CAE-Net: Cross-Modal Attention Enhancement Network for RGB-T Salient Object Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose a novel RGB-T salient object detection model, called a cross-modal attention enhancement network (CAE-Net), which consists of the cross-modal fusion (CMF), the single-/joint-modality decoder (SMD/JMD), and multi-stream fusion (MSF).
- To fuse the cross-modal features, we design a cross-modal fusion (CMF) module, where the cross-attention unit (CAU) is employed to filter incompatible information, and the channel attention is used to emphasize the significant modal features.
- To fuse cross-level features, we design the joint-modality decoder (JMD) module, where the multi-scale features are extracted and aggregated, and noisy information is filtered. Besides, two independent single-modality decoder (SMD) branches are employed to preserve more modality-specific information.
- To fully explore the complementary information between different decoder branches, we design a multi-stream fusion (MSF) module.
2. Related Works
2.1. RGB Salient Object Detection
2.2. RGB-D Salient Object Detection
2.3. RGB-T Salient Object Detection
3. The Proposed Method
3.1. Architecture Overview
3.2. Cross-Modal Fusion
3.3. Single-/Joint-Modality DECODER
3.4. Multi-Stream Fusion (MSF)
3.5. Loss Functions
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets and Implementation Details
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.2.1.
4.2.2.
4.2.3.
4.2.4.
4.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Arts
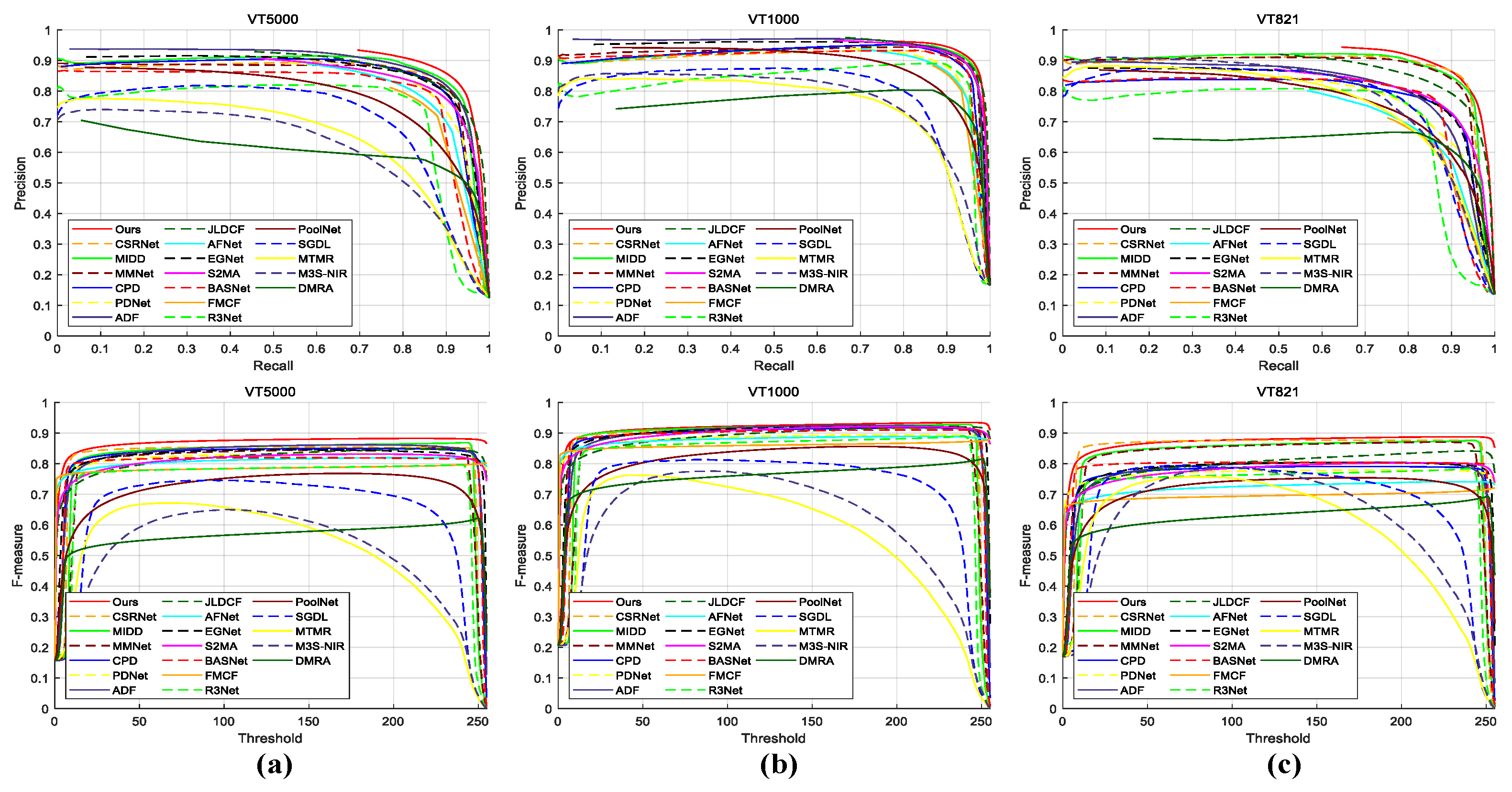
4.3.1. Quantitative Comparison
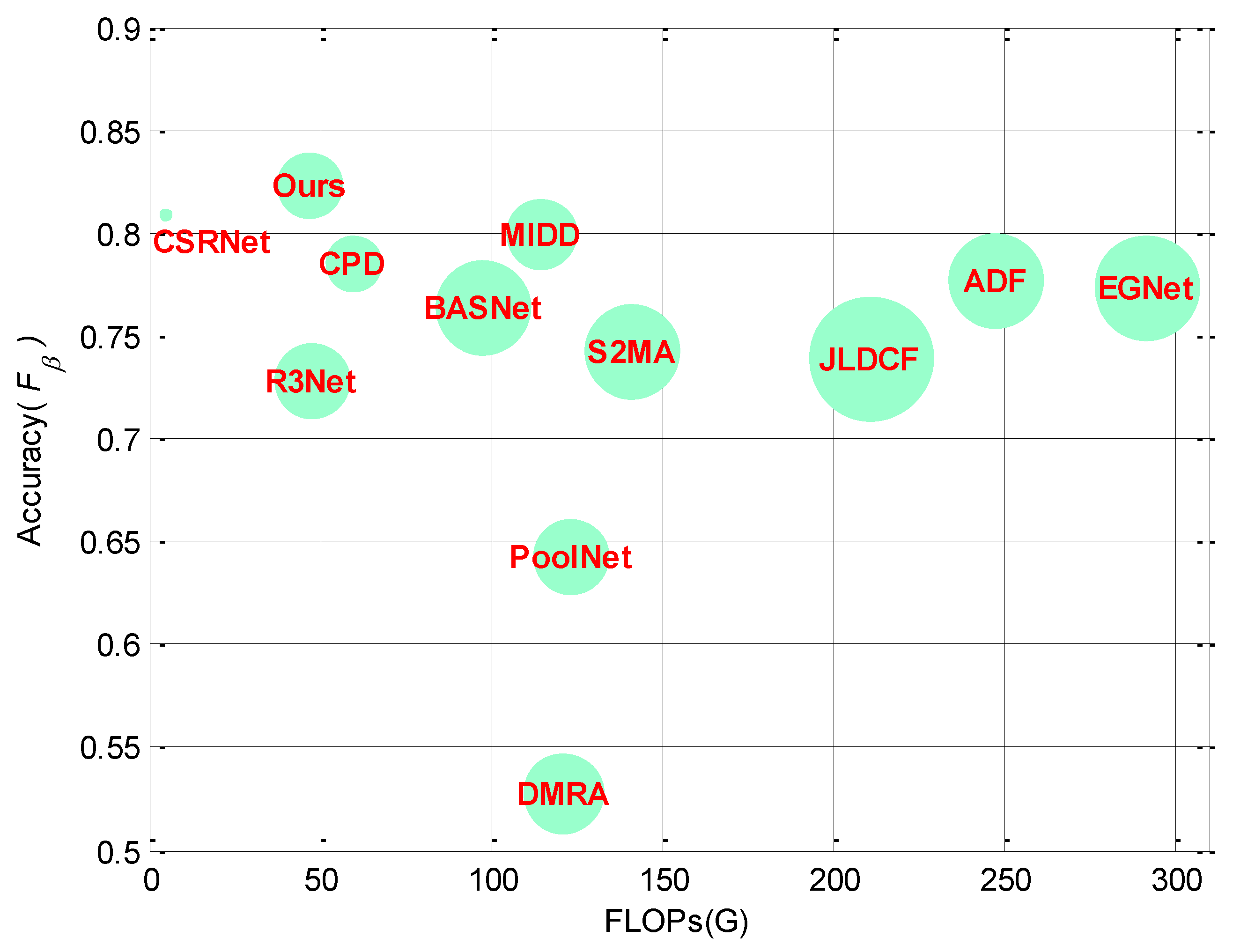
4.3.2. Complexity Analysis
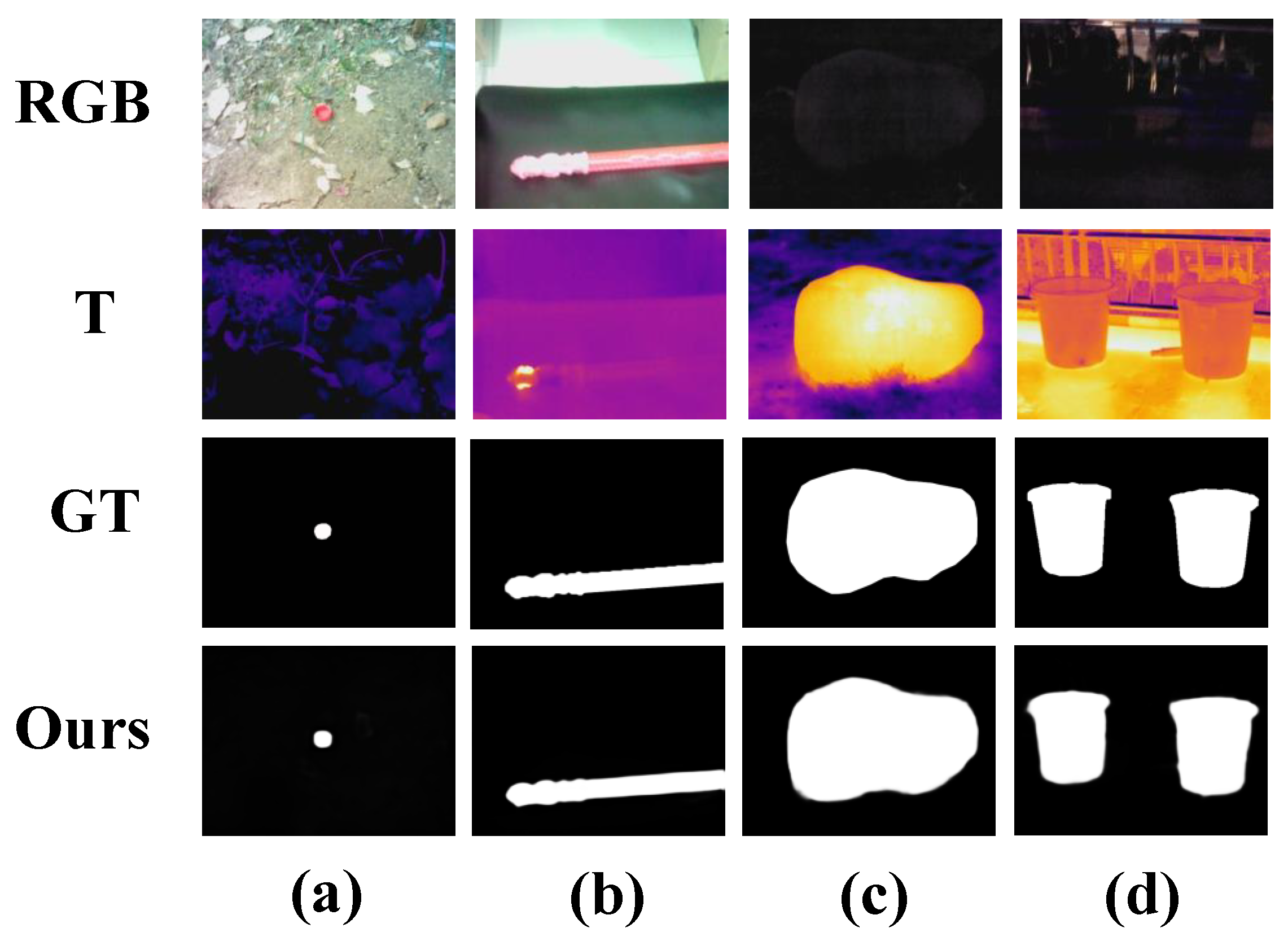
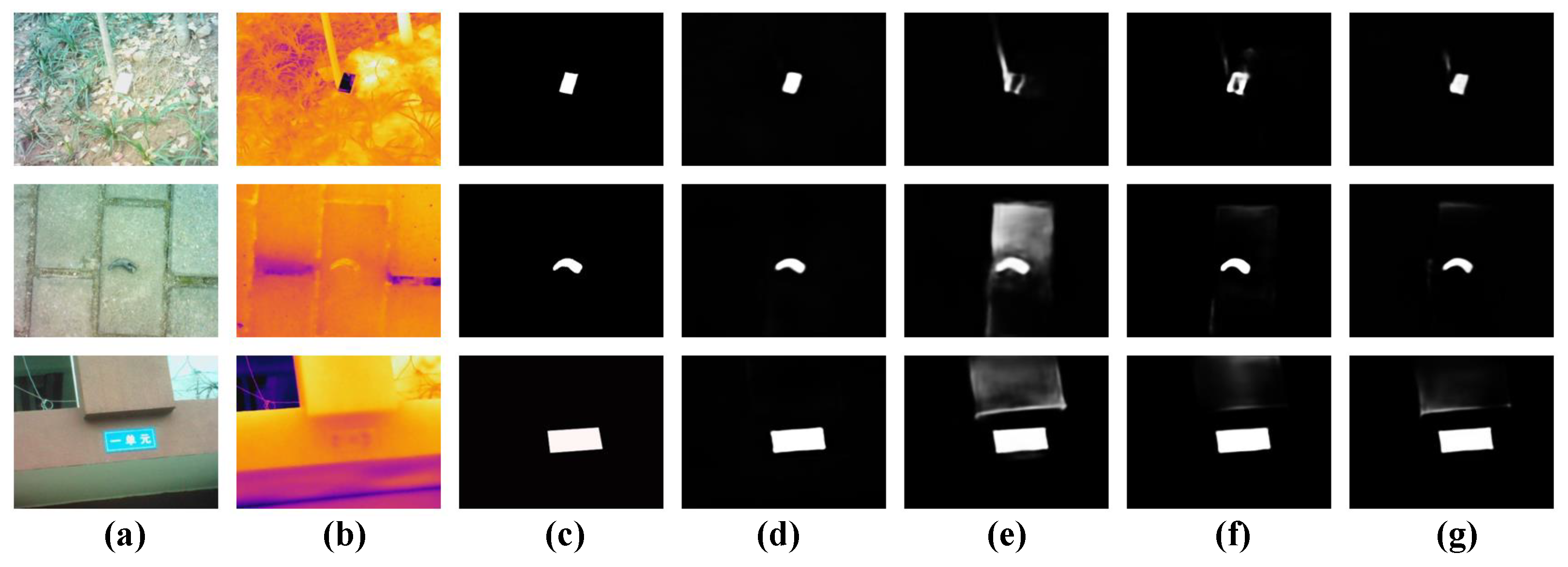
4.3.3. Qualitative Comparison
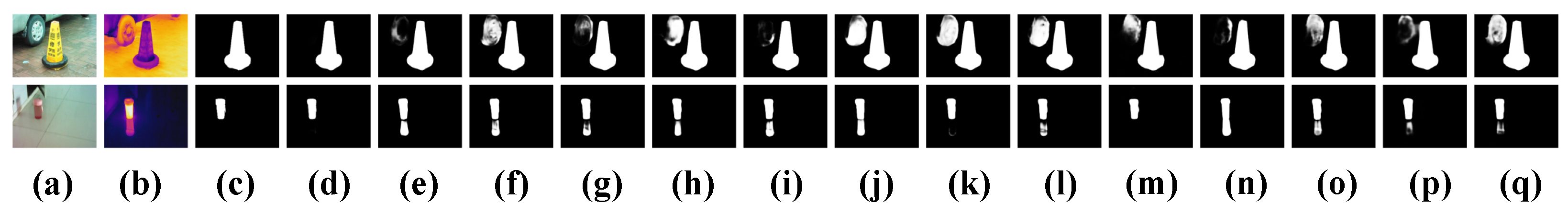
4.4. Ablation Studies
4.4.1. Effectiveness of cross-Modal Fusion (CMF)
4.4.2. Effectiveness of Single-/Joint-Modality Decoder (SMD/JMD)
4.4.3. Effectiveness of Multi-Stream Fusion (MSF)
4.4.4. Effectiveness of Backbone
4.4.5. Effectiveness of Loss Functions
4.5. Scalability Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Gong, S.; Guan, W.; Li, B.; Li, H.; Liu, J. Tracking and Localization based on Multi-angle Vision for Underwater Target. Electronics 2020, 9, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Sun, K.; Huang, S.; Wang, G.; Jiang, K. Quality Assessment of View Synthesis Based on Visual Saliency and Texture Naturalness. Electronics 2022, 11, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Hu, X.; Wang, M. Saliency Preprocessing Locality-Constrained Linear Coding for Remote Sensing Scene Classification. Electronics 2018, 7, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Liu, Y.; Xing, C.; Wang, Z. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Using Truncated Huber Penalty Function Smoothing and Visual Saliency Based Threshold Optimization. Electronics 2022, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Su, L.; Huang, Q. Cascaded partial decoder for fast and accurate salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3907–3916. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.J.; Hou, Q.; Cheng, M.M.; Feng, J.; Jiang, J. A simple pooling-based design for real-time salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 3917–3926. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Huang, D. Receptive field block net for accurate and fast object detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 385–400. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H. Multi-scale interactive network for salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 9413–9422. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.X.; Liu, J.J.; Fan, D.P.; Cao, Y.; Yang, J.; Cheng, M.M. EGNet: Edge guidance network for salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8779–8788. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Shen, K.; Liu, Z.; Gong, C.; Zhang, J.; Yan, C. Edge-aware multiscale feature integration network for salient object detection in optical remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2021, 60, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Lang, Y.; Tang, J. Multi-Interactive dual-decoder for RGB-Thermal salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 5678–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, F.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Shu, Y. Efficient Context-Guided Stacked Refinement Network for RGB-T Salient Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 3111–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Fu, H.; Chen, G.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, D.P.; Shao, L. Specificity-preserving rgb-d saliency detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual Conference, 10 March 2021; pp. 4681–4691. [Google Scholar]
- Itti, L.; Koch, C.; Niebur, E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1998, 20, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Yuan, Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N.; Tang, X.; Shum, H.Y. Learning to detect a salient object. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 33, 353–367. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, N.; Li, S. Salient object detection: A discriminative regional feature integration approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 2083–2090. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, C.; Gao, C.; Dehghan, M.; Jagersand, M. Basnet: Boundary-aware salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 7479–7489. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, B.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yan, C. Deeper feature integration network for salient object detection of strip steel surface defects. J. Electron. Imaging 2022, 31, 023013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, X.; Zhao, W. Salient object detection network with center pooling and distance-weighted affinity loss function. J. Electron. Imaging 2022, 31, 023008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Fang, H.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yan, C. Dense Attention-guided Cascaded Network for Salient Object Detection of Strip Steel Surface Defects. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 71, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Li, G.; Wang, W.; Wang, R. An innovative salient object detection using center-dark channel prior. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1509–1515. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, Y.; Ji, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Lu, H. Depth-induced multi-scale recurrent attention network for saliency detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 7254–7263. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Gong, X. Adaptive fusion for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 55277–55284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Cai, X.; Huang, K.; Li, T.H.; Li, G. PDNet: Prior-model guided depth-enhanced network for salient object detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Shanghai, China, 8–12 July 2019; pp. 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, N.; Han, J. Learning selective self-mutual attention for RGB-D saliency detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2020, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 13753–13762. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, K.; Fan, D.P.; Ji, G.P.; Zhao, Q. JL-DCF: Joint learning and densely-cooperative fusion framework for RGB-D salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 3052–3062. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Li, G.; Gong, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J. Attention-guided RGBD saliency detection using appearance information. Image Vis. Comput. 2020, 95, 103888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cong, R.; Piao, Y.; Xu, Q.; Loy, C.C. RGB-D salient object detection with cross-modality modulation and selection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 225–241. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.; Yan, C.; Zhou, X.; Cong, R.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, J.; Bao, Y.; Ding, G. Dynamic selective network for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 9179–9192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, C.