Dual-Level Viewpoint-Learning for Cross-Domain Vehicle Re-Identification
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To overcome the ambiguity of viewpoint information in human subjectivity, a dual-level viewpoint-annotation proposal is defined, one with a novel method for viewpoint measurement, and one which can alleviate the subjective error of manual annotations.
- A method of angle invariance pre-training is designed to explore identity similarity and difference between vehicles across angle-level viewpoints. During the whole pre-training procedure, the part-level pyramidal network (PLPNet) with angle bias metric loss is adopted to obtain the angle invariance feature, which provides more subtle angle-level discrimination for the downstream target domain.
- A meta-orientation adaptation learning strategy is proposed for extending Re-ID model generalization in a meta-learning manner by utilizing orientation-level viewpoint annotations.
2. Related Work
2.1. Multi-View Learning for Vehicle Re-ID
2.2. Cross-Domain Learning for Vehicle Re-ID
2.3. Meta-Learning for Vehicle Re-ID
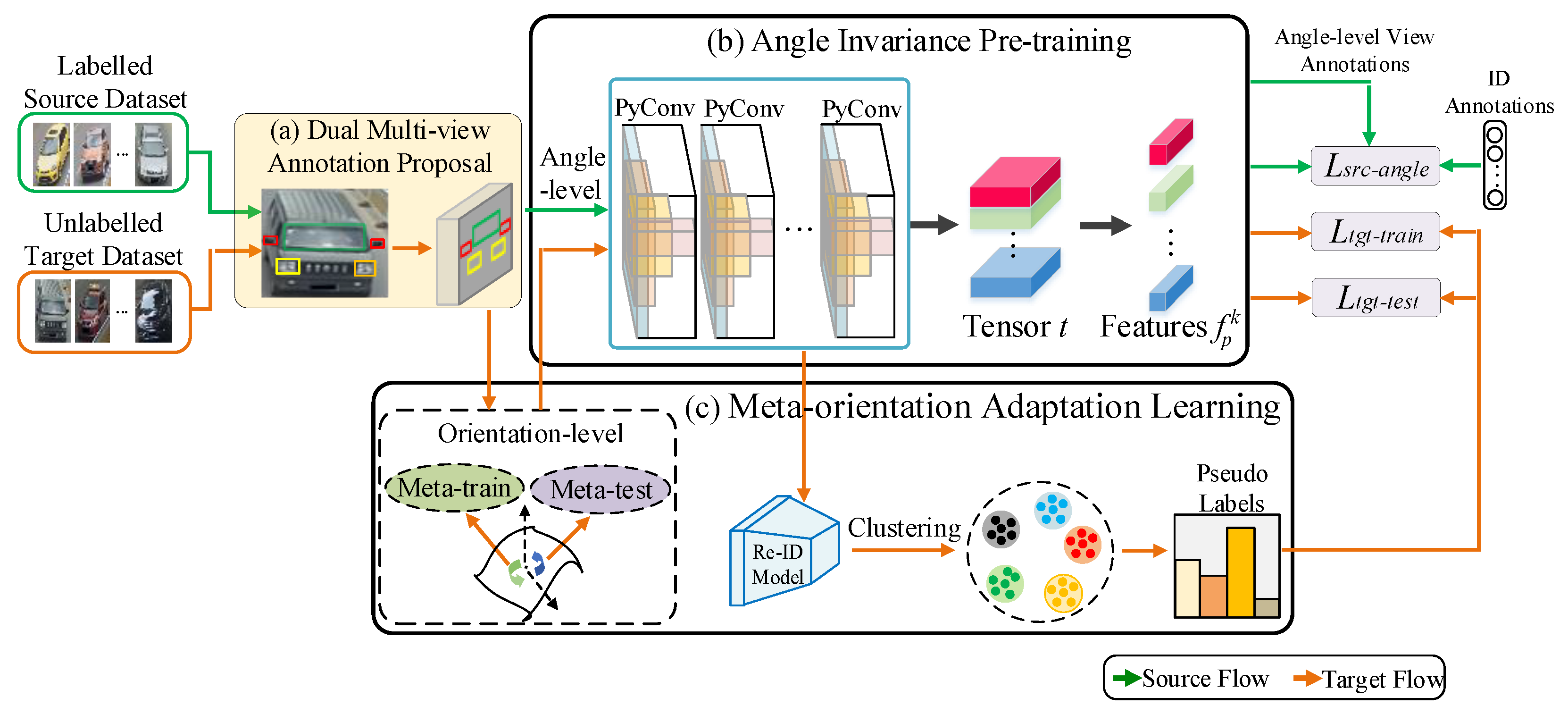
3. The Proposed Methods
3.1. The Overall Framework
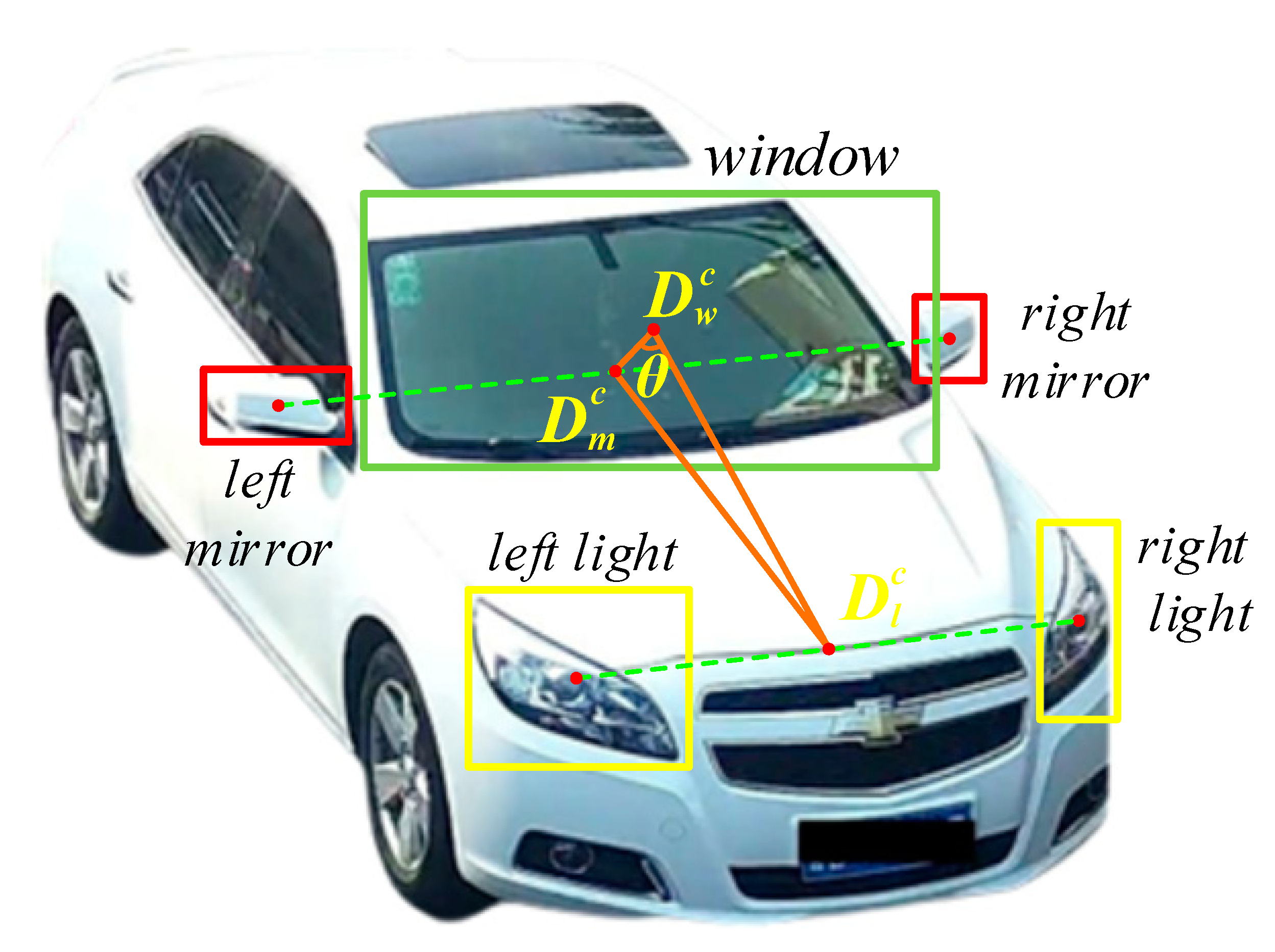
3.2. Dual-Level Viewpoint-Annotation Proposal
3.3. Angle Invariance Pre-Training for Source Domain
3.4. Meta-Orientation Adaptation Learning for Target Domain
3.5. Discussion
- The bounding box level of vehicle-part coordinates still belongs to the coarse-grained perspective calculation method as the basis for viewpoint calculation. There is a lack of utilization of pixel-level part detection for fine-grained viewpoint calculation.
- The proposed dual-level viewpoint-framework focuses on calculating viewpoint in scenarios where vehicle parts are visible, but does not fully consider the method of calculating vehicle viewpoint in occluded scenes. Furthermore, there are also cases where several bounding boxes are not detected.
