Multi-Frequency Spectral–Spatial Interactive Enhancement Fusion Network for Pan-Sharpening
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel multi-frequency spectrum–spatial interaction enhanced fusion network (MFSINet) is proposed, leveraging a multi-resolution analysis to integrate complementary features from both the spatial and frequency domains, thereby enhancing the quality of pan-sharpened fusion.
- A spectral–spatial interaction fusion block has been developed to construct multi-scale spatial and spectral interactions. This approach promotes the effective fusion and interaction of information across different scales at both the spectral and spatial levels.
- We propose a multi-frequency feature enhancement scheme that fully leverages the advantages of wavelet transform in multi-frequency analysis and edge-preserving fusion. This approach accurately represents image texture and structural information from both directional and spatial perspectives.
- Extensive experiments conducted on the IKONOS and WorldView-2 datasets demonstrate that our method is comparable to state-of-the-art algorithms in both qualitative and quantitative analyses.
2. Related Work
2.1. Spectral–Spatial Interactive Fusion
2.2. Multi-Frequency Feature Enhancement
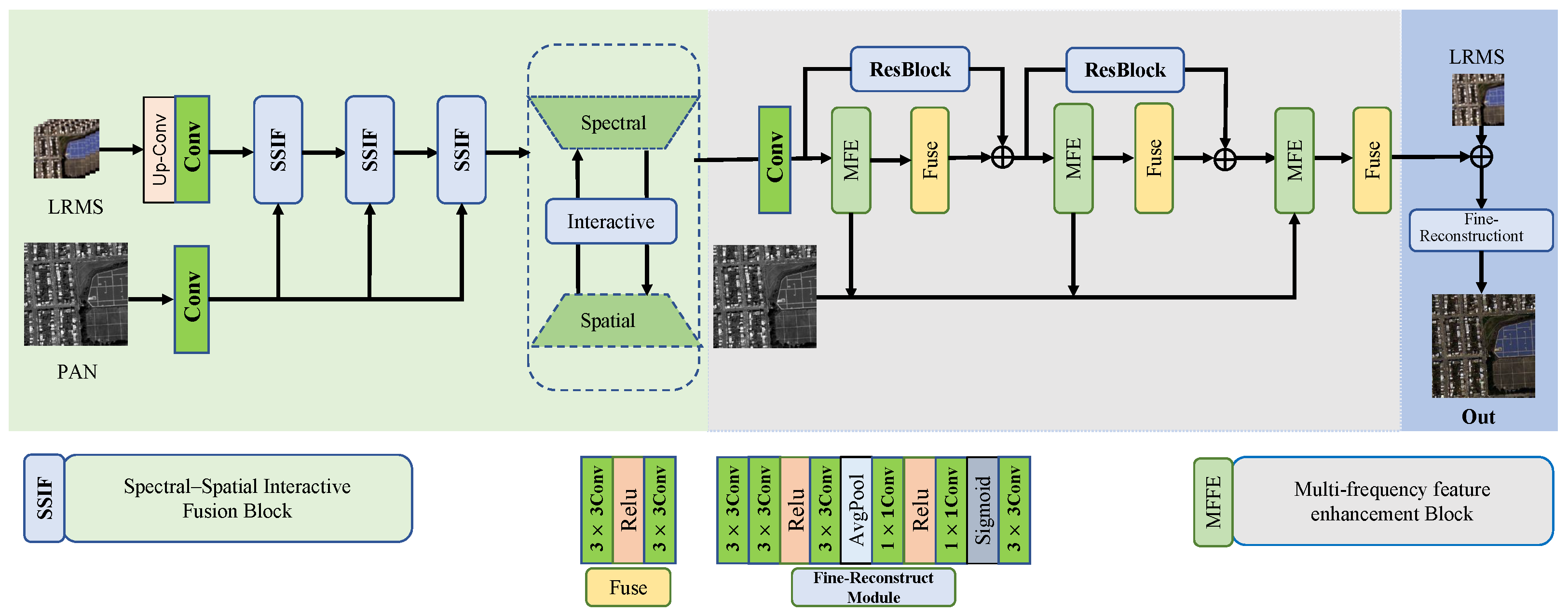
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Motivation
3.2. Network Framework
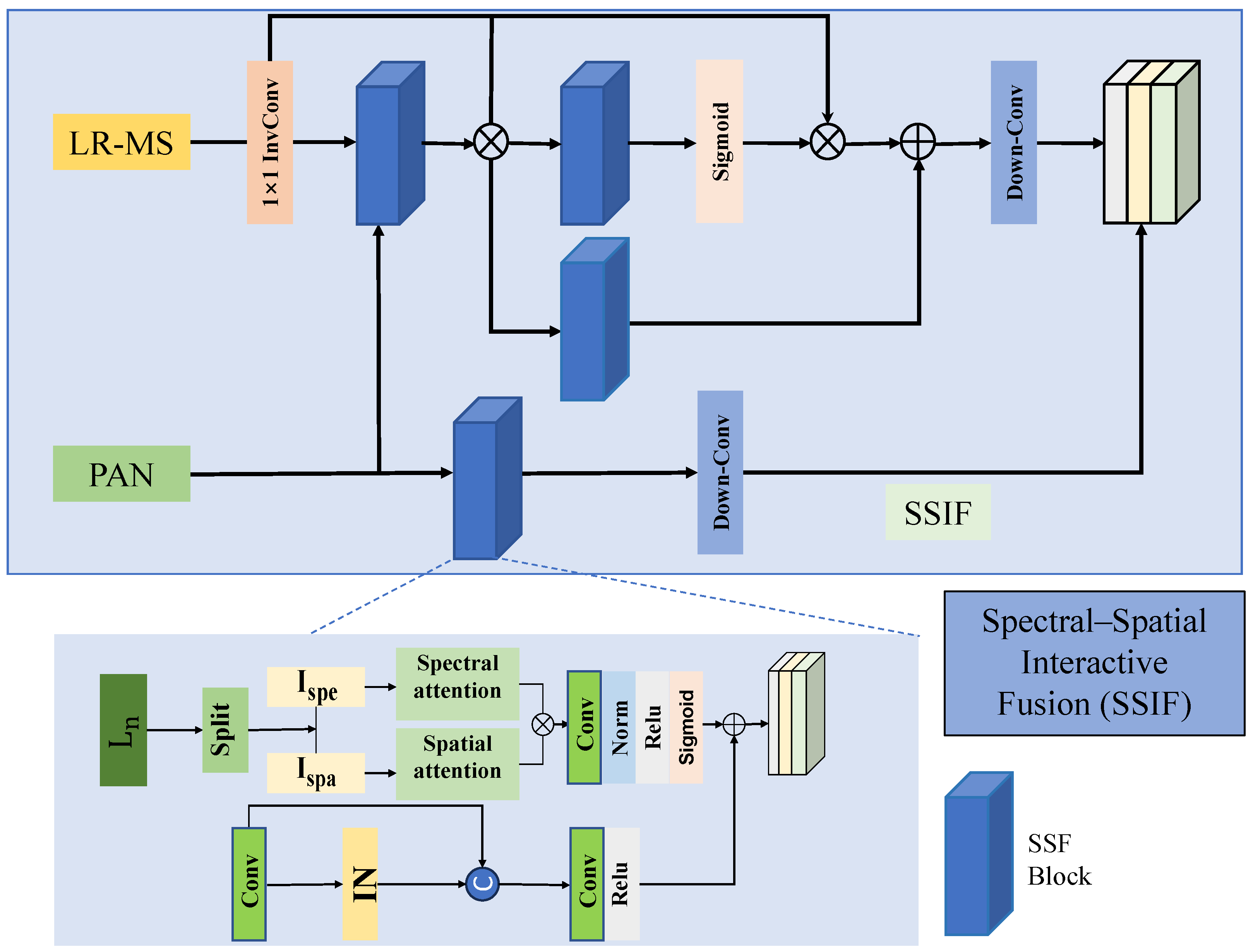
3.2.1. Spectral–Spatial Interactive Fusion Block (SSIF)
3.2.2. Multi-Frequency Feature Enhancement (MFFE)
3.2.3. Fine Reconstruction
3.3. Loss Function
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Details
4.1.1. Datasets
4.1.2. Implementation Details and Metrics
4.1.3. Compared Methods
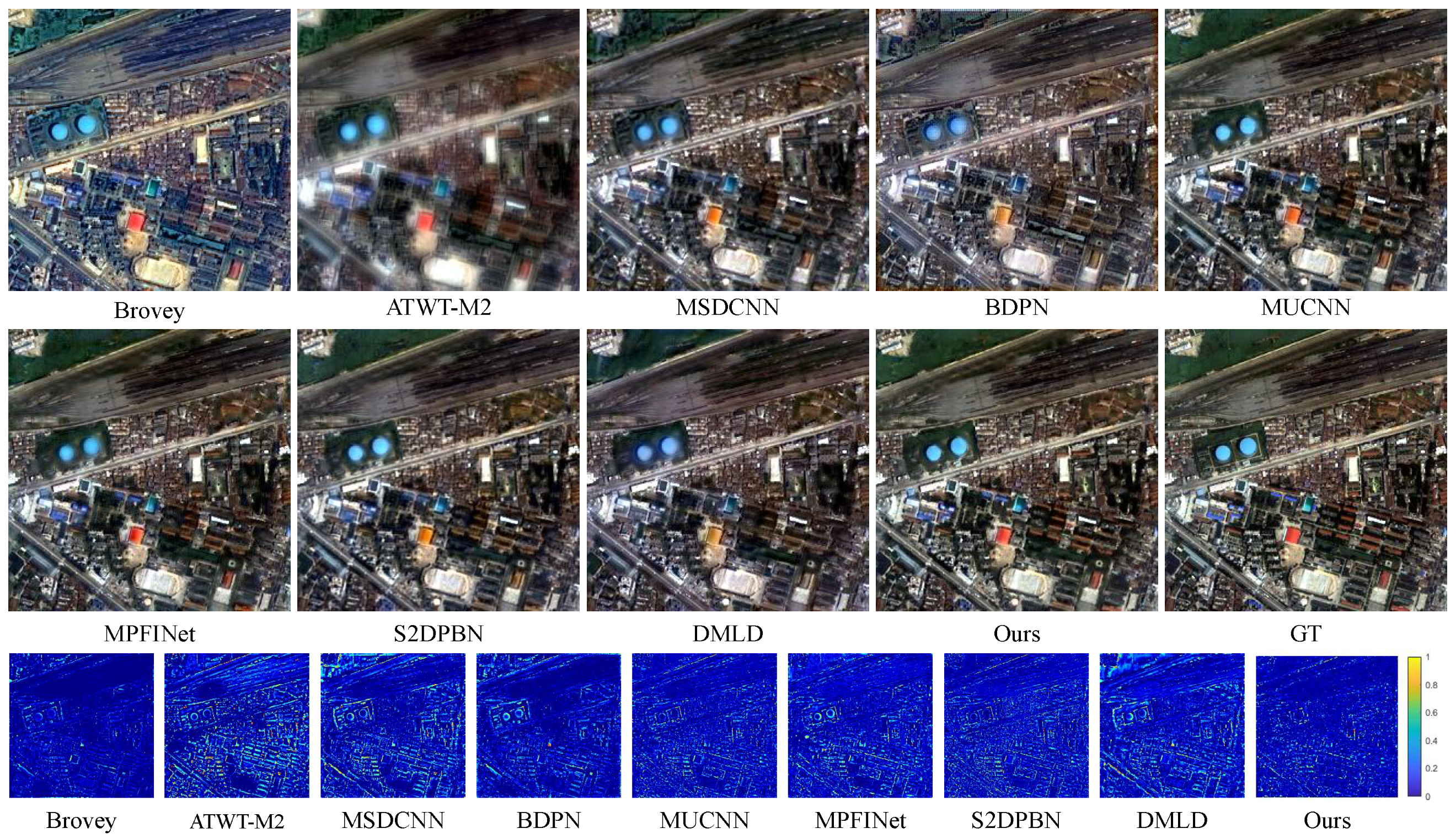
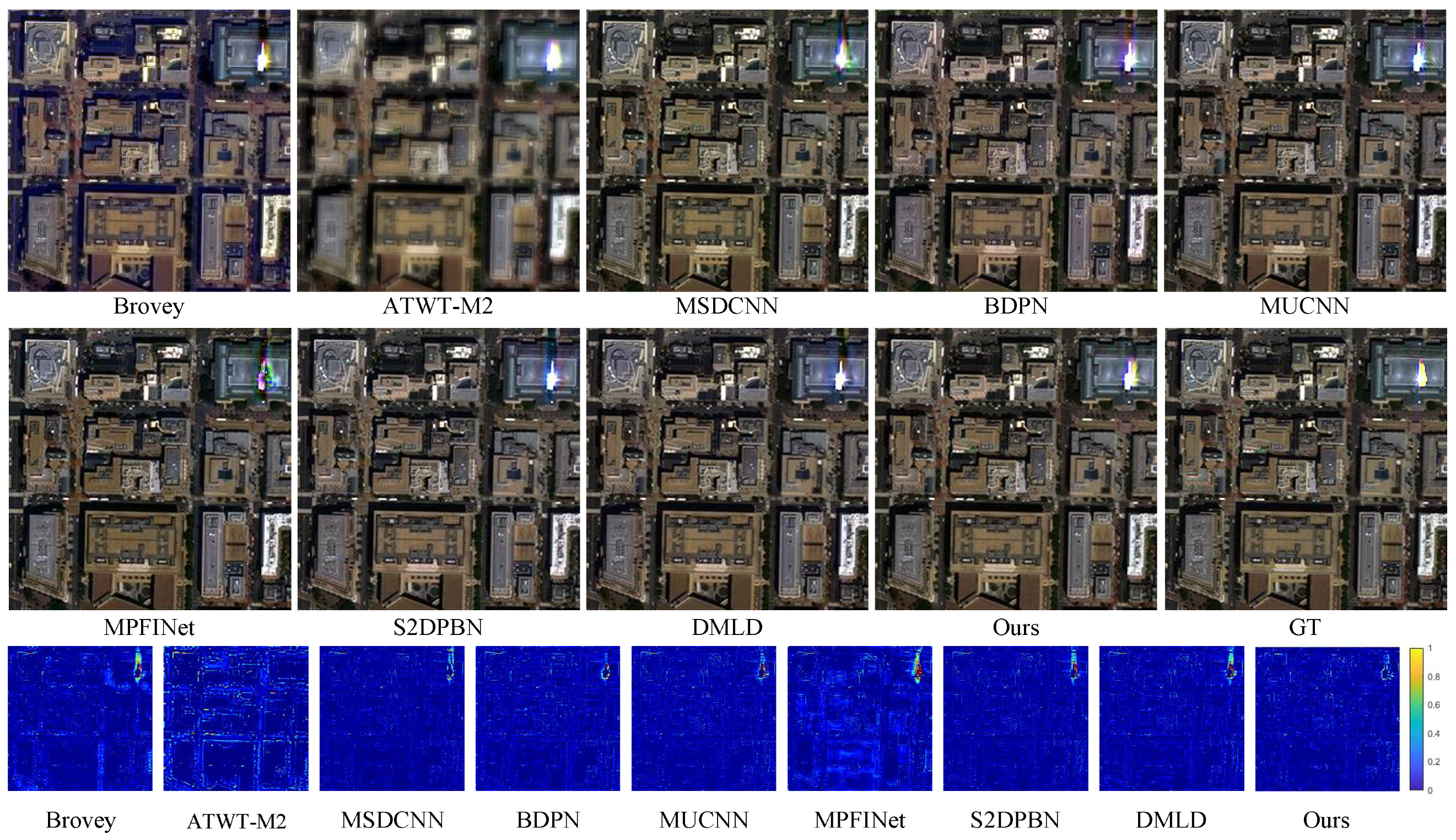
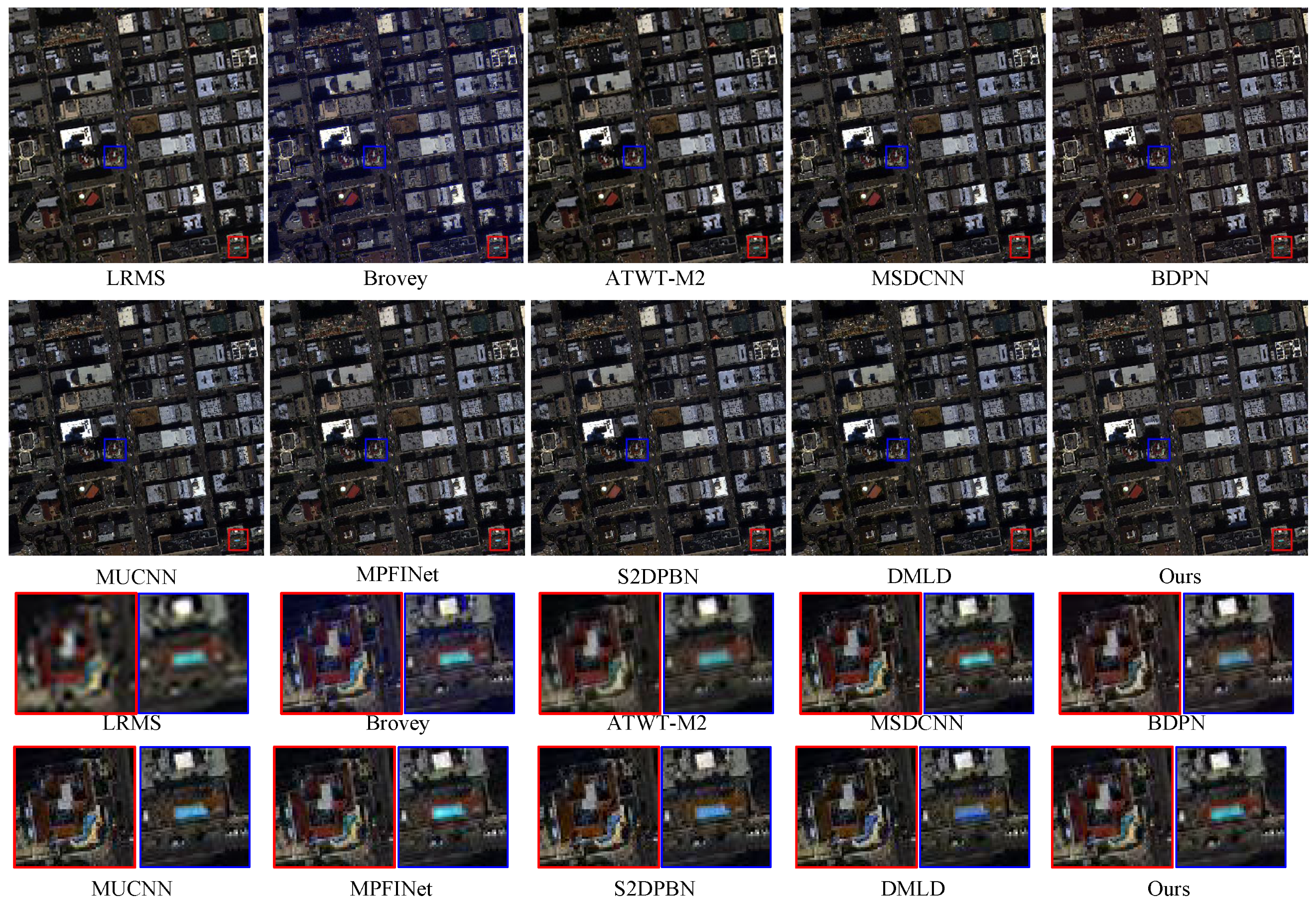
4.2. Comparative Analysis
4.2.1. Experiments on Reduced-Resolution Datasets
4.2.2. Experiments on Full-Resolution Datasets
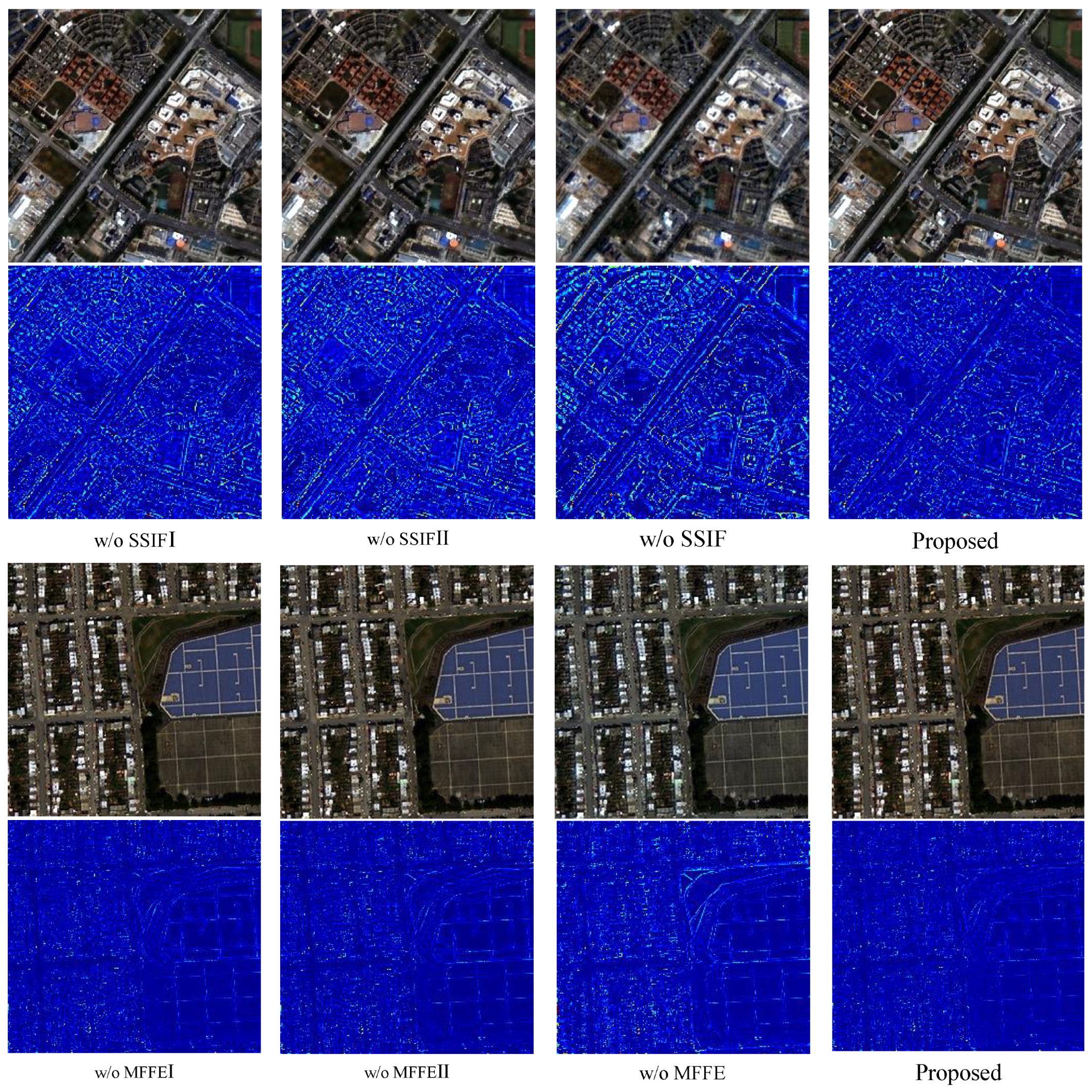
