The Use of TheraBracelet Upper Extremity Vibrotactile Stimulation in a Child with Cerebral Palsy—A Case Report
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participant
- ◦
- Manual Ability Classification System [56]: Level 3, he was able to handle objects with difficulty and needed help to prepare and/or modify activities. The child did not take any medications for spasticity, and he did not have a history of any movement disorders outside of hemiplegia.
- ◦
- Gross Motor Function Classification System [56]: Level 1, he was able to ambulate without limitations, not requiring the use of a mobility device.
- ◦
- Eating and Drinking Ability Classification Scale [57]: Level 1, he was able to eat and drink safely and efficiently.
- ◦
- Communication Function Classification System [56]: Level 1, he was an effective sender and receiver with unfamiliar and familiar partners.
- ◦
- Visual Function Classification System [58]: Level 1, he used visual functions easily without compensatory strategies.
2.2. Procedure
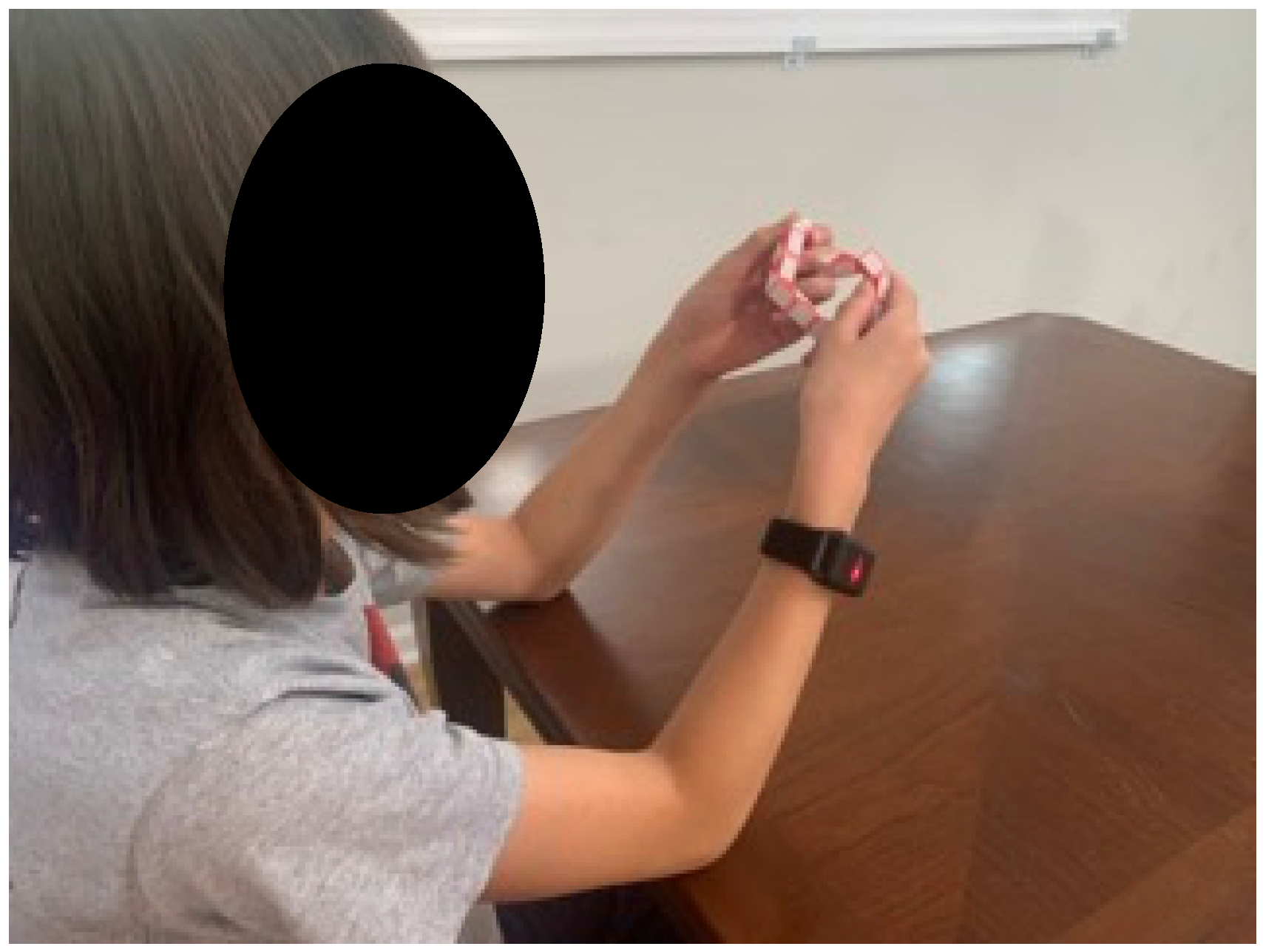
2.2.1. TheraBracelet Wearable and Smartphone App
2.2.2. Intervention
2.2.3. Assessments
- ◦
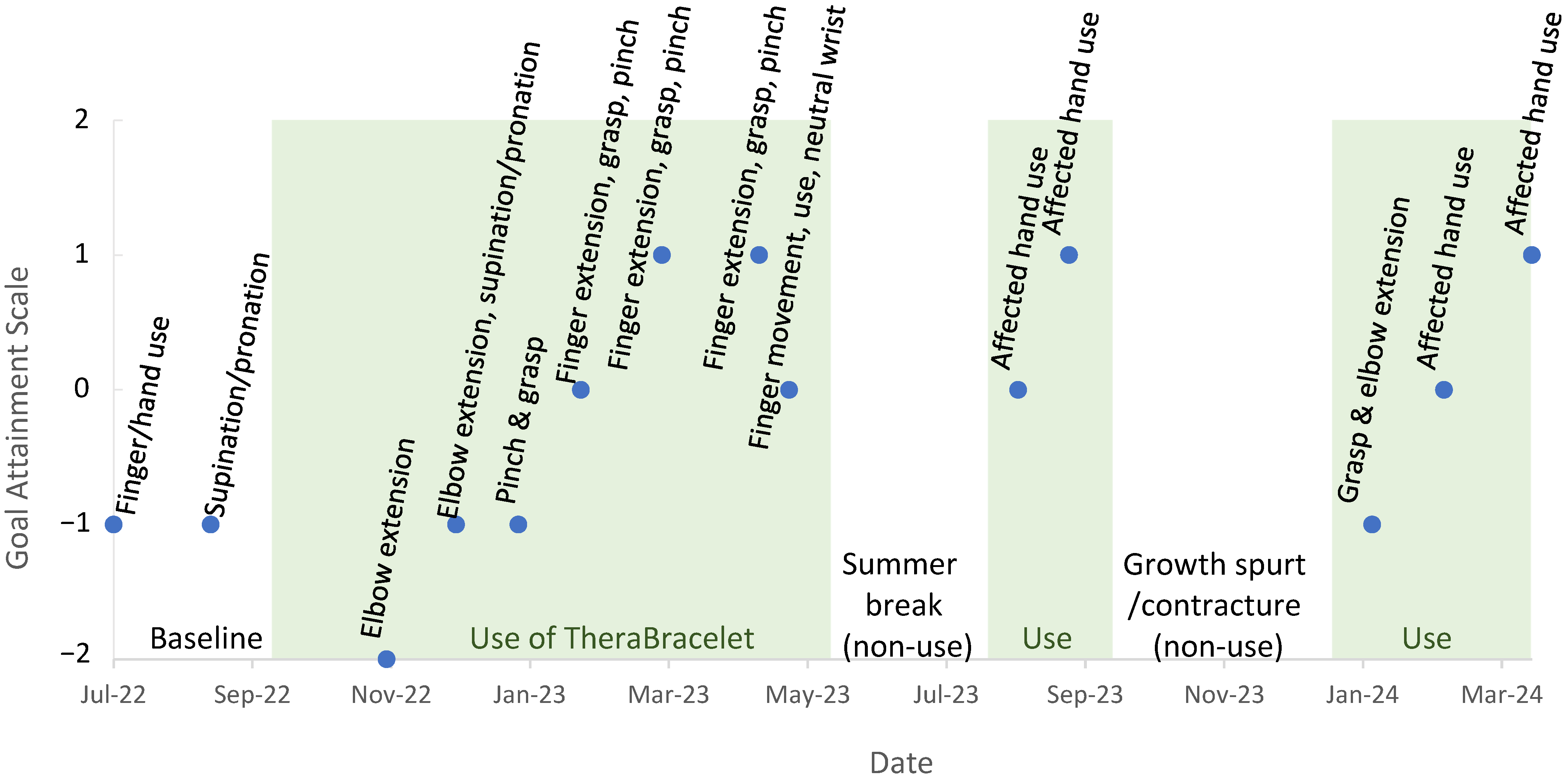
- GAS uses a 5-level incremental scale from −2 to +2 (−2, −1, 0, +1, +2) for each goal at each time point. The child’s baseline ability is the base score of –2. The child’s “expected progress” is a score of 0. A score < 0 indicates that “less than the expected goal” was achieved. A score of > 0 indicates that “more than the expected goal” was achieved. Individual goal scores can be averaged to produce a cumulative score indicating overall intervention effectiveness [70].