- In terms of data augmentation used to alleviate overfitting issues, we use random cropping, horizontal flipping, and erasing to expand the training set during the training process. This operation can encourage the Re-ID model to continuously learn more challenging generated data during each epoch process, thereby overcoming the overfitting issues.
- In terms of the proposed meta-learning strategy for alleviating the overfitting issues, we randomly divide different orientation-level viewpoint annotations according to the split ratio in each epoch of meta-learning. That is to say, the partitioning of the meta-orientation training set and meta-orientation testing set during each epoch process is dynamically changed based on directional viewpoint annotations. This design can continuously improve the generalization ability of the Re-ID model to changes in viewpoint, thereby alleviating overfitting issues during the training process.
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset and Evaluation Protocols
4.2. Experiment Settings
4.3. Ablation Studies
- “Direct Transfer” means adopting the traditional cross-domain Re-ID method, using ResNet-50 as the backbone.
- The term “w/o (O + A)” means adopting the traditional cross-domain Re-ID method, using PLPNet as the backbone.
- The term “w/o O” means not using the meta-orientation adaptation learning strategy and only using the angle invariance pre-training method for cross-domain Re-ID tasks.
- The term “w/o A” means not using the angle invariance pre-training method and only using the meta-orientation adaptation learning strategy for cross-domain Re-ID tasks.
- “Ours” means using all proposed modules.