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, A.; Tang, J.; Luo, B. RGB-T saliency detection benchmark: Dataset, baselines, analysis and a novel approach. In Proceedings of the 13th Conference on Image and Graphics Technologies and Applications, Beijing, China, 8–10 April 2018; pp. 359–369. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Z.; Xia, T.; Li, C.; Lu, Y.; Tang, J. M3S-NIR: Multi-modal multi-scale noise-insensitive ranking for RGB-T saliency detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Multimedia Information Processing and Retrieval (MIPR), San Jose, CA, USA, 28–30 March 2019; pp. 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Z.; Xia, T.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Tang, J. RGB-T image saliency detection via collaborative graph learning. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2019, 22, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, N.; Yao, L.; Zhang, D.; Shan, C.; Han, J. RGB-T salient object detection via fusing multi-level CNN features. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 3321–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Liao, G.; Ma, S.; Li, G.; Liang, Y.; Lin, W. Unified information fusion network for multi-modal RGB-D and RGB-T salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 2091–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y. RGBT salient object detection: A large-scale dataset and benchmark. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, J.; Nie, L.; Shao, J.; Liu, W.; Chua, T.S. Sca-cnn: Spatial and channel-wise attention in convolutional networks for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–6 July 2017; pp. 5659–5667. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2015, International Machine Learning Society (IMLS), Lile, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-local neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7794–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Cheng, M.M.; Hu, X.; Borji, A.; Tu, Z.; Torr, P.H. Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–16 July 2017; pp. 3203–3212. [Google Scholar]
- De Boer, P.T.; Kroese, D.P.; Mannor, S.; Rubinstein, R.Y. A tutorial on the cross-entropy method. Ann. Oper. Res. 2005, 134, 19–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.P.; Cheng, M.M.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Borji, A. Structure-measure: A new way to evaluate foreground maps. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4548–4557. [Google Scholar]
- Máttyus, G.; Luo, W.; Urtasun, R. Deeproadmapper: Extracting road topology from aerial images. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3438–3446. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 8026–8037. [Google Scholar]