- ◦
- The ABILHAND-Kids assesses the parent’s perception of the level of difficulty that a child experiences when performing activities of daily living either bimanually or unimanually [71].
- ◦
- ◦
3. Results
3.1. Feasibility and Usability
3.2. Safety
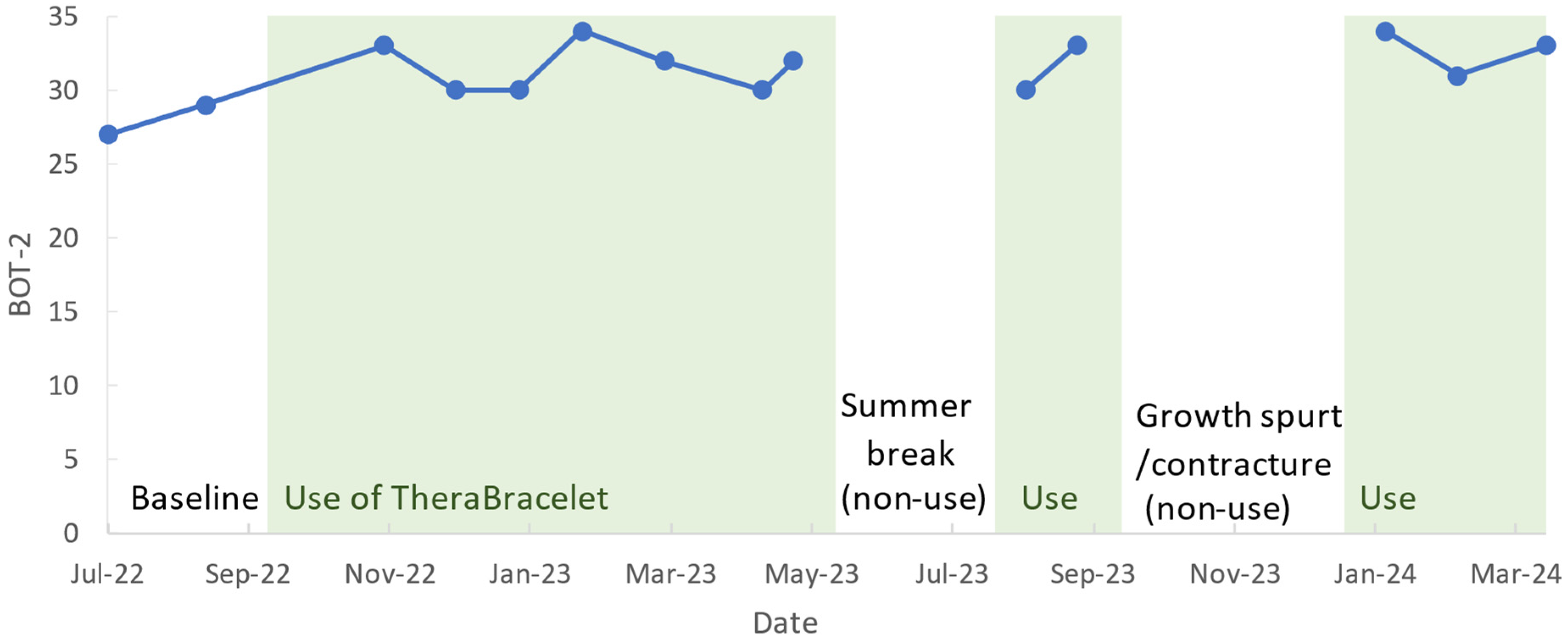
3.3. Upper Limb Motor Function Monitoring
4. Discussion
4.1. Feasibility, Usability, and Safety
4.2. Upper Limb Motor Function
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Durkin, M.S.; Benedict, R.E.; Christensen, D.; Dubois, L.A.; Fitzgerald, R.T.; Kirby, R.S.; Maenner, M.J.; Van Naarden Braun, K.; Wingate, M.S.; Yeargin-Allsopp, M. Prevalence of Cerebral Palsy among 8-Year-Old Children in 2010 and Preliminary Evidence of Trends in Its Relationship to Low Birthweight. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2016, 30, 496–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felling, R.J.; Sun, L.R.; Maxwell, E.C.; Goldenberg, N.; Bernard, T. Pediatric arterial ischemic stroke: Epidemiology, risk factors, and management. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2017, 67, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makki, D.; Duodu, J.; Nixon, M. Prevalence and pattern of upper limb involvement in cerebral palsy. J. Child. Orthop. 2014, 8, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbaum, P.L.; Livingston, M.H.; Palisano, R.J.; Galuppi, B.E.; Russell, D.J. Quality of life and health-related quality of life of adolescents with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 49, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.; Sarmiento, C.; Sanders, J.; Wang, L.; Fetsko, L.; Akamagwun, U. Navigating the complex care landscape: Addressing challenges and advancing adult care frameworks for individuals with cerebral palsy. Health Care Transit. 2024, 2, 100051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kancherla, V.; Amendah, D.D.; Grosse, S.D.; Yeargin-Allsopp, M.; Van Naarden Braun, K. Medical expenditures attributable to cerebral palsy and intellectual disability among Medicaid-enrolled children. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2012, 33, 832–840. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhusaini, A.A.; Fallatah, S.; Melam, G.R.; Buragadda, S. Efficacy of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation combined with therapeutic exercise on hand function in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy. Somat. Mot. Res. 2019, 36, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, T.; Caria, M.A.; Asanuma, H. Information processing within the motor cortex. II. Intracortical connections between neurons receiving somatosensory cortical input and motor output neurons of the cortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 1994, 345, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, T.; Caria, M.A.; Asanuma, H. Information processing within the motor cortex. I. Responses of morphologically identified motor cortical cells to stimulation of the somatosensory cortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 1994, 345, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyas, F.; Sreenivasan, V.; Marbach, F.; Wacongne, C.; Barsy, B.; Mateo, C.; Aronoff, R.; Petersen, C.C. Motor control by sensory cortex. Science 2010, 330, 1240–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemon, R.N. Functional properties of monkey motor cortex neurones receiving afferent input from the hand and fingers. J. Physiol. 1981, 311, 497–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenner, J.R.; Stephens, J.A. Cutaneous reflex responses and their central nervous pathways studied in man. J. Physiol. 1982, 333, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Ashby, P. Reflex responses in upper limb muscles to cutaneous stimuli. Le J. Can. Des Sci. Neurol. 1993, 20, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkranz, K.; Rothwell, J.C. Differential effect of muscle vibration on intracortical inhibitory circuits in humans. J. Physiol. 