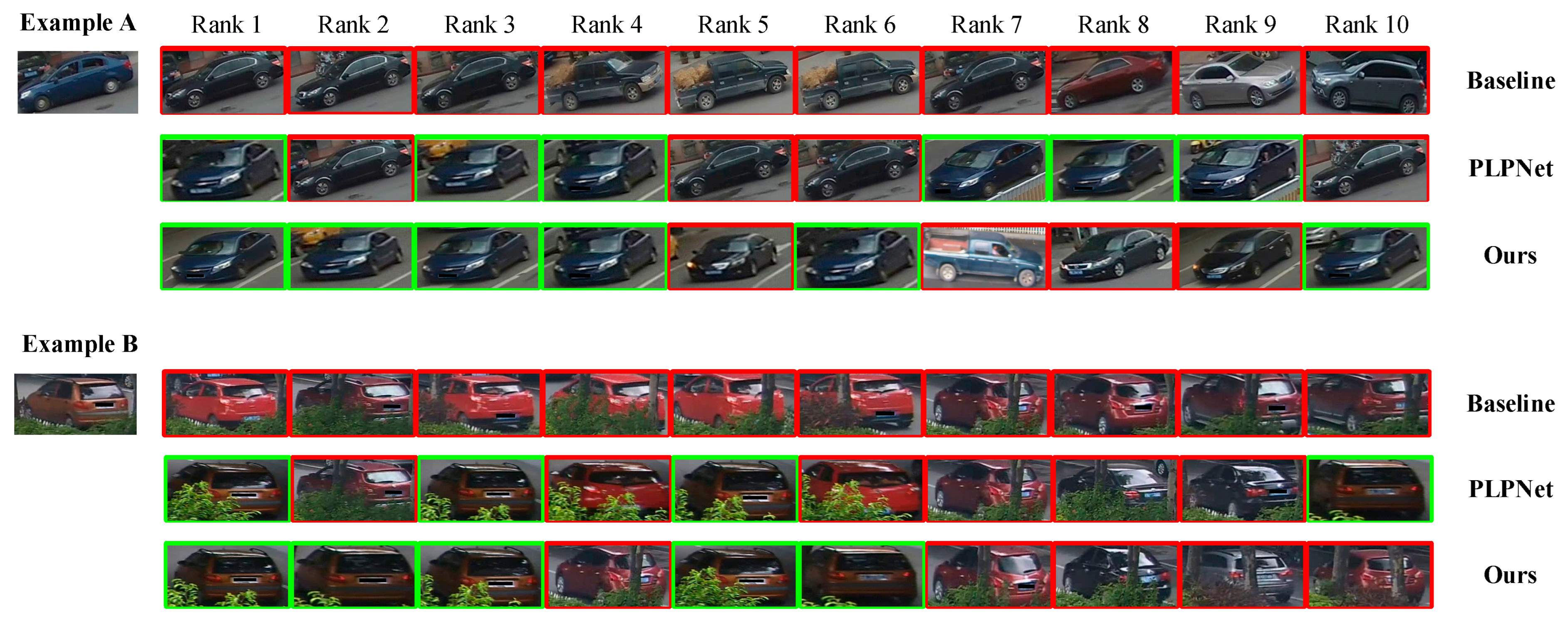
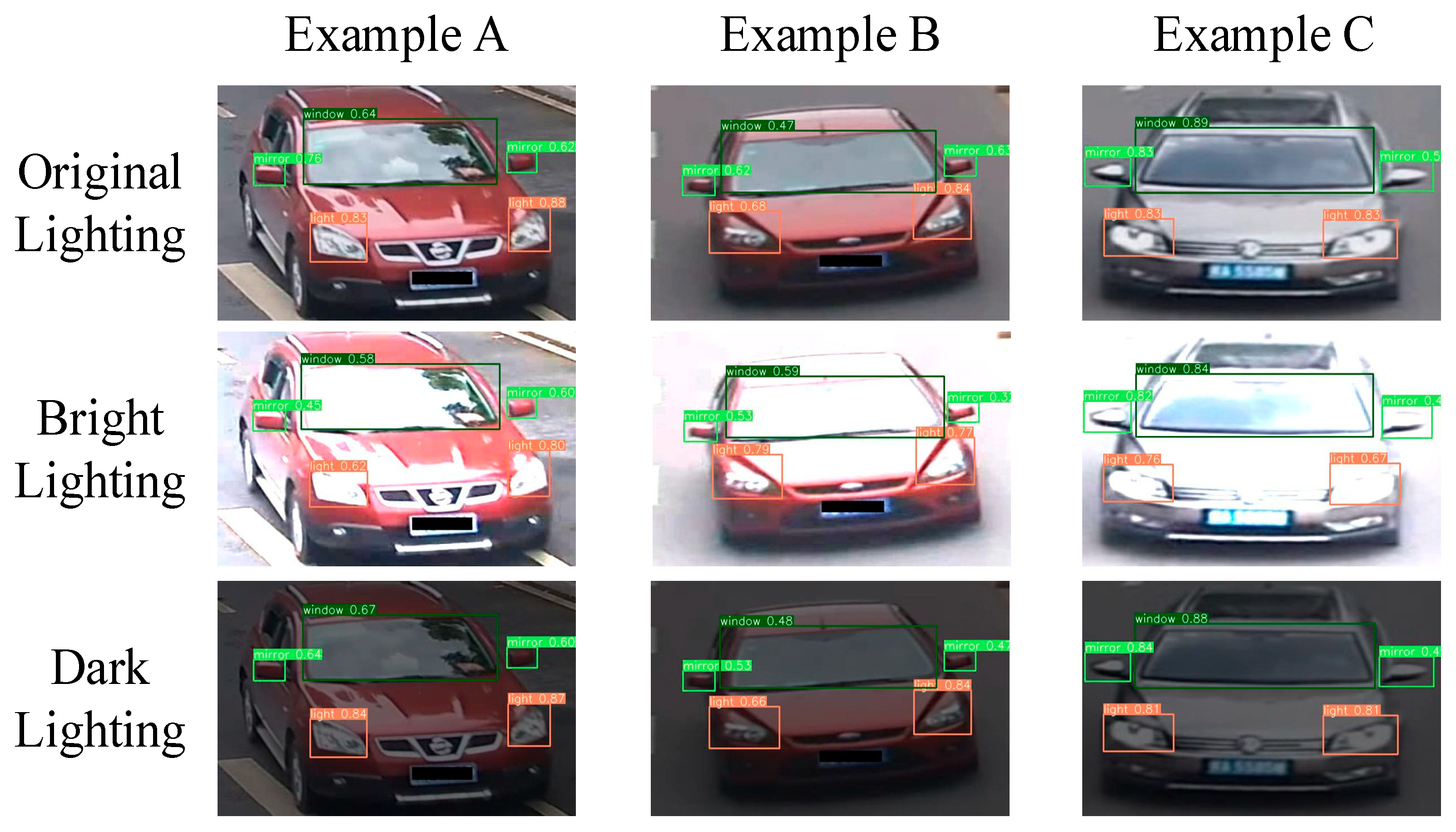
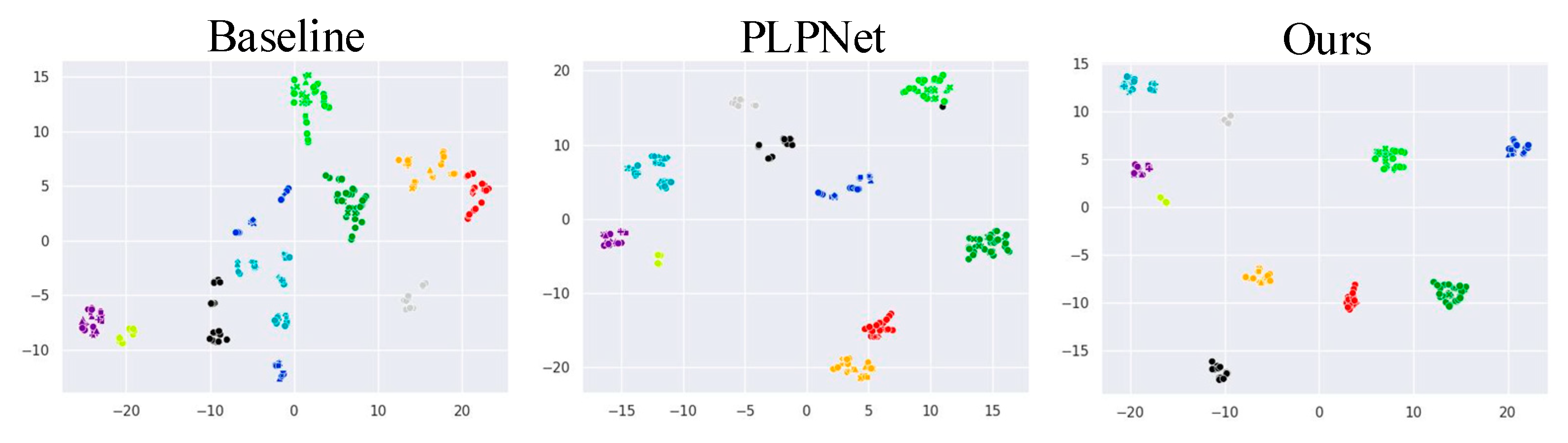
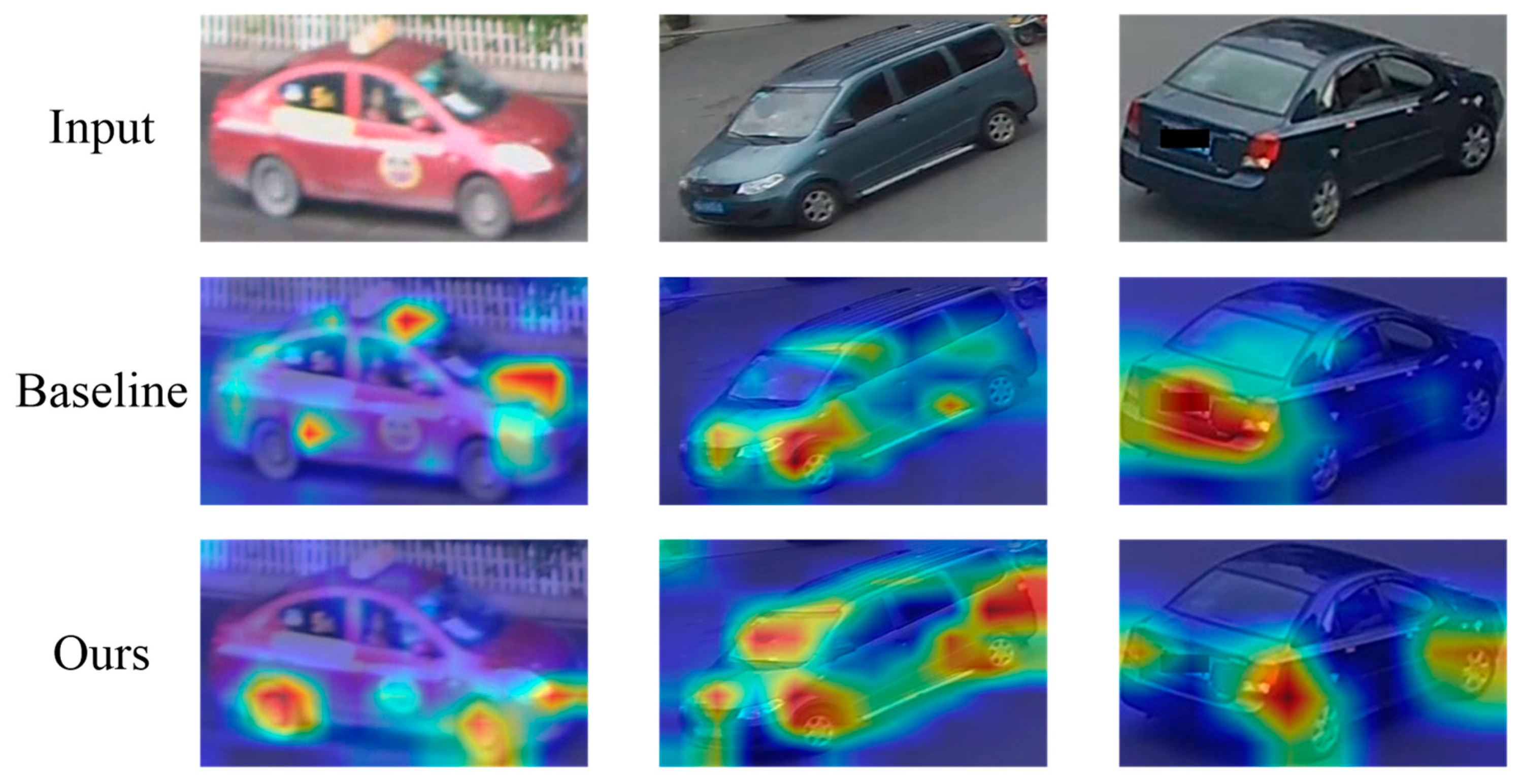
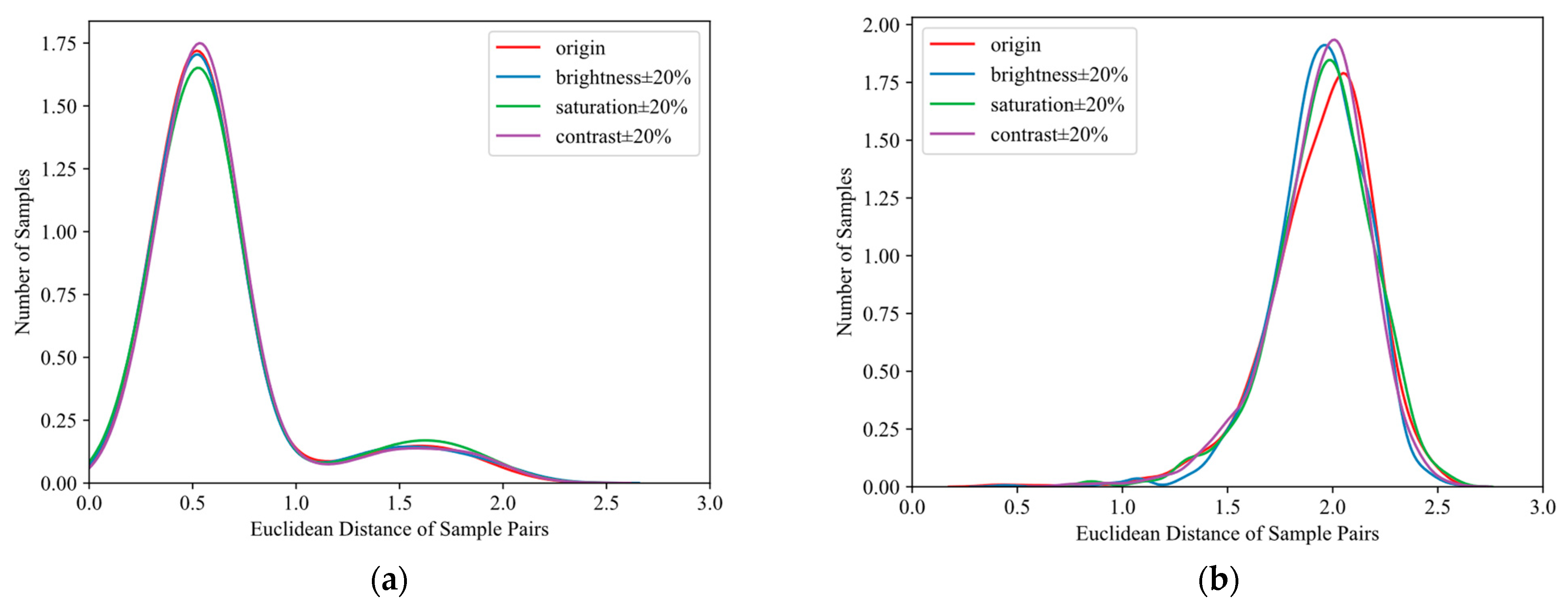
4.4. Qualitative Visualization Analysis
4.5. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Approaches
4.6. Further Studies in Unsupervised Setting
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiao, B.; Yang, L.; Gao, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y. Vehicle Re-Identification in Aerial Images and Videos: Dataset and Approach. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 1586–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Hu, H. Graph-Based Progressive Fusion Network for Multi-Modality Vehicle Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 12431–12447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Min, W.; Han, Q.; Liu, Q.; Zha, C.; Zhao, H.; Wei, Z. Inter-Domain Adaptation Label for Data Augmentation in Vehicle Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 24, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lan, C.; Zeng, W.; Chen, Z.; Chang, S.-F. Beyond Triplet Loss: Meta Prototypical N-Tuple Loss for Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 24, 4158–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, D.; Zhang, W.; Chen, D.; Ge, Z.; Boussaid, F.; Bennamoun, M.; Shen, J. Pseudo-Pair Based Self-Similarity Learning for Unsupervised Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 4803–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lin, Y.; Du, B. Unsupervised Person Re-Identification with Stochastic Training Strategy. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 4240–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Song, Y.; Chang, F.; Li, S.; Ke, R.; Wang, Y. Posture Calibration Based Cross-View & Hard-Sensitive Metric Learning for UAV-Based Vehicle Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 19246–19257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y. Pluggable Weakly-Supervised Cross-View Learning for Accurate Vehicle Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, Newark, NJ, USA, 27 June 2022; pp. 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Peng, P.; Giannopoulos, G.A. Model Latent Views with Multi-Center Metric Learning for Vehicle Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 1919–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, R.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wei, Y. Vehicle Re-Identification with Viewpoint-Aware Metric Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8281–8290. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Wang, Y.; Chau, L.-P. Weakly-Supervised Part-Attention and Mentored Networks for Vehicle Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 8887–8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, R.; Zheng, X.; Peng, P.; Wu, Y.; Huang, F.; Ji, R. Aggregating Global and Local Visual Representation for Vehicle Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 23, 3968–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, H.; Zhao, F.