4.3. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, F.; Xu, C.; Hang, R.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Q. Mining joint intra-and inter-image context for remote sensing change detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4403712. [Google Scholar]
- Hang, R.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q.; Ghamisi, P.; Bhattacharyya, S.S. Hyperspectral Image Classification With Attention-Aided CNNs. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 2281–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Xie, H.; Weng, Q. Urban Land Cover Classification with Airborne Hyperspectral Data: What Features to Use? IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3998–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Q.; Hang, R. Tropical Cyclone Intensity Estimation Using Two-Branch Convolutional Neural Network From Infrared and Water Vapor Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yang, Y.; Huang, S.; Tu, W.; Wan, W. A Unified Pansharpening Model Based on Band-Adaptive Gradient and Detail Correction. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 918–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javan, F.D.; Samadzadegan, F.; Mehravar, S.; Toosi, A.; Khatami, R.; Stein, A. A review of image fusion techniques for pan-sharpening of high-resolution satellite imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 171, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Y.; Yin, G.; Johnson, B.A. Deep learning in remote sensing applications: A meta-analysis and review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 152, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carper, W.; Lillesand, T.; Kiefer, R. The use of intensity-hue-saturation transformations for merging SPOT panchromatic and multispectral image data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1990, 56, 459–467. [Google Scholar]
