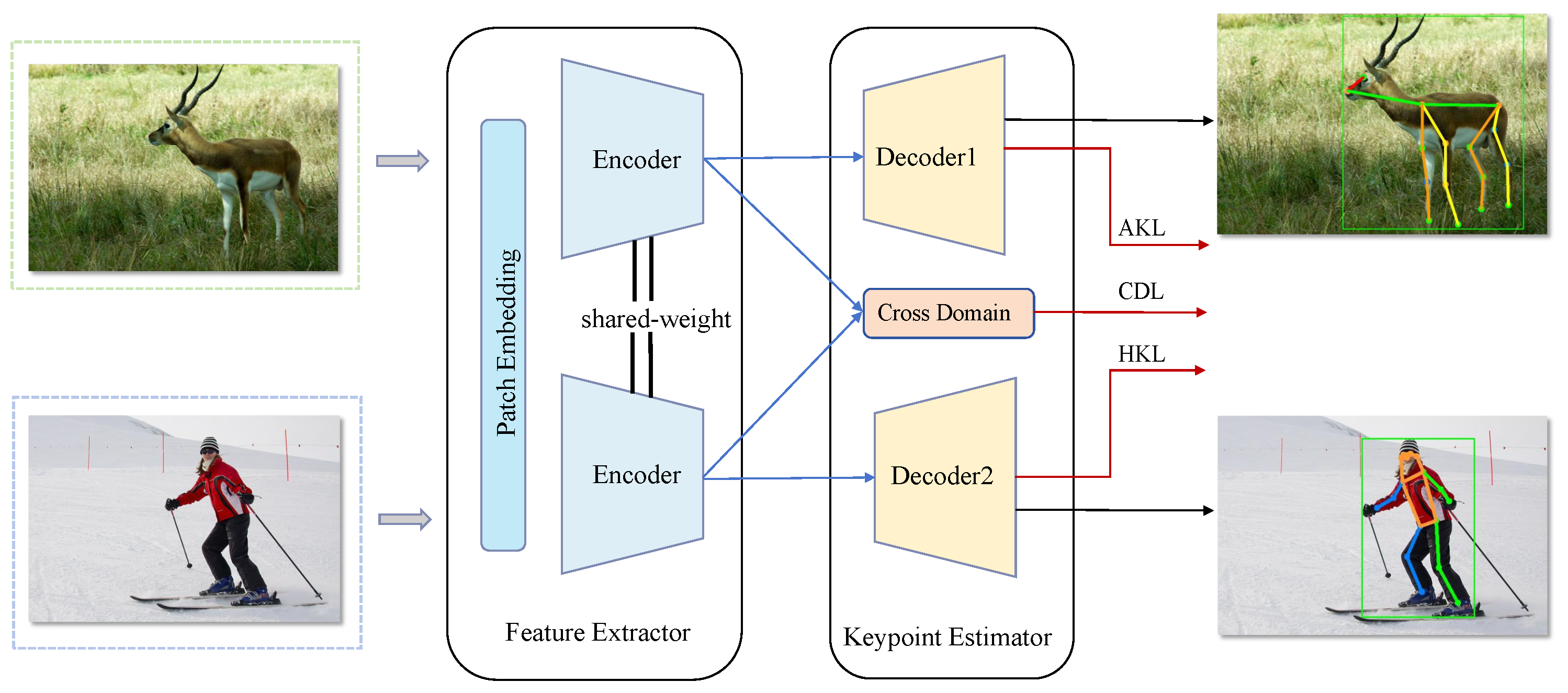
- We design a simple yet efficient multi-task encode–decoder transformer network, namely THANet, which simultaneously estimates human pose and animal pose.
- We propose a joint-learning strategy and cross-domain adaptation to transfer knowledge from the human domain to the animal domain to improve performance and generalization.
- The proposed THANet achieves promising results on the AP-10K and the Animal-Pose benchmarks, verifying the effectiveness of our proposed approach.