2003, 551 Pt 2, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkranz, K.; Pesenti, A.; Paulus, W.; Tergau, F. Focal reduction of intracortical inhibition in the motor cortex by selective proprioceptive stimulation. Exp. Brain Res. 2003, 149, 9–16. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaelin-Lang, A.; Luft, A.R.; Sawaki, L.; Burstein, A.H.; Sohn, Y.H.; Cohen, L.G. Modulation of human corticomotor excitability by somatosensory input. J. Physiol. 2002, 540 Pt 2, 623–633. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meesen, R.L.; Cuypers, K.; Rothwell, J.C.; Swinnen, S.P.; Levin, O. The effect of long-term TENS on persistent neuroplastic changes in the human cerebral cortex. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2011, 32, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golaszewski, S.M.; Siedentopf, C.M.; Koppelstaetter, F.; Rhomberg, P.; Guendisch, G.M.; Schlager, A.; Gallasch, E.; Eisner, W.; Felber, S.R.; Mottaghy, F.M. Modulatory effects on human sensorimotor cortex by whole-hand afferent electrical stimulation. Neurology 2004, 62, 2262–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schranz, C.; Vatinno, A.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Seo, N.J. Neuroplasticity after upper-extremity rehabilitation therapy with sensory stimulation in chronic stroke survivors. Brain Commun. 2022, 4, fcac191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, N.J.; Lakshminarayanan, K.; Lauer, A.W.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Schmit, B.D.; Hanlon, C.A.; George, M.S.; Bonilha, L.; Downey, R.J.; DeVries, W.; et al. Use of imperceptible wrist vibration to modulate sensorimotor cortical activity. Exp. Brain Res. 2019, 237, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos Conforto, A.; Nocelo Ferreiro, K.; Tomasi, C.; dos Santos, R.L.; Loureiro Moreira, V.; Nagahashi Marie, S.K.; Baltieri, S.C.; Scaff, M.; Cohen, L.G. Effects of somatosensory stimulation on motor function after subacute stroke. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2010, 24, 263–272. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celnik, P.; Hummel, F.; Harris-Love, M.; Wolk, R.; Cohen, L.G. Somatosensory stimulation enhances the effects of training functional hand tasks in patients with chronic stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 88, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marconi, B.; Filippi, G.M.; Koch, G.; Giacobbe, V.; Pecchioli, C.; Versace, V.; Camerota, F.; Saraceni, V.M.; Caltagirone, C. Long-term effects on cortical excitability and motor recovery induced by repeated muscle vibration in chronic stroke patients. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2011, 25, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conforto, A.B.; Cohen, L.G.; Santos, R.L.D.; Scaff, M.; Marie, S.K. Effects of somatosensory stimulation on motor function in chronic cortico-subcortical strokes. J. Neurol. 2007, 254, 333–339. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonde, L.; Gip, C.; Fernaeus, S.E.; Nilsson, C.G.; Viitanen, M. Stimulation with low frequency (1.7 Hz) transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation (low-tens) increases motor function of the post-stroke paretic arm. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 1998, 30, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yozbatiran, N.; Donmez, B.; Kayak, N.; Bozan, O. Electrical stimulation of wrist and fingers for sensory and functional recovery in acute hemiplegia. Clin. Rehabil. 2006, 20, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrico, C.; Chelette, K.C., II; Westgate, P.M.; Salmon-Powell, E.; Nichols, L.; Sawaki, L. Randomized Trial of Peripheral Nerve Stimulation to Enhance Modified Constraint-Induced Therapy After Stroke. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 95, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrico, C.; Chelette, K.C.; Westgate, P.M.; Powell, E.; Nichols, L.; Fleischer, A.; Sawaki, L. Nerve Stimulation Enhances Task-Oriented Training in Chronic, Severe Motor Deficit After Stroke: A Randomized Trial. Stroke 2016, 47, 1879–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peurala, S.H.; Pitkanen, K.; Sivenius, J.; Tarkka, I.M. Cutaneous electrical stimulation may enhance sensorimotor recovery in chronic stroke. Clin. Rehabil. 