- Chavez, P.; Sides, S.C.; Anderson, J.A. Comparison of three different methods to merge multiresolution and multispectral data: Landsat TM and SPOT panchromatic. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1991, 57, 295–303. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, F.; Feng, Z.; Sun, J.; Wu, Q. Fusion of panchromatic and multispectral images using multiscale convolution sparse decomposition. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, A.R.; Kahle, A.B.; Walker, R.E. Color enhancement of highly correlated images. II. Channel ratio and “chromaticity” transformation techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 1987, 22, 343–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, J.; Otazu, X.; Fors, O.; Prades, A.; Pala, V.; Arbiol, R. Multiresolution-based image fusion with additive wavelet decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 1204–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DadrasJavan, F.; Samadzadegan, F.; Fathollahi, F. Spectral and spatial quality assessment of IHS and wavelet based pan-sharpening techniques for high resolution satellite imagery. Image Video Process. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Yu, K.; Kim, Y. A new adaptive component-substitution-based satellite image fusion by using partial replacement. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, F.; Yang, S.; Zhang, K.; Su, X.; Jiao, L. Refined pan-sharpening with NSCT and hierarchical sparse autoencoder. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 5715–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranchin, T.; Wald, L. Fusion of high spatial and spectral resolution images: The ARSIS concept and its implementation. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 49–61. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Q.; Wei, Y.; Meng, X.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. A multiscale and multidepth convolutional neural network for remote sensing imagery pan-sharpening. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Sun, M.; Ou, Y. Pan-sharpening using an efficient bidirectional pyramid network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5549–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, L.J.; Zhang, T.J.; Wu, X. SSconv: Explicit spectral-to-spatial convolution for pansharpening. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual Event, China, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 4472–4480. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Jin, X.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Liu, L.; Yao, S. MPFINet: A Multilevel Parallel Feature Injection Network for Panchromatic and Multispectral Image Fusion. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, A.; Zhang, F.; Wan, W.; Sun, J.; Bruzzone, L. Spatial-Spectral Dual Back-Projection Network for Pansharpening. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5406015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, G.; Zhang, F.; Wan, W.; Zhou, M.; Sun, J.; Zhang, H. Learning Deep Multiscale Local Dissimilarity Prior for Pansharpening. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.; Jiang, M.; Li, J.; Yuan, Q.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, L. Spatial–spectral fusion by combining deep learning and variational model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6169–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Pan, E.; Ma, Y.; Dai, X.; Huang, J.; Fan, F.; Du, Q.; Zheng, H.; Ma, J. Spectral-spatial attention networks for hyperspectral image classification. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Chen, L.; Jeon, S.; Yang, X. Spectral-Spatial Interaction Network for Multispectral Image and Panchromatic Image Fusion. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yan, K.; Zhang, J.; Li, R.; Xie, C.; Zhou, M.; Hong, D. Multi-scale dual-domain guidance network for pan-sharpening. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, K.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C. Deep gradient projection networks for pan-sharpening. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 1366–1375. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Wang, N.; Shao, F.; Li, S. Vision Transformer for Pansharpening. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. A new saliency-driven fusion method based on complex wavelet transform for remote sensing images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2433–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsson, F.; Sveinsson, J.R.; Ulfarsson, M.O.; Benediktsson, J.A. Model-based fusion of multi- and hyperspectral images using PCA and wavelets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2652–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, X.; Yan, K.; Cao, K.; Li, R.; Xie, C.; Zhou, M.; Hong, D. Pan-Sharpening With Wavelet-Enhanced High-Frequency Information. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5402914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S.G. A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: The wavelet representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1989, 11, 674–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Z.; Lei, M. A new wavelet transform convolution algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Communication Software and Networks, Xi’an, China, 27–29 May 2011; pp. 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Seyed Mousavi, H.; Huu Vu, T.; Monga, V. Deep wavelet prediction for image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 104–113. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, H.; Lian, W.; Zuo, W. Multi-level wavelet convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 74973–74985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Grohnfeldt, C.; Bamler, R. Exploiting Joint Sparsity for Pansharpening: The J-SparseFI Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2664–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Leng, W.; Xu, Q.; Li, W.; Tao, R.; Sun, W. A Joint Optimization Based Pansharpening via Subpixel-Shift Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, M.; Liu, S.; Sheng, H.; Zheng, H. Spatial-spectral Attention Bilateral Network for Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 5507505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Luo, F. Spatial-Spectral Attention Graph U-Nets for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5528317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Huang, J.; Yan, K.; Yang, G.; Liu, A.; Li, C.; Zhao, F. Normalization-based feature selection and restitution for pan-sharpening. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 3365–3374. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Huang, J.; Fang, Y.; Fu, X.; Liu, A. Pan-sharpening with customized transformer and invertible neural network. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, Canada, 20–27 February 2022; Volume 36, pp. 3553–3561. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Dhariwal, P. Glow: Generative flow with invertible 1x1 convolutions. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.03039. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Nie, R.; Cao, J.; Li, H.; Li, J. A Deep Multi-Resolution Representation Framework for Pansharpening. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5517216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparone, L.; Wald, L.; Chanussot, J.; Thomas, C.; Gamba, P.; Bruce, L.M. Comparison of pansharpening algorithms: Outcome of the 2006 GRS-S data-fusion contest. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushparaj, J.; Hegde, A.V. Evaluation of pan-sharpening methods for spatial and spectral quality. Appl. Geomat. 2017, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuhas, R.H.; Goetz, A.F.; Boardman, J.W. Discrimination among semi-arid landscape endmembers using the spectral angle mapper (SAM) algorithm. In Proceedings of the JPL, Summaries of the Third Annual JPL Airborne Geoscience Workshop, Volume 1: AVIRIS Workshop, Pasadena, CA, USA, 1–5 June 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C. A universal image quality index. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2002, 9, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzelli, A.; Nencini, F. Hypercomplex quality assessment of multi/hyperspectral images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparone, L.; Aiazzi, B.; Baronti, S.; Garzelli, A.; Nencini, F.; Selva, M. Multispectral and panchromatic data fusion assessment without reference. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2008, 74, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Nie, R.; Cao, J.; Jin, B.; Han, Y. MPEFNet: Multi-level Progressive Enhancement Fusion Network for Pansharpening. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 9358–9368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, H.; Xie, M.; Yu, Z. DCPNet: A Dual-Task Collaborative Promotion Network for Pansharpening. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5404016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivone, G.; Alparone, L.; Chanussot, J.; Dalla Mura, M.; Garzelli, A.; Licciardi, G.A.; Restaino, R.; Wald, L. A critical comparison among pansharpening algorithms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 2565–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Methods | Reduced Resolution | Full Resolution | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q4↑ | ERGAS↓ | SAM↓ | SCC↑ | QNR↑ | ↓ | ↓ | |
| Brovey | 0.7347 | 2.5267 | 3.4047 | 0.8880 | 0.7084 | 0.2143 | 0.1097 |
| ATWT-M2 | 0.6919 | 2.8690 | 3.4583 | 0.8323 | 0.7605 | 0.1559 | 0.1089 |
| MSDCNN | 0.8766 | 1.6187 | 2.3738 | 0.9474 | 0.8563 | 0.1071 | 0.0468 |
| BDPN | 0.8434 | 1.9006 | 3.0374 | 0.9277 | 0.7802 | 0.1545 | 0.0802 |
| MUCNN | 0.8822 | 1.5532 | 2.2227 | 0.9476 | 0.8333 | 0.1026 | 0.0812 |
| MPFINet | 0.8754 | 1.6211 | 2.1946 | 0.9491 | 0.8405 | 0.1123 | 0.0624 |
| S2DPBN | 0.8655 | 1.6726 | 2.4063 | 0.9469 | 0.8409 | 0.0924 | 0.0788 |
| DMLD | 0.8560 | 1.8216 | 2.6823 | 0.9397 | 0.8387 | 0.1081 | 0.0694 |
| OURS | 0.8905 | 1.5405 | 2.1238 | 0.9493 | 0.8840 | 0.0713 | 0.0504 |
| Methods | Reduced Resolution | Full Resolution | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q8↑ | ERGAS↓ | SAM↓ | SCC↑ | QNR↑ | ↓ | ↓ | |
| Brovey | 0.8212 | 6.3161 | 7.9286 | 0.9007 | 0.8688 | 0.1088 | 0.0251 |
| ATWT-M2 | 0.7234 | 7.3883 | 7.9224 | 0.8382 | 0.8389 | 0.1088 | 0.0587 |
| MSDCNN | 0.9605 | 3.2738 | 5.1168 | 0.9632 | 0.8731 | 0.0940 | 0.0363 |
| BDPN | 0.9483 | 3.7056 | 5.8499 | 0.9470 | 0.8732 | 0.1005 | 0.0293 |
| MUCNN | 0.9543 | 3.4941 | 5.3528 | 0.9558 | 0.8709 | 0.0966 | 0.0360 |