- Achanta, R.; Hemami, S.; Estrada, F.; Susstrunk, S. Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 22–24 June 2009; pp. 1597–1604. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.P.; Gong, C.; Cao, Y.; Ren, B.; Cheng, M.M.; Borji, A. Enhanced-alignment measure for binary foreground map evaluation. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; pp. 698–704. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhu, L.; Xu, X.; Qin, J.; Han, G.; Heng, P.A. R3net: Recurrent residual refinement network for saliency detection. In Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; pp. 684–690. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, R.; Ge, L.; Geng, W.; Ren, T.; Wu, G. Depth saliency based on anisotropic center-surround difference. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 1115–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Li, B.; Xiong, W.; Hu, W.; Ji, R. Rgbd salient object detection: A benchmark and algorithms. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 92–109. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Geng, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, F. Leveraging stereopsis for saliency analysis. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 454–461. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.P.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Cheng, M.M. Rethinking RGB-D salient object detection: Models, data sets, and large-scale benchmarks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 2075–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Fu, Y. Progressively guided alternate refinement network for RGB-D salient object detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 520–538. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, Y.; Rong, Z.; Zhang, M.; Ren, W.; Lu, H. A2dele: Adaptive and attentive depth distiller for efficient RGB-D salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9060–9069. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Pang, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhang, L. A single stream network for robust and real-time RGB-D salient object detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 646–662. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Deng, Y.; Li, Y.; Hung, T.Y.; Lin, G. RGBD salient object detection via disentangled cross-modal fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 8407–8416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ren, W.; Piao, Y.; Rong, Z.; Lu, H. Select, supplement and focus for RGB-D saliency detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 3472–3481. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Liu, Z.; Ling, H. ICNet: Information conversion network for RGB-D based salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4873–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.X.; Cao, Y.; Fan, D.P.; Cheng, M.M.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, L. Contrast prior and fluid pyramid integration for RGBD salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3927–3936. [Google Scholar]