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z. Global–Local Discriminative Representation Learning Network for Viewpoint-Aware Vehicle Re-Identification in Intelligent Transportation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Pan, M.; Tong, W.; Law, R.; Wu, E.Q. URRNet: A Unified Relational Reasoning Network for Vehicle Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 11156–11168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Luo, Z.; Fu, P.; Ji, X. VOC-ReID: Vehicle Re-Identification Based on Vehicle-Orientation-Camera. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 2566–2573. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Oh, H. Camera-Tracklet-Aware Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Vehicle Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23 May 2022; pp. 905–911. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, S.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Q.; Sebe, N. Multi-View Spatial Attention Embedding for Vehicle Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Z. Self-Supervised Geometric Features Discovery via Interpretable Attention for Vehicle Re-Identification and Beyond. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 194–204. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Liu, J.; Zheng, C.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Z. Exploiting Multi-View Part-Wise Correlation via an Efficient Transformer for Vehicle Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 25, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, Y.; Shi, H.; Tu, Z. Multi-View Feature Complementary for Multi-Query Vehicle Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2023 8th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing (ICSP), Xi’an, China, 21 April 2023; IEEE Computer Society: Los Alamitos, CA, USA; pp. 1570–1573. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, D.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Gao, L.; Huang, Q. Viewpoint Alignment and Discriminative Parts Enhancement in 3D Space for Vehicle ReID. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 25, 2954–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, L.; Liu, X.; Yao, Z.; Yi, S.; Shao, J.; Yan, J.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Orientation Invariant Feature Embedding and Spatial Temporal Regularization for Vehicle Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 379–387. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, L.; Shao, L. Vehicle Re-Identification by Deep Hidden Multi-View Inference. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 3275–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Zheng, J.; Yan, C.; Mei, T. Beyond the Parts: Learning Multi-View Cross-Part Correlation for Vehicle Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12 October 2020; pp. 907–915. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, S.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Q.; Sebe, N. Viewpoint and Scale Consistency Reinforcement for UAV Vehicle Re-Identification. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 719–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, K.; Kou, G.; Wang, M.; Gupta, B.B. GAN-Siamese Network for Cross-Domain Vehicle Re-Identification in Intelligent Transport Systems. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2023, 10, 2779–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Gu, J.; He, S.; Jiang, W. Transformer-Based Domain-Specific Representation for Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Vehicle Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 2935–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Oh, H. Unsupervised Vehicle Re-Identification via Self-Supervised Metric Learning Using Feature Dictionary. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September 2021; pp. 3806–3813. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Peng, J.; Jiang, G.; Fu, X. Learning Multiple Semantic Knowledge for Cross-Domain Unsupervised Vehicle Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Virtual, 5 July 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bashir, R.M.S.; Shahzad, M.; Fraz, M.M. Vr-Proud: Vehicle Re-Identification Using Progressive Unsupervised Deep Architecture. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 90, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, A.; Sun, X.; Li, C.; Tang, J. Aware Progressive Clustering for Unsupervised Vehicle Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 11422–11435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, T.; Fu, X. Cross Domain Knowledge Transfer for Unsupervised Vehicle Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), Shanghai, China, 8–12 July 2019; pp. 453–458. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Zhong, Z.; Luo, Z.; Cai, Y.; Lin, Y.; Li, S.; Sebe, N. Joint Noise-Tolerant Learning and Meta Camera Shift Adaptation for Unsupervised Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 4853–4862. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Yang, F.; Luo, Z.; Lin, Y.; Li, S.; Sebe, N. Learning to Generalize Unseen Domains via Memory-Based Multi-Source Meta-Learning for Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 6273–6282. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Zhong, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Z.; Li, S.; Sebe, N.; Satoh, S. Learning to Attack Real-World Models for Person Re-Identification via Virtual-Guided Meta-Learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 3128–3135. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Jiao, J.; Ce, W.; Liu, J.; Lou, Y.; Feng, X.; Duan, L.-Y. Person30k: A Dual-Meta Generalization Network for Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 2123–2132. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:200410934. [Google Scholar]
- Duta, I.C.; Liu, L.; Zhu, F.; Shao, L. Pyramidal Convolution: Rethinking Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition. arXiv 2020, arXiv:200611538. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Mei, T.; Ma, H. A Deep Learning-Based Approach to Progressive Vehicle Re-Identification for Urban Surveillance. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 9906, pp. 869–884. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pang, L.; Huang, T. Deep Relative Distance Learning: Tell the Difference between Similar Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2167–2175. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Y.; Bai, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Duan, L. Veri-Wild: A Large Dataset and a New Method for Vehicle Re-Identification in the Wild. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3230–3238. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.; Zheng, L.; Ye, Q.; Kang, G.; Yang, Y.; Jiao, J. Image-Image Domain Adaptation with Preserved Self-Similarity and Domain-Dissimilarity for Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 994–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Du, B.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, C.; Wang, X. Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Reidentification: Theory and Practice. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 102, 107173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Zheng, L.; Luo, Z.; Li, S.; Yang, Y. Invariance Matters: Exemplar Memory for Domain Adaptive Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 598–607. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Liao, S.; Zhao, F.; Kang, C.; Shao, L. DomainMix: Learning Generalizable Person Re-Identification Without Human Annotations. In Proceedings of the 32nd British Machine Vision Conference 2021, BMVC 2021, Online, 22 November 2021; p. 355. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.; Zhu, F.; Chen, D.; Zhao, R.; Li, H. Self-Paced Contrastive Learning with Hybrid Memory for Domain Adaptive Object Re-ID. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Larochelle, H., Ranzato, M., Hadsell, R., Balcan, M.F., Lin, H., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Scotland, UK, 2020; Volume 33, pp. 11309–11321. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, H. Mutual Mean-Teaching: Pseudo Label Refinery for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation on Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 26 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Fan, H.; Xu, M.; Yang, Y. Adaptive Exploration for Unsupervised Person Re-Identification. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2020, 16, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Oh, H. Unsupervised Person Re-Identification via Multi-Label Prediction and Classification Based on Graph-Structural Insight. arXiv 2021, arXiv:210608798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ge, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Li, H. Refining Pseudo Labels with Clustering Consensus over Generations for Unsupervised Object Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 3435–3444. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Li, C.-G.; Guo, J. Cluster-Guided Asymmetric Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 3606–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Datasets | Image Size | Number of Cameras | Number of Images (Number of IDs) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Set | Training Set | Test Set | |||||
| VeRi-776 | 224 × 224 | 20 | 50,117 (776) | 37,778 (576) | 12,339 (200) | ||
| VehicleID | 224 × 224 | - | 221,763 (26,267) | 110,178 (13,134) | Test800 | Test1600 | Test2400 |
| 6532 (800) | 11,385 (1600) | 17,638 (2400) | |||||