2. Related Work
2.1. Human Pose Estimation
| Method (Dataset) | Keywords | Year | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Animal Pose Estimation | |||
| TigDog [30] | 2D joint, horse, tiger | 2015 | A keypoint dataset for horse and tiger. |
| WS-CDA [6] | 2D joint, weakly semi supervised, cross-domain | 2019 | Transfer knowledge from unlabeled animal data and provide a new Animal-Pose dataset. |
| CC-SSL [4] | Synthetic data, semi-supervised learning | 2020 | Consistency-constrained SSL framework for APE. |
| UDA [5] | Unsupervised learning, self-distillation | 2021 | Unsupervised learning pipeline for APE and online pseudo-label refinement strategy. |
| AP-10K [31] | 2D joint, mammal | 2021 | Large-scale mammal animal pose dataset. |
| Human Pose Estimation | |||
| Deeppose [15] | Single-person, regression | 2014 | The first HPE method via deep neural network. |
| CPM [17] | Top–down, sequential | 2016 | Sequential CNNs to learn spatial features in the end-to-end way. |
| SB [25] | Efficient, tracking | 2018 | Efficient pose estimation via CNN. |
| HRNet [26] | high-resolution representation | 2019 | Learning high-resolution representation from images. |
| DEKR [24] | Bottom–up, regression | 2021 | Directly regressing the keypoint position with bottom–up paradigm. |
| ViTPose [11] | Vision-transformer | 2022 | Effective pose estimation via vision transformer. |
2.2. Animal Pose Estimation
3. Method
3.1. Problem Definition
Human and Animal Pose Estimation
3.2. Vision Transformer Architecture
3.2.1. Encoder
3.2.2. Decoder
3.2.3. Joint Learning
3.3. Cross-Domain Adaptation
3.4. Overall Loss Function
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Implementation Details and Evaluation Metrics
4.2.1. Experimental Settings
4.2.2. Metrics
4.3. Quantitative Analysis
4.3.1. Comparison with the Methods Based on CNNs
4.3.2. Ablation Study
4.3.3. Generalize to Animal-Pose Dataset
4.4. Qualitative Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APE | Animal Pose Estimation |
| HPE | Human Pose Estimation |
| AKL | Animal Keypoint Loss |
| HKL | Human Keypoint Loss |
| CDL | Cross-Domain Loss |
| JL | Joint Learning |
| CD | Cross-Domain |
| AP | Average Precision |
| AR | Average Recall |
| OKS | Object Keypoint Similarity |
| PCK | Percentage of Correct Keypoints |
References
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Decoding complete reach and grasp actions from local primary motor cortex populations. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 9659–9669. [Google Scholar]
- Wenger, N.; Moraud, E.M.; Raspopovic, S.; Bonizzato, M.; DiGiovanna, J.; Musienko, P.; Morari, M.; Micera, S.; Courtine, G. Closed-loop neuromodulation of spinal sensorimotor circuits controls refined locomotion after complete spinal cord injury. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 255ra133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathis, A.; Mamidanna, P.; Cury, K.M.; Abe, T.; Murthy, V.N.; Mathis, M.W.; Bethge, M. DeepLabCut: Markerless pose estimation of user-defined body parts with deep learning. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, J.; Qiu, W.; Hager, G.D.; Yuille, A.L. Learning from synthetic animals. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 12386–12395. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Lee, G.H. From synthetic to real: Unsupervised domain adaptation for animal pose estimation. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 1482–1491. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Tang, H.; Fang, H.S.; Shen, X.; Lu, C.; Tai, Y.W. Cross-Domain Adaptation for Animal Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the ICCV, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the ICLR, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the ICCV, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, D. ViTPose: Simple Vision Transformer Baselines for Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Andriluka, M.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. Pictorial structures revisited: People detection and articulated pose estimation. In Proceedings of the CVPR, IEEE, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 1014–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Sapp, B.; Jordan, C.; Taskar, B. Adaptive pose priors for pictorial structures. In Proceedings of the CVPR, IEEE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantone, M.; Gall, J.; Leistner, C.; Van Gool, L. Human pose estimation using body parts dependent joint regressors. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 3041–3048. [Google Scholar]
- Toshev, A.; Szegedy, C. Deeppose: Human pose estimation via deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1653–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Tompson, J.; Goroshin, R.; Jain, A.; LeCun, Y.; Bregler, C. Efficient object localization using convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 648–656. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.E.; Ramakrishna, V.; Kanade, T.; Sheikh, Y. Convolutional pose machines. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4724–4732. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, A.; Yang, K.; Deng, J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the ECCV, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 483–499. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, G.; Sun, J. Cascaded Pyramid Network for Multi-Person Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Long, X.; Gao, Y.; Ding, E.; Wen, S. Graph-PCNN: Two Stage Human Pose Estimation with Graph Pose Refinement. In Proceedings of the ECCV, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 492–508. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Xu, W.; Tu, Z. Pose Recognition With Cascade Transformers. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 1944–1953. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, X.; Feng, J.; Zhang, J.; Yan, S. Single-Stage Multi-Person Pose Machines. In Proceedings of the ICCV, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kreiss, S.; Bertoni, L.; Alahi, A. PifPaf: Composite Fields for Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Z.; Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J. Bottom-Up Human Pose Estimation via Disentangled Keypoint Regression. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 14676–14686. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, B.; Wu, H.; Wei, Y. Simple baselines for human pose estimation and tracking. In Proceedings of the ECCV, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 466–481. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5693–5703. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, A.; Grimes, M.; Cipolla, R. PoseNet: A Convolutional Network for Real-Time 6-DOF Camera Relocalization. In Proceedings of the ICCV, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rieger, I.; Hauenstein, T.; Hettenkofer, S.; Garbas, J.U. Towards Real-Time Head Pose Estimation: Exploring Parameter-Reduced Residual Networks on In-the-wild Datasets. In Proceedings of the Advances and Trends in Artificial Intelligence. From Theory to Practice, Graz, Austria, 9–11 July 2019; Wotawa, F., Friedrich, G., Pill, I., Koitz-Hristov, R., Ali, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, A.; Moore, M.; Zhang, J.; Lancette, S.; Ward, V.P.; Chang, J. Toward a head movement-based system for multilayer digital content exploration. Comput. Animat. Virtual Worlds 2021, 32, e1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pero, L.; Ricco, S.; Sukthankar, R.; Ferrari, V. Articulated motion discovery using pairs of trajectories. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 2151–2160. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.; Guan, Z.; Tao, D. AP-10K: A Benchmark for Animal Pose Estimation in the Wild. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Fifth Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems Datasets and Benchmarks Track (Round 2), Virtual, 6–14 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, X.L.; Ong, K.E.; Zheng, Q.; Ni, Y.; Yeo, S.Y.; Liu, J. Animal Kingdom: A Large and Diverse Dataset for Animal Behavior Understanding. In Proceedings of the CVPR, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 19023–19034. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.; Yang, J.; Ranjan, A.; Pujades, S.; Pons-Moll, G.; Tang, S.; Black, M.J. Learning to dress 3d people in generative clothing. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6469–6478. [Google Scholar]
- Ba, J.L.; Kiros, J.R.; Hinton, G.E. Layer normalization. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.06450. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Lille, France, 7–9 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Agarap, A.F. Deep learning using rectified linear units (relu). arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.08375. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Tao, D. Towards high performance human keypoint detection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 2639–2662. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the ECCV, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Openmmlab Pose Estimation Toolbox and Benchmark. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmpose (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- He, K.; Chen, X.; Xie, S.; Li, Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Masked autoencoders are scalable vision learners. In Proceedings of the CVPR, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 16000–16009. [Google Scholar]
- Reddi, S.J.; Kale, S.; Kumar, S. On the convergence of adam and beyond. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.09237. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Guo, F.; Huang, G. The devil is in the details: Delving into unbiased data processing for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 5700–5709. [Google Scholar]




| Model | Backbone | Params (M) | Training Time (s) | Inference Time (ms) | Resolution | AP | AP | AR | AR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRNet | HRNet32 | 28.54 | 90.09 | 8.13 | 256 × 256 | 72.46 | 94.24 | 75.81 | 94.95 |
| HRNet | HRNet48 | 63.59 | 91.59 | 10.33 | 256 × 256 | 72.95 | 94.28 | 76.28 | 95.04 |
| SB | ResNet50 | 33.99 | 47.60 | 6.88 | 256 × 256 | 67.96 | 91.92 | 71.68 | 92.88 |
| SB | ResNet101 | 52.99 | 49.08 | 7.28 | 256 × 256 | 68.25 | 92.01 | 71.78 | 92.95 |
| Ours | ViT-B | 104.08 | 71.93 | 12.07 | 256 × 256 | 77.12 | 96.24 | 80.32 | 97.12 |
| ViT | JL | CD | AP | AR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ | 75.98 | 95.42 | 79.26 | 96.11 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | 74.22 | 94.72 | 77.71 | 95.31 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 77.12 | 96.24 | 80.32 | 97.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, J.; Xu, J.; Shen, Y.; Lin, S. THANet: Transferring Human Pose Estimation to Animal Pose Estimation. Electronics 2023, 12, 4210. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12204210
Liao J, Xu J, Shen Y, Lin S. THANet: Transferring Human Pose Estimation to Animal Pose Estimation. Electronics. 2023; 12(20):4210. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12204210
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Jincheng, Jianzhong Xu, Yunhang Shen, and Shaohui Lin. 2023. "THANet: Transferring Human Pose Estimation to Animal Pose Estimation" Electronics 12, no. 20: 4210. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12204210
APA StyleLiao, J., Xu, J., Shen, Y., & Lin, S. (2023). THANet: Transferring Human Pose Estimation to Animal Pose Estimation. Electronics, 12(20), 4210. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12204210