| Dataset | VT5000 | VT1000 | VT821 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metric | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | |
| RGB | PoolNet [9] | 0.0805 | 0.6431 | 0.8089 | 0.7881 | 0.063 | 0.7503 | 0.8552 | 0.8485 | 0.0828 | 0.6518 | 0.811 | 0.7884 |
| R3Net [53] | 0.0588 | 0.7283 | 0.8618 | 0.8128 | 0.0369 | 0.8325 | 0.9191 | 0.8865 | 0.0809 | 0.6815 | 0.8165 | 0.7823 | |
| BASNet [22] | 0.0542 | 0.764 | 0.8793 | 0.8385 | 0.0304 | 0.848 | 0.9244 | 0.9084 | 0.0673 | 0.7354 | 0.857 | 0.8228 | |
| EGNet [14] | 0.0528 | 0.7741 | 0.8885 | 0.8526 | 0.0339 | 0.8474 | 0.9226 | 0.9093 | 0.0661 | 0.7256 | 0.8583 | 0.829 | |
| CPD [8] | 0.0465 | 0.7859 | 0.8965 | 0.8547 | 0.0312 | 0.8617 | 0.9307 | 0.9071 | 0.0795 | 0.7173 | 0.8474 | 0.8185 | |
| RGB-D | DMRA [27] | 0.1845 | 0.5273 | 0.6869 | 0.6589 | 0.1241 | 0.7151 | 0.8197 | 0.7836 | 0.2165 | 0.5772 | 0.7144 | 0.6663 |
| S2MA [30] | 0.0533 | 0.7432 | 0.8703 | 0.8535 | 0.0297 | 0.848 | 0.9286 | 0.9182 | 0.098 | 0.7092 | 0.8376 | 0.8112 | |
| AFNet [28] | 0.0503 | 0.7488 | 0.8794 | 0.8323 | 0.0328 | 0.8382 | 0.9226 | 0.8891 | 0.0687 | 0.6616 | 0.8212 | 0.7787 | |
| JLDCF [31] | 0.0503 | 0.7391 | 0.8639 | 0.8615 | 0.0299 | 0.8291 | 0.9145 | 0.9127 | 0.0756 | 0.7265 | 0.8486 | 0.8389 | |
| PDNet [29] | 0.0474 | 0.7612 | 0.8836 | 0.845 | 0.0327 | 0.8362 | 0.9212 | 0.8974 | 0.0566 | 0.7126 | 0.8587 | 0.8099 | |
| RGB-T | M3S-NIR * [36] | 0.168 | 0.5752 | 0.7818 | 0.6527 | 0.1454 | 0.7167 | 0.8281 | 0.7263 | 0.1397 | 0.7339 | 0.8607 | 0.7238 |
| MTMR * [35] | 0.1143 | 0.5952 | 0.7948 | 0.6808 | 0.1194 | 0.7136 | 0.8356 | 0.7063 | 0.1083 | 0.662 | 0.8142 | 0.7258 | |
| SGDL * [37] | 0.0886 | 0.6712 | 0.8241 | 0.7517 | 0.0896 | 0.7626 | 0.857 | 0.7878 | 0.0849 | 0.7292 | 0.8472 | 0.7666 | |
| FMCF [38] | 0.0556 | 0.7326 | 0.8672 | 0.813 | 0.037 | 0.822 | 0.916 | 0.8723 | 0.0808 | 0.6405 | 0.8035 | 0.7596 | |
| ADF [40] | 0.0483 | 0.7774 | 0.891 | 0.8636 | 0.0339 | 0.8462 | 0.9222 | 0.9094 | 0.0765 | 0.7158 | 0.8442 | 0.8106 | |
| MMNet [39] | 0.0433 | 0.7823 | 0.8903 | 0.8639 | 0.0275 | 0.8607 | 0.9284 | 0.9173 | 0.04 | 0.7958 | 0.8931 | 0.8749 | |
| MIDD [16] | 0.0433 | 0.7994 | 0.8988 | 0.8679 | 0.0271 | 0.88 | 0.942 | 0.9155 | 0.0446 | 0.8032 | 0.8975 | 0.8712 | |
| CSRNet [17] | 0.0417 | 0.8092 | 0.9068 | 0.8676 | 0.0242 | 0.8751 | 0.9392 | 0.9183 | 0.0376 | 0.829 | 0.9116 | 0.8848 | |
| Ours | 0.0375 | 0.8233 | 0.9185 | 0.8802 | 0.0232 | 0.8813 | 0.9491 | 0.9234 | 0.0359 | 0.8201 | 0.9159 | 0.8837 | |