2002, 16, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordo, P.; Wolf, S.; Lou, J.S.; Bogey, R.; Stevenson, M.; Hayes, J.; Roth, E. Treatment of severe hand impairment following stroke by combining assisted movement, muscle vibration, and biofeedback. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2013, 37, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordo, P.; Lutsep, H.; Cordo, L.; Wright, W.G.; Cacciatore, T.; Skoss, R. Assisted movement with enhanced sensation (AMES): Coupling motor and sensory to remediate motor deficits in chronic stroke patients. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2009, 23, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes-Osman, J.; Field-Fote, E.C. Cortical vs. afferent stimulation as an adjunct to functional task practice training: A randomized, comparative pilot study in people with cervical spinal cord injury. Clin. Rehabil. 2015, 29, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, L.; Field-Fote, E. Effects of practice combined with somatosensory or motor stimulation on hand function in persons with spinal cord injury. Top. Spinal Cord Inj. Rehabil. 2013, 19, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conforto, A.B.; Dos Anjos, S.M.; Bernardo, W.M.; Silva, A.A.D.; Conti, J.; Machado, A.G.; Cohen, L.G. Repetitive Peripheral Sensory Stimulation and Upper Limb Performance in Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2018, 32, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kattenstroth, J.C.; Kalisch, T.; Sczesny-Kaiser, M.; Greulich, W.; Tegenthoff, M.; Dinse, H.R. Daily repetitive sensory stimulation of the paretic hand for the treatment of sensorimotor deficits in patients with subacute stroke: RESET, a randomized, sham-controlled trial. BMC Neurol. 2018, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, N.J.; Woodbury, M.L.; Bonilha, L.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Kautz, S.A.; Downey, R.J.; Dellenbach, B.H.; Lauer, A.W.; Roark, C.M.; Landers, L.E. TheraBracelet Stimulation During Task-Practice Therapy to Improve Upper Extremity Function After Stroke: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Study. Phys. Ther. 2019, 99, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scronce, G.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Vatinno, A.A.; Seo, N.J. Effect of Self-Directed Home Therapy Adherence Combined with TheraBracelet on Poststroke Hand Recovery: A Pilot Study. Stroke Res. Treat. 2023, 2023, 3682898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatinno, A.A.; Hall, L.; Cox, H.; Fluharty, A.; Taylor, C.; Wease, A.; Davis, A.; Cain, S.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Woodbury, M.; et al. Using Subthreshold Vibratory Stimulation During Poststroke Rehabilitation Therapy: A Case Series. OTJR 2022, 42, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.; Yick, K.L.; Ng, S.P.; Yip, J. Case study on the effects of fit and material of sports gloves on hand performance. Appl. Ergon. 2019, 75, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, H. Effect of gloves on prehensile forces during lifting and holding tasks. Ergonomics 1999, 42, 1372–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Sklar, G.E.; Oh, V.M.S.; Li, S.C. Factors affecting therapeutic compliance: A review from the patient’s perspective. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, N.J.; Enders, L.R.; Fortune, A.; Cain, S.; Vatinno, A.A.; Schuster, E.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Feng, W. Phase I Safety Trial: Extended Daily Peripheral Sensory Stimulation Using a Wrist-Worn Vibrator in Stroke Survivors. Transl. Stroke Res. 2020, 11, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enders, L.R.; Hur, P.; Johnson, M.J.; Seo, N.J. Remote vibrotactile noise improves light touch sensation in stroke survivors’ fingertips via stochastic resonance. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2013, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, F.; Ward, L.M.; Sannita, W.G. Stochastic resonance and sensory information processing: A tutorial and review of application. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 267–281. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, L.M. Physics of neural synchronisation mediated by stochastic resonance. Contemp. Phys. 2009, 50, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, N.J.; Lakshminarayanan, K.; Bonilha, L.; Lauer, A.W.; Schmit, B.D. Effect of imperceptible vibratory noise applied to wrist skin on fingertip touch evoked potentials—An EEG study. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3, e12624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, L.M.; MacLean, S.E.; Kirschner, A. Stochastic resonance modulates neural synchronization within and between cortical sources. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallbo, A.B.; Johansson, R.S. Properties of cutaneous mechanoreceptors in the human hand related to touch sensation. Hum. Neurobiol. 1984, 3, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vallbo, A.B. Microneurography: How it started and how it works. J. Neurophysiol. 2018, 120, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, P.; Motawar, B.; Seo, N.J. Muscular responses to handle perturbation with different glove condition. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2014, 24, 159–164. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayanan, K.; Lauer, A.W.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Webster, J.G.; Seo, N.J. Application of vibration to wrist and hand skin affects fingertip tactile sensation. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3, e12465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Lakshminarayanan, K.; Slota, G.P.; Seo, N.J.; Webster, J.G. An MRI-compatible hand sensory vibrotactile system. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, N15–N21. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, N.J.; Kosmopoulos, M.L.; Enders, L.R.; Hur, P. Effect of remote sensory noise on hand function post stroke. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 934. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, N.J.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Woodbury, M.L.; Bonilha, L.; Harvey, J.B.; Finetto, C.; Schranz, C.; Scronce, G.; Coupland, K.; Blaschke, J.; et al. Concomitant sensory stimulation during therapy to enhance hand functional recovery post stroke. Trials 2022, 23, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennington, A.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Scronce, G.; Coupland, K.; Vatinno, A.; Seo, N.J. Effect of using TheraBracelet on grasping vs. reaching in post-stroke rehabilitation. Occup. Ther. J. Res. 2023, 43, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscitelli, D.; Ferrarello, F.; Ugolini, A.; Verola, S.; Pellicciari, L. Measurement properties of the Gross Motor Function Classification System, Gross Motor Function Classification System-Expanded & Revised, Manual Ability Classification System, and Communication Function Classification System in cerebral palsy: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2021, 63, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, S.E.; Yi, Y.G.; Shin, H.-I. Reliability and Validity of the Eating and Drinking Ability Classification System in Adults with Cerebral Palsy. Dysphagia 2021, 36, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranello, G.; Signorini, S.; Tinelli, F.; Guzzetta, A.; Pagliano, E.; Rossi, A.; Foscan, M.; Tramacere, I.; Romeo, D.M.; Ricci, D.; et al. Visual Function Classification System for children with cerebral palsy: Development and validation. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2020, 62, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.J.; Imhoff, T.T.; Grigg, P. Noise-enhanced tactile sensation. Nature 1996, 383, 770. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, M.D.; Ward, L.M. The benefits of noise in neural systems: Bridging theory and experiment. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.J.; Imhoff, T.T.; Grigg, P. Noise-mediated enhancements and decrements in human tactile sensation. Phys. Rev. E 1997, 56, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, C.; Ward, L.M.; Chua, R.; Inglis, J.T. Touch noise increases vibrotactile sensitivity in old and young. Psychol. Sci. 2005, 16, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurita, Y.; Shinohara, M.; Ueda, J. Wearable Sensorimotor Enhancer for Fingertip Based on Stochastic Resonance Effect. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2013, 43, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lipsitz, L.A.; Montero-Odasso, M.; Bean, J.; Kerrigan, D.C.; Collins, J.J. Noise-enhanced vibrotactile sensitivity in older adults, patients with stroke, and patients with diabetic neuropathy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, J.J.; Priplata, A.A.; Gravelle, D.C.; Niemi, J.; Harry, J.; Lipsitz, L.A. Noise-enhanced human sensorimotor function. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2003, 22, 76–83. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.A.; Field-Fote, E.C.; Floeter, M.K. Patterned sensory stimulation induces plasticity in reciprocal ia inhibition in humans. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 2014–2018. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragert, P.; Kalisch, T.; Bliem, B.; Franzkowiak, S.; Dinse, H.R. Differential effects of tactile high- and low-frequency stimulation on tactile discrimination in human subjects. BMC Neurosci. 2008, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.R. The system usability scale: Past, present, and future. Int. J. Hum.—Comput. Interact. 2018, 34, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooke, J. SUS: A ‘Quick and Dirty’ Usability Scale. In Usability Evaluation in Industry, 1st ed.; Jordan, P.W., Thomas, B., Weerdmeester, B.A., McClelland, I.L., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 1996; pp. 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasny-Pacini, A.; Evans, J.; Sohlberg, M.M.; Chavignard, M. Proposed Criteria for Appraising Goal Attainment Scales Used as Outcome Measures in Rehabilitation Research. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 97, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleyenheuft, Y.; Gordon, A.M.; Rameckers, E.; Thonnard, J.L.; Arnould, C. Measuring changes of manual ability with ABILHAND-Kids following intensive training for children with unilateral cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2017, 59, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T. Structural validity of the Bruininks-Oseretsky test of motor proficiency—Second edition brief form (BOT-2-BF). Res. Dev. Disabil. 2019, 85, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruininks, R.H.; Bruininks, B.D. BOT2: Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency; Pearson Assessments: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, K.J.; Chen, H.L.; Shieh, J.Y.; Wang, T.N. Measurement properties of the box and block test in children with unilateral cerebral palsy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Sanchez, S.; Molina-Rueda, F.; Florencio, L.L.; Carratala-Tejada, M.; Cuesta-Gomez, A. Reliability and agreement of the Nine Hole Peg Test in patients with unilateral spastic cerebral palsy. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 2283–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauro, J. 5 Way to Interpret a SUS Score. Available online: https://measuringu.com/interpret-sus-score/ (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Bangor, A.; Kortum, P.T.; Miller, J.T. An Empirical Evaluation of the System Usability Scale. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2008, 24, 574–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teresi, J.A.; Yu, X.; Stewart, A.L.; Hays, R.D. Guidelines for Designing and Evaluating Feasibility Pilot Studies. Med. Care 2022, 60, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, D.J.; Kreuter, M.; Spring, B.; Cofta-Woerpel, L.; Linnan, L.; Weiner, D.; Bakken, S.; Kaplan, C.P.; Squiers, L.; Fabrizio, C.; et al. How we design feasibility studies. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2009, 36, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judy, L.M.; Morrow, C.; Seo, N.J. Development and evaluation of an efficient training program to facilitate the adoption of a novel neurorehabilitation device. J. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. Eng. 2023, 10, 20556683231158552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, C.M.; Johnson, E.; Simpson, K.N.; Seo, N.J. Determining Factors that Influence Adoption of New Post-Stroke Sensorimotor Rehabilitation Devices in the USA. IEEE Trans. Neural. Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.N.; Lin, K.C.; Wu, C.Y.; Chung, C.Y.; Pei, Y.C.; Teng, Y.K. Validity, responsiveness, and clinically important difference of the ABILHAND questionnaire in patients with stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2011, 92, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, P.B.; Rohrich, R.J.; Chung, K.C. The levels of evidence and their role in evidence-based medicine. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 128, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker-Bolt, P.; Downey, R.J.; Connolly, J.; Hoover, R.; Shelton, D.; Seo, N.J. Exploring the feasibility and use of accelerometers before, during, and after a camp-based CIMT program for children with cerebral palsy. J. Pediatr. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 10, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddell, K.J.; Strube, M.J.; Bailey, R.R.; Klaesner, J.W.; Birkenmeier, R.L.; Dromerick, A.W.; Lang, C.E. Does Task-Specific Training Improve Upper Limb Performance in Daily Life Poststroke? Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2017, 31, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaschke, J.; Vatinno, A.; Scronce, G.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Seo, N.J. Effect of Sensory Impairment on Hand Functional Improvement with Therapy and Sensory Stimulation. Neurol. Neurorehabilit. 2022, 4, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Jette, A.M.; Keysor, J.; Coster, W.; Ni, P.; Haley, S. Beyond function: Predicting participation in a rehabilitation cohort. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, N.J.; Coupland, K.; Finetto, C.; Scronce, G. Wearable Sensor to Monitor Quality of Upper Limb Task Practice for Stroke Survivors at Home. Sensors 2024, 24, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Scronce, G.; Finetto, C.; Coupland, K.; Zhong, M.; Lambert, M.E.; Baker, A.; Luo, F.; Seo, N.J. Application of Deep Learning Algorithm to Monitor Upper Extremity Task Practice. Sensors 2023, 23, 6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, S.P.; Dawe, J.; Musselman, K.E.; Petrevska, M.; Zariffa, J.; Andrysek, J.; Biddiss, E. Measuring functional hand use in children with unilateral cerebral palsy using accelerometry and machine learning. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, N.J.; Brinkhoff, M.; Fredendall, S.; Coker-Bolt, P.; McGloon, K.; Humanitzki, E. The Use of TheraBracelet Upper Extremity Vibrotactile Stimulation in a Child with Cerebral Palsy—A Case Report. Electronics 2024, 13, 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163147
Seo NJ, Brinkhoff M, Fredendall S, Coker-Bolt P, McGloon K, Humanitzki E. The Use of TheraBracelet Upper Extremity Vibrotactile Stimulation in a Child with Cerebral Palsy—A Case Report. Electronics. 2024; 13(16):3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163147
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Na Jin, Molly Brinkhoff, Savannah Fredendall, Patricia Coker-Bolt, Kelly McGloon, and Elizabeth Humanitzki. 2024. "The Use of TheraBracelet Upper Extremity Vibrotactile Stimulation in a Child with Cerebral Palsy—A Case Report" Electronics 13, no. 16: 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163147
APA StyleSeo, N. J., Brinkhoff, M., Fredendall, S., Coker-Bolt, P., McGloon, K., & Humanitzki, E. (2024). The Use of TheraBracelet Upper Extremity Vibrotactile Stimulation in a Child with Cerebral Palsy—A Case Report. Electronics, 13(16), 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163147