| MPFINet | 0.9601 | 3.3807 | 5.0055 | 0.9601 | 0.8886 | 0.0740 | 0.0403 |
| S2DPBN | 0.9587 | 3.3087 | 5.1763 | 0.9619 | 0.8614 | 0.0885 | 0.0550 |
| DMLD | 0.9552 | 3.4982 | 5.3348 | 0.9581 | 0.8660 | 0.1076 | 0.0296 |
| OURS | 0.9623 | 3.2097 | 4.9357 | 0.9643 | 0.8948 | 0.0796 | 0.0278 |
| Dataset | Versions | SSIF I | SSIF II | SSIF III | Q4↑ | ERGAS↓ | SAM↓ | SCC↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IKONOS | I | ✓ | × | × | 0.8820 | 1.5890 | 2.1990 | 0.9467 |
| II | ✓ | × | × | 0.8815 | 1.5948 | 2.2166 | 0.9461 | |
| III | × | ✓ | × | 0.7960 | 2.2295 | 3.0067 | 0.8942 | |
| Ours | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.8905 | 1.5405 | 2.1238 | 0.9493 | |
| Dataset | Versions | MFFEI | MFFEII | MFFE | Q8↑ | ERGAS↓ | SAM↓ | SCC↑ |
| WV-2 | I | ✓ | × | × | 0.9607 | 3.2439 | 4.9906 | 0.9623 |
| II | ✓ | × | × | 0.9603 | 3.2551 | 5.0307 | 0.9625 | |
| III | × | ✓ | × | 0.9398 | 4.0128 | 6.0383 | 0.9397 | |
| Ours | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.9623 | 3.2097 | 4.9357 | 0.9643 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, Y.; Li, H.; Xie, G.; Liu, P.; Li, T. Multi-Frequency Spectral–Spatial Interactive Enhancement Fusion Network for Pan-Sharpening. Electronics 2024, 13, 2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13142802
Tang Y, Li H, Xie G, Liu P, Li T. Multi-Frequency Spectral–Spatial Interactive Enhancement Fusion Network for Pan-Sharpening. Electronics. 2024; 13(14):2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13142802
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Yunxuan, Huaguang Li, Guangxu Xie, Peng Liu, and Tong Li. 2024. "Multi-Frequency Spectral–Spatial Interactive Enhancement Fusion Network for Pan-Sharpening" Electronics 13, no. 14: 2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13142802
APA StyleTang, Y., Li, H., Xie, G., Liu, P., & Li, T. (2024). Multi-Frequency Spectral–Spatial Interactive Enhancement Fusion Network for Pan-Sharpening. Electronics, 13(14), 2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13142802