| Models | PoolNet | R3Net | BASNet | EGNet | CPD | DMRA | S2MA | JLDCF | ADF | MIDD | CSRNet | Ours | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [9] | [53] | [22] | [14] | [8] | [27] | [30] | [31] | [40] | [16] | [17] | |||
| Param | (M) ↓ | 53.6 | 56.1 | 87.1 | 108.1 | 29.2 | 59.7 | 86.7 | 143.5 | 83.1 | 50 | 1 | 38.8 |
| FLOPs | (G) ↓ | 123.4 | 47.5 | 97.7 | 291.9 | 59.4 | 120.9 | 141.1 | 211.1 | 247.2 | 114.6 | 4.4 | 47.1 |
| Ablation Study | VT5000 | VT1000 | VT821 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ||
| No.1 | CI | 0.043 | 0.7955 | 0.9013 | 0.8639 | 0.0275 | 0.8647 | 0.9388 | 0.9111 | 0.046 | 0.7894 | 0.8884 | 0.8595 |
| w/o CMF | 0.039 | 0.8096 | 0.9091 | 0.873 | 0.0259 | 0.8682 | 0.9393 | 0.9132 | 0.0393 | 0.7889 | 0.8931 | 0.8653 | |
| Self | 0.0385 | 0.8155 | 0.9113 | 0.8763 | 0.0252 | 0.8733 | 0.9413 | 0.9176 | 0.0381 | 0.7977 | 0.8968 | 0.8712 | |
| No.2 | Unet | 0.0445 | 0.7679 | 0.8883 | 0.8516 | 0.0319 | 0.8426 | 0.9223 | 0.8989 | 0.0484 | 0.7412 | 0.8673 | 0.8433 |
| w/o SMD | 0.0386 | 0.8144 | 0.9103 | 0.8775 | 0.0233 | 0.8753 | 0.9411 | 0.9196 | 0.0387 | 0.8066 | 0.9023 | 0.8754 | |
| w/o RFB | 0.04 | 0.7995 | 0.9 | 0.8704 | 0.0281 | 0.8634 | 0.9295 | 0.9128 | 0.0406 | 0.7871 | 0.8882 | 0.8673 | |
| w/o Nonlocal | 0.0386 | 0.8153 | 0.9123 | 0.8735 | 0.0257 | 0.8771 | 0.9455 | 0.9178 | 0.0381 | 0.801 | 0.902 | 0.8698 | |
| No.3 | Only-J | 0.0382 | 0.8126 | 0.9106 | 0.8746 | 0.0246 | 0.8757 | 0.944 | 0.9188 | 0.0391 | 0.7971 | 0.8957 | 0.8688 |
| Only-R | 0.0442 | 0.7937 | 0.9001 | 0.8601 | 0.0278 | 0.8638 | 0.9338 | 0.9088 | 0.0575 | 0.7524 | 0.8704 | 0.84 | |
| Only-T | 0.0509 | 0.7644 | 0.8904 | 0.8335 | 0.0384 | 0.8354 | 0.9238 | 0.8816 | 0.0541 | 0.7424 | 0.8699 | 0.8176 | |
| Both-Avg | 0.0395 | 0.797 | 0.9002 | 0.8731 | 0.0271 | 0.8614 | 0.9304 | 0.9134 | 0.0378 | 0.7912 | 0.8936 | 0.8731 | |
| No.4 | Res50 | 0.0523 | 0.7486 | 0.8772 | 0.8361 | 0.0372 | 0.8277 | 0.9121 | 0.8866 | 0.0445 | 0.7796 | 0.8917 | 0.8501 |
| PS | 0.039 | 0.8098 | 0.9074 | 0.8738 | 0.0243 | 0.8781 | 0.9458 | 0.9193 | 0.0373 | 0.7987 | 0.8971 | 0.8738 | |
| No.5 | bce | 0.0393 | 0.7918 | 0.8981 | 0.8771 | 0.0268 | 0.8553 | 0.9299 | 0.9175 | 0.041 | 0.78 | 0.8861 | 0.8719 |
| bce+IoU | 0.0381 | 0.8138 | 0.9089 | 0.8805 | 0.0235 | 0.8737 | 0.9391 | 0.921 | 0.0383 | 0.8059 | 0.8992 | 0.8767 | |
| bce+SSIM | 0.0385 | 0.8041 | 0.9072 | 0.8781 | 0.0258 | 0.8595 | 0.9327 | 0.9206 | 0.0386 | 0.7884 | 0.8919 | 0.8738 | |
| Ours | 0.0375 | 0.8233 | 0.9185 | 0.8802 | 0.0232 | 0.8813 | 0.9491 | 0.9234 | 0.0359 | 0.8201 | 0.9159 | 0.8837 | |
| Datasets | Metric | CPFP | AFNet | S2MA | ICNet | DMRA | A2dele | DANet | SSF | DCMF | JLDCF | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [65] | [28] | [30] | [64] | [27] | [60] | [61] | [63] | [62] | [31] | |||