| VeRi-Wild | 224 × 224 | 176 | 416,314 (40,671) | 277,794 (30,671) | Test3000 | Test5000 | Test10000 |
| 41,816 (3000) | 69,389 (5000) | 138,517 (10,000) | |||||
| Different Modules | VeRi-776 | VERI-Wild | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R5 | mAP | Test3000 | Test5000 | Test10000 | |||||||
| R1 | R5 | mAP | R1 | R5 | mAP | R1 | R5 | mAP | ||||
| Direct Transfer | 65.40 | 73.50 | 25.50 | 50.97 | 70.57 | 20.74 | 29.34 | 49.72 | 12.06 | 27.46 | 46.25 | 9.36 |
| Ours w/o (O + A) | 77.80 | 84.90 | 34.10 | 52.10 | 74.80 | 27.00 | 45.10 | 68.20 | 23.10 | 35.30 | 58.30 | 18.10 |
| Ours w/o O | 78.10 | 85.60 | 34.20 | 53.60 | 75.50 | 27.50 | 46.80 | 69.80 | 23.90 | 35.50 | 58.00 | 17.60 |
| Ours w/o A | 80.80 | 87.10 | 36.80 | 55.80 | 77.50 | 28.70 | 48.70 | 71.10 | 24.90 | 39.90 | 62.90 | 20.90 |
| Ours | 83.10 | 89.00 | 37.80 | 59.90 | 80.70 | 31.40 | 51.90 | 74.90 | 27.30 | 41.80 | 65.80 | 21.70 |
| Different Pre-Training Models | VeRi-776 | VERI-Wild | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R5 | mAP | Test3000 | Test5000 | Test10000 | |||||||
| R1 | R5 | mAP | R1 | R5 | mAP | R1 | R5 | mAP | ||||
| ResNet-50 | 81.30 | 87.90 | 37.00 | 57.10 | 78.50 | 29.80 | 49.00 | 72.80 | 25.60 | 38.50 | 62.40 | 20.20 |
| PCB | 81.10 | 87.70 | 36.80 | 58.20 | 80.00 | 30.80 | 50.40 | 73.70 | 26.60 | 40.10 | 63.90 | 21.10 |
| DenseNet | 80.00 | 86.80 | 35.10 | 58.80 | 80.60 | 31.10 | 51.40 | 74.10 | 27.10 | 41.20 | 64.40 | 21.20 |
| PLPNet (Ours) | 83.10 | 89.00 | 37.80 | 59.90 | 80.70 | 31.40 | 51.90 | 74.90 | 27.30 | 41.80 | 65.80 | 21.70 |
| Orientation-Level View Partition N | VeRi-776 | VERI-Wild | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R5 | mAP | R1 | R5 | mAP | |
| 9 | 82.20 | 87.90 | 36.90 | 57.10 | 78.50 | 29.70 |
| 12 | 81.00 | 85.90 | 35.60 | 56.00 | 78.60 | 29.70 |
| 18 | 83.10 | 89.00 | 37.80 | 59.90 | 80.70 | 31.40 |
| 36 | 82.20 | 88.20 | 36.80 | 59.00 | 79.80 | 31.00 |
| Meta-Learning Split Ratio λ | VeRi-776 | VERI-Wild | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R5 | mAP | R1 | R5 | mAP | |
| 0.1 | 79.30 | 87.90 | 36.20 | 56.40 | 78.20 | 29.90 |
| 0.2 | 81.10 | 87.60 | 36.10 | 59.30 | 79.60 | 31.00 |
| 0.3 | 78.90 | 88.60 | 35.00 | 58.60 | 80.10 | 31.40 |
| 0.4 | 79.70 | 88.10 | 35.90 | 59.80 | 80.60 | 31.40 |
| 0.5 | 81.20 | 88.60 | 36.10 | 59.40 | 80.30 | 31.30 |
| 0.6 | 83.10 | 89.00 | 37.80 | 59.90 | 80.70 | 31.40 |
| 0.7 | 81.60 | 87.90 | 36.70 | 58.70 | 80.30 | 31.30 |
| 0.8 | 79.50 | 87.70 | 36.30 | 57.80 | 79.30 | 30.70 |
| 0.9 | 78.80 | 87.80 | 35.90 | 57.40 | 79.20 | 30.60 |
| Methods | VeRi-776 | VERI-Wild | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R5 | mAP | Test3000 | Test5000 | Test10000 | |||||||
| R1 | R5 | mAP | R1 | R5 | mAP | R1 | R5 | mAP | ||||
| Direct Transfer | 43.56 | 54.11 | 14.77 | 50.97 | 70.57 | 20.74 | 29.34 | 49.72 | 12.06 | 27.46 | 46.25 | 9.36 |
| SPGAN [42] | 50.72 | 62.63 | 15.83 | 28.77 | 48.27 | 10.63 | 24.60 | 42.96 | 8.97 | 23.40 | 40.78 | 7.13 |
| UDA_TP [43] | 51.85 | 64.54 | 18.12 | 46.30 | 59.20 | 12.30 | 16.20 | 29.00 | 5.21 | 17.65 | 29.99 | 4.53 |
| ECN [44] | 42.80 | 55.40 | 16.20 | 30.10 | 49.20 | 13.30 | 25.60 | 43.60 | 10.90 | 19.40 | 35.50 | 8.00 |
