Reliability Evaluation of Multi-State Solar Energy Generating System with Inverters Considering Common Cause Failures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Descriptions of the Model
2.1. Assumptions of the Model
2.2. Infinitesimal Generator
3. System Performance Metrics
3.1. Transient Regime
3.1.1. Transient Availability
3.1.2. Reliability and Mean Time between Consecutive System Failures
3.1.3. The Idle Probability of the Repairman
3.1.4. The Probability of the Repairman Comes Back to the System
3.2. Stationary Regime
3.2.1. Stationary Availability
3.2.2. The Stationary Idle Probability of the Repairman
3.2.3. The Stationary Probability of the Repairman Returning to the System
4. Numerical Examples
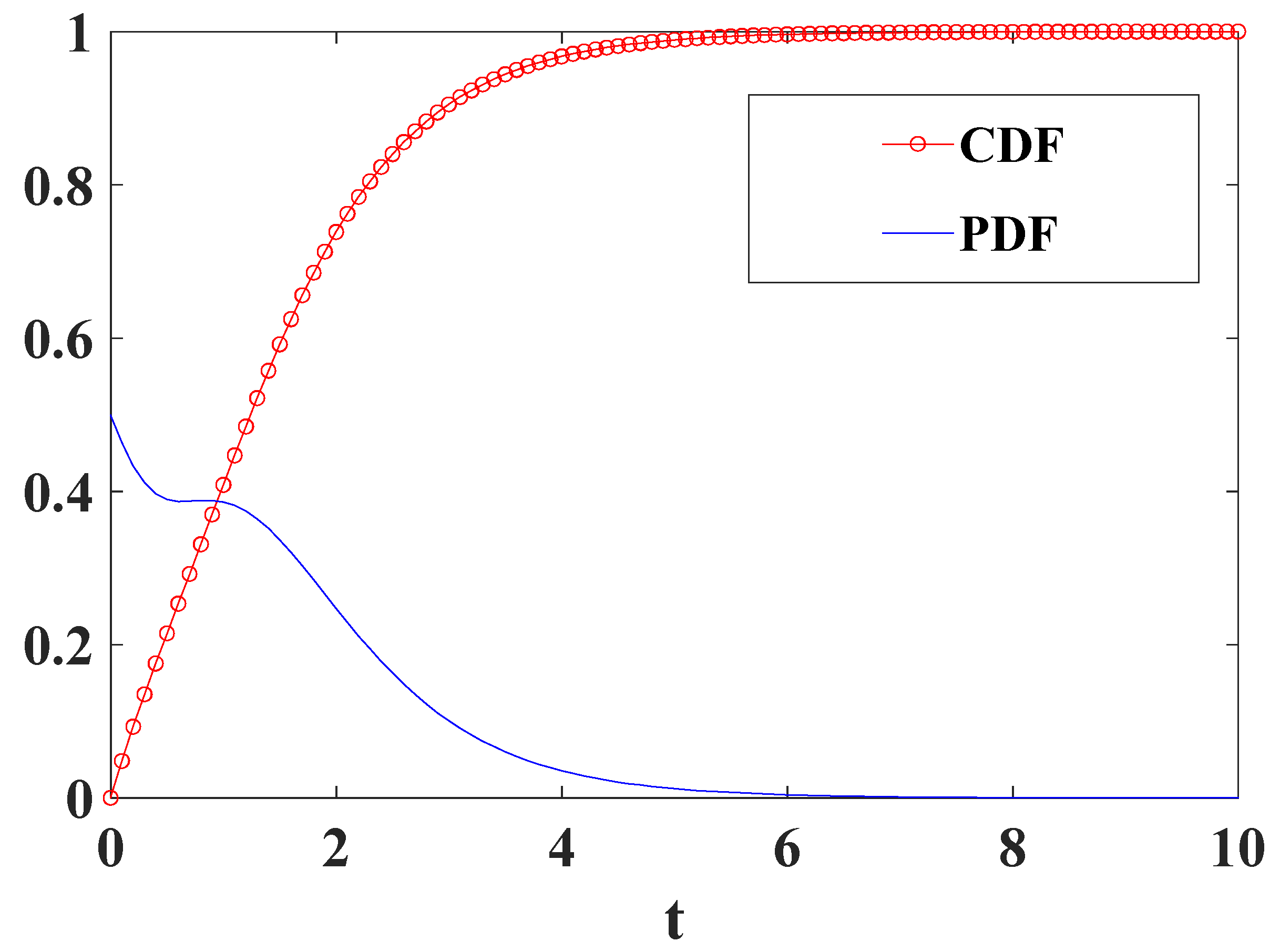
4.1. Performance Evaluation of the Newly Proposed System
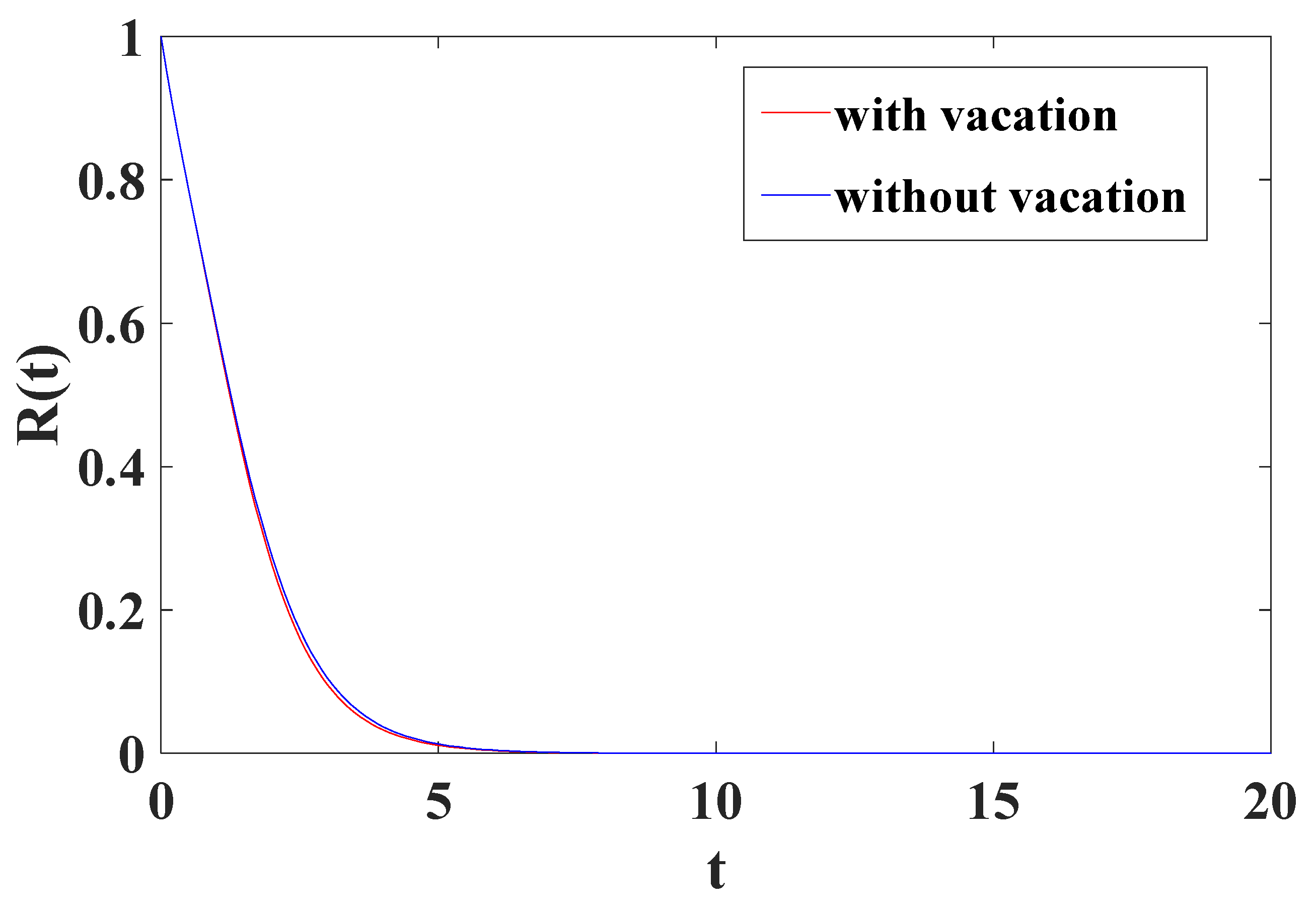
4.2. Comparison between the Proposed System and Existing Model with Repairman without Vacations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- IEA-PVPS T1-15:2006; Trends in Photovoltaic Applications: Survey Report of Selected IEA Countries between 1992 and 2005. The International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2006.