| NJU2K | ↓ | 0.0534 | 0.0533 | 0.0533 | 0.052 | 0.051 | 0.0509 | 0.0464 | 0.0435 | 0.0427 | 0.0415 | 0.0379 |
| ↑ | 0.8364 | 0.8672 | 0.8646 | 0.8676 | 0.8701 | 0.8709 | 0.8763 | 0.8827 | 0.8804 | 0.8841 | 0.9007 | |
| ↑ | 0.9002 | 0.9188 | 0.9163 | 0.9127 | 0.92 | 0.916 | 0.926 | 0.9335 | 0.9246 | 0.9347 | 0.9409 | |
| ↑ | 0.8777 | 0.8801 | 0.8942 | 0.8939 | 0.8859 | 0.871 | 0.8969 | 0.8984 | 0.9125 | 0.9025 | 0.9074 | |
| NLPR | ↓ | 0.036 | 0.033 | 0.03 | 0.0284 | 0.0315 | 0.0286 | 0.0285 | 0.0267 | 0.029 | 0.0219 | 0.0221 |
| ↑ | 0.8189 | 0.8203 | 0.8479 | 0.865 | 0.8494 | 0.87 | 0.8662 | 0.8672 | 0.849 | 0.8732 | 0.897 | |
| ↑ | 0.9227 | 0.9306 | 0.9407 | 0.9435 | 0.94 | 0.9441 | 0.9478 | 0.949 | 0.9381 | 0.9539 | 0.9606 | |
| ↑ | 0.8874 | 0.8994 | 0.9145 | 0.9215 | 0.8986 | 0.898 | 0.9137 | 0.9135 | 0.921 | 0.9239 | 0.9241 | |
| STERE | ↓ | 0.0514 | 0.0472 | 0.0508 | 0.0447 | 0.0477 | 0.0432 | 0.0476 | 0.0448 | 0.0427 | 0.0404 | 0.0392 |
| ↑ | 0.8296 | 0.8718 | 0.8545 | 0.8642 | 0.8658 | 0.8808 | 0.8581 | 0.878 | 0.8659 | 0.8688 | 0.8824 | |
| ↑ | 0.9071 | 0.9337 | 0.9254 | 0.9256 | 0.9332 | 0.9348 | 0.9263 | 0.9342 | 0.9298 | 0.9368 | 0.9403 | |
| ↑ | 0.8793 | 0.8914 | 0.8904 | 0.9025 | 0.8856 | 0.887 | 0.8922 | 0.8928 | 0.9097 | 0.9029 | 0.8993 | |
| DUT | ↓ | − | − | 0.044 | 0.0722 | 0.0478 | 0.0427 | 0.0467 | 0.034 | 0.0351 | 0.043 | 0.035 |
| ↑ | − | − | 0.8847 | 0.8298 | 0.8831 | 0.8901 | 0.8836 | 0.9129 | 0.9057 | 0.8827 | 0.916 | |
| ↑ | − | − | 0.9349 | 0.9012 | 0.9301 | 0.9296 | 0.929 | 0.9514 | 0.9505 | 0.9375 | 0.9498 | |
| ↑ | − | − | 0.903 | 0.8524 | 0.8889 | 0.8869 | 0.8894 | 0.9159 | 0.9279 | 0.9055 | 0.9141 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, C.; Wan, B.; Zhou, X.; Sun, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yan, C. CAE-Net: Cross-Modal Attention Enhancement Network for RGB-T Salient Object Detection. Electronics 2023, 12, 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12040953
Lv C, Wan B, Zhou X, Sun Y, Hu J, Zhang J, Yan C. CAE-Net: Cross-Modal Attention Enhancement Network for RGB-T Salient Object Detection. Electronics. 2023; 12(4):953. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12040953
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Chengtao, Bin Wan, Xiaofei Zhou, Yaoqi Sun, Ji Hu, Jiyong Zhang, and Chenggang Yan. 2023. "CAE-Net: Cross-Modal Attention Enhancement Network for RGB-T Salient Object Detection" Electronics 12, no. 4: 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12040953
APA StyleLv, C., Wan, B., Zhou, X., Sun, Y., Hu, J., Zhang, J., & Yan, C. (2023). CAE-Net: Cross-Modal Attention Enhancement Network for RGB-T Salient Object Detection. Electronics, 12(4), 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12040953