| DomainMix [45] | 53.30 | 64.60 | 15.40 | 33.20 | 53.80 | 14.10 | 28.40 | 48.10 | 12.20 | 21.10 | 38.90 | 9.00 |
| SpCL [46] | 58.90 | 68.00 | 24.40 | 48.80 | 72.80 | 25.10 | 42.00 | 66.10 | 21.50 | 32.70 | 55.70 | 16.60 |
| MMT [47] | 60.37 | 70.14 | 23.09 | 55.63 | 77.43 | 27.71 | 47.70 | 71.46 | 23.63 | 40.24 | 64.98 | 18.00 |
| AE [48] | 68.50 | 78.60 | 28.89 | 55.60 | 76.60 | 28.00 | 50.90 | 73.60 | 24.60 | 41.50 | 64.70 | 18.90 |
| Ours | 83.10 | 89.00 | 37.80 | 59.90 | 80.70 | 31.40 | 51.90 | 74.90 | 27.30 | 41.80 | 65.80 | 21.70 |
| Methods | VeRi-776 | |
|---|---|---|
| Time | Macro-F1 | |
| Direct Transfer | 5 h: 30 m: 03 s | 72.36 |
| SPGAN [42] | 7 h: 11 m: 22 s | 85.43 |
| UDA_TP [43] | 8 h: 22 m: 15 s | 81.71 |
| ECN [44] | 6 h: 47 m: 43 s | 78.16 |
| DomainMix [45] | 9 h: 28 m: 48 s | 85.22 |
| SpCL [46] | 14 h: 40 m: 39 s | 84.96 |
| MMT [47] | 12 h: 01 m: 30 s | 85.93 |
| AE [48] | 7 h: 33 m: 37 s | 74.98 |
| Ours | 10 h: 31 m: 00 s | 91.02 |
| Methods | VeRi-776 | VERI-Wild | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R5 | mAP | Test3000 | Test5000 | Test10000 | |||||||
| R1 | R5 | mAP | R1 | R5 | mAP | R1 | R5 | mAP | ||||
| MMT [47] | 25.40 | 61.70 | 71.60 | 23.30 | 46.70 | 70.90 | 19.80 | 39.70 | 64.20 | 15.10 | 30.10 | 53.20 |
| SPCL [46] | 25.80 | 65.60 | 74.30 | 27.80 | 52.60 | 76.50 | 23.60 | 45.30 | 69.70 | 18.20 | 34.70 | 59.30 |
| GSMLP-SMLC [49] | 13.30 | 44.30 | 51.60 | 15.80 | 37.60 | 54.10 | 13.60 | 32.60 | 49.90 | 10.30 | 25.40 | 41.90 |
| MetaCam [33] | 25.60 | 67.10 | 76.00 | 28.20 | 53.90 | 76.90 | 24.10 | 46.00 | 70.20 | 18.80 | 35.90 | 59.70 |
| SSML [28] | 20.20 | 60.90 | 69.80 | 13.90 | 35.80 | 57.20 | 11.70 | 30.70 | 50.10 | 8.70 | 23.20 | 41.10 |
| RLCC [50] | 25.60 | 64.00 | 73.30 | 28.20 | 53.80 | 78.10 | 24.00 | 45.60 | 71.60 | 18.70 | 35.50 | 60.50 |
| CACL [51] | 23.70 | 55.70 | 69.00 | 28.00 | 53.30 | 77.40 | 24.00 | 45.70 | 70.80 | 18.50 | 35.30 | 60.40 |
| Ours (Uns) | 28.80 | 72.20 | 79.10 | 30.60 | 56.30 | 79.00 | 25.30 | 47.80 | 72.10 | 19.80 | 37.20 | 61.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, R.; Wang, Q.; Cao, L.; Xu, J.; Zhu, X.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, Y. Dual-Level Viewpoint-Learning for Cross-Domain Vehicle Re-Identification. Electronics 2024, 13, 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13101823
Zhou R, Wang Q, Cao L, Xu J, Zhu X, Xiong X, Zhang H, Zhong Y. Dual-Level Viewpoint-Learning for Cross-Domain Vehicle Re-Identification. Electronics. 2024; 13(10):1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13101823
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Ruihua, Qi Wang, Lei Cao, Jianqiang Xu, Xiaogang Zhu, Xin Xiong, Huiqi Zhang, and Yuling Zhong. 2024. "Dual-Level Viewpoint-Learning for Cross-Domain Vehicle Re-Identification" Electronics 13, no. 10: 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13101823
APA StyleZhou, R., Wang, Q., Cao, L., Xu, J., Zhu, X., Xiong, X., Zhang, H., & Zhong, Y. (2024). Dual-Level Viewpoint-Learning for Cross-Domain Vehicle Re-Identification. Electronics, 13(10), 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13101823