- Atwa, Y.M.; El-Saadany, E.F.; Salama, M.M.A.; Seethapathy, R. Optimal renewable resources mix for distribution system loss minimization. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakammenos, D.J.; Dialynas, E.N. Reliability and cost assessment of power transmission networks in the competitive electrical energy market. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2004, 19, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, Y.G.; Salama, M.M.A.; Chikhani, A.Y. Adequacy assessment of distributed generation systems using Monte Carlo simulation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2003, 18, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-khattam, W.; Hegazy, Y.G.; Salama, M.M.A. Investigating distributed generation systems performance using Monte Carlo simulation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2006, 21, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Z.; Jirutitijaroen, P. Latin hypercube sampling techniques for power systems reliability analysis with renewable energy sources. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 26, 2066–2073. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, W. Comparative analysis of the reliability of grid-connected photovoltaic power systems. In Proceedings of the Power and Energy Society General Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 22–26 July 2012; pp. 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Rei, A.M.; Schilling, M.T. Reliability assessment of the Brazilian power system using enumeration and Monte Carlo. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2008, 23, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Zio, E. A multi-state model for the reliability assessment of a distributed generation system via universal generating function. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2012, 106, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Shen, W.; Levitin, G.; Wang, P.; Goel, L.; Wu, Q. Economical evaluation of large-scale photovoltaic systems using universal generating function techniques. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2013, 1, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotopoulou, M.; Rakopoulos, D.; Petridis, S.; Drosatos, P. Assessment of smart grid operation under emergency situations. Energy 2024, 287, 129661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, P.M.; Twaha, S.; Murphy, I.S. Analysis of the cost of reliable electricity: A new method for analyzing grid connected solar, diesel and hybrid distributed electricity systems considering an unreliable electric grid, with examples in Uganda. Energy 2014, 66, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adefarati, T.; Bansal, R.C. Reliability assessment of distribution system with the integration of renewable distributed generation. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, L.R.; Gupta, R.; Rana, V.S. Analysis of a multiunit solar energy system model. Microelectron. Reliab. 1993, 33, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Tang, Y.H.; Yu, M.M. The reliability of solar energy generating system with inverters in series under common cause failure. Appl. Math. Model. 2019, 68, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.A.; Li, R.; Zhao, X. Failure risk management: Adaptive performance control and mission abort decisions. Risk Anal. 2024, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Q.A.; Cui, L.R. Reliability evaluation based on a dependent two-stage failure process with competing failures. Appl. Math. Model. 2018, 64, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.A.; Cui, L.R. Gamma process based optimal mission abort policy. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2019, 190, 106496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuts, M.F. Matrix-Geometric Solutions in Stochastic Models—An Algorithmic Approach; The Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Juybari, M.N.; Hamadani, A.Z.; Ardakan, M.A. Availability analysis and cost optimization of a repairable system with a mix of active and warm-standby components in a shock environment. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 237, 109375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juybari, M.N.; Hamadani, A.Z.; Liu, B.L. A Markovian analytical approach to a repairable system under the mixed redundancy strategy with a repairman. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2022, 38, 3663–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.L.; Wen, Y.Q.; Qiu, Q.A.; Shi, H.Y.; Chen, J.H. Reliability analysis for multi-state systems under K-mixed redundancy strategy considering switching failure. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2022, 228, 108814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.Q.; Liu, B.L.; Shi, H.Y.; Kang, S.G.; Feng, Y.J. Reliability evaluation and optimization of a system with mixed run shock. Axioms 2022, 11, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.J.; Liu, B.L.; Yang, L.; Gao, K.Y. Customizing random replacement model and flexible warranty model from the perspective of screening reliability. Axioms 2023, 12, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ocón, R.; Castro, J.E.R. Two models for repairable two-system with phase-type sojourn time distributions. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2004, 84, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eryilmaz, S.; Kan, C. Reliability and optimal replacement policy for an extreme shock model with a change point. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2019, 190, 106513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, P. Reliability models for a nonrepairable system with heterogeneous components having phase-type time-to-failure distribution. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2017, 159, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.R.; Hu, L.M.; Zhang, T.T.; Wang, Y.Y. Reliability modeling for a repairable (k1, k2)-out-of-n: G system with phase-type vacation time. Appl. Math. Model. 2021, 91, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.M.; Tang, Y.H.; Liu, L.P.; Cheng, J. A phase-type geometric process repair model with spare device procurement and repairman’s multiple vacations. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2013, 225, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L. Reliability analysis for a k-out-of-n: G system with redundant dependency and repairmen having multiple vacations. Appl. Math. Comput. 2012, 218, 11959–11969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wang, J.T.; Zhang, J. Reliability analysis of a redundant series system with common cause failures and delayed vacation. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 239, 109467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Huang, H.Z.; Mi, J.H.; Peng, W.W.; Han, X.M. Reliability analysis of multi-state systems with common cause failures on Bayesian network and fuzzy probability. Ann. Oper. Res. 2022, 311, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Yang, S.K.; Bian, C.; Gou, X.D. Formal analysis of repairable phased-mission systems with common cause failures. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2021, 70, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colquhoun, D.; Hawkes, A.G. On the stochastic properties of bursts of single Ion Channel openings and of clusters of bursts. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond.–Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1982, 300, 1–59. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.R.; Du, S.J.; Liu, B.L. Multi-point and multi-interval availabilities. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2013, 62, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.L.; Cui, L.R.; Wen, Y.Q.; Shen, J.Y. A performance measure for Markov system with stochastic supply patterns and stochastic demand patterns. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2013, 119, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.L.; Cui, L.R.; Wen, Y.Q.; Shen, J.Y. A cold standby repairable system with working vacations and vacation interruption following Markovian arrival process. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2015, 142, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| t | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| 5 | 0.0212 | 0.0205 | 0.0197 | 0.0187 | 0.0174 | 0.0034 | 0.0088 | 0.0220 | 0.0777 | 0.0392 | 0.2946 | 0* |
| 10 | 0.0196 | 0.0190 | 0.0184 | 0.0177 | 0.0169 | 0.0032 | 0.0084 | 0.0224 | 0.0870 | 0.0265 | 0.3505 | 0* |
| 15 | 0.0188 | 0.0182 | 0.0176 | 0.0169 | 0.0160 | 0.0030 | 0.0080 | 0.0222 | 0.0901 | 0.0244 | 0.3723 | 0* |
| 20 | 0.0185 | 0.0179 | 0.0172 | 0.0165 | 0.0156 | 0.0030 | 0.0079 | 0.0220 | 0.0914 | 0.0236 | 0.3812 | 0* |
| 25 | 0.0183 | 0.0177 | 0.0171 | 0.0164 | 0.0155 | 0.0029 | 0.0078 | 0.0220 | 0.0919 | 0.0233 | 0.3849 | 0* |
| 0.0182 | 0.0176 | 0.0170 | 0.0163 | 0.0154 | 0.0029 | 0.0078 | 0.0219 | 0.0923 | 0.0231 | 0.3875 | 0* | |
| t | ||||||||||||
| 0 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.6000 |
| 5 | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0.0907 | 0.3649 | 0.2096 | 0.2279 | 0.1367 |
| 10 | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0.0697 | 0.3397 | 0.2127 | 0.1881 | 0.1128 |
| 15 | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0.0649 | 0.3267 | 0.2108 | 0.1769 | 0.1062 |
| 20 | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0.0631 | 0.3213 | 0.2100 | 0.1725 | 0.1035 |
| 25 | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0.0624 | 0.3190 | 0.2096 | 0.1708 | 0.1025 |
| 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0* | 0.0619 | 0.3174 | 0.2094 | 0.1695 | 0.1017 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, S.; Chen, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, H.; Liu, B.; Qiu, Q. Reliability Evaluation of Multi-State Solar Energy Generating System with Inverters Considering Common Cause Failures. Electronics 2024, 13, 3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163228
Zhao S, Chen J, Li B, Zhang H, Liu B, Qiu Q. Reliability Evaluation of Multi-State Solar Energy Generating System with Inverters Considering Common Cause Failures. Electronics. 2024; 13(16):3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163228
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Shenmiao, Jianhui Chen, Baoqin Li, Hui Zhang, Baoliang Liu, and Qingan Qiu. 2024. "Reliability Evaluation of Multi-State Solar Energy Generating System with Inverters Considering Common Cause Failures" Electronics 13, no. 16: 3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163228
APA StyleZhao, S., Chen, J., Li, B., Zhang, H., Liu, B., & Qiu, Q. (2024). Reliability Evaluation of Multi-State Solar Energy Generating System with Inverters Considering Common Cause Failures. Electronics, 13(16), 3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163228





